(C-D)(E-F) (C-D) (A-B)(C-D)(E-F) D. simulans. D. sechellia. D.melanogaster. D. yakuba. D. erecta. D. ananassae D. pseudoobscura.
|
|
|
- Erick Sims
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADDITIONAL FILE 1 Segmental duplication, microinversion and gene loss associated with a complex inversion breakpoint region in Drosophila Oriol Calvete; Josefa Gonzalez; Esther Betran; Alfredo Ruiz. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2012; doi: /molbev/mss067
2
3 D. simulans D. sechellia D.melanogaster D. yakuba (AB) [(C),CG6490] [(E),Syx18] [(D),CG1866] [(F),RhoL] (C-D)(E-F) D. erecta Sophophora (AB)(CD)(EF) (C-D) (A-B)(C-D)(E-F) D. ananassae D. pseudoobscura D. persimilis D. willistoni D. mojavensis D. buzzatii D. virilis (AB) (CD) (EF) [(C),CG6089] (AB) [(D),CG6966] (EF) (AB) (CD) (EF) (AC) (BE) (DF) Drosophila D. grimshawi (AB) (CD) (EF) mya
4 ΨCG exon L ΨCG exon 3 ΨCG exon L L 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1Kb 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1Kb 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1Kb ΨCG UTR L 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1Kb CG exons L 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1Kb L: ladder 1: Egg 0-1,30h 2: Egg 0-2,15h 3: Egg 0-2,30h 4: Egg 0-22h 5: Larvae 6: Pupae 7: Adult female 8: Adult male 9: DNA
5 1 L L (bp) L L: RNA ladder : mrna Adult (Female) 2: mrna Adult (Male) 3: mrna Pupa 4: mrna Larva 955 5: mrna Egg 623 6: mrna (D. mojavensis) 281 Figure S4. Analysis of CG4673 expression by Northern blot. Molecular weight of the hybridized bands is showed in the marker between membranes 1 and 2. mrna loaded in each lane is shown in the legend.
6 ΨCG exon L ΨCG exon 3 ΨCG exon L Gapdh L 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1 Kb 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1 Kb 1 Kb 0,5 Kb 0,1 Kb 1: D+/RT+ 2: D+/RT- 3: D+/RT+( N) 4: D+/RT+(T) 5: D-/RT+ 6: D-/RT- 7: D-/RT+(T) L: ladder
7 A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D A B C D A C B D
8 ADDITIONAL FILE 2 Segmental duplication, microinversion and gene loss associated with a complex inversion breakpoint region in Drosophila Oriol Calvete; Josefa Gonzalez; Esther Betran; Alfredo Ruiz. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2012; doi: /molbev/mss067
9 Additional file 2. Cloning and sequencing the inversion breakpoints To clone and sequence the breakpoints of inversions 2m and 2n we applied the following experimental approach: (i) Identification of D. buzzatii BAC clones encompassing the breakpoints. Three D. buzzatii BAC clones, 14B19, 20O19 and 16H04, encompassing the AC, BE and DF breakpoint regions, respectively, were identified by González et al (2007) For each inversion breakpoint, we used in situ hybridization to isolate from the BAC library two additional clones, overlapping the initial one, and also bearing the breakpoint regions (Figure S1 in Additional file 1). The names of the identified clones are given in Table 1 in the main text. (ii) BAC-end sequencing and localization of the sequences in the D. mojavensis genome. We successfully generated 14 BAC-end sequences (BES), out of the 18 possible, and mapped 10 of them by similarity searches onto unique sites within the D. mojavensis genome (Table S5 in additional file 3). All sequences were anchored in scaffold 6540 (~34 Mb long), corresponding to D. mojavensis chromosome 2 (Muller s element E; Schaeffer et al. 2008). The arrangement of BES on this scaffold allowed us to locate the AB, CD and EF breakpoints regions in three regions near coordinates 25.7 Mb, 16.8 Mb and 4.7 Mb respectively (Table S5 in additional file 3). In each of these region, the breakpoint was narrowed down to a specific segment with the aid of at least two BES (Figure 2 in main text): AB breakpoint region was located within the 152,933 bp-long region limited by BES 14B19-T7 and 22B03-T7 and; CD breakpoint region was located inside the 91,453 bp-long
10 region between BES 1N19-T7 and 14E21-SP6; and EF breakpoint region was located within the 111,770 bp-long region limited by BES 20O19-SP6 and 16H04-T7. (iii) Walking along the D. mojavensis genome and characterization of the breakpoint regions in the non-inverted genome. We carried out an in situ hybridization walk in order to locate precisely the breakpoint within the previously delimited regions of D. mojavensis scaffold 6540 (Figure 2 in main text). DNA probes were generated by PCR (Table S6 in additional file 3) along the region and then hybridized to D. buzzatii chromosomes to determine their location (Table S7 in additional file 3). In this way, the AB breakpoint region (inversion 2m distal breakpoint) was located within 10,256 bp-long region delimited by probes A5 and B2, designed downstream of gene msi (A5) and within the Ssadh (B2) coding sequence (Figure 2 in main text). An attempt to further narrow down the breakpoint region using probes B3 and B4, both of them designed in the CG4673 gene, failed (Figure 2 in main text). The CD breakpoint (2m/2n shared breakpoint) was located in the 1,551 bplong segment between probes C2 and D2 designed in the intergenic region upstream of the scrib gene (C2) and downstream of the Or98b gene (D2) (Figure 2 in main text). Finally, the EF breakpoint (2n proximal breakpoint) was located in the 2,138 bp-long segment between probes E3 and F4, downstream of genes Wsck (E3) and CG8147 (F4) (Figure 2 in main text). (iv) Isolation of the breakpoint regions in D. buzzatii by PCR. Once the breakpoint regions were pinpointed in the D. mojavensis genome, we attempted to isolate the three breakpoint regions in D. buzzati (AC, EB and DF) by PCR amplification using combinations of primers designed in the expected orientation according to Figure 1 (in main text). Primers were designed inside the probes used to narrow down the breakpoints
