CLASSIFICATION OF AGRICULTURAL CROPS. BY PROF.A.BALASUBRAMANIAN Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore
|
|
|
- Archibald Griffin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLASSIFICATION OF AGRICULTURAL CROPS BY PROF.A.BALASUBRAMANIAN Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore 1
2 Introduction: Agriculture is the backbone of India s economy. The history of agriculture dates back to several centuries. Since time immemorial, crops and plants were grown and domesticated by the people, in several parts of the world. Plants which are fully useful for human and animal consumption have been segregated and cultivated in farms and fields. In Geographic studies, the area of cultivation of crops and plants, factors of their growth, their distribution and yield are analyzed with reference to space and time. In this context, there is a need to classify the crops for a systematic geographical analysis. The International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) explains the principal ranks of taxa. According to them, plants are classified based on the following criteria: (1) botanical, (2) descriptive, and (3) agricultural. A common, well-defined system of crop classification is important in geography. Globally, major crop classifications are defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. For a better understanding of agricultural crops and their distribution in India and the globe, knowledge of the classification of plants and crops is needed. Hence, the objectives of studying this lesson are to know about: 1. Descriptive Classification 2. Ecological classification 3. Agronomic Classification 4. Horticultural Classification 5. Ornamental and plantation classification. 1. DESCRIPTIVE CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS The descriptive classification of crops is based on five criterions: a) Mode of Reproduction, b) Mode of Pollination, c) Life Span, d) Growth Habit and e) Leaf Retention. The method adopted according to the Mode of Reproduction, has classified the crops into two major divisions as sexual and asexual reproducing plants. The Sexual category of plants are developed from a seed or spore after undergoing union of male and female gametes. The typical examples include palms and ferns. The Asexual category of plants undergo reproduction by any vegetative means without the union of the sexual gametes or by apomixis. The Crop Classifications attempted according to the mode of pollination. This criteria divides plants into three categories as: 1. Naturally self-pollinated crops 2. Naturally cross-pollinated crops 3. Both self- and cross-pollinated crops 2
3 In the Naturally self-pollinated plants, both pollen and embryo sac are produced in the same floral structure or in different flowers but within the same plant. Typical Examples include: rice, most pulses, okra, tobacco, tomato. In the Naturally cross-pollinated crops, the pollen transfer is done from one flower to the stigma of another flower in a separate plant. Typical examples include, corn and many grasses, avocado, grape, mango, many plants with unisexual or imperfect flowers. In both self- and cross-pollinated crops, plants are largely self-pollinated but varying amounts of cross-pollination also occur. Examples include, cotton and sorghum. According to Life Span, crops are classified into annuals, biennial and perennial categories. The Annuals are plants which live within a short period of time, for a few weeks or months, perpetuated by seed, and which die soon after producing seeds. Examples include: rice, corn, cowpea, etc. The Biennials are plants which requires two growing seasons to complete its life cycle, the first for vegetative growth and accumulation of food reserves, and the second for the production of reproductive parts. Examples include: onion, cabbage, carrot, celery, and raddish. The Perennials include, a plant that lives indefinitely, including all trees and shrubs and many herbaceous plants with underground stems (e.g. corm, rhizome, tuber) like banana and clump-forming grasses. The Perennial plants continue growing and produce seeds year after year, either from a single plant or, in herbaceous plants, from succeeding regrowth. Based on Growth Habit crops classified into Herbs, Vines, Lianas, Shrubs and Trees. According to Leaf Retention, plants are classified into Evergreen plants and deciduous plants. The Evergreen plants are those that maintain their leaves throughout the year. Abscissed leaves are continually replaced by new flushes. Examples include pines, banana, papaya, palms and most tropical plants. The Deciduous plants are those which naturally shed off or lose leaves annually for extended periods. Natural leaf shedding is pronounced in deciduous trees of temperate regions. 2. Ecological Adaptation or Habitat: Geography and ecology are two inter-related subjects. Most of the ecosystems are studied under geographic contexts, The plants are also classified according to their ecological adaptation and habitat. The major classes of plants are: Aquatic / hydrophytic plants Epiphyte or epiphytic plants Halophyte or halophytic plants Lithophyte or lithophytic plants Mesophyte or mesophitic plants Parasite or parasitic plants Saprophyte or saprophytic plants Sciophyte or sciophytic plants Terrestrial or land plants Xerophyte/ xerophytic plants. The Aquatic/ hydrophytic plants are adapted to growing in water or waterlogged soil. They grow entirely in submerged, partly submerged or floating, or conditions. Examples: lotus and water lily. 3
4 The Epiphyte or epiphytic plants grow above ground on another plant but is not parasitic, usually deriving only physical support from the host and obtaining nourishment from the air and other sources. The most common epiphytes belong to the pineapple, orchid, and fern families. The Halophytes grow in habitats excessively rich in salts or under saline conditions. Mangrove vegetation are good examples. Coconut, cashew and tamarind have varying levels of tolerance to saline conditions. The Lithophytes are adapted to grow on rocks or in rocky terrain with little humus, absorbing nutrients from the atmosphere, rain, and decaying matter which accumulate on the rocks. The Mesophytes are terrestrial plants which are adapted to moderate conditions for growth, i.e. not too dry and not too wet (e.g. corn and most commercially-grown crops). The Parasite or parasitic plants grow on another plant from which it takes part or all nourishment. The Saprophyte or saprophytic crops grow on decaying organic matter and has no green tissue. This classification applies to the mushrooms, which are fungi. The Sciophytes grow in low light intensity or shade, e.g. most ferns and mosses, black pepper, coffee, hot pepper, gingers, and many orchids can tolerate or require shade. The Terrestrial or land plants grow on land. Most agricultural crops are terrestrial plants. They are further subclassified into various groups such as halophytes, mesophytes, etc. The Xerophytes are adapted to conditions with little or no water. Examples: cacti and many succulents. 3. Agricultural Classification A crop is any useful plant, or a plant which is grown for any purpose. It is utilized by people directly or indirectly, raw or processed. These plants are intentionally grown or managed for various uses. On the basis of tradition, extent of cultivation and intensity of culture, agricultural crops are classified into two main divisions: agronomic and horticultural. The Agronomic crops are also called as field crops. They are mostly annual herbaceous plants that are grown under extensive or large-scale culture. The agricultural classification of plants/ crops based on their primary uses include the following classes: 1. Food Crops 2. Cash Crops 3. Staple Crops 4. Cereal or Grain Crops 5. Legume Seed Crops or Pulses 6. Root and Tuber Crops or Tuberous Crops 7. Oil Seed Crops 8. Sugar and Sweetener Crops 9. Beverage Crops 10. Rubber Crops 11. Latex and Gum Crops 12. Dye and Tannin Crops 4
5 13. Fiber Crops 14. Pasture and Forage Crops 15. Biofuel Crops. The Food Crops are plants grown primarily for the harvesting of any part which is used by people as food or processed into food product. The Non-food Crops are mainly cash crops. These are plants grown for the production of non-food products such as fiber, fodder, alcohol and tobacco. The Staple Crops are food crops. These are regularly consumed in a traditional diet and from which people obtain a major proportion of their energy and nutrient requirements. Examples of other staple crops: wheat and millet. The Cereal or Grain Crops are mainly annual, herbaceous plants belonging to the grass family which are grown for their seeds or grains. Examples: corn, millet, rice, sorghum, wheat. The Legume Seed Crops or Pulses are leguminous plants which produce edible, protein-rich seeds. Examples: cowpea, peanut and peas. The Root and Tuber s us Crops are plants with modified, swollen root or underground stem. These organs are rich sources of carbohydrate and are commonly used as staple, livestock feed, or as raw materials for industrial purposes, such as starch and alcohol production, or processed into various food products. The Oil Seed Crops are plants grown for their seeds which are rich source of edible and industrial oil. Example: sunflower The Sugar and sweetener Crops are plants grown primarily for the production of sugar or other sweettasting products. Various forms of sugar are derived from various parts of certain plants such as from stems, bulb and other underground organs, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds, sap and resin. These are called as sugar crops. The Beverage Crops are plants which are sources of various drinks including fruit juices. Examples: coffee and tea. The Rubber Crops are another major type of plants that are grown for the production of latex which is processed into the industrial product called rubber. The Latex and Gum Crops are very typical plants. These plants are grown for the collection of latex which is processed into chewing gum, inelastic rubber and other industrial products such as surgical tapes and dental supplies, insulation, splints, pipes, golf balls, waterproofing, adhesives, etc. The Dye and Tannin Crops are special kinds of plants. These plants are grown as sources of tannin and coloring substances. Tannin is an aromatic, phenolic substance which is obtained from barks and other plant organs and variously used in tanning, medicines, dyeing, ink manufacture, etc. Fiber Crops are plants grown as sources of fiber used in making textiles, ropes, twine and similar materials. The fiber is extracted from the bark, leaves, or other organs including the husk of coconut. 5
