NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
|
|
|
- Abraham Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules and mitochondrial DNA represents circular molecules. All eukaryotic cells contain at least one nucleus. The contents of the nucleus are present as a viscous, amorphous mass of material enclosed by a complex nuclear envelope. Nucleus consists of: Chromosomes, which are present as extended nucleoprotein fibers, called chromatin; Nuclear matrix, which is a proteincontaining fibrillar network; Nucleolus (or some nucleoli) that are responsible for synthesis of rrna and assembling of ribosomes; Nucleoplasm (or karyoplasm) the fluid substance in which the solutes of nucleus are Fig. 1. Position of nucleus in the cell dissolved. CHROMATIN The eukaryotic cell nucleus is typically ~1mm in diameter. It contains a large amount of DNA (a total length of 1-2 meters), which must be efficiently packaged in such a way as to guarantee access to genetic information. Thus, each DNA molecule is packed forming chromatin, a densely staining material initially recognized in two different forms: highly condensed heterochromatin and more diffuse euchromatin. Chemically chromatin is organized from 30% DNA + 40% histones + 25% non-histones + 5% RNA. Chromatin fragments contain DNA (a negatively charged polymer) in complex with highly positively charged (basic) proteins called histones, and much smaller amounts of other DNAbinding proteins, collectively referred to as non-histone proteins. Human histone genes are represented as a family of moderately repeated sequences with variations in the structure, organization, and regulation of the different copies. The histones organize DNA into a regular repeating structure, the basic unit of which is the nucleosome, which wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. There are 5 classes of histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4. They contain Leucine, Lysine, Arginine and other basic amino acids. The quantity of histones is the same in all tissues and they have no tissuespecificity. They induce the tertiary structure of DNA (DNP). The non-histones are acid Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin 1
2 Nucleus. PL5. proteins, are very heterogeneous and comprise: enzymes (for replication, repair, transcription, RNA processing, biogenesis of ribosomes), site-specific proteins, scaffold proteins. More active tissues contain larger quantity and diversity of non-histones. Euchromatin represents the active part of chromatin; contain structural genes that are transcribed. It is less compacted and replicates early in the S period of interphase. Heterochromatin is tightly condensed and contains inactive sequences which are not transcribed. It replicates late in the S period. There are two types of heterochromatin: constitutive and facultative. Facultative heterochromatin contains genes that in some condition, in some tissues may be active, so it can be transformed into euchromatin. It contains coding but inactive sequences. Facultative heterochromatin assures cell differentiation, sexual differentiation, and control of ontogenesis. Constitutive heterochromatin contains repetitive sequences, which always remain condensed. It is represented by centromeres, telomeres, satellites, spacers between genes. Constitutive heterochromatin is the same in all cells. LEVELS OF DNA CONDENSATION I. Nucleosomal. Decondensed chromatin viewed in the electron microscope resembles beads on a string. Each bead is a nucleosome containing 146 bp of DNA wrapped around the core histone octamer, and sealed by a single molecule of linker histone (H1) bound at the point where the DNA enters and exits. H1 also binds to the linker DNA (the string connecting one bead to the next) (Fig. 2, 4). The histone octamer is composed of two molecules each of the four core histones: 2xH2A, 2xH2B, 2xH3 and 2xH4. These are small, basic proteins, which have been highly conserved during evolution. Histone H1, the linker histone, is not part of the nucleosome core (Fig. 5). It is very rich in lysine residues, less well conserved than the core histones, and is larger. The length of DNA in the core particle Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of nucleosome core is invariable (146 bp), but the average length of the linker DNA varies between species and tissues, giving rise to a characteristic repeat length (the average length of DNA in a nucleosome). II. Chromatin folding (Solenoid). Most of the chromatin in the nucleus is in the form of a highly condensed filament about 30-nm in diameter (the 30-nm filament). Formation of these highly condensed filaments is dependent on H1 (one H1 molecule per nucleosome). The condensed 30-nm filament is the result of solenoidal (helical) folding of the beads-on-a- Fig. 6. The solenoidal model of chromatin Fig. 3. Structure of nucleus Fig. 5. Binding of histone H1 to the linker DNA 2
