Chapter 19b Blood, cont d
|
|
|
- Oswin Reed
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 19b Blood, cont d White Blood Cells WBCs account for less than 1% of blood volume. There are two major histological categories of WBCs the granulocytes and the agranulocytes. GRANULOCYTES are Basophils, Eosinophils and Neutrophils (BEN) o Basophils account for less than 1% of the WBCs, and they take up basic due you see mostly the granules on the histology slide. Basophils release HISTAMINE, so they are part of the allergy response. Basophils circulate around, and their buddies, the Mast Cells are in tissues. An example of a Mast Cell is a Langerhans cell. o Eosinophils account for 2-4% of WBCs and they take up acidic dye (granules show up red.) They have a bi-lobed nucleus that pretty much looks like two nuclei, or an alien face. These cells are phagocytic, but don t kill their prey by phagocytosis. They use phagocytosis to clear up cellular debris, but for dealing with pathogens they attack it as a group and release their deadly enzymes. Eosinophils are high in response to PARASITE INFECTION! o Neutrophils account for the majority of WBCs 50-70%. They do not take up dyes! They are going to be present when you have a BACTERIAL INFECTION. Though they are smaller than the macrophages, there are so many of them that they can get the job done. They are also phagocytic, and they contain lysosomal enzymes as well as bactericides. AGRANULOCYTES are Lymphocytes and Monocytes o Lymphocytes are rather small compared to other leukocytes, but they have a huge round nucleus and you can t see much of the cytoplasm. They mostly live in lymphatic tissues, and there are three types: o B-Lymphocytes (B-cells) o T-Lymphocytes (T-cells) Specific immune response o NK Cells (macrophages) Nonspecific immune response o Monocytes have a large heart-shaped nucleus. These cells circulate temporarily but eventually enter tissues as MACROPHAGES. They are phagocytic! Specific and non-specific (general) immunity General immunity: Granulocytes (Basophils, Neutrophils and Acidophils) Monocytes An example of general immunity is inflammation. It occurs the same way for every injury, no matter where it is or how severe it is. The secretion of histamine causes inflammation the basophils and mast cells secrete histamine! Specific immunity: T-lymphocytes (cell-mediated immunity) B-lymphocytes (humoral immunity)
2 The T-cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, meaning they get involved in handto-hand combat with the pathogens. They come directly into contact with the invading cells and destroy them! The B-cells are involved in humoral immunity, which means they secrete antibodies (immunoglobulins) to do the dirty work for them. The antibodies then attack! Unique characteristics of WBCs (leukocytes) o WBCs are true cells. They have a nucleus and can divide/repair o Most WBCs are phagocytic o Large populations of WBCs are found in CT proper and lymphatic tissues o They are the only blood cells that can leave circulation and enter tissues through a process called diapedesis o They are called to action via chemotaxis attraction to specific chemical stimuli Production of WBCs All blood cells start with the stem cell which is the HEMOCYTOBLAST. It then branches to the two less-specialized stem cells the MYELOID stem cell produces the granulocytes and the monocytes. The LYMPHOID stem cell produces lymphocytes. The committed cell for each cell type is: MYELOBLAST produces eosinophils MYELOBLAST produces neutrophils MYELOBLAST produces basophils MONOBLAST produces monocytes LYMPHOBLAST produces lymphocytes Chemical messengers known as CSF (colony stimulating factors) tell the developing cells what kind of cell to specify. o EPO tells the progenitor cell to make erythroblasts. o EPO tells the blast cell to make erythroblasts o GMCSF tells the progenitor cell to make granulocytes and monocytes o GCSF tells the blast cell to make granulocytes o MCSF tells the blast cell to make monocytes So, the pathway for the production of blood cells for each of the cell types is as follows: Pluripotent Stem Cell Committed Produces Process Stem Cell Cell Hemocytoblast Myeloid S.C. Proerythroblast Erythrocyte Erythropoiesis Hemocytoblast Myeloid S.C. Myeloblast Basophil Leukopoiesis Hemocytoblast Myeloid S.C. Myeloblast Eisonophil Leukopoiesis Hemocytoblast Myeloid S.C. Myeloblast Neutrophil Leukopoiesis Hemocytoblast Myeloid S. C. Monoblast Monocyte Leukopoiesis Hemocytoblast Lymphoid S.C. Lymphoblast Lymphocyte Leukopoiesis Hemocytoblast Myeloid S.C. Megakaryoblast Platelet Thrombocytopoiesis
3 We can also make a synthetic GCSF (filgrastin or Neupogen). It is used by cancer patients to help them develop more neutrophils to support the immune system during chemotherapy. Recall that neutrophils are the major phagocyte in circulation. WBC disorders: o Leukopenia = not enough WBCs (results from chemotherapy) o Leukocytosis = too many WBCs can be because you are fighting an infection, or because of cancer causing the abnormal production of WBCs. Production of Platelets (thrombocytopoiesis) The production of platelets begins with the HEMOCYTOBLAST, and the committed cell is the MEGAKARYOBLAST. It then becomes a PROMEGAKARYOCYTES, but this is not a platelet yet! Next, it is a MEGAKARYOCYTE, which breaks off into pieces to become about 4,000 platelets. Platelets are little pieces of cells! These little pieces squeeze through capillary wall in the bone marrow to go out into circulation. The granules of platelets are chemical messengers and enzymes that are involved in