Supplemental figure 1. Dys-regulated signal pathways in MSCs from TNF-Tg. mice. 965 dys-regulated genes were uploaded to IPA and David bioinformatics
|
|
|
- Thomas Wright
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental figure 1. Dys-regulated signal pathways in MSCs from TN-Tg mice. 965 dys-regulated genes were uploaded to IPA and David bioinformatics esources software. The top 53 and top 11 dys-regulated pathways were identified by IPA (A) and David bioinformatics esources (B) analysis according to P value. The ratio is the number of genes found in our data set divided by the referenced genes in pathways of software data base. Supplemental figure 2. Expression of Notch genes in MSCs of TN-Tg mice via NAseq. mna levels of Notch-related factors in CD45-/Scal1+/CD15+ MSCs from TN-Tg mice and WT littermates by NA-sequencing. Values are means + SD of 3 mice. Supplemental figure 3. Characterization of 3rd passage of bone-derived MSCs. Bone-derived cells from WT mice were cultured in basal medium and passaged 3 times. (A) The expression profile of MSC surface markers was examined by ACS. MSC surface markers are CD45-/Sca1+/CD15+/CD44+/CD31-/CD11b-/CD117-. (B) The differentiation potential to osteoblasts, adipocytes and chondrocytes were examined by culturing cells in the appropriate inducing media for 2-4 weeks. Supplemental figure 4. The effect of long-term DAPT treatment on expression levels of Notch target genes. TN-Tg mice were treated with DAPT or vehicle by daily gavage for 3 months. Total NA was extracted from popliteal lymph nodes and spleens, and expression levels of Notch-related genes were examined by qpc. Values are means and SD of 3 samples. *p<.5 vs vehicle-treated mice. Supplemental figure 5. Characterization of CU colony cells. BM cells from WT mice were used. ed blood cells were lysed first to obtain BM mononuclear cells. Cells were cultured in basal condition for 3 weeks. Low cell density (1E4/1 cm dish)
2 was used in CU colony assay to generate colony cells (A). High cell density (1E6/ml) was used to generate BM stromal cells (B). Media were changed every 5 days. Primary BM mononuclear cells were isolated freshly from a separate WT mouse (C). Cells were stained with anti-cd45, Scal1 and CD15 antibodies and subjected to ACS analyses. Supplemental figure 6. In vivo bone repair model. Mice received bone scaffold alone (A) or bone scaffold plus WT CU cells (B) were sacrificed 6 weeks post surgery. H&E-stained sections show the bone defect area (black dash line) and newly formed bone (sold black line). The defects that were filled with bone scaffold alone have significantly lesser bone volume compared to those that were filled with bone scaffold plus CU cells (C). N= 5 mice/group. *p<.5 vs no cell group. Supplemental figure 7. The effect of long-term DAPT treatment on morphology of internal organs. WT mice were treated with DAPT or vehicle by daily gavage for 3 months. Internal organs were stained with H&E. epresentative sections were shown. Supplemental figure 8. Thapsigargin reduces Hes1 expression and revises decreased osteoblast differentiation of MSCs in TN-Tg mice. TN-Tg mice and WT littermates were i.p. injected with the new Notch inhibitor Thapsigargin (.4mg/kg/time) or vehicle daily for 4 days. (A) The inhibitory effect of Thapsigargin on Notch activation (Hes1 mna) was confirmed in the popliteal lymph nodes (positive Ctl) and in CD45- MSC-enriched cells by qpc. (B) epresentative photos and # of CU-ALP+ colonies in BM stromal cells from Thapsigargin- or vehicle-treated mice. TN-Tg mice and WT littermates were i.p. injected with Thapsigargin (.4mg/kg/time, 3 time/week) or vehicle for 2 months. (C) The expression levels of Hey1 in CU cells from Thapsigargin- or PBS-treated mice were examined by qpc. *p<.5 vs vehicle-treated mice, #p<.5 vs WT mice. Supplemental figure 9. Activation status of Notch signaling in cells at different 4
3 confluence. Expression levels of Hes1 and NICD (Notch-2) in C3H1T1/2 cells at different confluence levels were examined by Western blotting using anti-nicd (Notch-2) antibody. Supplemental figure 1. Correlation of gene expression levels in CD45- MSCs from BM and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. CD45- cells were isolated form BM mononuclear cells (BMMCs) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of TN-Tg mice and WT littermates. The expression levels of Hes1 and unx2 from BMMCs and paired PBMCs were determined by qpc. Values were calculated based the equation= ½ CT(gene of interest) CT(actin). 41
4 Supplemental figure 1A Ingenuity Canonical Pathways p-value HG Signaling.676 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Signaling.1 SAPK/JNK Signaling.1148 B Cell eceptor Signaling.263 ole of Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Chondrocytes in heumatoid Arthritis.32 Xenobiotic Metabolism Signaling.39 Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer.3236 PI3K/AKT Signaling.3548 p53 Signaling.4365 LPS/IL-1 Mediated Inhibition of X unction.5248 Assembly of NA Polymerase I Complex.6457 Phospholipid Degradation.6761 Insulin eceptor Signaling.6918 Notch Signaling.779 Type II Diabetes Mellitus Signaling.7762 Huntington's Disease Signaling.7762 Glioblastoma Multiforme Signaling.7943 IL-15 Production.8128 CD27 Signaling in Lymphocytes.8128 Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions.8128 N- B signaling.8511 JAK/Stat Signaling.9333 Histidine Metabolism.1 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Signaling.1471 PPAα/Xα Activation.1122 Production of Nitric Oxide and eactive Oxygen Species in Macrophages