6 The Pasture and Forage Crops are very essential varieties of plants. These plants are grown or managed as vegetable feed for grazing animals. Soilage Crops are the grasses grown, cut and directly fed to animals. Silage Crops are the grasses grown, cut, fermented and preserved before being fed to animals. The Biofuel Crops are special type of crops. These plants are grown for the production of fuel that is used as additive or replacement for petroleum products. Examples: sugarcane, corn, coconut, castor bean and Jatropha. 4. Horticultural Crops/ Plants: Horticultural crops have been referred to as garden crops. Horticultural crops are annual and perennial plants which are grown under an intensive system of agriculture. The following are the major kind of horticultural crops: Olericultural or Vegetable Crops Pomological or Fruit Crops and Nuts Spice Crops Essential-oil Crops Ornamental Crops Biocidal Crops Industrial Crops Plantation Crops. Vegetable Crops are (except mushroom) grown for their succulent and edible parts such as the roots, stems, leaves, young tops, fruits or seeds for use in culinary preparations either fresh or preserved in the fresh state. Vegetables are classified based on their edible parts, into several varieties. They are: a. Leafy Vegetables are crops that are grown mainly for their leaves. Examples: amaranth, lettuce, and raddish. b. Shoot Vegetables are plants grown primarily for their edible shoot, mainly the young, succulent stem. Examples: asparagus and celery. c. Pod and Seed Vegetables are generally members of Leguminosae or Fabaceae family. These plants are grown for their young pods and seeds. Examples: beans and sweet corn. d. Root and Bulb Vegetables are plants grown for their swollen underground roots and stems. Examples: carrot, potato, onion and raddish. e. Flower Vegetables are plants with edible flowers. Examples: rose and sunflower. f. Fruit Vegetables are grown for their fleshy, succulent fruits. Examples: eggplant, tomato, peppers and melons. Vegetables are also classified according to their families, into the following groups: a. Cole Crops or Crucifers. These vegetable crops belong to the Cruciferae or Brassicaceae (Mustard) family. They possess edible leaves or heads. Examples: cabbage, cauliflower, mustard, and raddish. 6
7 b. Cucurbits, belong to the Gourd and Squash family. They are grown mainly for their fruits but some have edible young shoots and flowers; also called Vine Crops. Examples: bottle gourd, cucumber and melons. c. Legume Vegetables are the members of the Leguminosae or Fabaceae (Bean) family. The seeds are rich in protein. Examples: kidney beans, pea and pole sitao. d. Lilies are members of the Liliaceae (Lily) family. Examples: asparagus, garlic and onion. e. Solanaceous Crops, belong to the Solanaceae (Nightshade or Eggplant) family and, with the exception of white potato, are also called Fruit Vegetables. Examples: eggplant, tomato, peppers and white potato. f. Mushrooms are edible fungi belonging to the division Basidiomycota (club fungi). The edible part commonly consist of an upright stalk and an umbrella- shaped cap. In addition to these, horticultural crops include a) fruits and nuts b) Spices c) Essential oil crops The Fruit Crops and Nuts include plants that are grown primarily for their edible fruits. Nuts are grown for their fruits which are high in fat. The nut is a simple, dry, indehiscent fruit with a hard outer covering. Example is the cashew. The Spice Crops are grown for the production of aromatic substances which are used as food flavoring, fragrance or preservative qualities. Spices are in solid or liquid forms. Examples: black pepper, garlic, ginger, hot pepper, onion and turmeric. The Essential-oil Crops are plants grown for the extraction of essential oils which are volatile, aromatic substances for perfumery and other uses. Examples: eucalyptus, peppermint, etc. 5. Ornamental and Other Plantation Crops Gardening is a part of agriculture. Horticultural cultivation of garden plants is a major area of economy. The Ornamental Crops are plants that are grown primarily for decoration or landscaping or to be appreciated because of their attractive flowers or foliage. They also include floricultural crops. The ornamental plants are further classified into several varieties, based on their usage, as: a) cutflowers, b) cut foliage, c) turfgrasses, d) groundcovers, e) hedges, f) accents, g) specimen plants, h) avenue trees, i) screens, j) topiaries, k) fillers and others. 7
8 Floricultural crops are valued for their attractive flowers, foliage ornamentals for their leaves. The Lawn or Turf Grasses are grasses grown for aesthetic purpose in the landscape or for any outdoor recreational use. They are usually maintained at a low height. Example: Bermuda grass. The Cutflowers are obtained from plants that are grown for their attractive flowers with long shelf life. Example: anthurium. The Cutfoliage are obtained from plants that are grown for their attractive foliage which are cut for floral decoration. Example: ferns. The Edge Crops are the short- statured plants that are grown to serve as barrier between the lawn and garden, to highlight gardens, or to create stand-alone gardens; also called border plants. Examples: mondo grass and dwarf cucharita. The Groundcovers are low-lying, aesthetically appealing plants grown in the landscape primarily to suppress weed growth and to control, retard or prevent soil erosion by covering and binding loose, bare soil. It is used to produce a carpeting effect. The Hedges are plants grown at the edges of pathways or boundaries and continuously pruned to kneehigh height or upper but below eye level. The Accents are plants with showy features distinct from the rest of the other plants. It immediately attracts attention and becomes a focal item in the landscape garden and at the same time provides the contrast which gives attention to other plants. The Specimens are obtained from plants that have showy features, or with unique characteristics which make them pieces of conversation or botanical curiosity, or otherwise desired as collector s item. The Screens are plants grown to serve as barrier against sun rays, to conceal certain parts of the landscape, or to obstruct view. The Shade crops are generally trees, shrubs, trellised vines and lianas which are grown mainly to provide shade singly or with supporting trellis. The Avenue Trees are mainly trees and shrubs grown, more or less equidistant, beside roads and streets. Palms are also used. In addition to these, there are two more categories of plantation crops. One is Biocidal Crops and Industrial Crops. The Biocidal Crops are plants containing organic compounds with pesticidal or anti-microbial properties. The effective parts are either directly applied or seeped in water for foliar spray. The Industrial Crops are plants grown to provide materials for industrial processing and production of non-food products, including drugs. The crop names which we use in the farmland are also included under the plantation crops category. They include: 1) Main Crop 2) Nursery crop 3) Intercrop 8
