Diseases of Soybean: Sudden Death Syndrome
|
|
|
- Elvin Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Purdue e-pubs Historical Documents of the Purdue Cooperative Extension Service Department of Agricultural Communication Diseases of Soybean: Sudden Death Syndrome Andreas Westphal Lijuan Xing T. Scott Abney Gregory Shaner Westphal, Andreas; Xing, Lijuan; Abney, T. Scott; and Shaner, Gregory, "Diseases of Soybean: Sudden Death Syndrome" (2016). Historical Documents of the Purdue Cooperative Extension Service. Paper For current publications, please contact the Education Store: This document is provided for historical reference purposes only and should not be considered to be a practical reference or to contain information reflective of current understanding. For additional information, please contact the Department of Agricultural Communication at, College of Agriculture: This document has been made available through Purdue e-pubs, a service of the Libraries. Please contact epubs@purdue.edu for additional information.
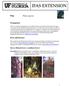
2 Diseases of Soybean Purdue Extension Sudden Death Syndrome Andreas Westphal, Lijuan Xing, T. Scott Abney, and Gregory Shaner Department of Botany and Plant Pathology, and USDA-ARS BP-58-W Sudden death syndrome (SDS) is one of the most important diseases of soybean in the Midwest. First discovered in Arkansas in 1971, SDS has spread throughout most of the North Central Region, including Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, Ohio, and Tennessee. SDS is most severe when soybean is planted early into cool, wet soils and when heavy midsummer rains saturate the soil. The fungus that causes SDS is now present in nearly all Indiana soybean fields, placing plants in high moisture areas of fields at risk for the disease (Figures 1 and 2). Symptoms The first noticeable symptoms of SDS are yellowing and defoliation of upper leaves (Figures 3 and 4). When symptoms first appear in a field, they may be confined to a few small areas or strips in the field, often in wetter or compacted areas, such as turn rows. Over the following two or three weeks, affected areas may enlarge, and other areas in the field may show symptoms. Because the SDS fungus can overwinter in soil, areas of a field that show symptoms of the disease often grow larger with each growing season until most of the field is affected. In disease development, early symptoms are mottling and mosaic of the leaves. Later, leaf tissue between the major veins turns yellow, then dies and turns brown. Soon after, Figure 1. A field infested with sudden death syndrome. Figure 2. This photo shows soybean plants with aborted leaves on a water-saturated slope in a field that has a history of SDS. the leaflets die and shrivel. In severe cases, the leaflets will drop off, leaving the petioles (leaf stalks) attached.
3 Examining the interior of the lower stem and taproot provides a more diagnostic symptom (Figure 5). When split, the lower stem and taproot of a plant infected with SDS will exhibit a slightly tan to light brown discoloration compared to a healthy plant. The pith (the central portion of the stem) will remain white or slightly cream-colored. It is important to look for these stem symptoms because other diseases (such as brown stem rot) or chemical burn can produce foliar symptoms similar to SDS (although in other diseases dead leaflets tend to remain attached to the petioles). For example, brown stem rot darkens the pith, but there is little discoloration of the cortex. If a plant with advanced foliar symptoms of SDS is dug up when soil is moist, there may be small, light blue patches on the taproot s surface near the soil line (Figure 5c). These patches are blue spore masses of the fungus that causes SDS. As the plant dries, the blue color will fade, but these blue spore masses, seen in conjunction with the other symptoms mentioned above, are strong indicators of SDS. Causal Agent SDS is caused by the soilborne fungus Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines, synonym: Fusarium virguliforme. This fungus grows slowly in culture and is difficult to isolate from diseased plants. Once pure cultures are obtained, blue spores and other cultural characteristics distinguish it from other Fusarium species that can infect soybean roots (Figure 6a). Disease Cycle Presumably, Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines survives the winter as chlamydospores in the crop residue or freely in the soil (Figure 6b). The thick-walled chlamydospores develop in the soil and on soybean roots during disease development and thereafter. The fungus also can survive in cysts of the soybean cyst nematode. Chlamydospores can withstand wide soil temperature fluctuations (including freezing) and resist desiccation. As soil temperatures rise in the spring, chlamydospores near soybean roots are stimulated to germinate, then infect soybean roots. The fungus may infect roots as early as one week after crop emergence, but aboveground symptoms of SDS rarely appear until mid-july, when soybean plants start to flower. Heavy rains during reproductive stages often are critical for SDS symptom development. When the soil is wet the fungus produces toxins in the roots that are translocated to the leaves. These toxins are what cause foliar symptoms; the fungus does not invade the stems above a few inches of the soil line. It does not invade leaves, flowers, pods, or seeds. a b Figure 3. Foliar symptoms of SDS: (a) View into a soybean stand with SDS (b) Note the loss of leaf blades and that only the leaf stalks remain on this view of the entire plant (c) A view into a canopy with SDS-symptomatic leaves (d) Note the dead tissue and green leaf veins on this single leaf with SDS symptoms Although the fungus may produce spores on the taproot s surface during the summer, these spores only spread short distances within a growing season. Over a period of years, flowing water and cultivation practices that move soil can move spores over longer distances, within or between fields. c d 2
4 Management SDS management options are limited. Although soybean varieties less sensitive to SDS have been developed, there are no highly resistant varieties. Fungicides applied in furrow during planting or as seed treatments have only limited effects, and fungicides applied to foliage have no effect on SDS, presumably because the fungal infection is restricted to root systems and fungicides typically do not move downward in the plant to reach the site of infection. However, there are several management practices that may reduce the risk of SDS damage, although they will not prevent the disease: Planting Date Early planting predisposes soybean to infection. Farmers have been planting soybean earlier every spring for the past few years. In cool, wet soils, young soybean plants are vulnerable to infection by Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines. If early spring conditions are favorable for rapid soybean growth, and if saturating rains do not occur during early reproductive stages of growth, the SDS risk is limited even though the fungus is in the soil. Conversely, if there is no Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines in a field, the disease will not develop even though other conditions may be favorable. So growers should plant fields with no history of SDS first, then later move into fields where SDS has been a problem. Tillage Compacted soils impede water percolation and restrict root growth. A heavy rain when soybean has reached the reproductive stage will saturate compacted areas, which promotes SDS development. Correcting soil compaction and water permeability problems may reduce the risk for SDS. Tile drainage or tillage may improve permeability. Soils react differently to tillage intensity. In some soils, no-tillage can be beneficial and increase soil water permeability. In other soils, tillage is mandatory for maintaining sufficient vertical water movement. Plowing, chiseling, or similar drastic soil disturbances strongly affect drainage, crop residue position, and the microbial composition of soil. Reports on the effects of tillage on SDS are contradictory. Some reports suggest the benefit of intensive tillage to improve soil drainage, which should reduce the risk for soil saturation after a rain. Other reports show that the improved soil tilth and drainage capability under continuous no-till reduces SDS risk. Growers should focus on how to create the best drainage in soil in some instances, that may require intensive tilling, and in other soil types this may be accomplished by adopting a no-till operation. Figure 4. These leaves show a range of foliar SDS symptoms, from very light yellowing to severe interveinal chlorosis. a c b Figure 5. Root symptoms of SDS: (a) Note the discoloration and lack of secondary roots on the infected root system (left) compared to the healthy root (b) The split stem on the right is infected with SDS note the light tan discoloration (c) Note the blue stains on the outside of this freshly dug root system, indicating the presence of sporulation of the SDS fungus Rotation There does not appear to be a rotation that significantly reduces SDS. In particular, corn does not reduce the incidence and severity of SDS, and severe outbreaks of the disease have occurred even after several years of continuous corn. However, crop rotation does reduce other soybean pathogens. It appears that shifting to twoyear rotations of corn and soybean (compared to longer rotations that involved small grains and perhaps forages) has favored the buildup of populations of Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines and other soilborne soybean pathogens in Indiana fields. 3