5 Continued Supplemental figure 1A Ingenuity Canonical Pathways p-value Acute Phase esponse Signaling Lymphotoxin β eceptor Signaling PDG Signaling G Signaling Atherosclerosis Signaling MSP-ON Signaling Pathway actors Promoting Cardiogenesis in Vertebrates Glycerophospholipid Metabolism IL-9 Signaling Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis Human Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency.2893 Androgen and Estrogen Metabolism Leptin Signaling in Obesity Assembly of NA Polymerase II Complex.2574 Colorectal Cancer Metastasis Signaling Type I Diabetes Mellitus Signaling GM-CS Signaling Estrogen eceptor Signaling Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Signaling Glioma Signaling PKCθ Signaling in T Lymphocytes.3819 Prostate Cancer Signaling.3819 Tyrosine Metabolism.3819 Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Signaling.3819 Thrombopoietin Signaling.3895 PX/X Activation Glucocorticoid eceptor Signaling
6 Supplemental figure 1B Supplemental figure 1. Dys-regulated signal pathways in MSCs from TN-Tg mice 51
7 Supplemental figure eceptors (PKM) Ligands and co-activators (PKM) WT TN-Tg Notch 1 Notch 2 Notch 3 Notch 4 4 Jag1 Delta1 Jag2 Delta4 Dtx1 Dtx2 Dtx3 Dtx Ligands Targets and inhibitors (PKM) Hes 6 Hes1 Hey1 Hey2 Target genes Co-activators Numb Numbl Inhibitors Supplemental figure 2. Expression of Notch genes in MSCs of TN-Tg mice via NAseq. 52
8 Supplemental figure 3 A 93.63% 73.65% 71.68% Isotype control Specific antibody CD45 Sca1 CD % 99.61% 96.3% 97.52% CD44 CD31 CD11b CD117 B Osteoblasts (Alizarin red) Adipocytes (Oil ed) Chondrocytes (Alcian blue) Supplemental figure 3. Characterization of 3rd passage of bone-derived MSCs. 53
9 Supplemental figure 4 elative expression level to GAPDH Lymph node Spleen Notch1 Notch2 Hey1 1.6 Hey2 Hes1 Hes2 * *.4 * * Vehicle DAPT Supplemental figure 4. The effect of long-term DAPT treatment on expression levels of Notch target genes. 54
10 Supplemental figure 5 A CU cells 5.4% 88.7% 88.6% B Bone marrow stromal cells 15.5% 12.7% 6.7% C Primary bone marrow mononuclear cells 5.6% 8.4% 1.9% CD45 Scal1 CD15 Isotype control Specific antibody Supplemental figure 5. Characterization of CU colony cells. 55
11 Supplemental figure 6 A Bone scaffold -cells B Bone scaffold + cells C New bone area (mm 2 ) * Bone scaffold cells Bone scaffold + cells Supplemental figure 6. In vivo bone repair model. 56
12 Supplemental figure 7 Intestine Lung Liver Kidney Vehicle DAPT Supplemental figure 7. The effect of long-term DAPT treatment on morphology of internal organs. 57
13 Supplemental figure 8 A Lymph nodes Hes1 (fold vs WT veh.) CD45- cells # * # * * * WT TN-Tg WT TN-Tg Vehicle Thapsigargin B Vehicle Thapsigargin WT 6 CU-ALP (#/well) * # 4 TN-Tg 2 WT TN-Tg C Hey1 expression fold change * # * WT TN-Tg Supplemental figure 8. Thapsigargin reduces Hes1 expression and revises decreased osteoblast differentiation of MSCs in TN-Tg mice. 58
14 Supplemental figure 9 Hes1 NICD GAPDH 5% 8% 1% Confluence Supplemental figure 9. Activation status of Notch signaling in cells at different confluence. 59
15 Supplemental figure 1.4 Hes unx2 WT TN-Tg BMMCs WT TN-Tg PBMCs WT TN-Tg WT TN-Tg BMMCs PBMCs Supplemental figure 1. Correlation of gene expression levels in CD45- MSCs from BM and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 6
16 Name / Sequences mhes1 GACCCAGATCAACGCCATGA TGGAAGCCGCCAAAAACCTT mhes2 CTGAAGGGTCTCGTATTGCCG CGCAGGTGCTCTAGTAGGC mhey1 GCGCGGACGAGAATGGAAA TCAGGTGATCCACAGTCATCTG mhey2 AAGCGCCCTTGTGAGGAAAC GGTAGTTGTCGGTGAATTGGAC mnotch1 CCCTTGCTCTGCCTAACGC GGAGTCCTGGCATCGTTGG mnotch2 ATGTGGACGAGTGTCTGTTGC GGAAGCATAGGCACAGTCATC malp CTTGCTGGTGGAAGGAGGCAGG CACGTCTTCTCCACCGTGGGTC munx2 CAAGAAGGCTCTGGCGTTTA TGCAGCCTTAAATGACTCGG mgapdh GGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG ATGAGCCCTTCCACAATG Supplemental table A. Murine primer sequences 61
17 B. Human primer sequences Name hhes1 / Sequences TGAGCCAGCTGAAAACACTG GTGCGCACCTCGGTATTAAC hhey1 GTTCGGCTCTAGGTTCCATGT CGTCGGCGCTTCTCAATTATTC hp52 ATGGAGAGTTGCTACAACCCA CTGTTCCACGATCACCAGGTA helb CCATTGAGCGGAAGATTCAACT CTGCTGGTCCCGATATGAGG halp ACCACCACGAGAGTGAACCA CGTTGTCTGAGTACCAGTCCC hunx2 TCAACGATCTGAGATTTGTGGG GGTCAAGGTGAAACTCTTGCC hgapdh AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAAC GGGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATA 62
Supplemental figure 1: Phenotype of IMC and MDSC after purification. A. Gating
 Supplemental Figure Legend: Supplemental figure 1: Phenotype of IMC and MDSC after purification. A. Gating strategy for mouse MDSC. CD11b + Ly6C high Ly6G - cells are defined as M-MDSC. CD11b + Ly6C low
Supplemental Figure Legend: Supplemental figure 1: Phenotype of IMC and MDSC after purification. A. Gating strategy for mouse MDSC. CD11b + Ly6C high Ly6G - cells are defined as M-MDSC. CD11b + Ly6C low
Figure S1: GM-CSF upregulates CCL17 expression in in vitro-derived and ex vivo murine macrophage populations
 Figure S1 A B C Figure S1: GM-CSF upregulates CCL17 expression in in vitro-derived and ex vivo murine macrophage populations (A-B) Murine bone cells were cultured in either M-CSF (5,000 U/ml) or GM-CSF
Figure S1 A B C Figure S1: GM-CSF upregulates CCL17 expression in in vitro-derived and ex vivo murine macrophage populations (A-B) Murine bone cells were cultured in either M-CSF (5,000 U/ml) or GM-CSF