hemostasis they create a plug until the tissue is fully repaired. They do this by facilitating clot formation and converting fibrinogen to fibrin. The chemical messenger for this pathway is thrombopoietin (TPO) TPO stimulates the development of platelets. Hemostasis Hemostasis is the process of stopping bleeding! It consists of three general phases: 1. Vasoconstriction just upstream from the break. This is an immediate response that lasts about 30 minutes. Smooth muscles cells have a vascular spasm when they are damaged this is another way of saying they undergo vasoconstriction. This constriction buys us time while we complete phase 2. Besides slowing the flow of blood, a few other things happen at this time: a. The endothelial cells release their chemical messenger (endothelin) that reinforce the smooth muscle spasm and cause a proliferation of cells and fibers for tissue repair. b. The endothelial cell membrane becomes sticky, which helps platelets plugs adhere to the injury site c. The basal lamina is exposed to blood flow 2. Platelet plug formation takes about 1 minute, but also starts immediately. In this stage the platelets adhere to the site of injury on exposed collagen fibers + basal lamina + sticky endothelial cells. This process is called platelet aggregation and it creates a platelet plug. Though not a great seal (it still needs the fibrin mesh), the platelets release: a. Ca ++ which promotes aggregation in a positive feedback loop b. Seratonin which enhances vasoconstriction of the vessel c. ADP which enhances aggregation and secretion, attracting more platelets. Also a positive feedback loop d. Clotting factors, which enhance vessel repair e. PDGF (platelet derived growth factor) that enhances vessel repair
4 f. Thromboxane A 2, which stimulates aggregation and secretion as well as secretion it is inhibited by aspirin (aspirin is an antiprostaglandin). This plug formation is regulated locally by prostacyclin from the endothelial cells, which work as a negative feedback loop to prevent the clot from getting too big and encroaching on non-injured tissues. 3. Coagulation is a delayed response delayed by about 30 seconds and takes about 5 minutes to complete. The reason it takes so long is that there are about 30 different clotting factors that all work in a complicated pathway to convert fibrinogen to fibrin. There are two components to the process the extrinsic pathway (stimulated by trigger outside the blood) and the intrinsic pathway (stimulated by trigger in the blood), and they converge at Clotting Factor 10. From there, prothrombinase converts prothombin to thrombin, and thrombin converts fibrinogin to fibrin. The final product in the coagulation phase is the fibrin mesh. Procoagulants are things that promote clot formation. These factors include Ca 2+ and various plasma proteins called proenzymes these are activated in the chain reaction. Anticoagulants are things that inhibit clot formation. These provide control in the form of negative feedback. Examples are heparin (from basophils and mast cells), Thrombomodulin (from endothelial cells) and Prosacyclin. The EXTRINSIC PATHWAY is faster and originates from the vessel wall. The INTRINSIC PATHWAY is not as fast, but is more robust. Though clotting can be initiated by either one, they usually work together and converge at a common pathway. The end result of both of them working together is that once prothombinase is produced, then clotting happens very fast in about seconds. The prothombinase pathway is: Prothombinase stimulates the synthesis of prothrombin which leads to thrombin, which leads to fibrinogen becoming fibrin, which creates the fibrin mesh! Recall that Vitamin-K is needed for the synthesis of prothrombin, and that fibrinogen is the dissolved plasma protein. Post Hemostasis is clot retraction and repair this happens within minutes. In this stage 1. Contractile proteins within the platelets contract, which pulls the vessel edges closer together this is called clot retraction. 2. Endothelium and smooth muscle regenerate and repair. This is stimulated in part by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), which is one of the chemical messengers from the platelet granules 3. Once healed, fibrinolysis removes the temporary clot. This is mediated by the enzyme plasmin.
5 Disorders of Hemostasis There are two major types of disorders of hemostasis thromboembolytic disorders and bleeding disorders. Thromboembolytic disorders have to do with inappropriate clot formation. When an abnormal clot forms on a vessel wall this is called a THROMBUS. If it breaks off and floats downstream it is called an EMBOLUS. When it lodges and blocks the blood flow causing all kinds of damage, this is called an EMBOLISM. Embolisms cause strokes and heart attacks. Bleeding disorders have to do with abnormal bleeding due to the inability to form clots. o Thrombocytopenia is a platelet deficiency. This is caused by damaged bone marrow which can t function properly. o Insufficient procoagulants can also affect one s ability to make clots. This happens with liver disease/dysfunction and Vit-K deficiency. Recall that the liver produces most of the blood proteins, including fibrinogen. No fibrinogen is a very bad situation to be in. o Hemophilias are genetic bleeding disorders that have similar signs and symptoms of the ones listed above. The individual is missing a clotting factor (it only takes one missing factor to screw up the pathway). Sometimes this factor can be given exogenously, or the person has to get frequent plasma/whole blood transfusions.
