CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION. Unit 5
|
|
|
- Reynold Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5
2 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells
3 THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle- series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cells leading to its division Interphase- Cell growths, accumulating nutrients for mitosis Replication of DNA- stage which the cell splits itself into 2 distinct cells
4 CELLULAR DIVISION Cellular division is a complicated process that cannot be done by simply pinching the cell in half Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes include distribution of genetic material known as DNA Into two identical daughter cells Gnome- is a cells genetic information Each Cell contains enough genetic material if all the DNA in the cell is stretched out from end to end it would be over 2 meters long or 250,000 times greater the cells length How then does the DNA fit in the cell?
5 CHROMOSOMES DNA is condensed and packaged into structures called Chromosomes A DNA strand can encode for several different proteins and consist of several hundred genes Chromatin- is the DNA and Protein used to pupils the chromosome
6 CHROMOSOMES Chromosomes are in the nucleus Every Eukaryotic species has a certain number of chromosomes in each cell Somatic Cells- body cells that aren't meant for reproduction Gamete- Sperm and Egg Cells Humans= 46 Chromosomes in Somatic Cells and 23 Chromosomes in Gamete Cells
7 DISTRIBUTION OF CHROMOSOMES DNA is in preparation for Cellular division all the time even when the cell is not in the act of division DNA is constantly being stretched out and replicated then condensed back down to chromatic fibers to make chromosomes Each duplicated chromosome has 2 sister chromosomes which are joined copies of the original chromosome Centromere- is the center region (protein) which the sister and original chromatin attach to
8 CELL CYCLE STAGES G1 phase (interphase) S phase (interphase) G2 phase (interphase) M phase (mitosis)
9 INTERPHASE G1, S, and G2 Phase S phase is the DNA Synthesis phase Takes up 90% of the time for the Cell Cycle
10 M PHASE Mitotic Phases when mitosis occurs Cytokinesis or cell splitting occurs at the end Result is 2 daughter cells Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase then Cytokinesis PMAT Cytokinesis
11 FROM G2 PHASE TO PROPHASE What needs to happen before mitosis can occur? 2 centromeres have formed from 1 Chromatin have not condensed to Chromosomes yet
12 PROPHASE Chromatin fibers become more condensed to form chromosomes The Nuclear Envelope starts to disappear Each chromosome has 2 identical Sister Chromatids Mitotic Spindle Fibers start to form Centromeres move away from each other
13 METAPHASE Centromeres are on opposite poles of the cell Chromosomes line up down the middle of the cell Spindle fibers attach to the center (kinetochore) of each chromosome
14 ANAPHASE Sister Chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends and become full fledge chromosomes The new chromosomes start to move toward opposite ends of the cell The cell starts to elongate At the end of this phase each end of the cell has a equivalent and complete set of chromosomes
15 TELOPHASE A nuclear envelope started to form around each set of chromosomes Chromosomes start to deco dense The net result is 2 genetically identical nuclei
16 CYTOKINESIS Cleavage Furrow is made and the cell is pinched in half 2 new cells have been made and the process of cellular division can start over again
17
18 CONTROLLING THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle Control System- molecules in the cell that both triggers and coordinates key events in the cell cycle These molecules create checkpoints in the cycle to check and make sure everything is replicating properly Once the Checkpoint has been reached the molecules will "tell" the cell whether to go ahead with replication or just to sit and await further instructions
19
20 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN THE CHECKPOINTS DON'T WORK? Cells continue to replicate They will replicate the error that would normally have stopped the replication This error can lead to a whole number of problems Unregulated cellular replication can and most of the time does result in Cancer
21 CANCER Cancer cells do not stop when the cell cycle tries to regulate it (they go a wall) These cells can divide rapidly and invade other tissues damaging them or inhibiting functions of them They don't stop growing just because they outgrow their resources Benign tumor- is a group of abnormal (Cancer) cells that remain at its original site and do not have enough genetic changes to survive in other tissues Malignant tumor- a group of abnormal (Cancer) cells whose genetic and cellular changes enable it to invade other tissues and spread
22 SOME EXTRA VOCABULARY Karyotypes- display of chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape Crossing over-the exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatides during Prophase 1 of Meiosis Haploid- a cell containing only 1 set of chromosomes Diploid- a cell that contains 2 sets of chromosomes 1 from each parent
23 MORE VOCABULARY Epithelium- a membranous cellular tissue that covers the free surface or lines at tube or cavity of an animal body Ploidy- degree of repetition ion of a panic number of chromosomes Apoptosis- Programed cell death, a genetically directed process of cellular self destruction
24 WHY DO CELLS DIVIDE? If a cell didn't divide rapidly and just grew, it would quickly out grow its resources or it would be so big the organelles would not be able to keep up with the cell This would lead to an inability to keep cellular homeostasis and result in apoptosis By having a lot of smaller cells it is easier to keep cellular homeostasis. It is not that big of an issue if a cell dies. Also if there is a genetic issue with one cell it is a lot more disposable then if there were only a few large cells.