Supplementary Information. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells
 Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diptiman Chanda 1*, Ashish Kurundkar 1, Sunad Rangarajan 1, Morgan Locy 1, Karen Bernard 1,
Developmental Reprogramming in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Human Subjects with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diptiman Chanda 1*, Ashish Kurundkar 1, Sunad Rangarajan 1, Morgan Locy 1, Karen Bernard 1,
Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis
 Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis Yan Liu 1,*, Zhipeng Han 1,*, Yingying Jing 1,*, Xue Yang 1, Shanshan Zhang 1, Chen
Contribution and Mobilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis Yan Liu 1,*, Zhipeng Han 1,*, Yingying Jing 1,*, Xue Yang 1, Shanshan Zhang 1, Chen
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES
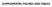 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
MicroRNAs Modulate Hematopoietic Lineage Differentiation
 Chen et al., page 1 MicroRNAs Modulate Hematopoietic Lineage Differentiation Chang-Zheng Chen, Ling Li, Harvey F. Lodish, David. Bartel Supplemental Online Material Methods Cell isolation Murine bone marrow
Chen et al., page 1 MicroRNAs Modulate Hematopoietic Lineage Differentiation Chang-Zheng Chen, Ling Li, Harvey F. Lodish, David. Bartel Supplemental Online Material Methods Cell isolation Murine bone marrow
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells. in the injured sites
 Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP2 transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP2 nucleotide sequence
 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP nucleotide sequence depicting the consensus sequence for
1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of the POP transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory elements. (A) POP nucleotide sequence depicting the consensus sequence for
(A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: WT; lower
 Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Fig. 1 (Li et al.)
 Supplementary Fig. 1 (Li et al.) Fcrg / Supplementary Figure 1 Microcomputed tomography (mct) images of the distal femurs isolated from the indicated bone marrow chimeric mice. indicates the Dap12 -/-
Supplementary Fig. 1 (Li et al.) Fcrg / Supplementary Figure 1 Microcomputed tomography (mct) images of the distal femurs isolated from the indicated bone marrow chimeric mice. indicates the Dap12 -/-
Supplementary Figures, Tables, and Legends:
 Supplementary Figures, Tables, and Legends: Supplementary Figure 1. RBPjκ is efficiently knocked down in RBPjk Prx1 mutant compact bones. Western blot analyses for RBPjk in protein extracts from femurs
Supplementary Figures, Tables, and Legends: Supplementary Figure 1. RBPjκ is efficiently knocked down in RBPjk Prx1 mutant compact bones. Western blot analyses for RBPjk in protein extracts from femurs
Supplemental Information Inventory
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Distinct Hematopoietic Stem Cell Subtypes Are Differentially Regulated by TGF-β1 Grant A. Challen, Nathan C. Boles, Stuart M. Chambers, and Margaret A.
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Distinct Hematopoietic Stem Cell Subtypes Are Differentially Regulated by TGF-β1 Grant A. Challen, Nathan C. Boles, Stuart M. Chambers, and Margaret A.
Wnt16 smact merge VK/AB
 A WT Wnt6 smact merge VK/A KO ctrl IgG WT KO Wnt6 smact DAPI SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE I: Wnt6 expression in MGP-deficient aortae. Immunostaining for Wnt6 and smooth muscle actin (smact) in aortae from 7 day
A WT Wnt6 smact merge VK/A KO ctrl IgG WT KO Wnt6 smact DAPI SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE I: Wnt6 expression in MGP-deficient aortae. Immunostaining for Wnt6 and smooth muscle actin (smact) in aortae from 7 day
Supplemental Figure 1: Diagram of full-length and predicted variant AR amino acid sequences.
 DNA-BD NLS LBD Supplemental Figure 1: Diagram of full-length and predicted variant AR amino acid sequences. The predicted amino acid sequence of AR v567es is compared to the known amino acid sequence for
DNA-BD NLS LBD Supplemental Figure 1: Diagram of full-length and predicted variant AR amino acid sequences. The predicted amino acid sequence of AR v567es is compared to the known amino acid sequence for
percentage of Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3728 Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 4 integrin expression in monocytes and macrophages from Cre + 4 f/f and Cre 4 f/f mice. a) Depicted is a representative histogram of flow cytometry analysis for α4 integrin expression
Supplementary Figure 1 4 integrin expression in monocytes and macrophages from Cre + 4 f/f and Cre 4 f/f mice. a) Depicted is a representative histogram of flow cytometry analysis for α4 integrin expression
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of the AARE-Gene system construct. (a) Position and sequence alignment of AAREs extracted from human Trb3, Chop or Atf3 promoters. AARE core sequences are boxed in grey.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of the AARE-Gene system construct. (a) Position and sequence alignment of AAREs extracted from human Trb3, Chop or Atf3 promoters. AARE core sequences are boxed in grey.
