Online Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Coral Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Online Supplementary Information NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting TBK1 for degradation via E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 Jun Cui 1,4,6,7, Yinyin Li 1,5,6,7, Liang Zhu 1, Dan Liu 3, Zhou Songyang 3, Helen Y. Wang 1,6 and Rong-Fu Wang 1,2,6* 1 The Center for Cell and Gene Therapy, 2 Departments of Pathology and Immunology, 3 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas 77030, USA. 4 State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Department of Biochemistry, Nanjing University, Nanjing China. 5 Institute of Biosciences and Technology, Texas A&M University Health Science Center, Houston, TX USA. 6 Center for Inflammation and Epigenetics, The Methodist Hospital Research Institute, Houston, TX 77030, USA 7 These authors contributed equally to this work. *Correspondence: rongfuw@bcm.edu, rwang3@tmhs.org Content Supplementary Figures S1-S14 Supplementary Methods - 1 -
2 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of NLRP4 in tissues and cell lines. (a) Human NLRP4 mrna levels in different tissues were determined by real-time PCR analysis. (b) Immunoblot analysis of human NLRP4 expression in the indicated cell lines or primary cells. Mouse RAW264.7 cells served as a negative control. The relative protein level of NLRP4 was quantified by band density scanning of immunoblot images. Results are representative of three independent experiments
3 Supplementary Figure 2. Knockdown of NLRP4 by NLRP4- specific shrnas and sirnas. (a) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged NLRP4 and indicated shrnas for 48 h. Knockdown efficiency was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-flag antibody. (b) 293T cells were transfected with indicated shrnas for 48 h. Total RNA was collected for real-time-pcr analysis. Ctrl, control. (c) THP-1 cells were transfected NLRP4-specific sirna or scrambled (scr) sirna for 48 h, and total RNA was collected for real-time-pcr analysis. Data from (b-c) are plotted as means ± s.d. All experiments were performed at least in three independent experiments. * P <0.001, versus controls
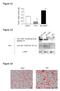
4 Supplementary Figure 3. NLRP4 inhibits STING-induced type I IFN signaling. 293T cells were transfected with IFN-β-luc or ISRE-luc, together with STING, along with NLRP4 or empty vector and analyzed for IFN-β-luc and ISRE-luc activity. Data is plotted as means ± s.d. All experiments were performed at least in three independent experiments. * P <0.01, ** P<0.001, versus controls
5 Supplementary Figure 4. NLRP4 mouse homologs inhibit TBK1-induced ISRE activity and induce TBK1 degradation. (a) The expression levels of Nlrp4a-g genes in MEFs and RAW264.7cells were determined by real-time PCR. Relative expression (fold) is calculated by the ratio of NLRP4 homolog mrna/gapdh mrna. (b) 293T cells were transfected with TBK1, NLRP4b or NLRP4g plasmids, along with ISRE-luc and analyzed for ISRE luciferase activity. Data from (b) are plotted as means ± s.d. * P <0.001, versus controls. (c) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-TBK1 and empty vector, HA-NLRP4, NLRP4b or NLRP4g. Cell extracts were harvested for immunoblot analysis. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments
6 Supplementary Figure T cells were transfected with an empty vector or HA-NLRP4, together with Flag-IKKα, Flag-IKKβ, Flag-TBK1 or Flag-IKKi. Cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot with the indicated antibodies. Results are representative of three independent experiments
7 Supplementary Figure 6. NLRP4 induced TBK1 degradation after VSV-eGFP infection. (a) 293T cells were transfected with different amounts of HA-NLRP4 plasmid (0, 100, 200 ng). Cell extracts were harvested for immunoblot analysis. (b) 293T cells transfected with GFP-NLRP4 or control vector were infected with VSV-eGFP for 10 h. Cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblot with indicated antibodies. Results are representative of three independent experiments
8 Supplementary Figure 7. NLRP4 can not induce the degradation of TBK1 deletion constructs. 293T cells were transfected with HA-NLRP4, Flag-TBK1 and its deletion constructs, and analyzed by immunoblotting. Results are representative of three independent experiments
9 Supplementary Figure 8. Identification of DTX4 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of TBK1. (a) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with shrna plasmids derived from a human RING domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligase shrna sub-library along with TBK1 and ISRE-luc reporter plasmid, followed by measurement of luciferase activity by a reporter assay. (b) Mapping target locations for different DTX4-specific shrna. (c) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged DTX4, DTX4-specific shrna1 or control (ctrl) shrna for 48 h. Knockdown efficiency was analyzed by immunoblot with anti-flag antibody. (d) 293T cells were transfected with indicated DTX4-specific shrnas or control (ctrl) shrna for 48 h. Total RNA was collected for real-time-pcr analysis. (e) Quantitative comparison of TBK1 protein level by density scanning of the blots in Fig 7a. Data from (d) are plotted as means ± s.d. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. * P <0.001, versus controls
