Proposed Algorithm with Standard Terminologies (SNOMED and CPT) for Automated Generation of Medical Bills for Laboratory Tests
|
|
|
- August Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Healthc Inform Res September;16(3): pissn eissn X Proposed Algorithm with Standard Terminologies (SNOMED and CPT) for Automated Generation of Medical Bills for Laboratory Tests Shine Young Kim, MD, MS 1, Hyung Hoi Kim, MD, PhD 1, In Keun Lee, PhD 2, Hwa Sun Kim, RN, PhD 2,3, Hune Cho, PhD 2,3 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine and Biomedical Informatics, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan; 2 MIPTH, Kyungpook National University, Daegu; 3 Department of Medical Informatics, College of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Deagu, Korea Objectives: In this study, we proposed an algorithm for mapping standard terminologies for the automated generation of medical bills. As the Korean and American structures of health insurance claim codes for laboratory tests are similar, we used Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) instead of the Korean health insurance code set due to the advantages of mapping in the English language. Methods: 1,149 CPT codes for laboratory tests were chosen for study. Each CPT code was divided into two parts, a Logical Observation Identifi ers Names and Codes (LOINC) matched part (matching part) and an unmatched part (unmatched part). The matching parts were assigned to LOINC axes. An ontology set was designed to express the unmatched parts, and a mapping strategy with Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT) was also proposed. Through the proceeding analysis, an algorithm for mapping CPT with SNOMED CT arranged by LOINC was developed. Results: 75% of the 1,149 CPT codes could be assigned to LOINC codes. Two hundred and twenty-five CPT codes had only one component part of LOINC, whereas others had more than two parts of LOINC. The system of LOINC axes was found in 309 CPT codes, scale 555, property 9, method 42, and time aspect 4. From the unmatched parts, three classes, types, objects, and subjects, were determined. By determining the relationship between the classes with several properties, all unmatched parts could be described. Since the subject to class was strongly connected to the six axes of LOINC, links between the matching parts and unmatched parts were made. Conclusions: The proposed method may be useful for translating CPT into concept-oriented terminology, facilitating the automated generation of medical bills, and could be adapted for the Korean health insurance claim code set. Keywords: Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine, Current Procedural Terminology, Health Insurance Received for review: September 2, 2010 Accepted for publication: September 27, 2010 Corresponding Author Hwa Sun Kim, RN, PhD Department of Medical Informatics & MIPTH, Kyungpook National University, Dongin-dong, Jung-gu, Deagu , Korea. Tel: , Fax: , pulala@paran.com This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. c 2010 The Korean Society of Medical Informatics I. Introduction Most medical billing processes are done electronically, but the manner of generating bills is still largely manual, even though the electronic medical record (EMR) and the order communication system (OCS) have been widely used. Achieving semantic interoperability not only among hospital systems (EMR, OCS, generation of bills), but also among many systems outside the hospital, requires that clinical data elements are captured in a standardized form [1]. However, several standards exist, even in areas of medical terminol-
2 Shine Young Kim et al ogy such as Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT), Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC), and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), which is used only in the US. Each standard has its own purpose and the structure fits its goals, so adoption of several standard terminologies simultaneously is inevitable. Their coverage, however, often overlaps [2-4]. For interoperable health information technology to become a reality, reference mapping among standard terminologies is necessary. SNOMED CT, LOINC, and CPT would seem to be the key terminologies for the automated generation of bills for laboratory tests in an EMR environment. Because CPT is the most widely accepted medical nomenclature used to report medical procedures and services under public and private health insurance programs, clinical data stored in SNOMED CT format should be translated to CPT for the automated generation of bills in the US. However, direct mapping between them would be difficult because SNOMED CT codes should be post-coordinated to express the CPT code and a CPT code can be expressed by numerous post-coordinated SNOMED CT code sets. The situation is similar in Korea; the only difference is the code set. If the automated generation of billing algorithms with CPT codes and other standard terminologies were possible, then it could also work with the Korean health insurance claim code set. Because the LOINC and SNOMED CT code have not been translated into Korean, CPT is more feasible for the purpose of determining the possibility of creating algorithms for automated bill generation. Therefore, we decided to first try using the CPT code. LOINC is concept-oriented terminology, and cross mapping tables exist between SNOMED CT concepts and LOINC concepts, provided by the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organization (IHTSDO) [5]. Also, the owners of SNOMED CT and LOINC have announced that they would cooperate in the generation of laboratory test terminology content [6]. Although the cross mapping table between SNOMED CT and LOINC is incomplete, the method of mapping between them can be reused to map between SNOMED CT and CPT, if the CPT codes for laboratory tests could be expressed in LOINC structure [7]. Thus our first action was to evaluate the utility of the LOINC semantic structure as a terminology model for representing CPT, by dividing CPT items into LOINC axes. Second, CPT codes for laboratory aspects have more information, which cannot be covered by LOINC, but is expressed by SNOMED CT, which has a larger coverage. We present a proposed ontology for the categorization of the area of CPT that is less covered by LOINC [8]. Finally, a proposed mapping strategy between CPT and SNOMED CT using LOINC structure is discussed. II. Methods 1. Analyzing Sentence of CPT Codes In total, 1,149 codes in the Pathology and Laboratory section (CPT code ) of CPT, except the surgical pathology, cytopathology, and anatomic pathology subsections, which are not laboratory tests, were analyzed. Two clinical laboratory medicine doctors dissected each sentence of the CPT codes, and discrepancies were discussed and mutual agreement was reached. Each part of the CPT sentence was assigned to the six LOINC axes (component, system, property, scale, time aspect, method); remaining parts of the sentence that could not be included in LOINC axes were recorded separately. 2. Assigning CPT Codes into LOINC Axes Because there are many synonyms in the CPT and LOINC codes, the individual parts of CPT were not mapped, but rather were manually assigned to one of the LOINC six axes, regardless of the presence of CPT words in the LOINC database. Component, one of the axes of LOINC, was force-assigned in all CPT codes, even in cases when CPT codes did not have a real component. For example, (CPT code), chemiluminescent assay ; this CPT code contains information only about a method, without information about component. In this case, the component was assumed to be any component available, and an annotation was attached and separately recorded for mapping with SNOMED CT (e.g., any component could be allowed was added as additional information as a subpart for SNOMED CT mapping). Rules in notes under each subsection of the CPT code book were applied to all subcodes in that subsection for assignment to LOINC axes. For example, notes in the therapeutic drug assays subsection state that examination is quantitative. Thus, we regarded all the codes under this subsection as quantitative tests and assigned them a quantitative scale (one of the LOINC axes). Another example is in the urinalysis subsection; if specific codes did not define the system (one of the LOINC axes), we deemed the system to be urine. CPT codes including words of unlisted tests in CPT were not dissected, and the full sentence was assigned to a component of LOINC if other parts existed that could match with the axes of LOINC. For example, (CPT code), Unlisted 186
3 Automated Generation of Medical Bills in Laboratory Test hematology and coagulation procedure was assigned to the component (force-assign, any component), and an annotation was recorded as a subpart for SNOMED CT mapping: any component could be allowed in the hematology and coagulation section. The following is a general example of dissecting a CPT code into the axes of LOINC: (CPT codes); Protein, total, except by refractometry: urine component; protein, total, system: urine, method: except by refractometry and annotation for SNOMED CT mapping: (method) other than refractometry. 