isolated from ctr and pictreated mice. Activation of effector CD4 +
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bystander inflammation conditioned T reg cells have normal functional suppressive activity and ex vivo phenotype. WT Balb/c mice were treated with polyi:c (pic) or PBS (ctr) via
Supplementary Figure 1 Bystander inflammation conditioned T reg cells have normal functional suppressive activity and ex vivo phenotype. WT Balb/c mice were treated with polyi:c (pic) or PBS (ctr) via
Blood transcriptional profiling of pediatric multiple sclerosis. Yulia Khavkin Mentor: Dr. Michael Gurevich
 Blood transcriptional profiling of pediatric multiple sclerosis Yulia Khavkin Mentor: Dr. Michael Gurevich Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common immunemediated inflammatory demyelinating
Blood transcriptional profiling of pediatric multiple sclerosis Yulia Khavkin Mentor: Dr. Michael Gurevich Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common immunemediated inflammatory demyelinating
F4/80, CD11b, Gr-1, NK1.1, CD3, CD4, CD8 and CD19. A-antigen was detected with FITCconjugated
 SDC MATERIALS AND METHODS Flow Cytometric Detection of A-Antigen Expression Single cell suspensions were prepared from bone marrow, lymph node and spleen. Peripheral blood was obtained and erythrocytes
SDC MATERIALS AND METHODS Flow Cytometric Detection of A-Antigen Expression Single cell suspensions were prepared from bone marrow, lymph node and spleen. Peripheral blood was obtained and erythrocytes
Tissue Engineering. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for. Tissue Engineering
 Tissue Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering Reference: Culture of Cells for Tissue Engineering (Culture of Specialized Cells), Chapter 2 Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Date: 03.20.2012 Institute
Tissue Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering Reference: Culture of Cells for Tissue Engineering (Culture of Specialized Cells), Chapter 2 Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Date: 03.20.2012 Institute
Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc)
 Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc) Introduction Over the past decade, stem cell research has provided new avenues for deeper investigation into tissue repair and aging processes,
Assuring Multipotency of human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hmsc) Introduction Over the past decade, stem cell research has provided new avenues for deeper investigation into tissue repair and aging processes,
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
GUGAUAAUGGAGCGAGAUUUUCUGUUGUGCUUGAUCUAACCAUGUGCUUGCGAGGUAUGA GAAAAACAUGGUUCCGUCAAGCACCAUGGAACGUCACGCAGCUUUCUACA
 Precursor mmu-mir-8- GUGAUAAUGGAGCGAGAUUUUCUGUUGUGCUUGAUCUAACCAUGUGCUUGCGAGGUAUGA GAAAAACAUGGUUCCGUCAAGCACCAUGGAACGUCACGCAGCUUUCUACA Precursor mmu-mir-8- GACCAGUUGCCGCGGGGCUUUCCUUUGUGCUUGAUCUAACCAUGUGGUGGAACGAUGGAA
Precursor mmu-mir-8- GUGAUAAUGGAGCGAGAUUUUCUGUUGUGCUUGAUCUAACCAUGUGCUUGCGAGGUAUGA GAAAAACAUGGUUCCGUCAAGCACCAUGGAACGUCACGCAGCUUUCUACA Precursor mmu-mir-8- GACCAGUUGCCGCGGGGCUUUCCUUUGUGCUUGAUCUAACCAUGUGGUGGAACGAUGGAA
Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in
 Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in mouse NOD/SCID/Jak3 null mice were transplanted with human CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells. (Top) Four weeks after the transplantation
Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in mouse NOD/SCID/Jak3 null mice were transplanted with human CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells. (Top) Four weeks after the transplantation
Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*.
 Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*. * Via PAR-1 & CXCR4 upregulation, SDF-1 secretion and EPCR shedding. By Tsvee Lapidot, Ph.D. Weizmann Institute
Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their Bone Marrow Niches by the Coagulation System*. * Via PAR-1 & CXCR4 upregulation, SDF-1 secretion and EPCR shedding. By Tsvee Lapidot, Ph.D. Weizmann Institute
Product datasheet. ARG30119 Pro-B Cell Marker Antibody panel (CD19, CD34, CD38, CD40, CD45)(FACS)
 Product datasheet info@arigobio.com Package: 1 kit ARG30119 Pro-B Cell Marker Antibody panel (CD19, CD34, CD38, CD40, CD45)(FACS) Component Cat. No. Component Name ARG62820 anti-cd34 antibody [4H11(APG)]
Product datasheet info@arigobio.com Package: 1 kit ARG30119 Pro-B Cell Marker Antibody panel (CD19, CD34, CD38, CD40, CD45)(FACS) Component Cat. No. Component Name ARG62820 anti-cd34 antibody [4H11(APG)]
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
MLN8237 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 827 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and polyploidization of a human erythroleukemia cell line with the activating
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 827 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and polyploidization of a human erythroleukemia cell line with the activating
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3342 EV O/E 13 4 B Relative expression 1..8.6.4.2 shctl Pcdh2_1 C Pcdh2_2 Number of shrns 12 8 4 293T mterc +/+ G3 mterc -/- D % of GFP + cells 1 8 6 4 2 Per2 p=.2 p>
DOI: 1.138/ncb3342 EV O/E 13 4 B Relative expression 1..8.6.4.2 shctl Pcdh2_1 C Pcdh2_2 Number of shrns 12 8 4 293T mterc +/+ G3 mterc -/- D % of GFP + cells 1 8 6 4 2 Per2 p=.2 p>
Keywords: mesenchymal, FGF2, MHC-classII, RANKL, osteoimmunology
 1 Supplementary data FGF2 induces RANKL gene expression as well as IL1 regulated MHC class II in bone marrow derived human mesenchymal progenitor stromal cells. 1,3 Chiara Bocelli-Tyndall, 1 Emanuele Trella,
1 Supplementary data FGF2 induces RANKL gene expression as well as IL1 regulated MHC class II in bone marrow derived human mesenchymal progenitor stromal cells. 1,3 Chiara Bocelli-Tyndall, 1 Emanuele Trella,
Supplementary Methods Antibodies for flow cytometry Cytotoxicity assay
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies for flow cytometry HLA-Cw3 and CD2 expression: LCL 72.22 cell lines were stained with anti-hla-abc-apc (clone G46-2.6, BD) or migg-apc (clone MOPC-2, BD) antibody, or with
Supplementary Methods Antibodies for flow cytometry HLA-Cw3 and CD2 expression: LCL 72.22 cell lines were stained with anti-hla-abc-apc (clone G46-2.6, BD) or migg-apc (clone MOPC-2, BD) antibody, or with
Supplementary Information
 1 2 Supplementary Information 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Loading of R837 into PLGA nanoparticles. The loading efficiency (a) and loading capacity (b) of R837 by PLGA nanoparticles obtained at
1 2 Supplementary Information 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Loading of R837 into PLGA nanoparticles. The loading efficiency (a) and loading capacity (b) of R837 by PLGA nanoparticles obtained at
