Dimensions of Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development of Assam
|
|
|
- Sydney Peregrine Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jour. Ind. Soc. Ag. Statistics 57 (Special Volume), 2004: Dimensions of Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development of Assam S.C. Rai and V.K. Bhatia Indian Society ofagricultural Statistics, New Delhi SUMMARY The status of of different districts of Assam has been estimated with the help of composite index based on optimum combination of forty-eight al indicators. The data on various socio-economic indicators of the year 2001 for different districts have been used in the study. The level of is separately estimated for agricultural sector, industrial sector, infrastructural facilities and overail socio-economic sectors. The district of Sonitpur is found to rank first and the district of NC Hills is on the last position in the overall socio-economic. There is positive significant association between the levels of in agriculture and.socio-economic fields. Wide disparities in the levels of have been observed in different districts of the State. For bringing about uniform regional in the State, model districts have been identified and potential targets for various indicators have been estimated for low developed districts. Key-words : Regional disparities, Potential targets, Composite index, Model districts, Developmental indicators. 1. Introduction Developmental programmes were taken up in the country in a planned way through various Five Year Plans with the main objective of enhancing the quality of life of people by providing the basic necessities of life as well as effecting improvement in their social and economic well being. Social is not a pre-determined stage but it is a continuous process of improvement of levels of living. Although resource transfers are being executed in the backward regions, it has been observed that the regional disparities in terms of economic is not declining over time. For focusing the attention of the scientists, planners, policy makers and administrators on the level of disparities in economic, a seminar was organized jointly by the Planning Commission, Government of India and State Planning Institute, Government of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow during Realizing the importance and seriousness of the problems of estimation of level
2 REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVEWPMENT OF ASSAM /79 of, the Indian Society of Agricultural Statistics conducted a series of studies for estimating the level of of different states. After analyzing the data on socio-economic variables of major 17 states for the year and ([1], [2]), it was felt that the regional variability in socioeconomic could better be explained through analyzing the data of district level of various states. The district level data on socia-economic variables have been analyzed in respect of the states of Orissa ([3], [4]), A.P. [5], Kerala [6], V.P. [7], Maharashtra [8], Karnataka [9], combined analysis of districts of Southern Region [10], Tamil Nadu [11] and M.P. [13]. The present study has been undertaken in the state of Assam where an attempt has been made to evaluate the level of in agricultural, industrial, infrastructural and overall socio-economic sectors for different districts. Assam is predominately rural and agrarian. As per 2001 Census, more than 80 per cent people of the State live in rural areas. The decadal growth rate of population from 1991 to 200I is about 19 per cent whereas. the growth rate of the population of the country during this period is about 21 per cent. The literacy rate in Assam is about 64 per cent against the all India literacy rate of about 65 per cent. The literacy rate among the female of the State is about 56 per cent and among male about 72 per cent. The estimatep annual birth rate in the State is about 27 against the death rate of 9.7 and infant mortality rate 76. The district has been taken as the unit of analysis. It would be of interest to measure the level of at district level since there has been a growing consensus about the need of district level planning in the State. A knowledge of the stages of at district level will help in identifying where a given district stands in relation to others. The study will also throw light on the relationships between the levels of of different sectors of economy of the State. An attempt will be made to identify the model districts for fixing up the potential targets of various al indicators of low developed districts. 2. Developmental Indicators Each district faces situational factors unique to it as well as common administrative and financial problems. Administrative and financial problems along with the situational factors common to all the districts have been included in the study for estimating the level of. The composite indices of for different districts have been obtained on the basis of following indicators of the year Percentage forest area 2. Percentage area not available for cultivation 3. Percentage uncultivated land
3 180 JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN SOCIElY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS 4. Percentage net area sown 5. Area sown more than once 6. Area under HYV of paddy 7. Fertilizer consumption 8. Area irrigated 9. Irrigation potential created 10. Number of seedling planted under social forestry 11. Fish production 12. Number of cattle 13. Number of buffaloes 14. Number of sheep 15. Number of goats 16. Number of pigs 17. Area under silk worm 18. Production of silk worm 19. Number of trainees in handloom training centre 20. Production of cloth 21. Number of weavers engaged whole time 22. Distribution of registered factories 23. Number of small scale industries 24. Registered area under tea 25. Number of motor vehicles on road 26. Road length per '00 sq. km. of area 27. Number of employment exchange 28. Registration of employment exchange 29. Number of hospitals 30. Number of beds in hospitals 31. Immunization performance 32. Number of teachers in primary schools 33. Total literacy rate 34. Female literacy rate 35. Incidence of crime reported 36. Per capita gross domestic product
4 REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVEWPMENT OF ASSAM Total allocation for DRDA 38. Percentage of expenditure over total final available 39. Number of habitations providing with drinking water 40. Flood affected area 41. Total value damaged due to flood 42. Sex ratio 43. Population density per sq. km. 44. Decadal growth rate of population ( ) 45. Number of male workers 46. Number of female workers 47. Percentage of S.C. population 48. Percentage of S.T. population A total of forty-eight al indicators depicting the progress of agricultural, industrial, infrastructural facilities and overall socio-economic have been included in the analysis. These indicators may not form an all inclusive list but these are the major interactive components of socio-economic in the State. 3. Estimation oflevel ofdevelopment and Fixation ofpotential Targets Indicators of are recorded in different units of measurement and they come from different population distributions. Hence the values of these indicators are not quite suitable for simple addition in estimating the level of. The values of the indicators are transformed in such a way that the transformed variables follow the standard normal distribution. Let f. be the 1 observed values of the indicators (i = 1, 2,..., n districts) and (j = 1, 2,..., k indicators). x -x Now Xij is transformed to Zij as Zij = IJ Sj Where Xj =mean ofjth indicator and Sj =S.D. ofjth indicator The best values of the transformed variables for each indicator (maximum/minimum value depending upon the direction of the impact of indicator on ) are identified and deviation of the transformed variables from their best value is obtained. The statistical technique given by Narain et al. ([4], [11]) is applied to construct the composite index of. The composite indices have been obtained for each district J
5 182 JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN SOCIETY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS separately in respect of agricultural, industrial. infrastructural and socio-economic. The value of the composite index is non-negative and it lies between 0 and 1. A value close to 0 indicates higher level of and value close to 1 indicates low level of. The al distances based on all the indicators are obtained for each pair of districts and the model districts have been identified on the basis of composite index of and the al distances. Model districts are better developed districts and the best value of the indicators of model districts are taken as potential targets of al indicators. 4.1 The Level of Oevelopment 4. Results and Discussion The composite indices of have been worked out for different districts separately for agricultural sector, industrial sector. infrastructural service sector and overall socio-economic sector. The districts have been ranked on the basis of al indices. The composite indices of along with the district ranks are presented in Table 1. It may be seen from the table that the district of Sonitpur was ranked first and district of NC Hills was ranked last in the overall socio-economic. The values of composite indices varied from 0.72 to In case of agricultural, the district of Nagaon occupied the first position and the district of N.C. Hills was on the last position. The composite indices varied from 0.46 to T.he district of Karnrup was placed on the first position whereas the district of Hailakandi was on the last place in industrial. The values of composite indices varied from 0.55 to In case of infrastructural facilities. the district of Karbi Anlong was on the first position and the district of HC Hills was on the last place. The composite indices varied from 0.70 to In case of socio-economic sector, three most developed districts in the State are Sonitpur. Karbi Anglong and Lakhimpur. 4.2 Relative Share of Area and Population under Different Level of Development For classificatory analysis, a simple ranking of districts on the basis of composite indices is sufficient but a suitable classification of the districts formed on the basis of mean and standard deviation of the composite indices will provide a more meaningful characterization of various stages of. For relative comparison, it appears appropriate to assume the districts having composite index less than or equal to (Mean - SO) as highly developed districts and the districts having composite index greater than (Mean + SO) as low developed districts. Similarly. districts with composite index lying between
6 REGIONAL DlSPARrrlES IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTOFASSAM 183 (Mean and Mean - SD) are cjassified as middle level developed and districts with composite index lying between (Mean and Mean + SD) are classified as developing districts. Table 1. Composite indices of S.No. District 01 Dhubri 02 Kokrajhar 03 Bongaigaon 04 Goalpara 05 Barpeta 06 Nalbari 07 Kamrup 08 Darrang 09 Sonitpur 10 Lakhimpur 11 Dhemaji 12 Morigaon 13 Nagaon 14 Golaghat 15 Jorhat 16 Sibsagar 17 Dibrugarh 18 Tinsukia 19 Karbi Anglong 20 NC Hills 21 Karimganj 22 Hailakandi 23 Cachar Agricultural C.I. IRank Industrial C.1. IRank Infrastructural C.I. IRank Socioeconomic C.1. IRank An important aspect of the study is to find out the relative share of area and population affected under various stages of in the State. The details regarding area and population under different levels of are given in Table 2 below for agricultural sector, industrial sector, infrastructural service sector and overall socio-economic sector.