3. Categorization of CPT Subpart for SNOMED CT Mapping Some CPT codes had extra information that could not be covered by the LOINC semantic structure including some annotations created during LOINC assign. All such information was collected, analyzed, and categorized. We created three classes for categorization of subparts for SNOMED CT mapping: types, subjects, and objects. We also defined properties to be used for specifying the meaning of sentences. The types class is defined as one of allowance or restriction and represents the general meaning of the subpart for SNOMED CT. The types class has one of the following properties: any, each, several, except for. The object class is the object of the types-class expression in the sentence. The subject class was created for presenting subparts of SNOMED CT mapping more clearly. Most subjects of collected data were concerned with the axes of LOINC, and to make definite relationships with LOINC axes and such information, the axes of LOINC were also used as key subjects. For example, the sentence, This CPT code allowed for any component (within assigned LOINC axes). can be expressed as Subjects (component) + Types (allowance, any) + Objects (component) (+ subparts of assigned LOINC axes). In this case, the subjects class is not meaningful. Here is another example: The sentence, This CPT code could be chargeable whenever each test is performed with another system. Can be expressed as Subjects (charge) + Types (allowance, each) + Objects (system). We simplified the subparts for SNOMED CT mapping with the rules described. III. Results 1. Assigning CPT Codes into LOINC Axes All of the analyzed CPT codes were forced to be assigned into a component part of LOINC, as described in the Methods. The system of LOINC axes was found in 309 CPT codes, scale 555, property 19, method 412, and time aspect 4. The scale was usually expressed in CPT codes as quantitative, qualitative, qualitative or semiquantitative, and ratio. The scale of the LOINC axes could be analogized from the properties of LOINC. For example, test results with a ratio property were assumed to be on a quantitative scale. Table Table 1. Pattern and number of CPT codes assigned with the axes of LOINC Six axes of LOINC Cases of CPT Component System Scale Property Time aspect Method codes X X 302 X 225 X X 194 X X X 112 X X X 109 X X 83 X X X 72 X X X X 29 X X 7 X X X 7 X X X X 5 X X X X 3 X X X 1 Total 1,149 CPT: Current Procedural Terminology, LOINC: Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes. Vol. 16 No. 3 September
4 Shine Young Kim et al 1 shows how the CPT codes were dissected into the six axes of LOINC. CPT codes containing component and scale only were the most common. 2. Categorization of CPT Subpart for SNOMED CT Mapping Of the 1,149 CPT codes we analyzed, 351 had additional information that did not match the axes of LOINC. We categorized the remaining sentences as described. The types class was defined as allowance or restriction. The contents (instances) of the object were determined, such as component, system, method, time, number, purpose, diagnosis, and XXX (other) in our study. We also determined the subjects class to be subject to combinations of type and object. The class of subjects was supposed to have firm instances in the six axes of LOINC and charge by definition. Table 2 presents the extracted combination of type, property, object, and subject to classes from the remaining sentences of CPT codes. All combinations of Type + Object + Subject to would be possible, at least theoretically, but those shown in Table 2 were the only combinations extracted in our study. The instance number and properties are flexible and changeable, as are combinations of them. 3. Schema for Mapping CPT with SNOMED CT SNOMED CT provides an integration table with LOINC. It contains concept identifiers from SNOMED CT that relate specific components of the LOINC test to the SNOMED CT hierarchy [9]. RelationshipType in SNOMED CT is a concept identifier (ConceptID) from the SNOMED CT concepts table and defines the relationship between the LOINC name and the target SNOMED concept. Because components of the subject to class, except charge, are the same as the six axes of LOINC, the relationship among components of the subject to class can be readily expressed by SNOMED CT RelationshipType. Then, if the relationship among types, property, and object and the relationship between charge (extracted from CPT, which is a part unmatched with LOINC) and the LOINC axes could be defined with SNOMED CT ConceptID, the sentences of CPT code could be translated into SNOMED CT without ambiguity (Figure 1). Table 2. A conceptual structured combinations of CPT sentences that were not directly dissected into LOINC axes Classes Types Objects Subjects Description No. Allowance (any) Component Component Any component would be allowed 22 Allowance (any) System System Any system would be allowed 43 Allowance (any, NOS) Component Component Any component would be allowed, not other specific 20 Allowance (each) Component Charge Charge whenever each component performed 41 Allowance (each) System Charge Charge whenever each test performed with other system 65 Allowance (each) Method Charge Charge whenever each test performed with other method 23 Allowance (each) Time Charge Charge per time 11 Allowance (several) Component Component Several component 78 Restriction (except) Component Component Other than some component 7 Restriction (except) Method Method Other than some method 12 Restriction (except) System System Other than some system 13 Restriction (for) NOS Charge Charge only when meeting XXX restriction 2 Restriction (for) System Charge Charge only when meeting restriction for system 4 Restriction (for) Number Component Restriction for component number is present 22 Restriction (for) NOS Component Other restriction for component is present 3 Restriction (for) Purpose Component Restriction for component purpose is present 21 Restriction (for) Diagnosis Component The component would not be allowed if it would not meet to 20 specific diagnosis, disease or clinical condition Restriction (for) System System Restriction for system of specific condition is present 13 Total 420 CPT: Current Procedural Terminology, LOINC: Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes
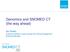
5 Automated Generation of Medical Bills in Laboratory Test Figure 1. Schema mapping CPT with SNOMED CT. CPT: Current Procedural Terminology, LOINC: Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, SNOMED CT: Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms. In this schema, the instances of parts are flexible. New instances in the property or object class did not break down the structure of the coordinated SNOMED CT codes system. We supposed that every instance (voluntarily created) of each class could be matched with SNOMED CT ConceptID or post-coordinated codes. IV. Discussion For the automated generation of bills for laboratory tests, we adapted the LOINC structure to CPT. A draft version of a mapping table between LOINC and CPT was published by the National Library of Medicine in 2006 [5]. However, it did not contain all possible matches, and it was just a mapping table, not a mapping method or algorithm. Thus, it was limited in that it could not keep up with a new version of LOINC or CPT, which is why we developed a mapping algorithm that would be less influenced by the contents of LOINC or CPT. In some studies, the relationship between the axes of LOINC has been analyzed for each test and has a different SNOMED CT code, case by case [10]. However what we wanted was not a real-world mapping with SNOMED CT, but CPT with SNOMED CT using the LOINC structure. This means that the role of SNOMED CT is not to express real things at this time. For the automated generation of bills, the role of SNOMED CT is cross bridging between CPT and LOINC. If the LOINC codes were used to order OCS, additional information for matching CPT is required. This seeking process would be possible by defining SNOMED RelationshipType of the type class, object class, and subject to class [9]. Each LOINC code fully describes its own meaning; the relationship among the six axes need not describe a real meaning, but describe only which axis is concerned, with SNOMED CT. This algorithm can be applied with any code set that represents laboratory tests, including the Korean code set, due to the excellence of the LOINC axes structure. In the results of dissecting CPT into LOINC axes, almost half of the CPT codes were dissected into more than three axes of LOINC (Table 1). If CPT codes have more matching parts for the axes of LOINC, the less LOINC codes can be mapped to CPT code (Generally, one CPT code can be mapped with multiple LOINC codes, which is also true for the Korean code set). About 25% of CPT codes had only one matching part of LOINC, component, and some concepts of CPT could not be found among LOINC items. At this time, like the procedure code, the SNOMED CT ConceptID could be used instead of LOINC to express concepts of CPT. Vol. 16 No. 3 September
6 Shine Young Kim et al Table 2 shows our suggestion for categorizing subparts for SNOMED CT mapping. It is just one option for categorization. We hope this can be developed further by experts in the field. The algorithm developed in this study has some limitations. First, to express instances of each class, post-coordination of SNOMED CT may be needed. Some relationships between type class and object class or charge and subject to class and other classes may not be found in SNOMED CT ConceptID. To minimize the use of post-coordination, more and more delicate categorizations of classes would be required. Second, this method can be applied only in the area of laboratory tests. Finally, the generated SNOMED CT code in our algorithm could not fully describe real things, and is only useful for generating bills. Our study presents a method for mapping between SNOMED CT and CPT laboratory test concepts through LOINC for automated coding to CPT from EMR data recorded with SNOMED CT for billing purposes. The CPT codes are used in the US, but not in Korea. Nonetheless, we suggest that the algorithm for mapping could be widely used, and would also work with the Korean health insurance claim code set. Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. Acknowledgments This article is based on research supported by the R&D Program of MKE/KEIT (KI , KI ). References 1. Garde S, Knaup P, Hovenga E, Heard S. Towards semantic interoperability for electronic health records. Methods Inf Med 2007; 46: Cimino JJ. Review paper: coding systems in health care. Methods Inf Med 1996; 35: American Medical Association. CPT: Current Procedural Terminology [Internet]. Chicago: American Medical Association; 2009 [cited 2010 Feb 23]. Available from: solutions-managing-your-practice/coding-billing-insurance/cpt.shtml. 4. Forrey AW, McDonald CJ, DeMoor G, Huff SM, Leavelle D, Leland D, Fiers T, Charles L, Griffin B, Stalling F, Tullis A, Hutchins K, Baenziger J. Logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC) database: a public use set of codes and names for electronic reporting of clinical laboratory test results. Clin Chem 1996; 42: National Library of Medicine (US). LOINC to CPT Mapping [Internet]. Bethesda, MD: National Library of Medicine (US); 2006 [cited 2010 Feb 23]. Available from: projects/loinc_to_cpt_map.html. 6. Regenstrief Institute, LOINC Committee, IFCC, IUPAC, IHTSDO. Owners of LOINC, NPU, and SNOMED CT begin trial of cooperative terminology development [Internet]. Indianapolis: The Regenstrief Institute, Inc.; 2009 [cited 2010 Feb 23]. Available from: org/news/owners-of-loinc-npu-and-snomed-ct-begintrial-of-cooperative-terminology-development-jointpress-release.html. 7. Donnelly K. SNOMED-CT: the advanced terminology and coding system for ehealth. Stud Health Technol Inform 2006; 121: Zhang S, Bodenreider O. Experience in aligning anatomical ontologies. Int J Semant Web Inf Syst 2007; 3: International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation (IHTSDO). SNOMED Clinical Terms Technical Reference Guide [Internet]. Copenhagen: IHTSDO; 2008 [cited 2010 Feb 23]. Available from: php?contentfileid= Bodenreider O. Issues in mapping LOINC laboratory tests to SNOMED CT. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2008:
Mapping Thai local laboratory codes with LOINC : the preliminary report
 Mapping Thai local laboratory codes with LOINC : the preliminary report Wanchana Ponthongmak, Boonchai Kijsanayotin, Win Min Thit, Panu Looareesuwan Thai Health Information Standards Development Center
Mapping Thai local laboratory codes with LOINC : the preliminary report Wanchana Ponthongmak, Boonchai Kijsanayotin, Win Min Thit, Panu Looareesuwan Thai Health Information Standards Development Center
Technical White Paper. Metadata management. Ontologies, measures, registries, and patient attribution
 Technical White Paper Ontologies, measures, registries, and patient attribution Contents 02 About Informatics and Analytics 02 Ontologies used by 04 Quality measures metadata 04 Clinical registry metadata
Technical White Paper Ontologies, measures, registries, and patient attribution Contents 02 About Informatics and Analytics 02 Ontologies used by 04 Quality measures metadata 04 Clinical registry metadata
Rooibos : Automated schedule broadcast software for clinical pharmacology studies
 TCP 2016;24(3):127-131 http://dx.doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2016.24.3.127 Rooibos : Automated schedule broadcast software for clinical pharmacology studies Ji-Hyoung Lee 1, Woo-Suk Chong 2, Jong Kwan Park 3,
TCP 2016;24(3):127-131 http://dx.doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2016.24.3.127 Rooibos : Automated schedule broadcast software for clinical pharmacology studies Ji-Hyoung Lee 1, Woo-Suk Chong 2, Jong Kwan Park 3,
Would SNOMED CT benefit from Realism-Based Ontology Evolution?
 Would SNOMED CT benefit from Realism-Based Ontology Evolution? Werner M. Ceusters, MD 1, Kent A. Spackman, MD, PhD 2, Barry Smith, PhD 1,3 1 Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Life Sciences, University
Would SNOMED CT benefit from Realism-Based Ontology Evolution? Werner M. Ceusters, MD 1, Kent A. Spackman, MD, PhD 2, Barry Smith, PhD 1,3 1 Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Life Sciences, University
GLOBAL HEALTH INFORMATICS STANDARDS FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INFORMATION
 GLOBAL HEALTH INFORMATICS STANDARDS FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INFORMATION Vikas Dwivedi (vikas_dwivedi@jsi.com) Boonchai Kijsanayotin (kijs0001@gmail.com) Derek Kunaka (derek_kunaka@za.jsi.com) What is Interoperability?
GLOBAL HEALTH INFORMATICS STANDARDS FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INFORMATION Vikas Dwivedi (vikas_dwivedi@jsi.com) Boonchai Kijsanayotin (kijs0001@gmail.com) Derek Kunaka (derek_kunaka@za.jsi.com) What is Interoperability?
Evaluation of a Proposed Method for Representing Drug Terminology
 Evaluation of a Proposed Method for Representing Drug Terminology James J. Cimino, M.D., 1 Timothy J. McNamara, M.D., M.P.H.&T.M., 2 Terri Meredith, R.Ph., 2 Carol A. Broverman, Ph.D., 3 Karen C. Eckert,
Evaluation of a Proposed Method for Representing Drug Terminology James J. Cimino, M.D., 1 Timothy J. McNamara, M.D., M.P.H.&T.M., 2 Terri Meredith, R.Ph., 2 Carol A. Broverman, Ph.D., 3 Karen C. Eckert,
StartUp America Challenge. Improvements to Information Structure Data Standards, Quality & Interoperability. Part 3 FINAL PROJECT PLAN
 StartUp America Challenge Improvements to Information Structure Data Standards, Quality & Interoperability Part 3 FINAL PROJECT PLAN Lyndia A. Hayden Northwestern University MED 407, Winter 2012 StartUp
StartUp America Challenge Improvements to Information Structure Data Standards, Quality & Interoperability Part 3 FINAL PROJECT PLAN Lyndia A. Hayden Northwestern University MED 407, Winter 2012 StartUp
The role of SNOMED CT in healthcare systems across the world Jan-Eric Slot MB MSc MBA CEO IHTSDO
 The role of SNOMED CT in healthcare systems across the world Jan-Eric Slot MB MSc MBA CEO IHTSDO International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation www.ihtsdo.org 1 Outline What is the
The role of SNOMED CT in healthcare systems across the world Jan-Eric Slot MB MSc MBA CEO IHTSDO International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation www.ihtsdo.org 1 Outline What is the
Technical White Paper. The data curation process. Watson Health Informatics overview of mapping, standardization, and indexing
 Technical White Paper Informatics overview of mapping, standardization, and indexing Contents 02 About Informatics and Analytics 02 Data mapping and extraction 03 04 The curation workflow 04 Curation transparency
Technical White Paper Informatics overview of mapping, standardization, and indexing Contents 02 About Informatics and Analytics 02 Data mapping and extraction 03 04 The curation workflow 04 Curation transparency
Information Paper. MAKING USE OF SNOMED CT: KEY QUESTIONS and STATUS as of SEPTEMBER 2013
 Information Paper MAKING USE OF SNOMED CT: KEY QUESTIONS and STATUS as of SEPTEMBER 2013 1. Introduction This document aims at explaining in a synthetic way why certain Member States (MS) have decided
Information Paper MAKING USE OF SNOMED CT: KEY QUESTIONS and STATUS as of SEPTEMBER 2013 1. Introduction This document aims at explaining in a synthetic way why certain Member States (MS) have decided
Pilot Study Concept Paper 1 Executive Summary. 2 Introduction. 2.1 Background: 2.2 Issue. MedDRA MSSO
 Pilot Study Concept Paper 1 Executive Summary The November 2006 Blue Ribbon Panel (BRP) recommended that the MSSO conduct a pilot study on the MedDRA concept attribute relationship, which allows the connection
Pilot Study Concept Paper 1 Executive Summary The November 2006 Blue Ribbon Panel (BRP) recommended that the MSSO conduct a pilot study on the MedDRA concept attribute relationship, which allows the connection
TCP Transl Clin Pharmacol
 TCP 2018;26(4):172-176 https://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2018.26.4.172 Trends of clinical trials from 2014 to 2016 in South Korea Ki Young Huh, Jun Gi Hwang and SeungHwan Lee* Department of Clinical Pharmacology
TCP 2018;26(4):172-176 https://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2018.26.4.172 Trends of clinical trials from 2014 to 2016 in South Korea Ki Young Huh, Jun Gi Hwang and SeungHwan Lee* Department of Clinical Pharmacology
Big Data & Clinical Informatics
 Big Data & Clinical Informatics Client Overview A leading clinical intelligence company that powers healthcare providers, life sciences and research organizations to make better-informed, more confident
Big Data & Clinical Informatics Client Overview A leading clinical intelligence company that powers healthcare providers, life sciences and research organizations to make better-informed, more confident
Monitoring Pig Body Temperature Using Infrared Sensors
 Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 40(4):368-372. (2015. 12) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2015.40.4.368 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Monitoring Pig Body Temperature
Original Article J. of Biosystems Eng. 40(4):368-372. (2015. 12) http://dx.doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2015.40.4.368 Journal of Biosystems Engineering eissn : 2234-1862 pissn : 1738-1266 Monitoring Pig Body Temperature
Identifying the Clinical Laboratory Tests from Unspecified Other Lab Test Data for Secondary Use
 Identifying the Clinical Laboratory Tests from Unspecified Other Lab Test Data for Secondary Use Xuequn Pan, PhD 1, 2, James J. Cimino, MD 1, 2 1 Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications,
Identifying the Clinical Laboratory Tests from Unspecified Other Lab Test Data for Secondary Use Xuequn Pan, PhD 1, 2, James J. Cimino, MD 1, 2 1 Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications,
Combining laboratory data sets from multiple institutions using the logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC)
 International Journal of Medical Informatics 51 (1998) 29 37 Combining laboratory data sets from multiple institutions using the logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC) David M. Baorto a,
International Journal of Medical Informatics 51 (1998) 29 37 Combining laboratory data sets from multiple institutions using the logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC) David M. Baorto a,
Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2017
 Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2017 An Easy-to-Use Tool for Coding and Reimbursement Compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East
Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2017 An Easy-to-Use Tool for Coding and Reimbursement Compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of Panacea Healthcare Solutions, Inc. 287 East
Guidance on use of SNOMED CT and LOINC together
 Guidance on use of SNOMED CT and LOINC together OCTOBER 2014 Date: 2014-10-14 Version: 0.30 Status: DRAFT TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 4 1.1 Purpose of this guide... 4 1.2 Who should read this guide...