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A P1 NOD - SCID(X*X*)(0/0) NOD - SCID(X*Y)(A*0201/A*0201) B F1 (X*X)(A*0201/0) (X*X*)(0/0) F2 (X*X*)(0/0) (X*Y)(0/0) (X*X*)(A*0201/0) (X*X*)(A*0201/0) F3 (X*X*)(0/0) (X*X)(A*0201/0)
Supplemental Figure 1 A P1 NOD - SCID(X*X*)(0/0) NOD - SCID(X*Y)(A*0201/A*0201) B F1 (X*X)(A*0201/0) (X*X*)(0/0) F2 (X*X*)(0/0) (X*Y)(0/0) (X*X*)(A*0201/0) (X*X*)(A*0201/0) F3 (X*X*)(0/0) (X*X)(A*0201/0)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tomura et al. 1.173/pnas.8227815 WT CFSE Con A stimulation Before After 2 3 1 CFSE Kaede- Tg No photoconversion Photoconversion Kaede Red Fig. S1. Dilution of photoconverted Kaede
Supporting Information Tomura et al. 1.173/pnas.8227815 WT CFSE Con A stimulation Before After 2 3 1 CFSE Kaede- Tg No photoconversion Photoconversion Kaede Red Fig. S1. Dilution of photoconverted Kaede
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs
 FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1
 Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1 a His-ORMDL3 ~ 17 His-ORMDL3 GST-ORMDL3 - + - + IPTG GST-ORMDL3 ~ b Integrated Density (ORMDL3/ -actin) 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1 a His-ORMDL3 ~ 17 His-ORMDL3 GST-ORMDL3 - + - + IPTG GST-ORMDL3 ~ b Integrated Density (ORMDL3/ -actin) 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
Flow cytometry Stained cells were analyzed and sorted by SORP FACS Aria (BD Biosciences).
 Mice C57BL/6-Ly5.1 or -Ly5.2 congenic mice were used for LSK transduction and competitive repopulation assays. Animal care was in accordance with the guidelines of Keio University for animal and recombinant
Mice C57BL/6-Ly5.1 or -Ly5.2 congenic mice were used for LSK transduction and competitive repopulation assays. Animal care was in accordance with the guidelines of Keio University for animal and recombinant
ClustalW algorithm. The alignment statistics are 96.9% for both pairwise identity and percent identical sites.
 Identity Human Mouse Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence alignment of -MyHC. The alignment was created using the ClustalW algorithm. The alignment statistics are 96.9% for both pairwise identity
Identity Human Mouse Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence alignment of -MyHC. The alignment was created using the ClustalW algorithm. The alignment statistics are 96.9% for both pairwise identity
a Lamtor1 (gene) b Lamtor1 (mrna) c WT Lamtor1 Lamtor1 flox Lamtor2 A.U. p = LysM-Cre Lamtor3 Lamtor4 Lamtor5 BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO β-actin WT BMDMs
 a Lamtor (gene) b Lamtor (mrna) c BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor flox 8 bp LysM-Cre 93 bp..5 p =.4 WT BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor (protein) BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor 8 kda Lamtor 4 kda Lamtor3 4 kda Lamtor4 kda Lamtor5.5
a Lamtor (gene) b Lamtor (mrna) c BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor flox 8 bp LysM-Cre 93 bp..5 p =.4 WT BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor (protein) BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor 8 kda Lamtor 4 kda Lamtor3 4 kda Lamtor4 kda Lamtor5.5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Expression of single HLA loci in shns- and shb 2 m-transduced MKs. Expression of HLA class I antigens (HLA-ABC) as well as
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Flow cytometric analysis of HLA class I single locus expression Expression of single HLA loci (HLA-A and HLA-B) by shns- and shb 2 m-transduced megakaryocytes (MKs)
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Flow cytometric analysis of HLA class I single locus expression Expression of single HLA loci (HLA-A and HLA-B) by shns- and shb 2 m-transduced megakaryocytes (MKs)
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ex2 promotor region Cre IRES cherry pa Ex4 Ex5 Ex1 untranslated Ex3 Ex5 untranslated EYFP pa Rosa26 STOP loxp loxp Cre recombinase EYFP pa Rosa26 loxp 1 kb Interleukin-9 fate reporter
Supplementary Figure 1 Ex2 promotor region Cre IRES cherry pa Ex4 Ex5 Ex1 untranslated Ex3 Ex5 untranslated EYFP pa Rosa26 STOP loxp loxp Cre recombinase EYFP pa Rosa26 loxp 1 kb Interleukin-9 fate reporter
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and
 Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Eight-week-old wildtype mice were kept under standard diet (SD) for 4 weeks, or fed Western
 Supplemental information M. Itoh et al. 0 Supplemental Methods Inducible NASH model using wildtype mice Eight-week-old wildtype mice were kept under standard diet (SD) for weeks, or fed Western diet (WD)
Supplemental information M. Itoh et al. 0 Supplemental Methods Inducible NASH model using wildtype mice Eight-week-old wildtype mice were kept under standard diet (SD) for weeks, or fed Western diet (WD)
Matrix IGF-1 regulates bone mass by activation of mtor in. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Supplemental information Matrix IGF-1 regulates bone mass by activation of mtor in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Lingling Xian, Xiangwei Wu, Lijuan Pang, Michael Lou, Clifford Rosen, Tao Qiu, Janet Crane, Frank
Supplemental information Matrix IGF-1 regulates bone mass by activation of mtor in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Lingling Xian, Xiangwei Wu, Lijuan Pang, Michael Lou, Clifford Rosen, Tao Qiu, Janet Crane, Frank
TITLE: Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Tyk2: Lucrative Therapeutic Target in Lupus
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0609 TITLE: Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Tyk2: Lucrative Therapeutic Target in Lupus PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Abhishek Trigunaite CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: SRI International
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0609 TITLE: Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Tyk2: Lucrative Therapeutic Target in Lupus PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Abhishek Trigunaite CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: SRI International
Dual PI3K/ERK inhibition induces necroptotic cell death of Hodgkin Lymphoma cells through IER3 downregulation
 Dual PI3K/ERK inhibition induces necroptotic cell death of Hodgkin Lymphoma cells through IER3 downregulation *Silvia Laura Locatelli, 1 Giuseppa Careddu, 1 Giuliano Giuseppe Stirparo, 1 Luca Castagna,
Dual PI3K/ERK inhibition induces necroptotic cell death of Hodgkin Lymphoma cells through IER3 downregulation *Silvia Laura Locatelli, 1 Giuseppa Careddu, 1 Giuliano Giuseppe Stirparo, 1 Luca Castagna,