6 Marieb, E. N. (2006). Essentials of human anatomy & physiology (8th ed.). San Francisco: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. Martini, F., & Ober, W. C. (2006). Fundamentals of anatomy & physiology (7th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow. Baroreceptor reflex. Veins returning blood
 Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time. Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO
 Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides.
 These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
The Story of the Platelet Clump. Wayne Hall MTN Network Laboratory Magee-Womens Research Institute Pittsburgh, PA
 The Story of the Platelet Clump Wayne Hall MTN Network Laboratory Magee-Womens Research Institute Pittsburgh, PA Reason for Alarm? Platelet Clumping was occurring in multiple African sites 1-2 times per
The Story of the Platelet Clump Wayne Hall MTN Network Laboratory Magee-Womens Research Institute Pittsburgh, PA Reason for Alarm? Platelet Clumping was occurring in multiple African sites 1-2 times per
BLOOD COAGULATION. 1. The initial phase of the process is vascular constriction. This limits the flow of blood to the area of injury.
 BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
1 Adequate. Some key words were used and used correctly. Some errors were made in the use of key words.
 Peer Assessment Form for Antibiotics Activity Q1 Key Words platelets clot white blood cells engulf digest capillaries Microbes lymphocytes antibodies clump (agglutination) lysis signal Phagocytes infection
Peer Assessment Form for Antibiotics Activity Q1 Key Words platelets clot white blood cells engulf digest capillaries Microbes lymphocytes antibodies clump (agglutination) lysis signal Phagocytes infection
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management. Objectives
 Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Overview of hemostasis Initiated when trauma, surgery or disease disrupts the vascular endothelium, exposing blood to the subendothelial connective tissue Achieved by: 1)Vasconstriction
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Overview of hemostasis Initiated when trauma, surgery or disease disrupts the vascular endothelium, exposing blood to the subendothelial connective tissue Achieved by: 1)Vasconstriction
Haemostasis. The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels. to stop bleeding. to prevent thrombosis
 Haemostasis Haemostasis The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels to stop bleeding to prevent thrombosis Haemostasis blood endothelium basement membrane subendothelium
Haemostasis Haemostasis The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels to stop bleeding to prevent thrombosis Haemostasis blood endothelium basement membrane subendothelium
VIII. Validation Evaluation Comparative Chart Application Fields of PRP Advantages of MiroPRP for skin treatments MicroPRP and Mico-Mesotherapy
 The New Technology for Safe Platelet Activation INDEX I. Blood Composition II. What is PRP Therapy? III. Growth Factors Present in PRP IV. Why is PRP concentration significant? V. How are Platelets Activated?
The New Technology for Safe Platelet Activation INDEX I. Blood Composition II. What is PRP Therapy? III. Growth Factors Present in PRP IV. Why is PRP concentration significant? V. How are Platelets Activated?
At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to:
 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to: Understand the key terms and definitions regarding stem cells Differentiate between the adult and embryonic stem cells Differentiate
Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lesson you should be able to: Understand the key terms and definitions regarding stem cells Differentiate between the adult and embryonic stem cells Differentiate
Rheological and biochemical analyses on blood coagulation ~ Discovery of a new pathway under stagnant flow conditions ~
 Rheological and biochemical analyses on blood coagulation ~ Discovery of a new pathway under stagnant flow conditions ~ Computer and Information Division, RIKEN Hiroki Iwata Supramolecular Science Laboratory,
Rheological and biochemical analyses on blood coagulation ~ Discovery of a new pathway under stagnant flow conditions ~ Computer and Information Division, RIKEN Hiroki Iwata Supramolecular Science Laboratory,
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance. DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: Technical Support:
 Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders
 CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
Drugs used in Thromboembolic Disease. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Department of Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine October 2014
 Drugs used in Thromboembolic Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Department of Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine October 2014 Drugs used in Thromboembolic Disease Anticoagulants: Heparin. Oral anticoagulants.
Drugs used in Thromboembolic Disease Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Department of Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine October 2014 Drugs used in Thromboembolic Disease Anticoagulants: Heparin. Oral anticoagulants.
