Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
|
|
|
- Marvin Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA and proteins u Structural motifs of TF DNA-binding domains (helixturn-helix; zinc fingers; bzip; helix-loop-helix; betascaffold) u DNA-protein interactions in transcription u RNA polymerase and preinitiation complex for transcription u Mechanism of gene activation by transcription factors
2 Proteins are the processing units for transcription cnx.org 2
3 Protein-DNA interactions DNA-binding proteins Transcription factors Polymerases & nucleases Transcription factors utilize a wide range of DNA-binding structural motifs Interaction between dimeric proteins and palindromic sequences are common. Binding often leads to the conformational changes in the protein and DNA. λ repressor PDB 2OR1 3
4 Transcription factors Sequence-specific DNA-binding factor that controls the rate of transcription by promoting (activator) or blocking (repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase Other proteins critical for regulating transcription lack DNA-binding domains: coactivators, corepressors, deacetylases, methylases, chromatin remodelers Bind either promoter or enhancer regions of DNA Regulatory mechanism Stabilize or block RNA polymerase association with DNA Catalyze, directly or by recruitment, acetylation or deacetylation of histones Recruit coactivator or corepressor proteins to the complex Function: basal level transcription, development, signaling, cell cycle control Activation of TFs: 4 may be activated or deactivated by ligand binding to a sensing domain (hormone receptors), chemical modification (e.g. STAT proteins must be phosphorylated to bind DNA) Interaction coregulatory proteins PHRM or 836, with 22 Sept other 2015 TFs (homo- or hetero-dimerization)
5 Eukaryotic transcription factors have modular structure: CREB example DNA binding domain (bzip) Recognize specific sequences in DNA for sequence-specific binding. (e.g. HLH) Basis of structural classification Dimerization domain (bzip) Promotes the formation of heterodimer or homodimers. Activation domain (Q1 and Q2) Interact with general transcription factors, RNA polymerase II, or other regulators of transcription. e.g. acidic domains, glutamine-rich domains, and proline-rich domains. Protein interaction domain (KID) Associate with proteins like histone acetyltransferases or coactivators. 5 camp response element binding protein, CREB Order varies
6 DNA sequence-specificity of DNAbinding proteins Sequence-specific interactions Frequently involve DNA major groove Base-specific H-bond donor, acceptors, and nonpolar groups are recognized by DNA-binding proteins DNA structure can deviate from classic B-form helix, and therefore be specifically recognized by a protein. No simple recognition code between DNA and protein sequences. Nonspecific interactions interactions with DNA phosphate backbones 6
7 Helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif ~20 amino-acid long DNA-binding motif. Formed by two helices connected by a short turn. The second helix is the recognition helix that binds in a sequence-specific manner in the major groove. The first helix stabilizes the motif. Examples E. coli lactose repressor Homeobox domains: appear in developmentally important transcription factors e.g. antennapedia Figure
8 Helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif Homeobox domains: appear in developmentally important transcription factors e.g. antennapedia PDB entry 9ANT. Sequence specific interactions 8
9 Zinc fingers (ZnFs) PDB-101 entry Classic ZnF is ~30 amino-acid domain A two-stranded antiparallel β-sheet and short α-helix The α-helix makes sequence-specific contacts along the major groove. Initially known as sequence-specific DNA-binding motifs Now known that ZnFs also recognize RNA and other proteins Small modules in which zinc plays a structural role Structural diverse: ~8 fold groups Present in ~1000 different proteins A Zn 2+ ion coordinated by 4 Cys or 2 Cys and 2 His residues. Often occur as tandem repeats with two, three, or more fingers. ZnFs designed to bind targeted DNA sequences with ultimate goal of therapeutics 9
10 Basic region-leucine zippers (bzip) Contain leucine residues every 7 th position in an α-helix. Form homo- or heterodimers with coiled coil structure (blue region) The basic region with arginine and lysine residues bind to the major groove of DNA The basic amino acids interact with the phosphate backbone of DNA through electrostatic interactions and also the DNA bases through hydrogen bonding. Examples fos and jun camp response element-binding protein (CREB) 10
11 Helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif Two amphipathic α-helices connected by a loop. Forms homo- or heterodimers. Dimerization domain has a fourhelix bundle structure. Extension of one of the α-helices from DNA binding domain binds the major groove of DNA. Examples of HLH transcription factors myod myc max PDB entry 1MDY 11