3 string nucleosomal (10 nm) filament, having 6-12 nucleosomes per turn (Fig. 6). Nucleus. PL5. III. Chromatin Loops. The interphase chromosomes are organized into loops of chromatin filament attached to the nuclear skeleton (nuclear matrix) at their bases and projecting into the interior of the nucleus (Fig. 7). Each loop may contain a gene or related cluster of genes whose expression may in principle be regulated at the level of loop structure. The regions of DNA, which interact with matrix, are called MARs (matrix attachment regions) or SARs (scaffold attachment regions), while. The loops contain an average of bp. IV. Metaphase Chromosomes. When the nuclear membrane breaks down during mitosis, chromatin is reorganized to form metaphase chromosomes in which a chromosomal metaphase scaffold is folded to form a quite regular helical coil, to which chromatin loops are attached at their bases (Fig. 8). Sister chromatids are usually of opposite helical handedness. The organization of DNA into the organelle, which is a chromosome, is most obvious at metaphase when the chromosome is condensed into a highly structured body. At this point in the cell cycle important chromosomal elements are visible: two arms (short p and long q), centromere and telomere. The telomeres are special sequences responsible for preventing the shortening of chromosomes during replication, protect linear molecules of DNA against actions of exonucleases and prevent joining of different chromosomes. Structurally, the telomeres are rich in tandemly repeated G/C sequences with a total length of 3 20 kb. The centromere is the genetic element (formed by constitutive heterochromatin) responsible for chromosome Fig. 8. Structure of a chromosome Fig. 7. Attachment of solenoid fiber to scaffold segregation during cell division. It is visible at metaphase as a constriction in mammalian chromosomes and is the site of attachment of spindle microtubules to the proteins that make up the kinetochore. Centromere contains A/T rich repetitive sequences. Within centromeres, H3 histone is substituted by CENP-A histone. Chromatine activation: Gene activity depends on: the stage of ontogenetic period, type of cell, environment. It also depends on the level of DNA condensation. Transcription is associated with nucleosomal level only. Transcriptionally active chromatin regions have core histones undergoing high rates of acetylation and deacetylation. Histone acetylation (which is a type of post-translational modification of histones) is generally linked to gene activation. The enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group (functional group COCH 3 ) are called histone acetyltransferases (HAT), which can also acetylate non-histone proteins, such as transcription factors and nuclear receptors to facilitate gene expression. Removal of the acetyl group by histone deacetylases (HDACs) condenses DNA structure, thereby preventing transcription. Another common way to block DNA and inhibit gene transcription is DNA methylation, which involves the addition of a methyl group (CH 3 ) to cytosine or adenine. 3
4 So, the post-translational modifications of histones include: Methylation of H3 (Lys4) active expression of a gene; Methylation of H3 (Lys9) diminishing of transcription; Histone acetylation assisting the transcription, gene activation; Histone deacetylation chromatin condensation, inactivation of transcription; Phosphorylation of H1 chromatin supercoiling Dephosphorylation of H1 chromatin decondensation. Nucleus. PL5. NUCLEAR ENVELOPE Nuclear envelope is a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus during most of the cell's lifecycle. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), having numerous ribosomes attached to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pores that perforate the nuclear envelope. These pores regulate the selective passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, The space between the outer and inner membranes is termed the perinuclear space and is connected with the lumen of the rough ER. Structural support is provided to the nuclear envelope by two different networks of intermediate filaments. Along the inner surface of the nucleus, one of these networks is organized into the nuclear lamina (made of fibrous proteins nuclear lamins and membrane associated proteins), which binds to chromatin, integral membrane proteins, and other nuclear components. The nuclear lamina is also thought to play a role in directing materials inside the nucleus toward the nuclear pores for export and in the disintegration of the nuclear envelope during cell division and its subsequent reformation at the end of the process. The other intermediate filament network is located on the outside of the outer nuclear membrane and is not organized in such a systemic way as the nuclear lamina. The amount of traffic that must pass through the nuclear envelope on a continuous basis in order for the eukaryotic cell to function properly is considerable. RNA and ribosomal subunits must be constantly transferred from the nucleus where they are made to the cytoplasm, and histones, gene regulatory proteins, DNA and RNA polymerases, and other substances required for nuclear activities must be imported from the cytoplasm. An active mammalian cell can synthesize about 20,000 ribosome subunits per minute, and at certain points in the cell cycle, as many as 30,000 histones per minute are required by the nucleus. In order for such a tremendous number of molecules to pass through the nuclear envelope in a timely manner, the nuclear pores must be highly efficient at selectively allowing the passage of materials to and from the nucleus. Nuclear Pores It is generally thought that a protein structure called the nuclear pore complex (NPCs) that surrounds each pore plays a key role in allowing the active transport of a selected set of large molecules into and out of the nucleus. The nuclear pore proteins are called nucleoporins, which are not only engaged in nucleocytoplasmic transport, but also in transcription regulation, kinetochore organization and other cellular events. Given the various functions of nucleoporins, it is not surprising to find them involved in a wide variety of human disease. 4
