The Polymerase Chain Reaction. Chapter 6: Background
|
|
|
- Alban Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Polymerase Chain Reaction Chapter 6: Background
2 Invention of PCR Kary Mullis Mile marker in April of 1983 Pulled off the road and outlined a way to conduct DNA replication in a tube Worked for Cetus, which was purchased by Chiron and is now part of Novartis 2
3 What is PCR? Polymerase chain reaction or PCR Simplified version of bacterial DNA replication Copies a specific sequence of DNA Target sequence PCR products Amplicons Target is determined by the primers Short sequences of single-strand DNA To amplify a defined segment, two are required Annealing is when the primers bind to the target sequence The two primers are referred to as forward and reverse primers 3
4 Challenges of DNA Replication in a Tube Normal replication uses enzymes that are heat sensitive Using heat to denature the double strands of DNA, would damage the enzymes Heat-stable DNA polymerases were the key to developing in vitro method of replication Thermus aquaticus was the bacteria from which the first heat-stable DNA polymerase was isolated and the enzyme was named Taq polymerase 4
5 Normal Bacterial Replication Steps: Topoisomerase gradually unwinds the DNA helix ahead of the replication fork. Helicase unzips the strands by breaking hydrogen bonds Single-stranded binding proteins prevent DNA from reannealing Primase adds RNA nucleotides in the 5'3' direction DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides to the ends of the RNA primers DNA polymerase I corrects mistakes and removes RNA nucleotides and replaces them with DNA nucleotides Ligase links the leading and lagging strands (Okazaki fragments) 5
6 Normal Bacterial Replication 6
7 Components of a PCR Reaction Template DNA Nucleotides (dntps) PCR buffer Magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) Forward and reverse primers DNA polymerase 7
8 Thermal Cyclers Initially water baths were used, but that was very labor intensive Thermal cyclers are electronically controlled heat blocks that can quickly change from one temperature to another They are programmable and are in many different configurations depending upon their purpose They most commonly have graphical interfaces that make them very easy to program 8
9 Types of PCR There are many variations of traditional PCR Real-time or quantitative PCR (qpcr) Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) Multiplex PCR Degenerate PCR Nested PCR Random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Fast PCR 9
10 Real-Time PCR Allows for quantitation of the amount of initial DNA in a sample The amount of PCR product is measured at the end of each cycle 10
11 Reverse Transcription PCR Uses retroviral enzyme reverse transcriptase to reverse transcribe mrna into DNA before the PCR begins When DNA is made this way it is referred to as cdna RT-PCR is often used in combination with real-time PCR to measure levels of gene expression Reverse transcription DNA RNA Protein Trait 11
12 Other Types of PCR Multiplex PCR Multiple sets of primers are used to target and amplify different sequences Often used in GMO detection Degenerate PCR Uses sets of primers that have almost the same sequence as each other differing in only 1 3 bases. They are used when working with closely related species and improve the likelihood of amplification 12
13 Other Types of PCR Nested PCR Sometimes PCR is not optimal and two rounds are required. The first set of primers might amplify target and non-target DNA. A second set of primers is used that will bind within the target region using the first round as template DNA Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) This is a method of DNA fingerprinting that uses a collection of random primers. These primers are 10 base pairs long (decamers) and will randomly amplify products if they bind close enough on the template DNA. Closely related species will have similar products while others might not 13
14 Other Types of PCR Fast PCR Total running time for traditional three-cycle PCR is relatively long (2.5 4 hours) In Fast PCR, the run time can be hours with new advancements This can be achieved by using two steps where the annealing temperature and extension temperature are close to each other This type of reaction must be highly optimized and only works for some reactions 14