Guidance on use of SNOMED CT and LOINC together OCTOBER 2014 Date: 2014-10-14 Version: 0.30 Status: DRAFT TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 4 1.1 Purpose of this guide... 4 1.2 Who should read this guide...
Dr. Karen DeSalvo Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
 March 20, 2015 Dr. Karen DeSalvo Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology U.S. Department of Health and Human Services RE: A Shared Nationwide Interoperability Roadmap Draft
March 20, 2015 Dr. Karen DeSalvo Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology U.S. Department of Health and Human Services RE: A Shared Nationwide Interoperability Roadmap Draft
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #70 (NQF 0379): Hematology: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Baseline Flow Cytometry National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Quality ID #70 (NQF 0379): Hematology: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Baseline Flow Cytometry National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2018
 Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2018 An Easy-to-Use Tool for Coding and Reimbursement Compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street,
Coding Essentials for Laboratories 2018 An Easy-to-Use Tool for Coding and Reimbursement Compliance Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street,
GLEE A Model-Driven Execution System for Computer-Based Implementation of Clinical Practice Guidelines
 A Model-Driven Execution System for Computer-Based Implementation of Clinical Practice Guidelines Dongwen Wang, M.Phil., Edward H. Shortliffe, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Medical Informatics, Columbia University
A Model-Driven Execution System for Computer-Based Implementation of Clinical Practice Guidelines Dongwen Wang, M.Phil., Edward H. Shortliffe, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Medical Informatics, Columbia University
A SWOT Analysis of the Various Backup Scenarios Used in Electronic Medical Record Systems
 Original Article Healthc Inform Res. 2011 September;17(3):162-171. http://dx.doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.3.162 pissn 2093-3681 eissn 2093-369X A SWOT Analysis of the Various Backup Scenarios Used in Electronic
Original Article Healthc Inform Res. 2011 September;17(3):162-171. http://dx.doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.3.162 pissn 2093-3681 eissn 2093-369X A SWOT Analysis of the Various Backup Scenarios Used in Electronic
Drug development is a lengthy, expensive, and complex process, and clinical development is
 J Korean Med Assoc 2010 September; 53(9): 753-760 DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.9.753 pissn: 1975-8456 eissn: 2093-5951 http://jkma.org Focused Issue of This Month New drug development and clinical trial Dong-Hyun
J Korean Med Assoc 2010 September; 53(9): 753-760 DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2010.53.9.753 pissn: 1975-8456 eissn: 2093-5951 http://jkma.org Focused Issue of This Month New drug development and clinical trial Dong-Hyun
Similarity Analysis of Korean Medical Literature and Its Association with Efforts to Improve Research and Publication Ethics
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Editing, Writing & Publishing https://doi.org/1.3346/jkms.217.32.6.887 J Korean Med Sci 217; 32: 887-892 Similarity Analysis of Korean Medical Literature and Its Association with Efforts
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Editing, Writing & Publishing https://doi.org/1.3346/jkms.217.32.6.887 J Korean Med Sci 217; 32: 887-892 Similarity Analysis of Korean Medical Literature and Its Association with Efforts
What is the Coverage of SNOMED CT on Scientific Medical Corpora?
 MIE 2011, Oslo, Norway What is the Coverage of SNOMED CT on Scientific Medical Corpora? DIMITRIOS KOKKINAKIS Centre for Language Technology (CLT) & Språkbanken Department of Swedish dimitrios.kokkinakis@svenska.gu.se
MIE 2011, Oslo, Norway What is the Coverage of SNOMED CT on Scientific Medical Corpora? DIMITRIOS KOKKINAKIS Centre for Language Technology (CLT) & Språkbanken Department of Swedish dimitrios.kokkinakis@svenska.gu.se
Approved by: Thomas M. Driskill, Jr. President & CEO
 HAWAII HEALTH SYSTEMS C O R P O R A T I O N Touching Lives Everyday" Policies and Procedures Subject: Unlisted Laboratory Procedure Codes Quality Through Compliance Issued by: Corporate Compliance Committee
HAWAII HEALTH SYSTEMS C O R P O R A T I O N Touching Lives Everyday" Policies and Procedures Subject: Unlisted Laboratory Procedure Codes Quality Through Compliance Issued by: Corporate Compliance Committee
Laboratory QA. Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience
 Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience Brian E. Dixon, MPA, PhD, 1* John Hook, BS, 2 Daniel J. Vreeman, PT, DPT, MSc 3 Lab Med Spring 2015;46:168-174 DOI: 10.1309/LMWJ730SVKTUBAOJ
Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience Brian E. Dixon, MPA, PhD, 1* John Hook, BS, 2 Daniel J. Vreeman, PT, DPT, MSc 3 Lab Med Spring 2015;46:168-174 DOI: 10.1309/LMWJ730SVKTUBAOJ
Laboratory QA. Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience
 Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience Brian E. Dixon, MPA, PhD, 1* John Hook, BS, 2 Daniel J. Vreeman, PT, DPT, MSc 3 Lab Med Spring 2015;46:168-174 DOI: 10.1309/LMWJ730SVKTUBAOJ
Learning From the Crowd in Terminology Mapping: The LOINC Experience Brian E. Dixon, MPA, PhD, 1* John Hook, BS, 2 Daniel J. Vreeman, PT, DPT, MSc 3 Lab Med Spring 2015;46:168-174 DOI: 10.1309/LMWJ730SVKTUBAOJ
Agenda. Background SNOMED International Collaborations developments Information models Extensions
 Agenda Background SNOMED International Collaborations 2018 developments Information models Extensions SNOMED International International not-for-profit association, based in the UK Owns and maintains SNOMED
Agenda Background SNOMED International Collaborations 2018 developments Information models Extensions SNOMED International International not-for-profit association, based in the UK Owns and maintains SNOMED
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Exploring Complexity in Health: An Interdisciplinary Systems Approach
 Aalborg Universitet Applying the SNOMED CT concept model to represent value sets for head and neck cancer documentation Højen, Anne Randorff; Brønnum, Dorthe Scavenius; Gøeg, Kirstine Rosenbeck; Elberg,
Aalborg Universitet Applying the SNOMED CT concept model to represent value sets for head and neck cancer documentation Højen, Anne Randorff; Brønnum, Dorthe Scavenius; Gøeg, Kirstine Rosenbeck; Elberg,
Clinical Information Interoperability Council (CIIC) Providing a Shared Repository of Detailed Clinical Models for all of Health and Healthcare
 Clinical Information Interoperability Council (CIIC) Providing a Shared Repository of Detailed Clinical Models for all of Health and Healthcare NIH HCS Collaboratory and PCORnet December 1, 2017 Stanley
Clinical Information Interoperability Council (CIIC) Providing a Shared Repository of Detailed Clinical Models for all of Health and Healthcare NIH HCS Collaboratory and PCORnet December 1, 2017 Stanley
Current Development of Medical Terminology
 Current Development of Medical Terminology Yun Sik Kwak, MD, PhD Dept Med. Info.,Kyungpook Nat l Univ Sch Med ISO/TC 215, Health Informatics APAMI HL7-Korea (yskwak@knu.ac.kr) October 27, 2006 APAMI MIC2006