5 Nucleus. PL5. In addition to their role in nuclear transport, nuclear pores are important as sites where the outer membrane and inner membrane of the nuclear envelope are fused together. Due to this fusion, the membranes can be considered continuous with one another although they have different biochemical characteristics and can function in distinctive ways. Since the outer nuclear membrane is also continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), both it and the inner nuclear membrane can exchange membranous materials with the ER. This capability enables the nuclear envelope to grow bigger or smaller when necessary to accommodate the dynamic contents of the nucleus. KARYOPLASM The karyoplasm or nucleoplasm or nuclear sap is a highly viscous liquid contained within the nucleus that surrounds the chromosomes and other subnuclear organelles. A network of fibers known as the nuclear matrix (scaffold, skeleton) can also be found in the nucleoplasm. Nuclear Scaffold The skeleton maintains the overall size and shape of the nucleus. The matrix acts as a structural attachment site for the DNA loops during the interphase: evolutionary highly conserved bp long DNA sequences, referred to as SARs (Scaffold Associated Regions), have been identified that define the base of DNA loops, anchoring them to specific proteins (SAPs - Scaffold Associated Proteins). By means of such chromosomal attachment sites, the matrix might help to organize chromosomes, localize genes, and regulate DNA transcription and replication within the nucleus. NUCLEOLUS Nucleolus is a part of nucleus responsible for biogenesis of ribosomes. It is the place of: transcription of ribosomal genes and synthesis of precursor rrna (45S), followed by processing of 45S rrna and formation of 3 types of rrna: 5.8S + 18S + 28S. As a result of assembling the RNP is formed: rrna 18S + 33 ribosomal proteins = 40S RNP (small ribosomal subunit) and rrna 28S + rrna 5.8S +rrna 5S + 49 ribosomal proteins =60S RNP (large ribosomal subunit). Sequences of DNA containing ribosomal genes (tandem repeats of rrna genes) form the nucleolar organizer region (NOR). The human genome contains more than 200 clustered copies of the rrna genes on five different chromosomes (13, 14, 15, 21, 22). Transcription of rrna genes is executed by RNA-polymerase I (rrna 45S) and III (for rrna 5S). Further processing is needed to generate the 18S RNA, 5.8S and 28S RNA molecules. This processing involves the function of a 5
6 Nucleus. PL5. class of small nucleolar RNAs (snornas) which are complexed with proteins and exist as smallnucleolar-ribonucleoproteins (snornps). Once the rrna subunits are processed, they are ready to be assembled into larger ribosomal subunits. Fig. 9. Scheme of ribosome biogenesis. 6
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome
 Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome Ashley Soosay This OpenCourseWare@UNIMAS and its related course materials are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0
Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome Ashley Soosay This OpenCourseWare@UNIMAS and its related course materials are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0
Cell Nucleus. Chen Li. Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine
 Cell Nucleus Chen Li Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Structure of the nucleus: nuclear pore complex (NPC), lamina, nucleolus,
Cell Nucleus Chen Li Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Structure of the nucleus: nuclear pore complex (NPC), lamina, nucleolus,
The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure
 The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure Size of the human genom: The diploid human genome contains approximately 6 billion base pairs of DNA packaged into 23 chromosome pairs. Each diploid cell therefore
The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure Size of the human genom: The diploid human genome contains approximately 6 billion base pairs of DNA packaged into 23 chromosome pairs. Each diploid cell therefore
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year
 Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Chromosomes. M.Sc. Biotechnology. Hawler Medical University, Iraq
 Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
 Chromosomes exist in different states throughout the life of a cell Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
Chromosomes exist in different states throughout the life of a cell Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about genes is correct? Question #1 (A) Genes carry the information for protein
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about genes is correct? Question #1 (A) Genes carry the information for protein
Chapter 2 The Structure of Genes and Genomes. Electron micrograph of a metaphase chromosome
 Chapter 2 The Structure of Genes and Genomes Electron micrograph of a metaphase chromosome Genetic information is stored in double stranded DNA DNA structure, building blocks: (A) Bases DNA structure,
Chapter 2 The Structure of Genes and Genomes Electron micrograph of a metaphase chromosome Genetic information is stored in double stranded DNA DNA structure, building blocks: (A) Bases DNA structure,
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 10
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
AP Biology. The BIG Questions. Chapter 19. Prokaryote vs. eukaryote genome. Prokaryote vs. eukaryote genome. Why turn genes on & off?