7 184 JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN SOCIETY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS Table 2. Area and population under different levels of Level of No. of districts Area % Population % Agriculture High Medium Developing Low Industry High Medium Developing Low Infrastructural facilities High Medium Developing Low Socio-economic High Medium Developing Low With regard to overall socio-economic, three districts namely Sonitpur, Lakhimpur and Karbi Anglong were found to be better developed and these districts are classified as highly developed in the State. These districts cover about 23 per cent area and 13 per cent population of the State. Similarly three districts namely Kamrup, Tinsukia and N.C. Hills are observed to be low developed. These districts cover about 17 per cent area and 20 per cent population. Thirteen districts namely Kokrajhar, Bongaigaon, Goalpara, Barpeta, Nalbari, Darrang, Morigaon, Nagaon, Golaghat, Sibsagar, Dibrugarh, Karimganj and Cachar are classified as medium level developed districts. They cover about 47 per cent area and 53 per cent population of the State. The remaining four districts namely Dhubri, Dhemaji, Jorhat and Hailakandi are grouped into developing districts. They cover about 13 per cent area and 14 per cent population of the State. In agricultural, three districts namely Barpeta, Sonitpur and Nagaon are found to be better developed. They are grouped as highly developed districts. They cover about 14 per cent area and 21 per cent population of the
8 REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN SOCIO ECONOMIC DEVEWPMENT OF ASSAM 185 State. Similarly three districts namely Dhemaji, NC Hills and Hailakandi are observed to be low developed districts. They cover about 12 per cent area and 11 per cent population of the State. Nine districts namely Dhubri, Kokrajhar, Nalbari, Kamrup, Darrang, Lakhimpur, Golaghat, Jorhat and Cachar are middle level developed and they cover about 38 per cent area and 35 per cent population of the State. The remaining eight districts namely Bongaigaon, Goalpara, Morigaon, Sibsagar, Dibrugarh, Tinsukia, Karbi Anglong and Hailakandi are also low developed but these districts are having tendency to improve the level of and they can be classified as developing districts. These districts cover about 36 per cent area and 33 per cent population of the State. In the case of industrial, two districts namely Kamrup and Sonitpur are found to be highly developed and eleven districts namely Dhubri, Kokrajhar, Bongaigaon, Barpeta, Nalbari, Darrang, Nagaon, Golaghat, Sibsagar, Dibrugarh and Karbi Anglong are middle level developed. The districts of Goalpara, Lakhimpur, Morigaon, Jorhat, Tinsukia and Cachar are observed to be in the developing stage whereas the districts of Dhamagi, NC Hills, Karimganj and Hailakandi are low developed. The area and population covered under highly developed districts are 12 per cent and 16 per cent respectively whereas the area and population covered by the middle level districts are about 53 per cent and 47 per cent respectively. Developing districts cover about 21 per cent area and 22 per cent population and low developed districts occupy 14 per cent area and they cover about 15 per cent population. Infrastructural facilities are very important and they play significant role in enhancing the level of. Two districts namely Lakhimpur and Karbi Anglong are found to be highly developed in infrastructural facilities and these districts cover about 16 per cent area and 6 per cent population. Fifteen districts namely Kokrajhar, Bongaingaon, Goalpara, Barpeta, Nalbari, Darrang, Sonitpur, Dhemaji, Morigaon, Nagaon, Golaghat, Sibsagar, Dibrugarh, Karimganj and Cachar are having middle level facilities and they cover about 58 per cent area and 64 per cent population of the State. Three districts namely Dhubri, Jorhat and Hailakandi are in the developing stage and these districts cover about 9 per cent area and 12 per cent population. The remaining three districts namely Kamrup. Tinsukia and NC Hills are low developed and they cover about 17 per cent area and 18 per cent population. In order to improve the level of, infrastructural facilities should be enhanced in the rural areas. 4.3 Inter-relationship among Different Sectors of Economy For proper and effective, it is desirable that agriculture, industry, infrastrucutral facilities and overall socio-economic should prosper together. The correlation coefficients between agricultural, industrial, infrastructural facilities, socio-economic and literacy level have been worked out and presented in Table 3.
9 186 JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN SOCIElY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS Table 3. Correlation coefficients Factors Agricultural Industrial Infrastructural Socio Literacy economic Agricultural Industrial Infrastructural Socioeconomic Literacy... Significant at 0.01 probability level The correlation coefficient between agricultural and industrial is highly significant. This indicates that the area. which is well developed in agricultural sector is also better developed in the industrial sector. The significant association between agricultural and industrial s also indicates that agriculture and industry are flowering together in the State. Industries provide basic inputs for agricultural improvement and use agricultural produce as the principal raw material for producing finished goods. Agricultural is also found to be very highly associated with the socio-economic in the State. Infrastructural facilities such as electrification of villages, construction of roads, provision of medical help, enhancement in literacy level etc. are not associated with the agricultural. These facilities are also not associated with the industrial. Socioeconomic is also not associated with the industrial. Infrastructural facilities are very highly associated with the socio-economic in the State. The level of literacy is not found to affect the status of any sector in the State. Agricultural has played a positive role in improving the overall socio-economic. 4.4 Model Districts and Potential Targets for Low Developed Districts For enhancing the level of of low developed districts, model districts have been identified on the basis of composite index of and the distance between different pairs of districts. Three districts covering about 13 per cent area and 16 per cent population of the State are found to be low developed in the socio-economic field. List of model districts for the low developed districts is given in Table 4.
10 REGIONAL DISPARrrlES IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVEWPMENT OF ASSAM 187 Table 4. List of model districts for low developed districts Low developed districts NC Hills Hailakandi Tinsukia Model districts Cachar, Morigaon, Goalpara, Karimganj Karimganj, Golaghat, Sibsagar, Barpeta Dibrugarh, Morigaon, Golaghat, Barpeta In comparison with low developed districts, model districts are better developed. The best values of the. al indicators of the model districts are taken as potential targets for the low developed districts. Improvements required in different indicators for the low developed districts are presented in Table 5.. Table S. Improvements required in low developed districts S.No. Developmental indicators N.C. Hills Hailakandi Tinsukia 01 Net area sown (%) 5.2 (62.8) 34.9 (53.4) 25.2 (62.8) 02 Area under HYVP 5.0 (68.0) 26.0 (102.0) 31.0 (102.0) 03 Fertilizer consumption 1.0 (92.0) 13.0 (103.0) 61.0 (103.0) 04 Area irrigated (345.0) 8.0 (8199.0) 18.0 (819.0) 05 Production of fish 1.0 (115.0) 50.0 (294.0) 53.0 (256.0) 06 No. of cattle 51.0 (428.0) (497.0) (497.0) 07 No. of buffaloes 24.0 (87.0) 34.0 (177.0) 31.0 (177.0) 08 Production of silk warm 38.0 (107.0) 2.0 (107.0) 26.0 (107.0) 09 Production of cloth 10.0 (197.0) 15.0 (197.0) 80.0 (197.0) 10 No. of weavers engaged (320.0) (320.0) (320.0) 11 No. of small scale industries (2838.0) (1242.0) (1242.0) 12 Road length 33.0 (56.0) 33.0 (67.0) 35.0 (42.0) 13 Registration in Employment 1.0 (10.0) 2.0 (10.0) 6.0 (10.0) Exchange 14 No. of hospital beds (986.0) 80.0 (368.0) (1395.0) 15 No. of teachers in primary 24.0 (38.0) 30.0 (87.0) 26.0 (44.0) schools 16 Total literacy rate 69.0 (69.0) 60.0 (75.0) 63.0 (71.0) 17 Female literacy rate 59.0 (60.0) 51.0 (68.0) 53.0 (62.0) 18 Per capita gross domestic 5.8 (16.6) 7.9 (17.0) 5.8 (16.6) product 19 Total main workers (418.0) (339.0) (339.0) Note: Figures in bracket indicate the best values of the model districts It may be seen from the above table that in al indicators, large improvements are required in the low developed districts to attain the level of model districts. However, steps should be taken to improve the al indicators in future planning. The following specific improvements are required in the low developed districts.
