Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism
|
|
|
- Clyde Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question: Draw a general pathway for converting carbohydrates to fatty acids in a liver cell, and indicate which processes occur in the cytosol and which occur in mitochondria. Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-3 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2
2 Introduction The nucleotides Introduction The nucleotides Introduction The nucleotides Introduction The nucleotides RNA 3-4 DNA 3
3 Introduction The nucleotides Introduction Nucleotide metabolism provides us with some nice examples of biochemically intricate and creative pathways. We will focus on a couple of examples 18.1 Synthesis of Purine Nucleotides (Inosine Monophosphate, IMP) 18.2 Other Purine Nucleotides are Synthesized from IMP 18.3 (Uridine monophosphate, UMP) 18.4 CTP is Synthesized from UMP 18.5 Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides 4 4 Introduction We will not cover nucleotide degradation or the salvage pathways As we will see, the nucleotide biosynthesis pathways are very energy intensive. The salvage pathways are used to recycle nucleotides and conserve energy in rapidly growing cells. 5 5 Working out the details of purine biosynthesis started with the investigation the uric acid biosynthesis pathway in birds. 6 6
4 Radioactively labeled precursors were fed to pigeons to see where the labels ended up in uric acid. 13 CO 2 H 13 COO - (formate) H3N + -CH 2-13 COO - (glycine) Radioactively labeled precursors were fed to pigeons to see where the labels ended up in uric acid. 13 CO 2 H 13 COO - (formate) H3N + -CH 2-13 COO - (glycine) Radioactively labeled precursors were fed to pigeons to see where the labels ended up in uric acid. 13 CO 2 H 13 COO - (formate) H3N + -CH 2-13 COO - (glycine) Purines are synthesized on top of the ribose phosphate. Ribose 5-phosphate This starts with the activation of ribose 5- phosphate to 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) The final product is inosine-5 - monophosphate
5 Purines are synthesized on top of the ribose phosphate. Ribose 5-phosphate This starts with the activation of ribose 5- phosphate to 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) The final product is inosine-5 - monophosphate Purines are synthesized on top of the ribose phosphate. Ribose 5-phosphate This starts with the activation of ribose 5- phosphate to 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) The final product is inosine-5 - monophosphate Purines are synthesized on top of the ribose phosphate. Ribose 5-phosphate This starts with the activation of ribose 5- phosphate to 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) The final product is inosine-5 - monophosphate Purines are synthesized on top of the ribose phosphate. Ribose 5-phosphate This starts with the activation of ribose 5- phosphate to 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) The final product is inosine-5 - monophosphate
6 Starting with PRPP, the complete synthesis of IMP is done in 10 steps Starting with PRPP, the complete synthesis of IMP is done in 10 steps Step 1: Glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase. 10 An amido nitrogen is transferred form glutamine to the C1 position of PRPP. Note the inversion of the chirality of the ribose from α to β. Reaction is driven by the hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate 10 Step 2: Glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase. 11 A peptide bond is formed between the glycine and the ribosylamine. The reaction requires activation of the glycine carboxylate with ATP. 11
7 Step 3: Glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase. 12 A formyl group is transferred from 10-formyltetetrahydrofolate 12 Step 4: Formylglycinamidine ribonucleotide synthetase. 13 The amide is converted to an amidine The nitrogen is donated by glutamine. This reaction requires the hydrolysis of ATP 13 Step 5: Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase. 14 Ring closure requires the hydrolysis of ATP 14 Step 6: Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide carboxylase Surprisingly, this carboxylase does not involve the use of biotin. The reaction does require the hydrolysis of ATP 15
8 Step 6: Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide carboxylase Surprisingly, this carboxylase does not involve the use of biotin. The reaction does require the hydrolysis of ATP 15 Step 6: Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide carboxylase Surprisingly, this carboxylase does not involve the use of biotin. The reaction does require the hydrolysis of ATP 15 Step 7: Aminoimidazole succinylcarboxamide ribonucleotide synthetase. 16 The newly added carboxylate group is activated with ATP and condensed with aspartate to become succinylated. 16 Step 8: Adenylosuccinate lyase Coupled to the last reaction, these two reactions resemble two that we saw in the urea cycle. 17
9 Step 8: Adenylosuccinate lyase Coupled to the last reaction, these two reactions resemble two that we saw in the urea cycle. 17 Step 8: Adenylosuccinate lyase Coupled to the last reaction, these two reactions resemble two that we saw in the urea cycle. 17 Step 9: Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase. 18 Similar to Step 3, a formyl group is transferred from 10- formyl-tetrahydrofolate to an amino group 18 Step 10: Inosine 5 -monophosphate cyclohydrolase. 19 Like Schiff base formation, this is a condensation reaction between an aldehyde and an amine. 19
10 The synthesis of IMP requires a considerable amount of energy in the form of ATP, (11 ATP s in all) 2 ATP equivalents for the activation of PRPP 2 for glutamine-prpp amidotransferase 1 each for steps 2, 4, 5, 6 & 7 (=5 ATP s) 2 ATP for the two glutamine synthetase reactions The synthesis of IMP requires a considerable amount of energy in the form of ATP, (11 ATP s in all) 2 ATP equivalents for the activation of PRPP 2 for glutamine-prpp amidotransferase 1 each for steps 2, 4, 5, 6 & 7 (=5 ATP s) 2 ATP for the two glutamine synthetase reactions The synthesis of IMP requires a considerable amount of energy in the form of ATP, (11 ATP s in all) 2 ATP equivalents for the activation of PRPP 2 for glutamine-prpp amidotransferase 1 each for steps 2, 4, 5, 6 & 7 (=5 ATP s) 2 ATP for the two glutamine synthetase reactions Other Purines Synthesized from IMP