5 Figure 6. Spores of the SDS-pathogen: (a) Numerous macrospores like these make the blue stain that s visible on the outside of soybean roots with severe SDS (b) Chlamydospores are long-lasting and can survive in soil and plant debris Purdue studies have found that soybean roots were not visually healthier after a rotation with corn compared to continuous soybean. When corn is grown in the field, soilborne soybean pathogen populations may decline, but not enough to substantially reduce the problem when soybean is grown in the field the following year. Although a twoyear rotation may hold soybean cyst nematode populations below threshold levels when its initial population is low, such a rotation appears to be too short to reduce populations of Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines during the year corn is grown. It is not understood why SDS can be severe even after several years of continuous corn. Resistant Soybean Varieties Soybean breeders are developing SDS-resistant varieties, but progress has been slow. While most seed companies have removed highly susceptible varieties from their inventories, no highly resistant varieties are available. Because seed companies continually introduce new varieties, and retire older ones, it is critical that growers seek accurate information about how each variety reacts to SDS. Read variety descriptions carefully, and when looking at a variety described as resistant, ask seed dealers how extensively it was tested under conditions known to favor SDS. Interactions with Other Soilborne Organisms The combined action of Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines and soybean cyst nematode (SCN) will damage a soybean variety susceptible to both pathogens much more than either pathogen could on its own. Both pathogens are considered present in at least half of Indiana s fields. Production practices that maintain SCN at low levels may reduce the risk for SDS, but much more work is necessary to better understand the nature of the interaction of the two pathogens. If a field infested with the SDS pathogen has not been evaluated for SCN, it should be, and if SCN is present, a management strategy for both pests should be implemented. Conclusions Growers should keep good field records of when and where SDS and other soilborne diseases occur. Growers also should map problem fields or areas within fields. Handheld GPS receivers work well, but even simple sketched maps will help record problem areas. Documenting problem areas will allow growers to determine if management practices are reducing problems, holding them steady, or are failing to provide suppression. Fields severely affected by SDS should be earmarked for later planting when they are scheduled for soybean planting in the future, and every operation improving water permeability should be considered including compactioncorrecting tillage or tile drainage. Finally, varieties with some degree of resistance should be planted in these fields. Acknowledgements SDS research has been supported by the Indiana Soybean Board, North Central Soybean Research Program, and United Soybean Board. Purdue Agriculture 4/06 It is the policy of the Cooperative Extension Service, David C. Petritz, Director, that all persons shall have equal opportunity and access to the programs and facilities without regard to race, color, sex, religion, national origin, age, marital status, parental status, sexual orientation, or disability. is an Affirmative Action employer. This material may be available in alternative formats EXT-INFO
No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year.
 No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year. This presentation focuses on integrated pest management of corn and soybean
No matter the weather conditions, there will be problematic diseases every year. Which disease may change from year to year. This presentation focuses on integrated pest management of corn and soybean
Charcoal Rot Management in the North Central Region
 A4037 Charcoal Rot Management in the North Central Region Damon Smith, Marty Chilvers, Anne Dorrance, Teresa Hughes, Daren Mueller, Terry Niblack, Kiersten Wise Introduction Charcoal rot of soybean (figure
A4037 Charcoal Rot Management in the North Central Region Damon Smith, Marty Chilvers, Anne Dorrance, Teresa Hughes, Daren Mueller, Terry Niblack, Kiersten Wise Introduction Charcoal rot of soybean (figure
Disease Management In Irrigated Row Crops
 Disease Management In Irrigated Row Crops Melvin A. Newman, Ph.D. Professor University of Tennessee Extension Entomology and Plant Pathology Dept. Jackson, TN 6 Soybean Disease Loss Estimate for Tennessee,
Disease Management In Irrigated Row Crops Melvin A. Newman, Ph.D. Professor University of Tennessee Extension Entomology and Plant Pathology Dept. Jackson, TN 6 Soybean Disease Loss Estimate for Tennessee,
CPN Charcoal Rot
 S OY B E A N D I S E A S E M A N A G E M E N T CPN-1004 Charcoal Rot Charcoal rot of soybean (Figure 1) is caused by the soilborne fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Figure 2), which can infect more than
S OY B E A N D I S E A S E M A N A G E M E N T CPN-1004 Charcoal Rot Charcoal rot of soybean (Figure 1) is caused by the soilborne fungus Macrophomina phaseolina (Figure 2), which can infect more than
DISEASE FORECASTER Purdue Extension
 BP-64-W Melcast uses hourly leaf wetness and temperature data to help melon growers schedule fungicide applications for managing Alternaria leaf blight, anthracnose, and gummy stem blight. The system is
BP-64-W Melcast uses hourly leaf wetness and temperature data to help melon growers schedule fungicide applications for managing Alternaria leaf blight, anthracnose, and gummy stem blight. The system is
Wheat Disease Identification
 Wheat Disease Identification Contents Diseases affecting heads and grain Common bunt... 1 Fusarium head blight... 2 Loose smut... 3 Sooty head molds... 4 Stagonospora nodorum blotch... 5 Diseases affecting
Wheat Disease Identification Contents Diseases affecting heads and grain Common bunt... 1 Fusarium head blight... 2 Loose smut... 3 Sooty head molds... 4 Stagonospora nodorum blotch... 5 Diseases affecting
Grain Yield. Soybean Growth and Development. Yield Components of Soybean. Plants/Branches per area Lauer
 Soybean yield is a complex series of interactions Soybean Growth and Development Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weather YIELD Weeds Insects Variety Diseases SCN Yield Components of Soybean Soybean
Soybean yield is a complex series of interactions Soybean Growth and Development Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weather YIELD Weeds Insects Variety Diseases SCN Yield Components of Soybean Soybean
Corn and Soybean Disease Concerns
 Atlantic Corn, Soybean, Cereal & Oilseed Growers Symposium February 12 th, 2014 Corn and Soybean Disease Concerns Bill Thomas Corn: Anthracnose Northern Corn Leaf Blight Eye spot Yield reductions, reduced
Atlantic Corn, Soybean, Cereal & Oilseed Growers Symposium February 12 th, 2014 Corn and Soybean Disease Concerns Bill Thomas Corn: Anthracnose Northern Corn Leaf Blight Eye spot Yield reductions, reduced
Soybean. yield-limiting FactorS in WiSconSin
 Soybean yield-limiting FactorS in WiSconSin Authors Shawn Conley, Ph.D. Eileen Cullen, Ph.D. Vince Davis, Ph.D. Paul Esker, Ph.D. State Soybean Specialist Extension Field Crops Entomologist Cropping Systems
Soybean yield-limiting FactorS in WiSconSin Authors Shawn Conley, Ph.D. Eileen Cullen, Ph.D. Vince Davis, Ph.D. Paul Esker, Ph.D. State Soybean Specialist Extension Field Crops Entomologist Cropping Systems
Disease in this heat? John Damicone, Extension Plant Pathologist
 Entomology and Plant Pathology, Oklahoma State University 127 Noble Research Center, Stillwater, OK74078 405.744.5527 Vol. 10, No. 18 http://entoplp.okstate.edu/pddl/ Aug 4, 2011 Disease in this heat?