Current Development of Medical Terminology Yun Sik Kwak, MD, PhD Dept Med. Info.,Kyungpook Nat l Univ Sch Med ISO/TC 215, Health Informatics APAMI HL7-Korea (yskwak@knu.ac.kr) October 27, 2006 APAMI MIC2006
Ontologies examples and applications
 Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Ontologies examples and applications 2 UMLS - Unified Medical Language System Framework consisting of several knowledge bases and according
Web Science & Technologies University of Koblenz Landau, Germany Ontologies examples and applications 2 UMLS - Unified Medical Language System Framework consisting of several knowledge bases and according
HOW TO MITIGATE YOUR ED REIMBURSEMENT RISK
 HOW TO MITIGATE YOUR ED REIMBURSEMENT RISK Tips to Automate and Improve Emergency Services Billing and Coding Workflow IN PARTNERSHIP WITH How to Mitigate Your ED Reimbursement Risk 1 Emergency Reimbursement
HOW TO MITIGATE YOUR ED REIMBURSEMENT RISK Tips to Automate and Improve Emergency Services Billing and Coding Workflow IN PARTNERSHIP WITH How to Mitigate Your ED Reimbursement Risk 1 Emergency Reimbursement
The UMLS and the Semantic Web
 W3C Semantic Web Health Care and Life Sciences Interest Group BioRDF Teleconference September 25, 2008 The UMLS and the Semantic Web Olivier Bodenreider Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications
W3C Semantic Web Health Care and Life Sciences Interest Group BioRDF Teleconference September 25, 2008 The UMLS and the Semantic Web Olivier Bodenreider Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #70: Hematology: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Baseline Flow Cytometry National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions
Quality ID #70: Hematology: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Baseline Flow Cytometry National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions
Implementing SNOMED CT for Quality Reporting: Avoiding Pitfalls
 Research Article Applied Clinical Informatics 5 Implementing SNOMED CT for Quality Reporting: Avoiding Pitfalls G. Wade Clinical Informatics Consulting, Atlanta, GA, USA Keywords SNOMED CT, electronic
Research Article Applied Clinical Informatics 5 Implementing SNOMED CT for Quality Reporting: Avoiding Pitfalls G. Wade Clinical Informatics Consulting, Atlanta, GA, USA Keywords SNOMED CT, electronic
emerge Data Dictionary Harmonization and Best Practices for Standardized Phenotype Data Representation Jyoti Pathak April 13 th, 2010
 emerge Data Dictionary Harmonization and Best Practices for Standardized Phenotype Data Representation Jyoti Pathak April 13 th, 2010 Chris Chute Dan Masys Janey Wang Sudha Kashyap Melissa Basford Acknowledgment
emerge Data Dictionary Harmonization and Best Practices for Standardized Phenotype Data Representation Jyoti Pathak April 13 th, 2010 Chris Chute Dan Masys Janey Wang Sudha Kashyap Melissa Basford Acknowledgment
The Use of Automated SNOMED CT Clinical Coding in Clinical Decision Support Systems for Preventive Care
 The Use of Automated SNOMED CT Clinical Coding in Clinical Decision Support Systems for Preventive Care The Use of Automated SNOMED CT Clinical Coding in Clinical Decision Support Systems for Preventive
The Use of Automated SNOMED CT Clinical Coding in Clinical Decision Support Systems for Preventive Care The Use of Automated SNOMED CT Clinical Coding in Clinical Decision Support Systems for Preventive
An Ontology for Clinical Laboratory Standard Operating Procedures
 An Ontology for Clinical Laboratory Standard Operating Procedures Fatima S. MAIKORE a,b,1, Gantigmaa SELENGE a, Adebola OLAYINKA c, Pamela ABBOTT d, and Larisa SOLDATOVA a a Brunel University, London,
An Ontology for Clinical Laboratory Standard Operating Procedures Fatima S. MAIKORE a,b,1, Gantigmaa SELENGE a, Adebola OLAYINKA c, Pamela ABBOTT d, and Larisa SOLDATOVA a a Brunel University, London,
IHE LAB face to face meeting Usage of reference terminologies SNOMED-CT, LOINC - UCUM. Filip Migom Product Manager GLIMS 15 October 2013
 IHE LAB face to face meeting Usage of reference terminologies SNOMED-CT, LOINC - UCUM Filip Migom Product Manager GLIMS 15 October 2013 History : IHE Chicago 4 Febr. 2013 by Filip Migom IHE-LABORATORY
IHE LAB face to face meeting Usage of reference terminologies SNOMED-CT, LOINC - UCUM Filip Migom Product Manager GLIMS 15 October 2013 History : IHE Chicago 4 Febr. 2013 by Filip Migom IHE-LABORATORY
Comparing Pharmacologic Classes in NDF-RT and SNOMED CT
 Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Semantic Mining in Biomedicine (SMBM 2010) 2010:119-124. Comparing Pharmacologic Classes in NDF-RT and SNOMED CT Jonathan Mortensen 1, Olivier Bodenreider
Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Semantic Mining in Biomedicine (SMBM 2010) 2010:119-124. Comparing Pharmacologic Classes in NDF-RT and SNOMED CT Jonathan Mortensen 1, Olivier Bodenreider
Template for comments
 WHO concept note and collaboration proposal for International Nomenclature, coding and classification of medical devices (ICMD) Name of person(s) submitting comments Eileen G. Erinoff Institution/organization:
WHO concept note and collaboration proposal for International Nomenclature, coding and classification of medical devices (ICMD) Name of person(s) submitting comments Eileen G. Erinoff Institution/organization:
BELGIAN USE CASE BASED APROACH AND APPROACH TO TRANSLATION
 Federal Public Service of Health, Food Chain Safety and Environment Directorate-General Health Care Department Datamanagement Arabella D Havé, chief of Terminology, Classification, Grouping & Audit arabella.dhave@health.belgium.be
Federal Public Service of Health, Food Chain Safety and Environment Directorate-General Health Care Department Datamanagement Arabella D Havé, chief of Terminology, Classification, Grouping & Audit arabella.dhave@health.belgium.be
Has no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
 Public Health and Support for Meaningful Use in Health Information Exchange Noam H. Arzt, PhD, FHIMSS President HLN Consulting, LLC San Diego, CA June 10, 2010 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Noam H. Arzt,
Public Health and Support for Meaningful Use in Health Information Exchange Noam H. Arzt, PhD, FHIMSS President HLN Consulting, LLC San Diego, CA June 10, 2010 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Noam H. Arzt,
Health Information Exchange Based on Cloud Computing System
 Health Information Exchange Based on Cloud Computing System Syeda Mariya Tanzil B.Tech, Department of CSE, Lords Institute of Engineering and Technology. Zehra Fatima B.Tech, Department of CSE, Lords Institute
Health Information Exchange Based on Cloud Computing System Syeda Mariya Tanzil B.Tech, Department of CSE, Lords Institute of Engineering and Technology. Zehra Fatima B.Tech, Department of CSE, Lords Institute
School of Industrial and Information Engineering Master of Science in Information Engineering Master of Science in Biomedical Engineering
 School of Industrial and Information Engineering Master of Science in Information Engineering Master of Science in Biomedical Engineering Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria ICT for
School of Industrial and Information Engineering Master of Science in Information Engineering Master of Science in Biomedical Engineering Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria ICT for
MedDRA and Ontology. Anna Zhao-Wong, MD, PhD Deputy Director MedDRA MSSO
 MedDRA and Ontology Anna Zhao-Wong, MD, PhD Deputy Director MedDRA MSSO anna.zhao-wong@meddra.org What is MedDRA? Med = Medical D = Dictionary for R = Regulatory A = Activities 2 What Is MedDRA Used For?