25 HEREDITY Genetics- is the Scientific study of heredity (the transmission of traits from one generation to the next) Asexual reproduction- reproduction where the offspring is an exact genetic copy of the parent Sexual reproduction- two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combination of genes inherited from the two parents.
26 VOCABULARY Homologous Chromosomes- a pair of chromosomes that are the same length and have the same centromere position Sex chromosomes- These are the homologous chromosomes that determine sex (X &Y) (Female = XX Male = XY) Zygote- Male and Female diploid sex cells (egg and sperm)
27 MEIOSIS Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from diploid to haploid Meiosis closely resembles mitosis stepwise However after interphase meiosis unlike mitosis will go through 2 consecutive cell divisions (meiosis 1 and meiosis 2) This results in 4 daughter cells (instead of 2 with mitosis) that are haploid cells This only occurs in sex cells
28 MEIOSIS 1 Separates homologous Chromosomes Prophase 1 Metaphase 1 Anaphase 1 Telophase 1 Cytokinesis (cell splits)
29 MEIOSIS 2 Separates sister chromatids Prophase. 2 Metaphase2 Anaphase 2 Telophase 2 Cytokinesis
30 PROPHASE 1& 2 Chromosomes begin to condense and prophase proceeds as it did in mitosis Crossing over occurs as homologous chromosomes start to connect to one another only occurs in prophase 1
31 METAPHASE 1 & 2 Just like in mitosis the chromosomes start to line up along the center of the cell Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes Because of the crossing over in prophase 1 there are not genetically equal chromatids in metaphase 2
32 ANAPHASE 1 & 2 Just like in mitosis the chromatids are moved to opposite poles guided by the spindle fibers Anaphase 1 & 2 are exactly the same
33 TELOPHASE 1 & 2 AND CYTOKINESIS Both proceed as in mitosis but remember that after telophase 1 & cytokinesis there is no reproduction of existing chromosomes they go right into Meiosis 2 and Prophase 2 2 daughter cells after telophase 1 4 daughter cells after telophase 2
34
35 WHY DOES MEIOSIS MAKE SENSE? With Sex Cells we are only needing haploid cells so they don't need a full set of chromosomes Sex Cells are needed in vast quantities because of their rapid disposal rate Increases genetic diversity of each individual cell because of crossing over and having different sets of genes in each cell opposed to a replicate of the original
36
37 DNA DNA is also know as Deoxyribonuleic acid Double Stranded helix that contained the genetic information for cellular function growth and division Watson and Crick were the first scientist that provided a model for DNA
38 WATSON AND CRICKS MODEL 2 anti-parallel strands Nucleotides 5-carbon sugar (backbone of DNA) Nitrogen base pair A phosphate group
39 NUCLEIC ACID Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nuclei can acids These consist of sugars phosphate groups and nitrogen bases
40 SUGAR AND PHOSPHATE PORTION
41 NITROGEN BASE PAIRS Think of theses as rungs in a ladder (2 come together to form the full rung) Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine These base pair up to form the rungs in "the ladder" Adenine always pairs with Thymine & Cytosine Always pairs with Guanine We uses their first letters to shorten their names A-T and C- G
42
43
44 VOCABULARY Purine- 1 of 2 types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides characterized by a 6 member ring fused to a 5 member ring (Adenine and Guanine) Pyrimidine- 1 of 2 types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides characterized by 6 member ring ( Cytosine and Thymine) Complementary Strands- a strand of DNA that completes the DNA Helix by having a complementary set of nucleotides Nuclease- an enzyme that cuts damaged section of DNA and Replicants Telomeres- special nucleotide sequences at the end of DNA strands these act as a buffer between genes it acts as a stop signal
45
46 WHAT WOULD BE THE COMPLEMENTARY DNA STRAND TO THESE SINGLE STRANDS OF DNA TGCCAAATGTGCTAATC ATAAGAGCCTCGTCAAA TTCACCGAGCTTACCCT
47 DNA REPLICATION In order for DNA to replicate the double helix must be split to 2 separate templates Once the strands are separated a complementary strand is made on each template