9 4) Filler Crop 5) Relay Crop 6) Companion crop 7) Green manure crop 8) Trap crop or Decoy crop 9) Insect pest repellant crops 10) Natural enemies attractant crops. Any crop which is intended by the grower to become his main source of revenue is called as the Main Crop. A plant which is temporarily grown in the nursery and later planted in the field or garden or used for ornamental display, when it reaches the proper age and size, is called as a Nursery crop. The Intercrop is any crop which is planted simultaneously with or before the flowering season of the main crop in intercropping. The Filler Crop is any crop which is planted to fill a gap. The Relay Crop is the crop which is planted after the flowering period or harvest of the main crop in relay cropping. The Companion crop is any crop which is planted close to the main crop to complement the latter s growth and production, or to maximize utilization of space because they do not compete. The Cover crop is a crop grown mainly to control soil erosion, regulate soil temperature, control weeds and reduce evaporative losses. The Green manure crop is a leguminous crop grown to be plowed under the soil to increase organic matter and serve as organic fertilizer. Mungbean (mungo) is ideal for this purpose. The Trap crop or Decoy crop are plants grown to attract certain insect pests or parasites because they are favorite hosts. They act as decoys to lure pests away from the main crop. The Insect pest repellant crops are plants grown along the borders and at strategic places in the farm to repel insect pests because of their strong aroma and anti-herbivory properties. The Natural enemies attractant crops are flowering plants grown at strategic places in the farm to attract natural enemies of insect pests. The extent of cultivation of these crops vary from place to place and depends on such factors as the level of mechanization, adoption of technological advances, farm size, market stability and availability of capital. The classifications of crops are used in collecting the basic data of agriculture and analyse them geographically. We will see the distribution of these crops in India, one by one, later. 9
Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013
 Farming in India Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013 Location of India in World Map States in India Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA 28 states and seven union territories Annual Rainfall in India Rivers in India River
Farming in India Sreedhar Patil 5/30/2013 Location of India in World Map States in India Bangalore, Karnataka, INDIA 28 states and seven union territories Annual Rainfall in India Rivers in India River
Organic Crop Production: Crop Rotation
 Organic Crop Production: Crop Rotation Annette Wszelaki Vegetable Specialist Well thought out crop rotation is worth 75% of everything else that might be done, including fertilization, tillage and pest
Organic Crop Production: Crop Rotation Annette Wszelaki Vegetable Specialist Well thought out crop rotation is worth 75% of everything else that might be done, including fertilization, tillage and pest
Joyce Kinabo Sokoine University of Agriculture Morogoro, Tanzania
 Joyce Kinabo Sokoine University of Agriculture Morogoro, Tanzania 4/18/2013 Background Agricultural production systems: from local diversified (cereals, roots, horticulture) systems to monoculture farming
Joyce Kinabo Sokoine University of Agriculture Morogoro, Tanzania 4/18/2013 Background Agricultural production systems: from local diversified (cereals, roots, horticulture) systems to monoculture farming
JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection
 JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection This document is the first (draft) version of the JECAM Guidelines for field data collection. It has been prepared based
JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection This document is the first (draft) version of the JECAM Guidelines for field data collection. It has been prepared based
AGRICULTURE (CODE NO. 01) PAPER - I
 AGRICULTURE (CODE NO. 01) PAPER - I There will be two parts PART I, Compulsory for all the candidates. PART II, There will be two optional sections (A & B) Candidate will have to answer all the questions
AGRICULTURE (CODE NO. 01) PAPER - I There will be two parts PART I, Compulsory for all the candidates. PART II, There will be two optional sections (A & B) Candidate will have to answer all the questions
Myanmar Agriculture and Future Prospect of Agricultural Development in Kayah State
 Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation Department of Agriculture 1 Myanmar Agriculture and Future Prospect of Agricultural Development in Kayah State Myint Myint Aye Assistant Director Department
Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation Department of Agriculture 1 Myanmar Agriculture and Future Prospect of Agricultural Development in Kayah State Myint Myint Aye Assistant Director Department
Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van
 Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van Introduction Agriculture has been the basic source for the subsistence of man for thousand of years. Even today, it provides livelihood to
Group 3: Anuradha Rucku Gupta Marvis Dan Xiao Duong Nguyen Van Introduction Agriculture has been the basic source for the subsistence of man for thousand of years. Even today, it provides livelihood to
Adding Value with Horticulture Farming
 Adding Value with Horticulture Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-881-8909 byerspl@missouri.edu Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine
Adding Value with Horticulture Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-881-8909 byerspl@missouri.edu Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine
Nature of the Agriculture/Horticulture Industry
 Nature of the Agriculture/Horticulture Industry Interest Approach Have the students create their own definition of agriculture. Ask for volunteers to share their definitions with the rest of the class.
Nature of the Agriculture/Horticulture Industry Interest Approach Have the students create their own definition of agriculture. Ask for volunteers to share their definitions with the rest of the class.
Crop Rotation - Chapter 7 7. Crop Rotation
 Crop Rotation - Chapter 7 7. Crop Rotation P roper crop rotation is Fundamental #1. It will beat the disease and pest cycle while promoting nutrient cycling. This is a forgotten age-old method to assure
Crop Rotation - Chapter 7 7. Crop Rotation P roper crop rotation is Fundamental #1. It will beat the disease and pest cycle while promoting nutrient cycling. This is a forgotten age-old method to assure
Sunil Jain, Sankarsana Sahoo, Kumar Sundaram, Pramod Kumar
 Sunil Jain, Sankarsana Sahoo, Kumar Sundaram, Pramod Kumar Plan of Presentation Methodology of GVA Estimation of Crop Sector Methodology for GVA of Crop sector on Financial Year basis. Methodology for
Sunil Jain, Sankarsana Sahoo, Kumar Sundaram, Pramod Kumar Plan of Presentation Methodology of GVA Estimation of Crop Sector Methodology for GVA of Crop sector on Financial Year basis. Methodology for
Decadal Shift in Cropping Pattern in Karnataka Research Report July 2016
 Karnataka Agriculture Price Commission Decadal Shift in Cropping Pattern in Karnataka Research Report July 2016 This is a comprehensive analysis of the shift in the area of agriculture & horticulture crops
Karnataka Agriculture Price Commission Decadal Shift in Cropping Pattern in Karnataka Research Report July 2016 This is a comprehensive analysis of the shift in the area of agriculture & horticulture crops
Tall Harvest, SumaGrow Inside
 Tall Harvest, SumaGrow Inside Product Application Rates Recommendations for Crops & Cultivation Practices 1. Organic Applications 2. Cotton 3. Field Corn, Sweet Corn, Milo 4. Soybeans 5. Summer Grasses
Tall Harvest, SumaGrow Inside Product Application Rates Recommendations for Crops & Cultivation Practices 1. Organic Applications 2. Cotton 3. Field Corn, Sweet Corn, Milo 4. Soybeans 5. Summer Grasses
This presentation is sponsored by the Beginning Farmer and Rancher Development Program INTEGRATED FARMS
 This presentation is sponsored by the Beginning Farmer and Rancher Development Program INTEGRATED FARMS Integrated Farms In the 20 th century, farming saw a gradual separation and specialization of production
This presentation is sponsored by the Beginning Farmer and Rancher Development Program INTEGRATED FARMS Integrated Farms In the 20 th century, farming saw a gradual separation and specialization of production
Table 10: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM CANADA, 1995 AND 1996
 Table 10: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM CANADA, 1995 AND 1996 Canada Canada Commodity / Calendar year Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Change from Change from Share of total Share of total
Table 10: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM CANADA, 1995 AND 1996 Canada Canada Commodity / Calendar year Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Change from Change from Share of total Share of total
Table 8: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM MEXICO, 1995 AND 1996
 Table 8: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM MEXICO, 1995 AND 1996 Mexican Mexican Commodity / Calendar year Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Change from Change from Share of total Share of total
Table 8: U.S. AGRICULTURAL IMPORTS FROM MEXICO, 1995 AND 1996 Mexican Mexican Commodity / Calendar year Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Jan.- Jan. Change from Change from Share of total Share of total
Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops
 LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
CINNERATE KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN CAUTION
 CINNERATE CINNERATE IS A BROAD SPECTRUM, CONTACT FOLIAR FUNGICIDE, FOR CONTROL OF A VARIETY OF DISEASES AND MITICIDE ON AGRICULTURAL CROPS, TERRESTRIAL AND ORNAMENTAL PLANTS ACTIVE INGREDIENTS: Cinnamon
CINNERATE CINNERATE IS A BROAD SPECTRUM, CONTACT FOLIAR FUNGICIDE, FOR CONTROL OF A VARIETY OF DISEASES AND MITICIDE ON AGRICULTURAL CROPS, TERRESTRIAL AND ORNAMENTAL PLANTS ACTIVE INGREDIENTS: Cinnamon
Horticultural Production in Nebraska Organic Vegetable Production Integrated, Sustainable Production Systems. Considering Organic Production?