11 188 JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN SOCIETY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS (a) District N.C. Hills This district is low developed in agricultural and industrial sectors. Most of the areas of the district are covered by hills and forest and only 5 per cent area is net sown. Irrigation system is poor and fertilizer use is low. Improvements are needed to enhance the agricultural by creating additional irrigation potential and also popularizing the use of manure and chemical fertilizer. Developmental programmes suitable for hilly and forest area should be taken in the district. About 66 per cent population of the district belongs to SC and ST. Developmental programmes suitable to these communities should be enhanced. Literacy rate is quite high in the district. (b) District Hailakandi The district is low developed in agricultural and industrial sectors. About 48 per cent area of the district is covered by forest and about 35 per cent area is available for cultivation. Irrigation facilities are not sufficient for enhancing the agricultural production. Irrigation potential should be enhanced in the district. Medical facilities and employment opportunities are very low. Developmental programmes for creating new job opportunities should be undertaken in the district. (c) District Tinsukia Agricultural and industrial in the district is quite low. Infrastructural facilities are also poor. About 35 per cent area of the district is covered by forest and only 25 per cent area is available for cultivation. Irrigation facilities should be increased. Industrial in the district requires improvement and medical as well as transport facilities need enhancement. 5. Conclusions The broad conclusions emerging from the study are as follows (i) With reference to overall socio-economic, three districts namely Sonitpur, Karbi Anglong and Lakhimpur are found to be better developed and three districts namely NC Hills, Hailakandi and Tinsukia are observed to be low developed. (ii) In agricultural, three districts namely Nagaon. Barpeta and Sonitpur are better developed. The districts of NC Hills, Dhemaji and Hailakandi are found to be low developed. (iii) In industrial, two districts are found to be better developed and four districts are low developed. In case of infrastructural facilities, two districts are better developed and three districts are low developed. (iv) The overall socio-economic is found to be positively associated with agricultural and infrastructural facilities. The
12 REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF ASSAM 189 in agricultural and industrial sectors are also observed to be highly correlated. The literacy level has not influenced the status of in agricultural, industrial and overall socio-economic sectors. (v) It is observed that the entire part of the low developed district are not low developed but some parts are middle level or high level developed. (vi) Wide disparities in the level of have been observed in different districts of the State. (vii) In order to reduce the disparities in the level of, model districts have been identified and potential targets of various indicators of have been fixed. The low developed districts require improvement of various dimensions in the al indicators. REFERENCES [I] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1991). Statistical evaluation of on socio-economic front. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 43, [2] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1992). Evaluation of economic in India. Souvenir of 11th Economic Development Conference in Complementarity of Agriculture and Industry in Development, Instt. Trade & Industrial Development, New Delhi, [3] Narain, P., Rai, S.c. and Shanti Sarup (1992). Classification of districts based on socio-economic in Orissa. Yojana, 36, 23, [4] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1993). Evaluation of economic in Orissa. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 45, [5] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1994). Regional dimensions of socioeconomic in Andhra Pradesh. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 46, [6] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1994). Inter-districts disparities in socio-economic in Kerala. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 46, [7] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1995). Regional disparities in the levels of in Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 47, [8] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Shanti Sarup (1996). Dynamics of socio-economic in Maharashtra. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 48, [9] Narain, P., Rai, S.C. and Bhatia, V.K. (1997). Regional pattern of socioeconomic in Karnataka. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., SO, [101 Narain, P., Rai, S.c. and Bhatia, V.K. (1999). Inter district variation of in Southern Region. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 52,
13 190 JOURNAL OF THE 1NDJAN SOC1ErY OF AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS [11] Narain, P., Sharma, S.D., Rai, S.C. and Bhatia, V.K. (2000). Regional disparities in socio-economic in Tamil Nadu. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 53, [12] Narain, P., Shanna, S.D., Rai, S.C. and Bhatia, V.K. (2001). Regional dimensions of disparities in crop productivity in Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 54, [13] Narain, P., Sharma. S.D., Rai, S.c. and Bhatia, V.K. (2002). Dimensions of regional disparities in socio-economic in Madhya Pradesh. Jour. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat., 55, [14] Regional dimensions of India's economic. Proc. ofseminar held on April 22-24, 1982 sponsored by Planning Commission, Govt. of India and State Planning Institute, Govt. ofu.p. [15] Statistical Handbook Assam (2002). Directorate of Economics & Statistics, Govt. of Assam, Guwahati.
Dimensions of Socio-Economic Development in Jammu & Kashmir*
 J. Inti. Soc. Agri/. Statist. 59(3), 2005 : 243-250 Dimensions of Socio-Economic in Jammu & Kashmir* Prem Narain, S.D. Sharma, S.C. Rai and V.K. Bhatia Indian Society ofagricultural Statistics, New Delhi
J. Inti. Soc. Agri/. Statist. 59(3), 2005 : 243-250 Dimensions of Socio-Economic in Jammu & Kashmir* Prem Narain, S.D. Sharma, S.C. Rai and V.K. Bhatia Indian Society ofagricultural Statistics, New Delhi
GOVERNMENT OF ASSAM REPORT
 GOVERNMENT OF ASSAM REPORT ON AGRICULTURAL CENSUS 2010-11 ON NUMBER AND AREA OF OPERATIONAL HOLDINGS (Phase-I) DIRECTORATE OF ECONOMICS AND STATISTICS GOVERNMENT OF ASSAM GUWAHATI-28. FOREWORD Agricultural
GOVERNMENT OF ASSAM REPORT ON AGRICULTURAL CENSUS 2010-11 ON NUMBER AND AREA OF OPERATIONAL HOLDINGS (Phase-I) DIRECTORATE OF ECONOMICS AND STATISTICS GOVERNMENT OF ASSAM GUWAHATI-28. FOREWORD Agricultural
Statistical Evaluation ofsocio-economic Development of Different States in India
 1. /nd. Soc. Agril. Statist. 6/ (3), 2007: 328-335 Statistical Evaluation ofsocio-economic Development of Different States in India Prem Narain, S.D. Sharma, S.C. Rai and Y.K. Bhatia Indian Society of
1. /nd. Soc. Agril. Statist. 6/ (3), 2007: 328-335 Statistical Evaluation ofsocio-economic Development of Different States in India Prem Narain, S.D. Sharma, S.C. Rai and Y.K. Bhatia Indian Society of
Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development A Statistical Evaluation of Kashmir Valley, J&K
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. I, Issue 10/ January 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 0.485 (GIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development A Statistical
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. I, Issue 10/ January 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 0.485 (GIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development A Statistical
STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN ASIAN COUNTRIES
 STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN ASIAN COUNTRIES Bhatia, V.K. Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute Library Avenue, Pusa, New Delhi-110012 (INDIA) E-mail: vkbhatia@iasri.res.in
STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN ASIAN COUNTRIES Bhatia, V.K. Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute Library Avenue, Pusa, New Delhi-110012 (INDIA) E-mail: vkbhatia@iasri.res.in
Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development in Tamil Nadu 1
 Jour. Ind. Soc. Ag. Sralislics 53(1), 2()()() : 35-46 Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development in Tamil Nadu 1 Prem Narain, S.D. Shanna, S.C. Rai and V.K. Bhatia Indian Society of Agricultural
Jour. Ind. Soc. Ag. Sralislics 53(1), 2()()() : 35-46 Regional Disparities in Socio-Economic Development in Tamil Nadu 1 Prem Narain, S.D. Shanna, S.C. Rai and V.K. Bhatia Indian Society of Agricultural
Economic implications of land degradation on sustainability and food security in India
 Agropedology 23, 13(2), 19-27 Economic implications of land degradation on sustainability and food security in India A. K. VASISHT, R. P. SINGH AND V. C. MATHUR Division of Agricultural Economics, Indian
Agropedology 23, 13(2), 19-27 Economic implications of land degradation on sustainability and food security in India A. K. VASISHT, R. P. SINGH AND V. C. MATHUR Division of Agricultural Economics, Indian
Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis
 Volume 3, Issue 1 June 2014 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis M. Borah* and R.A. Halim Dept. of Agricultural Economics
Volume 3, Issue 1 June 2014 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis M. Borah* and R.A. Halim Dept. of Agricultural Economics
Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted?