11 in D. mojavensis (Figure 2 in main text and Table S8 in additional file 3). Only the DF breakpoint could be successfully amplified. The DF PCR product was ~4.4 kb in size and correspond to the expected intergenic region between genes Or98b and CG8147. Comparison of this 4.4 kb region with the CD and EF regions of D. mojavensis allowed us to further narrow down the breakpoint region to a ~3 kb segment as follows. The first 1,050 bp of the 4.4 kb DF region show similarity with CD region and the last 165 bp of the DF sequence are homologous to the last exon and 3 UTR of gene CG8147 from D. mojavensis EF region. Thus the DF breakpoint is located in a 3,185 bp-long segment between coordinates 1,051 bp and 4,235 bp of D. buzzatii DF sequence (Figure 4 in main text). The AC and EB breakpoint regions could not be amplified although several attempts using different primers were made. We also attempted to locate in D. buzzatii the D. mojavensis region between A and B containing CG4673 (Figure 2 in main text). We combined primers A and B with primers from B3 and B4 probes but this region could not be amplified. (v) Sequencing and annotation of the BAC clones containing AC and EB breakpoints. To isolate and characterize the AC and EB breakpoint regions we sequenced and annotated BAC clones 1N19 and 20O19, respectively (Table S9 in additional file 3). Clone 1N19 has a 138,724-bp long insert and contains exons 1-5 of the gene scribbled (scrib, CG4562), genes CG5071, CG12250 and CG4582, and exons 2-5 of musashi (msi, CG5099) (Figure 3 in main text). In D. melanogaster, msi encodes two transcripts, RA and RB. D. buzzatii BAC 1N19 fully contains the three exons (3-5) encoding transcript RA and four of the five exons (1-5) encoding transcript RB (only exon 1 is lacking). The complex organization of the genes msi, CG12250 and CG4582 seems
12 conserved between D. buzzatii and D. mojavensis, with CG4582 fully nested within intron 2 of msi and CG12250 exons interleaved with those of msi. The short (63 bp) exon 1 of CG12250 is not present in the current annotation of the D. mojavensis genome (CG12250 lacks the ATG start codon) giving the false impression that this gene is fully nested within msi intron 2. However we have detected and annotated downstream of the msi stop codon the putative initial exon of CG12250 that is conserved between D. mojavensis and D. buzzatii. Therefore in D. buzzatii CG12250 is closest to the breakpoint than msi. Comparison of BAC clone 1N19 containing AC breakpoint region with AB and CD regions of D. mojavensis allowed us to further narrow down the breakpoint to a ~700 bp segment as follows. The similarity between D. buzzatii AC region and D. mojavensis AB region reaches 12,841 bp upstream of the CG12250 start codon. When the AC breakpoint region was compared to the D. mojavensis CD region, the similarity reached 1,808 bp upstream of scrib start codon. These observations place the D. buzzatii AC breakpoint in a 693 bp-long segment between coordinates 113,151 and 113,843 of BAC 1N19 (Figure 4 in main text). Clone 20O19 insert is 143,293 bp long and contains the complete coding sequences of 22 genes: CG4774, CG31258, Rpl27 (CG4743), CG5828, CG4743, CG5039, CG4730, Lgr3 (CG31096), CG5053, tankyrase (CG4719), jigr1 (CG17383), Ssadh (CG4585), CG4673, Wsck (CG31127), at1 (CG6668), CG8721, CG5794, ash2 (CG6677), CG31125, CG6695, CG31126 and Ppox (CG5796) (see Figure 3 in main text). In addition it contains the first 7 exons of the gene slowpoke (slo, CG10693) a 45,122 bp-long gene comprising 28 exons in D. mojavensis. Sequence comparison between D. buzzatii 20O19 BAC clone containing EB breakpoint and D. mojavensis AB and EF regions allowed us to narrow down the
13 breakpoint to a ~1.1 kb segment. D. mojavensis AB region extends 5,108 bp downstream from the Ssadh stop codon. On the other hand, the similarity with D. mojavensis EF region extends 2,019 downstream from the stop codon of Wsck. Thus the EB breakpoint is located in a 1,114 bp-long segment between coordinates 79,447 bp and 80,560 bp of BAC 20O19 (Figure 4 in main text). References cited in this file 1. Gonzalez J, Casals F, Ruiz A: Testing chromosomal phylogenies and inversion breakpoint reuse in Drosophila. Genetics 2007, 175: Schaeffer SW, Bhutkar A, McAllister BF, Matsuda M, Matzkin LM, O'Grady PM, Rohde C, Valente VL, Aguade M, Anderson WW, et al: Polytene chromosomal maps of 11 Drosophila species: the order of genomic scaffolds inferred from genetic and physical maps. Genetics 2008, 179:
14 ADDITIONAL FILE 3 Segmental duplication, microinversion and gene loss associated with a complex inversion breakpoint region in Drosophila Oriol Calvete; Josefa Gonzalez; Esther Betran; Alfredo Ruiz. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2012; doi: /molbev/mss067
15 Additional file 3. Table S1. Similarity blocks between the CG4673 gene region of D. mojavensis as query and the AC breakpoint region (BAC 1N19) of D. buzzatii as subject. Search was carried out using BLAST (Bl2seq). Only hits with a minimum size of 45 bp and E-value 1e-04 are included in this list. CG4673 region Coordinates in Coordinates Identity (%) E-value in D. mojavensis D. mojavensis scaffold in 6540 D. buzzatii BAC 1N19 Exon UTR 25,756,516-25,756,613 12,802-12,704 72/99 (72.7) 2e-07 Exon ,757,533-25,757,920 12,632-12, /393 (69.5) 2e-37 Intron 6 25,759,443-25,759,569 11,708-11,583 99/128 (77.3) 5e-21 Intron 6 25,759,465-25,759,577 10,089-9,966 91/124 (73.4) 7e-13 Intron 6 25,760,725-25,760,896 10,246-10, /196 (67.3) 3e-10 Intron 6 25,761,139-25,761,215 9,726-9,652 59/77 (76.6) 4e-09 Intron 6 25,761,270-25,761,379 9,643-9,549 79/110 (71.8) 3e-10 CG ,761,635-25,762,277 8,571-7, /643 (80.9) 1e-173 CG ,762,432-25,762,593 6,719-6, /168 (72.6) 2e-20 Intron 6 25,763,858-25,763,918 4,202-4,148 47/61 (77.0) 6e-07 Intron 6 a 25,766,399-25,766,446 3,679-3,726 39/48 (81.2) 2e-06 CG ,764,640-25,764,730 2,991-2,895 71/97 (73.2) 3e-10 Intron 6 25,765,297-25,765,341 2,490-2,446 39/45 (86.7) 4e-09 Intron 6 25,765,806-25,765,925 2,129-2,007 90/127 (70.9) 8e-12 Intron 6 25,767,941-25,768, /187 (65.2) 3e-10 Intron 6 25,768,145-25,768, /54 (88.9) 5e-14 Intron 6 25,768,279-25,768, /60 (75.0) 9e-05 Exon 7 25,768,450-25,768, /125 (78.4) 4e-22 3 UTR 25,769,034-25,769, /61 (86.9) 4e-15 a This fragment is inverted
16 Table S2. Structure and comparison of the CG4673 gene of D. buzzatii (EB breakpoint region) with D. mojavensis and D. melanogaster. Exons 1 to 8 encode RA transcript. Exons 0 and 2 to 8 encode transcript RB and RD. Dbuz Dmoj Dmel Dbuz/Dmoj Dbuz/Dmel Region (bp) (bp) (exon a ) Identity (%) Identity (%) Exon (11) Intron Exon (10) Intron Exon (8) Intron Exon (7) Intron Exon (6) Intron Exon (5) Intron Exon (4) Intron Exon (3) Intron Exon (2/1) a exon number according to FlyBase.