10 Supplementary Figure 9. The RING domain of DTX4 is critically required for inhibition of TBK1 activity as well as interaction with NLRP4. (a) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-DTX4, HA-NLRP4 and its deletion constructs, and analyzed by coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. (b) Schematic diagram showing deletion constructs of DTX4 containing different domains. (c) 293T cells were transfected with ISRE-luc, Flag-TBK1, HA-NLRP4, with Flag-DTX4 or its deletion constructs, and analyzed for ISRE-dependent luciferase activity. (d-e) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-DTX4 and its deletion constructs, and HA-NLRP4 (d) or HA-NLRP4(Nod) (e), and analyzed by coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Data from (c) are plotted as means ± s.d. Similar results were obtained from three independent experiments. * P <0.01, ** P <0.001, versus controls
11 Supplementary Figure 10. NLRP4 mediates K48-linked ubiquitination of TBK1 in a DTX4-dependent manner. (a) 293T cells were transfected with c-myc-tbk1, HA-K48-linked ubiquity together with control vector, Flag-DTX4 alone, GFP-NLRP4 alone, or Flag-DTX4 plus GFP-NLRP4. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-myc antibody, and immunoblotted with anti-ha antibody. (b) 293T cells were transfected with c-myc-tbk1, HA-K63-linked ubiquitin together with control vector, GFP-NLRP4 alone, or Flag-DTX4 plus GFP-NLRP4. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-myc antibody, and immunoblotted with anti-ha antibody. (c-d) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-TBK1, GFP-NLRP4, HA-K48-linked ubiquitin (c) or HA-K63-linked ubiquitin (d) together with DTX4-specific shrna or control shrna. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-flag beads, and immunoblotted with anti-ha antibody. Results are representative of three independent experiments
12 Supplementary Figure T cells were transfected with HA-NLRP4 together with Flag-TBK1, Flag-MyD88 or empty vector. After immunoprecipitation with anti-ha or anti-flag beads, Flag-MyD88 or HA-NLRP4 was analyzed by immunoblot using anti-flag or anti-ha. Results are representative of three independent experiments
13 - 13 -
14 - 14 -
15 - 15 -
16 Supplementary Figure 12. NLRP4-DTX4 specifically inhibits TBK1-dependent type I IFN signaling, but not TLR9-Myd88-IRF7 signaling. (a) PBMCs or THP-1 cells were transfected with NLRP4-specific sirna, DTX4-specific sirna or scrambled (scr) sirna for 36 h, and total RNA was collected for real-time PCR analysis. (b) PBMCs were transfected with NLRP4-specific sirna, DTX4-specific sirna or scrambled (scr) sirna. After VSV-eGFP, Sendai virus (SV), ploy(da:dt) or CpG-A-DOTAP treatment, cell extracts were harvested and analyzed by immunoblot with the indicated antibodies. UT, untreated. (c) PBMCs were transfected with NLRP4-specific sirna or scrambled (scr) sirna, followed by VSV-eGFP, CpG-A-DOTAP or CpG-A treatment and total RNA was collected at different time points (0, 5, 15 h) for real-time PCR analysis. (d-f) PBMCs or THP-1 cells were transfected with NLRP4-specific sirna, DTX4-specific sirna or scrambled (scr) sirna, followed by VSV-eGFP, Sendai virus (SV), ploy(da:dt) or CpG-A-DOTAP treatment. The concentrations of IFN-α, IFN-β, IL-6 and IL-1β were determined by ELISA. NS, not significant, ND, not detected. Data from (a, c-f) are plotted as means ± s.d. All experiments were performed at least in three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, versus controls
17 Supplementary Figure 13. TBK1 ubiquitination at Lysine 670 is essential for NLRP4 mediated inhibition of type I IFN signaling. (a) Generation of TBK1 point mutations. (b) 293T cells were transfected with ISRE-luc, an empty vector or HA-NLRP4, together with Flag-TBK1 and its mutants. Cell extracts were analyzed by luciferase assay. Data from (b) are plotted as means ± s.d from three independent experiments. * P<0.01, ** P<0.001, versus controls
18 Supplementary Figure 14. Proposed model illustrating how NLRP4/DTX4 negatively regulates type I IFN signaling pathways through ubiquitination and degradation of activated TBK