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (Conference Number) 2013 pp 1-11 Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted? M.L. Nithyashree* and
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (Conference Number) 2013 pp 1-11 Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted? M.L. Nithyashree* and
Presentation on Rural Roads: Changing Scenario & Challenges Ahead
 Presentation on Rural Roads: Changing Scenario & Challenges Ahead By: N C Solanki Director (Projects-I) National Rural Roads Development Agency Ministry of Rural Development 1 Government of India Status
Presentation on Rural Roads: Changing Scenario & Challenges Ahead By: N C Solanki Director (Projects-I) National Rural Roads Development Agency Ministry of Rural Development 1 Government of India Status
Knowledge of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Practices among Chilli Farmers in Raichur District of Karnataka, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2397706 Volume 7 Number 03 (208) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/0.20546/ijcmas.208.703.259
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2397706 Volume 7 Number 03 (208) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/0.20546/ijcmas.208.703.259
Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India
 Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Geospatial Situational Analysis of Flood in Asam and Challenges
 Geospatial Situational Analysis of Flood in Asam and Challenges Dr.Mukta Girdhar, Assistant Professor, GGSIP University New Delhi Word Limit of the Paper should not be more than 3000 Words = 7/8 Pages)
Geospatial Situational Analysis of Flood in Asam and Challenges Dr.Mukta Girdhar, Assistant Professor, GGSIP University New Delhi Word Limit of the Paper should not be more than 3000 Words = 7/8 Pages)
Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States,
 University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Economics Department Working Paper Series Economics 2016 Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States, 1995-2011 Deepankar
University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Economics Department Working Paper Series Economics 2016 Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States, 1995-2011 Deepankar
DISTRICT PROFILE OF UTTARA KANANDA
 DISTRICT PROFILE OF UTTARA KANANDA 1. Name of the District : UTTARA KANNADA 2. Geographical Position* North Latitude Between 13 o 52 52 and 15 o 30 o East Longitude Between 74 05 and 75 o 05 3. Total Geographical
DISTRICT PROFILE OF UTTARA KANANDA 1. Name of the District : UTTARA KANNADA 2. Geographical Position* North Latitude Between 13 o 52 52 and 15 o 30 o East Longitude Between 74 05 and 75 o 05 3. Total Geographical
Liberalization, Growth and Regional Disparities in India
 Liberalization, Growth and Regional Disparities in India India Studies in Business and Economics VOLUME 1 For further volumes: http://www.springer.com/series/11234 Madhusudan Ghosh Liberalization, Growth
Liberalization, Growth and Regional Disparities in India India Studies in Business and Economics VOLUME 1 For further volumes: http://www.springer.com/series/11234 Madhusudan Ghosh Liberalization, Growth
Socio-Economic Profile of Sugarcane Growers in District Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 6 Number 9 (17) pp. 1217-1229 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.546/ijcmas.17.69.148
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 6 Number 9 (17) pp. 1217-1229 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.546/ijcmas.17.69.148
CENTRAL BUDGET AND FARMERS SUICIDE IN INDIA
 CENTRAL BUDGET AND FARMERS SUICIDE IN INDIA Dr. Sunil Gosavi Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Kamaveer Bhaurao Patil College, Navi Mumbai Email: sunil.gosavi070@gamil.com ABSTRACT Farmers
CENTRAL BUDGET AND FARMERS SUICIDE IN INDIA Dr. Sunil Gosavi Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, Kamaveer Bhaurao Patil College, Navi Mumbai Email: sunil.gosavi070@gamil.com ABSTRACT Farmers
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis
 Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
CITIZEN S CHARTER (Year -2013)
 GOVT. OF ASSAM CITIZEN S CHARTER (Year -2013) DIRECTORATE OF AGRICULTURE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, ASSAM KHANAPARA GUWAHATI-22 tahbildarctzncharter Page 1 Citizen s Charter of the Directorate of Agriculture
GOVT. OF ASSAM CITIZEN S CHARTER (Year -2013) DIRECTORATE OF AGRICULTURE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, ASSAM KHANAPARA GUWAHATI-22 tahbildarctzncharter Page 1 Citizen s Charter of the Directorate of Agriculture
WOMEN PARTICIPATION IN CARP CULTURE ACTIVITIES IN INDIA
 WOMEN PARTICIPATION IN CARP CULTURE ACTIVITIES IN INDIA M. C. Nandeesha Fisheries College and Research Institute Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University Tuticorin 628 008, Tamil Nadu, India.
WOMEN PARTICIPATION IN CARP CULTURE ACTIVITIES IN INDIA M. C. Nandeesha Fisheries College and Research Institute Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University Tuticorin 628 008, Tamil Nadu, India.
Problems and Agriculture Land Holding Pattern among BPL Households in Hill Rural Areas: A Study of Pauri District of Uttarakhand Ajay Kumar Salgotra
 International Journal of Humanities & Social Science Studies (IJHSSS) A Peer-Reviewed Bi-monthly Bi-lingual Research Journal ISSN: 2349-6959 (Online), ISSN: 2349-6711 (Print) ISJN: A4372-3142 (Online)
International Journal of Humanities & Social Science Studies (IJHSSS) A Peer-Reviewed Bi-monthly Bi-lingual Research Journal ISSN: 2349-6959 (Online), ISSN: 2349-6711 (Print) ISJN: A4372-3142 (Online)
Output and Employment Growth in Registered Manufacturing Industries in India: Testing Kaldor s Hypothesis
 Output and Employment Growth in Registered Manufacturing Industries in India: Testing Kaldor s Hypothesis Dr. Panchanan Das Taki Government College West Bengal This paper carries out GMM estimation in
Output and Employment Growth in Registered Manufacturing Industries in India: Testing Kaldor s Hypothesis Dr. Panchanan Das Taki Government College West Bengal This paper carries out GMM estimation in
Economics of production of Alphonso mango in Sindhudurg district
 2017; 5(4): 544-549 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(4): 544-549 2017 JEZS Received: 05-05-2017 Accepted: 06-06-2017 SS Dhuri Student M.Sc. (Agri.). Department of Agricultural Economics,
2017; 5(4): 544-549 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(4): 544-549 2017 JEZS Received: 05-05-2017 Accepted: 06-06-2017 SS Dhuri Student M.Sc. (Agri.). Department of Agricultural Economics,
Livestock sector development and implications for rural poverty alleviation in India
 Livestock Research for Rural Development 19 (2) 2007 Guidelines to authors LRRD News Citation of this paper Livestock sector development and implications for rural poverty alleviation in India Jabir Ali
Livestock Research for Rural Development 19 (2) 2007 Guidelines to authors LRRD News Citation of this paper Livestock sector development and implications for rural poverty alleviation in India Jabir Ali
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture.
 1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
An economic analysis of production of sugarcane under different method of irrigation in Durg division of Chhattisgarh
 2018; 6(1): 1389-1393 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(1): 1389-1393 2018 IJCS Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Umesh Jaiswal Jayant Nishad AK Koshta Professor, Department of Vijay
2018; 6(1): 1389-1393 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(1): 1389-1393 2018 IJCS Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Umesh Jaiswal Jayant Nishad AK Koshta Professor, Department of Vijay
A Balance Sheet of Performance of Large dams in India The case of irrigation and flood control
 1 A Balance Sheet of Performance of Large dams in India The case of irrigation and flood control Over the last 51 years of water resources development in Independent India, the nation has spent over Rs.