17 Table S3. PCR and sequences of primers designed for the analysis of CG4673 and ΨCG4673 of D. buzzatii. PCR Primer Sequence (5-3 ) Annotation 2 2R TTACAGCGTACAAAATGTGT Exon 2 of ΨCG4673 2L GAGTTCTGCCCACCAGCTCA Exon 2 of ΨCG R GCACGAGTACCACAGCCAAA Exon 3 of ΨCG4673 3L CCTGATTACTTCAATGTATT Exon 3 of ΨCG R GCCGCTGCAGCCGCACATTC Exon 7 of ΨCG4673 7L GATAGATGGCTGATCAACAC Exon 7 of ΨCG UTR 3 UTR-R TCCAACTGTCAGCTTGACAC 3 UTR of ΨCG UTR-L CATGCTTATTGAATCTTTAT 3 UTR of ΨCG R CTGACCGCTCAGGAGTGCAT Exon 5 of CG4673 6L GGTGCATCCTTGGTAGGTAT Exon 6 of CG RACE Outer 8R GACGACCAGCTATCCCAGTG Exon 8 of CG Outer Adapter GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGACT * 3 RACE Inner 8Rint TGGACCTGCAACCACTGCAC Exon 8 of CG Inner Adapter CGCGGATCCGAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGG * 5 RACE Outer 1L GCAGACTGCACGCGTATTAG Exon 1 of CG Outer Adapter GCTGATGGCGATGAATGAACACTG * 5 RACE Inner 1Lint GAAGAGACGATGTCGCACAA Exon 1 of CG Inner Adapter CGCGGATCCGAACACTGCGTTTGCTGGCTTTGATG * 3 RACE Outer 7R GCCGCTGCAGCCGCACATTC Exon 7 of ΨCG4673
18 3 Outer Adapter GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGACT * 3 RACE Inner 7Rint ACGAAAGACGCCAGCCATTG Exon 7 of ΨCG Inner Adapter CGCGGATCCGAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGG * 5 RACE Outer 2L GAGTTCTGCCCACCAGCTCA Exon 2 of ΨCG Outer Adapter GCTGATGGCGATGAATGAACACTG * 5 RACE Inner 2Lint CTTTAGCTCCGTGGCCAAGC Exon 2 of ΨCG Inner Adapter CGCGGATCCGAACACTGCGTTTGCTGGCTTTGATG * Gapdh H1 ATGTCGAAGATTGGTATTAATGG Gapdh H2 GTTCGACACGACCTTCATGT Gapdh *primers from the RLM-RACE kit of Ambion (AM1700).
19 Table S4. Functional information of the genes located nearby the 2mn inversion breakpoints (FlyBase r5.36). Gene CG12250 (A) Ssadh (B) CG4673 (AB) CG5079 (AB) CG5071 (AB) Scrib (C) Molecular Function - catalytic step 2 spliceosome - precatalytic spliceosome a succinatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase activity b - structural constituent of nuclear pore - zinc ion binding GO annotation Biological Process nuclear mrna splicing, via spliceosome - gammaaminobutyric acid catabolic process - oxidationreduction process InterPro domains Evidence of Cellular expresion component none none High expression level in 1-5 day-old adult males (not expressed in adult females) mitochondrion - Aldehyde dehydrogenase domain none nuclear pore - Zinc finger, RanBP2-type - NPL4, zincbinding putative - Polyubiquitintagged protein recognition complex, Npl4 component High expression in L2 and L3 larvae Very highly expressed in adult male and female none none none none Low expression in pupae - peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity - zinc ion binding Protein binding protein folding intracellular - Zinc finger, B- box and RINGtype - Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, cyclophilin-type - cell cycle process - olfactory behaviou r - plasma membrane f - PDZ/DHR/GLGF - Leucine-rich repeat Moderately high expressed in males (no expression in adult females) High expression in embryo Other information None None Nonsense-mediated mrna decay (NMD) down-regulates CG4673- RB transcript c RNAi generated by PCR using primers directed to this gene causes a cell growth and viability phenotype when assayed in Kc167 and S2R + cells d. None Essential for odour guided behaviou r
20 Or98b (D) Wsck (E) CG8147 (F) - odorant binding - olfactory receptor activity - ATP binding - protein tyrosine kinase activity - alkaline phosphatase activity - sensory perception of smell - protein phosphorylation - metabolic process a Inferred from direct assay (Herold et al. 2009) a Inferred from direct assay (Rothacker 2008) - integral to membrane - membrane - plasma membrane none - olfactory receptor, drosophila - Protein kinase, catalytic domain - Carbohydratebinding WSC - Fibronectin, type III - Serinethreonine/tyrosineprotein kinase - Immunoglobulinlike fold - Alkaline phosphatase Extremely low expression in larvae and pupae Moderately high in embryo High in L2 larvae none none Identified in S2/cycloheximide assay as a direct target of Clk (circadian regulation of gene expression) mediated transcriptional regulation c Hansen et al 2009 d Boutros et al e Infered from mutant phenotype f Inferred from direct assay g Ganguly et al. 2003
21 Table S5. Mapping of the D. buzzatii BAC ends by similarity search to the D. mojavensis genome sequence. All D. mojavensis coordinates belong to scaffold Note that in D. mojavensis scaffold 6540 numbering increases from centromere to telomere (Schaeffer et al. 2008). Breakpoint BAC End Read length (bp) Hit on D. mojavensis genome (scaffold 6540) Annotation Score E-value Identity (%) AC 14B19 T ,824,685-25,824,451 msi 339 2e /240 (94.1) AC 1N19 T ,861,094-16,861,229 scrib 150 7e /135 (85.9) AC 14B19 SP ,810,607-16,811,089 Intergenic (Twd1-CG5467) 335 2e /500 (81.6) AC 15L19 T ,761,866-16,762,001 Intergenic (beat-vii-twd1) 329 9e /219 (92.7) BE 22B03 T ,671,558-25,671,752 CG e /200 (84.5) BE 2N19 SP ,823,128-4,822,869 slo 183 7e /267 (82.4) BE 20O19 SP ,804,621-4,804,495 slo 220 4e /127 (96.8) DF 14E21 SP ,952,682-16,952,590 Intergenic (Cyp6d5-beat-VI) 90 1e-16 79/93 (84.9) DF 16H04 T ,692,135-4,692,725 CG /592 (90.4) DF 14E21 T ,644,326-4,6445,63 Intergenic (alpha-manii-ps) 361 3e /238 (94.1)