12 Beta-scaffold with minor groove contacts: e.g. TATA binding protein (TBP) PDB-101 entry Uses a large β-sheet surface to recognize DNA by binding in the minor grove. Recognizes T-A-T-A-a/t-A-a/t and variations of it Function=control of which gene gets transcribed. TATA box is in front of start site of transcription and TBP binding creates a marks for transcription start Binding induces significant changes in the DNA structure Enables good fit between the protein and DNA bases. The binding of TBP directs assembly of the initiation complex by ordered addition of several general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. TFIIA, a transcription activator (pdb 1YTF) TATA-binding protein DNA Transcription regulator (inhibitor) 12 pdb 1JFI
13 Beta-scaffold with minor groove contacts: e.g. TATA binding protein (TBP) Lys and Arg interact with phosphate groups Phe groups jam into the DNA minor groove and kink the DNA; TATA is relatively flexible sequence 13 pdb 1YTB
14 General transcription Eukaryotic RNA polymerases RNA polymerase I transcribes the rrna genes. RNA polymerase II transcribes the protein-encoding genes to produce mrna. RNA polymerase III transcribes the genes for trnas and other small RNAs. Preinitiation complex: binding of RNA polymerase II to a promoter region of DNA requires the initial contact of the promoter with transcription factors (TFs). TFIID : multi-subunit complex with TATA binding protein (TBP) and different TBP-associated factors (TAFs). TATA box Located ~27 bp upstream of the transcription start site. Recognized by TATA binding protein. Needs to be dissociated from histones for transcription. 14
15 Bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase (PDB entry 1MSW) RNA polymerase, ~880 residues DNA, ~20 base pairs transcribed strand not transcribed strand RNA, ~10 bases PDB entry 1MSW 15
16 RNA polymerase II elongation complex PDB-101 entry PDB entry 1I6H 3521 amino acid residues (10 subunits), 9 RNA bases, 13 DNA bases 16 Core part of Pol II from yeast unwinds DNA, builds RNA
17 RNA polymerase II elongation complex PDB entry 1I6H 3521 amino acid residues (10 subunits), 9 RNA bases, 13 DNA bases 17 Core part of Pol II from yeast unwinds DNA, builds RNA
18 RNA polymerase II elongation complex A mechanism for translocation was speculated from seeing the structure! Gnatt, Cramer, Fu, Bushnell and Roger Kornberg (2006 Nobel Prize) Science 8 June 2001: This yeast complex has common Vol. 292 no pp features with the bacterial complex 18
19 Multiple transcription factor-binding sites regulate eukaryotic transcription Promoter regulatory regions on DNA (example of LDL receptor gene) In addition to preinitiation-complex assembly site, other TF-binding sites close to the TATA box (e.g. CAAT box and GB box) play a role in transcription TF Sp1 binds GC boxes via ZnFs; a glu-rich activation domain thought to recruit TFIID with help from CRSP Some TFs are regulated by signaling molecules (e.g. hormones) or chemical modification (e.g. phosphorylation) Bind to DNA response elements such as SRE (sterol response element) or CRE (camp response element) Examples: SREBP-1A moves to nucleus when cholesterol levels are low; binds SRE via HLH motifs; recruits CBP, which couples chromatin remodeling to transcription factor recognition 19
20 Multiple transcription factor-binding sites regulate eukaryotic transcription Promoter regulatory regions on DNA (example of LDL receptor gene) Other proteins can bridge between the TF and the preinitiation complex (rather than TF direct interaction). Recruitment of histone remodeling enzymes, e.g. CBP-p300 complex has histone acetylase activity, which modifies chromatin structure. Enhancer elements: bind TFs that activate transcription by increasing the rate of assembly of the preinitiation complex. Unlike promoter sequences, can be located many thousands of bp from initiation assembly site (TATA-like site); brought close to preinitiation complex by DNA loop 20
21 Summary: DNA binding proteins, structure and function A number of proteins recognize DNA using a variety of structural motifs Dimeric interactions; palindromes Flexibility of structures, both DNA and protein Sequence specific or not Motifs include HTH, zinc-fingers, leucine zipper, TATA binding protein Transcription factors regulate transcription through binding certain DNA regions and involve interactions with other proteins RNA polymerase recognition of DNA during transcription involves a promoter region and a multi-subunit complex (machine) to conduct a complex process (unwinding DNA, RNA elongation, accurate translation of DNA via proofreading) Numerous proteins involved in regulation of transcription including CBP, Sp1, etc 21
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators
 Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Gene expression DNA RNA. Protein DNA. Replication. Initiation Elongation Processing Export. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Degradation.