Supplementary Data. In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods. Results. Conclusions
 Supplementary Data In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods Induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like progenitor cells (impcs) (1 10 6 M-iMPC-GMs in 10
Supplementary Data In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods Induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like progenitor cells (impcs) (1 10 6 M-iMPC-GMs in 10
TIB6 B16F1 LLC EL4. n=2 n=7 n=9 n=6
 Shojaei et al., Supplemental Fig. 1 9 Mean Inhibition by anti-vegf (%) 7 5 3 1 TIB6 n=2 n=7 n=9 n=6 Supplemental Figure 1 Differential growth inhibition by anti-vegf treatment. The percent of tumor growth
Shojaei et al., Supplemental Fig. 1 9 Mean Inhibition by anti-vegf (%) 7 5 3 1 TIB6 n=2 n=7 n=9 n=6 Supplemental Figure 1 Differential growth inhibition by anti-vegf treatment. The percent of tumor growth
The genetic code of gene regulatory elements
 The genetic code of gene regulatory elements Ivan Ovcharenko Computational Biology Branch National Center for Biotechnology Information National Institutes of Health October 23, 2008 Outline Gene deserts
The genetic code of gene regulatory elements Ivan Ovcharenko Computational Biology Branch National Center for Biotechnology Information National Institutes of Health October 23, 2008 Outline Gene deserts
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM
 Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM of Cx3cr1 GFP/+ mice related to Fig. 1a. MDP was defined
Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM of Cx3cr1 GFP/+ mice related to Fig. 1a. MDP was defined
Supplementary Fig S1: Bone marrow macrophages and liver Kupffer cells increase IL-1 in response to adenosine signaling. (a) Murine bone marrow
 Supplementary Fig S1: Bone marrow macrophages and liver Kupffer cells increase IL-1 in response to adenosine signaling. (a) Murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were primed with LPS for 16 hrs,
Supplementary Fig S1: Bone marrow macrophages and liver Kupffer cells increase IL-1 in response to adenosine signaling. (a) Murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were primed with LPS for 16 hrs,
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
0.9 5 H M L E R -C tr l in T w is t1 C M
 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
Development of NOG mice
 Development of NOG mice General characteris5cs of NOG mice 1. T and B cell deficient 2. NK cell deficient 3. Reduced macrophage and dendri;c cell func;on 4. Complement ac;vity deficient 5. No incidence
Development of NOG mice General characteris5cs of NOG mice 1. T and B cell deficient 2. NK cell deficient 3. Reduced macrophage and dendri;c cell func;on 4. Complement ac;vity deficient 5. No incidence
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by
 PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
PRIME-XV Cell Therapy Products by Product List 2017 TRINOVA BIOCHEM now distributes the PRIME-XV Cell Therapy line by Irvine Scientific in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Irvine Scientific is a worldwide
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10772 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1. Location of CNS1 within of the Foxp3 locus highlighting CNS1 and indicating transcription factor binding motifs downstream of TCR,
doi:10.1038/nature10772 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1. Location of CNS1 within of the Foxp3 locus highlighting CNS1 and indicating transcription factor binding motifs downstream of TCR,
Table S1. Antibodies and recombinant proteins used in this study
 Table S1. Antibodies and recombinant proteins used in this study Labeled Antibody Clone Cat. no. Streptavidin-PerCP BD Biosciences 554064 Biotin anti-mouse CD25 7D4 BD Biosciences 553070 PE anti-mouse
Table S1. Antibodies and recombinant proteins used in this study Labeled Antibody Clone Cat. no. Streptavidin-PerCP BD Biosciences 554064 Biotin anti-mouse CD25 7D4 BD Biosciences 553070 PE anti-mouse
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis
 Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
Impact of Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) on Regulators of Metabolism and Adipogenesis The mammalian system undergoes ~24 hour cycles known as circadian rhythms that temporally orchestrate metabolism, behavior,
To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated
 Supplementary Methods Tolerogenic effect of MDSC To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated MDSC in vivo, we used a model described previously
Supplementary Methods Tolerogenic effect of MDSC To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated MDSC in vivo, we used a model described previously
Supplemental Information. Targeting HIF1 Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells. in Hematological Malignancies. Inventory of Supplemental Information
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Targeting HIF1 Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells in Hematological Malignancies Yin Wang, Yan Liu, Sami N. Malek, Pan Zheng, and Yang Liu Inventory of Supplemental
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Targeting HIF1 Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells in Hematological Malignancies Yin Wang, Yan Liu, Sami N. Malek, Pan Zheng, and Yang Liu Inventory of Supplemental
True Confessions: Ancillary Materials in a Cell Processing Lab. Cell Processing Section, DTM, CC, NIH David Stroncek, MD Chief, CPS, DTM, CC
 True Confessions: Ancillary Materials in a Cell Processing Lab Cell Processing Section, DTM, CC, NIH David Stroncek, MD Chief, CPS, DTM, CC Mission Provide cellular and gene therapy products and services
True Confessions: Ancillary Materials in a Cell Processing Lab Cell Processing Section, DTM, CC, NIH David Stroncek, MD Chief, CPS, DTM, CC Mission Provide cellular and gene therapy products and services
Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
DC enriched CD103. CD11b. CD11c. Spleen. DC enriched. CD11c. DC enriched. CD11c MLN
 CD CD11 + CD + CD11 d g CD CD11 + CD + CD11 CD + CD11 + Events (% of max) Events (% of max) CD + CD11 Events (% of max) Spleen CLN MLN Irf fl/fl e Irf fl/fl h Irf fl/fl DC enriched CD CD11 Spleen DC enriched
CD CD11 + CD + CD11 d g CD CD11 + CD + CD11 CD + CD11 + Events (% of max) Events (% of max) CD + CD11 Events (% of max) Spleen CLN MLN Irf fl/fl e Irf fl/fl h Irf fl/fl DC enriched CD CD11 Spleen DC enriched
Supplementary Figure and Table Legends
 1 Supplementary Figure and Table Legends Figure S1: Whole-animal metabolic analysis. 12 week old WT and Dvl1 / were singly housed in CLAMS cages (Comprehensive Laboratory Animals Monitoring System) for