48 WHERE DOES IT START? The Origins of Replication is a short set of nucleotides that cold for starting vise verse for when to stop On a strand of DNA the start code codes for replication going both ways on the strand this area where replication starts diverging is called a replication bubble
49 At each end of the replication bubble is a replication fork (a y shape region where the parental strands of DNA are being unwound) Helicases are enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forms separating the 2 parental strands making hem available for replication DNA Polymerase is an enzyme that catalyze so the synthesis of the new DNA by adding Nucleotides to the Preexisting chains
50
51 ANTIPARALLEL STRANDS The 2 ends of DNA strands are Different this gives each strand directionality (3' end and a 5' end) The 2 strands are opposite of on another Polymerase can only go from 3' - 5' Leading strand is the strand in which goes from 3' to 5' into the replication fork Lagging strand is the opposite from the leading strands where fragments are constantly being made to fill in the holes in the replicant
52
53 PROOF READING Errors happen one and every 1,000,000 nucleotides DNA Polymerase proof reads each nucleotide agains it's template as son as it is added to the growing of strands After all their other enzymes proofread the proofread and replace any mismatched nucleotides Permanent changed in the DNA are called Mutations
54
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION What are Chromosomes? Cell structures that contain genetic material. Where are they found? Found inside a cell, inside the nucleus. VOCABULARY Somatic cells (body cells) Sex cells
UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION What are Chromosomes? Cell structures that contain genetic material. Where are they found? Found inside a cell, inside the nucleus. VOCABULARY Somatic cells (body cells) Sex cells
Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS
 Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS 1/2/2018 Bell Work What is a Gene? Genes as Medicine As you watch the film, complete the questions on the film guide. When you
Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS 1/2/2018 Bell Work What is a Gene? Genes as Medicine As you watch the film, complete the questions on the film guide. When you
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction
 Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity
 What is DNA? DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity DNA is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and
What is DNA? DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity DNA is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
DNA STRUCTURE. Nucleotides: Nitrogenous Bases (Carry the Genetic Code) Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle. I can statements: Basic Information:
 Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Chapter 3. DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA?
 Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Name: Block: PACKET #9 Reading: Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit you will be able to: Date: Introduction to the cell cycle 1.
Name: Block: PACKET #9 Reading: Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit you will be able to: Date: Introduction to the cell cycle 1.
Cell Division. Use Target Reading Skills. This section explains how cells grow and divide.
 Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES
 DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
4.1 CELL DIVISION AND GENETIC MATERIAL
 4.1 CELL DIVISION AND GENETIC MATERIAL GENETICS Field of biology Study how genetic information is passed from one generation of organism/cells to the next THE CELL THEORY developed in mid-1800s 1. All
4.1 CELL DIVISION AND GENETIC MATERIAL GENETICS Field of biology Study how genetic information is passed from one generation of organism/cells to the next THE CELL THEORY developed in mid-1800s 1. All
Keeping Cells Identical The instructions for making cell parts are encoded in the DNA, so each new cell must get a complete set of the DNA molecules.