 Horticultural Production in Nebraska 2002 Organic Vegetable Production Integrated, Sustainable Production Systems Laurie Hodges & Liz Sarno University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension Vegetables, melons,
Horticultural Production in Nebraska 2002 Organic Vegetable Production Integrated, Sustainable Production Systems Laurie Hodges & Liz Sarno University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension Vegetables, melons,
Common millet management
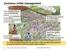 Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
Common millet management Soil compaction due to tracking animals and tractors No protection measures against wind and soil erosion Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of harvested fields No soil water
A brief focus on Georgia s agricultural industry
 A brief focus on Georgia s agricultural industry 2010 Total Farm Gate Value $200,000,000 - $475,048,630 $80,000,000 - $200,000,000 $45,000,000 - $80,000,000 $20,000,000 - $45,000,000 $313,000 - $20,000,000
A brief focus on Georgia s agricultural industry 2010 Total Farm Gate Value $200,000,000 - $475,048,630 $80,000,000 - $200,000,000 $45,000,000 - $80,000,000 $20,000,000 - $45,000,000 $313,000 - $20,000,000
Gardening. What We Will Cover
 08 08 Gardening Gardening is a therapeutic, outdoor hobby and a great way to enjoy the beauty of plants. In order to have a flourishing garden, you must have a keen grasp of the two most important aspects
08 08 Gardening Gardening is a therapeutic, outdoor hobby and a great way to enjoy the beauty of plants. In order to have a flourishing garden, you must have a keen grasp of the two most important aspects
Fruit origin and domestication; Plant propagation; Production systems; Plant conduction and pruning; Cultural practices.
 LPV0156 Plant Raw Materials Keigo Minami The role of cultivated plants; Origin and classification of cultivated plants; Structure and function in plants; Reproduction of plants; Plant protection; Grain
LPV0156 Plant Raw Materials Keigo Minami The role of cultivated plants; Origin and classification of cultivated plants; Structure and function in plants; Reproduction of plants; Plant protection; Grain
Table 70. Summary by Tenure of Operators: 1998
 Summary by Tenure of Operators: 1998 FARMS AND LAND IN FARMS Farms number 19 951 15 620 2 207 2 124 Land in farms cuerdas 865 478 457 786 246 494 161 198 Average size of farm cuerdas 43.4 29.3 111.7 75.9
Summary by Tenure of Operators: 1998 FARMS AND LAND IN FARMS Farms number 19 951 15 620 2 207 2 124 Land in farms cuerdas 865 478 457 786 246 494 161 198 Average size of farm cuerdas 43.4 29.3 111.7 75.9
Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity
 Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity Brief prepared for the Entry phase of the project: Strengthening Agricultural Water Efficiency and Productivity on the African and Global Level The Project The GCP/INT/166/SWI
Thematic Brief 2 Water Productivity Brief prepared for the Entry phase of the project: Strengthening Agricultural Water Efficiency and Productivity on the African and Global Level The Project The GCP/INT/166/SWI
KEEPING livestock well fed during the
 Forage Production KEEPING livestock well fed during the winter months can be one of the largest costs associated with livestock operations. Forage can provide much needed nutrients, so it is critical in
Forage Production KEEPING livestock well fed during the winter months can be one of the largest costs associated with livestock operations. Forage can provide much needed nutrients, so it is critical in
{ } Introduction to. Livestock
 { } Introduction to Livestock 1 February 2015 { } Glossary of Grazing Terms February 2015 2 A Accessibility (n) The ease with which an area of vegetation can be accessed for grazing. Acre (n) A unit of
{ } Introduction to Livestock 1 February 2015 { } Glossary of Grazing Terms February 2015 2 A Accessibility (n) The ease with which an area of vegetation can be accessed for grazing. Acre (n) A unit of
Tropical Horticulture HORT 423
 Initial Student Questionaire - 2003 HORT 423 Tropical Horticulture NAME----------------------------------------------------------------- Tropical Horticulture HORT 423 Telephone number: email address:
Initial Student Questionaire - 2003 HORT 423 Tropical Horticulture NAME----------------------------------------------------------------- Tropical Horticulture HORT 423 Telephone number: email address:
Founded in Houston, TX as a biotechnological, innovative
 REZFREE INC. Founded in Houston, TX as a biotechnological, innovative result based company, Rezfree Inc. discovers, develops and commercializes innovative products in agriculture. Rezfree Inc. is committed
REZFREE INC. Founded in Houston, TX as a biotechnological, innovative result based company, Rezfree Inc. discovers, develops and commercializes innovative products in agriculture. Rezfree Inc. is committed
Protecting Pollinators
 Protecting Pollinators A how-to-help guide for non-beekeepers. Narrated by Valerie Duever Member of the Missouri Farm Bureau Beekeeper/Pollinator Workgroup Missouri Farm Bureau Beekeeper/Pollinator Workgroup
Protecting Pollinators A how-to-help guide for non-beekeepers. Narrated by Valerie Duever Member of the Missouri Farm Bureau Beekeeper/Pollinator Workgroup Missouri Farm Bureau Beekeeper/Pollinator Workgroup
An overview of horticultural crops with emphasis on vegetables production in Ethiopia. A country report
 An overview of horticultural crops with emphasis on vegetables production in Ethiopia A country report Presented at the workshop Tuta absoluta: Meeting the challenge of the tomato leafminer By Endale Gebre
An overview of horticultural crops with emphasis on vegetables production in Ethiopia A country report Presented at the workshop Tuta absoluta: Meeting the challenge of the tomato leafminer By Endale Gebre
How can cover crops contribute to a healthy garden?