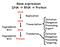 Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Transcription factors
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Transcription factors I Introduction * II Initiation of transcription III Transcription factors family pdf version I Introduction III.1 Helix-Turn-Helix
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Transcription factors I Introduction * II Initiation of transcription III Transcription factors family pdf version I Introduction III.1 Helix-Turn-Helix
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs. Effector Domain. Zinc Fingers. Zinc Fingers, continued. Zif268
 DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Regulation of gene expression. (Lehninger pg )
 Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
Eukaryotic transcription (II)
 Eukaryotic transcription (II) Transcription factors Prokaryote: Sigma factors they are similar to general transcription factor of eukaryotes, they help bring RNA pol to the promoter Transcription factors
Eukaryotic transcription (II) Transcription factors Prokaryote: Sigma factors they are similar to general transcription factor of eukaryotes, they help bring RNA pol to the promoter Transcription factors
Enhancers. Activators and repressors of transcription
 Enhancers Can be >50 kb away from the gene they regulate. Can be upstream from a promoter, downstream from a promoter, within an intron, or even downstream of the final exon of a gene. Are often cell type
Enhancers Can be >50 kb away from the gene they regulate. Can be upstream from a promoter, downstream from a promoter, within an intron, or even downstream of the final exon of a gene. Are often cell type
Differential Gene Expression
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II
 The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
DNA & DNA : Protein Interactions BIBC 100
 DNA & DNA : Protein Interactions BIBC 100 Sequence = Information Alphabet = language L,I,F,E LIFE DNA = DNA code A, T, C, G CAC=Histidine CAG=Glutamine GGG=Glycine Protein = Protein code 20 a.a. LIVE EVIL
DNA & DNA : Protein Interactions BIBC 100 Sequence = Information Alphabet = language L,I,F,E LIFE DNA = DNA code A, T, C, G CAC=Histidine CAG=Glutamine GGG=Glycine Protein = Protein code 20 a.a. LIVE EVIL
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs
 Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs 1. Helix-turn-helix proteins 2. Zinc finger proteins 3. Leucine zipper proteins 4. Beta-scaffold factors 5. Others λ-repressor AND CRO
Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs 1. Helix-turn-helix proteins 2. Zinc finger proteins 3. Leucine zipper proteins 4. Beta-scaffold factors 5. Others λ-repressor AND CRO
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes. Chapter 12
 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes Chapter 12 Techniques Run-off transcription Primer extension Quantitative S1 mapping Modular Protein domain is an independingly folding region. DA binding domain
Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes Chapter 12 Techniques Run-off transcription Primer extension Quantitative S1 mapping Modular Protein domain is an independingly folding region. DA binding domain
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression
 Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Synthetic cells: do bacteria need all its genes? No.
 NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
Complex Transcription Machinery
 Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Resources. This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11
 Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302. March 6, 2006
 Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302 March 6, 2006 Common structural motifs associated with transcriptional regulatory proteins Helix-turn-helix Prokaryotic repressors and activators Eukaryotic homeodomain
Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302 March 6, 2006 Common structural motifs associated with transcriptional regulatory proteins Helix-turn-helix Prokaryotic repressors and activators Eukaryotic homeodomain
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1
 Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2
 Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
 Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
- all cells express large number of the same genes - housekeeping or common genes - many cells also express cell-type-specific genes
 Developmental Biology - Biology 4361 Lecture 8 - Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 The principle of genomic equivalence states that all cells in a developing organism have the same genetic
Developmental Biology - Biology 4361 Lecture 8 - Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 The principle of genomic equivalence states that all cells in a developing organism have the same genetic
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes The latest estimates are that a human cell, a eukaryotic cell, contains 20,000 25,000 genes. Some of these are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes The latest estimates are that a human cell, a eukaryotic cell, contains 20,000 25,000 genes. Some of these are expressed in all cells all the time. These so-called housekeeping
Transcription steps. Transcription steps. Eukaryote RNA processing
 Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
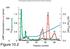 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words).