 CELLULAR DIVISION Cell Theory Pro/Euk review Cells are the basic unit of life. All living things have cell(s). All cells are formed from existing cells. Keeping Cells Identical The instructions for making
CELLULAR DIVISION Cell Theory Pro/Euk review Cells are the basic unit of life. All living things have cell(s). All cells are formed from existing cells. Keeping Cells Identical The instructions for making
These molecules make up the ladder of the DNA Bound by weak hydrogen bonds. 4 Different Types (2 specific matches) look at the
 B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
Part2. University of Technology Applied Sciences Department Biotechnology Division. Genetics. 2 nd class. Produced by L. Wasnaa H.
 University of Technology Applied Sciences Department Biotechnology Division 2 nd class Produced by L. Wasnaa H. Mohammad Part 2 2013 Cell Division or cell cycle When cells reproduce, the genetic material
University of Technology Applied Sciences Department Biotechnology Division 2 nd class Produced by L. Wasnaa H. Mohammad Part 2 2013 Cell Division or cell cycle When cells reproduce, the genetic material
Lecture 4 04/12/2018
 Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis nucleus chromosomes Genes DNA
 Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
Bio Study Guide. What is the structure of a DNA. A nitrogen base (ATCG/AUCG) connected to a sugar and a phosphate. nucleotide?
 What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
The Cell Cycle. Study Guide: Cell Division and DNA Structure
 A. Review Materials 1. Text: Chapter 2, section 3. 2. EOS questions: cell division and DNA (online) 3. Any videos linked from the website 4. Labs: review conclusions and notes (DNA Candy, Flipbooks, Scum)
A. Review Materials 1. Text: Chapter 2, section 3. 2. EOS questions: cell division and DNA (online) 3. Any videos linked from the website 4. Labs: review conclusions and notes (DNA Candy, Flipbooks, Scum)
Cell Division. embryo: an early stage of development in organisms
 Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Lesson Overview DNA Replication
 12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Copying the Code What role does DNA polymerase play in copying DNA?
12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Copying the Code What role does DNA polymerase play in copying DNA?
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
DNA and Replication 1
 DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
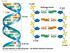 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA Structure and Replication. Higher Human Biology
 DNA Structure and Replication Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine 1 Division and differentiation
DNA Structure and Replication Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine 1 Division and differentiation
Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics
 Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics Information Overload : Cells store information in DNA. Information is used to build molecules needed for cell growth. As cell size increases, the demands on that
Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics Information Overload : Cells store information in DNA. Information is used to build molecules needed for cell growth. As cell size increases, the demands on that
copyright cmassengale 2
 1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
Purines vs. Pyrimidines
 Introduction to Genetics/DNA Replication The DNA molecule is found in the nucleus and is composed of nucleotides The DNA Molecule Composed of 2 polymers of nucleotides Polymers are oriented in antiparallel
Introduction to Genetics/DNA Replication The DNA molecule is found in the nucleus and is composed of nucleotides The DNA Molecule Composed of 2 polymers of nucleotides Polymers are oriented in antiparallel
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
 Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Lesson Overview DNA Replication
 12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Review Question! At what stage of the cell cycle do cells duplicate
12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Review Question! At what stage of the cell cycle do cells duplicate
Vocab Word 1: Interphase
 Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
The Molecule of Heredity. Chapter 12 (pg. 342)
 The Molecule of Heredity Chapter 12 (pg. 342) What is DNA? DNA contains instructions for assembling proteins. Proteins tell our cells how to function and act. The Roles of DNA DNA has three jobs in heredity:
The Molecule of Heredity Chapter 12 (pg. 342) What is DNA? DNA contains instructions for assembling proteins. Proteins tell our cells how to function and act. The Roles of DNA DNA has three jobs in heredity:
Chapter 10. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity. Lectures by Gregory Ahearn. University of North Florida. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
Biology Semester Exam Study Guide--January 2016
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