19 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Molecular Cloning of Full-Length Human NLRP4 and Other Related Genes. A complete open reading frame of human NLRP4 was obtained from human PBMC cdna by RT-PCR and subsequently subcloned into pcdna-ha, pcdna-flag and pegfp-c2 vectors. The full-length and deletion domains of human NLRP4, Flag-tagged and GFP-tagged DTX4, deletion domains of TBK1 and DTX4 were generated by PCR using the following primers: NLRP4 forward primer, 5 CGATATGTTTAAACATGGACTACAAAGACGAT; NLRP4 reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGTCAGATCTCTACCCTTG; NLRP4-GFP forward primer, 5 AATTCTCGAGCGCAGCCTCTTTC; NLRP4-GFP reverse primer, 5 GGCCGAATTCTCAGATCTCTACCCT; NLRP4(PYD) forward primer, 5 GTGGTACCGCAGCCTCTTTCTTCTCT NLRP4(PYD) reverse primer, 5 CGCTCGAGTCACTGTTTCCCAGTTTCCTT NLRP4(Nod) forward primer, 5 GTGGTACCCAGCCACGTACAGTGATT NLRP4(Nod) reverse primer, 5 CCGCTCGAGTCAAAAACAGAGTTTCCTCAA NLRP4(LRR) forward primer, 5 GTGGTACCTGCTCCAGCTTGAGGAAA NLRP4(LRR) reverse primer, 5 CGCTCGAGTCAGATCTCTACCCTTGT TBK1-(1-301) forward primer, 5 CGATATGGATCCATGCAGAGCACTTCTAA TBK1-(1-301) reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGCTATTCTGCAAAAAACT TBK1-(1-383) forward primer, 5 CGATATGGATCCATGCAGAGCACTTCTAA TBK1-(1-383) reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGCTAGCTTACTACAAATA TBK1-( ) forward primer, 5 CGATATGGATCCATGCGGGAACCTCTGAATA
20 TBK1-( ) reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGCTAAAGACAGTCAACGTTG DTX4 forward primer, 5 CGATATAAGCTTGAAGTGGGCATCACCAT DTX4 reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGGTCCTTCTCCTGGGCAG DTX4-GFP forward primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGCGAAGTGGGCATCACCAT DTX4-GFP reverse primer, 5 CGATATAAGCTTTCAGTCCTTCTCCTGGGCAG DTX4-(1-301) forward primer, 5 CGATATAAGCTTGAAGTGGGCATCACCAT DTX4-(1-301) reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGTCACTCATCTGGTGGGTGCCGGA DTX4-( ) forward primer, 5 CGATATAAGCTTGACTGCATGCACCATCTGATGGAA DTX4-( ) reverse primer, 5 CGATATCTCGAGGTCCTTCTCCTGGGCAG Real-time PCR Analysis Total RNA was isolated from cells or tissues, and first-strand cdna was generated from total RNA using oligo-dt primers and reverse transcriptase II (Invitrogen). Real-time PCR was conducted with the SYBR GreenER qpcr Super Mix Universal (Invitrogen) and specific primers using the ABI Prism 7000 analyzer (Applied Biosystems). The values of the target gene expression were normalized to hgapdh. The following primers were used for real-time PCR: hnlrp4 forward primer, 5 AGAAAGGATCTCTGCATGAAGGT hnlrp4 reverse primer, 5 GCGGTCCAAATGGTCACATTC hgapdh forward primer, 5 TCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG hgapdh reverse primer, 5 GAGGGGAGATTCAGTGTGGT hisg54 forward primer, 5 GGAGGGAGAAAACTCCTTGGA
21 hisg54 reverse primer, hisg15 forward primer, hisg15 reverse primer, hisg56 forward primer, hisg56 reverse primer, 5 GGCCAGTAGGTTGCACATTGT 5 TCCTGGTGAGGAATAACAAGGG 5 GTCAGCCAGAACAGGTCGTC 5 TCAGGTCAAGGATAGTCTGGAG 5 AGGTTGTGTATTCCCACACTGTA hrantes forward primer, hrantes reverse primer, 5 ATCCTCATTGCTACTGCCCTC 5 GCCACTGGTGTAGAAATACTCC hifn-β forward primer, 5 CATTACCTGAAGGCCAAGGA; hifn-β reverse primer, 5 CAATTGTCCAGTCCCAGAGG; hdtx4 forward primer, 5 TTAAGGCAGCCGTGGTCAATG hdtx4 reverse primer, 5 CTTCAGTGGGCCTCGAATGG Knockdown of NLRP4 and DTX4 by RNA interference NLRP4-specific, DTX4-specific and control (2-scramble mix) sirna oligonucleotides, were obtained from Invitrogen and Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT). Two NLRP4-specific shrna plasmids, four DTX4-specific shrna plasmids and control shrna plasmids were obtained from Openbiosystems. They were transfected into 293T or THP-1 cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) or Nucleofector kit V respectively according to the manufacturer s instruction
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplementary Material. TRIB3 inhibits proliferation and promotes osteogenesis in hbmscs by regulating the. ERK1/2 signaling pathway
 Supplementary Material TRIB3 inhibits proliferation and promotes osteogenesis in hbmscs by regulating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway Cui Zhang 1, Fan-Fan Hong 1, Cui-Cui Wang 1, Liang Li 1, Jian-Ling Chen
Supplementary Material TRIB3 inhibits proliferation and promotes osteogenesis in hbmscs by regulating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway Cui Zhang 1, Fan-Fan Hong 1, Cui-Cui Wang 1, Liang Li 1, Jian-Ling Chen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Zranb1 gene targeting.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
Transcriptional Regulation of Pro-apoptotic Protein Kinase C-delta: Implications for Oxidative Stress-induced Neuronal Cell Death
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Transcriptional Regulation of Pro-apoptotic Protein Kinase C-delta: Implications for Oxidative Stress-induced Neuronal Cell Death Huajun Jin 1, Arthi Kanthasamy 1, Vellareddy Anantharam
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Transcriptional Regulation of Pro-apoptotic Protein Kinase C-delta: Implications for Oxidative Stress-induced Neuronal Cell Death Huajun Jin 1, Arthi Kanthasamy 1, Vellareddy Anantharam
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
GFP CCD2 GFP IP:GFP
 D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research.
 Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research. by Altogen Labs, 11200 Manchaca Road, Suite 203 Austin TX 78748 USA Tel. (512) 433-6177
Comparison of Commercial Transfection Reagents: Cell line optimized transfection kits for in vitro cancer research. by Altogen Labs, 11200 Manchaca Road, Suite 203 Austin TX 78748 USA Tel. (512) 433-6177
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon Song, Richard M. Amasino, Bosl Noh, and Yoo-Sun Noh
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MLL histone methylases regulate expression of HDLR- in presence of estrogen and control plasma cholesterol in vivo Khairul I. Ansari 1, Sahba Kasiri 1, Imran Hussain 1, Samara
Supplementary Information MLL histone methylases regulate expression of HDLR- in presence of estrogen and control plasma cholesterol in vivo Khairul I. Ansari 1, Sahba Kasiri 1, Imran Hussain 1, Samara
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplemental Information. HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form. a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates. DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response
 Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response Mehdi Morchikh, Alexandra Cribier,
Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response Mehdi Morchikh, Alexandra Cribier,
SOD1 as a Molecular Switch for Initiating the Homeostatic ER Stress Response under Zinc Deficiency
 Molecular Cell, Volume 52 Supplemental Information SOD1 as a Molecular Switch for Initiating the Homeostatic ER Stress Response under Zinc Deficiency Kengo Homma, Takao Fujisawa, Naomi Tsuburaya, Namiko
Molecular Cell, Volume 52 Supplemental Information SOD1 as a Molecular Switch for Initiating the Homeostatic ER Stress Response under Zinc Deficiency Kengo Homma, Takao Fujisawa, Naomi Tsuburaya, Namiko
IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p53 activity
 IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p5 activity H6 5 5 H58 A59 H6 H58 A59 anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα
IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-induced lung cancer with disrupted p5 activity H6 5 5 H58 A59 H6 H58 A59 anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα anti-ikkβ anti-panras anti-gapdh anti-ikkα
Contents... vii. List of Figures... xii. List of Tables... xiv. Abbreviatons... xv. Summary... xvii. 1. Introduction In vitro evolution...
 vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Liu et al. 10.1073/pnas.0901216106 SI Materials and Methods Reagents. Thioglycolate and LPS from Escherichia coli 0111:B4 were from Sigma-Aldrich. PAM3CSK4 and poly(i:c) were from
Supporting Information Liu et al. 10.1073/pnas.0901216106 SI Materials and Methods Reagents. Thioglycolate and LPS from Escherichia coli 0111:B4 were from Sigma-Aldrich. PAM3CSK4 and poly(i:c) were from
Hsp90 Regulates Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and TBK-1 Stabilization in Sendai Virus-infected Cells
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 17, 1461 1471, March 2006 Hsp90 Regulates Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and TBK-1 Stabilization in Sendai Virus-infected Cells Kai Yang, Hexin Shi, Rong
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 17, 1461 1471, March 2006 Hsp90 Regulates Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and TBK-1 Stabilization in Sendai Virus-infected Cells Kai Yang, Hexin Shi, Rong
NTM486-04, NTM174-04,
 Transfection of transformed human trabecular meshwork TM5, and primary human NTM210-05, NTM486-04, NTM174-04, and NTM153-00 cells with Metafectene Easy Adnan Dibas1A,C, Ming Jiang1A,C, Thomas Yorio1A,C.
Transfection of transformed human trabecular meshwork TM5, and primary human NTM210-05, NTM486-04, NTM174-04, and NTM153-00 cells with Metafectene Easy Adnan Dibas1A,C, Ming Jiang1A,C, Thomas Yorio1A,C.
