Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
|
|
|
- Henry Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the same functional pathway (leading to a particular phenotype), or physical interactions, in which there is direct physical contact between two proteins (or between protein and DNA). 2. Complementation groups Using forward saturation genetics, you may recover several independent mutants with the same (or similar) phenotype. There are two possibilities: a) mutations are in the same gene b) mutations are in different genes involved in the same pathway. Scenario (b) can be tested genetically with a complementation test: - Cross two homozygous mutants and observe heterozygous offspring phenotypes - Mutations in the same gene will not complement -> offspring have mutant phenotype - Mutations in different genes will complement -> offspring have wild-type phenotype - Do pairwise crosses for all mutants to identify complementation groups - Typically each complementation group represents a different gene - If many mutations are recovered in the same genes, this implies saturation 3. Modifier screens This is a way to find new genes involved in the pathway leading to a mutant phenotype. It can also identify epistatic interactions. Forward saturation mutagenesis is performed in the background of a particular mutant phenotype, then new mutants that alter the phenotype of the original mutant are identified. Types of mutations that can be uncovered: Back mutations a second mutation in the same gene that corrects the previous mutation and restores phenotype to wild-type. This is rare; modifying mutations are typically in other genes. Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme Example: Drosophila Bar eye. The Bar mutation in Drosophila causes flies to have narrow eyes that are shaped like a bar. Enhancer of Bar mutations cause the eyes to be even narrower, while suppressor of Bar mutations cause the eye to be wider and more like wildtype. Epistasis = interactions between genes (non-additive). A mutation in one gene allows a mutation in a second gene to be revealed. The double mutant has a unique phenotype or one more extreme than expected from the two single mutations. Example: Drosophila eye color. Drosophila eyes contain two color pigments, brown and red. When both are present, the eyes are dark red (wild-type). The vermilion mutation prevents production of the brown pigment, resulting in eyes that are bright red. The brown mutation 1
2 prevents production of the red pigment, resulting in eyes that are brown. When both pigments are missing, the eyes are white. Example: synthetic lethals. Two mutations are viable individually, but lethal in combination. This has been extensively studied in yeast and is thought to be caused by redundancy of function of some genes. In yeast, over 80% of the 6200 predicted genes are non-essential when knocked out individually. Large-scale array crosses of each single knockout to every other knockout can reveal interactions through synthetic lethals, however there are 20 million pairwise combinations. A large-scale screen for genetic interactions in yeast was carried out in This covered not only synthetic lethals, but also interactions that were not lethal, but affected growth in combination. About 170,000 interactions were identified. Interacting genes tended to be of similar biological processes and formed coherent clusters. See: Costanzo et al. (2010) The genetic landscape of a cell. Science 327: Protein interactions The above classical genetics methods identify genes that interact in the generation of a particular phenotype, but the genes or their protein products may not physically interact with each other. Some possibilities are that the mutations affect: a) different steps in same enzymatic pathway b) steps in different enzymatic pathways, the products of each required for phenotype c) cis or trans acting factors in gene expression d) different components of a signal transduction pathway e) different peptides that physically interact with each other f) many more possibilities Many of the above types of interactions are difficult to test on a large, genomic scale. Probably the most progress has been made in the detection of (e), protein-protein interactions. Some approaches: Affinity chromatography purify a target protein by passing through a chromatography column. Then see what other proteins come out with the target. This approaches detects direct or indirect interactions (protein complexes). Some methods: - Co-immunoprecipitation: requires that specific antibodies to the target protein be linked to the column. This causes the target protein (and all proteins bound to it) to be retained in the column. - Biotin-affinity chromatography: biotin is chemically linked to the target protein. The column contains the protein streptavidin, which has a very high binding affinity for biotin. Thus, the target protein (and all proteins bound to it) is retained in the column. This method is good for large-scale applications; commercial streptavidin columns are available. - GST-fusion chromatography a recombinant DNA encoding the target protein is joined to DNA encoding GST (glutathione S-transferase). The resulting fusion protein is run through a column containing glutathione. The strong binding between GST and glutathione causes the 2