MedDRA and Ontology Anna Zhao-Wong, MD, PhD Deputy Director MedDRA MSSO anna.zhao-wong@meddra.org What is MedDRA? Med = Medical D = Dictionary for R = Regulatory A = Activities 2 What Is MedDRA Used For?
National Program of Cancer Registries Advancing E-cancer Reporting and Registry Operations (NPCR-AERRO)
 National Program of Cancer Registries Advancing E-cancer Reporting and Registry Operations (NPCR-AERRO) Sandy Thames, CDC October 5 th, 2009 Cancer Surveillance Branch Division of Cancer Prevention and
National Program of Cancer Registries Advancing E-cancer Reporting and Registry Operations (NPCR-AERRO) Sandy Thames, CDC October 5 th, 2009 Cancer Surveillance Branch Division of Cancer Prevention and
Enhancing Laboratory Data Infrastructure to Access Real-World Evidence (RWE) for in vitro Diagnostics (IVDs): Three Models for RWE Use
 Enhancing Laboratory Data Infrastructure to Access Real-World Evidence (RWE) for in vitro Diagnostics (IVDs): Three Models for RWE Use Michael Waters, Ph.D. Michael.Waters@fda.hhs.gov Office of In Vitro
Enhancing Laboratory Data Infrastructure to Access Real-World Evidence (RWE) for in vitro Diagnostics (IVDs): Three Models for RWE Use Michael Waters, Ph.D. Michael.Waters@fda.hhs.gov Office of In Vitro
Profiling Structured Product Labeling with NDF-RT and RxNorm
 Profiling Structured Product Labeling with NDF-RT and RxNorm Qian Zhu, PhD, Guoqian Jiang, MD, PhD and Christopher G. Chute, MD, Dr. PH Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, MN, USA ICBO VDOSME 2012,
Profiling Structured Product Labeling with NDF-RT and RxNorm Qian Zhu, PhD, Guoqian Jiang, MD, PhD and Christopher G. Chute, MD, Dr. PH Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, MN, USA ICBO VDOSME 2012,
SNOMED CT Editorial Guide
 SNOMED CT Editorial Guide January 2015 International Release (GB English) This document may have been updated since you received it. The latest versions of IHTSDO documents are available online. Latest
SNOMED CT Editorial Guide January 2015 International Release (GB English) This document may have been updated since you received it. The latest versions of IHTSDO documents are available online. Latest
What Mapping and Modeling Means to the HIM Professional
 What Mapping and Modeling Means to the HIM Professional 1 What Mapping and Modeling Means to the HIM Professional by Patricia S. Wilson, RT(R), CPC, PMP Objective The processes of data mapping and concept
What Mapping and Modeling Means to the HIM Professional 1 What Mapping and Modeling Means to the HIM Professional by Patricia S. Wilson, RT(R), CPC, PMP Objective The processes of data mapping and concept
Validating drug repurposing signals using electronic health records: a case study of metformin associated with reduced cancer mortality
 Validating drug repurposing signals using electronic health records: a case study of metformin associated with reduced cancer mortality Hua Xu, PhD School of Biomedical Informatics, UTHealth JAMIA Journal
Validating drug repurposing signals using electronic health records: a case study of metformin associated with reduced cancer mortality Hua Xu, PhD School of Biomedical Informatics, UTHealth JAMIA Journal
SNOMED Clinical Terms National Release Centre of Ireland. Governance Group Strategy for 2018
 SNOMED Clinical Terms National Release Centre of Ireland Governance Group Strategy for 2018 December 2017 Document Management Document Control The controlled copy of this document is maintained by the
SNOMED Clinical Terms National Release Centre of Ireland Governance Group Strategy for 2018 December 2017 Document Management Document Control The controlled copy of this document is maintained by the
STI ecr Learning Community: Webinar 2. April 27, 2017 Noon 1 p.m. EDT
 STI ecr Learning Community: Webinar 2 April 27, 2017 Noon 1 p.m. EDT STI ecr Learning Community Webinar 2 Please use the link below to register for the webinar: https://attendee.gotowebinar.com/register/1084681796879085313
STI ecr Learning Community: Webinar 2 April 27, 2017 Noon 1 p.m. EDT STI ecr Learning Community Webinar 2 Please use the link below to register for the webinar: https://attendee.gotowebinar.com/register/1084681796879085313
Leading healthcare terminology, worldwide
 Leading healthcare terminology, worldwide Table of Contents 3 Chairman s Report 4 CEO Report 6 Background 7 Development in Activities and Financial Position 8 Strategy, Objectives, and Future Prospects
Leading healthcare terminology, worldwide Table of Contents 3 Chairman s Report 4 CEO Report 6 Background 7 Development in Activities and Financial Position 8 Strategy, Objectives, and Future Prospects
Semantic Enrichment and the Information Manager
 WHITEPAPER Semantic Enrichment and the Information Manager Turning Content into Insight It is more resource intensive to bring a drug to market than ever before: Pharmaceutical companies spend an average
WHITEPAPER Semantic Enrichment and the Information Manager Turning Content into Insight It is more resource intensive to bring a drug to market than ever before: Pharmaceutical companies spend an average
Terminology Needs in Clinical Decision Support. Samson Tu Senior Research Scientist Center for Biomedical Informatics Research Stanford University
 Terminology Needs in Clinical Decision Support Samson Tu Senior Research Scientist Center for Biomedical Informatics Research Stanford University 11th International Protégé Conference Workshop Amsterdam,
Terminology Needs in Clinical Decision Support Samson Tu Senior Research Scientist Center for Biomedical Informatics Research Stanford University 11th International Protégé Conference Workshop Amsterdam,
Immunization Information System Interoperability
 Immunization Information System Interoperability AIRA Pre-conference Workshop 42 nd National Immunization Conference Noam H. Arzt, Ph.D. March 16, 2008 1 Table of Contents Evolution of IIS & Systems Integration
Immunization Information System Interoperability AIRA Pre-conference Workshop 42 nd National Immunization Conference Noam H. Arzt, Ph.D. March 16, 2008 1 Table of Contents Evolution of IIS & Systems Integration
Published in: Building Continents of Knowledge in Oceans of Data: The Future of Co-Created ehealth
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 17, 2019 Aalborg Universitet An empirical approach to enhancing terminology binding An HL7 FHIR SNOMED CT example Gøeg, Kirstine Rosenbeck; Hummeluhr, Mark Published
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 17, 2019 Aalborg Universitet An empirical approach to enhancing terminology binding An HL7 FHIR SNOMED CT example Gøeg, Kirstine Rosenbeck; Hummeluhr, Mark Published
Genomics and SNOMED CT (the way ahead) Ian Green Customer Relations Lead, Europe and Clinical Engagement Business Manager
 Genomics and SNOMED CT (the way ahead) Ian Green Customer Relations Lead, Europe and Clinical Engagement Business Manager Agenda The changing face of medicine The Genomics standards landscape Accessing
Genomics and SNOMED CT (the way ahead) Ian Green Customer Relations Lead, Europe and Clinical Engagement Business Manager Agenda The changing face of medicine The Genomics standards landscape Accessing
DENOMINATOR: All final reports for patients, regardless of age, undergoing a CT procedure
 Quality ID #363: Optimizing Patient Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: Search for Prior Computed Tomography (CT) Studies Through a Secure, Authorized, Media-Free, Shared Archive National Quality Strategy
Quality ID #363: Optimizing Patient Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: Search for Prior Computed Tomography (CT) Studies Through a Secure, Authorized, Media-Free, Shared Archive National Quality Strategy
The Future of Reimbursement for Lab Developed Mass Spec Assays
 The Future of Reimbursement for Lab Developed Mass Spec Assays Charles Root, PhD CodeMap, LLC Schaumberg, IL AACC/MSSS Mass Spectrometry and Separation Sciences for Lab Medicine Oct 1 2, 2015 1 The Future
The Future of Reimbursement for Lab Developed Mass Spec Assays Charles Root, PhD CodeMap, LLC Schaumberg, IL AACC/MSSS Mass Spectrometry and Separation Sciences for Lab Medicine Oct 1 2, 2015 1 The Future
Author s response to reviews
 Author s response to reviews Title: Assessment of laparoscopic stomach preserving surgery with sentinel basin dissection versus standard gastrectomy with lymphadenectomy in early gastric cancer-a multicenter