1 A Balance Sheet of Performance of Large dams in India The case of irrigation and flood control Over the last 51 years of water resources development in Independent India, the nation has spent over Rs.
Rural Livelihoods Approach and Health and Nutrition
 Rural Livelihoods Approach and Health and Nutrition Overview of the Rural Livelihoods Portfolio Leveraging Institutional platforms of the poor to deliver livelihood outcomes Specific Investments in Financial
Rural Livelihoods Approach and Health and Nutrition Overview of the Rural Livelihoods Portfolio Leveraging Institutional platforms of the poor to deliver livelihood outcomes Specific Investments in Financial
Chapter 4 Agriculture
 Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
Proceedings of the Annual Conference of NEEA held at Dibrugarh, Assam in February POVERTY AND ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION IN RURAL INDIA: A NEXUS
 POVERTY AND ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION IN RURAL INDIA: A NEUS Purusottam Nayak Abstract Inspired by the worldwide debate on the issue, the present paper is a humble attempt to test the nexus between poverty
POVERTY AND ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION IN RURAL INDIA: A NEUS Purusottam Nayak Abstract Inspired by the worldwide debate on the issue, the present paper is a humble attempt to test the nexus between poverty
Demography Introduction Demographic Transition in Tamil Nadu Human Development Index
 9 9.1. Introduction The population growth rate in Tamil Nadu had started declining in eighties itself. In 1991 the decadal growth rate was 15.4 per cent for Tamil Nadu compared to the All-India rate of
9 9.1. Introduction The population growth rate in Tamil Nadu had started declining in eighties itself. In 1991 the decadal growth rate was 15.4 per cent for Tamil Nadu compared to the All-India rate of
Estimation of agricultural resource inequality in India using Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient approach
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 4 (April-2015) pp. 174-184 www.ijcrar.com Estimation of agricultural resource inequality in India using Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient approach Mada Melkamu 1 * and Richard
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 4 (April-2015) pp. 174-184 www.ijcrar.com Estimation of agricultural resource inequality in India using Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient approach Mada Melkamu 1 * and Richard
DEMONSTRATION OF CROP CUTTING EXPERIMENT
 18: Demonstration of Crop Cutting Experiment DEMONSTRATION OF CROP CUTTING EXPERIMENT Man Singh Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, New Delhi-110012 1.0 INTRODUCTION Agricultural statistics
18: Demonstration of Crop Cutting Experiment DEMONSTRATION OF CROP CUTTING EXPERIMENT Man Singh Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, New Delhi-110012 1.0 INTRODUCTION Agricultural statistics
Chapter 4 SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIES AND WOMEN EMPOWERMENT IN INDIA
 Chapter 4 SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIES AND WOMEN EMPOWERMENT IN INDIA 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Role of Small Scale Industrial Units in Indian Economy 4.3 Role of Small Scale Industries in Women Empowerment in India
Chapter 4 SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIES AND WOMEN EMPOWERMENT IN INDIA 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Role of Small Scale Industrial Units in Indian Economy 4.3 Role of Small Scale Industries in Women Empowerment in India
Farm Power and Machinery Availability on Indian Farms
 Vol. 39(1), 2015 Farm and Machinery Availability on Indian Farms R S Singh 1 (LM-10492), Surendra Singh 2 (F-143) and S P Singh 3 (LM-10002) 1 CIAE, Nabi Bagh, Bhopal-462038 2 Ex Project Coordinator, AICRP
Vol. 39(1), 2015 Farm and Machinery Availability on Indian Farms R S Singh 1 (LM-10492), Surendra Singh 2 (F-143) and S P Singh 3 (LM-10002) 1 CIAE, Nabi Bagh, Bhopal-462038 2 Ex Project Coordinator, AICRP
A Comprehensive Impact Assessment Study of Assam Rural Infrastructure Agricultural Services Project
 A Comprehensive Impact Assessment Study of Assam Rural Infrastructure Agricultural Services Project M. K. Awasthi* I INTRODUCTION Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.61, No.3, July-Sept. 2006 Socio-economically
A Comprehensive Impact Assessment Study of Assam Rural Infrastructure Agricultural Services Project M. K. Awasthi* I INTRODUCTION Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.61, No.3, July-Sept. 2006 Socio-economically
Quality of Water and Water Related Diseases in Urban Areas
 5.1.2 Incidence of water borne diseases in states of India The water borne diseases in India are occurring over the years despite various water quality management plans by the Government of India. Regardless
5.1.2 Incidence of water borne diseases in states of India The water borne diseases in India are occurring over the years despite various water quality management plans by the Government of India. Regardless
Participation of Farm Women in Animal Husbandry in Anand District of Gujarat
 Journal of Community Mobilization and Sustainable Development Vol. 6(2), 117-121, July-December, 2011 Participation of Farm Women in Animal Husbandry in Anand District of Gujarat Sangeeta Upadhyay 1 and
Journal of Community Mobilization and Sustainable Development Vol. 6(2), 117-121, July-December, 2011 Participation of Farm Women in Animal Husbandry in Anand District of Gujarat Sangeeta Upadhyay 1 and
CHRONIC POVERTY AND SOCIALLY DISADVANTAGED GROUPS: ANALYSIS OF CAUSES AND REMEDIES. Sukhadeo Thorat Motilal Mahamallik
 WORKING PAPER CHRONIC POVERTY AND SOCIALLY DISADVANTAGED GROUPS: ANALYSIS OF CAUSES AND REMEDIES Sukhadeo Thorat Motilal Mahamallik Working Paper 33 CPRC-IIPA Chronic Poverty Research Centre Indian Institite
WORKING PAPER CHRONIC POVERTY AND SOCIALLY DISADVANTAGED GROUPS: ANALYSIS OF CAUSES AND REMEDIES Sukhadeo Thorat Motilal Mahamallik Working Paper 33 CPRC-IIPA Chronic Poverty Research Centre Indian Institite
Cost of cultivation of sugarcane crop in Meerut district of Uttar Pradesh
 IJF CI International Journal of Forestry and Crop Improvement Volume 6 Issue 1 June, 2015 41-48 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in e ISSN-2230-9411 RESEARCH ARTICLE DOI: 10.15740/HAS/IJFCI/6.1/41-48
IJF CI International Journal of Forestry and Crop Improvement Volume 6 Issue 1 June, 2015 41-48 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in e ISSN-2230-9411 RESEARCH ARTICLE DOI: 10.15740/HAS/IJFCI/6.1/41-48
Constraints faced by the farmers in adoption of Integrated crop Management in Chilli crop in Telangana
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Sowjanya and Kumari Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1135-1140 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5662 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Sowjanya and Kumari Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1135-1140 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5662 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App.