3 target protein (and all proteins bound to it) to be retained in the column. An advantage of this method is that one does not need to start with purified target protein, only the gene encoding it. This method is good for large-scale applications; commercial glutathione columns are available. - Direct purification this approach typically requires much work to purify individual protein complexes by chromatography or sedimentation. An advantage is that you don t have to start with a particular target protein. Yeast 2-hybrid screen this method detects direct protein-protein interactions. cdna libraries are used to make fusions of bait and prey proteins to the DNA-binding domain (BD) and activator domain (AD) of a transcriptional activator. The recombinant proteins are expressed in yeast. If there is a bait-prey interaction, transcription of a reporter gene will be induced. Note that, although the assay is performed in yeast, it can be used to detect interactions between proteins from any organism. False positives bait alone activates transcription due to chance interactions False negatives normally interacting proteins change structure when fused to bait or prey and no longer interact Can be used to make protein interaction maps. Examples: YEAST See Uetz et al. (2000) Nature 403: Yeast has about 6000 genes. Pairwise comparisons = n(n-1)/2 18 million Yeast-2-hybrid (Y2H) method with two approaches: i) Array Screening a) Fused 6000 ORFs to activator domain (Prey) and transformed them into separate yeast cells. Grew cells in 384-well plates. b) Fused 192 (half of 384) ORFs to DNA binding domain (Bait). Added each separately to the 6000 Prey cells. 192 x 6000 > 1 million interaction tests. Look for positives (cells expressing His3 gene, which allows them to grow on media lacking histidine). c) Independently repeat the experiment. Consider only interactions identified in both replicates to be real. d) 87 of the 192 had 1 or more interaction. Total = 281 interacting pairs. ii) Library Screening a) 6000 Prey cells pooled together and pools grown in 96-well plates b) Same 6000 ORFs fused to DNA binding domain (Bait). Each separately added to the pooled Prey cells. c) Cells expressing reporter gene selected and Prey sequenced. 3
4 d) 817 ORFs had 1 or more interaction. Total = 692 discrete interacting pairs (472 identified two or more times. Comparison Array method produced a higher percentage of interactions (87/192 = 45% vs. 817/6000 = 14%), but library method had much higher throughput. DROSOPHILA See Giot et al. (2003) Science 302: Drosophila has about 14,000 genes 100 million pairwise comparisons. Used Y2H with two library screening methods: i) cdna Screen a) Designed primers to 14,000 predicted ORFs, amplified from cdna and cloned into Bait fusion vector b) Cloned random cdnas into Prey vectors. c) Tested every Bait with random cdna library Prey. Sequence Prey that gives reporter gene expression. d) 5,200 ORFs had 1 or more interaction. Total = 10,782 interactions. High confidence, non-self = 1,344 ORFs. Total = 1,673 interactions. ii) Collection Screen a) Cloned 14,000 ORFs into both Bait and Prey vectors b) Each Bait was added to pooled Prey cells. c) Cells expressing reporter gene selected and Prey sequenced. d) 4,500 ORFs had 1 or more interaction. Total = 10,021 interactions. High confidence, non-self = 3,402 ORFs. Total = 3,319 interactions. Combined Total 7,048 ORFs had 1 or more interaction. Total = 20,405 interactions. High confidence, non-self = 4,655 ORFs. Total = 4,677 interactions. Only high confidence interactions used to make a protein interaction map. Limitations of Y2H Autoactivation. Some Baits may activate transcription by themselves. Some Baits or Preys may be lethal when expressed in yeast. Only detects direct, pairwise protein-protein interactions. Some complexes may require 3 or more proteins. Does not detect protein-dna or protein-rna interactions. 4
5 Interaction in yeast does not guarantee interaction in other cell/organism (proteins can only interact if they are expressed at same place/time). Fusion of proteins (Bait-binding domain or Prey-Activator domain) may alter protein structure/function. 5. Protein microarrays - proteins can be purified and immobilized on glass slides in a manner similar to DNA microarrays. The arrays can then be used to test for protein or small-molecule binding. Typically, many different proteins are placed on an array, but only a single antibody, protein, protein co-factor, small molecule, etc. is used as a target for hybridization to the array. This approach can identify proteins that interact with the target. Some problems with protein microarrays: unlike with DNA arrays, where it is relatively easy to do PCR or synthesize oligonucleotides on a large scale, it is difficult to produce large amounts of purified proteins to put on arrays. Do the proteins maintain their structure/function after attaching them to the array? Typically they need to be kept hydrated and cannot be dried and stored like DNA arrays. 6. 2D-PAGE (two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) Total proteins are separated by charge (isoelectric point), then by size on an acrylamide gel. The proteins are stained with a general silver or fluorescent stain. The result is a complex pattern of 1000 s of spots that is semi-quantitative. Good for head-to-head comparison of two samples, such as control vs. treatment or human vs. chimpanzee. Quantitative change = size of spot (amount of protein) Qualitative change = location of spot (size or charge of protein) 5
27041, Week 02. Review of Week 01
 27041, Week 02 Review of Week 01 The human genome sequencing project (HGP) 2 CBS, Department of Systems Biology Systems Biology and emergent properties 3 CBS, Department of Systems Biology Different model
27041, Week 02 Review of Week 01 The human genome sequencing project (HGP) 2 CBS, Department of Systems Biology Systems Biology and emergent properties 3 CBS, Department of Systems Biology Different model
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH TECHNIQUES IN CELL BIOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LIGHT MICROSCOPE A light microscope uses light waves and magnification to view specimens Can be used to visualize transparent, and some cellular components - Can visualize
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LIGHT MICROSCOPE A light microscope uses light waves and magnification to view specimens Can be used to visualize transparent, and some cellular components - Can visualize
Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III
 Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand full of genes.
Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand full of genes.
Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ
 Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Genome Biology and Biotechnology
 Genome Biology and Biotechnology 10. The proteome Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
Genome Biology and Biotechnology 10. The proteome Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
Design. Construction. Characterization
 Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
[Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale]
![[Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale]](/thumbs/96/128035026.jpg) Mutational Dissection [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] Introduction What is the point of Mutational Dissection? It allows understanding of normal biological functions
Mutational Dissection [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] Introduction What is the point of Mutational Dissection? It allows understanding of normal biological functions
Motivation From Protein to Gene
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
Yeast 2-Hybrid Kayla Nygaard
 Yeast 2-Hybrid 2.26.18 Kayla Nygaard Y2H - What is it? A method to screen for protein-protein interactions in yeast Capitalizes on GAL4 system in yeast. GAL4 has 2 domains DNA-Binding Domain (DB) Transcriptional
Yeast 2-Hybrid 2.26.18 Kayla Nygaard Y2H - What is it? A method to screen for protein-protein interactions in yeast Capitalizes on GAL4 system in yeast. GAL4 has 2 domains DNA-Binding Domain (DB) Transcriptional
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks. Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger
 Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger This Lecture Protein-protein interactions Characteristics Experimental detection methods Databases Biological networks Ulf Leser: Introduction
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger This Lecture Protein-protein interactions Characteristics Experimental detection methods Databases Biological networks Ulf Leser: Introduction
Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis. Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada
 Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada Community website: The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) at http://www.arabidopsis.org Can order
Experimental Tools and Resources Available in Arabidopsis Manish Raizada, University of Guelph, Canada Community website: The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) at http://www.arabidopsis.org Can order
7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV
 1 Fall 2006 7.03 7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that
1 Fall 2006 7.03 7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that
7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV
 7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand
7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand
11/22/13. Proteomics, functional genomics, and systems biology. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 11
 Proteomics, functional genomics, and systems biology Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 11 1 Figure 6.1 The future of genomics Functional Genomics The field of functional genomics represents the
Proteomics, functional genomics, and systems biology Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 11 1 Figure 6.1 The future of genomics Functional Genomics The field of functional genomics represents the
Genome Analysis. Bacterial genome projects
 Genome Analysis Bacterial Genome sequencing does this help us in the investigation of adaptive responses/regulatory systems? Genome Sequencing Projects strategy & methods annotation Comparative genomics
Genome Analysis Bacterial Genome sequencing does this help us in the investigation of adaptive responses/regulatory systems? Genome Sequencing Projects strategy & methods annotation Comparative genomics
Gene expression analysis. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5. Gene expression analysis
 Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Selected Techniques Part I
 1 Selected Techniques Part I Gel Electrophoresis Can be both qualitative and quantitative Qualitative About what size is the fragment? How many fragments are present? Is there in insert or not? Quantitative
1 Selected Techniques Part I Gel Electrophoresis Can be both qualitative and quantitative Qualitative About what size is the fragment? How many fragments are present? Is there in insert or not? Quantitative
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES
 MODULE 4 LECTURE 5 SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES 4-5.1. Introduction Library screening is the process of identification of the clones carrying the gene of interest. Screening relies on a
MODULE 4 LECTURE 5 SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES 4-5.1. Introduction Library screening is the process of identification of the clones carrying the gene of interest. Screening relies on a
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology
 CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
CH 8: Recombinant DNA Technology Biotechnology the use of microorganisms to make practical products Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources What is Recombinant DNA Technology? modifying genomes
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks. Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger
 Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger This Lecture Protein-protein interactions Characteristics Experimental detection methods Databases Protein-protein interaction networks Ulf
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger This Lecture Protein-protein interactions Characteristics Experimental detection methods Databases Protein-protein interaction networks Ulf
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
NPTEL VIDEO COURSE PROTEOMICS PROF. SANJEEVA SRIVASTAVA
 LECTURE-26 Interactomics: Yeast two-hybrid immunoprecipitation protein microarrays TRANSCRIPT Welcome to the proteomics course. Today we will talk about interactomics, which is studying interactions of
LECTURE-26 Interactomics: Yeast two-hybrid immunoprecipitation protein microarrays TRANSCRIPT Welcome to the proteomics course. Today we will talk about interactomics, which is studying interactions of
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
Introduction to Microarray Analysis
 Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
 CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
Genome Biology and Biotechnology
 Genome Biology and Biotechnology Functional Genomics Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
Genome Biology and Biotechnology Functional Genomics Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
Recent technology allow production of microarrays composed of 70-mers (essentially a hybrid of the two techniques)
 Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Computing with large data sets
 Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 14 (week 8): genomics 1 Central dogma Gene expression DNA RNA Protein v22.0480: computing with data, Richard Bonneau Lecture 14 places
Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 14 (week 8): genomics 1 Central dogma Gene expression DNA RNA Protein v22.0480: computing with data, Richard Bonneau Lecture 14 places
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.15 GENOMES AND GENOMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
12/11/12. Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava. IIT Bombay 2. Interactomics Yeast Two-Hybrid Immunoprecipitation Protein microarrays. Proteomics Course NPTEL
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Interactomics Yeast Two-Hybrid Immunoprecipitation Protein microarrays IIT Bombay 2 1 IIT Bombay Tremendous effect of interactions IIT Bombay 4 2 Complex formation Protein
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Interactomics Yeast Two-Hybrid Immunoprecipitation Protein microarrays IIT Bombay 2 1 IIT Bombay Tremendous effect of interactions IIT Bombay 4 2 Complex formation Protein
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques
 Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II
 Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II High-throughput RNAi screens High-throughput insertional/chemical screens Homologous recombination (yeast and mouse) - Other methods in discerning gene function Activation
Lecture 15: Functional Genomics II High-throughput RNAi screens High-throughput insertional/chemical screens Homologous recombination (yeast and mouse) - Other methods in discerning gene function Activation
Bi 8 Lecture 4. Ellen Rothenberg 14 January Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8
 Bi 8 Lecture 4 DNA approaches: How we know what we know Ellen Rothenberg 14 January 2016 Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8 Central concept: DNA or RNA polymer length as an identifying feature RNA has intrinsically
Bi 8 Lecture 4 DNA approaches: How we know what we know Ellen Rothenberg 14 January 2016 Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8 Central concept: DNA or RNA polymer length as an identifying feature RNA has intrinsically
4 Mutant Hunts - To Select or to Screen (Perhaps Even by Brute Force)
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 4 Mutant Hunts - To Select or to Screen
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 4 Mutant Hunts - To Select or to Screen
Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology
 3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology Scientists have discovered that one of the differences between healthy and cancer is which genes are turned on in each. Scientists can compare the gene expression patterns
3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology Scientists have discovered that one of the differences between healthy and cancer is which genes are turned on in each. Scientists can compare the gene expression patterns
Fatchiyah
 Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Proteomics. Manickam Sugumaran. Department of Biology University of Massachusetts Boston, MA 02125
 Proteomics Manickam Sugumaran Department of Biology University of Massachusetts Boston, MA 02125 Genomic studies produced more than 75,000 potential gene sequence targets. (The number may be even higher
Proteomics Manickam Sugumaran Department of Biology University of Massachusetts Boston, MA 02125 Genomic studies produced more than 75,000 potential gene sequence targets. (The number may be even higher
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
CAP BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE. 10/5/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1
 CAP 5510-9 BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 10/5/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Basic BioTech Processes Hybridization PCR Southern blotting (spot or stain) 10/5/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 10/5/2005 Su-Shing
CAP 5510-9 BIOINFORMATICS Su-Shing Chen CISE 10/5/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Basic BioTech Processes Hybridization PCR Southern blotting (spot or stain) 10/5/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 10/5/2005 Su-Shing
Kinetics Review. Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets)
 Quiz 1 Kinetics Review Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets) I will post the problems with solutions on Toolkit for those that can t make
Quiz 1 Kinetics Review Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets) I will post the problems with solutions on Toolkit for those that can t make
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish
 Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
Who, When, and Where. Section Days & Times
 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Who, When, and Where Section 01 02 Days & Times Professors Teaching Assistants Laboratory Coordinator M 12:20 4:25 pm W 1:25 4:25 pm Sam Hazen Assistant Professor, Biology 409A Morrill
1 GENERAL INFORMATION Who, When, and Where Section 01 02 Days & Times Professors Teaching Assistants Laboratory Coordinator M 12:20 4:25 pm W 1:25 4:25 pm Sam Hazen Assistant Professor, Biology 409A Morrill
BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY
 BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY 1. Variation in tail length is characteristic of some dog breeds, such as Pembroke Welsh Corgis, which sometimes show a bob tail (short tail) phenotype (see illustration
BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY 1. Variation in tail length is characteristic of some dog breeds, such as Pembroke Welsh Corgis, which sometimes show a bob tail (short tail) phenotype (see illustration
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Lecture 25 (11/15/17)
 Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr.
 MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
Technical tips Session 5
 Technical tips Session 5 Chromatine Immunoprecipitation (ChIP): This is a powerful in vivo method to quantitate interaction of proteins associated with specific regions of the genome. It involves the immunoprecipitation
Technical tips Session 5 Chromatine Immunoprecipitation (ChIP): This is a powerful in vivo method to quantitate interaction of proteins associated with specific regions of the genome. It involves the immunoprecipitation
Technical tips Session 4
 Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing. Outline
 XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
XXII DNA cloning and sequencing 1) Deriving DNA for cloning Outline 2) Vectors; forming recombinant DNA; cloning DNA; and screening for clones containing recombinant DNA [replica plating and autoradiography;
The Two-Hybrid System
 Encyclopedic Reference of Genomics and Proteomics in Molecular Medicine The Two-Hybrid System Carolina Vollert & Peter Uetz Institut für Genetik Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe PO Box 3640 D-76021 Karlsruhe
Encyclopedic Reference of Genomics and Proteomics in Molecular Medicine The Two-Hybrid System Carolina Vollert & Peter Uetz Institut für Genetik Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe PO Box 3640 D-76021 Karlsruhe
7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Contents... vii. List of Figures... xii. List of Tables... xiv. Abbreviatons... xv. Summary... xvii. 1. Introduction In vitro evolution...
 vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
Experimental Techniques 2
 Experimental Techniques 2 High-throughput interaction detection Yeast two-hybrid - pairwise organisms as machines to learn about organisms yeast, worm, fly, human,... low intersection between repeated
Experimental Techniques 2 High-throughput interaction detection Yeast two-hybrid - pairwise organisms as machines to learn about organisms yeast, worm, fly, human,... low intersection between repeated
Parallel analysis of translated ORF (PLATO)
 Parallel analysis of translated ORF (PLATO) Technical Journal Club 16.04.2013 Mary-Aude Rochat, PhD student Speck group Proteomics Rationale: Increase in the DNA sequence information Understand biological
Parallel analysis of translated ORF (PLATO) Technical Journal Club 16.04.2013 Mary-Aude Rochat, PhD student Speck group Proteomics Rationale: Increase in the DNA sequence information Understand biological
12 Interaction of Genes
 12 Interaction of Genes Yeast genetics has been particularly amenable for identifying and characterizing gene products that directly or indirectly interact with each other, especially when two mutations
12 Interaction of Genes Yeast genetics has been particularly amenable for identifying and characterizing gene products that directly or indirectly interact with each other, especially when two mutations
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks. Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger
 Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger SHK Stelle frei Ab 1.9.2015, 2 Jahre, 41h/Monat Verbundprojekt MaptTorNet: Pankreatische endokrine Tumore Insb. statistische Aufbereitung und
Protein-Protein-Interaction Networks Ulf Leser, Samira Jaeger SHK Stelle frei Ab 1.9.2015, 2 Jahre, 41h/Monat Verbundprojekt MaptTorNet: Pankreatische endokrine Tumore Insb. statistische Aufbereitung und
3. human genomics clone genes associated with genetic disorders. 4. many projects generate ordered clones that cover genome
 Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lectures 30 and 31 Genome analysis I. Genome analysis A. two general areas 1. structural 2. functional B. genome projects a status report 1. 1 st sequenced: several viral genomes 2. mitochondria and chloroplasts
Supplemental Data. Cui et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc a b c d. Stem UBC32 ACTIN
 A Root Stem Leaf Flower Silique Senescence leaf B a b c d UBC32 ACTIN C * Supplemental Figure 1. Expression Pattern and Protein Sequence of UBC32 Homologues in Yeast, Human, and Arabidopsis. (A) Expression
A Root Stem Leaf Flower Silique Senescence leaf B a b c d UBC32 ACTIN C * Supplemental Figure 1. Expression Pattern and Protein Sequence of UBC32 Homologues in Yeast, Human, and Arabidopsis. (A) Expression
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
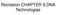 Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
A) (5 points) As the starting step isolate genomic DNA from
 GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
Applicazioni biotecnologiche
 Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
AD BD TOC1. Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between
 AD X BD TOC1 AD BD X PIFΔAD PIF TOC1 TOC1 PIFΔAD PIF N TOC1 TOC1 C1 PIFΔAD PIF C1 TOC1 TOC1 C PIFΔAD PIF C TOC1 Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between PIF and TOC1