Entomology and Plant Pathology, Oklahoma State University 127 Noble Research Center, Stillwater, OK74078 405.744.5527 Vol. 10, No. 18 http://entoplp.okstate.edu/pddl/ Aug 4, 2011 Disease in this heat?
Maximizing the Value of Foliar Fungicides in Corn by Mark Jeschke, Agronomy Research Manager
 CROP INSIGHTS Summary Maximizing the Value of Foliar Fungicides in Corn by Mark Jeschke, Agronomy Research Manager Pioneer Hi-Bred has conducted extensive research to better understand the value of foliar
CROP INSIGHTS Summary Maximizing the Value of Foliar Fungicides in Corn by Mark Jeschke, Agronomy Research Manager Pioneer Hi-Bred has conducted extensive research to better understand the value of foliar
Back to Basics: Root rots, Leaf blights and the Disease Triangle. Drs. Anne Dorrance and Pierce Paul
 Back to Basics: Root rots, Leaf blights and the Disease Triangle Drs. Anne Dorrance and Pierce Paul Key Root Rot Pathogens Factors that favor development AND Moist conditions after planting. SCN populations
Back to Basics: Root rots, Leaf blights and the Disease Triangle Drs. Anne Dorrance and Pierce Paul Key Root Rot Pathogens Factors that favor development AND Moist conditions after planting. SCN populations
1. Symptoms of take-all in wheat 1 2. Assessing early-season hail damage on corn 4 3. Effect of stand loss on corn yields 6
 Number 194 May 29, 2009 1. Symptoms of take-all in wheat 1 2. Assessing early-season hail damage on corn 4 3. Effect of stand loss on corn yields 6 1. Symptoms of take-all in wheat In years with a wet
Number 194 May 29, 2009 1. Symptoms of take-all in wheat 1 2. Assessing early-season hail damage on corn 4 3. Effect of stand loss on corn yields 6 1. Symptoms of take-all in wheat In years with a wet
Pest & Crop. Newsletter IN THIS ISSUE. Purdue Cooperative Extension Service. Insects, Mites, and Nematodes. Home Current Year Past Years Subscribe
 Home Current Year Past Years Subscribe Pest & Crop Newsletter Purdue Cooperative Extension Service IN THIS ISSUE Issue 21, August 26, 2016 USDA-NIFA Extension IPM Grant Insects, Mites, and Nematodes VIDEO:
Home Current Year Past Years Subscribe Pest & Crop Newsletter Purdue Cooperative Extension Service IN THIS ISSUE Issue 21, August 26, 2016 USDA-NIFA Extension IPM Grant Insects, Mites, and Nematodes VIDEO:
2019 SOYBEANS SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE AND INSECT GUIDE VARIETY SELECTION AND POSITIONING
 2019 SOYBEANS SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE AND INSECT GUIDE VARIETY SELECTION AND POSITIONING Table of contents Yield and performance 3 Final population recommendations by management zone 4 Plant
2019 SOYBEANS SEED- AND SOIL-BORNE SOYBEAN DISEASE AND INSECT GUIDE VARIETY SELECTION AND POSITIONING Table of contents Yield and performance 3 Final population recommendations by management zone 4 Plant
Assessment of Certified Crop Adviser Experience with and Knowledge of Early and Mid-season Soybean Diseases Caused by Oomycetes
 Sociology Technical Reports Sociology 10-2012 Assessment of Certified Crop Adviser Experience with and Knowledge of Early and Mid-season Soybean Diseases Caused by Oomycetes J. Gordon Arbuckle Iowa State
Sociology Technical Reports Sociology 10-2012 Assessment of Certified Crop Adviser Experience with and Knowledge of Early and Mid-season Soybean Diseases Caused by Oomycetes J. Gordon Arbuckle Iowa State
2018 Soybeans. Variety Selection and Positioning
 2018 Soybeans Variety Selection and Positioning Yield & Performance = 2 Variety Plant Types Thin Varieties Branching Varieties Between Varieties 3 Soil Type Population recommendations by management zone
2018 Soybeans Variety Selection and Positioning Yield & Performance = 2 Variety Plant Types Thin Varieties Branching Varieties Between Varieties 3 Soil Type Population recommendations by management zone
Indiana Soil and Water
 EXTENSION AY-363-W Indiana Soil and Water Authors Jennifer Woodyard and Eileen Kladivko Four Strategies to Improve Your Field s Soil Health Purdue Agronomy ag.purdue.edu/agry What Is Soil Health? The definition
EXTENSION AY-363-W Indiana Soil and Water Authors Jennifer Woodyard and Eileen Kladivko Four Strategies to Improve Your Field s Soil Health Purdue Agronomy ag.purdue.edu/agry What Is Soil Health? The definition
Southwest MN IPM STUFF
 Southwest MN IPM STUFF All the pestilence that s fit to print IPM STUFF 2017-14 Volume 20 number 14 08/18/2017 This newsletter and the advice herein are free. You usually get what you pay for. Crop weather
Southwest MN IPM STUFF All the pestilence that s fit to print IPM STUFF 2017-14 Volume 20 number 14 08/18/2017 This newsletter and the advice herein are free. You usually get what you pay for. Crop weather
Soybean IPM Elements Revised March, 2012
 Soybean IPM Elements Revised March, 2012 Edited by Jim Jasinski Contributing Authors: Ron Hammond, Andy Michels (Entomology); Mark Loux, Mark Sulc, Peter Thomison (Horticulture & Crop Science); Robert
Soybean IPM Elements Revised March, 2012 Edited by Jim Jasinski Contributing Authors: Ron Hammond, Andy Michels (Entomology); Mark Loux, Mark Sulc, Peter Thomison (Horticulture & Crop Science); Robert
This presentation is available at Borges, University of Wisconsin Agronomy
 SOYBEAN YIELD IS A COMPLEX SERIES OF INTERACTIONS Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weeds YIELD Weather Insects Variety Diseases SCN WISCONSIN SOYBEAN PRODUCTION KEYS TO SUCCESS Fertilize and lime
SOYBEAN YIELD IS A COMPLEX SERIES OF INTERACTIONS Management Soil type Fertility Herbicide Weeds YIELD Weather Insects Variety Diseases SCN WISCONSIN SOYBEAN PRODUCTION KEYS TO SUCCESS Fertilize and lime
Soil Fertility: Current Topic June 19, 2010
 IS IN-SEASON FERTILIZATION FOR SOYBEAN EFFECTIVE? Antonio Mallarino, Professor, Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Questions often arise in June about "emergency or catch-up" fertilization for
IS IN-SEASON FERTILIZATION FOR SOYBEAN EFFECTIVE? Antonio Mallarino, Professor, Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Questions often arise in June about "emergency or catch-up" fertilization for
Public Soybean Varieties for Indiana (1997)
 Agronomy Guide Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service CROPS (SOYBEANS) AY-270 Public Soybean Varieties for Indiana (1997) J. R. Wilcox, T. S Abney and E. P. Christmas USDA-Agricultural Research
Agronomy Guide Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service CROPS (SOYBEANS) AY-270 Public Soybean Varieties for Indiana (1997) J. R. Wilcox, T. S Abney and E. P. Christmas USDA-Agricultural Research
BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GUIDE
 WISCONSIN BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GUIDE BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES The mission of the Wisconsin Soybean Marketing Board (WSMB) is to maximize the profitability of Wisconsin s soybean producers by investing
WISCONSIN BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GUIDE BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES The mission of the Wisconsin Soybean Marketing Board (WSMB) is to maximize the profitability of Wisconsin s soybean producers by investing
STATUS OF APHANOMYCES ROOT ROT IN WISCONSIN. C.R. Grau 1. Introduction
 STATUS OF APHANOMYCES ROOT ROT IN WISCONSIN C.R. Grau 1 Introduction Alfalfa is the primary forage crop in Wisconsin and is a key element in the state s dairy industry. The yield of new varieties is greater
STATUS OF APHANOMYCES ROOT ROT IN WISCONSIN C.R. Grau 1 Introduction Alfalfa is the primary forage crop in Wisconsin and is a key element in the state s dairy industry. The yield of new varieties is greater
Fall-Applied Herbicide Applications in Indiana
 WS-8-W Fall-Applied Herbicide Applications in Indiana Gregory J. Bossaer White County Extension Educator Jerry N. Nelson Knox County Extension Educator Steven D. Siegelin Former Adams County Extension
WS-8-W Fall-Applied Herbicide Applications in Indiana Gregory J. Bossaer White County Extension Educator Jerry N. Nelson Knox County Extension Educator Steven D. Siegelin Former Adams County Extension
Oomycete Diseases in the North-Central Region: A Survey of Certified Crop Advisers
 Sociology Technical Reports Sociology 12-2011 Oomycete Diseases in the North-Central Region: A Survey of Certified Crop Advisers J. Gordon Arbuckle Iowa State University, arbuckle@iastate.edu Alison E.