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie
 De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S-1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S-1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development
 Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
Strategies for Assessment of Immunotoxicology in Preclinical Drug Development Rebecca Brunette, PhD Scientist, Analytical Biology SNBL USA Preclinical Immunotoxicology The study of evaluating adverse effects
Adrenal Gland. MEDULLA Epinephrine CORTEX. Zona reticularis --adrenal androgen. Zona fasciculata --glucocorticoids
 STRESS AND IMMUNITY STRESS Defined as life under tension Homeostatic range: normal physiological balance Stressors: physical and emotional stimuli that disrupt homeostasis Eustress vs Distress Stress response:
STRESS AND IMMUNITY STRESS Defined as life under tension Homeostatic range: normal physiological balance Stressors: physical and emotional stimuli that disrupt homeostasis Eustress vs Distress Stress response:
Immunoglobulins. Biological Properties
 Immunoglobulins Biological Properties Introduction Many important biological properties are attributed to antibodies that differ depending on isotype These include; - Neutralization of toxins - Immobilization
Immunoglobulins Biological Properties Introduction Many important biological properties are attributed to antibodies that differ depending on isotype These include; - Neutralization of toxins - Immobilization
Sergeant System s Immune System Defense Team Webquest
 Name Sergeant System s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Hello! I m Sergeant Cell and I am in charge of the Special Operations Teams here at the ImmunoSystem Police Station. 2 Thanks so much for coming
Name Sergeant System s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Hello! I m Sergeant Cell and I am in charge of the Special Operations Teams here at the ImmunoSystem Police Station. 2 Thanks so much for coming
Changes in coagulation and tissue plasminogen activator after the treatment of cerebral infarction with lumbrokinase
 Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation 23 (2000) 213 218 213 IOS Press Changes in coagulation and tissue plasminogen activator after the treatment of cerebral infarction with lumbrokinase Lirong Jin
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation 23 (2000) 213 218 213 IOS Press Changes in coagulation and tissue plasminogen activator after the treatment of cerebral infarction with lumbrokinase Lirong Jin
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
Basic Antibody Structure. Multiple myeloma = cancerous plasma cells Monomer = 150,000. Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function
 Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function. Functional Regions. Types of chains. Constant & Variable regions 4. Glycoprotein * * * Heavy chain= 446 aa Light chain= 4aa Each heavy and light chain
Chapter 4. Immunoglobulin Structure and Function. Functional Regions. Types of chains. Constant & Variable regions 4. Glycoprotein * * * Heavy chain= 446 aa Light chain= 4aa Each heavy and light chain
COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES. Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology
 COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology 1395 Haemostasis overview: BV Injury Neural Contact/ Tissue Factor Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced Blood flow Platelet
COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology 1395 Haemostasis overview: BV Injury Neural Contact/ Tissue Factor Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced Blood flow Platelet
Blood Product Utilization
 Who gets what & when Why not to give blood? Volume Expander For specific number (except as related to procedures) To patients with religious objections to blood transfusions Blood given only when necessary
Who gets what & when Why not to give blood? Volume Expander For specific number (except as related to procedures) To patients with religious objections to blood transfusions Blood given only when necessary
BACTERIA. NO or membrane bound WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF PROKARYOTES? TYPES EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA. bilayer embedded with
 Bacteria and Virus Notes WHAT ARE PROKARYOTES? ALWAYS organisms BACTERIA NO or membrane bound Very compared to cells WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF PROKARYOTES? TYPES EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA MAJOR DIFFERENCES
Bacteria and Virus Notes WHAT ARE PROKARYOTES? ALWAYS organisms BACTERIA NO or membrane bound Very compared to cells WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF PROKARYOTES? TYPES EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA MAJOR DIFFERENCES
Phylogenetic Assessment of Innate Immunity s Complement Component C3 and Factor B (Bf)
 Phylogenetic Assessment of Innate Immunity s Complement Component C3 and Factor B (Bf) In Cnidarians 3D! Sarah McAnulty Innate Immunity Organism is born with its innate immune system No development over
Phylogenetic Assessment of Innate Immunity s Complement Component C3 and Factor B (Bf) In Cnidarians 3D! Sarah McAnulty Innate Immunity Organism is born with its innate immune system No development over
Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation, the MLS student will be able to:
 Clinical Performance Objectives in Clinical Hematology Department of Medical and Research Technology University of Maryland School of Medicine Spring 2015 Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation,
Clinical Performance Objectives in Clinical Hematology Department of Medical and Research Technology University of Maryland School of Medicine Spring 2015 Upon completion of the Clinical Hematology rotation,
Laboratory Manual Selected Experiments in General Physiology, Basics of Hematology & Nerve-Muscle Physiology
 Laboratory Manual Selected Experiments in General Physiology, Basics of Hematology & Nerve-Muscle Physiology (For medical students) Written by E.S.Prakash, MBBS, MD Associate Professor of Physiology, Mercer
Laboratory Manual Selected Experiments in General Physiology, Basics of Hematology & Nerve-Muscle Physiology (For medical students) Written by E.S.Prakash, MBBS, MD Associate Professor of Physiology, Mercer
Rheological Properties of Fibrin Clots
 Rheological Properties of Fibrin Clots A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF PHILOSOPHY IN THE FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Year of submission 2012
Rheological Properties of Fibrin Clots A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF PHILOSOPHY IN THE FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Year of submission 2012
ROTEM Basic Interpretation Guide
 ROTEM Basic Interpretation Guide Parameter: Clotting Time CT - Clotting Time (seconds) The time from the start of the test until first significant levels of a clot are detected. This measurement is initiated
ROTEM Basic Interpretation Guide Parameter: Clotting Time CT - Clotting Time (seconds) The time from the start of the test until first significant levels of a clot are detected. This measurement is initiated
RegenACR. autologous cellular regeneration. RegenACR A-PRP treatment. collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength.