AD X BD TOC1 AD BD X PIFΔAD PIF TOC1 TOC1 PIFΔAD PIF N TOC1 TOC1 C1 PIFΔAD PIF C1 TOC1 TOC1 C PIFΔAD PIF C TOC1 Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between PIF and TOC1
Lecture 8: Affinity Chromatography-III
 Lecture 8: Affinity Chromatography-III Key words: Chromatography; Affinity chromatography; Protein Purification During this lecture, we shall be studying few more examples of affinity chromatography. The
Lecture 8: Affinity Chromatography-III Key words: Chromatography; Affinity chromatography; Protein Purification During this lecture, we shall be studying few more examples of affinity chromatography. The
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Supplemental Figure 1. Immunoblot analysis of wild-type and mutant forms of JAZ3
 Supplemental Data. Chung and Howe (2009). A Critical Role for the TIFY Motif in Repression of Jasmonate Signaling by a Stabilized Splice Variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis.
Supplemental Data. Chung and Howe (2009). A Critical Role for the TIFY Motif in Repression of Jasmonate Signaling by a Stabilized Splice Variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis.
DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3. GUS activity. Time h (ZT) Cluster 1. Cluster 2 Cluster 3. Cluster 4. Cluster 5. Cluster 6
 Supplemental Data. Giraud et al. (21). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.11.74518 A) B) 6 5 4 3 2 1 DAY 1 2 15 1 5 IP SITE II DAY 2 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 IP SITE II DAY 3 IP SITE II ealtive transcript abundance 12 1 75 5 25
Supplemental Data. Giraud et al. (21). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.11.74518 A) B) 6 5 4 3 2 1 DAY 1 2 15 1 5 IP SITE II DAY 2 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 IP SITE II DAY 3 IP SITE II ealtive transcript abundance 12 1 75 5 25
VOLUME 2. Molecular Clonin g A LABORATORY MANUA L THIRD EDITIO N. Joseph Sambrook. David W. Russell
 VOLUME 2 Molecular Clonin g A LABORATORY MANUA L THIRD EDITIO N Joseph Sambrook David W. Russell Chapter 8 In Vitro Amplification of DNA by the Polymerase 8. 1 Chain Reaction 1 The Basic Polymerase Chain
VOLUME 2 Molecular Clonin g A LABORATORY MANUA L THIRD EDITIO N Joseph Sambrook David W. Russell Chapter 8 In Vitro Amplification of DNA by the Polymerase 8. 1 Chain Reaction 1 The Basic Polymerase Chain
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Supplemental Data. Benstein et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Purification of the heterologously expressed PGDH1, PGDH2 and PGDH3 enzymes by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. Protein extracts (2 µl) of different fractions (lane 1 = total extract,
Supplemental Figure 1. Purification of the heterologously expressed PGDH1, PGDH2 and PGDH3 enzymes by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. Protein extracts (2 µl) of different fractions (lane 1 = total extract,
(i) A trp1 mutant cell took up a plasmid containing the wild type TRP1 gene, which allowed that cell to multiply and form a colony
 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Supplemental Data. Hu et al. Plant Cell (2017) /tpc
 1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Gene expression. What is gene expression?