22 Table S6. Sequences of primers used to generate probes for the BAC walking (see Figure 2 in main text). PCR Forward (5 3 ) Reverse (5 3 ) A5 GCCGTACGCGTTCTCTATAA TGCCGAACTTGTTAGACGTA A4 CCGATTGACTAACGTTAAGA GTCTCACGTTTCGCATACCA A3 TGGTATGCGAAACGTGAGAC TTGACTGGAGCAGCATGTAC A2 GTTGTTGTCAGGCAGTTGCA TGGTCCAAGTAAAACACAC A1 ATATTGCAGGTTTCAGACAC TTGTCATTATCGCCGATTAC B1 GCGAGGATCCAGATTATGAA GCCATGCAGACCATCATAAC B2 GCTCGAGCAATTCATCTACA TTATCACGAACCAGAGCCAT B3 CCAGCACTTCGATACCATCA GCGATACTCCACAGCTATTG B4 GTGGAGTATCTGCTAGTTGA TATAGAGAACGCGTACGGCA C2 GCTTGCATGCTAACGAGTTG AAAAAGAGTTCCTCGAGGGT C1 TATGACAACGCGGAAATTGT CAGGTGGAATTCGTGGACAA D1 GGCATGGCCATCTACGATAT GGATCCGGGAAGTATTCCTC D2 GACAAGGCCAGAAGCATAAT GCTCTAATTAGGCGCACATA E3 TATTGTGCTAATCTGGCAAG TTACGTTCATCGCTAACAGA E2 TACTATTACGTTGGCTGCTA GAGGAGAGGTCATCAGCTGA E1 CTTACTCAATCTCATGTCCA TTGAAGTAGGTGTGCTCGAA F1 TACGACACACATCGGAACTC GCGCCAATACGAGTAGAGTA F2 GCTGATGAAGTGAAAGTCAA GATAGACACGCCTTGTAAGT F3 AAGGATAAACGTTGCCGAAG GACTTTTGGTTGGCTTGTCA F4 CGAATATGTCGTTCTTGCGA TATGGAACCGTGCTCGACTA
23 Table S7. In situ hybridization of PCR probes for the BAC walking along the breakpoint regions from anchored BAC ends. PCR reactions were carried out using DNA from D. buzzatii BAC clones as template. See Table S6 in this file for sequences of PCR primers used to produce the probes. (-): No amplification product obtained. *In situ hybridization using D. mojavensis probe due to lack of amplification in D. buzzatii. PCR Coordinates of Annotation Expected length of Length of PCR Length of PCR Location of the in primers in D. PCR product in D. in bp (BAC product in bp situ hybridization mojavensis mojavensis (bp) used as (BAC used as signal in D. template) template) buzzatii F CG ~2100 (16H04) - (20O19) F6h/F2a F Intergenic (CG16779-CG8147) 1697 ~1800 (16H04) - (20O19) F6h/F2a F Intergenic (CG16779-CG8147) 813 ~820 (16H04) - (20O19) F6h/F2a F CG ~1500 (16H04) - (20O19) F6h/F2a E Intergenic (CG8147- Wsck) (16H04) ~1200 (20O19) D3e/F6h E Wsck (16H04) - (20O19) D3e/F6h* E CG (16H04) ~2000 (20O19) D3e/F6h D Cyp6d (1N19) ~1500 (16H04) No signal D Or98b (1N19) ~2400 (16H04) F6h/F2a C scrib (1N19) - (16H04) D3e/F2a* C scrib (1N19) ~2100 (16H04) D3e/F2a B Intergenic (jigr1-ssadh) 1539 ~1500 (20O19) - (1N19) D3e/F6h
24 B Ssadh 1622 ~1850 (20O19) - (1N19) D3e/F6h B CG5071-CG (20O19) - (1N19) No signal* B CG ~750 (20O19) ~750 (1N19) no signal A CG (20O19) - (1N19) D3e/F2a* A CG (20O19) ~3500 (1N19) D3e/F2a A msi (20O19) ~2050 (1N19) D3e/F2a A msi (20O19) - (1N19) no signal* A msi (20O19) ~2000 (1N19) D3e/F2a
25 Table S8. Primers used to attempt to amplify the breakpoints of inversions 2m and 2n (AC, EB and DF) in D. buzzatii. All primers were designed in D. mojavensis. Only the DF breakpoint was successfully amplified. Breakpoint Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Annotation AC EB DF A GCAACAACAAGTCACAATGA Intergenic (msi-cg4673) C TGAATTAGAAACCACCGTCA scrib B GGCATACGTCAGCTGATGAC Ssadh E ATCAATATGGCAACGAGGTG CG31127 D TGTTCGAGCAGCACTACATA Or98b conserved downstream region F AATAAGCAGCAAGTGCACAG CG8147
26 Table S9. Details of the sequencing results of the 1N19 and 20O19 BAC clones. Note that the actual size of the BAC clones is similar to the original estimates (given in brackets) BAC clone 1N19 20O19 Corresponding breakpoint of D. buzzatii AC EB Size of BAC clone (bp) 138,724 (138,197) 143,293 (142,697) Size of fragments selected from the partial digestion to 2 to 5 2 to 5 construct the library (kb) Number of reads in shotgun sequencing 1,536 1,344 Number of reads excluded Trimmed Read length mean (std) bases 869± ±150 Coverage 8.47x 7.56x Number of contigs 2 3 Gaps 1 2 References cited in this file 1. Schaeffer SW, Bhutkar A, McAllister BF, Matsuda M, Matzkin LM, O'Grady PM, Rohde C, Valente VL, Aguade M, Anderson WW, et al: Polytene chromosomal maps of 11 Drosophila species: the order of genomic scaffolds inferred from genetic and physical maps. Genetics 2008, 179:
Outline. Annotation of Drosophila Primer. Gene structure nomenclature. Muller element nomenclature. GEP Drosophila annotation projects 01/04/2018
 Outline Overview of the GEP annotation projects Annotation of Drosophila Primer January 2018 GEP annotation workflow Practice applying the GEP annotation strategy Wilson Leung and Chris Shaffer AAACAACAATCATAAATAGAGGAAGTTTTCGGAATATACGATAAGTGAAATATCGTTCT
Outline Overview of the GEP annotation projects Annotation of Drosophila Primer January 2018 GEP annotation workflow Practice applying the GEP annotation strategy Wilson Leung and Chris Shaffer AAACAACAATCATAAATAGAGGAAGTTTTCGGAATATACGATAAGTGAAATATCGTTCT
Drosophila White Paper 2003 August 13, 2003
 Drosophila White Paper 2003 August 13, 2003 Explanatory Note: The first Drosophila White Paper was written in 1999. Revisions to this document were made in 2000 and the final version was published as the
Drosophila White Paper 2003 August 13, 2003 Explanatory Note: The first Drosophila White Paper was written in 1999. Revisions to this document were made in 2000 and the final version was published as the
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Genome annotation & EST
 Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
3. human genomics clone genes associated with genetic disorders. 4. many projects generate ordered clones that cover genome
 Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
7.012 Problem Set 5. Question 1