1 Supplementary Figure and Table Legends Figure S1: Whole-animal metabolic analysis. 12 week old WT and Dvl1 / were singly housed in CLAMS cages (Comprehensive Laboratory Animals Monitoring System) for
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN 1 PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF2 ACTIVATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology
 Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology Outline: 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Biopharming 8.3 Models of Human Disease 8.4 Detecting and Diagnosing Human Disease 8.5 Monoclonal Antibodies 8.6 Gene Therapy 8.7 Tissue
Chapter 8 Healthcare Biotechnology Outline: 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Biopharming 8.3 Models of Human Disease 8.4 Detecting and Diagnosing Human Disease 8.5 Monoclonal Antibodies 8.6 Gene Therapy 8.7 Tissue
Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood
 Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood Tahereh Foroutan 1 *, Aysan Farhadi 1, Bahram- Mohammad
Adipose Stem Cells as a Feeder Layer Reduce Apoptosis and p53 Gene Expression of Human Expanded Hematopoietic Stem Cells Derived from Cord Blood Tahereh Foroutan 1 *, Aysan Farhadi 1, Bahram- Mohammad
BD MOSAIC h MSC CELL CULTURE ENVIRONMENT DEFINED SERUM FREE
 BD MOSAIC h MSC CELL CULTURE ENVIRONMENT DEFINED SERUM FREE As the promise of stem cell therapy grows, so does the need for reliable tools for cell expansion in both research and clinical applications.
BD MOSAIC h MSC CELL CULTURE ENVIRONMENT DEFINED SERUM FREE As the promise of stem cell therapy grows, so does the need for reliable tools for cell expansion in both research and clinical applications.
Mouse expression data were normalized using the robust multiarray algorithm (1) using
 Supplementary Information Bioinformatics statistical analysis of microarray data Mouse expression data were normalized using the robust multiarray algorithm (1) using a custom probe set definition that
Supplementary Information Bioinformatics statistical analysis of microarray data Mouse expression data were normalized using the robust multiarray algorithm (1) using a custom probe set definition that
Figure S Relative MUC4 transcript level* CD18/HPAF CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4
 Figure S1 Relative MUC4 transcript level* 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 CD18/HPAF CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 Figure S2 * * CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 Figure S3 CD18/HPAF-Scr
Figure S1 Relative MUC4 transcript level* 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 CD18/HPAF CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 Figure S2 * * CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 CD18/HPAF-Scr CD18/HPAF-siMUC4 Figure S3 CD18/HPAF-Scr
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Song et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218131110 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Dislodgment Assays. In vivo dislodgement experiments were performed as previously described (1) using function
Supporting Information Song et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218131110 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Dislodgment Assays. In vivo dislodgement experiments were performed as previously described (1) using function
Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor
 Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Nicholas Love 11/28/01 A. What is p21? Introduction - p21 is a gene found on chromosome 6 at 6p21.2 - this gene
Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Nicholas Love 11/28/01 A. What is p21? Introduction - p21 is a gene found on chromosome 6 at 6p21.2 - this gene
About ATCC. Established partner to global researchers and scientists
 Discovering ATCC Primary Immunology Cells - Model Systems to Study the Immune and Cardiovascular Systems James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC July 14, 2016 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Discovering ATCC Primary Immunology Cells - Model Systems to Study the Immune and Cardiovascular Systems James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC July 14, 2016 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
B Vehicle 1V270 (35 μg) 1V270 (100 μg) Days post tumor implantation. Vehicle 100μg 1V270 biweekly 100μg 1V270 daily
 Supplemental Figure 1 A 1 1V7 (8 μg) 1 1V7 (16 μg) 8 6 4 B 1 1 8 6 4 1V7 (35 μg) 1V7 (1 μg) 5 1 15 5 1 15 C Biweekly 8 11 14 17 Days Implant SCC7 cells Daily 8 9 1 11 1 Implant SCC7 cells 1V7 i.t. treatment
Supplemental Figure 1 A 1 1V7 (8 μg) 1 1V7 (16 μg) 8 6 4 B 1 1 8 6 4 1V7 (35 μg) 1V7 (1 μg) 5 1 15 5 1 15 C Biweekly 8 11 14 17 Days Implant SCC7 cells Daily 8 9 1 11 1 Implant SCC7 cells 1V7 i.t. treatment
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cheng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1207354109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of Stim1 Stim2 Double-KO Mice and Assessment of Saliva Secretion. T-cell specific deletion of Stim1 and Stim2
Supporting Information Cheng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1207354109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of Stim1 Stim2 Double-KO Mice and Assessment of Saliva Secretion. T-cell specific deletion of Stim1 and Stim2
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b expression on different B cell subsets in anti-snrnp Ig Tg mice. (a) Highly purified follicular (FO) and marginal zone (MZ) B cells were sorted from
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b expression on different B cell subsets in anti-snrnp Ig Tg mice. (a) Highly purified follicular (FO) and marginal zone (MZ) B cells were sorted from
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/275/275ra20/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Targeted nanoparticles containing the proresolving peptide Ac2-26 protect against advanced atherosclerosis
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/275/275ra20/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Targeted nanoparticles containing the proresolving peptide Ac2-26 protect against advanced atherosclerosis
Autocrine Complement Inhibits IL10-Dependent T-Cell Mediated. Antitumor Immunity to Promote Tumor Progression
 Supplemental Information Autocrine Complement Inhibits IL10-Dependent T-Cell Mediated Antitumor Immunity to Promote Tumor Progression Yu Wang, Sheng-Nan Sun, Qing Liu, Yang-Yang Yu, Jian Guo, Kun Wang,
Supplemental Information Autocrine Complement Inhibits IL10-Dependent T-Cell Mediated Antitumor Immunity to Promote Tumor Progression Yu Wang, Sheng-Nan Sun, Qing Liu, Yang-Yang Yu, Jian Guo, Kun Wang,
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Figure S1- Targeting strategy for generating SIK1-T182A, SIK2-T175A and SIK3-T163A KI mice.