15 PCR Optimization Each reaction is very different and the components and conditions must be adjusted Factors that must be taken into account vary with the purpose of the reaction If the goal is to clone a gene, then the PCR product should have no errors so no mutations are introduced Enzymes with proofreading features are used to ensure accuracy 15
16 PCR Optimization Conditions and factors to optimize: Template quality Template concentration Primer concentration Primer design Magnesium concentration Annealing temperature Cycling times 16
17 PCR Optimization Template quality If DNA is ancient, usually the template is broken into smaller fragments Designing primers to amplify small PCR products should be the goal 17
18 PCR Optimization Template concentration Generally there is an optimal concentration of template Too little concentration is often an issue depending upon the length of the target being amplified Too much template can inhibit a reaction Adjusting the concentration to see which concentration yields the best amplification is the goal with template concentration optimization 18
19 PCR Optimization Primer concentration The normal range is from 0.1 µm to 1 µm Increasing the concentration can lead to Nonspecific binding Formation of primer dimer Primer dimer is when the primers bind to each other 19
20 PCR Optimization Primer design The sequence of the primers is crucial to the success of PCR Primer sequences must be complementary to each end of the target region The melting temperature (T m ) of each primer must be within a few degrees of the other primers The T m is the temperature at which half of the primers dissociate from the template DNA The annealing temperature is usually 3 5ºC lower than the T m 20
21 PCR Optimization Primer design Primers should be designed without intra- or intercomplementary sequences 21
22 PCR Optimization Magnesium concentration Magnesium is a cofactor for the polymerase enzyme The normal concentration used is between 1 6 mm This should be adjusted to find which concentration yields the best results 22
23 PCR Optimization Annealing temperature The temperature that is used for the primers to bind is called the annealing temperature. These are calculated using the formula: Annealing temperatures are often adjusted up and down a few degrees to optimize them. Many thermal cyclers have a gradient function that will allow multiple annealing temperatures to be tested at one time 23
24 PCR Optimization Annealing temperature Many thermal cyclers have a gradient function that will allow multiple annealing temperatures to be tested at one time 24
25 PCR Optimization Cycling temperatures and times The amount of time that each step is held depends on the length of PCR product and the amount of time it would take to amplify that length. Shorter lengths require shorter times Generally only the annealing temperature is adjusted 25
26 PCR Optimization Denature DNA Bind primers Extend primers Finish any products To ensure all DNA is denatured Repeat this 40 times Hold until ready to remove from thermal cycler 26
27 Techniques Based on PCR DNA microarrays Small spots of identical pieces of DNA are annealed to a slide and arranged in order to determine which spots had a complementary binding event The spots of DNA fragments can represent variations in gene sequences, mrna complementary sequences, viral sequences, bacterial sequences, etc. 27
28 Microarrays PCR is used to amplify the sequence of interest They are spotted on a slide Sequences from other samples that have been amplified with labeled nucleotides are washed The results are detected 28
29 DNA Sequencing Modern sequencing techniques use PCR to amplify the sequence to be determined A mixture of terminating and nonterminating nucleotides are used in the reaction Each terminating nucleotide has a different color dye added to it, a dideoxynucleotide triphosphate (ddntp). Once the growing chain terminates, the nucleotide will have a unique color associated with it 29
30 DNA Sequencing Since the primer is known, each successive terminated fragment should be one nucleotide longer Automated sequencers read the colors as they electrophorese past a detector 30
31 Other Applications of PCR PCR in medicine Detection of disease-causing organisms Species-specific primers help isolate genes Amplification of disease-causing organisms for quick diagnosis Real-time PCR confirmed H1N1 outbreak Amplification of genes of interest for cloning Roles of genes in cancer can be explored 31