B. Articles. Identification of Predominant Farming Systems and their Economics in Telangana Region of Andhra Pradesh
 B. Articles Identification of Predominant Farming Systems and their Economics in Telangana Region of Andhra Pradesh V. RAJENDRA PRASAD, M. MALLA REDDY AND M. V. RAMANA* Introduction Telangana is one of
B. Articles Identification of Predominant Farming Systems and their Economics in Telangana Region of Andhra Pradesh V. RAJENDRA PRASAD, M. MALLA REDDY AND M. V. RAMANA* Introduction Telangana is one of
Farmers information needs in rural Manipur: an assessment
 Annals of Library and Information Studies Vol. 56, March 2009, MEITEI pp. 35-40 & DEVI: FARMERS INFORMATION NEEDS IN RURAL MANIPUR: AN ASSESSMENT 35 Farmers information needs in rural Manipur: an assessment
Annals of Library and Information Studies Vol. 56, March 2009, MEITEI pp. 35-40 & DEVI: FARMERS INFORMATION NEEDS IN RURAL MANIPUR: AN ASSESSMENT 35 Farmers information needs in rural Manipur: an assessment
Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 15 (2), May, Perception of Farming Youth towards Farming
 Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 15 (2), May, 2015 105 RESEARCH NOTE Perception of Farming Youth towards Farming Sarju Narain 1, A.K. Singh 2 and S.R.K. Singh 3 1. Astt. Prof. (Agril. Ext.), Brahmanand Mahavidyalaya,
Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 15 (2), May, 2015 105 RESEARCH NOTE Perception of Farming Youth towards Farming Sarju Narain 1, A.K. Singh 2 and S.R.K. Singh 3 1. Astt. Prof. (Agril. Ext.), Brahmanand Mahavidyalaya,
STATE OF ENVIRONMENT ATLAS OF INDIA-OUTLINE
 STATE OF ENVIRONMENT ATLAS OF INDIA-OUTLINE Sl. No. Maps Themes Features Data Source I: GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS I. Administrative Divisions International, States, Districts Survey of Boundaries with State
STATE OF ENVIRONMENT ATLAS OF INDIA-OUTLINE Sl. No. Maps Themes Features Data Source I: GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS I. Administrative Divisions International, States, Districts Survey of Boundaries with State
Sericulture An Ideal Enterprise for Sustainable Income in Erode District of Tamil Nadu
 ================================================================== Language in India www.languageinindia.com ISSN 1930-2940 Vol. 14:9 September 2014 ==================================================================
================================================================== Language in India www.languageinindia.com ISSN 1930-2940 Vol. 14:9 September 2014 ==================================================================
National Dairy Development Board. Dairying In. Punjab. A Statistical Profile 2014
 Dairying In National Dairy Development Board Punjab A Statistical Profile 2014 PUNJAB Formation of districts: Census 1991 to 2011 Foreword In this compilation of the statistical profile of the dairy sector
Dairying In National Dairy Development Board Punjab A Statistical Profile 2014 PUNJAB Formation of districts: Census 1991 to 2011 Foreword In this compilation of the statistical profile of the dairy sector
The agricultural production can be increased
 Agriculture Update August & November, 2010 Vol. 5 Issue 3 & 4 370-374 Constraints in various integrated farming systems J. PUSHPA RESEARCH ARTICLE Correspondence to : J. PUSHPA Department of Extension
Agriculture Update August & November, 2010 Vol. 5 Issue 3 & 4 370-374 Constraints in various integrated farming systems J. PUSHPA RESEARCH ARTICLE Correspondence to : J. PUSHPA Department of Extension
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction of Bricks Brick, the most important tiny piece for construction works is used by human for many years back.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction of Bricks Brick, the most important tiny piece for construction works is used by human for many years back. Its history goes back to some of the earliest times in
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction of Bricks Brick, the most important tiny piece for construction works is used by human for many years back. Its history goes back to some of the earliest times in
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF PLANTATION SECTOR IN KERALA
 Economic importance of plantation sector in Kerala Contents Chapter 2 ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF PLANTATION SECTOR IN KERALA 2.1 Contribution of Agriculture to Kerala State GDP 2.2 Income Share of Main Agriculture
Economic importance of plantation sector in Kerala Contents Chapter 2 ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF PLANTATION SECTOR IN KERALA 2.1 Contribution of Agriculture to Kerala State GDP 2.2 Income Share of Main Agriculture
Working Papers Series Center on Globalization and Sustainable Development
 Agricultural Performance in Uttar Pradesh: A Historical Account Nirupam Bajpai and Nicole Volavka CGSD Working Paper No. 23 April 2005 Working Papers Series Center on Globalization and Sustainable Development
Agricultural Performance in Uttar Pradesh: A Historical Account Nirupam Bajpai and Nicole Volavka CGSD Working Paper No. 23 April 2005 Working Papers Series Center on Globalization and Sustainable Development
CROPPING PATTERN OF NORTH EAST INDIA: AN APPRAISAL
 AMERICAN RESEARCH THOUGHTS ISSN: 2392 876X Volume 1 Issue 1 November 2014 Available online at: www.researchthoughts.us CROPPING PATTERN OF NORTH EAST INDIA: AN APPRAISAL Lh. Seitinthang Research Scholar,
AMERICAN RESEARCH THOUGHTS ISSN: 2392 876X Volume 1 Issue 1 November 2014 Available online at: www.researchthoughts.us CROPPING PATTERN OF NORTH EAST INDIA: AN APPRAISAL Lh. Seitinthang Research Scholar,
COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION OF J&K STATE IN INDIA
 Received: 16 th August-2012 Revised: 19 th August -2012 Accepted: 24 th August -2012 Research article COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION
Received: 16 th August-2012 Revised: 19 th August -2012 Accepted: 24 th August -2012 Research article COST AND RETURN FROM MILK PRODUCTION AMONG TRIBALS (GUJJARS) IN DIFFERENT DISTRICTS OF JAMMU REGION
MICRO ANALYSIS OF YIELD GAP AND PROFITABILITY IN PULSES AND CEREALS
 Legume Res., 37 (5) : 532-536, 2014 doi:10.5958/0976-0571.2014.00671.7 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.legumeresearch.in MICRO ANALYSIS OF YIELD GAP AND PROFITABILITY
Legume Res., 37 (5) : 532-536, 2014 doi:10.5958/0976-0571.2014.00671.7 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.legumeresearch.in MICRO ANALYSIS OF YIELD GAP AND PROFITABILITY
Demand for Fertilisers in India: Determinants and Outlook for 2020
 Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.66, No.4, Oct.-Dec. 2011 Demand for Fertilisers in India: Determinants and Outlook for 2020 Vijay Paul Sharma and Hrima Thaker* I INTRODUCTION The role of chemical fertilisers
Ind. Jn. of Agri. Econ. Vol.66, No.4, Oct.-Dec. 2011 Demand for Fertilisers in India: Determinants and Outlook for 2020 Vijay Paul Sharma and Hrima Thaker* I INTRODUCTION The role of chemical fertilisers
Page 1 of 6. Agriculture. I. Answer the Following
 Agriculture Page 1 of 6 I. Answer the Following Q1. What is the importance of agriculture in the Indian economy? Ans. Two-thirds of India s population is engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture
Agriculture Page 1 of 6 I. Answer the Following Q1. What is the importance of agriculture in the Indian economy? Ans. Two-thirds of India s population is engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture
Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) is a comparative analysis of environmental achievements, challenges
 Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) for Indian States 2011 Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) is a comparative analysis of environmental achievements, challenges and priorities of Indian states.
Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) for Indian States 2011 Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI) is a comparative analysis of environmental achievements, challenges and priorities of Indian states.