 RegenACR autologous cellular regeneration RegenACR A-PRP treatment collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength. 4,5 WHAT IS A-PRP Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Plasma contains many
RegenACR autologous cellular regeneration RegenACR A-PRP treatment collagen fibers. 1,2 texture and elasticity. 3 volume & strength. 4,5 WHAT IS A-PRP Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Plasma contains many
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Transformed Pre- Ig Surface Surface Secreted B- ALL Macroglobulinemia Myeloma
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Arthrex Angel TM System. Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations
 Arthrex Angel TM System Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations Arthrex Angel TM System The Arthrex Angel TM System is a revolutionary production system for platelet-rich plasma (PRP) formulations
Arthrex Angel TM System Indication-specific PRP and PRF gel preparations Arthrex Angel TM System The Arthrex Angel TM System is a revolutionary production system for platelet-rich plasma (PRP) formulations
From Stem Cell to Any Cell
 sciencenewsforkids.org http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/2005/10/from-stem-cell-to-any-cell-2/ From Stem Cell to Any Cell By Emily Sohn / October 11, 2005 For maybe a day, about 9 months before you were
sciencenewsforkids.org http://www.sciencenewsforkids.org/2005/10/from-stem-cell-to-any-cell-2/ From Stem Cell to Any Cell By Emily Sohn / October 11, 2005 For maybe a day, about 9 months before you were
Immunotherapy in myeloma
 Immunotherapy in myeloma This Horizons Infosheet contains information on immunotherapy, a type of treatment being investigated in myeloma. The Horizons Infosheet series provides information relating to
Immunotherapy in myeloma This Horizons Infosheet contains information on immunotherapy, a type of treatment being investigated in myeloma. The Horizons Infosheet series provides information relating to
LEARN. about. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 3-5 and enclosed full Prescribing Information.
 LEARN about on pages 3-5 and enclosed 2 3? What is ZARXIO (filgrastim-sndz)? ZARXIO is a man-made form of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) called filgrastim. G-CSF is a substance produced
LEARN about on pages 3-5 and enclosed 2 3? What is ZARXIO (filgrastim-sndz)? ZARXIO is a man-made form of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) called filgrastim. G-CSF is a substance produced
CHAPTER 5 COMPLEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 COMPLEMENT See APPENDIX (8) COMPLEMENT FIXATION ASSAY The complex of serum proteins known as COMPLEMENT plays key roles in the lytic and inflammatory properties of antibodies. The CLASSICAL pathway
CHAPTER 5 COMPLEMENT See APPENDIX (8) COMPLEMENT FIXATION ASSAY The complex of serum proteins known as COMPLEMENT plays key roles in the lytic and inflammatory properties of antibodies. The CLASSICAL pathway
Immunology: Antibody Basics
 e-learning JABSOM Immunology: Antibody Basics One :: General Structure Identify the Parts of an Antibody Two :: Isotypes Identify Antibody Isotypes Three :: Function Match Antibody Functions With Isotypes
e-learning JABSOM Immunology: Antibody Basics One :: General Structure Identify the Parts of an Antibody Two :: Isotypes Identify Antibody Isotypes Three :: Function Match Antibody Functions With Isotypes
Our detailed aims were:
 1 Fortsatt utveckling och validering av screeningtester för evaluering av industriellt och miljö producerade partiklars toxicitet (diarienr 150144 - Bo Nilsson) Aim The original aim of the study was to
1 Fortsatt utveckling och validering av screeningtester för evaluering av industriellt och miljö producerade partiklars toxicitet (diarienr 150144 - Bo Nilsson) Aim The original aim of the study was to
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
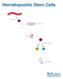 Hematopoietic Stem Cells Isolate Culture Verify Differentiate Investigate a brand Hematopoietic Stem Cells Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are multipotent, self-renewing progenitor cells from which all
Hematopoietic Stem Cells Isolate Culture Verify Differentiate Investigate a brand Hematopoietic Stem Cells Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are multipotent, self-renewing progenitor cells from which all
Basic coagulation applications and case studies
 Basic coagulation applications and case studies Jing Jin Clinical laboratory Scientist (MLS, ASCP) - Coagulation/Hematology Stanford University Hospital and Clinics 1 Agenda Overview about 3 major phases
Basic coagulation applications and case studies Jing Jin Clinical laboratory Scientist (MLS, ASCP) - Coagulation/Hematology Stanford University Hospital and Clinics 1 Agenda Overview about 3 major phases
XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story
 XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story Barbara J Connell MS, MT(ASCP)SH Senior Product Manager Technical Marketing & Communications Sysmex America, Inc Objectives Describe the advantages
XN Hematology Case Studies Every Picture Tells a Story Barbara J Connell MS, MT(ASCP)SH Senior Product Manager Technical Marketing & Communications Sysmex America, Inc Objectives Describe the advantages
Disclosures. Thromboelastography. TEG Methodology. TEG Output. Thromboelastography (TEG): Basics & Clinical Applications
 Thromboelastography (TEG): Basics & Clinical Applications Paula J. Santrach MD Associate Professor, Laboratory Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Disclosures Relevant financial relationships NONE Off label
Thromboelastography (TEG): Basics & Clinical Applications Paula J. Santrach MD Associate Professor, Laboratory Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Disclosures Relevant financial relationships NONE Off label