32 Other Applications of PCR PCR in agriculture GMO detection in foods Compliance with reporting requirements Can verify levels of genetic modifications in exports Can identify percentages of genetic modification to meet various countries reporting requirements 32
33 Other Applications of PCR PCR in forensics Short tandem repeats (STR) analysis Short tandem repeats are amplified and used as a method of identification They have repetitive regions from 2-6 bp They are inherited from parents They display lots of variety 33
34 Other Applications of PCR PCR in forensics Allele frequencies Vary between different ethic groups Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) Indexes 13 different STR loci Maintains national sample database FBI uses to statistically calculate random match probability 34
35 Other Applications of PCR PCR in paternity Samples are amplified using STR analysis Children are a combination of parents In example, the child is possible from the mother and father shown Method is often use to exclude paternity 35
36 Other Applications of PCR PCR in human migration Short interspersed repetitive elements (SINEs) have been inserted randomly into our human genome over millions of years. Alu is one such element PV92 is one specific Alu repetitive element Can be used to trace migration of humans 36
37 Other Applications of PCR PCR in wildlife conservation Poaching endangers many animals in the world today STR analysis can determine legality of animal parts to possess or sell 37
38 Chapter 6 Summary Background Invention of PCR What is PCR Challenges of PCR PCR DNA Replication Components of PCR Optimization Types of PCR Real-Time PCR Reverse Transcription PCR Other Types Applications Medical Agricultural Others 38
The Polymerase Chain Reaction. Chapter 6: Background
 The Polymerase Chain Reaction Chapter 6: Background PCR Amplify= Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Invented in 1984 Applications Invention of PCR Kary Mullis Mile marker 46.58 in April of 1983 Pulled off
The Polymerase Chain Reaction Chapter 6: Background PCR Amplify= Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Invented in 1984 Applications Invention of PCR Kary Mullis Mile marker 46.58 in April of 1983 Pulled off
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.20 - BIOTECHNOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
PCR in the Classroom. UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003
 PCR in the Classroom UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003 A little history In 1983, Kary B. Mullis conceived the procedure. He went on to Cetus Corp in Emeryville, CA where it was developed
PCR in the Classroom UC Davis - PCR Workshop Friday, September 26, 2003 A little history In 1983, Kary B. Mullis conceived the procedure. He went on to Cetus Corp in Emeryville, CA where it was developed
Polymerase chain reaction
 Core course BMS361N Genetic Engineering Polymerase chain reaction Prof. Narkunaraja Shanmugam Dept. Of Biomedical Science School of Basic Medical Sciences Bharathidasan University The polymerase chain
Core course BMS361N Genetic Engineering Polymerase chain reaction Prof. Narkunaraja Shanmugam Dept. Of Biomedical Science School of Basic Medical Sciences Bharathidasan University The polymerase chain
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
 Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR What is PCR? An in vitro process that detects, identifies, and copies (amplifies) a specific piece of DNA in a biological sample. Discovered by Dr. Kary Mullis in 1983. A
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR What is PCR? An in vitro process that detects, identifies, and copies (amplifies) a specific piece of DNA in a biological sample. Discovered by Dr. Kary Mullis in 1983. A
INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist
 INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist Objective of PCR To provide a solution to one of the most pressing
INTRODUCTION TO REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION PCR (RT-PCR) ABCF 2016 BecA-ILRI Hub, Nairobi 21 st September 2016 Roger Pelle Principal Scientist Objective of PCR To provide a solution to one of the most pressing
Covalently bonded sugar-phosphate backbone with relatively strong bonds keeps the nucleotides in the backbone connected in the correct sequence.
 Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Experiment (5): Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BCH361 [Practical] Experiment (5): Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Aim: Amplification of a specific region on DNA. Primer design. Determine the parameters that may affect he specificity, fidelity and efficiency
BCH361 [Practical] Experiment (5): Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Aim: Amplification of a specific region on DNA. Primer design. Determine the parameters that may affect he specificity, fidelity and efficiency
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications
 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications What is PCR? PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by Dr. Kary Mullis,
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications What is PCR? PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by Dr. Kary Mullis,
Polymerase Chain Reaction-361 BCH
 Polymerase Chain Reaction-361 BCH 1-Polymerase Chain Reaction Nucleic acid amplification is an important process in biotechnology and molecular biology and has been widely used in research, medicine, agriculture
Polymerase Chain Reaction-361 BCH 1-Polymerase Chain Reaction Nucleic acid amplification is an important process in biotechnology and molecular biology and has been widely used in research, medicine, agriculture
B. Incorrect! Ligation is also a necessary step for cloning.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 15: The Techniques in Molecular Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is not part of the normal process of cloning recombinant DNA in bacteria? (A) Restriction endonuclease
Genetics - Problem Drill 15: The Techniques in Molecular Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is not part of the normal process of cloning recombinant DNA in bacteria? (A) Restriction endonuclease
Polymerase Chain Reaction
 Polymerase Chain Reaction Problem Suppose you have a patient with an infection or a heritable disease. You want to know which infection or disease it is and.. you want to know it fast and... from as little
Polymerase Chain Reaction Problem Suppose you have a patient with an infection or a heritable disease. You want to know which infection or disease it is and.. you want to know it fast and... from as little
Polymerase Chain Reaction
 Polymerase Chain Reaction = multiple rounds of in vitro DNA replication = a region of DNA lying between two regions of known sequence is amplified hundreds of millions of time within a matter of several
Polymerase Chain Reaction = multiple rounds of in vitro DNA replication = a region of DNA lying between two regions of known sequence is amplified hundreds of millions of time within a matter of several
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design
 Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
Journal Club & MSc Seminar
 Journal Club & MSc Seminar 2 The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was not a discovery, but rather an invention A special DNA polymerase (Taq) is used to make many copies of a short length of DNA (100-10,000
Journal Club & MSc Seminar 2 The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was not a discovery, but rather an invention A special DNA polymerase (Taq) is used to make many copies of a short length of DNA (100-10,000
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) May 23, 2017
 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) May 23, 2017 Outline History of PCR Uses of PCR How PCR works How to set up and run PCR The structure of DNA PCR Polymerase chain reaction Selective amplification of target
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) May 23, 2017 Outline History of PCR Uses of PCR How PCR works How to set up and run PCR The structure of DNA PCR Polymerase chain reaction Selective amplification of target
DNA Analysis Students will learn:
 DNA Analysis Students will learn: That DNA is a long-chain polymer found in nucleated cells, which contain genetic information. That DNA can be used to identify or clear potential suspects in crimes. How
DNA Analysis Students will learn: That DNA is a long-chain polymer found in nucleated cells, which contain genetic information. That DNA can be used to identify or clear potential suspects in crimes. How
Overview. Background ~30 min. Lab activity ~50 min. DNA profiling Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis PCR
 Overview Day 1: Tuesday Introduction to DNA profiling How do we use DNA to solve crimes? Background Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis Set up PCR Day 2: Wednesday Make and Run Agarose
Overview Day 1: Tuesday Introduction to DNA profiling How do we use DNA to solve crimes? Background Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Gel Electrophoresis Set up PCR Day 2: Wednesday Make and Run Agarose
Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us!
 Name Per Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us! Introduction The human genome (the total sum of our genetic makeup) is made up of approximately 6 billion base pairs distributed on 46 chromosomes.
Name Per Ah, Lou! There really are differences between us! Introduction The human genome (the total sum of our genetic makeup) is made up of approximately 6 billion base pairs distributed on 46 chromosomes.
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Laboratory #7 PCR PCR
 1 Laboratory #7 Polymerase chain reaction () is DNA replication in a test tube. In vitro enzymatic amplification of a specific segment of DNA. Many Applications. direct cloning from DNA or cdna. Mutagenesis
1 Laboratory #7 Polymerase chain reaction () is DNA replication in a test tube. In vitro enzymatic amplification of a specific segment of DNA. Many Applications. direct cloning from DNA or cdna. Mutagenesis
PCR. CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D.
 PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
DNA Replication. Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow!
 DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
DNA Replication Back ground.. Single celled zygote goes from being single celled to 100 trillion more cells in over 240 days in humans! Wow! Must be fast! six billion base pairs in a single human cell
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter Introduction Table of Contents Introduction Page. Principles of PCR and RT-PCR...9.2 The Evolution of PCR....3 Purpose of this PCR Applications Manual...5 8 PCR Applications Manual Principles of
Chapter Introduction Table of Contents Introduction Page. Principles of PCR and RT-PCR...9.2 The Evolution of PCR....3 Purpose of this PCR Applications Manual...5 8 PCR Applications Manual Principles of
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
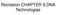 Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
Proposed Models of DNA Replication. Conservative Model. Semi-Conservative Model. Dispersive model
 5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
5.2 DNA Replication Cell Cycle Life cycle of a cell Cells can reproduce Daughter cells receive an exact copy of DNA from parent cell DNA replication happens during the S phase Proposed Models of DNA Replication
PCR KIT/REAGENTS/BUFFERS/PRIMERS
 PCR KIT/REAGENTS/BUFFERS/PRIMERS 114330 DNA Amplification Kit DNA amplification kit is suitable for amplification of DNA size about 100bp to 5kb. It can be also used to RAPD PCR. This kit contains all
PCR KIT/REAGENTS/BUFFERS/PRIMERS 114330 DNA Amplification Kit DNA amplification kit is suitable for amplification of DNA size about 100bp to 5kb. It can be also used to RAPD PCR. This kit contains all
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
Fun with DNA polymerase
 Fun with DNA polymerase Why would we want to be able to make copies of DNA? Can you think of a situation where you have only a small amount and would like more? Enzymatic DNA synthesis To use DNA polymerase
Fun with DNA polymerase Why would we want to be able to make copies of DNA? Can you think of a situation where you have only a small amount and would like more? Enzymatic DNA synthesis To use DNA polymerase
POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION PCR. (Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering) Edemhanria, Lawrence
 POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION PCR. (Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering) Edemhanria, Lawrence Biochemistry Unit Chemical Sciences Department Samuel Adegboyega University Ogwa, Edo State, Nigeria. Outline
POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION PCR. (Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering) Edemhanria, Lawrence Biochemistry Unit Chemical Sciences Department Samuel Adegboyega University Ogwa, Edo State, Nigeria. Outline
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses. Prepared by Woojoo Choi
 Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses Prepared by Woojoo Choi Polymerase chain reaction 1) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): artificial amplification of a DNA sequence by repeated
Chapter 17. PCR the polymerase chain reaction and its many uses Prepared by Woojoo Choi Polymerase chain reaction 1) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): artificial amplification of a DNA sequence by repeated
Chapter 10 Genetic Engineering: A Revolution in Molecular Biology
 Chapter 10 Genetic Engineering: A Revolution in Molecular Biology Genetic Engineering Direct, deliberate modification of an organism s genome bioengineering Biotechnology use of an organism s biochemical
Chapter 10 Genetic Engineering: A Revolution in Molecular Biology Genetic Engineering Direct, deliberate modification of an organism s genome bioengineering Biotechnology use of an organism s biochemical
Human Genomics. 1 P a g e
 Human Genomics What were the aims of the human genome project? To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in Human DNA. To find where each gene is located To determine the sequences of the 3
Human Genomics What were the aims of the human genome project? To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in Human DNA. To find where each gene is located To determine the sequences of the 3
PV92 PCR Bio Informatics
 Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
PCR Amplifies Targeted Sequence
 PCR Amplifies Targeted Sequence Target Sequence Supercoiled DNA Strand DNA Strand Double Helix DNA Strand Chromosome P C R PCR PCR = Polymerase Chain Reaction. A primer directed-extension reaction for
PCR Amplifies Targeted Sequence Target Sequence Supercoiled DNA Strand DNA Strand Double Helix DNA Strand Chromosome P C R PCR PCR = Polymerase Chain Reaction. A primer directed-extension reaction for
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5. Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology -
 Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Biotechnology. Explorer Program. Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1
 Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
Biotechnology Explorer Program Serious About Science Education 5/17/09 1 Chromosome 8: PCR TM PCR Workshop Kirk Brown,, Tracy High School; Tracy, Ca Stan Hitomi,, Monte Vista High School; Danville, CA
PCR OPTIMIZATION AND TROUBLESHOOTING
 PCR OPTIMIZATION AND TROUBLESHOOTING Amplification of each DNA fragment can occur only under the defined conditions which are provided by a reaction mixture. If no positive PCR result can be obtained,
PCR OPTIMIZATION AND TROUBLESHOOTING Amplification of each DNA fragment can occur only under the defined conditions which are provided by a reaction mixture. If no positive PCR result can be obtained,