Sociology Technical Reports Sociology 12-2011 Oomycete Diseases in the North-Central Region: A Survey of Certified Crop Advisers J. Gordon Arbuckle Iowa State University, arbuckle@iastate.edu Alison E.
Long term impact of soybean rust on the Midwest corn-soybean rotation system
 Long term impact of soybean rust on the Midwest corn-soybean rotation system Gary Munkvold, Associate Professor and Seed Science Endowed Chair Dept. of Plant Pathology, Iowa State University Outline Factors
Long term impact of soybean rust on the Midwest corn-soybean rotation system Gary Munkvold, Associate Professor and Seed Science Endowed Chair Dept. of Plant Pathology, Iowa State University Outline Factors
Canola Diseases. Kurtis Schroeder Department of Plant Pathology Washington State University Pullman, WA
 Canola Diseases Kurtis Schroeder Department of Plant Pathology Washington State University Pullman, WA Outline General overview of disease situation Soilborne Diseases Rhizoctonia Sclerotinia Potential
Canola Diseases Kurtis Schroeder Department of Plant Pathology Washington State University Pullman, WA Outline General overview of disease situation Soilborne Diseases Rhizoctonia Sclerotinia Potential
REPORT TO THE OREGON PROCESSED VEGETABLE COMMISSION:
 REPORT TO THE OREGON PROCESSED VEGETABLE COMMISSION: Title: Impact of biological control on white mold sclerotial survival and disease severity in subsequent resistant and susceptible bean crops. Principal
REPORT TO THE OREGON PROCESSED VEGETABLE COMMISSION: Title: Impact of biological control on white mold sclerotial survival and disease severity in subsequent resistant and susceptible bean crops. Principal
BEFORE USING ANY PESTICIDE STOP READ THE LABEL I Prepared by Furney A. Todd, Extension Professor of Plant Pathology North Carolina State University at
 CONTROL BLACK IN BU RLEY / TOBACCO BEFORE USING ANY PESTICIDE STOP READ THE LABEL I Prepared by Furney A. Todd, Extension Professor of Plant Pathology North Carolina State University at Raleigh and the
CONTROL BLACK IN BU RLEY / TOBACCO BEFORE USING ANY PESTICIDE STOP READ THE LABEL I Prepared by Furney A. Todd, Extension Professor of Plant Pathology North Carolina State University at Raleigh and the
Daren Mueller, ISU Extension Field Crop
 Integrated management of sudden death syndrome of soybean Daren Mueller, ISU Extension Field Crop Pathologist Crop Advantage Series 2010 @dsmuelle Symptoms SDS Root Rot Yield Loss Disease incidence and
Integrated management of sudden death syndrome of soybean Daren Mueller, ISU Extension Field Crop Pathologist Crop Advantage Series 2010 @dsmuelle Symptoms SDS Root Rot Yield Loss Disease incidence and
In This Issue. Insects, Mites, And Nematodes. Purdue Cooperative Extension Service. September 19, Issue 24. Agronomy Tips
 Purdue Cooperative Extension Service September 19, 2008 - Issue 24 In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Hessian Fly Continues to Spread Black Light Trap Catch Report Plant Diseases Impact of Heavy
Purdue Cooperative Extension Service September 19, 2008 - Issue 24 In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Hessian Fly Continues to Spread Black Light Trap Catch Report Plant Diseases Impact of Heavy
Interpreting Nitrate Concentration in Tile Drainage Water
 Agronomy Guide AY-318-W SOILS (TILLAGE) Sylvie Brouder, Brenda Hofmann, Eileen Kladivko, Ron Turco, Andrea Bongen, Purdue University Department of Agronomy; Jane Frankenberger, Purdue University Department
Agronomy Guide AY-318-W SOILS (TILLAGE) Sylvie Brouder, Brenda Hofmann, Eileen Kladivko, Ron Turco, Andrea Bongen, Purdue University Department of Agronomy; Jane Frankenberger, Purdue University Department
1. Potassium deficiency in corn and soybeans 1 2. Residue treatment in continuous no-till wheat systems 3
 Number 61 December 15, 2006 1. Potassium deficiency in corn and soybeans 1 2. Residue treatment in continuous no-till wheat systems 3 1. Potassium deficiency in corn and soybeans We have been seeing a
Number 61 December 15, 2006 1. Potassium deficiency in corn and soybeans 1 2. Residue treatment in continuous no-till wheat systems 3 1. Potassium deficiency in corn and soybeans We have been seeing a
Expert views on Root Health from around the world. Dr. Melanie Goll Development Support Manager, Syngenta
 Expert views on Root Health from around the world Dr. Melanie Goll Development Support Manager, Syngenta Content The invisible half of the plant Cause and consequence The complexity challenge Holistic
Expert views on Root Health from around the world Dr. Melanie Goll Development Support Manager, Syngenta Content The invisible half of the plant Cause and consequence The complexity challenge Holistic
Apr
 MISSISSIPPI SOYBEAN PROMOTION BOARD PROJECT NO. 78-2014 (YEAR 1) 2014 Annual Report Title: Identification and characterization of mystery disease pathogen that is prevalent in Mississippi soybean fields
MISSISSIPPI SOYBEAN PROMOTION BOARD PROJECT NO. 78-2014 (YEAR 1) 2014 Annual Report Title: Identification and characterization of mystery disease pathogen that is prevalent in Mississippi soybean fields
Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops
 1 of 7 29/06/2007 16:33 Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops Author: OMAFRA Staff Creation Date: 01 March 2002 Last Reviewed: 01 March 2002 Agronomy Guide > Pub 811: Soil Management and Fertilizer
1 of 7 29/06/2007 16:33 Soil Management and Fertilizer Use: Cover Crops Author: OMAFRA Staff Creation Date: 01 March 2002 Last Reviewed: 01 March 2002 Agronomy Guide > Pub 811: Soil Management and Fertilizer
February, 2007, Volume 7, Issue 1. Available online at:
 Corn & Soybean News February, 00, Volume, Issue 1 Available online at: www.uky.edu/ag/cornsoy Cooperating Departments: Agricultural Economics, Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering, Entomology, Plant
Corn & Soybean News February, 00, Volume, Issue 1 Available online at: www.uky.edu/ag/cornsoy Cooperating Departments: Agricultural Economics, Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering, Entomology, Plant
AGRONOMY 375 Exam II Key November 2, 2018
 1 AGRONOMY 375 Exam II Key November 2, 2018 3 pts 1. a) Latitude, previous crop residue, and soil drainage all influence soil temperature, which is critical in determining early season corn crop growth
1 AGRONOMY 375 Exam II Key November 2, 2018 3 pts 1. a) Latitude, previous crop residue, and soil drainage all influence soil temperature, which is critical in determining early season corn crop growth
Nematode Management in Field Crops