From Gene to Protein. Making Sense of DNA
 From Gene to Protein Making Sense of DNA The 4 th Macromolecule DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) carbohydrates lipids The 4 major organic macromolecules nucleic acids proteins the building blocks of organisms
From Gene to Protein Making Sense of DNA The 4 th Macromolecule DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) carbohydrates lipids The 4 major organic macromolecules nucleic acids proteins the building blocks of organisms
Adenine % Guanine % Thymine % Cytosine %
 1. Explain each of the following statements in terms of your knowledge of the structure and function of DNA. (i) In all living organisms the ratio species to another. A C T G is constant but the ratio
1. Explain each of the following statements in terms of your knowledge of the structure and function of DNA. (i) In all living organisms the ratio species to another. A C T G is constant but the ratio
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013
 REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION
 DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION A MODEL OF DNA In 1953, two scientists named Watson & Crick built a model of DNA that demonstrates its exact structure and function. They called this model a double helix, which
DNA STRUCTURE & REPLICATION A MODEL OF DNA In 1953, two scientists named Watson & Crick built a model of DNA that demonstrates its exact structure and function. They called this model a double helix, which
10-2 Cell Division (Pages )
 10-2 Cell Division (Pages 244-245) What do you think would happen if a cell were simply to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive?
10-2 Cell Division (Pages 244-245) What do you think would happen if a cell were simply to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive?
8.1 Why Do Cells Divide?
 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division. One cell gives rise to two or more cells, called daughter cells. Each daughter cell receives a complete set of heredity information identical
8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division. One cell gives rise to two or more cells, called daughter cells. Each daughter cell receives a complete set of heredity information identical
Biology Lecture 2 Genes
 Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Structure and Replication
 Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
DNA and DNA Replication
 Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
DNA Structure and Replica2on
 DNA Structure and Replica2on Structure of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick (with Maurice Wilkins) awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962 for the construc2on of the double helix model of DNA Rosalind Franklin
DNA Structure and Replica2on Structure of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick (with Maurice Wilkins) awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962 for the construc2on of the double helix model of DNA Rosalind Franklin
CH 4 - DNA. DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells
 CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
Essential Question. What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance?
 DNA Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance? What is the role of DNA in hereditary? Transformation Transformation is the process
DNA Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance? What is the role of DNA in hereditary? Transformation Transformation is the process
What Are the Yeast Cells Doing?
 Cell Division Reading Preview Key Concepts What events take place during the three stages of the cell cycle? How does the structure of DNA help account for the way in which DNA copies itself? Key Terms
Cell Division Reading Preview Key Concepts What events take place during the three stages of the cell cycle? How does the structure of DNA help account for the way in which DNA copies itself? Key Terms
Genetics and Heredity. Mr. Gagnon
 Genetics and Heredity Mr. Gagnon Key Terms: Traits Heredity Genetics Purebred Genes Alleles Recessive Allele Dominant Allele Hybrids Key Concepts: What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms?
Genetics and Heredity Mr. Gagnon Key Terms: Traits Heredity Genetics Purebred Genes Alleles Recessive Allele Dominant Allele Hybrids Key Concepts: What factors control the inheritance of traits in organisms?
N O T E S STUDENT S NAME: TOPIC: INHERITANCE. BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 1 of 24
 GRADE: 12 TOPIC: INHERITANCE N O T E S SUBJECT: BIOLOGY DATE: STUDENT S NAME: BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 1 of 24 BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 2 of 24 Inheritance BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 3
GRADE: 12 TOPIC: INHERITANCE N O T E S SUBJECT: BIOLOGY DATE: STUDENT S NAME: BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 1 of 24 BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 2 of 24 Inheritance BIO - Notes - Inheritance Page 3
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid.