Author s response to reviews Title: Assessment of laparoscopic stomach preserving surgery with sentinel basin dissection versus standard gastrectomy with lymphadenectomy in early gastric cancer-a multicenter
COST Action IC0604 Euro-Telepath 10th Working Group 4 Meeting
 COST Action IC0604 Euro-Telepath 10th Working Group 4 Meeting Innovation Center of the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Univ. Belgrade. Serbia. 2/March/2011 WG4 Agenda Scanning technology Collaboration
COST Action IC0604 Euro-Telepath 10th Working Group 4 Meeting Innovation Center of the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Univ. Belgrade. Serbia. 2/March/2011 WG4 Agenda Scanning technology Collaboration
Initiatives to Speed up Data Mining. Ségolène Aymé ICORD 2014, Ede, Netherlands 9 October 2014
 Initiatives to Speed up Data Mining Ségolène Aymé ICORD 2014, Ede, Netherlands 9 October 2014 1 Objectives Make the most of remarkable advances in the molecular basis of human diseases dissect the physiological
Initiatives to Speed up Data Mining Ségolène Aymé ICORD 2014, Ede, Netherlands 9 October 2014 1 Objectives Make the most of remarkable advances in the molecular basis of human diseases dissect the physiological
Certification in Healthcare Revenue Integrity (CHRI) Exam Outline
 Certification in Healthcare Revenue Integrity (CHRI) Exam Outline I. EDUCATION 30 items (16 recall/10 application/4 analysis) a. Rules and Regulations 1. Provide expert advice in coding guidelines and
Certification in Healthcare Revenue Integrity (CHRI) Exam Outline I. EDUCATION 30 items (16 recall/10 application/4 analysis) a. Rules and Regulations 1. Provide expert advice in coding guidelines and
Organizational Track Definitions, Assumptions and Issues
 Organizational Track Definitions, Assumptions and Issues 10a.m. 11a.m. Use Case Specification Robert Dolin,, MD National Clinical Information Systems and Physician Lead for Enterprise Terminology Services,
Organizational Track Definitions, Assumptions and Issues 10a.m. 11a.m. Use Case Specification Robert Dolin,, MD National Clinical Information Systems and Physician Lead for Enterprise Terminology Services,
The knowledge-driven exploration of integrated biomedical knowledge sources facilitates the generation of new hypotheses
 The knowledge-driven exploration of integrated biomedical knowledge sources facilitates the generation of new hypotheses Vinh Nguyen 1, Olivier Bodenreider 2, Todd Minning 3, and Amit Sheth 1 1 Kno.e.sis
The knowledge-driven exploration of integrated biomedical knowledge sources facilitates the generation of new hypotheses Vinh Nguyen 1, Olivier Bodenreider 2, Todd Minning 3, and Amit Sheth 1 1 Kno.e.sis
NLM Funded Research Projects Involving Text Mining/NLP
 NLM Funded Research Projects Involving Text Mining/NLP Jane Ye, PhD Program Officer Division of Extramural Programs 2017 BioCreative VI Workshop Funding Stakeholders Panel 1 NLM Grant Programs in Biomedical
NLM Funded Research Projects Involving Text Mining/NLP Jane Ye, PhD Program Officer Division of Extramural Programs 2017 BioCreative VI Workshop Funding Stakeholders Panel 1 NLM Grant Programs in Biomedical
Is Your Healthcare Analytics System Missing the Gold in Your EHRs? A Special Report for Healthcare Executives
 Is Your Healthcare Analytics System Missing the Gold in Your EHRs? A Special Report for Healthcare Executives Contents Executive Summary 3 Checklist: Are You Mining All the Gold in Your EHRs? 4 What s
Is Your Healthcare Analytics System Missing the Gold in Your EHRs? A Special Report for Healthcare Executives Contents Executive Summary 3 Checklist: Are You Mining All the Gold in Your EHRs? 4 What s
PCORI Methodology Standards: Academic Curriculum Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. All Rights Reserved.
 PCORI Methodology Standards: Academic Curriculum 2016 Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. All Rights Reserved. Module 5: Architecture for Data Networks Category 7: Data Networks as Research-Facilitating
PCORI Methodology Standards: Academic Curriculum 2016 Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. All Rights Reserved. Module 5: Architecture for Data Networks Category 7: Data Networks as Research-Facilitating
Terminology Services: Standard Terminologies to Control Health Vocabulary
 227 2018 IMIA and Schattauer GmbH Terminology Services: Standard Terminologies to Control Health Vocabulary Experience at the Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires Fernán González Bernaldo de Quirós, Carlos
227 2018 IMIA and Schattauer GmbH Terminology Services: Standard Terminologies to Control Health Vocabulary Experience at the Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires Fernán González Bernaldo de Quirós, Carlos
Critical appraisal checklist for papers on biological variation
 Biological Variation Working Group Critical appraisal checklist for papers on biological variation Dr Bill Bartlett Biological Variation Working Group EFLM Biological Variation Working Group Member These
Biological Variation Working Group Critical appraisal checklist for papers on biological variation Dr Bill Bartlett Biological Variation Working Group EFLM Biological Variation Working Group Member These
Ontology-Based Model of Law Retrieval System for R&D Projects
 Ontology-Based Model of Law Retrieval System for R&D Projects Wooju Kim Yonsei University 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea +82-2-2123-5716 wkim@yonsei.ac.kr Minjae Won INNOPOLIS Foundation
Ontology-Based Model of Law Retrieval System for R&D Projects Wooju Kim Yonsei University 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea +82-2-2123-5716 wkim@yonsei.ac.kr Minjae Won INNOPOLIS Foundation
Implementing Biomedical Informatics Approaches to Facilitate Translational and Clinical Research
 Implementing Biomedical Informatics Approaches to Facilitate Translational and Clinical Research Institute of Medicine May 30, 2014 David A. Fenstermacher, Ph.D. Chief Research Information Officer Professor,
Implementing Biomedical Informatics Approaches to Facilitate Translational and Clinical Research Institute of Medicine May 30, 2014 David A. Fenstermacher, Ph.D. Chief Research Information Officer Professor,
Digital Health and the Challenge of Interoperability
 Digital Health and the Challenge of Interoperability Theodoros N. Arvanitis, RT, DPhil, CEng, MIET, AMIA, NYAS, FRSM Professor of e-health Innovation & Head of Research Institute of Digital Healthcare,
Digital Health and the Challenge of Interoperability Theodoros N. Arvanitis, RT, DPhil, CEng, MIET, AMIA, NYAS, FRSM Professor of e-health Innovation & Head of Research Institute of Digital Healthcare,
Interoperability for clinical research Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI)
 9 ème École d'eté Méditerranéenne d'information en Santé Corte, France July 18, 2017 Interoperability for clinical research Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) Olivier Bodenreider
9 ème École d'eté Méditerranéenne d'information en Santé Corte, France July 18, 2017 Interoperability for clinical research Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) Olivier Bodenreider
Citation Discovery Tools for Conducting Adaptive Metaanalyses to Update Systematic Reviews
 Brief Report J Prev Med Public Health 2016;49:129-133 http://dx.doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.15.074 pissn 1975-8375 eissn 2233-4521 Journal of Preventive Medicine & Public Health Citation Discovery Tools for
Brief Report J Prev Med Public Health 2016;49:129-133 http://dx.doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.15.074 pissn 1975-8375 eissn 2233-4521 Journal of Preventive Medicine & Public Health Citation Discovery Tools for
The Wonderful World of Informatics
 The Wonderful World of Informatics VI Jornadas Universitarias de Sistemas de Informción en Salud 31 de octubre, 1 y 2 de noviembre 2011 W. Ed Hammond, PhD, FACMI, FAIMI, FAIMBE, FHL7 Director, Duke Center
The Wonderful World of Informatics VI Jornadas Universitarias de Sistemas de Informción en Salud 31 de octubre, 1 y 2 de noviembre 2011 W. Ed Hammond, PhD, FACMI, FAIMI, FAIMBE, FHL7 Director, Duke Center
SNOMED CT Editorial Guide
 SNOMED CT Editorial Guide Latest web browsable version: http://snomed.org/eg SNOMED CT document library: http://snomed.org/doc Publication date: 2017-08-01 Copyright 2017 International Health Terminology
SNOMED CT Editorial Guide Latest web browsable version: http://snomed.org/eg SNOMED CT document library: http://snomed.org/doc Publication date: 2017-08-01 Copyright 2017 International Health Terminology