 Gene expression What is gene expression? Methods for measuring a single gene. Northern Blots Reporter genes Quantitative RT-PCR Operons, regulons, and stimulons. DNA microarrays. Expression profiling Identifying
Gene expression What is gene expression? Methods for measuring a single gene. Northern Blots Reporter genes Quantitative RT-PCR Operons, regulons, and stimulons. DNA microarrays. Expression profiling Identifying
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Value Correct Answer Feedback. Student Response. A. Dicer enzyme. complex. C. the Dicer-RISC complex D. none of the above
 1 RNA mediated interference is a post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism Which component of the RNAi pathway have been implicated in cleavage of the target mrna? A Dicer enzyme B the RISC-siRNA complex
1 RNA mediated interference is a post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism Which component of the RNAi pathway have been implicated in cleavage of the target mrna? A Dicer enzyme B the RISC-siRNA complex
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5. Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology -
 Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Genetics and Biotechnology. Section 1. Applied Genetics
 Section 1 Applied Genetics Selective Breeding! The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations is called selective breeding. Section
Section 1 Applied Genetics Selective Breeding! The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations is called selective breeding. Section
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics. If we can, should we?
 Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
1a. What is the ratio of feathered to unfeathered shanks in the offspring of the above cross?
 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
LARGE-SCALE PROTEIN INTERACTOMICS. Karl Frontzek Institute of Neuropathology
 LARGE-SCALE PROTEIN INTERACTOMICS Karl Frontzek Institute of Neuropathology STUDYING THE INTERACTOME A yeast 2 hybrid (DB: DNA binding domain, AD: activation domain) B tandem affinity purification (dashed
LARGE-SCALE PROTEIN INTERACTOMICS Karl Frontzek Institute of Neuropathology STUDYING THE INTERACTOME A yeast 2 hybrid (DB: DNA binding domain, AD: activation domain) B tandem affinity purification (dashed
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
Methods for Working with DNA and RNA
 Methods for Working with DNA and RNA 1. Gel electrophoresis A. Materials: agarose (large DNAs) vs. acrylamide (high resolution, DNA sequencing) B. Separated by its sieving property and charge: both are
Methods for Working with DNA and RNA 1. Gel electrophoresis A. Materials: agarose (large DNAs) vs. acrylamide (high resolution, DNA sequencing) B. Separated by its sieving property and charge: both are
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
BSCI410-Liu/Spring 06 Exam #1 Feb. 23, 06
 Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Analysis of gene function
 Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
SGN-6106 Computational Systems Biology I
 SGN-6106 Computational Systems Biology I A View of Modern Measurement Systems in Cell Biology Kaisa-Leena Taattola 21.2.2007 1 The cell a complex system (Source: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 4th
SGN-6106 Computational Systems Biology I A View of Modern Measurement Systems in Cell Biology Kaisa-Leena Taattola 21.2.2007 1 The cell a complex system (Source: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 4th
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.20 - BIOTECHNOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
BIOINF/BENG/BIMM/CHEM/CSE 184: Computational Molecular Biology. Lecture 2: Microarray analysis
 BIOINF/BENG/BIMM/CHEM/CSE 184: Computational Molecular Biology Lecture 2: Microarray analysis Genome wide measurement of gene transcription using DNA microarray Bruce Alberts, et al., Molecular Biology
BIOINF/BENG/BIMM/CHEM/CSE 184: Computational Molecular Biology Lecture 2: Microarray analysis Genome wide measurement of gene transcription using DNA microarray Bruce Alberts, et al., Molecular Biology
Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes
 Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