 1 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid. DNA controls the kind of cell which is formed (i.e. muscle, blood, nerve). DNA controls the type of organism which is produced (i.e. buttercup, giraffe, herring,
1 DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid. DNA controls the kind of cell which is formed (i.e. muscle, blood, nerve). DNA controls the type of organism which is produced (i.e. buttercup, giraffe, herring,
amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide glucose
 Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast
 1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast
1. Describe the structure of DNA. Be sure to include what forms the skeleton and how are the strands held together? 2. Compare and contrast chromosomes, chromatids, genes, and alleles. 3. Compare and contrast
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When bases on an
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When bases on an
Outline. Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage
 Genetics Outline Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage Chromosomes are composed of chromatin, which is DNA and associated
Genetics Outline Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage Chromosomes are composed of chromatin, which is DNA and associated
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1
 What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1
 DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
DNA & RNA. Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One
 DNA & RNA Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One I. DNA Structure A. DNA monomers = nucleotides *1. sugar bonded to PO4 & one of four possible nitrogen bases 2. bases = Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
DNA & RNA Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One I. DNA Structure A. DNA monomers = nucleotides *1. sugar bonded to PO4 & one of four possible nitrogen bases 2. bases = Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology
 DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology Let s Think!!!! What does DNA stand for? Where is DNA located in the cell? What is DNA to you? Where do we find DNA? 1928- Fredrick Griffith s Experiment
DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology Let s Think!!!! What does DNA stand for? Where is DNA located in the cell? What is DNA to you? Where do we find DNA? 1928- Fredrick Griffith s Experiment
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Unit 5 DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 1 Biology Unit 5 DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 5:1 History of DNA Discovery Fredrick Griffith-conducted one of the first experiment s in 1928 to suggest that bacteria are capable of transferring genetic
1 Biology Unit 5 DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 5:1 History of DNA Discovery Fredrick Griffith-conducted one of the first experiment s in 1928 to suggest that bacteria are capable of transferring genetic
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
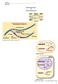 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Quiz 1. Bloe8 Chapter question online student quizzes
 Bloe8 Chapter 9 2 15-question online student quizzes Questions are organized by section number and have an (F), (C), or (A) at the beginning to designate the modified Bloom categories used in the test
Bloe8 Chapter 9 2 15-question online student quizzes Questions are organized by section number and have an (F), (C), or (A) at the beginning to designate the modified Bloom categories used in the test
DNA. Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
 DNA Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Biomolecules Remember 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Nucleic acids hold genetic information; code for proteins 4. Proteins History of DNA Who Discovered DNA Rosalind Franklin
DNA Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Biomolecules Remember 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Nucleic acids hold genetic information; code for proteins 4. Proteins History of DNA Who Discovered DNA Rosalind Franklin
ADENINE, THYMINE,CYTOSINE, GUANINE
 MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular Genetics - the branch of genetics concerned with the structure and activity of genetic material at the molecular level Genetic Material - chromatin (chromosomes) within the
MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular Genetics - the branch of genetics concerned with the structure and activity of genetic material at the molecular level Genetic Material - chromatin (chromosomes) within the
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions Concept 16.1: DNA is the genetic material The Search for the Genetic Material: Scientific Inquiry
 Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
Overview: Life s Operating Instructions In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick introduced an elegant double-helical model for the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA DNA, the substance of inheritance,
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 16 Objectives Describe the contributions of the following people: Griffith; Avery, McCary, and MacLeod; Hershey and Chase; Chargaff; Watson and Crick; Franklin;
Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 2. How did Mendel s scientific work differ from the work of T. A. Knight?