 Figure S1- Targeting strategy for generating SIK1-T12A, SIK2-T175A and SIK3-T163A mice. Left panel represents a depiction of the genomic loci of each gene, the targeting strategy and the final recombined
Figure S1- Targeting strategy for generating SIK1-T12A, SIK2-T175A and SIK3-T163A mice. Left panel represents a depiction of the genomic loci of each gene, the targeting strategy and the final recombined
Dec 04, 2013
 Stem Cells Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Research Center of Stem Cell and Developmental Biology School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cn Dec 04, 2013 Totipotent Pluripotent
Stem Cells Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Research Center of Stem Cell and Developmental Biology School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cn Dec 04, 2013 Totipotent Pluripotent
immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Rabbit anti-kor-1
 Supplemental Tables Table S1. List of primary antibodies used for immunohistochemistry, FACS, and immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Bioss USA bs-13041r
Supplemental Tables Table S1. List of primary antibodies used for immunohistochemistry, FACS, and immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Bioss USA bs-13041r
Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study
 Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplemental Table S1. RT-PCR primers used in this study -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/353/353ra113/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Thymidine phosphorylase exerts complex effects on bone resorption and formation in myeloma Huan Liu,
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/353/353ra113/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Thymidine phosphorylase exerts complex effects on bone resorption and formation in myeloma Huan Liu,
Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Tracking mesenchymal stem cell contributions to regeneration in an immunocompetent cartilage regeneration model Daniela Zwolanek, María Satué, Verena Proell, Josè R. Godoy, Kathrin
Supplementary material Tracking mesenchymal stem cell contributions to regeneration in an immunocompetent cartilage regeneration model Daniela Zwolanek, María Satué, Verena Proell, Josè R. Godoy, Kathrin
Background. Background. Background. Background. Background 3/4/2013
 3/4/213 Human Very Small Embryonic-like Stem Cells (s) Capacity to Regenerate Bone Tissue: A Potential Cell-based Therapy for Autogenous Bone Grafting Aaron M. Havens, DMD Need to discover an improved
3/4/213 Human Very Small Embryonic-like Stem Cells (s) Capacity to Regenerate Bone Tissue: A Potential Cell-based Therapy for Autogenous Bone Grafting Aaron M. Havens, DMD Need to discover an improved
Gene Forward (5 to 3 ) Reverse (5 to 3 ) Accession # PKA C- TCTGAGGAAATGGGAGAACC CGAGGGTTTTCTTCCTCTCAA NM_011100
 Supplementary Methods: Materials. BRL37344, insulin, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, dibutyryl camp (Bt2-cAMP) and 8-Bromoadenosine 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate sodium (8-br-cAMP), cilostamide, adenosine deaminase,
Supplementary Methods: Materials. BRL37344, insulin, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, dibutyryl camp (Bt2-cAMP) and 8-Bromoadenosine 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate sodium (8-br-cAMP), cilostamide, adenosine deaminase,
Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture.
 Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
Imaging the immune system with a Two photon (2P) microscope
 Imaging the immune system with a Two photon (2P) microscope QuickTime et un décompresseur Cinepak sont requis pour visionner cette image. Main advantages of 2P microscopy : 1/ Deep penetration into tissue
Imaging the immune system with a Two photon (2P) microscope QuickTime et un décompresseur Cinepak sont requis pour visionner cette image. Main advantages of 2P microscopy : 1/ Deep penetration into tissue
Supplemental methods:
 Supplemental methods: ASC-J9 treatment ASC-J9 was patented by the University of Rochester, the University of North Carolina, and AndroScience Corp., and then licensed to AndroScience Corp. Both the University
Supplemental methods: ASC-J9 treatment ASC-J9 was patented by the University of Rochester, the University of North Carolina, and AndroScience Corp., and then licensed to AndroScience Corp. Both the University
Rorα is essential for nuocyte development
 Rorα is essential for nuocyte development See Heng Wong,,, Jennifer A. Walker,, Helen E. Jolin,, Lesley F. Drynan, Emily Hams 3, Ana Camelo, Jillian L. Barlow, Daniel R. Neill,6, Veera Panova, Ute Koch,
Rorα is essential for nuocyte development See Heng Wong,,, Jennifer A. Walker,, Helen E. Jolin,, Lesley F. Drynan, Emily Hams 3, Ana Camelo, Jillian L. Barlow, Daniel R. Neill,6, Veera Panova, Ute Koch,
Supplementary Fig. 1: Characterization of Asxl2 -/- mouse model. (a) HSCs and their
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Characterization of Asxl2 -/- mouse model. (a) HSCs and their differentiated cell populations were sorted from the BM of WT mice using respective surface markers, and Asxl2 mrna expression
Supplementary Fig. 1: Characterization of Asxl2 -/- mouse model. (a) HSCs and their differentiated cell populations were sorted from the BM of WT mice using respective surface markers, and Asxl2 mrna expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Interferon- -producing immature myeloid cells confer protection. against severe invasive group A Streptococcus infections. Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Interferon- -producing immature myeloid cells confer protection against severe invasive group A Streptococcus infections Takayuki Matsumura, Manabu Ato, Tadayoshi Ikebe, Makoto
Supplementary Information Interferon- -producing immature myeloid cells confer protection against severe invasive group A Streptococcus infections Takayuki Matsumura, Manabu Ato, Tadayoshi Ikebe, Makoto