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
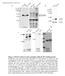 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
SANTA CRUZ BIOTECHNOLOGY, INC.
 TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
TECHNICAL SERVICE GUIDE: Western Blotting 2. What size bands were expected and what size bands were detected? 3. Was the blot blank or was a dark background or non-specific bands seen? 4. Did this same
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview
 SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
SureSilencing sirna Array Technology Overview Pathway-Focused sirna-based RNA Interference Topics to be Covered Who is SuperArray? Brief Introduction to RNA Interference Challenges Facing RNA Interference
Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami
 Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami hanialhadrami@kau.edu.sa www.hanialhadrami.kau.edu.sa Overview Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques
Reverse transcription-pcr (rt-pcr) Dr. Hani Alhadrami hanialhadrami@kau.edu.sa www.hanialhadrami.kau.edu.sa Overview Several techniques are available to detect and analyse RNA. Examples of these techniques
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
A probability-based approach for the analysis of large-scale RNAi screens
 A probability-based approach for the analysis of large-scale RNAi screens Renate König, Chih-yuan Chiang, Buu P Tu, S Frank Yan, Paul D DeJesus, Angelica Romero, Tobias Bergauer, Anthony Orth, Ute Krueger,
A probability-based approach for the analysis of large-scale RNAi screens Renate König, Chih-yuan Chiang, Buu P Tu, S Frank Yan, Paul D DeJesus, Angelica Romero, Tobias Bergauer, Anthony Orth, Ute Krueger,
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm
 Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Description of the observed lymphatic metastases in two different SIX1-induced MCF7 metastasis models (Nude and NOD/SCID). Supplementary Figure 2. MCF7-SIX1
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Description of the observed lymphatic metastases in two different SIX1-induced MCF7 metastasis models (Nude and NOD/SCID). Supplementary Figure 2. MCF7-SIX1
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5910/124/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Regulation of Neuronal Survival Factor MEF2D by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Qian Yang, Hua She, Marla Gearing, Emanuela
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5910/124/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Regulation of Neuronal Survival Factor MEF2D by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Qian Yang, Hua She, Marla Gearing, Emanuela
Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by. Regulating Occludin
 Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Occludin Chaithanya Chelakkot 1,ǂ, Jaewang Ghim 2,3,ǂ, Nirmal Rajasekaran 4, Jong-Sun Choi 5, Jung-Hwan
Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Occludin Chaithanya Chelakkot 1,ǂ, Jaewang Ghim 2,3,ǂ, Nirmal Rajasekaran 4, Jong-Sun Choi 5, Jung-Hwan
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS)
 Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS) KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS USE OF KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS - how to use Annhyb to save and manage sequences - how to use BLAST to compare sequences - how to get
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS) KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS USE OF KNOWLEDGE AND LEARNING SKILLS - how to use Annhyb to save and manage sequences - how to use BLAST to compare sequences - how to get
Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit
 Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1137999/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Disrupting the Pairing Between let-7 and Enhances Oncogenic Transformation Christine Mayr, Michael T. Hemann, David P. Bartel*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1137999/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Disrupting the Pairing Between let-7 and Enhances Oncogenic Transformation Christine Mayr, Michael T. Hemann, David P. Bartel*
Supplemental Data. LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory. and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons
 Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
Neuron, Volume 61 Supplemental Data LMO4 Controls the Balance between Excitatory and Inhibitory Spinal V2 Interneurons Kaumudi Joshi, Seunghee Lee, Bora Lee, Jae W. Lee, and Soo-Kyung Lee Supplemental
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines
 ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
Supplementary Information Design of small molecule-responsive micrornas based on structural requirements for Drosha processing
 Supplementary Information Design of small molecule-responsive micrornas based on structural requirements for Drosha processing Chase L. Beisel, Yvonne Y. Chen, Stephanie J. Culler, Kevin G. Hoff, & Christina
Supplementary Information Design of small molecule-responsive micrornas based on structural requirements for Drosha processing Chase L. Beisel, Yvonne Y. Chen, Stephanie J. Culler, Kevin G. Hoff, & Christina
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Lecture 25 (11/15/17)
 Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 9/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 9/2000 LightCycler Optimization Strategy Introduction Purpose of this Note Table of Contents The LightCycler system provides different detection formats
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 9/2000 LightCycler Optimization Strategy Introduction Purpose of this Note Table of Contents The LightCycler system provides different detection formats
pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide
 pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide NOTE: PLEASE READ THE ENTIRE PROTOCOL CAREFULLY BEFORE USE Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Vector Overview... 1 3. Vector Maps 2 4. Materials Provided...
pdsipher and pdsipher -GFP shrna Vector User s Guide NOTE: PLEASE READ THE ENTIRE PROTOCOL CAREFULLY BEFORE USE Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Vector Overview... 1 3. Vector Maps 2 4. Materials Provided...
Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Deletion of the B-B and C-C regions of inverted terminal repeats reduces raav productivity but increases transgene expression Qingzhang Zhou 1, Wenhong Tian 2, Chunguo Liu 3,
Supplementary Information Deletion of the B-B and C-C regions of inverted terminal repeats reduces raav productivity but increases transgene expression Qingzhang Zhou 1, Wenhong Tian 2, Chunguo Liu 3,
Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN SYBR Green SYBR Green is a cyanine dye that binds to double stranded DNA. When it is bound to D.S. DNA it has a much greater fluorescence than when bound to
Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN SYBR Green SYBR Green is a cyanine dye that binds to double stranded DNA. When it is bound to D.S. DNA it has a much greater fluorescence than when bound to
Yue Wang, Zhenyu Xu, Junfeng Jiang, Chen Xu, Jiuhong Kang, Lei Xiao, Minjuan Wu, Jun Xiong, Xiaocan Guo, and Houqi Liu
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Endogenous mirna Sponge lincrna-ror Regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in Human Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal Yue Wang, Zhenyu Xu, Junfeng Jiang,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Endogenous mirna Sponge lincrna-ror Regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in Human Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal Yue Wang, Zhenyu Xu, Junfeng Jiang,
Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease MTERMS 2012
 Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease MTERMS 2012 Gene Medicine Group: Oxford University Deborah Gill Steve Hyde UK Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy Consortium Edinburgh University To develop a clinical
Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease MTERMS 2012 Gene Medicine Group: Oxford University Deborah Gill Steve Hyde UK Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy Consortium Edinburgh University To develop a clinical
HCT116 SW48 Nutlin: p53
 Figure S HCT6 SW8 Nutlin: - + - + p GAPDH Figure S. Nutlin- treatment induces p protein. HCT6 and SW8 cells were left untreated or treated for 8 hr with Nutlin- ( µm) to up-regulate p. Whole cell lysates
Figure S HCT6 SW8 Nutlin: - + - + p GAPDH Figure S. Nutlin- treatment induces p protein. HCT6 and SW8 cells were left untreated or treated for 8 hr with Nutlin- ( µm) to up-regulate p. Whole cell lysates
Figure S2. Response of mouse ES cells to GSK3 inhibition. Mentioned in discussion
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 1 Supplemental Information Robust Self-Renewal of Rat Embryonic Stem Cells Requires Fine-Tuning of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition Yaoyao Chen, Kathryn Blair, and Austin
Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS
 Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS Email: ggabriely@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Outline: microrna overview microrna expression analysis microrna functional analysis microrna (mirna) Characteristics mirnas discovered
Galina Gabriely, Ph.D. BWH/HMS Email: ggabriely@rics.bwh.harvard.edu Outline: microrna overview microrna expression analysis microrna functional analysis microrna (mirna) Characteristics mirnas discovered
Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplemental Information. The TRAIL-Induced Cancer Secretome. Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Immune. Microenvironment via CCR2
 Molecular Cell, Volume 65 Supplemental Information The TRAIL-Induced Cancer Secretome Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Immune Microenvironment via CCR2 Torsten Hartwig, Antonella Montinaro, Silvia von Karstedt,
Molecular Cell, Volume 65 Supplemental Information The TRAIL-Induced Cancer Secretome Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Immune Microenvironment via CCR2 Torsten Hartwig, Antonella Montinaro, Silvia von Karstedt,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132
 Neuron, Volume 65 Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132 Dieter Edbauer, Joel R. Neilson, Kelly A. Foster, Chi-Fong Wang, Daniel P. Seeburg, Matthew
Neuron, Volume 65 Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132 Dieter Edbauer, Joel R. Neilson, Kelly A. Foster, Chi-Fong Wang, Daniel P. Seeburg, Matthew
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr.
 MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
Lentiviral shrna expression Cloning Kit User Manual for generating shrna expression lentivectors
 Lentiviral shrna expression Cloning Kit User Manual for generating s Cat# Product Name Amount Application LTSH-H1-GB peco-lenti-h1-shrna(gfp-bsd) cloning kit with GFP-Blasticidin selection LTSH-H1-GP peco-lenti-h1-shrna(gfp-puro)
Lentiviral shrna expression Cloning Kit User Manual for generating s Cat# Product Name Amount Application LTSH-H1-GB peco-lenti-h1-shrna(gfp-bsd) cloning kit with GFP-Blasticidin selection LTSH-H1-GP peco-lenti-h1-shrna(gfp-puro)
MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference
 Page 1 of 6 Page 1 of 6 Return to Web Version MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference By: Stephanie Uder, Henry George, Betsy Boedeker, LSI Volume 6 Article 2 Introduction The technology
Page 1 of 6 Page 1 of 6 Return to Web Version MISSION shrna Library: Next Generation RNA Interference By: Stephanie Uder, Henry George, Betsy Boedeker, LSI Volume 6 Article 2 Introduction The technology
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of RaPID with EDEN15
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of RaPID with EDEN15 (a) Full Western Blot of conventional biotinylated RNA pulldown with EDEN15 and scrambled control (n=3 biologically independent experiments, representative
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of RaPID with EDEN15 (a) Full Western Blot of conventional biotinylated RNA pulldown with EDEN15 and scrambled control (n=3 biologically independent experiments, representative
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
Microarrays: since we use probes we obviously must know the sequences we are looking at!