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 8 DIRECTED READING Mendel and Heredity Section 8-1: The Origins of Genetics Mendel and Others Studied Garden-Pea Traits 1. What did T. A. Knight discover? 2. How did Mendel s scientific
Name Date Class CHAPTER 8 DIRECTED READING Mendel and Heredity Section 8-1: The Origins of Genetics Mendel and Others Studied Garden-Pea Traits 1. What did T. A. Knight discover? 2. How did Mendel s scientific
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
2. Structure and Replication of DNA. Higher Human Biology
 2. Structure and Replication of DNA Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine Today we are moving
2. Structure and Replication of DNA Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine Today we are moving
Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose
 Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose Chapter 3 Genetics: Reproducing Life and Producing Variation Our Origins By Clark Spencer Larsen Natural Selection operates on the levels of the 1. living, behaving
Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose Chapter 3 Genetics: Reproducing Life and Producing Variation Our Origins By Clark Spencer Larsen Natural Selection operates on the levels of the 1. living, behaving
Structure of DNA Introductory Videos:
 Structure of DNA Introductory Videos: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy8dk5is1f0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zghkhmoyc5i DNA is a macromolecule made of nucleotides. Each human cell carries a complete
Structure of DNA Introductory Videos: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy8dk5is1f0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zghkhmoyc5i DNA is a macromolecule made of nucleotides. Each human cell carries a complete
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
II. DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Located in the nucleus of the cell Codes for your genes Frank Griffith- discovered DNA in 1928
 HEREDITY = passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and Genes DNA = blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) Chromatin= uncoiled DNA
HEREDITY = passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and Genes DNA = blueprint of life (has the instructions for making an organism) Chromatin= uncoiled DNA
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1
 DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. We have also
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. We have also
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.2 Chromosomes and DNA Replication
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.2 Chromosomes and DNA Replication Cell reproduction involves a series of steps that always begin with the processes of interphase. During interphase the
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.2 Chromosomes and DNA Replication Cell reproduction involves a series of steps that always begin with the processes of interphase. During interphase the
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs to be constantly making new skin cells.
 Name: Cells and Reproduction A. The Cell Life Cycle The many cells in your body are constantly and. For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs
Name: Cells and Reproduction A. The Cell Life Cycle The many cells in your body are constantly and. For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION
 Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
Chapter 8 DNA STRUCTURE AND CHROMOSOMAL ORGANIZATION Chapter Summary Even though DNA has been known as a biochemical compound for over 100 years, it was not implicated as the carrier of hereditary information
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 4: DNA and Cell Cycle
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 4: Cell Cycle Essential Question: Questions: - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. DNA RNA Mitosis Meiosis Homozygous Heterozygous Gene Chromosome
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 4: Cell Cycle Essential Question: Questions: - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. DNA RNA Mitosis Meiosis Homozygous Heterozygous Gene Chromosome
translation The building blocks of proteins are? amino acids nitrogen containing bases like A, G, T, C, and U Complementary base pairing links
 The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes. Vocabulary
 Vocabulary Big Ideas Heredity and Reproduction Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes
Vocabulary Big Ideas Heredity and Reproduction Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes
What is a chromosome and where is it located and what does it
 What is a chromosome and where is it located and what does it do? A general overview for neophytes A chromosome is one of the components of the cell inside the nucleus which codes for proteins and controls
What is a chromosome and where is it located and what does it do? A general overview for neophytes A chromosome is one of the components of the cell inside the nucleus which codes for proteins and controls
DNA Chapter 12. DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B Griffith s Experiment
 DNA Chapter 12 DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B.1.27 To truly understand genetics, biologists after Mendel had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. In 1928, Frederick Griffith was trying
DNA Chapter 12 DNA and RNA B.1.4, B.1.9, B.1.21, B.1.26, B.1.27 To truly understand genetics, biologists after Mendel had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. In 1928, Frederick Griffith was trying
DNA Structure and Replication 1
 Name: # Date: Per: Why? DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied? Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life.
Name: # Date: Per: Why? DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied? Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life.
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE. Link
 DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE Link STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
DNA- THE MOLECULE OF LIFE Link STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): DNA is a long, stringy, twisted molecule made up of nucleotides that carries genetic information. DISCOVERIES Rosalind Franklin,
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division. DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis
 Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