 Nematode Management in Field Crops Hillary L. Mehl, Extension Plant Pathologist, Virginia Tech Tidewater AREC Plant parasitic nematodes can be highly damaging to crops and reduce yields. Aboveground signs
Nematode Management in Field Crops Hillary L. Mehl, Extension Plant Pathologist, Virginia Tech Tidewater AREC Plant parasitic nematodes can be highly damaging to crops and reduce yields. Aboveground signs
A closer look at pulse diseases. Barbara Ziesman Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease 2017 Regional Pulse Meetings
 A closer look at pulse diseases Barbara Ziesman Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease 2017 Regional Pulse Meetings Seed quality Quality can mean different things depending on whether you are talking about
A closer look at pulse diseases Barbara Ziesman Provincial Specialist, Plant Disease 2017 Regional Pulse Meetings Seed quality Quality can mean different things depending on whether you are talking about
Robyne Bowness. Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development Lacombe, AB. Agronomy Update January 18 th, 2011
 Robyne Bowness Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development Lacombe, AB Agronomy Update January 18 th, 2011 Field Peas and Lentils Pulse crops grown for feed, food, and ingredients Valuable in crop rotation
Robyne Bowness Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development Lacombe, AB Agronomy Update January 18 th, 2011 Field Peas and Lentils Pulse crops grown for feed, food, and ingredients Valuable in crop rotation
Pinus species. Propagation. Pests and Diseases. Borers (flathead borers, roundhead borers)
 Pine Pinus species Propagation Pines are usually propagated by seed collected in the autumn from kiln dried cones and sown in the spring. Seeds should germinate in 2-6 weeks with a seed treatment of 40F
Pine Pinus species Propagation Pines are usually propagated by seed collected in the autumn from kiln dried cones and sown in the spring. Seeds should germinate in 2-6 weeks with a seed treatment of 40F
Natural Resources Conservation Service
 Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Health 101 What is soil health and how do we measure it? Name: Tom Roth Title: Conservation Agronomist Location, Salina Kansas Email: thomas.roth@ks.usda.gov
Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Health 101 What is soil health and how do we measure it? Name: Tom Roth Title: Conservation Agronomist Location, Salina Kansas Email: thomas.roth@ks.usda.gov
Soybean Seeding Rates and Seed Treatments: What Did We Learn?
 Soybean Seeding Rates and Seed Treatments: What Did We Learn? Freeport, IL- In 2018, Highland Community College decided to develop their 8-acre research farm in order to provide an outdoor classroom for
Soybean Seeding Rates and Seed Treatments: What Did We Learn? Freeport, IL- In 2018, Highland Community College decided to develop their 8-acre research farm in order to provide an outdoor classroom for
Biology and Ecology of Soilborne Organisms
 Identification, Assessment and Management of Soilborne Plant Pathogens in Vegetable Production Systems Biology and Ecology of Soilborne Organisms Beth K. Gugino Department of Plant Pathology and Environmental
Identification, Assessment and Management of Soilborne Plant Pathogens in Vegetable Production Systems Biology and Ecology of Soilborne Organisms Beth K. Gugino Department of Plant Pathology and Environmental
Pea root rot in Alberta: surveys, research and recommendations
 Pea root rot in Alberta: surveys, research and recommendations S. Chatterton, M.W. Harding and R. Bowness Agronomy Update January 21 st, Lethbridge, AB Root rot development during late flowering Stunting,
Pea root rot in Alberta: surveys, research and recommendations S. Chatterton, M.W. Harding and R. Bowness Agronomy Update January 21 st, Lethbridge, AB Root rot development during late flowering Stunting,
Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions
 Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions Rocky Lemus 1 and Jason Weirich 1 Extension Forage Specialist Visit us at http://msucares.com/crops/forages/index.html As we approach spring growth, weed control becomes
Making Pasture Weed Control Decisions Rocky Lemus 1 and Jason Weirich 1 Extension Forage Specialist Visit us at http://msucares.com/crops/forages/index.html As we approach spring growth, weed control becomes
Institute of Ag Professionals
 Institute of Ag Professionals Proceedings of the 2012 Crop Pest Management Shortcourse & Minnesota Crop Production Retailers Association Trade Show www.extension.umn.edu/agprofessionals Do not reproduce
Institute of Ag Professionals Proceedings of the 2012 Crop Pest Management Shortcourse & Minnesota Crop Production Retailers Association Trade Show www.extension.umn.edu/agprofessionals Do not reproduce
Wheat Foliar Fungicides
 Wheat Foliar s Robert L. Bowden, Extension Plant Pathologist Leaf rust, tan spot, Septoria leaf blotch (also called speckled leaf blotch) and powdery mildew are important fungal foliar diseases of wheat
Wheat Foliar s Robert L. Bowden, Extension Plant Pathologist Leaf rust, tan spot, Septoria leaf blotch (also called speckled leaf blotch) and powdery mildew are important fungal foliar diseases of wheat
Soybean Production in Michigan
 Extension Bulletin E-549, October 98, File. Soybean Production in Michigan By Z. R. Helsel, T. J. Johnston, and L. P. Hart Departments of Crop and Soil Sciences f'formerjyj and botany and Plant Pathology
Extension Bulletin E-549, October 98, File. Soybean Production in Michigan By Z. R. Helsel, T. J. Johnston, and L. P. Hart Departments of Crop and Soil Sciences f'formerjyj and botany and Plant Pathology
Cotton Cultural Practices and Fertility Management 1
 SS-AGR-194 1 David Wright, I. Small, and Nick Dufault 2 Cotton production and management requires much planning and timely action throughout the season. Preparation for planting cotton can be done by strip-tilling
SS-AGR-194 1 David Wright, I. Small, and Nick Dufault 2 Cotton production and management requires much planning and timely action throughout the season. Preparation for planting cotton can be done by strip-tilling
Bob Pearce, David Ditsch, Jack Zeleznik, and Wade Turner
 Vol. 34, No. 1, 2002 Burn Down Management of Winter Cereal Cover Crops for No-tillage Burley Tobacco Production Bob Pearce, David Ditsch, Jack Zeleznik, and Wade Turner INTRODUCTION Recent developments
Vol. 34, No. 1, 2002 Burn Down Management of Winter Cereal Cover Crops for No-tillage Burley Tobacco Production Bob Pearce, David Ditsch, Jack Zeleznik, and Wade Turner INTRODUCTION Recent developments