 These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Introduction to Microarray Analysis
 Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Supplementary Information
 Journal : Nature Biotechnology Supplementary Information Targeted genome engineering in human cells with RNA-guided endonucleases Seung Woo Cho, Sojung Kim, Jong Min Kim, and Jin-Soo Kim* National Creative
Journal : Nature Biotechnology Supplementary Information Targeted genome engineering in human cells with RNA-guided endonucleases Seung Woo Cho, Sojung Kim, Jong Min Kim, and Jin-Soo Kim* National Creative
A novel two-step genome editing strategy with CRISPR-Cas9 provides new insights into telomerase action and TERT gene expression
 Xi et al. Genome Biology (2015) 16:231 DOI 10.1186/s13059-015-0791-1 RESEARCH A novel two-step genome editing strategy with CRISPR-Cas9 provides new insights into telomerase action and TERT gene expression
Xi et al. Genome Biology (2015) 16:231 DOI 10.1186/s13059-015-0791-1 RESEARCH A novel two-step genome editing strategy with CRISPR-Cas9 provides new insights into telomerase action and TERT gene expression
Genome Editing: Cas9 Stable Cell Lines for CRISPR sgrna Validation, Library Screening, and More. Ed Davis, Ph.D.
 TECHNICAL NOTE Genome Editing: Cas9 Stable Cell Lines for CRISPR sgrna Validation, Library Screening, and More Introduction Ed Davis, Ph.D. The CRISPR-Cas9 system has become greatly popular for genome
TECHNICAL NOTE Genome Editing: Cas9 Stable Cell Lines for CRISPR sgrna Validation, Library Screening, and More Introduction Ed Davis, Ph.D. The CRISPR-Cas9 system has become greatly popular for genome
Supplemental Online Material. The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/-
 #1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
#1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure A Name Location Start position End position Oct4P Chr 3 29433673 29435 Annotation Mus musculus predicted gene 572 (Gm572), noncoding RNA RefSeq accession number NR_33594. Oct4P2 Chr
Supplementary Figure A Name Location Start position End position Oct4P Chr 3 29433673 29435 Annotation Mus musculus predicted gene 572 (Gm572), noncoding RNA RefSeq accession number NR_33594. Oct4P2 Chr
Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04
 Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04 Author(s): Claire Reardon Reviewers: Christian Daly Contact: claire@cgr.harvard.edu
Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04 Author(s): Claire Reardon Reviewers: Christian Daly Contact: claire@cgr.harvard.edu
Construction of plant complementation vector and generation of transgenic plants
 MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
Genome research in eukaryotes
 Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
Bronchial epithelium and its associated tissues act as a
 The Journal of Immunology A JNK-Independent Signaling Pathway Regulates TNF -Stimulated, c-jun-driven FRA-1 Protooncogene Transcription in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells 1 Pavan Adiseshaiah,* Dhananjaya V.
The Journal of Immunology A JNK-Independent Signaling Pathway Regulates TNF -Stimulated, c-jun-driven FRA-1 Protooncogene Transcription in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells 1 Pavan Adiseshaiah,* Dhananjaya V.