 Cover Crops for Tompkins County Gardens What are cover crops? Cover crops are close-growing crops planted either in rotation with food crops, or between food crops to enrich the soil. Before planting the
Cover Crops for Tompkins County Gardens What are cover crops? Cover crops are close-growing crops planted either in rotation with food crops, or between food crops to enrich the soil. Before planting the
Cover Crops in Vegetable Production Systems
 Cover Crops in Vegetable Production Systems T. Casey Barickman, Ph.D. Assistant Research/Extension Professor North Mississippi Research and Extension Center What is a Cover Crop A crop whose main purpose
Cover Crops in Vegetable Production Systems T. Casey Barickman, Ph.D. Assistant Research/Extension Professor North Mississippi Research and Extension Center What is a Cover Crop A crop whose main purpose
Intellectual Property Protection for Plants in U.S.
 Intellectual Property Protection for Plants in U.S. Plant Variety Protection Awareness Program Myanmar December 5, 2016 Kitisri Sukhapinda Attorney Advisor Office of Policy and International Affairs 2
Intellectual Property Protection for Plants in U.S. Plant Variety Protection Awareness Program Myanmar December 5, 2016 Kitisri Sukhapinda Attorney Advisor Office of Policy and International Affairs 2
Biology Booster. Higher Yields Improved Soil Health Sustainable Farming
 Biology Booster Higher Yields Improved Soil Health Sustainable Farming Conventional high intensity farming has led to the destruction of natural soil ecosystems. Such a decline in the soil biology leads
Biology Booster Higher Yields Improved Soil Health Sustainable Farming Conventional high intensity farming has led to the destruction of natural soil ecosystems. Such a decline in the soil biology leads
Farm Eligibility Table. Fire & Allied. Classification. FL/GL Auto
 Animal - General Farms, Primarily Livestock and Animal Specialties - general animal specialty and livestock farms; general livestock and animal specialty farms. See also - (Animal Specialty)/(Livestock)/
Animal - General Farms, Primarily Livestock and Animal Specialties - general animal specialty and livestock farms; general livestock and animal specialty farms. See also - (Animal Specialty)/(Livestock)/
CHAPTER 6: Irrigation scheduling
 Pressurized Irrigation Techniques 6.1 CHAPTER 6: Irrigation scheduling Irrigation scheduling is one of the factors that influence the agronomic and economic viability of small farms. It is important for
Pressurized Irrigation Techniques 6.1 CHAPTER 6: Irrigation scheduling Irrigation scheduling is one of the factors that influence the agronomic and economic viability of small farms. It is important for
Environmental influences on plant health
 Environmental influences on plant health Wind Poor crop on poor soil in an exposed environment Healthy crop on fertile deep soil in a natural environment A healthy soil is the basis for healthy plants
Environmental influences on plant health Wind Poor crop on poor soil in an exposed environment Healthy crop on fertile deep soil in a natural environment A healthy soil is the basis for healthy plants
Global Status of Commercialized Biotech Crops. International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications
 Global Status of Commercialized Biotech Crops International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications Outline of Presentation Introduction Global Perspective and Status Trends and Indicators
Global Status of Commercialized Biotech Crops International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications Outline of Presentation Introduction Global Perspective and Status Trends and Indicators
PLANTS for Food and Fiber UNIT TEST
 PLANTS for Food and Fiber UNIT TEST Student Name Class Plant structures and Life Processes 1. The largest group of plants in the world is seed plants. The structure in seed plants that function to produce
PLANTS for Food and Fiber UNIT TEST Student Name Class Plant structures and Life Processes 1. The largest group of plants in the world is seed plants. The structure in seed plants that function to produce
CROPPING SYSTEM LECTURE 7
 CROPPING SYSTEM LECTURE 7 What is a cropping system? A cropping system refers to growing a combination of crops in space and time. It comprises all cropping patterns grown on the farm and their interaction
CROPPING SYSTEM LECTURE 7 What is a cropping system? A cropping system refers to growing a combination of crops in space and time. It comprises all cropping patterns grown on the farm and their interaction
IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA
 IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA Rozhan Abu Dardak Director General Office, MARDI Head Quarters, Persiaran MARDI-UPM 43400 Serdang. E-mail: rozhan@mardi.gov.my
IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA Rozhan Abu Dardak Director General Office, MARDI Head Quarters, Persiaran MARDI-UPM 43400 Serdang. E-mail: rozhan@mardi.gov.my
Crops. Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide
 Crops Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide Crops The purpose of irrigation is to supplement natural precipitation so that the moisture
Crops Information contained in this presentation came from the National Engineering Handbook Irrigation Guide Crops The purpose of irrigation is to supplement natural precipitation so that the moisture
Organic Vegetable Intensive. Michael Bomford
 Organic Vegetable Intensive Michael Bomford Sir Albert Howard inspired by Eastern agriculture Small farms Mix of people, plants and animals; wastes recycled as nutrients Human and animal labor, not machines
Organic Vegetable Intensive Michael Bomford Sir Albert Howard inspired by Eastern agriculture Small farms Mix of people, plants and animals; wastes recycled as nutrients Human and animal labor, not machines
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming. Introduction. Outline. Introduction. Introduction
 Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-859-2044 byerspl@missouri.edu Upcoming Programs of Interest FSMA trainings, 1/29 (Springfield),
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-859-2044 byerspl@missouri.edu Upcoming Programs of Interest FSMA trainings, 1/29 (Springfield),
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming
 Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-859-2044 byerspl@missouri.edu Upcoming Programs of Interest FSMA trainings, 1/29 (Springfield),
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension 417-859-2044 byerspl@missouri.edu Upcoming Programs of Interest FSMA trainings, 1/29 (Springfield),
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON D.C., 20460
 MEMORANDUM UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON D.C., 20460 OFFICE OF PREVENTION, PESTICIDES AND TOXIC SUBSTANCES SUBJECT: FROM: BEAD s Planned Impact Assessments on Agricultural Sites
MEMORANDUM UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON D.C., 20460 OFFICE OF PREVENTION, PESTICIDES AND TOXIC SUBSTANCES SUBJECT: FROM: BEAD s Planned Impact Assessments on Agricultural Sites
ECOROST ТЕL.: +7 (4912) LIQUID HUMIC FERTILIZER
 RECOMMENDATIONS ON THE USE OF IN CROP GROWING ТЕL.: +7 (4912) 51-18-59 LIQUID HUMIC FERTILIZER EKOROST.RU.RZN@YANDEX.RU CETRUE AND PULSE CROPS Wheat, rye, barley, oats +10 L of 400 ml of per of 1. The
RECOMMENDATIONS ON THE USE OF IN CROP GROWING ТЕL.: +7 (4912) 51-18-59 LIQUID HUMIC FERTILIZER EKOROST.RU.RZN@YANDEX.RU CETRUE AND PULSE CROPS Wheat, rye, barley, oats +10 L of 400 ml of per of 1. The
FOLTRON Global Training Module
 FOLTRON Global Training Module Biostimulant to enhance vegetative growth 1. Presentation & Composition: - Liquid formula for foliar spray - Contents: Folcisteine (0.275%) Macronutrients: N (ammonium 5.6%);
FOLTRON Global Training Module Biostimulant to enhance vegetative growth 1. Presentation & Composition: - Liquid formula for foliar spray - Contents: Folcisteine (0.275%) Macronutrients: N (ammonium 5.6%);
TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: TIPS 2: TIPS 3: TIPS 4 TIPS 5
 TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: To control Rhinocerous Beetle in coconut, 5 kg cowdung and 1kg Castor can be mixed in water and kept in pots at the 4 corners of the Farm. This will attract the Beetles in to the
TIPS OF THE DAY TIPS 1: To control Rhinocerous Beetle in coconut, 5 kg cowdung and 1kg Castor can be mixed in water and kept in pots at the 4 corners of the Farm. This will attract the Beetles in to the
1. LEGAL STATUS OF THE FARM (to confirm, write ``x``)
 69 1 LEGAL STATUS OF THE FARM (to confirm write ``x``) 1 LEGAL PERSON 3 FAMILY FARM (OPG) 2 FARM INFORMATION (to confirm write ``x``) 4 Farm is no longer engaged in agricultural production 8 Other (out
69 1 LEGAL STATUS OF THE FARM (to confirm write ``x``) 1 LEGAL PERSON 3 FAMILY FARM (OPG) 2 FARM INFORMATION (to confirm write ``x``) 4 Farm is no longer engaged in agricultural production 8 Other (out
Crop Statistics in Germany
 Crop Statistics in Germany Follow up regional workshop on crop statistics Zagreb, 17 18 April 2008 Ute Walsemann Head of Subdivision Land use and Crop statistics Federal Statistical Office of Germany Federal
Crop Statistics in Germany Follow up regional workshop on crop statistics Zagreb, 17 18 April 2008 Ute Walsemann Head of Subdivision Land use and Crop statistics Federal Statistical Office of Germany Federal
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming. Outline. Introduction. Introduction. Inventory Your Resources. Introduction
 Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Horticulture Field Specialist University of Missouri Extension Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine the cropping system Considerations
Profitable Specialty Crop Farming Patrick Byers Horticulture Field Specialist University of Missouri Extension Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine the cropping system Considerations
B. Sc. (Ag.) Hons. Part- II Batch A-- AGRON 4211 Field Crops-I (Kharif) 3(2+1) Name of teacher Dr. L.R.Yadav Lecture schedule :Theory S.No.