Corn and Soybean Practices following Severe Drought. Roger Elmore and Andy Lenssen Department of Agronomy, ISU
 Corn and Soybean Practices following Severe Drought Roger Elmore and Andy Lenssen Department of Agronomy, ISU Shawn Macha 2012 growing season Corn & Soybean Dry fall, 2011 & spring 2012. Early-planting
Corn and Soybean Practices following Severe Drought Roger Elmore and Andy Lenssen Department of Agronomy, ISU Shawn Macha 2012 growing season Corn & Soybean Dry fall, 2011 & spring 2012. Early-planting
Why is Rhizoctonia increasing? Favorable weather Susceptible crops sown in rotations - Crops affect populations of R. solani in soil Management Rhizoc
 RHIZOCTONIA FORUM: EPIDEMIOLOGY AND ROTATION CROPS Carol Windels University of Minnesota NW Research & Outreach Center Crookston, Minnesota Moderator: Gary Franc Why is Rhizoctonia increasing? Favorable
RHIZOCTONIA FORUM: EPIDEMIOLOGY AND ROTATION CROPS Carol Windels University of Minnesota NW Research & Outreach Center Crookston, Minnesota Moderator: Gary Franc Why is Rhizoctonia increasing? Favorable
4-H CROPS RECORD Record for Year
 4-H 626-W 4-H CROPS RECORD Record for Year Corn Soybeans Oats Wheat Alfalfa (Other) Name Grade (as of Jan. 1) Address Project Leader Signature Years in this project and/or Division enrolled 1. Select the
4-H 626-W 4-H CROPS RECORD Record for Year Corn Soybeans Oats Wheat Alfalfa (Other) Name Grade (as of Jan. 1) Address Project Leader Signature Years in this project and/or Division enrolled 1. Select the
AGRONOMY 375. October 2, Exam 1
 Name AGRONOMY 375 October 2, 2015 Exam 1 There are 14 questions. One bonus question is also included at the end of the exam. A total of 100 points is possible. Best wishes for your success! 6 pts 1. What
Name AGRONOMY 375 October 2, 2015 Exam 1 There are 14 questions. One bonus question is also included at the end of the exam. A total of 100 points is possible. Best wishes for your success! 6 pts 1. What
TIMELY INFORMATION Agriculture & Natural Resources
 PLANT PATHOLOGY SERIES TIMELY INFORMATION Agriculture & Natural Resources EXTENSION PLANT PATHOLOGY, 961 S. DONAHUE DRIVE, AUBURN UNIVERSITY, AL 36849-5624 May 24, 2011 PP-698 2011 Peanut Disease Risk
PLANT PATHOLOGY SERIES TIMELY INFORMATION Agriculture & Natural Resources EXTENSION PLANT PATHOLOGY, 961 S. DONAHUE DRIVE, AUBURN UNIVERSITY, AL 36849-5624 May 24, 2011 PP-698 2011 Peanut Disease Risk
Management of southern rust and frogeye leaf spot. Dr. Carl A. Bradley, University of Kentucky
 Management of southern rust and frogeye leaf spot Dr. Carl A. Bradley, University of Kentucky Carl.Bradley@uky.edu Southern rust of corn New Southern Rust Extension Publication Crop Protection Network
Management of southern rust and frogeye leaf spot Dr. Carl A. Bradley, University of Kentucky Carl.Bradley@uky.edu Southern rust of corn New Southern Rust Extension Publication Crop Protection Network
2011 Pennsylvania Vegetable Marketing and Research Program Pennsylvania Vegetable Growers Association Report December 7, 2011
 2011 Pennsylvania Vegetable Marketing and Research Program Pennsylvania Vegetable Growers Association ort December 7, 2011 Title: Extended season management of snap bean root pathogens using combinations
2011 Pennsylvania Vegetable Marketing and Research Program Pennsylvania Vegetable Growers Association ort December 7, 2011 Title: Extended season management of snap bean root pathogens using combinations
Soybean Nematode Management
 Soybean Nematode Management Terry Kirkpatrick and Travis Faske Plant Pathologist/Nematologist The foundation of any nematode control program is the identification of the types of nematodes that are present
Soybean Nematode Management Terry Kirkpatrick and Travis Faske Plant Pathologist/Nematologist The foundation of any nematode control program is the identification of the types of nematodes that are present
EQIP application information by state
 IPM Plan Guide Sheet Practices for Field Crop Production Introduction This tool has been designed as a guide for evaluating on-farm pest management practices for farmers interested in a Natural Resource
IPM Plan Guide Sheet Practices for Field Crop Production Introduction This tool has been designed as a guide for evaluating on-farm pest management practices for farmers interested in a Natural Resource
Timing of Strobilurin Fungicide for Control of Top Dieback in Corn
 Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 3 Issue 6 Kansas Field Research Article 6 217 Timing of Strobilurin Fungicide for Control of Top Dieback in Corn Eric Adee Kansas State University,
Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 3 Issue 6 Kansas Field Research Article 6 217 Timing of Strobilurin Fungicide for Control of Top Dieback in Corn Eric Adee Kansas State University,
Nitrogen Management for Winter Wheat: Principles and Recommendations
 Nitrogen Management for Winter Wheat: Principles and Recommendations M. M. Alley, Soil and Crop Management Research, Virginia Tech Peter Scharf, Research Associate, Virginia Tech D. E. Brann, Extension
Nitrogen Management for Winter Wheat: Principles and Recommendations M. M. Alley, Soil and Crop Management Research, Virginia Tech Peter Scharf, Research Associate, Virginia Tech D. E. Brann, Extension
1. Vertical tillage: What is it and how does it work? 1 2. Potential for wheat die-out during the winter 4 3. Blackleg found in winter canola fields 6
 Number 222 December 11, 2009 1. Vertical tillage: What is it and how does it work? 1 2. Potential for wheat die-out during the winter 4 3. Blackleg found in winter canola fields 6 1. Vertical tillage:
Number 222 December 11, 2009 1. Vertical tillage: What is it and how does it work? 1 2. Potential for wheat die-out during the winter 4 3. Blackleg found in winter canola fields 6 1. Vertical tillage:
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D2-4 Conservation Tillage Practices Interest Approach Ask students what challenges the first farmers faced as colonists moved across North America. Some of the challenges involved
Replanting Options for Corn Chad Lee, James Herbek, J.D. Green, and James Martin, Plant and Soil Sciences; Paul Vincelli, Plant Pathology
 AGR-195 Replanting Options for Corn Chad Lee, James Herbek, J.D. Green, and James Martin, Plant and Soil Sciences; Paul Vincelli, Plant Pathology Evaluating damaged corn stands and determining when to
AGR-195 Replanting Options for Corn Chad Lee, James Herbek, J.D. Green, and James Martin, Plant and Soil Sciences; Paul Vincelli, Plant Pathology Evaluating damaged corn stands and determining when to
Agronomy 375 Key - Exam I February 15, 2013