International Journal of Commerce and Business Management. Volume 8 Issue 1 April, RESEARCH PAPER
 IJCBM e ISSN 0976 7940 International Journal of Commerce and Business Management Volume 8 Issue 1 April, 2015 17-22 DOI: 10.15740/HAS/IJCBM/8.1/17-22 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in RESEARCH PAPER
IJCBM e ISSN 0976 7940 International Journal of Commerce and Business Management Volume 8 Issue 1 April, 2015 17-22 DOI: 10.15740/HAS/IJCBM/8.1/17-22 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in RESEARCH PAPER
An Overview of Agricultural Universities of North East India
 Chapter-4 An Overview of Agricultural Universities of North East India 4.1 Introduction: Agriculture is a source of livelihood to the majority of population in India. Today India is self sufficient in
Chapter-4 An Overview of Agricultural Universities of North East India 4.1 Introduction: Agriculture is a source of livelihood to the majority of population in India. Today India is self sufficient in
ECONOMICS OF SUGARCANE CULTIVATION IN ANDHRA PRADESH (A Case Study of Visakhapatnam District)
 Synopsis of the thesis entitled ECONOMICS OF SUGARCANE CULTIVATION IN ANDHRA PRADESH (A Case Study of Visakhapatnam District) By KARRI NARASIMHA PUSAPPA Research Director Prof. M.BHAVANI SHANKAR RAO M.A.,
Synopsis of the thesis entitled ECONOMICS OF SUGARCANE CULTIVATION IN ANDHRA PRADESH (A Case Study of Visakhapatnam District) By KARRI NARASIMHA PUSAPPA Research Director Prof. M.BHAVANI SHANKAR RAO M.A.,
Labour Demand and Labour-saving Options: A Case of Groundnut Crop in India
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 24 (Conference Number) 2011 pp 423-428 Labour Demand and Labour-saving Options: A Case of Groundnut Crop in India G. Govindaraj* and A.P. Mishra Directorate
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 24 (Conference Number) 2011 pp 423-428 Labour Demand and Labour-saving Options: A Case of Groundnut Crop in India G. Govindaraj* and A.P. Mishra Directorate
An Analysis of Cost and Returns of Sugarcane Production in Krishnagiri District of Tamil Nadu
 An Analysis of Cost and Returns of Sugarcane Production in Krishnagiri District of Tamil Nadu *Dr.K.Saravanan M.A., M.Phil., Ph.D Associate Professor of Economics, Kandaswami Kandar s College, Velur-638
An Analysis of Cost and Returns of Sugarcane Production in Krishnagiri District of Tamil Nadu *Dr.K.Saravanan M.A., M.Phil., Ph.D Associate Professor of Economics, Kandaswami Kandar s College, Velur-638
Country Profile: Food Security Indicators
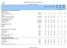 Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Do clinical trials conducted in India match its healthcare needs? An audit of the Clinical Trials Registry of India
 Original Article Do clinical trials conducted in India match its healthcare needs? An audit of the Clinical Trials Registry of India Mansi Chaturvedi, Nithya J. Gogtay, Urmila M. Thatte Department of Clinical
Original Article Do clinical trials conducted in India match its healthcare needs? An audit of the Clinical Trials Registry of India Mansi Chaturvedi, Nithya J. Gogtay, Urmila M. Thatte Department of Clinical
ADOPTION OF AZOLLA CULTIVATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE FARMERS FIELD: AN ANALYSIS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 5, 2016, 3081 3087 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) ADOPTION OF AZOLLA CULTIVATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE FARMERS FIELD: AN ANALYSIS
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 5, 2016, 3081 3087 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) ADOPTION OF AZOLLA CULTIVATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE FARMERS FIELD: AN ANALYSIS
Agricultural Productivity and Productivity Regions in West Bengal
 ISSN. 0972-8406 The NEHU Journal, Vol XIII, No. 2, July-December 2015, pp-49-61 49 Agricultural Productivity and Productivity Regions in West Bengal Introduction NASIM AKTAR* Abstract The green revolution
ISSN. 0972-8406 The NEHU Journal, Vol XIII, No. 2, July-December 2015, pp-49-61 49 Agricultural Productivity and Productivity Regions in West Bengal Introduction NASIM AKTAR* Abstract The green revolution
METEOROLOGICAL DROUGHT OCCURRENCES IN TURA, MEGHALAYA, INDIA ABSTRACT
 METEOROLOGICAL DROUGHT OCCURRENCES IN TURA, MEGHALAYA, INDIA Lala I P Ray* 1, P K Bora 1, V Ram 1, A K Singh 1, Ram Singh 2 and S M Feroze 2 * 1 School of Natural Resource Management, College of Post Graduate
METEOROLOGICAL DROUGHT OCCURRENCES IN TURA, MEGHALAYA, INDIA Lala I P Ray* 1, P K Bora 1, V Ram 1, A K Singh 1, Ram Singh 2 and S M Feroze 2 * 1 School of Natural Resource Management, College of Post Graduate
Instability and Regional Variation in Indian Agriculture
 Policy Paper 26 Instability and Regional Variation in Indian Agriculture Ramesh Cnd S S Raju Sanjeev Garg Lal Mani Pandey National Centre for Agricultural Economics and Policy Research Ne w De l h i-110
Policy Paper 26 Instability and Regional Variation in Indian Agriculture Ramesh Cnd S S Raju Sanjeev Garg Lal Mani Pandey National Centre for Agricultural Economics and Policy Research Ne w De l h i-110
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE
 6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
Country Profile: Food Security Indicators
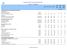 Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Country Profile: Food Security Indicars I. FOOD DEPRIVATION AND CONSUMPTION INDICATORS Food Deprivation Proportion of undernourishment - - - - na na na Number of undernourished millions ns ns ns ns na
Sustainability of Farming Systems in Kolar District of Karnataka. National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS) Rating : 3. 03
 I J T A Serials Publications Sustainability of Farming Systems in Kolar District of Karnataka National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS) Rating : 3. 03 Sustainability of Farming Systems in Kolar District
I J T A Serials Publications Sustainability of Farming Systems in Kolar District of Karnataka National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS) Rating : 3. 03 Sustainability of Farming Systems in Kolar District
Ch-2 SECTORS OF THE INDIAN ECONOMY
 Ch-2 SECTORS OF THE INDIAN ECONOMY 1. What are the different sectors of an economy? Or How are economic activities classified on the basis of the nature of the activity? i. Primary Sector: When we produce
Ch-2 SECTORS OF THE INDIAN ECONOMY 1. What are the different sectors of an economy? Or How are economic activities classified on the basis of the nature of the activity? i. Primary Sector: When we produce
National Vegetable Initiative for Urban Clusters. Value chain integration, technology dissemination and accessing investments and markets
 National Vegetable Initiative for Urban Clusters Value chain integration, technology dissemination and accessing investments and markets Progress and Prospects Vegetable Initiative for Urban Clusters FPO
National Vegetable Initiative for Urban Clusters Value chain integration, technology dissemination and accessing investments and markets Progress and Prospects Vegetable Initiative for Urban Clusters FPO
S. Rajendran* and B Gandhimathy**
 Journal of Economic and Social Development, Vol. VII, No. 1, 2011 SWOT Analysis of Coir Cooperative Marketing Society A Case Study from Salem Region S. Rajendran* and B Gandhimathy** India is the largest
Journal of Economic and Social Development, Vol. VII, No. 1, 2011 SWOT Analysis of Coir Cooperative Marketing Society A Case Study from Salem Region S. Rajendran* and B Gandhimathy** India is the largest
Estimates on State-Specific Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines (PCV) Coverage in the Private Sector in the Year 2012: Evidence from PCV Utilization Data
 Brief Research Article Estimates on State-Specific Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines (PCV) Coverage in the Private Sector in the Year 2012: Evidence from PCV Utilization Data Habib Hasan Farooqui 1, Sanjay
Brief Research Article Estimates on State-Specific Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines (PCV) Coverage in the Private Sector in the Year 2012: Evidence from PCV Utilization Data Habib Hasan Farooqui 1, Sanjay
Integrated Fish Farming in Jorhat District of Assam: Problems and Policy Options
 Economic Affairs: 58(4): 405-409 December, 2013 DOI Number 10.5958/J.0976-4666.58.4.024 Integrated Fish Farming in Jorhat District of Assam: Problems and Policy Options Jyotismita Bora 1 * and Anup Kumar
Economic Affairs: 58(4): 405-409 December, 2013 DOI Number 10.5958/J.0976-4666.58.4.024 Integrated Fish Farming in Jorhat District of Assam: Problems and Policy Options Jyotismita Bora 1 * and Anup Kumar
Agricultural Growth and Regional Disparity in India: A Convergence Analysis
 Agricultural Growth and Regional Disparity in India: A Convergence Analysis Arpita Banerjee 1 and Pravat Kumar Kuri 2 ABSTRACT The deceleration in growth trends in agricultural output and yield rate is
Agricultural Growth and Regional Disparity in India: A Convergence Analysis Arpita Banerjee 1 and Pravat Kumar Kuri 2 ABSTRACT The deceleration in growth trends in agricultural output and yield rate is
Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows
 Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows Dr. B. Rajender, Joint Secretary (Crops & Oilseeds) Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers
Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows Dr. B. Rajender, Joint Secretary (Crops & Oilseeds) Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers
GROWTH, POVERTY AND EMPLOYMENT IN UTTARAKHAND
 Working paper NO. 39 GROWTH, POVERTY AND EMPLOYMENT IN UTTARAKHAND Rajendra P. Mamgain INSTITUTE FOR HUMAN DEVELOPMENT NEW DELHI 2007 GROWTH, POVERTY AND EMPLOYMENT IN UTTARAKHAND Rajendra P. Mamgain
Working paper NO. 39 GROWTH, POVERTY AND EMPLOYMENT IN UTTARAKHAND Rajendra P. Mamgain INSTITUTE FOR HUMAN DEVELOPMENT NEW DELHI 2007 GROWTH, POVERTY AND EMPLOYMENT IN UTTARAKHAND Rajendra P. Mamgain
Contemporary Research in India (ISSN ): Vol. 7: Issue: 3 September, 2017
 IMPACT OF IMPROVED TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION FOR WHEAT IN MAHARASHTRA Dr. Y. C. Sale 1, Prof. N. K. Kale 2 and Prof. P. N. Shendage 3 College of Agriculture, Pune (Maharashtra) Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth,
IMPACT OF IMPROVED TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION FOR WHEAT IN MAHARASHTRA Dr. Y. C. Sale 1, Prof. N. K. Kale 2 and Prof. P. N. Shendage 3 College of Agriculture, Pune (Maharashtra) Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth,
Factors responsible for the performance of cooperative sugar factories in North-Eastern Karnataka
 Factors responsible for the performance of cooperative sugar factories in North-Eastern Karnataka Yasmeen*, Suresh S. Patil and N. Vijaykumar Department of Agricultural Economics, College of Agriculture,
Factors responsible for the performance of cooperative sugar factories in North-Eastern Karnataka Yasmeen*, Suresh S. Patil and N. Vijaykumar Department of Agricultural Economics, College of Agriculture,
CHAPTER II PROFILE OF THE STUDY AREA. state of Tamil Nadu. By its very location, the district
 CHAPTER II PROFILE OF THE STUDY AREA 2.0 Ranyakumari is the smallest district in the state of Tamil Nadu. By its very location, the district occupies a unique place among the other districts of Tamil Nadu.