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
MODULE 5: TRANSLATION
 MODULE 5: TRANSLATION Lesson Plan: CARINA ENDRES HOWELL, LEOCADIA PALIULIS Title Translation Objectives Determine the codons for specific amino acids and identify reading frames by looking at the Base
MODULE 5: TRANSLATION Lesson Plan: CARINA ENDRES HOWELL, LEOCADIA PALIULIS Title Translation Objectives Determine the codons for specific amino acids and identify reading frames by looking at the Base
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name peptidylprolyl isomerase A (cyclophilin A) Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID PPIA Human This gene encodes a member
Gene Information Gene Name peptidylprolyl isomerase A (cyclophilin A) Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID PPIA Human This gene encodes a member
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.15 GENOMES AND GENOMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
Reading Lecture 8: Lecture 9: Lecture 8. DNA Libraries. Definition Types Construction
 Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Agenda. Web Databases for Drosophila. Gene annotation workflow. GEP Drosophila annotation projects 01/01/2018. Annotation adding labels to a sequence
 Agenda GEP annotation project overview Web Databases for Drosophila An introduction to web tools, databases and NCBI BLAST Web databases for Drosophila annotation UCSC Genome Browser NCBI / BLAST FlyBase
Agenda GEP annotation project overview Web Databases for Drosophila An introduction to web tools, databases and NCBI BLAST Web databases for Drosophila annotation UCSC Genome Browser NCBI / BLAST FlyBase
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 February 15, 2013 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are not true Transcriptomes consist of mrnas Proteomes consist
1 February 15, 2013 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) 1. Which of the following statements are not true Transcriptomes consist of mrnas Proteomes consist
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Part I: Definitions. Homology: Reverse transcriptase. Allostery: cdna library
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 6b Sequence Libraries
 PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 6b Sequence Libraries Molecular Biotechnology (Ch 4) Analysis of Genes and Genomes (Ch 5) Unless otherwise cited or referenced, all content of this presenataion is licensed under the
PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 6b Sequence Libraries Molecular Biotechnology (Ch 4) Analysis of Genes and Genomes (Ch 5) Unless otherwise cited or referenced, all content of this presenataion is licensed under the
BENG 183 Trey Ideker. Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping
 BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping Reasons for sequencing Complete genome sequencing!!! Resequencing (Confirmatory) E.g., short regions containing single nucleotide polymorphisms
BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping Reasons for sequencing Complete genome sequencing!!! Resequencing (Confirmatory) E.g., short regions containing single nucleotide polymorphisms
7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I
 7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I For the last several lectures we have been looking at how one can manipulate prokaryotic genomes and how prokaryotic genes are regulated. In the next
7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I For the last several lectures we have been looking at how one can manipulate prokaryotic genomes and how prokaryotic genes are regulated. In the next
Fine scale structural variants distinguish the genomes of Drosophila melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura
 RESEARCH Open Access Fine scale structural variants distinguish the genomes of Drosophila melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura Stuart J Macdonald * and Anthony D Long Abstract Background: A primary objective
RESEARCH Open Access Fine scale structural variants distinguish the genomes of Drosophila melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura Stuart J Macdonald * and Anthony D Long Abstract Background: A primary objective
Draft 3 Annotation of DGA06H06, Contig 1 Jeannette Wong Bio4342W 27 April 2009
 Page 1 Draft 3 Annotation of DGA06H06, Contig 1 Jeannette Wong Bio4342W 27 April 2009 Page 2 Introduction: Annotation is the process of analyzing the genomic sequence of an organism. Besides identifying
Page 1 Draft 3 Annotation of DGA06H06, Contig 1 Jeannette Wong Bio4342W 27 April 2009 Page 2 Introduction: Annotation is the process of analyzing the genomic sequence of an organism. Besides identifying
Annotation of contig62 from Drosophila elegans Dot Chromosome
 Abstract: Annotation of contig62 from Drosophila elegans Dot Chromosome 1 Maxwell Wang The goal of this project is to annotate the Drosophila elegans Dot chromosome contig62. Contig62 is a 32,259 bp contig
Abstract: Annotation of contig62 from Drosophila elegans Dot Chromosome 1 Maxwell Wang The goal of this project is to annotate the Drosophila elegans Dot chromosome contig62. Contig62 is a 32,259 bp contig
Question 2: There are 5 retroelements (2 LINEs and 3 LTRs), 6 unclassified elements (XDMR and XDMR_DM), and 7 satellite sequences.