 Agronomy 375 Key - Exam I February 15, 2013 6 pts 1. A producer can monitor input use efficiency by following the cost of production per bushel. Optimum input mix efficiency and maximum profit are associated
Agronomy 375 Key - Exam I February 15, 2013 6 pts 1. A producer can monitor input use efficiency by following the cost of production per bushel. Optimum input mix efficiency and maximum profit are associated
Foliar Fungicide Use and Management in Field Crops
 Foliar Fungicide Use and Management in Field Crops Alyssa Collins Director, PSU SE Research & Extension Center Assistant Professor, Department of Plant Pathology & Environmental Microbiology Resistance
Foliar Fungicide Use and Management in Field Crops Alyssa Collins Director, PSU SE Research & Extension Center Assistant Professor, Department of Plant Pathology & Environmental Microbiology Resistance
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science. Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices
 Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 8: Employing Conservation Tillage Practices 1 Terms Conservation tillage Continuous cropping Conventional tillage Crop rotation Double cropping Organic farming
ONION DISEASE MANAGEMENT HOWARD F. SCHWARTZ PROFESSOR EMERITUS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
 ONION DISEASE MANAGEMENT HOWARD F. SCHWARTZ PROFESSOR EMERITUS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Monitor Pests and Diseases in Relation to Crop Growth Stages Priority 1 IYSV & Thrips Monitor Pests and Diseases
ONION DISEASE MANAGEMENT HOWARD F. SCHWARTZ PROFESSOR EMERITUS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Monitor Pests and Diseases in Relation to Crop Growth Stages Priority 1 IYSV & Thrips Monitor Pests and Diseases
Wheat Management. Anthony Ohmes University of Missouri Extension
 Wheat Management Anthony Ohmes University of Missouri Extension Wheat Yield Components Head Size Feekes 3 (tillering) # of Heads and Kernels - Feekes 6 (jointing) Kernel Size Feekes 8 Feekes Scale Wheat
Wheat Management Anthony Ohmes University of Missouri Extension Wheat Yield Components Head Size Feekes 3 (tillering) # of Heads and Kernels - Feekes 6 (jointing) Kernel Size Feekes 8 Feekes Scale Wheat
Industry-Leading BREEDING PLAN PLANT PROTECT PERFORM
 Industry-Leading PLAN PLANT PROTECT PERFORM Industry-Leading As an Asgrow brand soybean breeder, I have worked in Soybean Variety Development for seven years with Monsanto. Iowa is unique because there
Industry-Leading PLAN PLANT PROTECT PERFORM Industry-Leading As an Asgrow brand soybean breeder, I have worked in Soybean Variety Development for seven years with Monsanto. Iowa is unique because there
Review of lecture 1: Significance of Plant Disease. Lecture 2: Disease Concept
 Review of lecture 1: Significance of Plant Disease 10% of all food production is lost to disease (30% to all pests) The introduction of exotic plant pathogens has caused great losses: e.g., American chestnut
Review of lecture 1: Significance of Plant Disease 10% of all food production is lost to disease (30% to all pests) The introduction of exotic plant pathogens has caused great losses: e.g., American chestnut
Soybean Production in Missouri
 1 of 9 8/12/2010 11:42 AM University of Missouri Extension G4410, Reviewed October 1993 Soybean Production in Missouri Zane R. Helsel and Harry C. Minor Department of Agronomy In recent years, farmers
1 of 9 8/12/2010 11:42 AM University of Missouri Extension G4410, Reviewed October 1993 Soybean Production in Missouri Zane R. Helsel and Harry C. Minor Department of Agronomy In recent years, farmers
In This Issue. Insects, Mites, And Nematodes. Purdue Cooperative Extension Service USDA-NIFA Extension IPM Grant. August 24, Issue 22
 Purdue Cooperative Extension Service USDA-NIFA Extension IPM Grant August 24, 2012 - Issue 22 In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Bits & Pieces Bean Leaf Beetle Pod Feeding Harvesting and Storing
Purdue Cooperative Extension Service USDA-NIFA Extension IPM Grant August 24, 2012 - Issue 22 In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Bits & Pieces Bean Leaf Beetle Pod Feeding Harvesting and Storing
In This Issue. Insects, Mites, and Nematodes. September 29, No. 26& Crop. Purdue Cooperative Extension Service. Insects, Mites, and Nematodes
 Pest September 29, 2000 - No. 26& Crop In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Stalk Lodging and Postmortem Insect Damage Diagnosis Weeds Managing Winter Annual Weeds, Are Fall Herbicide Treatments
Pest September 29, 2000 - No. 26& Crop In This Issue Insects, Mites, and Nematodes Stalk Lodging and Postmortem Insect Damage Diagnosis Weeds Managing Winter Annual Weeds, Are Fall Herbicide Treatments
Crop Profile for Alfalfa in Nebraska
 Prepared: April, 2000 Crop Profile for Alfalfa in Nebraska General Production Information Nebraska is ranked second in the nation for alfalfa meal production and fifth for alfalfa hay production in 1998.
Prepared: April, 2000 Crop Profile for Alfalfa in Nebraska General Production Information Nebraska is ranked second in the nation for alfalfa meal production and fifth for alfalfa hay production in 1998.
Fertilizer Management
 2 5 Section 5 Fertilizer Management Lloyd Murdock, John Grove, and Greg Schwab The most important first step in your fertilizer management program is to take a soil sample. Except for nitrogen (N), your
2 5 Section 5 Fertilizer Management Lloyd Murdock, John Grove, and Greg Schwab The most important first step in your fertilizer management program is to take a soil sample. Except for nitrogen (N), your
USDA Acreage & Stocks Report
 Wednesday June 30 th 2010 Acreage & Grain Stocks Estimates Bullish for Corn Mildly Friendly Old Soybeans, Bearish New Soybeans Bearish Wheat Corn stock reported 288 million less than average trade estimates.
Wednesday June 30 th 2010 Acreage & Grain Stocks Estimates Bullish for Corn Mildly Friendly Old Soybeans, Bearish New Soybeans Bearish Wheat Corn stock reported 288 million less than average trade estimates.
Arkansas soybean producers use several
 Chapter 16 Production Systems and Economics by L. Ashlock, W. Mayhew, T. Windham, T. Keisling, R. Klerk, D. Beaty and G. Lorenz Arkansas soybean producers use several different irrigated and non-irrigated
Chapter 16 Production Systems and Economics by L. Ashlock, W. Mayhew, T. Windham, T. Keisling, R. Klerk, D. Beaty and G. Lorenz Arkansas soybean producers use several different irrigated and non-irrigated
One of the foundations for an IPM system is scouting your fields. This presentation will outline some of the basics of scouting.