11 Other Purines Synthesized from IMP Regulation of Purine Synthesis 22 Purine synthesis is regulated by a web of feedback inhibition of key branch-point reactions Unlike purine synthesis, pyrimidines are synthesized first and then attached to the phosphoribose. Like purine synthesis, the atoms in the pyrimidine ring come from a number of different sources Unlike purine synthesis, pyrimidines are synthesized first and then attached to the phosphoribose. Like purine synthesis, the atoms in the pyrimidine ring come from a number of different sources. 23
12 23-3 Unlike purine synthesis, pyrimidines are synthesized first and then attached to the phosphoribose. Like purine synthesis, the atoms in the pyrimidine ring come from a number of different sources. 23 Pyrimidine synthesis is a 6-step process that leads to UMP Pyrimidine synthesis is a 6-step process that leads to UMP Pyrimidine synthesis is a 6-step process that leads to UMP
13 Pyrimidine synthesis is a 6-step process that leads to UMP Step 1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II Step 1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. This reaction is synthesized by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II in mammals. This enzyme is found in the cytosol instead of the mitochondrial matrix Unlike the reaction in the urea cycle, the sources of the nitrogen is glutamine instead of free ammonia Step 1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. Site 1 Site 2 Site 3 27
14 27-2 Step 1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. Glutamine + H 2 O Site 1 glutamate + NH 3 Site 1 NH 3 + HCO ATP H 2 N-COOH + ADP + P i Site 2 H 2 N-COOH + ATP carbamoyl phosphate + ADP Site 3 O Site O 2 H 2 N C O P O O glutamine + HCO HSite 2 O + 32 ATP carbamoyl phosphate + glutamate + 2 ADP + P i Step 1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. Site 1 Site 2 Site Step 2: Aspartate transcarboylase (ATCase) Step 2: Aspartate transcarboylase (ATCase). The activated carbamoyl phosphate condenses with aspartate. 28
15 29-1 Step 3: Dihydroorotase Step 3: Dihydroorotase. The carboxylate and amide -NH2 condense to close the ring and form a cyclic imide Step 3: Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase Step 3: Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase The ring is oxidized to form the aromatic orotate ring In eukaryotes, this reaction occurs at the inner mitochondrial membrane 30
16 31-1 Step 5: Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase Step 5: Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase The orotate is condensed with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) Step 6: Orotidine 5 -monophosphate decarboxylase Decarboxylation of orotidine 5 - monophosphate produces UMP UMP is phosphorylated to UTP 33
17 34-1 UTP is converted to CTP by CTP synthetase This reaction is analogous to Step 4 in purine biosynthesis UTP is converted to CTP by CTP synthetase This reaction is analogous to Step 4 in purine biosynthesis UTP is converted to CTP by CTP synthetase This reaction is analogous to Step 4 in purine biosynthesis Regulation of pyrimidine synthesis in prokaryotes. 35
18 36-1 Regulation ATCase in E.coli ACTase is one the most thoroughly studied examples of allosteric enzyme regulation Regulation ATCase in E.coli ACTase is one the most thoroughly studied examples of allosteric enzyme regulation Regulation ATCase in E.coli ACTase is one the most thoroughly studied examples of allosteric enzyme regulation In prokaryotes ATCase is branch point between pyrimidine synthesis and arginine synthesis Regulation of ATCase controls the flow of material in these two pathways Both pathways share the same carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. In eukaryotes this is not the case carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I mitochondria (arginine synthesis) carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II cytoplasm (pyrimidine synthesis) 37
19 37-2 In prokaryotes ATCase is branch point between pyrimidine synthesis and arginine synthesis Regulation of ATCase controls the flow of material in these two pathways Both pathways share the same carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. In eukaryotes this is not the case carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I mitochondria (arginine synthesis) carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II cytoplasm (pyrimidine synthesis) In prokaryotes ATCase is branch point between pyrimidine synthesis and arginine synthesis Regulation of ATCase controls the flow of material in these two pathways Both pathways share the same carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. In eukaryotes this is not the case carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I mitochondria (arginine synthesis) carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II cytoplasm (pyrimidine synthesis) 37 Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Reduction occurs at the diphosphate level The same system is used for all four ribonucleotides ADP, GDP, CDP & UDP The system involves three enzymes ribonucleotide reductase thioredoxin thioredoxin reductase Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase
20 Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase 39-2 View 3-D model 39 Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase The enzyme mechanism involves free radicals. 40 X Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides. Ribonucleotide reductase has two regulatory sites An activity site A specificity site 41 X
21 Methylation of dump to dtmp 42 dudp is first converted to dump in a way the prevents the buildup of dutp. This done to head off the incorporation of dutp into DNA in place of dttp. 40 Methylation of dump to dtmp 43 dump is converted to dtmp by Thymidylate synthase. The source of the methyl group is serine, by way of 5,10- methylenetetrahydrofolate 41 Methylation of dump to dtmp Both thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase are prime targets for anticancer drugs Next Up Exam III (Lectures 7-10) 45 43
Biosynthesis of nucleotides
 Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
I. NUCLEOTIDES. Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below:
 Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp
 Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
Nucleotide Metabolism
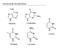 Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
 http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only.
 GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010
 Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition
 Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Biosynthesis. Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides
 Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
BIOC 312. Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12
 Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Nucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons. See: for supplementary course materials.
 1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
Enzymes Part III: regulation I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 16 Monday 1 March
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
Nucleic acids -1 Purines
 Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License.
 Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
ATP GTP UTP CTP
 Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life
 Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
Proteins Amides from Amino Acids
 Chapter 26 and Chapter 28 Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group Joined as amides between the ¾NH 2 of one amino acid and the ¾CO 2 H to the
Chapter 26 and Chapter 28 Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group Joined as amides between the ¾NH 2 of one amino acid and the ¾CO 2 H to the
Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0
 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B. Subject: Chemistry. Teacher Signature. Page 1 of 10
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS. Fiezah M. Alahmry
 IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
What is necessary for life?
 Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
The Transition to Life
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life? Chemical Evolution Biological Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids Replicable
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life? Chemical Evolution Biological Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids Replicable
What is necessary for life?
 Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
The Transition to Life!
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution Biological Evolution? Interacting Chemical Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution Biological Evolution? Interacting Chemical Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis
 Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
Biochemistry 694:301. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase!
 Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam Sweder & Deis Tue. Dec. 18, 2001 Name last 5 digits I.D. Num Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam Sweder & Deis Tue. Dec. 18, 2001 Name last 5 digits I.D. Num Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
Translation Mechanisms
 Translation Mechanisms Biology I Hayder A. Giha Translation The translation is the process of protein synthesis, where information in nucleotides sequences of a mrna is translated into amino acids sequence
Translation Mechanisms Biology I Hayder A. Giha Translation The translation is the process of protein synthesis, where information in nucleotides sequences of a mrna is translated into amino acids sequence
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS. Abdullah K. Shamsuddin
 CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS by Abdullah K. Shamsuddin A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle Tennessee State University in Partial
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS by Abdullah K. Shamsuddin A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle Tennessee State University in Partial
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids
 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
DNA and RNA Structure Guided Notes
 Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Redacted for privacy
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Richard K. Bestwick for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biochemistry and Biophysics presented on July 23, 1982. Title: DNA Precursor Compartmentation in Mammalian Cells:
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Richard K. Bestwick for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biochemistry and Biophysics presented on July 23, 1982. Title: DNA Precursor Compartmentation in Mammalian Cells:
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
A. Incorrect! A sugar residue is only part of a nucleotide. Go back and review the structure of nucleotides.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Central Dogma. 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below.
 Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
The Transition to Life
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution? Biological Evolution Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution? Biological Evolution Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
SURVEY AND SUMMARY Regulation of mammalian nucleotide metabolism and biosynthesis
 2466 2485 Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, Vol. 43, No. 4 Published online 27 January 2015 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv047 SURVEY AND SUMMARY Regulation of mammalian nucleotide metabolism and biosynthesis Andrew
2466 2485 Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, Vol. 43, No. 4 Published online 27 January 2015 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv047 SURVEY AND SUMMARY Regulation of mammalian nucleotide metabolism and biosynthesis Andrew
Nucleic Acids. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1
 Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Regulation of Mammalian Nucleotide Metabolism and Biosynthesis
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Toxicology and Cancer Biology Faculty Publications Toxicology and Cancer Biology 2-27-2015 Regulation of Mammalian Nucleotide Metabolism and Biosynthesis Andrew N. Lane
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Toxicology and Cancer Biology Faculty Publications Toxicology and Cancer Biology 2-27-2015 Regulation of Mammalian Nucleotide Metabolism and Biosynthesis Andrew N. Lane
Human tissue information processing
 Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
The Transition to Life
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution? Biological Evolution Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection 1 Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution? Biological Evolution Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection 1 Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Name. Student ID. Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004
 Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Isolation of Nucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska)
 Isolation of ucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska) by Zahrah M. Altawil A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle
Isolation of ucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska) by Zahrah M. Altawil A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle
Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora crassa
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 78-85 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 78-85 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids W. H. Freeman and Company
 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
CHAPTER 31 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND HEREDITY SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS. ƒ H. Guanine H O. Uracil
 CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN. SEEDS (Glycine max L.) Lola S. JarAllah
 CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN SEEDS (Glycine max L.) by Lola S. JarAllah A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Chemistry
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN SEEDS (Glycine max L.) by Lola S. JarAllah A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Chemistry
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
2012 GENERAL [5 points]
![2012 GENERAL [5 points] 2012 GENERAL [5 points]](/thumbs/75/72452386.jpg) GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
Chapter 1 -- Life. Chapter 2 -- Atoms, Molecules and Bonds. Chapter 3 -- Water
 Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication
 Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Highlights Translation I
 Highlights Translation I 1. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a 70S multi-protein, multi-rna complex, consisting of a large 50S subunit (31 proteins + 23S rrna + 5S rrna) and a smaller 30S subunit (21 proteins
Highlights Translation I 1. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a 70S multi-protein, multi-rna complex, consisting of a large 50S subunit (31 proteins + 23S rrna + 5S rrna) and a smaller 30S subunit (21 proteins
Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase
 Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page /14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1
 DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Take-Home Quiz II. Spring 2005 Semester
 Take-Home Quiz II General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name and quiz version on the
Take-Home Quiz II General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name and quiz version on the
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017
 Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017 Correct answers in multiple choice questions are indicated in RED and underlined. Correct answers to essay questions
Examination I Key MCMP 208 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences I February 7, 2017 Correct answers in multiple choice questions are indicated in RED and underlined. Correct answers to essay questions
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Nucleic Acids. OpenStax College. 1 DNA and RNA
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44403 1 Nucleic Acids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m44403 1 Nucleic Acids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation
 Polimernet Plastik San.Tic.Ltd.Şti. Tel:+90 216 393 77 46 / Email: info@polimernet.com www.polimernet.com 1 Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation This document provides an in depth explanation, detailing
Polimernet Plastik San.Tic.Ltd.Şti. Tel:+90 216 393 77 46 / Email: info@polimernet.com www.polimernet.com 1 Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation This document provides an in depth explanation, detailing
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
MARY ELLEN JONES
 NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES MARY ELLEN JONES 1922 1996 A Biographical Memoir by THOMAS W. TRAUT Any opinions expressed in this memoir are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of
NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES MARY ELLEN JONES 1922 1996 A Biographical Memoir by THOMAS W. TRAUT Any opinions expressed in this memoir are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of
DNA and RNA Structure. Unit 7 Lesson 1
 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
6 Enzymes II W. H. Freeman and Company
 6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
DNA and RNA are both made of nucleotides. Proteins are made of amino acids. Transcription can be reversed but translation cannot.
 INFORMATION TRANSFER Information in cells Properties of information Information must be able to be stored, accessed, retrieved, transferred, read and used. Information is about order, it is basically the
INFORMATION TRANSFER Information in cells Properties of information Information must be able to be stored, accessed, retrieved, transferred, read and used. Information is about order, it is basically the
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Dr. Deis Thu. Aug. 19, 2004 Row Seat
 Biochemistry 694:301 Name Final Exam, Dr. Deis Thu. Aug. 19, 2004 Row Seat This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the Part I
Biochemistry 694:301 Name Final Exam, Dr. Deis Thu. Aug. 19, 2004 Row Seat This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the Part I
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
9/3/2009. DNA RNA Proteins. DNA Genetic program RNAs Ensure synthesis of proteins Proteins Ensure all cellular functions Carbohydrates (sugars) Energy
 Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
* What are the nucleic acids?
 Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Please contact us if any parts are missing or damaged. DNA Backbone
 DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
STRUCTURE OF RNA. Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units. A ribonucleotide unit has: 5-Carbon ribose sugar.
 STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
Student Number: a) Indicate which, if any, of the six proteins would be found in these three fractions.
 Name: Student Number: April 23, 2009, 9:00 AM -12:00 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Laboratory Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. J. Galka 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided. 2. The back
Name: Student Number: April 23, 2009, 9:00 AM -12:00 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Laboratory Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. J. Galka 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided. 2. The back
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Biomolecules: nucleotides
 Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