 Bio4342 Exercise 1 Answers: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology (Answers prepared by Wilson Leung) Question 1: Low complexity DNA can be described as sequences that consist primarily of one or
Bio4342 Exercise 1 Answers: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology (Answers prepared by Wilson Leung) Question 1: Low complexity DNA can be described as sequences that consist primarily of one or
Fatchiyah
 Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Construction of plant complementation vector and generation of transgenic plants
 MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein kinase N1 PKN1 Human The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the protein
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein kinase N1 PKN1 Human The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the protein
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name keratin 78 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT78 Human This gene is a member of the type II keratin gene family
Gene Information Gene Name keratin 78 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT78 Human This gene is a member of the type II keratin gene family
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Transcriptomics. Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
 Transcriptomics Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Central dogma of molecular biology Central dogma of molecular biology Genome Complete DNA content of
Transcriptomics Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Central dogma of molecular biology Central dogma of molecular biology Genome Complete DNA content of
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name sortilin 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORT1 Human This gene encodes a protein that is a multi-ligand type-1
Gene Information Gene Name sortilin 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORT1 Human This gene encodes a protein that is a multi-ligand type-1
Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3
 Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3 Jeff Howenstein March 30, 2007 BIO434W Genomics 1 Introduction We received region 2_3 of the ChimpChunk sequence, and the first step we performed was to run RepeatMasker
Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3 Jeff Howenstein March 30, 2007 BIO434W Genomics 1 Introduction We received region 2_3 of the ChimpChunk sequence, and the first step we performed was to run RepeatMasker
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 9 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID CHRNA9 Human This gene is a member of
Gene Information Gene Name cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 9 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID CHRNA9 Human This gene is a member of
Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size.
 Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
Annotating Fosmid 14p24 of D. Virilis chromosome 4
 Lo 1 Annotating Fosmid 14p24 of D. Virilis chromosome 4 Lo, Louis April 20, 2006 Annotation Report Introduction In the first half of Research Explorations in Genomics I finished a 38kb fragment of chromosome
Lo 1 Annotating Fosmid 14p24 of D. Virilis chromosome 4 Lo, Louis April 20, 2006 Annotation Report Introduction In the first half of Research Explorations in Genomics I finished a 38kb fragment of chromosome
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase PAM Human This gene encodes a multifunctional
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase PAM Human This gene encodes a multifunctional
Molecular Genetics of Disease and the Human Genome Project
 9 Molecular Genetics of Disease and the Human Genome Project Fig. 1. The 23 chromosomes in the human genome. There are 22 autosomes (chromosomes 1 to 22) and two sex chromosomes (X and Y). Females inherit
9 Molecular Genetics of Disease and the Human Genome Project Fig. 1. The 23 chromosomes in the human genome. There are 22 autosomes (chromosomes 1 to 22) and two sex chromosomes (X and Y). Females inherit
CHAPTER 21 GENOMES AND THEIR EVOLUTION
 GENETICS DATE CHAPTER 21 GENOMES AND THEIR EVOLUTION COURSE 213 AP BIOLOGY 1 Comparisons of genomes provide information about the evolutionary history of genes and taxonomic groups Genomics - study of
GENETICS DATE CHAPTER 21 GENOMES AND THEIR EVOLUTION COURSE 213 AP BIOLOGY 1 Comparisons of genomes provide information about the evolutionary history of genes and taxonomic groups Genomics - study of
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID STE20-related kinase adaptor alpha STRADA Human The protein encoded by this gene
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID STE20-related kinase adaptor alpha STRADA Human The protein encoded by this gene
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh Rat This gene encodes a member of
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase Gapdh Rat This gene encodes a member of
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Deng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102117108 Fig. S1. Predicted structure of Arabidopsis bzip60 RNA. Lowest free energy form (ΔG = 309.72 (initially 343.10) of bzip60 mrna folded by M-Fold
Supporting Information Deng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102117108 Fig. S1. Predicted structure of Arabidopsis bzip60 RNA. Lowest free energy form (ΔG = 309.72 (initially 343.10) of bzip60 mrna folded by M-Fold
Drosophila ficusphila F element
 5/2/2016 CONTIG52 Drosophila ficusphila F element Vahag Kechejian BIO434W Abstract Contig52 is a 35,000 bp region located on the F element of Drosophila ficusphila. Genscan predicts six features in the
5/2/2016 CONTIG52 Drosophila ficusphila F element Vahag Kechejian BIO434W Abstract Contig52 is a 35,000 bp region located on the F element of Drosophila ficusphila. Genscan predicts six features in the
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for t
 Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
Genome annotation. Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013)
 Genome annotation Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013) Genome annotation AGACAAAGATCCGCTAAATTAAATCTGGACTTCACATATTGAAGTGATATCACACGTTTCTCTAAT AATCTCCTCACAATATTATGTTTGGGATGAACTTGTCGTGATTTGCCATTGTAGCAATCACTTGAA
Genome annotation Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013) Genome annotation AGACAAAGATCCGCTAAATTAAATCTGGACTTCACATATTGAAGTGATATCACACGTTTCTCTAAT AATCTCCTCACAATATTATGTTTGGGATGAACTTGTCGTGATTTGCCATTGTAGCAATCACTTGAA
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS)
 Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS) KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS USE OF KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS - how to use Annhyb to save and manage sequences - how to use BLAST to compare sequences - how to get
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS) KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS USE OF KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS - how to use Annhyb to save and manage sequences - how to use BLAST to compare sequences - how to get
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Source of D. littoralis fosmid clones
 Source of D. littoralis fosmid clones Libby Slawson Bio 4342 January 28, 2004 Overview What is a fosmid? Library construction Selection of target genes Probing the Library Confirming clones What is a fosmid?