 The BIG Questions Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
The BIG Questions Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Need a little extra help?
 Need a little extra help? Extra office hours! MWRF from 11:00 till 1:00 or by appointment: Marion.Brodhagen@wwu.edu. edu Tutoring center in Old Main 387: BIOL 205 drop-in tutoring at the following times:
Need a little extra help? Extra office hours! MWRF from 11:00 till 1:00 or by appointment: Marion.Brodhagen@wwu.edu. edu Tutoring center in Old Main 387: BIOL 205 drop-in tutoring at the following times:
The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
 Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
DNA AND CHROMOSOMES. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a prof S. Presciuttini
 DNA AND CHROMOSOMES This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. The Building Blocks
DNA AND CHROMOSOMES This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. The Building Blocks
A) The constituent monomer of DNA and RNA. C) The basic structural unit of chromatin with "bead-on-a-string" morphology
 MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Please select the best match for each term. 1) Centromere 2) Nucleoid 3) Nucleotide 4) Chromosome 5) Nucleosome A) The constituent
MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Please select the best match for each term. 1) Centromere 2) Nucleoid 3) Nucleotide 4) Chromosome 5) Nucleosome A) The constituent
The wrong file for Lecture 8 was posted on the website. I ve sent the correct file and it should be posted by the time class is out.
 The wrong file for Lecture 8 was posted on the website. I ve sent the correct file and it should be posted by the time class is out. Grade Distribution for EXAM 1 45 40 38 No. Scores/Grade 35 30 25 20
The wrong file for Lecture 8 was posted on the website. I ve sent the correct file and it should be posted by the time class is out. Grade Distribution for EXAM 1 45 40 38 No. Scores/Grade 35 30 25 20
Chromatin. Structure and modification of chromatin. Chromatin domains
 Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology. Chromatin: functional organization of the genome
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology I. Introduction II. III. The nucleosome Histone proteins III.1. Core histones III.2. Linker histones IV. Chromatin: functional organization
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology I. Introduction II. III. The nucleosome Histone proteins III.1. Core histones III.2. Linker histones IV. Chromatin: functional organization
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Vocab Word 1: Interphase
 Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the structure of the DNA molecule and how this structure allows for the storage of information,
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the structure of the DNA molecule and how this structure allows for the storage of information,
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Packing ratio the length of DNA divided by the length into which it is packaged
 DNA Structure DNA Replication Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Study Questions DNA Structure, Replication and Eukaryotic Chromatin Structure Overheads DNA Structure, Replication and Eukaryotic Chromatin
DNA Structure DNA Replication Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Study Questions DNA Structure, Replication and Eukaryotic Chromatin Structure Overheads DNA Structure, Replication and Eukaryotic Chromatin
The Nucleus and Nuclear Transport. The brain of the cell
 The Nucleus and Nuclear Transport The brain of the cell Form relating to function: Spherical nucleus is approximately 10% of the whole cell s volume, making it the central prominent feature. Functions
The Nucleus and Nuclear Transport The brain of the cell Form relating to function: Spherical nucleus is approximately 10% of the whole cell s volume, making it the central prominent feature. Functions
Biochemistry 401G Lecture 32 Andres
 Biochemistry 401G Lecture 32 Andres Lecture Summary: Discuss RNA structure and how the chemical differences between DNA and RNA make DNA the better choice for the storage of genetic information. DNA chromatin
Biochemistry 401G Lecture 32 Andres Lecture Summary: Discuss RNA structure and how the chemical differences between DNA and RNA make DNA the better choice for the storage of genetic information. DNA chromatin
Control of Eukaryotic Genes
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Questions from the last lecture. PHAR2811 Dale s lecture 3. Folate conversions. Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes
 PAR2811 Dale s lecture 3 Genome Structure MMWEALT F AUSTRALIA opyright Regulation WARIG This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to