4/26/2015. Cut DNA either: Cut DNA either:
 Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
Genetic Identity. Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology
 Genetic Identity Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology Comparison of Organisms ORGANISM GENES BASE PAIRS Lambda Phage 40 50,000 E.coli 400 5,000,000 Yeast 13,000 15,000,000 Human 20,000 3,000,000,000 (3 billion)
Genetic Identity Steve Harris SPASH - Biotechnology Comparison of Organisms ORGANISM GENES BASE PAIRS Lambda Phage 40 50,000 E.coli 400 5,000,000 Yeast 13,000 15,000,000 Human 20,000 3,000,000,000 (3 billion)
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Basic Steps of the DNA process
 As time pasted technology has improve the methods of analyzing DNA. One of the first methods for the analysis of DNA is known as Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP). This technique analyzed
As time pasted technology has improve the methods of analyzing DNA. One of the first methods for the analysis of DNA is known as Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP). This technique analyzed
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Appendix A. Introduction to PCR
 Appendix A Introduction to PR In 1983, Kary Mullis at etus orporation developed the molecular biology technique that has since revolutionized genetic research, earning him the Nobel Prize in 1993. This
Appendix A Introduction to PR In 1983, Kary Mullis at etus orporation developed the molecular biology technique that has since revolutionized genetic research, earning him the Nobel Prize in 1993. This
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
Unit 1. DNA and the Genome
 Unit 1 DNA and the Genome National 5 Knowledge Learners should have a clear understanding of the following areas of content from their previous learning: *Cell division (mitosis) and chromosomes *Base
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome National 5 Knowledge Learners should have a clear understanding of the following areas of content from their previous learning: *Cell division (mitosis) and chromosomes *Base
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication
 Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA Replication. The Organization of DNA. Recall:
 Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes:
 DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics. If we can, should we?
 Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication
 Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944)
Chapter 13 DNA The Genetic Material Replication Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944)
Human Genomics. Higher Human Biology
 Human Genomics Higher Human Biology Learning Intentions Explain what is meant by human genomics State that bioinformatics can be used to identify DNA sequences Human Genomics The genome is the whole hereditary
Human Genomics Higher Human Biology Learning Intentions Explain what is meant by human genomics State that bioinformatics can be used to identify DNA sequences Human Genomics The genome is the whole hereditary
Genetic Fingerprinting
 Genetic Fingerprinting Introduction DA fingerprinting In the R & D sector: -involved mostly in helping to identify inherited disorders. In forensics: -identification of possible suspects involved in offences.
Genetic Fingerprinting Introduction DA fingerprinting In the R & D sector: -involved mostly in helping to identify inherited disorders. In forensics: -identification of possible suspects involved in offences.
Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases)
 In order to understand and eventually manipulate DNA (human or otherwise) an array of DNA technologies have been developed. Here are some of the tools: Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases) In order to manipulate
In order to understand and eventually manipulate DNA (human or otherwise) an array of DNA technologies have been developed. Here are some of the tools: Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases) In order to manipulate
DNA Technology. Asilomar Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg
 DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
Chapter 4 DNA Structure & Gene Expression
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 4 DNA Structure & Gene Expression Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 108-153 4.1 DNA Structure pages 112-114 1. DNA stands for and is the genetic material
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 4 DNA Structure & Gene Expression Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 108-153 4.1 DNA Structure pages 112-114 1. DNA stands for and is the genetic material
Molecular Biology (2)
 Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Chapter 8: Recombinant DNA. Ways this technology touches us. Overview. Genetic Engineering
 Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA and Genetic Engineering Genetic manipulation Ways this technology touches us Criminal justice The Justice Project, started by law students to advocate for DNA testing of Death
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA and Genetic Engineering Genetic manipulation Ways this technology touches us Criminal justice The Justice Project, started by law students to advocate for DNA testing of Death
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics
 Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics There was a time when to amplify DNA, You had to grow tons and tons of tiny cells. (Oooh) Then along came a guy named Dr. Kary Mullis, Said you can amplify in vitro just as well.
Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics There was a time when to amplify DNA, You had to grow tons and tons of tiny cells. (Oooh) Then along came a guy named Dr. Kary Mullis, Said you can amplify in vitro just as well.
DNA Replication. DNA Replication. Meselson & Stahl Experiment. Contents
 DNA Replication Contents 1 DNA Replication 1.1 Meselson & Stahl Experiment 1.2 Replication Machinery 2 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) 3 External Resources: DNA Replication Meselson & Stahl Experiment
DNA Replication Contents 1 DNA Replication 1.1 Meselson & Stahl Experiment 1.2 Replication Machinery 2 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) 3 External Resources: DNA Replication Meselson & Stahl Experiment
Moayyad Al-shafei. Mohammad Tarabeih. Dr Ma'mon Ahram. 1 P a g e
 3 Moayyad Al-shafei Mohammad Tarabeih Dr Ma'mon Ahram 1 P a g e In this sheet, we are going to discuss 2 main topics: 1- The advantages of restriction endonucleases. 2- DNA replication. Before we start
3 Moayyad Al-shafei Mohammad Tarabeih Dr Ma'mon Ahram 1 P a g e In this sheet, we are going to discuss 2 main topics: 1- The advantages of restriction endonucleases. 2- DNA replication. Before we start
PCR. What is PCR? What is PCR? Why chain? What is PCR? Why Polymerase?
 What is PCR? PCR the swiss army knife Claudia Stäubert, Institute for biochemistry PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by
What is PCR? PCR the swiss army knife Claudia Stäubert, Institute for biochemistry PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by
1
 1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
ASIC200 PERSONAL GENOMICS LECTURE (PART 2/PCR LAB).
 ASIC200 PERSONAL GENOMICS LECTURE (PART 2/PCR LAB). Essentially covering the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Gel Electrophoresis. As mentioned earlier, Sanger sequencing, and Next Gen sequencing will not
ASIC200 PERSONAL GENOMICS LECTURE (PART 2/PCR LAB). Essentially covering the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Gel Electrophoresis. As mentioned earlier, Sanger sequencing, and Next Gen sequencing will not
Introduction to PCR. ABCF Training Module. Leah Kago Research Associate BecA-ILRI Hub
 Introduction to PCR ABCF Training Module Leah Kago Research Associate BecA-ILRI Hub What is PCR? Polymerase Chain Reaction An in vitro process that detects, identifies, and copies (amplifies) a specific
Introduction to PCR ABCF Training Module Leah Kago Research Associate BecA-ILRI Hub What is PCR? Polymerase Chain Reaction An in vitro process that detects, identifies, and copies (amplifies) a specific
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March :24 pm
 Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material
 Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time
 qpcr qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time Differs from endpoint PCR gel on last cycle Used to determines relative amount of template
qpcr qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time Differs from endpoint PCR gel on last cycle Used to determines relative amount of template
Report of Analyzing Short Tandem Repeats for Parentage Testing
 1 Alex Michael Tseng Department of Forensic Medicine, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University Report of Analyzing Short Tandem Repeats for Parentage Testing Introduction In the three billion letter
1 Alex Michael Tseng Department of Forensic Medicine, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University Report of Analyzing Short Tandem Repeats for Parentage Testing Introduction In the three billion letter
Amplification Products for PCR and RT-PCR
 Selection guide Polymerase Hot start Comment UptiTherm DNA pol. no Most economic. Lower error rate than Taq polymerase Available in several formats, master mix including or not dntp, Mg 2+..., in gel format
Selection guide Polymerase Hot start Comment UptiTherm DNA pol. no Most economic. Lower error rate than Taq polymerase Available in several formats, master mix including or not dntp, Mg 2+..., in gel format
Exploring Genetic Variation in a Caffeine Metabolism gene LAB TWO: POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION
 Exploring Genetic Variation in a Caffeine Metabolism gene LAB TWO: POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION Purpose: In this laboratory, we will set up a polymerase chain reaction to amplify the region of the caffeine
Exploring Genetic Variation in a Caffeine Metabolism gene LAB TWO: POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION Purpose: In this laboratory, we will set up a polymerase chain reaction to amplify the region of the caffeine
Biotechnology Chapter 20
 Biotechnology Chapter 20 DNA Cloning DNA Cloning AKA Plasmid-based transformation or molecular cloning First off-let s sum up what happens. A plasmid is taken from a bacteria A gene is inserted into the
Biotechnology Chapter 20 DNA Cloning DNA Cloning AKA Plasmid-based transformation or molecular cloning First off-let s sum up what happens. A plasmid is taken from a bacteria A gene is inserted into the
Chapter 7 DNA Fingerprinting By the end of this chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 7 DNA Fingerprinting By the end of this chapter you will be able to: explain how crime scene evidence is collected and processed to obtain DNA describe how radioactive probes are used in DNA fingerprinting
Chapter 7 DNA Fingerprinting By the end of this chapter you will be able to: explain how crime scene evidence is collected and processed to obtain DNA describe how radioactive probes are used in DNA fingerprinting
Molecular biology lecture #2
 Molecular biology lecture #2 In the previous lecture, we got to chapter 12. We talked about DNA structure and reached the Watson and Crick model and the double helix. Today, we are going to finish chapter
Molecular biology lecture #2 In the previous lecture, we got to chapter 12. We talked about DNA structure and reached the Watson and Crick model and the double helix. Today, we are going to finish chapter
DNA FINGERPRINTING MADE EASY FOR FORENSICS
 DNA FINGERPRINTING MADE EASY FOR FORENSICS Presented by Eilene Lyons The St. Louis Community College Florissant Valley Biotechnology Program Some slides are from a downloaded PPT presentation from The
DNA FINGERPRINTING MADE EASY FOR FORENSICS Presented by Eilene Lyons The St. Louis Community College Florissant Valley Biotechnology Program Some slides are from a downloaded PPT presentation from The
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
..C C C T C A T T C A T T C A T T C A T T C A..
 Polymerase Chain Reaction Lab: a Forensic Application INTRODUCTION PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a technique that scientists use to amplify particular segments of DNA. This process can produce large
Polymerase Chain Reaction Lab: a Forensic Application INTRODUCTION PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a technique that scientists use to amplify particular segments of DNA. This process can produce large
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing. Outline
 XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
Appendix A DNA and PCR in detail DNA: A Detailed Look
 Appendix A DNA and PCR in detail DNA: A Detailed Look A DNA molecule is a long polymer consisting of four different components called nucleotides. It is the various combinations of these four bases or
Appendix A DNA and PCR in detail DNA: A Detailed Look A DNA molecule is a long polymer consisting of four different components called nucleotides. It is the various combinations of these four bases or
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
DNA Profiling with PCR
 Name: DNA Profiling with PCR OBJECTIVES To review the structure and function of DNA. Understand and perform the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) To gain experience using the micropipettes, thermocycler,
Name: DNA Profiling with PCR OBJECTIVES To review the structure and function of DNA. Understand and perform the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) To gain experience using the micropipettes, thermocycler,
P HENIX. PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide Tools For Life Science Discovery RESEARCH PRODUCTS
 PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
