Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
|
|
|
- Robyn Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good luck! 1. (5) Describe how the restriction-modification system works and what it is used for in bacterial cells. Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences. These sequences are also recognized by methylases, which methylate A or C residues. This methylation blocks restriction enzymes from cutting at their target sequences. Bacteria use the restriction-modification system to protect their own DNA and destroy invading phage DNA that is not methylated. 2. (3) Name three essential components of a plasmid vector. 1) Origin of replication 2) Site to insert foreign DNA (MCS) 3) Selectable marker (i.e. ampicillin resistance) 3. (2) Which of the following would be most appropriate for making a genomic library? a) pbr322 b) M13 phage c) cosmid answer - c 4. (6) α-amanatin is used at the concentrations below. For each concentration, state ALL of the RNA polymerases that will continue to function and what RNAs will be transcribed. Concentration Functional RNA polymerases RNAs transcribed 0.1µg/mL Pol I, Pol III rrna, 5SRNA/tRNA 200µg/mL Pol I rrna µg/mL Pol I, Pol II, Pol III rrna, mrna, 5SRNA/tRNA 1
2 5. (2) What happens to the C-terminal domain of RPB1, a core subunit of yeast RNA polymerase II, to stimulate transcription? It is phosphorylated. 6. (4) Pol II promoters can have up to four functional elements. Draw a generic Pol II promoter with all four elements and their positions relative to the start of transcription (+1) /-70-30/-25 upstream element TATA box Initiation downstream element region 7. (2) The typical RNA Pol I promoter contains a core element which overlaps the start of transcription and a upstream control element which lies between -156bp and -107bp upstream of the start of transcription. 8. (2) You have discovered a regulatory element within the first intron of a gene which increases the transcription rate when mutated so it is non-functional. What is the name for this type of element? Silencer/represseor/inhibitor 9. (5) Describe DNase footprint analysis and how it was used to show that TFIID binds to the TATA box. 1) Label TATA box containing promoter DNA such that only one strand is labeled 2) Incubate DNA with TFIID (experimental) or without TFIID (control) 3) Cut with dilute DNase so that you get ~1 cut/dna strand 4) Run DNA on gel to separate DNA fragments by size. 5) Postions where DNase couldn t cut due to protection by TFIID are seen as blank areas, which will be found at the position of the TATA box. 10. (2) What is the function of TAF II s at TATA-less promoters? TAF II s bind to the initiation region of to factors bound to other promoter elements so that TBP (TFIID) will be correctly positioned upstream of the start of transcription (where the TATA box is in TATA box containing genes). 2
3 11. (6) Match the following Pol II transcription factors with their function/activity. c TFIIA a) Phosphorylates Pol II d TFIIB b) Binds immediately before TFIIH b TFIIE c) Stabilizes TFIID binding e TFIIF d) Binds after TFIIA/TFIID a TFIIH e) Brings Pol II to preinitiation complexes 12. (4) Describe an experiment that shows TFIIH has helicase activity? A single strand plasmid (unlabelled) was hybridized to a labeled oligonucleotide and incubated with or without TFIIH. TFIIH unwinds the oligonucleotide with it s helicase activity. Thus when you run the TFIIH treated and untreated samples on a gel to separate by size, the sample without TFIIH will have a large labeled band representing plasmid and hybridized oligonucleotide, whereas the sample incubated with TFIIH will have a labeled band corresponding to the size of the oligonucleotide. 13. (3) Define what the parts of following acronym mean: TAF I 63. TAF TBP associated factor I Polymerase I kilodalton molecular weight 14. (4) Describe the steps involved in the initation of trna transcription including the relevant factors and promoter sequences. 1) TFIIIC binds to the internal promoter elements box a and box B 2) TFIIIC attracts TFIIIB to the upstream region where it binds 3) TFIIIB allows Pol III to bind upstream 4) Transcription begins and removes TFIIIC from the internal promoter 15. (3) TBP is associated with which transcription factors in Class I, Class II and Class III preinitiation complexes? Class I SLI Class II TFIID Class III TFIIIB 3