 One of the foundations for an IPM system is scouting your fields. This presentation will outline some of the basics of scouting. 1 This presentation covers three things: Do your homework to prepare for
One of the foundations for an IPM system is scouting your fields. This presentation will outline some of the basics of scouting. 1 This presentation covers three things: Do your homework to prepare for
The University of Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences
 The University of Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences July 3, 2012 www.ugacotton.com Irrigation Management for the 2012 Crop 1 US and Georgia 2012 Cotton Acreage
The University of Georgia Cooperative Extension College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences July 3, 2012 www.ugacotton.com Irrigation Management for the 2012 Crop 1 US and Georgia 2012 Cotton Acreage
Number 142 May 30, 2008
 Number 142 May 30, 2008 1. Wheat disease update 1 2. Causes of white heads in wheat 2 3. New web site for Soil Testing Lab 4 4. Agronomy Field Day in Manhattan: August 22, 2008 6 1. Wheat disease update
Number 142 May 30, 2008 1. Wheat disease update 1 2. Causes of white heads in wheat 2 3. New web site for Soil Testing Lab 4 4. Agronomy Field Day in Manhattan: August 22, 2008 6 1. Wheat disease update
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this lesson:
 Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 1: Understanding Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1.
Unit G: Pest Management Lesson 1: Understanding Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1.
Foliar Fertilization of Soybean Where, When, and Why? Antonio P. Mallarino Iowa State University
 Foliar Fertilization of Soybean Where, When, and Why? Antonio P. Mallarino Iowa State University Foliar Fertilization Crops can use foliar-applied nutrients. High salt or ammonia concentrations damage
Foliar Fertilization of Soybean Where, When, and Why? Antonio P. Mallarino Iowa State University Foliar Fertilization Crops can use foliar-applied nutrients. High salt or ammonia concentrations damage
Site and application information. 1 of 10 8/5/2010 8:46 AM. Trial: SBAseedearl, SBAseedlate
 1 of 10 8/5/2010 8:46 AM myu One Stop Directories Search U of M Print this page using Acrobat Reader Trial: 2002-1SBAseedearl, 2002-1SBAseedlate Seed applied insecticide control of the Soybean Aphid (Aphis
1 of 10 8/5/2010 8:46 AM myu One Stop Directories Search U of M Print this page using Acrobat Reader Trial: 2002-1SBAseedearl, 2002-1SBAseedlate Seed applied insecticide control of the Soybean Aphid (Aphis
Pest Management in Indiana Soybean Production Systems
 1 of 10 9/22/2009 4:10 PM SEARCH JOE HOME JOURNAL GUIDELINES ABOUT JOE CONTACT NATIONAL JOB BANK Current Issue Back Issues Search Subscribe August 2007 // Volume 45 // Number 4 // Research in Brief //
1 of 10 9/22/2009 4:10 PM SEARCH JOE HOME JOURNAL GUIDELINES ABOUT JOE CONTACT NATIONAL JOB BANK Current Issue Back Issues Search Subscribe August 2007 // Volume 45 // Number 4 // Research in Brief //
Improving Canola Yields and Quality Through Best Management Practices for Diseases. Dr. Madeleine Smith
 Improving Canola Yields and Quality Through Best Management Practices for Diseases Dr. Madeleine Smith Talk Outline Results of 2014 Disease Survey In Minnesota Important Diseases in MN Canola Disease Nursery
Improving Canola Yields and Quality Through Best Management Practices for Diseases Dr. Madeleine Smith Talk Outline Results of 2014 Disease Survey In Minnesota Important Diseases in MN Canola Disease Nursery
Development of Plant Diseases Disease of a plant could simply be defined as any alteration of one or more of the ordered series of physiological
 Development of Plant Diseases Disease of a plant could simply be defined as any alteration of one or more of the ordered series of physiological process resulting in a loss of co-ordination of the energy
Development of Plant Diseases Disease of a plant could simply be defined as any alteration of one or more of the ordered series of physiological process resulting in a loss of co-ordination of the energy
MINIMIZING DISEASES OF PEANUT IN THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES. The 2015 Version of the Peanut Disease Risk Index (Peanut Rx)
 MINIMIZING DISEASES OF PEANUT IN THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES The 2015 Version of the Peanut Disease Risk Index (Peanut Rx) Robert Kemerait, Albert Culbreath, Eric Prostko, Tim Brenneman, Nathan Smith,
MINIMIZING DISEASES OF PEANUT IN THE SOUTHEASTERN UNITED STATES The 2015 Version of the Peanut Disease Risk Index (Peanut Rx) Robert Kemerait, Albert Culbreath, Eric Prostko, Tim Brenneman, Nathan Smith,
KNOWING YOUR FIELD A Guide to On-Farm Testing for Peanut Growers
 A Guide to On-Farm Testing for Peanut Growers KNOWING YOUR FIELD A Guide to On-Farm Testing for Peanut Growers To maximize profit when growing peanuts, farmers rely on recommendations for variety selection,
A Guide to On-Farm Testing for Peanut Growers KNOWING YOUR FIELD A Guide to On-Farm Testing for Peanut Growers To maximize profit when growing peanuts, farmers rely on recommendations for variety selection,
Predicting the Last Irrigation of the Season using Watermark Soil Moisture Sensors
 Predicting the Last Irrigation of the Season using Watermark Soil Moisture Sensors This is the last of a series of three factsheets on Watermark Soil Moisture Sensors. The first factsheets details How
Predicting the Last Irrigation of the Season using Watermark Soil Moisture Sensors This is the last of a series of three factsheets on Watermark Soil Moisture Sensors. The first factsheets details How
Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter
 Resources Conservation Practices Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter Conservation Quiz 1. What are the two classes of soil organic matter? 2. How does soil disturbance by tillage decrease soil organic
Resources Conservation Practices Tillage Management and Soil Organic Matter Conservation Quiz 1. What are the two classes of soil organic matter? 2. How does soil disturbance by tillage decrease soil organic
Response of Broad Spectrum and Target Specific Seed Treatments and Seeding Rate on Soybean Seed Yield, Profitability and Economic Risk
 Response of Broad Spectrum and Target Specific Seed Treatments and Seeding Rate on Soybean Seed Yield, Profitability and Economic Risk Adam P. Gaspar*, Daren S. Mueller, Kiersten A. Wise, Martin I. Chilvers,
Response of Broad Spectrum and Target Specific Seed Treatments and Seeding Rate on Soybean Seed Yield, Profitability and Economic Risk Adam P. Gaspar*, Daren S. Mueller, Kiersten A. Wise, Martin I. Chilvers,
Other. Issues. Wheat Other and Issues Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide
 Wheat Other and Issues Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide 52 52 Other Issues www.lsuagcenter.com/wheatoats Waterlogging stress in wheat and oats Occurrence: Waterlogging stress occurs in wheat and
Wheat Other and Issues Oat Weed, Insect and Disease Field Guide 52 52 Other Issues www.lsuagcenter.com/wheatoats Waterlogging stress in wheat and oats Occurrence: Waterlogging stress occurs in wheat and
Soybean Objective Yield Survey Data,
 Washington, D.C. Soybean Objective Yield Survey Data, 1992-2006 Released July 27, 2007, by the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS),, U.S. Department of Agriculture. For information on call
Washington, D.C. Soybean Objective Yield Survey Data, 1992-2006 Released July 27, 2007, by the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS),, U.S. Department of Agriculture. For information on call