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
DNA Technology. B. Using Bacteria to Clone Genes: Overview:
 DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
Myeloma Bone Disease Current and Future Treatment. A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation
 Myeloma Bone Disease Current and Future Treatment A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation What Is Multiple Myeloma? Multiple Myeloma is a cancer that results from a malignant change in a particular
Myeloma Bone Disease Current and Future Treatment A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation What Is Multiple Myeloma? Multiple Myeloma is a cancer that results from a malignant change in a particular
Biological evaluation of medical devices. Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10993-4 Third edition 2017-04 Biological evaluation of medical devices Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood Évaluation biologique
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10993-4 Third edition 2017-04 Biological evaluation of medical devices Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood Évaluation biologique
Platelet transfusion therapy. Orieji Illoh, M.D. January 23, 2007
 Platelet transfusion therapy Orieji Illoh, M.D. January 23, 2007 The Eighteenth Century Transfusions were done only sporadically, and were generally animal to human. Transfusion was generally thought of
Platelet transfusion therapy Orieji Illoh, M.D. January 23, 2007 The Eighteenth Century Transfusions were done only sporadically, and were generally animal to human. Transfusion was generally thought of
SEED Coagulation. Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development April 2014
 SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development April 2014 The Thrombin Time Test and Reptilase Test what is their role in coagulation testing? Baseline screening tests of coagulation The
SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development April 2014 The Thrombin Time Test and Reptilase Test what is their role in coagulation testing? Baseline screening tests of coagulation The
Residual Serum Thrombin
 Residual Serum Thrombin Activity Murray Weiner N RECENT YEARS a remarkable number of blood and tissue components have been found to play a role in the formation of thrombin, the enzyme ultimately responsible
Residual Serum Thrombin Activity Murray Weiner N RECENT YEARS a remarkable number of blood and tissue components have been found to play a role in the formation of thrombin, the enzyme ultimately responsible
IMMUNOBIOLOGY : AN INTRODUCTION
 Immunobiology : An Introduction MODULE - 5 30 IMMUNO : AN INTRODUCTION We all get infections, but some of us fall sick more frequently than others. This is related to the immune system. Proper functioning
Immunobiology : An Introduction MODULE - 5 30 IMMUNO : AN INTRODUCTION We all get infections, but some of us fall sick more frequently than others. This is related to the immune system. Proper functioning
Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC
 Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC 1 Monitoring hemostasis Bleeding Clotting 2 Picture courtesy of Helena Laboratories 3 Extrinsic Pathway Monitor with ACT / aptt WARFARIN Monitor with PT Common Pathway
Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC 1 Monitoring hemostasis Bleeding Clotting 2 Picture courtesy of Helena Laboratories 3 Extrinsic Pathway Monitor with ACT / aptt WARFARIN Monitor with PT Common Pathway
American Association of Immunology Heidi Anderson: Lesson Plan for Cell Signaling and Immune System
 B cell Modeling of Cell Communication and Signal Transduction Pathways: How can students visualize cellular discussions? Heidi M. Anderson 1 and Dr. Subbarao Bondada 2 1 Paul Laurence Dunbar High School,
B cell Modeling of Cell Communication and Signal Transduction Pathways: How can students visualize cellular discussions? Heidi M. Anderson 1 and Dr. Subbarao Bondada 2 1 Paul Laurence Dunbar High School,
PV92 PCR Bio Informatics
 Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Guidelines for the use of blood warming devices(aabb) Reference: 2002 AABB
 Guidelines for the use of blood warming devices(aabb) Reference: 2002 AABB 1 Hypothermia Introduction Induced by rapid, large-volume transfusion of refrigerated blood components A potential source of serious
Guidelines for the use of blood warming devices(aabb) Reference: 2002 AABB 1 Hypothermia Introduction Induced by rapid, large-volume transfusion of refrigerated blood components A potential source of serious
Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC
 Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC 1 Explain why ACTs from different systems are not the same Develop a plan for switching from one ACT system to another Describe why ACT and aptt are not interchangeable
Marcia L. Zucker, Ph.D. ZIVD LLC 1 Explain why ACTs from different systems are not the same Develop a plan for switching from one ACT system to another Describe why ACT and aptt are not interchangeable
Fibrin Glue Based Clotting Factor Cocktail for High Throughput in vitro. Thrombogenicity Screening. Yvette Michelle Beben
 Fibrin Glue Based Clotting Factor Cocktail for High Throughput in vitro Thrombogenicity Screening by Yvette Michelle Beben Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: William (Monty)
Fibrin Glue Based Clotting Factor Cocktail for High Throughput in vitro Thrombogenicity Screening by Yvette Michelle Beben Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: William (Monty)
FORENSIC SEROLOGY. Chapter PRENTICE HALL 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458
 Chapter 8 FORENSIC SEROLOGY 8-1 Nature of Blood The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. Plasma, which is the fluid portion of blood, is