Nucleic Acid Research Group Study: A Follow Up on the Comparison of Different Priming Strategies for cdna synthesis by Reverse Transcriptase
 Nucleic Acid Research Group 2008-2009 Study: A Follow Up on the Comparison of Different Priming Strategies for cdna synthesis by Reverse Transcriptase NARG Survey Results for Types of Primers Used for
Nucleic Acid Research Group 2008-2009 Study: A Follow Up on the Comparison of Different Priming Strategies for cdna synthesis by Reverse Transcriptase NARG Survey Results for Types of Primers Used for
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Introduction To Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Samuel Rulli, Ph.D. Samuel.Rulli@QIAGEN.com Technical Support: BRCsupport@qiagen.com The products described in this webinar are intended for molecular
Introduction To Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Samuel Rulli, Ph.D. Samuel.Rulli@QIAGEN.com Technical Support: BRCsupport@qiagen.com The products described in this webinar are intended for molecular
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna
 Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFPHigh cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Functional characterisation
 Me Me Ac Ac Functional characterisation How can we know if measured changes in DNA methylation and function (phenotype) and linked, and in what way? DNMT Dianne Ford Professor of Molecular Nutritional
Me Me Ac Ac Functional characterisation How can we know if measured changes in DNA methylation and function (phenotype) and linked, and in what way? DNMT Dianne Ford Professor of Molecular Nutritional
Convoy TM Transfection Reagent
 Convoy TM Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.25ml (40-80 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
Convoy TM Transfection Reagent Catalog No.11103 0.25ml (40-80 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11105 0.5 ml (80-165 transfections in 35mm dishes) Catalog No.11110 1.0 ml (165-330 transfections
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Jae Myoung Suh, Daniel Zeve, Renee McKay, Jin Seo, Zack Salo, Robert Li, Michael Wang, and Jonathan M. Graff
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 6 Supplemental Data Adipose Is a Conserved, Dosage-Sensitive Antiobesity Gene Jae Myoung Suh, Daniel Zeve, Renee McKay, Jin Seo, Zack Salo, Robert Li, Michael Wang, and Jonathan
Cell Metabolism, Volume 6 Supplemental Data Adipose Is a Conserved, Dosage-Sensitive Antiobesity Gene Jae Myoung Suh, Daniel Zeve, Renee McKay, Jin Seo, Zack Salo, Robert Li, Michael Wang, and Jonathan
Bacterial DNA replication
 Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Unit 6: Molecular Genetics & DNA Technology Guided Reading Questions (100 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1240933/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Is an Innate Immune Sensor of HIV and Other Retroviruses Daxing Gao, Jiaxi Wu, You-Tong Wu, Fenghe
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1240933/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Is an Innate Immune Sensor of HIV and Other Retroviruses Daxing Gao, Jiaxi Wu, You-Tong Wu, Fenghe
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A B 50 * 40 30 20 10 0 NeurofilamentM/βactin Relative expression control D neurogenic cond. PPARγ/ Relative expression C PPARγ Hprt OilRedO adipogenic cond. control 125 * 100 75 50
Supplemental Figure 1 A B 50 * 40 30 20 10 0 NeurofilamentM/βactin Relative expression control D neurogenic cond. PPARγ/ Relative expression C PPARγ Hprt OilRedO adipogenic cond. control 125 * 100 75 50
A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells
 Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells Anna Týcová a,b, Rajen J. J. Piernikarczyk c, Michael
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) A 5 P degradation hot spot influences molecular farming of anticancerogenic nuclease TBN1 in tobacco cells Anna Týcová a,b, Rajen J. J. Piernikarczyk c, Michael
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr)
 For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA
 sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
Supplemental Information
 Molecular Cell, Volume 54 Supplemental Information BRD7, a Tumor Suppressor, Interacts with p85 and Regulates PI3K Activity Yu-Hsin Chiu, Jennifer Y. Lee, and Lewis C. Cantley Supplemental Materials Supplemental
Molecular Cell, Volume 54 Supplemental Information BRD7, a Tumor Suppressor, Interacts with p85 and Regulates PI3K Activity Yu-Hsin Chiu, Jennifer Y. Lee, and Lewis C. Cantley Supplemental Materials Supplemental
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
SideStep Lysis and Stabilization Buffer
 SideStep Lysis and Stabilization Buffer INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #400900 Revision B.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 400900-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
SideStep Lysis and Stabilization Buffer INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #400900 Revision B.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 400900-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
 Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Supplementary Figure 1: MYCER protein expressed from the transgene can enhance
 Relative luciferase activity Relative luciferase activity MYC is a critical target FBXW7 MYC Supplementary is a critical Figures target 1-7. FBXW7 Supplementary Material A E-box sequences 1 2 3 4 5 6 HSV-TK
Relative luciferase activity Relative luciferase activity MYC is a critical target FBXW7 MYC Supplementary is a critical Figures target 1-7. FBXW7 Supplementary Material A E-box sequences 1 2 3 4 5 6 HSV-TK
The lineage-defining factors T-bet and Bcl-6 collaborate to regulate Th1 gene expression patterns
 The lineage-defining factors T-bet and Bcl-6 collaborate to regulate Th1 gene expression patterns Kenneth J. Oestreich, 1 Albert C. Huang, 1,2 and Amy S. Weinmann 1,2 1 Department of Immunology and 2 Molecular
The lineage-defining factors T-bet and Bcl-6 collaborate to regulate Th1 gene expression patterns Kenneth J. Oestreich, 1 Albert C. Huang, 1,2 and Amy S. Weinmann 1,2 1 Department of Immunology and 2 Molecular