Source of D. littoralis fosmid clones Libby Slawson Bio 4342 January 28, 2004 Overview What is a fosmid? Library construction Selection of target genes Probing the Library Confirming clones What is a fosmid?
Agenda. Annotation of Drosophila. Muller element nomenclature. Annotation: Adding labels to a sequence. GEP Drosophila annotation projects 01/03/2018
 Agenda Annotation of Drosophila January 2018 Overview of the GEP annotation project GEP annotation strategy Types of evidence Analysis tools Web databases Annotation of a single isoform (walkthrough) Wilson
Agenda Annotation of Drosophila January 2018 Overview of the GEP annotation project GEP annotation strategy Types of evidence Analysis tools Web databases Annotation of a single isoform (walkthrough) Wilson
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
Supporting Information SI Materials and Methods RT-qPCR The 25 µl qrt-pcr reaction mixture included 1 µl of cdna or DNA, 12.5 µl of 2X SYBER Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems ), 5 µm of primers and
Chapter 5. Structural Genomics
 Chapter 5. Structural Genomics Contents 5. Structural Genomics 5.1. DNA Sequencing Strategies 5.1.1. Map-based Strategies 5.1.2. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing 5.2. Genome Annotation 5.2.1. Using Bioinformatic
Chapter 5. Structural Genomics Contents 5. Structural Genomics 5.1. DNA Sequencing Strategies 5.1.1. Map-based Strategies 5.1.2. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing 5.2. Genome Annotation 5.2.1. Using Bioinformatic
Chapter 20 Biotechnology
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
Annotating 7G24-63 Justin Richner May 4, Figure 1: Map of my sequence
 Annotating 7G24-63 Justin Richner May 4, 2005 Zfh2 exons Thd1 exons Pur-alpha exons 0 40 kb 8 = 1 kb = LINE, Penelope = DNA/Transib, Transib1 = DINE = Novel Repeat = LTR/PAO, Diver2 I = LTR/Gypsy, Invader
Annotating 7G24-63 Justin Richner May 4, 2005 Zfh2 exons Thd1 exons Pur-alpha exons 0 40 kb 8 = 1 kb = LINE, Penelope = DNA/Transib, Transib1 = DINE = Novel Repeat = LTR/PAO, Diver2 I = LTR/Gypsy, Invader
Important gene-information's
 Sequences, domains and databases. How to gather information on a gene. Jens Bohnekamp, Institute for Biochemistry Important gene-information's Protein sequence Nucleotide sequence Gene structure Protein
Sequences, domains and databases. How to gather information on a gene. Jens Bohnekamp, Institute for Biochemistry Important gene-information's Protein sequence Nucleotide sequence Gene structure Protein
Erhard et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes
 Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Results WCP (Whole chromosome paint) FISH
 Results 61 3 Results The proband as well as her mother and grand mother with an inversion chromosome 3 and short stature were studied in this project to characterize the breakpoints. Cytogenetic analysis
Results 61 3 Results The proband as well as her mother and grand mother with an inversion chromosome 3 and short stature were studied in this project to characterize the breakpoints. Cytogenetic analysis
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1A PPM1A Human The protein encoded by
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1A PPM1A Human The protein encoded by
Annotation of a Drosophila Gene
 Annotation of a Drosophila Gene Wilson Leung Last Update: 12/30/2018 Prerequisites Lecture: Annotation of Drosophila Lecture: RNA-Seq Primer BLAST Walkthrough: An Introduction to NCBI BLAST Resources FlyBase:
Annotation of a Drosophila Gene Wilson Leung Last Update: 12/30/2018 Prerequisites Lecture: Annotation of Drosophila Lecture: RNA-Seq Primer BLAST Walkthrough: An Introduction to NCBI BLAST Resources FlyBase:
Annotating the D. virilis Fourth Chromosome: Fosmid 99M21
 Sonal Singhal 3 May 2006 Bio 4342W Annotating the D. virilis Fourth Chromosome: Fosmid 99M21 Abstract In this project, I annotated a chunk of the D. virilis fourth chromosome (fosmid 99M21) by considering
Sonal Singhal 3 May 2006 Bio 4342W Annotating the D. virilis Fourth Chromosome: Fosmid 99M21 Abstract In this project, I annotated a chunk of the D. virilis fourth chromosome (fosmid 99M21) by considering
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.17 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID BDH1 Human This gene encodes a member of
Gene Information Gene Name 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, type 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID BDH1 Human This gene encodes a member of
Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb
 Cell Reports Supplemental Information Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb Hirotsugu Ishizu, Yuka W. Iwasaki, Shigeki Hirakata, Haruka Ozaki, Wataru Iwasaki,
Cell Reports Supplemental Information Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb Hirotsugu Ishizu, Yuka W. Iwasaki, Shigeki Hirakata, Haruka Ozaki, Wataru Iwasaki,
Supplemental Information. Autoregulatory Feedback Controls. Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules. at the brinker Locus
 Developmental Cell, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Autoregulatory Feedback Controls Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules at the brinker Locus Leslie Dunipace, Abbie Saunders, Hilary L. Ashe,
Developmental Cell, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Autoregulatory Feedback Controls Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules at the brinker Locus Leslie Dunipace, Abbie Saunders, Hilary L. Ashe,
3 -end. Sau3A. 3 -end TAA TAA. ~9.1kb SalI TAA. ~12.6kb. HindШ ATG 5,860bp TAA. ~12.7kb
 Supplemental Data. Chen et al. (2008). Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. A pcam-cah/cah Sau3A Promoter
Supplemental Data. Chen et al. (2008). Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. A pcam-cah/cah Sau3A Promoter
d. reading a DNA strand and making a complementary messenger RNA
 Biol/ MBios 301 (General Genetics) Spring 2003 Second Midterm Examination A (100 points possible) Key April 1, 2003 10 Multiple Choice Questions-4 pts. each (Choose the best answer) 1. Transcription involves:
Biol/ MBios 301 (General Genetics) Spring 2003 Second Midterm Examination A (100 points possible) Key April 1, 2003 10 Multiple Choice Questions-4 pts. each (Choose the best answer) 1. Transcription involves:
Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing
 Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing Author: Prof Marinda Oosthuizen Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. SEQUENCING OF LARGE TEMPLATES As we have seen, we can obtain up to 800 nucleotides
Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing Author: Prof Marinda Oosthuizen Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. SEQUENCING OF LARGE TEMPLATES As we have seen, we can obtain up to 800 nucleotides
Finishing Drosophila Ananassae Fosmid 2728G16
 Finishing Drosophila Ananassae Fosmid 2728G16 Kyle Jung March 8, 2013 Bio434W Professor Elgin Page 1 Abstract For my finishing project, I chose to finish fosmid 2728G16. This fosmid carries a segment of
Finishing Drosophila Ananassae Fosmid 2728G16 Kyle Jung March 8, 2013 Bio434W Professor Elgin Page 1 Abstract For my finishing project, I chose to finish fosmid 2728G16. This fosmid carries a segment of
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
Genome Sequence Assembly
 Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Bi 8 Lecture 5. Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 5 MORE ON HOW WE KNOW WHAT WE KNOW and intro to the protein code Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016 SIZE AND PURIFICATION BY SYNTHESIS: BASIS OF EARLY SEQUENCING complex mixture of aborted DNA
Bi 8 Lecture 5 MORE ON HOW WE KNOW WHAT WE KNOW and intro to the protein code Ellen Rothenberg 19 January 2016 SIZE AND PURIFICATION BY SYNTHESIS: BASIS OF EARLY SEQUENCING complex mixture of aborted DNA
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
Drosophila Board White Paper 2007
 Drosophila Board White Paper 2007 December 2007 Explanatory Note: The first Drosophila White Paper was written in 1999. Revisions to this document were made in 2001, 2003 and 2005. http://flybase.bio.indiana.edu/static_pages/news/whitepapers/drosboardwp2001.pdf
Drosophila Board White Paper 2007 December 2007 Explanatory Note: The first Drosophila White Paper was written in 1999. Revisions to this document were made in 2001, 2003 and 2005. http://flybase.bio.indiana.edu/static_pages/news/whitepapers/drosboardwp2001.pdf
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name laminin, beta 3 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID LAMB3 Human The product encoded by this gene is a laminin that
Gene Information Gene Name laminin, beta 3 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID LAMB3 Human The product encoded by this gene is a laminin that
ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis. Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas
 ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas Introduction Challenges and Motivation D melanogaster Promoter Dataset Expanding promoter sequences
ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas Introduction Challenges and Motivation D melanogaster Promoter Dataset Expanding promoter sequences
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 6 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SOX6 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Gene Information Gene Name SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 6 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SOX6 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Biol 478/595 Intro to Bioinformatics
 Biol 478/595 Intro to Bioinformatics September M 1 Labor Day 4 W 3 MG Database Searching Ch. 6 5 F 5 MG Database Searching Hw1 6 M 8 MG Scoring Matrices Ch 3 and Ch 4 7 W 10 MG Pairwise Alignment 8 F 12
Biol 478/595 Intro to Bioinformatics September M 1 Labor Day 4 W 3 MG Database Searching Ch. 6 5 F 5 MG Database Searching Hw1 6 M 8 MG Scoring Matrices Ch 3 and Ch 4 7 W 10 MG Pairwise Alignment 8 F 12
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GAPDH Human The product of this gene catalyzes
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase GAPDH Human The product of this gene catalyzes
Annotation of contig27 in the Muller F Element of D. elegans. Contig27 is a 60,000 bp region located in the Muller F element of the D. elegans.
 David Wang Bio 434W 4/27/15 Annotation of contig27 in the Muller F Element of D. elegans Abstract Contig27 is a 60,000 bp region located in the Muller F element of the D. elegans. Genscan predicted six
David Wang Bio 434W 4/27/15 Annotation of contig27 in the Muller F Element of D. elegans Abstract Contig27 is a 60,000 bp region located in the Muller F element of the D. elegans. Genscan predicted six
Branches of Genetics
 Branches of Genetics 1. Transmission genetics Classical genetics or Mendelian genetics 2. Molecular genetics chromosomes, DNA, regulation of gene expression recombinant DNA, biotechnology, bioinformatics,
Branches of Genetics 1. Transmission genetics Classical genetics or Mendelian genetics 2. Molecular genetics chromosomes, DNA, regulation of gene expression recombinant DNA, biotechnology, bioinformatics,
Problem Set 8. Answer Key
 MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
The fourth chromosome: targeting heterochromatin formation in Drosophila. Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes
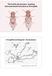 The fourth chromosome: targeting heterochromatin formation in Drosophila Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes modified from TS Painter, 1934, J. Hered 25: 465-476. 1 DNA packaging domains HATs Euchromatin
The fourth chromosome: targeting heterochromatin formation in Drosophila Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes modified from TS Painter, 1934, J. Hered 25: 465-476. 1 DNA packaging domains HATs Euchromatin
Design. Construction. Characterization
 Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures
 Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
Name AP Biology Mrs. Laux Take home test #11 on Chapters 14, 15, and 17 DUE: MONDAY, DECEMBER 21, 2009
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 11; 20 November 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P310-B2 TCOF1 Lot B2-0614, B2-0511. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0110), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Treacher Collins-Franceschetti 1 syndrome
SALSA MLPA probemix P310-B2 TCOF1 Lot B2-0614, B2-0511. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0110), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Treacher Collins-Franceschetti 1 syndrome
Quick Review of Protein Synthesis
 Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