Chapter 8 FORENSIC SEROLOGY 8-1 Nature of Blood The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. Plasma, which is the fluid portion of blood, is
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS
 OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors
 Venkat Living Venkat with Hemophilia Living with Hemophilia The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors Tami Livnat 1, Alfica
Venkat Living Venkat with Hemophilia Living with Hemophilia The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors Tami Livnat 1, Alfica
The clinical utility of IPF in thrombocytopenia
 The clinical utility of IPF in thrombocytopenia Platelets platelets Platelets are the smallest blood cells which are released by cytoplasmic blebbing of megakaryocytes with an average size of 2um. Normal
The clinical utility of IPF in thrombocytopenia Platelets platelets Platelets are the smallest blood cells which are released by cytoplasmic blebbing of megakaryocytes with an average size of 2um. Normal
Section 8. To introduce the basic theory and principles of collecting blood for Intraoperative Cell Salvage (ICS)
 Section 8 Practicalities Blood Collection Aim To introduce the basic theory and principles of collecting blood for Intraoperative Cell Salvage (ICS) Learning Outcomes To identify the equipment used for
Section 8 Practicalities Blood Collection Aim To introduce the basic theory and principles of collecting blood for Intraoperative Cell Salvage (ICS) Learning Outcomes To identify the equipment used for
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells ISOLATE & CULTURE VERIFY DIFFERENTIATE INVESTIGATE ISOLATE AND CULTURE Mouse Hematopoietic Cell Lineage Depletion Kit ( MAGM29) Both positive and negative selection methods can
Hematopoietic Stem Cells ISOLATE & CULTURE VERIFY DIFFERENTIATE INVESTIGATE ISOLATE AND CULTURE Mouse Hematopoietic Cell Lineage Depletion Kit ( MAGM29) Both positive and negative selection methods can
Inhibition of the prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH potentiates tissue regeneration. JournalClub Emilie Hrdliczka
 Inhibition of the prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH potentiates tissue regeneration JournalClub 14.12.2015 Emilie Hrdliczka Facts Author: Yongyou Zhang Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve
Inhibition of the prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH potentiates tissue regeneration JournalClub 14.12.2015 Emilie Hrdliczka Facts Author: Yongyou Zhang Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve
Category Storage Shelf Life Additional Criteria
 CE Update [blood banking/transfusion medicine] Blood Components for Hemostasis Jun Teruya, MD, DSc, and Glenn Ramsey, MD From the Department of Pathology, Northwestern University Medical School, Chicago.
CE Update [blood banking/transfusion medicine] Blood Components for Hemostasis Jun Teruya, MD, DSc, and Glenn Ramsey, MD From the Department of Pathology, Northwestern University Medical School, Chicago.
MISSION - Set (align) the arm bone, then apply the blue cast. The cast needs to be all the way down, and it needs to completely cover the break.
 2010 FLL CHALLENGE robot game Missions Biomedical engineering is the use of various engineering disciplines to help doctors and hospitals help patients. The fields of chemical, mechanical, electrical,
2010 FLL CHALLENGE robot game Missions Biomedical engineering is the use of various engineering disciplines to help doctors and hospitals help patients. The fields of chemical, mechanical, electrical,
Anticlotting mechanisms 1: physiology and pathology
 : physiology and pathology J Adanma Ezihe-Ejiofor FRCA, FWACS, MBBS Nevil Hutchinson FRCA 1A01 Key points Anticlotting mechanisms are important in restricting clot formation to the site of injury. The
: physiology and pathology J Adanma Ezihe-Ejiofor FRCA, FWACS, MBBS Nevil Hutchinson FRCA 1A01 Key points Anticlotting mechanisms are important in restricting clot formation to the site of injury. The
A Level. A Level Biology. Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY
 OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY by JOANNE VAN RYN-McKENNA, B.Sc., M.Sc. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
OERMATAN SULFATE: A NEW CONCEPT IN ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY by JOANNE VAN RYN-McKENNA, B.Sc., M.Sc. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser with fluorescence technology
 XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser Fig. 1: sysmex xs-1000i Since the introduction of fluorescence technology for leukocyte differentiation by sysmex in the year 1999, thousands of laboratories
XS-1000i New Sysmex 5-part diff haematology analyser Fig. 1: sysmex xs-1000i Since the introduction of fluorescence technology for leukocyte differentiation by sysmex in the year 1999, thousands of laboratories
No-wash, no-lyse detection of phagocytic cells via a phrodo BioParticles functional assay in human whole blood on the
 APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of phagocytic cells via a phrodo BioParticles functional assay in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Analysis
APPLICATION NOTE Attune NxT Flow Cytometer No-wash, no-lyse detection of phagocytic cells via a phrodo BioParticles functional assay in human whole blood on the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer Introduction Analysis
Appendix B. Glossary of Acronyms and Terms
 Appendix B. Glossary of Acronyms and Terms Glossary of Acronyms AABB ABC ABRA ACT ADP AHF AIDS ALT AMA AMS ARC ASCP ATIII ATP BTS CBC CCBC cdna CDC CFR CMV CPDA-1 CRC DBDR DHEW DHHS DNA DRG EBV EIA ELISA
Appendix B. Glossary of Acronyms and Terms Glossary of Acronyms AABB ABC ABRA ACT ADP AHF AIDS ALT AMA AMS ARC ASCP ATIII ATP BTS CBC CCBC cdna CDC CFR CMV CPDA-1 CRC DBDR DHEW DHHS DNA DRG EBV EIA ELISA
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
"Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin."