 B. Sc. (Ag.) Hons. Part- II Batch A-- AGRON 4211 Field Crops-I (Kharif) 3(2+1) Name of teacher Dr. L.R.Yadav Lecture schedule :Theory S.No. Date of Topic lectures 1 Pearl millet-importance, origin, distribution,production,
B. Sc. (Ag.) Hons. Part- II Batch A-- AGRON 4211 Field Crops-I (Kharif) 3(2+1) Name of teacher Dr. L.R.Yadav Lecture schedule :Theory S.No. Date of Topic lectures 1 Pearl millet-importance, origin, distribution,production,
Sub-theme 1.2. Plant Production and Health
 Sub-theme 1.2. Plant Production and Health Rationale Ethiopia has diverse agro-ecologies, agro-biodiversity and water resources, and great potential for agricultural production including food security
Sub-theme 1.2. Plant Production and Health Rationale Ethiopia has diverse agro-ecologies, agro-biodiversity and water resources, and great potential for agricultural production including food security
Lecture 13 - Different methods of Nematode Control
 Lecture 13 - Different methods of Nematode Control Plant parasitic nematodes can be controlled by several methods. The nematode control aims to improve growth, quality and yield by keeping the nematode
Lecture 13 - Different methods of Nematode Control Plant parasitic nematodes can be controlled by several methods. The nematode control aims to improve growth, quality and yield by keeping the nematode
Balancing the Nitrogen Budget
 University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
University of California Tulare County Cooperative Extension Balancing the Nitrogen Budget Bill Peacock Pub. NG2-96 Sources of nitrogen in the soil/water system other than fertilizer should be considered
Farm Profile. Name: Mailing Address: Phone: Cell phone: County (or counties) in which you farm:
 Farm Profile This profile will provide the basic information for understanding your farm operation and will give you a head start on pulling together the information you will need for applying to federal
Farm Profile This profile will provide the basic information for understanding your farm operation and will give you a head start on pulling together the information you will need for applying to federal
Tropical Agro-Ecosystems
 ropical Agro-Ecosystems to Dry ropical Vegetation Acid soils Alkaline soils From ain Forests to Deserts 3000+ - 1000 mm 12-10 months 2000-500 mm 9-4 months 500-0 mm 4-0 months to Dry ropical Vegetation
ropical Agro-Ecosystems to Dry ropical Vegetation Acid soils Alkaline soils From ain Forests to Deserts 3000+ - 1000 mm 12-10 months 2000-500 mm 9-4 months 500-0 mm 4-0 months to Dry ropical Vegetation
General Vegetable Gardening Practices. Consider the Location. Consider the Location. Black Walnut Toxicity
 General Vegetable Gardening Practices Level 2 Master Gardener Volunteer Training - February 19, 2013 Consider the Location Craig Saxe UW-Extension, Juneau Co. 211 Hickory Street Mauston WI 53948 (608)
General Vegetable Gardening Practices Level 2 Master Gardener Volunteer Training - February 19, 2013 Consider the Location Craig Saxe UW-Extension, Juneau Co. 211 Hickory Street Mauston WI 53948 (608)
International Research and Development. Designing a Crop Rotation Plan with Farmers
 International Research and Development Designing a Crop Rotation Plan with Farmers University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, June, 2011 Definition A system of farming in which a regular succession of different
International Research and Development Designing a Crop Rotation Plan with Farmers University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, June, 2011 Definition A system of farming in which a regular succession of different
Details of Training Programmes Soil Sampling and its importance 28 19
 Details of Training Programmes 200- Training Area 04.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 28 2 Soil science 0.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 29 3 22.02.20 Soil Sampling and its importance 28
Details of Training Programmes 200- Training Area 04.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 28 2 Soil science 0.2.200 Soil Sampling and its importance 29 3 22.02.20 Soil Sampling and its importance 28
General Vegetable Gardening Practices
 General Vegetable Gardening Practices Level 2 Master Gardener Volunteer Training - February 19, 2013 Craig Saxe UW-Extension, Juneau Co. 211 Hickory Street Mauston WI 53948 (608) 847-9329 craig.saxe@ces.uwex.edu
General Vegetable Gardening Practices Level 2 Master Gardener Volunteer Training - February 19, 2013 Craig Saxe UW-Extension, Juneau Co. 211 Hickory Street Mauston WI 53948 (608) 847-9329 craig.saxe@ces.uwex.edu
JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection
 JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection This document is the first version of the JECAM Guidelines for field data collection. It has been prepared based on 24 JECAM
JECAM Guidelines for cropland and crop type definition and field data collection This document is the first version of the JECAM Guidelines for field data collection. It has been prepared based on 24 JECAM
PLANT ENTERPRISES PRODUCTION
 s COTTON Lint - Non-irrigated 11,539.0 910.00 10,500,490 lbs. $5,460,255 Seed - Non-irrigated 11,539.0 1,456.00 16,800,784 lbs. $924,043 Cotton () 9 11,539.0 $6,384,298 FORESTRY Pulpwood Hardwood 44,476
s COTTON Lint - Non-irrigated 11,539.0 910.00 10,500,490 lbs. $5,460,255 Seed - Non-irrigated 11,539.0 1,456.00 16,800,784 lbs. $924,043 Cotton () 9 11,539.0 $6,384,298 FORESTRY Pulpwood Hardwood 44,476
Volume -1, Issue-4 (October-December), 2013 Available online at popularkheti.info
 Popular Kheti Volume -1, Issue-4 (October-December), 2013 Available online at www.popularkheti.info 2013 popularkheti.info Intercropping: An Alternative Pathway for Sustainable Agriculture Priyanka Gautam
Popular Kheti Volume -1, Issue-4 (October-December), 2013 Available online at www.popularkheti.info 2013 popularkheti.info Intercropping: An Alternative Pathway for Sustainable Agriculture Priyanka Gautam
Sunlight. Air. The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth.