 1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 31 Transcription and Regulation of Gene Expression 2 Messenger RNA Central Dogma (Francis Crick, 1958) DNA RNA Protein (Fig 31.1) Jacob-Monod Hypothesis:
BCH 4054 Fall 2000 Chapter 31 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 31 Transcription and Regulation of Gene Expression 2 Messenger RNA Central Dogma (Francis Crick, 1958) DNA RNA Protein (Fig 31.1) Jacob-Monod Hypothesis:
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 MODULAR STRUCTURE OF UPSTREAM TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS Experimental
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 MODULAR STRUCTURE OF UPSTREAM TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS Experimental
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Expression of the genome. Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell
 Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Prof. Michael Hampsey
 The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
RNA does not adopt the classic B-DNA helix conformation when it forms a self-complementary double helix
 Reason: RNA has ribose sugar ring, with a hydroxyl group (OH) If RNA in B-from conformation there would be unfavorable steric contact between the hydroxyl group, base, and phosphate backbone. RNA structure
Reason: RNA has ribose sugar ring, with a hydroxyl group (OH) If RNA in B-from conformation there would be unfavorable steric contact between the hydroxyl group, base, and phosphate backbone. RNA structure
Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004
 Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004 This exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions worth 2.5 points each, for a total of 100 points. Good luck. Name SS# 1. Which of the following statements
Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004 This exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions worth 2.5 points each, for a total of 100 points. Good luck. Name SS# 1. Which of the following statements
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks
 Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone:
 Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone: 453-6437 Email: bbartholomew@siumed.edu Class notes http://www.siumed.edu/~bbartholomew/hbtxn.html Other references Principles
Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone: 453-6437 Email: bbartholomew@siumed.edu Class notes http://www.siumed.edu/~bbartholomew/hbtxn.html Other references Principles
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
All Rights Reserved. U.S. Patents 6,471,520B1; 5,498,190; 5,916, North Market Street, Suite CC130A, Milwaukee, WI 53202
 Secondary Structure In the previous protein folding activity, you created a hypothetical 15-amino acid protein and learned that basic principles of chemistry determine how each protein spontaneously folds
Secondary Structure In the previous protein folding activity, you created a hypothetical 15-amino acid protein and learned that basic principles of chemistry determine how each protein spontaneously folds
Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact?
 Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires that Gal4-VP16 be present. Primer extension
Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires that Gal4-VP16 be present. Primer extension
Chapter 11. Transcription. The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU
 Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms
 Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chromatin and Transcription
 Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Part IV => DNA and RNA. 4.7 Gene Regulation 4.7a Chromatin Remodeling 4.7b Transcriptional Control
 Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.7 Gene Regulation 4.7a Chromatin Remodeling 4.7b Transcriptional Control Overview of Gene regulation - The expression of the so-called housekeeping genes (eg basal transcription
Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.7 Gene Regulation 4.7a Chromatin Remodeling 4.7b Transcriptional Control Overview of Gene regulation - The expression of the so-called housekeeping genes (eg basal transcription
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES V. Lecture 7. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES V Lecture 7 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University 2 CELL NUCLEUS AND THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION An Overview of Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
1 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES V Lecture 7 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University 2 CELL NUCLEUS AND THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION An Overview of Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
The Structure of Proteins The Structure of Proteins. How Proteins are Made: Genetic Transcription, Translation, and Regulation
 How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription
 Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 12 Transcription
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
Prokaryotic Transcription
 Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Nucleic Acids. Information specifying protein structure
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats) Genome - the genetic information of an organism Information
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats) Genome - the genetic information of an organism Information
Information specifying protein structure. Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Nucleotides Are the Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
 Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Information specifying protein structure Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats)
Chapter 19 Nucleic Acids Information specifying protein structure Nucleic acids represent the fourth major class of biomolecules (other major classes of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, fats)
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015
 Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Section 3: DNA Replication
 Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
Lesson 8. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity. Gene Expression and Regulation. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 8 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Gene Expression and Regulation Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Genes and DNA Hereditary information is found in discrete units called genes Genes are segments
Lesson 8 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Gene Expression and Regulation Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Genes and DNA Hereditary information is found in discrete units called genes Genes are segments
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0
 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression
 Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
Class: _ Date: _ CH 12 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 6 c. 3 b. 12
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
From Gene to Protein
 8.2 Structure of DNA From Gene to Protein deoxyribonucleic acid - (DNA) - the ultimate source of all information in a cell This information is used by the cell to produce the protein molecules which are
8.2 Structure of DNA From Gene to Protein deoxyribonucleic acid - (DNA) - the ultimate source of all information in a cell This information is used by the cell to produce the protein molecules which are
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Unit 1. DNA and the Genome
 Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