 "Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin." Carrasco, Joaquin phd Dp. Surgery Universitat de València. Presenter Bonete, Daniel MD Hospital La Fe de València Gomar, Francisco MD Hospital
"Release of growth factors in PRP activated with thrombin." Carrasco, Joaquin phd Dp. Surgery Universitat de València. Presenter Bonete, Daniel MD Hospital La Fe de València Gomar, Francisco MD Hospital
Improving Outcomes of Cardiac Surgery with a Point-of-Care Based Transfusion Algorithm
 Improving Outcomes of Cardiac Surgery with a Point-of-Care Based Transfusion Algorithm Summer Syed (local PI) Keyvan Karkouti Deputy Anesthesiologist-in-Chief, Toronto General Hospital, University Health
Improving Outcomes of Cardiac Surgery with a Point-of-Care Based Transfusion Algorithm Summer Syed (local PI) Keyvan Karkouti Deputy Anesthesiologist-in-Chief, Toronto General Hospital, University Health
2 Thomas G. DeLoughery
 Tests of Hemostasis and Thrombosis 2 Thomas G. DeLoughery A routine laboratory test once well-established is often slavishly adhered to, with little further thought about how it originated, why it is done
Tests of Hemostasis and Thrombosis 2 Thomas G. DeLoughery A routine laboratory test once well-established is often slavishly adhered to, with little further thought about how it originated, why it is done
Sepsis-Associated Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Thromboembolic Disease
 MEDITERRANEAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES www.mjhid.org ISSN 2035-3006 Review article Sepsis-Associated Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Thromboembolic Disease and Nicola Semeraro,
MEDITERRANEAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES www.mjhid.org ISSN 2035-3006 Review article Sepsis-Associated Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Thromboembolic Disease and Nicola Semeraro,
Bioreactors in tissue engineering
 Bioreactors in tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
Bioreactors in tissue engineering S. Swaminathan Director Centre for Nanotechnology & Advanced Biomaterials School of Chemical & Biotechnology SASTRA University Thanjavur 613 401 Tamil Nadu Joint Initiative
Apheresis Anticoagulant Removal. Oluwatoyosi Onwuemene, MD MS May 6th, 2017
 Apheresis Anticoagulant Removal Oluwatoyosi Onwuemene, MD MS May 6th, 2017 Talk Outline Case presentation Factors associated with drug removal TPE s effects on hematologic parameters Anticoagulant properties
Apheresis Anticoagulant Removal Oluwatoyosi Onwuemene, MD MS May 6th, 2017 Talk Outline Case presentation Factors associated with drug removal TPE s effects on hematologic parameters Anticoagulant properties
Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Immunology, Microbiology and Biotechnology
 Biyani's Think Tank Concept based notes Immunology, Microbiology and Biotechnology (B.Sc. Part-II) Naresh Kumar Nirmal Revised By: Priyanka Khan Deptt. of Science Biyani Girls College, Jaipur 2 Published
Biyani's Think Tank Concept based notes Immunology, Microbiology and Biotechnology (B.Sc. Part-II) Naresh Kumar Nirmal Revised By: Priyanka Khan Deptt. of Science Biyani Girls College, Jaipur 2 Published
Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords
 Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords Dr. Vasiliki E Kalodimou, Head of Flow Cytometry-Research and Regenerative Medicine Department, IASO-Maternity
Adipose rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of the chronic scar tissue of the vocal cords Dr. Vasiliki E Kalodimou, Head of Flow Cytometry-Research and Regenerative Medicine Department, IASO-Maternity
The Hollow Fiber Bioreactor and Cell Co-Cultivation
 The Hollow Fiber Bioreactor and Cell Co-Cultivation June 12, 2012 John J.S. Cadwell Historically, the scientific method had been based upon the reduction of complex systems to their simplest forms in order
The Hollow Fiber Bioreactor and Cell Co-Cultivation June 12, 2012 John J.S. Cadwell Historically, the scientific method had been based upon the reduction of complex systems to their simplest forms in order
2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives
 CHAPTER 15 2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives SECTION Gene Technologies and Human Applications KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: For what purposes are genes and proteins manipulated?
CHAPTER 15 2 Gene Technologies in Our Lives SECTION Gene Technologies and Human Applications KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: For what purposes are genes and proteins manipulated?
STRUCTURE-FUNCTION RELATIONSHIPS OF INTERSTITIAL TRANSPORT AND MECHANICS IN BLOOD CLOTS
 STRUCTURE-FUNCTION RELATIONSHIPS OF INTERSTITIAL TRANSPORT AND MECHANICS IN BLOOD CLOTS by Adam Wufsus A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial
STRUCTURE-FUNCTION RELATIONSHIPS OF INTERSTITIAL TRANSPORT AND MECHANICS IN BLOOD CLOTS by Adam Wufsus A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial
Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
Neutrophil support for patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy
 Appropriate dosing of NEUPOGEN in recovery of neutrophil counts in myelosuppressive regimens Neutrophil support for patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy Indication NEUPOGEN is indicated
Appropriate dosing of NEUPOGEN in recovery of neutrophil counts in myelosuppressive regimens Neutrophil support for patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy Indication NEUPOGEN is indicated