PAR2811 Dale s lecture 3 Genome Structure MMWEALT F AUSTRALIA opyright Regulation WARIG This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
B. Incorrect! Centromeric DNA is largely heterochromatin, which is inactive DNA.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Unit 7. Genetic Regulation, Development, and Biotechnology. AP Biology
 Unit 7 Genetic Regulation, Development, and Biotechnology The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes and prokaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely
Unit 7 Genetic Regulation, Development, and Biotechnology The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes and prokaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
9/3/2009. DNA RNA Proteins. DNA Genetic program RNAs Ensure synthesis of proteins Proteins Ensure all cellular functions Carbohydrates (sugars) Energy
 Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
Chapter 3. DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression
 Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
الحمد هلل رب العالميه الذي هداوا لهذا وما كىا لىهتدي لىال أن هداوا اهلل والصالة والسالم على أشزف األوبياء. 222Cell Biolgy 1
 الحمد هلل رب العالميه الذي هداوا لهذا وما كىا لىهتدي لىال أن هداوا اهلل والصالة والسالم على أشزف األوبياء 222Cell Biolgy 1 Lecture 13 222Cell Biolgy 2 Nucleosome Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating
الحمد هلل رب العالميه الذي هداوا لهذا وما كىا لىهتدي لىال أن هداوا اهلل والصالة والسالم على أشزف األوبياء 222Cell Biolgy 1 Lecture 13 222Cell Biolgy 2 Nucleosome Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating
CHAPTERS , 17: Eukaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics
 Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
1/24/2012. Cell. Plasma Membrane
 Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division Cell Basic unit of structure and function in body
Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division Cell Basic unit of structure and function in body
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s
 GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
DNA REPLICATION. DNA structure. Semiconservative replication. DNA structure. Origin of replication. Replication bubbles and forks.
 DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Chapter 2. An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
 PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL
 EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes - Genetic organization in eukaryote - Transcription in eukaryote - - RNA processing in eukaryote - Translation
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes - Genetic organization in eukaryote - Transcription in eukaryote - - RNA processing in eukaryote - Translation
Chapter 3.5. Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3.5 Protein Synthesis Summary of Protein Synthesis How chemical Information is transfer during protein synthesis DNA mrna protein transcription the step from DNA to mrna occurs in the nucleus where
Chapter 3.5 Protein Synthesis Summary of Protein Synthesis How chemical Information is transfer during protein synthesis DNA mrna protein transcription the step from DNA to mrna occurs in the nucleus where
GATE SCIENCE - BIOTECHNOLOGY SAMPLE THEORY
 GATE SCIENCE - BIOTECHNOLOGY SAMPLE THEORY GENOME ORGANIZATION MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF GENE CHROMOSOMES AND CHROMATIN For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary
GATE SCIENCE - BIOTECHNOLOGY SAMPLE THEORY GENOME ORGANIZATION MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF GENE CHROMOSOMES AND CHROMATIN For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams 1-C-8, Sheela Chowdhary
CELL BIOLOGY: DNA. Generalized nucleotide structure: NUCLEOTIDES: Each nucleotide monomer is made up of three linked molecules:
 BIOLOGY 12 CELL BIOLOGY: DNA NAME: IMPORTANT FACTS: Nucleic acids are organic compounds found in all living cells and viruses. Two classes of nucleic acids: 1. DNA = ; found in the nucleus only. 2. RNA
BIOLOGY 12 CELL BIOLOGY: DNA NAME: IMPORTANT FACTS: Nucleic acids are organic compounds found in all living cells and viruses. Two classes of nucleic acids: 1. DNA = ; found in the nucleus only. 2. RNA
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Judy Wieber. Department of Computational Biology. May 28, 2008
 Review III: Cellular Processes Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 28, 2008 Outline Metabolism Cell cycle Transcription
Review III: Cellular Processes Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 28, 2008 Outline Metabolism Cell cycle Transcription
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
Cells and Tissues. Overview CELLS
 Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Chapter 18. Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document.
 Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 26, 2014 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 September 26, 2014 1 / 21 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 26, 2014 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 11 September 26, 2014 1 / 21 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin
 6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin Individual chromosomes can be seen only during mitosis. During interphase, the general mass of chromatin is in the form of euchromatin. Euchromatin
6.2 Chromatin is divided into euchromatin and heterochromatin Individual chromosomes can be seen only during mitosis. During interphase, the general mass of chromatin is in the form of euchromatin. Euchromatin
Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein)
 Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein) I. Review A. Cells copy their DNA (in S phase of Interphase)-Why? Prepare for Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis) Genes
Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein) I. Review A. Cells copy their DNA (in S phase of Interphase)-Why? Prepare for Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis) Genes
Lecture 6. Chromosome Structure and Function in Mitosis
 Lecture 6 Chromosome Structure and Function in Mitosis Outline: Chromosome Organization and Function in Interphase Chromatin effects on replication Effects of nuclear organization on gene expression Chromosomes
Lecture 6 Chromosome Structure and Function in Mitosis Outline: Chromosome Organization and Function in Interphase Chromatin effects on replication Effects of nuclear organization on gene expression Chromosomes
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
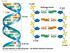 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
UNIT 2 HUMAN BIOLOGY NOTES
 DNA, genes and chromosomes CHAPTER 13 DNA THE CODE FOR LIFE - DNA is short for deoxyribonucleic acid found in cells of organisms. The DNA is embedded within the nucleus of a cell. - DNA is a long stranded
DNA, genes and chromosomes CHAPTER 13 DNA THE CODE FOR LIFE - DNA is short for deoxyribonucleic acid found in cells of organisms. The DNA is embedded within the nucleus of a cell. - DNA is a long stranded
Types of nucleic acid
 RNA STRUCTURE 1 Types of nucleic acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA ribonucleic acid HOCH 2 O OH HOCH 2 O OH OH OH OH (no O) ribose deoxyribose 2 Nucleic acids consist of repeating nucleotide that have
RNA STRUCTURE 1 Types of nucleic acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA ribonucleic acid HOCH 2 O OH HOCH 2 O OH OH OH OH (no O) ribose deoxyribose 2 Nucleic acids consist of repeating nucleotide that have
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome. AP Biology
 Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells. Section 1 Introduction
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302. January 20, 2006
 Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
Biology Lecture 2 Genes
 Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Information specifying protein structure. Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Nucleotides Are the Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Information specifying protein structure Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats)
Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Information specifying protein structure Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats)
Chromatin Remodeling Factors and DNA Replication
 Chromatin Remodeling Factors and DNA Replication Patrick Varga-Weisz Abstract Chromatin structures have to be precisely duplicated during DNA replication to maintain tissue-specific gene expression patterns
Chromatin Remodeling Factors and DNA Replication Patrick Varga-Weisz Abstract Chromatin structures have to be precisely duplicated during DNA replication to maintain tissue-specific gene expression patterns
The Structure of RNA. The Central Dogma
 12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information. Chapter 3
 Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
There are four major types of introns. Group I introns, found in some rrna genes, are self-splicing: they can catalyze their own removal.
 1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
The Nucleus and DNA Replication
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46073 1 The Nucleus and DNA Replication OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46073 1 The Nucleus and DNA Replication OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
12 2 Chromosomes and DNA Replication Chromosomes and DNA Replication. Slide 1 of 21. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 12-2 Chromosomes and 1 of 21 DNA and Chromosomes DNA and Chromosomes In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell
12-2 Chromosomes and 1 of 21 DNA and Chromosomes DNA and Chromosomes In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell
PRINCIPLES O F NUCLEAR STRUCTUR E AND FUNCTIO N. Peter R. Cook
 PRINCIPLES O F NUCLEAR STRUCTUR E AND FUNCTIO N Peter R. Cook Preface xii i Acknowledgments xv 1. SOME PRINCIPLES 1 Overview of the Cell Nucleus 1 Box 1-1. Discovery of Cells, Nuclei, and DNA 2 A Sense
PRINCIPLES O F NUCLEAR STRUCTUR E AND FUNCTIO N Peter R. Cook Preface xii i Acknowledgments xv 1. SOME PRINCIPLES 1 Overview of the Cell Nucleus 1 Box 1-1. Discovery of Cells, Nuclei, and DNA 2 A Sense
Nucleic Acids. Information specifying protein structure
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats) Genome - the genetic information of an organism Information
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats) Genome - the genetic information of an organism Information
Cell Division. embryo: an early stage of development in organisms
 Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes
 Chapter 8. DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes 1. Function of the Genetic Material 2. The Structures of DNA and RNA 3. Chemical Composition of Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Three Levels of DNA Packaging
Chapter 8. DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes 1. Function of the Genetic Material 2. The Structures of DNA and RNA 3. Chemical Composition of Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Three Levels of DNA Packaging
The Journey of DNA Sequencing. Chromosomes. What is a genome? Genome size. H. Sunny Sun
 The Journey of DNA Sequencing H. Sunny Sun What is a genome? Genome is the total genetic complement of a living organism. The nuclear genome comprises approximately 3.2 * 10 9 nucleotides of DNA, divided
The Journey of DNA Sequencing H. Sunny Sun What is a genome? Genome is the total genetic complement of a living organism. The nuclear genome comprises approximately 3.2 * 10 9 nucleotides of DNA, divided
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3
 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