 Sunlight The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth. Sunlight is important on a farm, because the growing plants require the sun or a source of light energy to make
Sunlight The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth. Sunlight is important on a farm, because the growing plants require the sun or a source of light energy to make
Sorghum grown under poor management
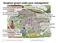 Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Sorghum grown under poor management Compaction of soil with tracking animals and tractors Use of poor seeds No hedges to protect the soil from erosion by wind Burning of crop residues or overgrazing of
Getting Started in Produce Farming. Outline. Introduction. Introduction. Inventory Your Resources. Introduction
 Getting Started in Produce Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine the cropping system Considerations
Getting Started in Produce Farming Patrick Byers Regional Horticulture Specialist University of Missouri Extension Outline Introduction Inventory your resources Determine the cropping system Considerations
BIOZYME Global Training Module
 BIOZYME Global Training Module Biostimulant to enhance plant and crop performance 1. Presentation & Composition: - Liquid formula for seed treatment, foliar spray, in furrow or drip irrigation application
BIOZYME Global Training Module Biostimulant to enhance plant and crop performance 1. Presentation & Composition: - Liquid formula for seed treatment, foliar spray, in furrow or drip irrigation application
Agricultural Regions
 Agricultural Regions Derwent Wittlesey s 11 Agricultural Regions Images: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:agricultural_map_by_whittlesey,_d.s.png Agriculture in the Developing World 5 types Poorer
Agricultural Regions Derwent Wittlesey s 11 Agricultural Regions Images: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:agricultural_map_by_whittlesey,_d.s.png Agriculture in the Developing World 5 types Poorer
Market opportunities for Queensland agribusiness from FTAs with China, Japan and South Korea. Queensland Production
 Market opportunities for Queensland agribusiness from FTAs with China, Japan and South Korea Queensland Production Scope Australia recently signed Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with China (June 2015), Japan
Market opportunities for Queensland agribusiness from FTAs with China, Japan and South Korea Queensland Production Scope Australia recently signed Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with China (June 2015), Japan
Organic Standards require that certain principles are observed when designing and implementing a crop rotation:
 Organic Crop Rotation Why do I need a crop rotation? A balanced rotation is the cornerstone of an organic system. It; Varies the demands on the soil Provides the nutritional requirements of each crop Limits
Organic Crop Rotation Why do I need a crop rotation? A balanced rotation is the cornerstone of an organic system. It; Varies the demands on the soil Provides the nutritional requirements of each crop Limits
Netherlands Training Placements 2017
 Dairy farming Dairy (milk cows) breeding and propagation of ornamental flowers ; modern company Arable and Field vegetables production Biological arable farming and field vegetable prod Dairy Biological
Dairy farming Dairy (milk cows) breeding and propagation of ornamental flowers ; modern company Arable and Field vegetables production Biological arable farming and field vegetable prod Dairy Biological
Cover Crops Grow Your Own Fertilizer
 Cover Crops Grow Your Own Fertilizer Overview Cover crops have many potential benefits in agriculture. They can improve numerous soil physical, chemical, and biological characteristics, improve water retention
Cover Crops Grow Your Own Fertilizer Overview Cover crops have many potential benefits in agriculture. They can improve numerous soil physical, chemical, and biological characteristics, improve water retention
Water Management in Horticultural Crops
 CHAPTER 7 Water Management in Horticultural Crops OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Learn about water management and various methods of irrigation including micro irrigation
CHAPTER 7 Water Management in Horticultural Crops OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Learn about water management and various methods of irrigation including micro irrigation
Netaji IAS. Civil Service Mains Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2001
 www.netajiias.com 1 Netaji IAS Civil Service Mains Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2001 Click here to download PDF Paper-I Section A 1. Write short notes in about 200 words each on any three of the
www.netajiias.com 1 Netaji IAS Civil Service Mains Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2001 Click here to download PDF Paper-I Section A 1. Write short notes in about 200 words each on any three of the
M. Sc. (Ag.) Horticulture (Vegetable Science)
 1 st Semester M. Sc. (Ag.) Horticulture (Vegetable Science) 1. Spices and Plantation Crops HORT 701 2 0 2 = 3 2. Principles & Technology of Seed Production of Vegetable Crops HORT 703 2 0 2 = 3 Basic Supporting
1 st Semester M. Sc. (Ag.) Horticulture (Vegetable Science) 1. Spices and Plantation Crops HORT 701 2 0 2 = 3 2. Principles & Technology of Seed Production of Vegetable Crops HORT 703 2 0 2 = 3 Basic Supporting
Archival copy: for current recommendations see or your local extension office.
 Fact Sheet RF-AA006 Vegetable Crops 1 George Hochmuth 2 VEGETABLE CROPS SERVICE PROGRAMS Non-parasitic Disorders Clinics for Vegetable Crops This service diagnoses disorders (other than parasitic diseases,
Fact Sheet RF-AA006 Vegetable Crops 1 George Hochmuth 2 VEGETABLE CROPS SERVICE PROGRAMS Non-parasitic Disorders Clinics for Vegetable Crops This service diagnoses disorders (other than parasitic diseases,
Preserve the Rain Forest
 The Rain Forests are very special places on Earth. This teaching module discusses the ecology, value and preservation of the World s Rain Forests 1. Importance of the Rain Forest 2. How the Rain Forests
The Rain Forests are very special places on Earth. This teaching module discusses the ecology, value and preservation of the World s Rain Forests 1. Importance of the Rain Forest 2. How the Rain Forests
Mississippi Fresh Produce Availability Calendar
 Mississippi Fresh Produce Availability Calendar Product Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec FRUITS Apples 15th ------- 15th Blueberries 25th ------- 25th Muscadines 5th 15th Peaches 15th -------
Mississippi Fresh Produce Availability Calendar Product Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec FRUITS Apples 15th ------- 15th Blueberries 25th ------- 25th Muscadines 5th 15th Peaches 15th -------
Plant Breeding as an integral part of Sustainable Agriculture
 2 Plant Breeding as an integral part of Sustainable Agriculture Dr. Dirk Zimmermann Sustainable Agriculture Campaigner Greenpeace Germany International Cotton Conference, Bremen, 17.03.2016 dirk.zimmermann@greenpeace.de
2 Plant Breeding as an integral part of Sustainable Agriculture Dr. Dirk Zimmermann Sustainable Agriculture Campaigner Greenpeace Germany International Cotton Conference, Bremen, 17.03.2016 dirk.zimmermann@greenpeace.de
Executive Summary. Fruits and Berries
 Executive Summary This report provides historical perspective, including acreage, operation count, cash receipts, production and yields, for Missouri-grown specialty crops. Data are reported for all facets
Executive Summary This report provides historical perspective, including acreage, operation count, cash receipts, production and yields, for Missouri-grown specialty crops. Data are reported for all facets
ORGANIC PLANT PRODUCTION
 TS24(EC)V03en_Plant Production ORGANIC PLANT PRODUCTION Guidelines no. 24: Plant Production & Organic Farming Ecocert Organic Standard (EOS) 1 I. Rules for organic conversion If you have not started the
TS24(EC)V03en_Plant Production ORGANIC PLANT PRODUCTION Guidelines no. 24: Plant Production & Organic Farming Ecocert Organic Standard (EOS) 1 I. Rules for organic conversion If you have not started the