CHAPTER II PROFILE OF THE STUDY AREA 2.0 Ranyakumari is the smallest district in the state of Tamil Nadu. By its very location, the district occupies a unique place among the other districts of Tamil Nadu.
Kharif Sorghum in Karnataka: An Economic Analysis
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 18 July-December 2005 pp 223-240 Kharif Sorghum in Karnataka: An Economic Analysis H. Basavaraja 1, A.Y. Hugar 2, S.B. Mahajanshetti 3, V.V. Angadi 4 and B.
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 18 July-December 2005 pp 223-240 Kharif Sorghum in Karnataka: An Economic Analysis H. Basavaraja 1, A.Y. Hugar 2, S.B. Mahajanshetti 3, V.V. Angadi 4 and B.
FLOOD DISASTER IN ASSAM: SOCIO- ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND CONTROL MEASURES
 147 FLOOD DISASTER IN ASSAM: SOCIO- ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND CONTROL MEASURES Abstract Manuranjan Gogoi 1 Flood is the major recurrent natural disaster of Assam. The economy of Assam mainly is based
147 FLOOD DISASTER IN ASSAM: SOCIO- ECONOMIC VULNERABILITY AND CONTROL MEASURES Abstract Manuranjan Gogoi 1 Flood is the major recurrent natural disaster of Assam. The economy of Assam mainly is based
8) The fixed capital investment indicated that land, implements and building are contributing more than 94 per cent to the total assets.
 CHAPTER VI SUMMARY The relationship between man and forest has always changed with socioeconomic development and will certainly continue to change. The reason in that man/land ratio will continue to be
CHAPTER VI SUMMARY The relationship between man and forest has always changed with socioeconomic development and will certainly continue to change. The reason in that man/land ratio will continue to be
IMPO P RT R AN A C N E C E O F G RO R UN U D N W
 Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
AN ANALYSIS OF AGRICULURAL SCHEMES RUN BY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA FOR FARMERS: A CASE STUDY OF DISTRICT SIRSA
 International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 7 Issue 5, May 17, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.81 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 7 Issue 5, May 17, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.81 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
JICA s Support to India (Forestry Sector)
 JICA s Support to India (Forestry Sector) January 6, 2015 JICA India office 1 Introduction of JICA Japan International Cooperation Agency President: Akihiko Tanaka Establishment: August 1974 and Reorganized
JICA s Support to India (Forestry Sector) January 6, 2015 JICA India office 1 Introduction of JICA Japan International Cooperation Agency President: Akihiko Tanaka Establishment: August 1974 and Reorganized
NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India. Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad
 NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad This Paper This paper argues that NREGA could be an important first step of a full
NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad This Paper This paper argues that NREGA could be an important first step of a full
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE. LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON 09.08.2016 Ecological Impact of Mining *334. SHRI JANARDAN SINGH SIGRIWAL state:
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENT, FOREST AND CLIMATE CHANGE LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION No. 334 TO BE ANSWERED ON 09.08.2016 Ecological Impact of Mining *334. SHRI JANARDAN SINGH SIGRIWAL state:
Research Article. Abdul Rauf 1 *, S. A. Saraf 1, P. A. Khan 2, and Q. J. A. Peer 3
 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Managerial Approach in Small and Large Apple Orchards of Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir States of India an Economic Perspective Abdul Rauf 1 *, S. A. Saraf
Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Managerial Approach in Small and Large Apple Orchards of Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir States of India an Economic Perspective Abdul Rauf 1 *, S. A. Saraf
SOCIO ECONOMIC PROFILE OF THE SAMPLE HOUSEHOLDS
 CHAPTER - V SOCIO ECONOMIC PROFILE OF THE SAMPLE HOUSEHOLDS 46 SOCIO ECONOMIC PROFILE OF THE SAMPLE HOUSEHOLDS In this chapter an attempt is made to present socio, demographic and economic profile of sample
CHAPTER - V SOCIO ECONOMIC PROFILE OF THE SAMPLE HOUSEHOLDS 46 SOCIO ECONOMIC PROFILE OF THE SAMPLE HOUSEHOLDS In this chapter an attempt is made to present socio, demographic and economic profile of sample
A GEOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN SATARA DISTRICT OF MAHARASHTRA
 Available online at: http://euroasiapub.org Vol. 8 Issue, April - 8 ISSN(o): -78 Impact Factor:. A GEOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN SATARA DISTRICT OF MAHARASHTRA K. C. Ramotra Former
Available online at: http://euroasiapub.org Vol. 8 Issue, April - 8 ISSN(o): -78 Impact Factor:. A GEOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN SATARA DISTRICT OF MAHARASHTRA K. C. Ramotra Former
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: X: ( )
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENI SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: X: (2018-2019) WKSHEET: No. 08 ECONOMICS CHAPTER: 2: SECTS OF INDIAN ECONOMY (APRIL-2018) ***Write answers to the following questions
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENI SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: X: (2018-2019) WKSHEET: No. 08 ECONOMICS CHAPTER: 2: SECTS OF INDIAN ECONOMY (APRIL-2018) ***Write answers to the following questions
Temporal Land Use and Cropping Pattern in Amravati District of Maharashtra State
 Temporal Land Use and Cropping Pattern in Amravati District of Maharashtra State National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS) Rating : 3. 03 Serials Publications Temporal Land Use and Cropping Pattern
Temporal Land Use and Cropping Pattern in Amravati District of Maharashtra State National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS) Rating : 3. 03 Serials Publications Temporal Land Use and Cropping Pattern
Organic by Design TEXTILE EXCHANGE
 Organic by Design TEXTILE EXCHANGE We work closely with organic cotton producer groups to help build supply and closer value chain relations. Five years of production growth Fiber (mt) Over the past five
Organic by Design TEXTILE EXCHANGE We work closely with organic cotton producer groups to help build supply and closer value chain relations. Five years of production growth Fiber (mt) Over the past five
Climate Change and Variability: Mapping Vulnerability of Agriculture using Geospatial Technologies
 Climate Change and Variability: Mapping Vulnerability of Agriculture using Geospatial Technologies Vinay Kumar Sehgal*, Malti Rani Singh, Niveta Jain and Himanshu Pathak ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research
Climate Change and Variability: Mapping Vulnerability of Agriculture using Geospatial Technologies Vinay Kumar Sehgal*, Malti Rani Singh, Niveta Jain and Himanshu Pathak ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research
A Study on Farm Households Coping Strategies Against the Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture: A Study in Cuddalore District
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, ECONOMICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Vol. 3, No. 1, January-June 2011: 151-156 A Study on Farm Households Coping Strategies Against the Impact of Climate Change
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, ECONOMICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Vol. 3, No. 1, January-June 2011: 151-156 A Study on Farm Households Coping Strategies Against the Impact of Climate Change