Reflections on Improving the Interoperability and Use of the Data Dividend
 Reflections on Improving the Interoperability and Use of the Data Dividend Betsy L. Humphreys Acting Director National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
Reflections on Improving the Interoperability and Use of the Data Dividend Betsy L. Humphreys Acting Director National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
Building an Enterprise Architecture of Statistics Korea
 Distr. GENERAL WP.7 12 April 2010 ENGLISH ONLY UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE (UNECE) CONFERENCE OF EUROPEAN STATISTICIANS EUROPEAN COMMISSION STATISTICAL OFFICE OF THE EUROPEA UNION (EUROSTAT)
Distr. GENERAL WP.7 12 April 2010 ENGLISH ONLY UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE (UNECE) CONFERENCE OF EUROPEAN STATISTICIANS EUROPEAN COMMISSION STATISTICAL OFFICE OF THE EUROPEA UNION (EUROSTAT)
ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS. Selec g and zing an Electronic Medical Records. A WHITE PAPER by CureMD. CureMD Healthcare
 ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS Selec g and zing an Electronic Medical Records n A WHITE PAPER by CureMD CureMD Healthcare 120 Broadway, 35th Floor New York City, NY 10271 Overview United States of America
ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS Selec g and zing an Electronic Medical Records n A WHITE PAPER by CureMD CureMD Healthcare 120 Broadway, 35th Floor New York City, NY 10271 Overview United States of America
Health Data Management
 Western Technical College 10530176 Health Data Management Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 2.00 Total Hours 54.00 Introduces the use
Western Technical College 10530176 Health Data Management Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 2.00 Total Hours 54.00 Introduces the use
Integrating RAPID Common Data Elements and Modeling with the Goals of HSPC. MDEpiNet RAPID Sept 14, 2016 Stanley M. Huff, MD
 Integrating RAPID Common Data Elements and Modeling with the Goals of HSPC MDEpiNet RAPID Sept 14, 2016 Stanley M. Huff, MD Why? To help people live the healthiest lives possible. 4 Healthcare Services
Integrating RAPID Common Data Elements and Modeling with the Goals of HSPC MDEpiNet RAPID Sept 14, 2016 Stanley M. Huff, MD Why? To help people live the healthiest lives possible. 4 Healthcare Services
OMOP Specifications for Implementation of Standard Vocabularies in Observational Data Analysis
 OMOP Specifications for Implementation of Standard Vocabularies in Observational Data Analysis June 2010 - License 2010 Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH). Licensed under the Apache
OMOP Specifications for Implementation of Standard Vocabularies in Observational Data Analysis June 2010 - License 2010 Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH). Licensed under the Apache
Distribution Gwen Smith Head of Technical Services
 UK Terminology Release & Distribution K Term minolo ogy Ce entre Gwen Smith Head of Technical Services NHS Connecting for Health, Technology Office April 2009 U Outline UK Term minolo ogy Ce entre Concept
UK Terminology Release & Distribution K Term minolo ogy Ce entre Gwen Smith Head of Technical Services NHS Connecting for Health, Technology Office April 2009 U Outline UK Term minolo ogy Ce entre Concept
The Impact of Interoperability / HIE to a Health System s Strategic Roadmap: Lessons from the OpenHIE Project
 The Impact of Interoperability / HIE to a Health System s Strategic Roadmap: Lessons from the OpenHIE Project Shaun Grannis, MD, MS, FAAFP FACMI Biomedical Informatics Scientist Regenstrief Institute /
The Impact of Interoperability / HIE to a Health System s Strategic Roadmap: Lessons from the OpenHIE Project Shaun Grannis, MD, MS, FAAFP FACMI Biomedical Informatics Scientist Regenstrief Institute /
Innovation and Technology in Breast Cancer 2019 A research initiative from Breast Cancer Foundation NZ.
 Request for Proposals Innovation and Technology in Breast Cancer 2019 A research initiative from Breast Cancer Foundation NZ. Overview Breast Cancer Foundation NZ (BCFNZ) is committed to funding research
Request for Proposals Innovation and Technology in Breast Cancer 2019 A research initiative from Breast Cancer Foundation NZ. Overview Breast Cancer Foundation NZ (BCFNZ) is committed to funding research
Modeling the Form and Function of Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Ontological Model to Computerize Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Modeling the Form and Function of Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Ontological Model to Computerize Clinical Practice Guidelines Syed Sibte Raza Abidi 1 and Shapoor Shayegani 1 Abstract. Computerization
Modeling the Form and Function of Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Ontological Model to Computerize Clinical Practice Guidelines Syed Sibte Raza Abidi 1 and Shapoor Shayegani 1 Abstract. Computerization
Committee Subcommittee on Nomenclature for Properties and Units (C-SC-NPU)
 IUPAC Chemistry and Human Health Division IFCC Scientific Division Committee Subcommittee on Nomenclature for Properties and Units (C-SC-NPU) Draft minutes for the meeting in Paris 2009-04-26 28 Item 1.
IUPAC Chemistry and Human Health Division IFCC Scientific Division Committee Subcommittee on Nomenclature for Properties and Units (C-SC-NPU) Draft minutes for the meeting in Paris 2009-04-26 28 Item 1.
Organizational Track. 10a.m. 11a.m. TRAINING
 Organizational Track 10a.m. 11a.m. TRAINING 1 Qualifications for a Terminology Analyst Veterans Health Administration Melanie Loucks, RHIT VHA Enterprise Terminology Services Enterprise Terminology Services
Organizational Track 10a.m. 11a.m. TRAINING 1 Qualifications for a Terminology Analyst Veterans Health Administration Melanie Loucks, RHIT VHA Enterprise Terminology Services Enterprise Terminology Services
Healthcare Analytics Adoption: Start Small and Start Now
 Healthcare Analytics Adoption: Start Small and Start Now A modular approach that starts with small-scope projects can help mid-sized healthcare enterprises expand their analytics competency while adding
Healthcare Analytics Adoption: Start Small and Start Now A modular approach that starts with small-scope projects can help mid-sized healthcare enterprises expand their analytics competency while adding
Thank you for the opportunity to provide input into the review of NEHTA.
 Professor Siaw-Teng Liaw PhD, FRACGP, FACHI President, Australian College of Health Informatics The University of Melbourne Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry & Health Sciences Phone: 03-83443019 Fax: 03-83443785
Professor Siaw-Teng Liaw PhD, FRACGP, FACHI President, Australian College of Health Informatics The University of Melbourne Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry & Health Sciences Phone: 03-83443019 Fax: 03-83443785
Value of a statistical life estimation of carcinogenic chemicals for socioeconomic analysis in Korea
 eiss: 2233-6567 Environmental Health and Toxicology Brief Report Open Access Volume: 30 Suppl, Article ID: s2015005, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5620/eht.s2015005 Value of a statistical life estimation
eiss: 2233-6567 Environmental Health and Toxicology Brief Report Open Access Volume: 30 Suppl, Article ID: s2015005, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5620/eht.s2015005 Value of a statistical life estimation
Spring House, PA 19477, USA 3 School of Biomedical Informatics, The University of Texas Health Science. Center at Houston, Houston, TX 77030, USA
 Editorial: International Workshop on Biomedical Data Mining, Modeling, and Semantic Integration: A Promising Approach to Solving Unmet Medical Needs (BDM2I 2015), Co-located with the 2015 International
Editorial: International Workshop on Biomedical Data Mining, Modeling, and Semantic Integration: A Promising Approach to Solving Unmet Medical Needs (BDM2I 2015), Co-located with the 2015 International
RE: Draft Local Coverage Determination Molecular Diagnostic Tests (MDT) (DL33599)
 December 17, 2014 Elaine Jeter, MD Medical Director Palmetto GBA PO Box 100190 Columbia, SC 29202 elaine.jeter@palmettogba.com J11B.policy@PalmettoGBA.com RE: Draft Local Coverage Determination Molecular
December 17, 2014 Elaine Jeter, MD Medical Director Palmetto GBA PO Box 100190 Columbia, SC 29202 elaine.jeter@palmettogba.com J11B.policy@PalmettoGBA.com RE: Draft Local Coverage Determination Molecular