THE MYSTERY OF THE FREAK POTATOES & VEGETABLES. Amber Vallotton VCE-Rockingham
 THE MYSTERY OF THE FREAK POTATOES & VEGETABLES Amber Vallotton VCE-Rockingham Can you come and look at my potatoes Something really STRANGE is going on!! Healthy potato plants Abnormal Leaf Expansion Leaf
THE MYSTERY OF THE FREAK POTATOES & VEGETABLES Amber Vallotton VCE-Rockingham Can you come and look at my potatoes Something really STRANGE is going on!! Healthy potato plants Abnormal Leaf Expansion Leaf
Affordability of Nutritious Diets in Africa: Mainstreaming New Metrics in Ghana s food price monitoring institutions
 Affordability of Nutritious Diets in Africa: Mainstreaming New Metrics in Ghana s food price monitoring institutions Daniel Bruce SARPONG University of Ghana Anna Herforth Columbia University Collaborators:
Affordability of Nutritious Diets in Africa: Mainstreaming New Metrics in Ghana s food price monitoring institutions Daniel Bruce SARPONG University of Ghana Anna Herforth Columbia University Collaborators:
Integrated Management of Fruit fly and Its Impact on Yield of Crops with Effective Microorganisms (A Case Study)
 Integrated Management of Fruit fly and Its Impact on Yield of Crops with Effective Microorganisms (A Case Study) K. Hamamoto 1 and H. Nago 2 1 Hamamoto Farms, P.O. Box 142, Kurtistown, Hawaii, 9676 2 EM
Integrated Management of Fruit fly and Its Impact on Yield of Crops with Effective Microorganisms (A Case Study) K. Hamamoto 1 and H. Nago 2 1 Hamamoto Farms, P.O. Box 142, Kurtistown, Hawaii, 9676 2 EM
Drought and salinity in crop production. February 14 th 2017, Greet Blom-Zandstra
 Drought and salinity in crop production February 14 th 2017, Greet Blom-Zandstra Outline Drought and salinity Plant responses Farm management strategies WUR projects in cooperation with public and private
Drought and salinity in crop production February 14 th 2017, Greet Blom-Zandstra Outline Drought and salinity Plant responses Farm management strategies WUR projects in cooperation with public and private
Organic Foods: Understanding Organic Food Labels, Benefits, and Claims
 Organic Foods: Understanding Organic Food Labels, Benefits, and Claims Organic food has become very popular. But navigating the maze of organic food labels, benefits, and claims can be confusing. Is organic
Organic Foods: Understanding Organic Food Labels, Benefits, and Claims Organic food has become very popular. But navigating the maze of organic food labels, benefits, and claims can be confusing. Is organic
Advanced Biology: Bahe & Deken. Agriculture & Nutrition. Chapter 9. Text Page
 Agriculture & Nutrition Chapter 9 Text Page - 107 - 9.1 Strategy of Agriculture What does it take to put food on the table at your house? Think about this question in terms of economics, energy, and ecology.
Agriculture & Nutrition Chapter 9 Text Page - 107 - 9.1 Strategy of Agriculture What does it take to put food on the table at your house? Think about this question in terms of economics, energy, and ecology.
Sampoorna International Institute of Agri Science & Horticultural Technology
 science & Technology or Table- for B.Sc. Honors in Horticulture science & Technology. I Curriculum TABLE : B.Sc. HONORS IN AGRICULTURE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Title Introductory Agriculture Principles of
science & Technology or Table- for B.Sc. Honors in Horticulture science & Technology. I Curriculum TABLE : B.Sc. HONORS IN AGRICULTURE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Title Introductory Agriculture Principles of
The Green Revolution
 The Green Revolution Since the 1950s, most increases in global food production have come from increased yields per unit area of cropland. This green revolution has been brought about through the development
The Green Revolution Since the 1950s, most increases in global food production have come from increased yields per unit area of cropland. This green revolution has been brought about through the development
Benefits of the UPOV System of Plant Variety Protection for farmers and growers: U.S. Perspective Bangkok, Thailand February 23, 2017
 Benefits of the UPOV System of Plant Variety Protection for farmers and growers: U.S. Perspective Bangkok, Thailand February 23, 2017 Kitisri Sukhapinda, Ph.D., J.D. Office of Policy and International
Benefits of the UPOV System of Plant Variety Protection for farmers and growers: U.S. Perspective Bangkok, Thailand February 23, 2017 Kitisri Sukhapinda, Ph.D., J.D. Office of Policy and International
Green Manuring. Reviving Our Time Tested Practices
 Green Manuring Reviving Our Time Tested Practices What Is Green Manuring This is a technique where we grow the manure in the field itself and plough it back in. Traditionally, we grow a green manure crop
Green Manuring Reviving Our Time Tested Practices What Is Green Manuring This is a technique where we grow the manure in the field itself and plough it back in. Traditionally, we grow a green manure crop
NQF Level: 1 US No:
 NQF Level: 1 US No: 116199 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Physiology Assessor:............................................ Workplace / Company:.................................. Commodity:...................
NQF Level: 1 US No: 116199 Assessment Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Physiology Assessor:............................................ Workplace / Company:.................................. Commodity:...................
10/19/ Not volatile and do not photo-decompose. -Ionic moderately adsorbed to soil. -Problems with ground water contamination
 Angela R. Post PLNT 4013 Principles of Weed Science Many different chemical groups Many of our most important herbicides Uses in crop and non-crop situations Applied PPI, Pre, Post, Post-directed Introduced
Angela R. Post PLNT 4013 Principles of Weed Science Many different chemical groups Many of our most important herbicides Uses in crop and non-crop situations Applied PPI, Pre, Post, Post-directed Introduced
Activity 27 GROWING PLANTS. How long does it take for a seed to sprout and what can I do to help it grow into a healthy plant?
 Activity 27 GROWING PLANTS STUDY QUESTION: THE ACTIVITY: How long does it take for a seed to sprout and what can I do to help it grow into a healthy plant? In this activity children plant seeds in two
Activity 27 GROWING PLANTS STUDY QUESTION: THE ACTIVITY: How long does it take for a seed to sprout and what can I do to help it grow into a healthy plant? In this activity children plant seeds in two
AGRIBUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES
 AGRIBUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AGRICULTURE PROMOTION CENTRE (CEPAGRI) 1 Content Introduction: Mozambique s economy & agricultural sector Principal crops Market Opportunities Agri-businesses
AGRIBUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AGRICULTURE PROMOTION CENTRE (CEPAGRI) 1 Content Introduction: Mozambique s economy & agricultural sector Principal crops Market Opportunities Agri-businesses
2/11/2015. Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program for 2015 and Subsequent Crop years
 Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program for 2015 and Subsequent Crop years 1 NAP Overview Reauthorized by the 2014 Farm Bill Provides financial assistance to producers of noninsurable crops to protect
Noninsured Crop Disaster Assistance Program for 2015 and Subsequent Crop years 1 NAP Overview Reauthorized by the 2014 Farm Bill Provides financial assistance to producers of noninsurable crops to protect
Permaculture Guidebook 2008 edition Table of Contents
 Aim of the guidebook 6 How to use the guidebook 6 Some ideas for implementing techniques 8 01 Ethics and principles of permaculture 19 1. Care for the land Kuidadu ba rai 21 2. Care for the people Kuidadu
Aim of the guidebook 6 How to use the guidebook 6 Some ideas for implementing techniques 8 01 Ethics and principles of permaculture 19 1. Care for the land Kuidadu ba rai 21 2. Care for the people Kuidadu