4 16. (3) A transcriptional activator binds to the sequence TAAGGTACCTTA as a homodimer. Which functional domains must this protein contain? 1) DNA binding domain, 2) dimerization domain, 3) activation domain 17. (4) The glucocorticoid receptor is a transcription factor that is typically found in the cytoplasm in the absence of glucocorticoid hormone. When glucocorticoid is present, describe the process by which glucocorticoid receptor activates transcription. 1) Glucocorticoid binds to the glucocorticoid receptor 2) Binding of glucocorticoid releases the hsp90 inhibitor from binding the receptor 3) The glucocorticoid receptor- glucocorticoid complex moves into the nucleus 4) The glucocorticoid receptor- glucocorticoid complex dimerizes and binds to enhancer elements to activate transcription 18. (2) Zinc fingers bind a zinc ion using two histidines amino acid residues in the alpha helix and two cysteines amino acid residues in the beta strand. 19. (4) bzip proteins contain a basic domain that uses positively charged amino acids to bind DNA, and a zipper domain consisting of alpha helices with leucines every seven amino acids which enable _interactions/dimerization_ between proteins. 20. (4) Derive the function of Gal4 in transcription activation based on the following run-off transcription experiment (i.e. What does Gal4 do and why?). Factors: D D,B B Run-off result Gal4: Incubation Wash Gal4 recruits TFIIB to the complex if Gal4 is bound first. Gal4 dependent Gal4: binding of TFIIB is also dependent Missing factors on TFIID. Incubation Run-off analysis NTPs 4
5 21. (2) A control region was deletion mapped and shown to have three enhancers: A, B and C. Enhancer binding proteins for site A and site C alone can stimulate transcription, but the protein that binds site B can not stimulate transcription. The protein that binds to site B is what type of transcription factor? The evidence is consistent with an architectural transcription factor. 22. (5) Describe the sequence of events that enable CREB to activate transcription. 1) CREB is present in the nucleus on the CRE enhancer element 2) PKA phosphorylates CREB 3) Phosphorylated CREB is bound by the mediator/co-activator CBP 4) CBP interacts with TAFII s to promote the formation of an initiation complex 5) Transcription is activated. 23. (2) The MAPK signal transduction pathway is initiated when growth factor binds to receptor. 24. (6) Match the term on the right that describes the term on the left. f Histone H3 a) formed by interactions among H1 histones e 50nm fiber b) histone octamer plus 146bp of DNA d Nucleosomes c) histone that is easily removed in low salt a Solenoids d) histone octamer, histone H1 and 200bp of DNA b Core particle e) comprised of 35kb 85kb loops c Histone H1 f) one of the core histones 25. (2) What is the function of an antirepressor? It removes nucleosomes from the promoter or prevents nucleosomes from binding. 5
6 26. (2) What assay would you use to reveal a nuclease free region in a promoter? DNAse hypersensitivity assay. 27. (5) Describe how an in vivo footprinting experiment is done and what it shows. In vivo footprinting is used to determine if nucleosomes are precisely positioned in a promoter of interest. Chromatin is treated with micrococcal nuclease at a concentration that cuts incompletely. Chromatin is then digested with restriction enzymes that bound a promoter fragment of interest. The chromatin fragments are size separated by gel electrophoresis and probed with a radioactive probe specific for you promoter region of interest. If bands are seen, that means that nucleosomes are precisely positioned within the promoter. If bands are not seen, then nucleosomes are randomly distributed along the promoter. Nucleosomes are typically precisely positioned in promoters of actively transcribed genes. 28. (4) Describe how histone acetylases function to activate transcription. They acetylate lysines on the N-terminal tails of H3 and H4, thus masking the + charges of the lysines. This masking of charge both decreases the strength of octamer binding to the DNA and decreases the interactions between nucleosomes. 29. (2) Sin3 and NcoR/SMRT are histone deacetylases that function to repress transcription. 6
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
Differential Gene Expression
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Enhancers. Activators and repressors of transcription
 Enhancers Can be >50 kb away from the gene they regulate. Can be upstream from a promoter, downstream from a promoter, within an intron, or even downstream of the final exon of a gene. Are often cell type
Enhancers Can be >50 kb away from the gene they regulate. Can be upstream from a promoter, downstream from a promoter, within an intron, or even downstream of the final exon of a gene. Are often cell type
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs. Effector Domain. Zinc Fingers. Zinc Fingers, continued. Zif268
 DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression
 Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Chapter 9-II - Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression 9.3 RNA Polymerase II Promoters and General Transcription Factors Three types of promoter sequences
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time.
 All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Synthetic cells: do bacteria need all its genes? No.
 NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Resources. This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11
 Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Transcription Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell's Biochemistry, Chapter 11 2 Definition of a gene The entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
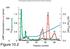 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Gene expression DNA RNA. Protein DNA. Replication. Initiation Elongation Processing Export. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Degradation.
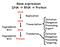 Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
- all cells express large number of the same genes - housekeeping or common genes - many cells also express cell-type-specific genes
 Developmental Biology - Biology 4361 Lecture 8 - Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 The principle of genomic equivalence states that all cells in a developing organism have the same genetic
Developmental Biology - Biology 4361 Lecture 8 - Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 The principle of genomic equivalence states that all cells in a developing organism have the same genetic
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Unit 6: Molecular Genetics & DNA Technology Guided Reading Questions (100 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Eukaryotic Gene Expression John O. Thomas I) RNA polymerases A) There are four RNA polymerases in human cells. 1) RNA polymerase I, located in the nucleolar region of the nucleus, is responsible for the
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004
 Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004 This exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions worth 2.5 points each, for a total of 100 points. Good luck. Name SS# 1. Which of the following statements
Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004 This exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions worth 2.5 points each, for a total of 100 points. Good luck. Name SS# 1. Which of the following statements
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015
 Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Eukaryotic transcription (II)
 Eukaryotic transcription (II) Transcription factors Prokaryote: Sigma factors they are similar to general transcription factor of eukaryotes, they help bring RNA pol to the promoter Transcription factors
Eukaryotic transcription (II) Transcription factors Prokaryote: Sigma factors they are similar to general transcription factor of eukaryotes, they help bring RNA pol to the promoter Transcription factors
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Prof. Michael Hampsey
 The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
The RNA Polymerase II General Transcription Machinery Michael Hampsey, PhD Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Piscataway, New Jersey 1 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA Stores genetic information
Complex Transcription Machinery
 Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Chromatin and Transcription
 Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression
 Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription
 Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
Lecture 21 Regulation of transcription Key learning goals: Understand what a promoter sequence is Understand the role of sigma factors in prokaryotic RNAP initiation Understand what an open complex is,
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
BIOLOGY 205 Midterm II - 19 February Each of the following statements are correct regarding Eukaryotic genes and genomes EXCEPT?
 BIOLOGY 205 Midterm II - 19 February 1999 Name Multiple choice questions 4 points each (Best 12 out of 13). 1. Each of the following statements are correct regarding Eukaryotic genes and genomes EXCEPT?
BIOLOGY 205 Midterm II - 19 February 1999 Name Multiple choice questions 4 points each (Best 12 out of 13). 1. Each of the following statements are correct regarding Eukaryotic genes and genomes EXCEPT?
B. Incorrect! Centromeric DNA is largely heterochromatin, which is inactive DNA.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites
 17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated February 2013)
 URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
URS AACTGT ATATTA - 35-10 transcription Pribnow Box discriminator +1 AGGAGGT TTA TCCTCCA ATT Gene C TGA TAG ACT ATC rho or GC hairpin loop transcription termination DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated
CONTENTS. LIST OF FIGURES... i. LIST OF TABLES... iii. SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi
 CONTENTS SECTION ~ LIST OF FIGURES... i LIST OF TABLES... iii LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED... ~... iv SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi 1. INTROD UCTION... :.................................... 1 1.1. AN OVERVIEW
CONTENTS SECTION ~ LIST OF FIGURES... i LIST OF TABLES... iii LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED... ~... iv SUMMARY OF THE WORK DONE... vi 1. INTROD UCTION... :.................................... 1 1.1. AN OVERVIEW
Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302. March 6, 2006
 Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302 March 6, 2006 Common structural motifs associated with transcriptional regulatory proteins Helix-turn-helix Prokaryotic repressors and activators Eukaryotic homeodomain
Gene regulation V Biochemistry 302 March 6, 2006 Common structural motifs associated with transcriptional regulatory proteins Helix-turn-helix Prokaryotic repressors and activators Eukaryotic homeodomain
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
Unit 8: Genomics Guided Reading Questions (150 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 18 The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Unit 8: Genomics Guided
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 18 The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria Unit 8: Genomics Guided
Chapter 18. Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Announcement Structure Analysis
 Announcement Structure Analysis BSC 4439/BSC 5436: Biomedical Informatics: Structure Analysis Spring 2019, CB117 Monday and Wednesday 12:00 1:15pm Office hour: Monday and Wednesday 1:15 2pm Topics include
Announcement Structure Analysis BSC 4439/BSC 5436: Biomedical Informatics: Structure Analysis Spring 2019, CB117 Monday and Wednesday 12:00 1:15pm Office hour: Monday and Wednesday 1:15 2pm Topics include
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
(c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/ :57 PM
 C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
DNA Evolution of knowledge about gene. Contains information about RNAs and proteins. Polynucleotide chains; Double stranded molecule;
 Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
Evolution of knowledge about gene G. Mendel Hereditary factors W.Johannsen, 1909 G.W.Beadle, E.L.Tatum, 1945 Ingram, 1957 Actual concepts The gene hereditary unit located in chromosomes Hypotheses One
Chapter 12 Packet DNA 1. What did Griffith conclude from his experiment? 2. Describe the process of transformation.
 Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0)
 Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0) 1. The lac operon. (PT1-5) a. Is found only in eukaryotic cells b. Codes for the sequence of amino acids in lactase c. Regulates the transcription of mrna d. Regulates transcription
Unit IIB Exam (v. 1.0) 1. The lac operon. (PT1-5) a. Is found only in eukaryotic cells b. Codes for the sequence of amino acids in lactase c. Regulates the transcription of mrna d. Regulates transcription
STSs and ESTs. Sequence-Tagged Site: short, unique sequence Expressed Sequence Tag: short, unique sequence from a coding region
 STSs and ESTs Sequence-Tagged Site: short, unique sequence Expressed Sequence Tag: short, unique sequence from a coding region 1991: 609 ESTs [Adams et al.] June 2000: 4.6 million in dbest Genome sequencing
STSs and ESTs Sequence-Tagged Site: short, unique sequence Expressed Sequence Tag: short, unique sequence from a coding region 1991: 609 ESTs [Adams et al.] June 2000: 4.6 million in dbest Genome sequencing
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs
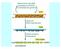 Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
مع اطيب امنيا تي لكم بالتوفيق
 Philadelphia University Faculty of Science Department of Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering Lecturer: Dr. Marwan Abu-halaweh Student Name: Student Number: Course Name: Animal Biotechnology Course Number:
Philadelphia University Faculty of Science Department of Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering Lecturer: Dr. Marwan Abu-halaweh Student Name: Student Number: Course Name: Animal Biotechnology Course Number:
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt
 BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Lecture 11. Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription. Transcription Initiation Complex
 Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact?
 Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires that Gal4-VP16 be present. Primer extension
Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires that Gal4-VP16 be present. Primer extension
Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL
 EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks
 Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
Regulatory Dynamics in Engineered Gene Networks The Physico-chemical Foundation of Transcriptional Regulation with Applications to Systems Biology Mads Kærn Boston University Center for BioDynamics Center
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators
 Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Control of Eukaryotic Genes
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Overlap with exam 1 begins
 Exam 2 begins here Overlap with exam 1 begins Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires
Exam 2 begins here Overlap with exam 1 begins Another groups asks with what does Gal4- VP16 interact? DNA attached to agarose beads Now add components in steps Ask if the recruitment of a component requires
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes. Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory
 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Why does this matter?
 Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
Problem Set 8. Answer Key
 MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
The Little Things About the Little Things Inside of Us The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression
 The Little Things About the Little Things Inside of Us The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression What Are the Characteristics of the Eukaryotic Genome? Key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic
The Little Things About the Little Things Inside of Us The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression What Are the Characteristics of the Eukaryotic Genome? Key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
DNA Bending and Wrapping around RNA Polymerase: a Revolutionary Model Describing Transcriptional Mechanisms
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1999, p. 457 478 Vol. 63, No. 2 1092-2172/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DNA Bending and Wrapping around
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 1999, p. 457 478 Vol. 63, No. 2 1092-2172/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DNA Bending and Wrapping around
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information. Chapter 3
 Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
CHapter 14. From DNA to Protein
 CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone:
 Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone: 453-6437 Email: bbartholomew@siumed.edu Class notes http://www.siumed.edu/~bbartholomew/hbtxn.html Other references Principles
Contact information Blaine Bartholomew Office: Neckers Bldg., Rm. 211 Phone: 453-6437 Email: bbartholomew@siumed.edu Class notes http://www.siumed.edu/~bbartholomew/hbtxn.html Other references Principles
