ICC CODE CORNER 2012 IFC Code & Commentary
|
|
|
- Emery Franklin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION 1005 MEANS OF EGRESS SIZING [B] General. All portions of the means of egress system shall be sized in accordance with this section. Exception: Means of egress complying with Section This section is a charging paragraph for sizing for the means of egress system in a tenant space, floor or building. The exception is based on the understanding that the criteria for spaces that serve as assembly areas have unique criteria based on the high occupant load and possibility of stepped or sloped aisles. [B] Minimum width based on component. The minimum width, in inches (mm), of any means of egress component shall not be less than that specified for such component elsewhere in this code or the International Building Code. The code requires the utilization of two methods to determine the minimum width of egress components. While this section provides a methodology for determining required widths based on the design occupant load, calculated in accordance with Section , other sections provide minimum widths of various components. The actual width that is provided is to be the larger of the two widths. [B] Required capacity based on occupant load. The required capacity, in inches (mm), of the means of egress for any room, area, space or story shall not be less than that determined in accordance with Sections and For this section, the sum of the capacities of the means of egress components that serve each space must equal or exceed the occupant load of that space. For example, the combined width of all the exit stairways from a floor need to be considered to determine if the stairways have adequate capacity for everyone to evacuate the building. All
2 elements must meet the minimum width requirements specified in other sections (e.g., Section for doors; Sections and for stairs). This section establishes the necessary width of each egress component on a per-occupant basis. Means of egress components are separated between stairs and other; other being doors, doorways, corridors, ramps, aisles, etc. The traditional unit of measurement of egress capacity was based on a unit exit width that was to simulate the body ellipse with a basic dimensional width of 22 inches (559 mm) approximately the shoulder width of an average adult male. This unit exit width was combined with assumed egress movement (such as single file or staggered file) to result in an egress capacity per unit exit width for various occupancies. This assumption simplifies the dynamic egress process since contemporary studies have indicated that people do not egress in such precise and predictable movements. As traditionally used in the codes, the method of determining capacity per unit of clear width implies a higher level of accuracy than can realistically be achieved. The resulting factors preserve the features of the past practices that can be documented, while providing a more straightforward method of determining egress capacity. [B] Stairways. The capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress stairways shall be calculated by multiplying the occupant load served by such stairway by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.3 inch (7.6 mm) per occupant. Where stairways serve more than one story, only the occupant load of each story considered individually shall be used in calculating the required capacity of the stairways serving that story. Exception: For other than Group H and I-2
3 occupancies, the capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress stairways shall be calculated multiplying the occupant load served by such stairway by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.2 inch ( 5.1 mm) per occupant in buildings equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system installed in accordance with Section or and an emergency voice/alarm communication system in accordance with Section The capacity factor for stairways is larger than other egress components due to the slowdown of travel to negotiate the steps. When the required occupant capacity of an egress component is determined, multiplication by the results in the required clear width of the component in inches, based on capacity. Similarly, if the clear width of a component is known, division by the results in the permitted capacity of that component. Per the exception, other than in Group H or I-2, if the building is sprinklered and has an emergency voice/alarm communication system, the capacity factor for stairways is permitted to be reduced to 0.2 inches (5.1 mm) per occupant. The 2009 edition of the code did not include the exception for sprinklered buildings; however, editions previous to 2009 included similar allowances in a table. The following illustrate typical calculations for stairways from a nonsprinklered, twostory, two-exit office building: 1. Determine the minimum required stairway width with a second-floor occupant load of 350: 350 occupants divided by 0.3 inches = 105 inches (2667 mm) minimum; 105 inches divided by two stairways is 521/2 inches (1334 mm) minimum per stairway; or Section
4 prescribes that the width of an interior stairway cannot be less than 44 inches (1118 mm). The capacity criteria are more restrictive and, therefore, the minimum required width for each stairway is 521/2 inches (1334 mm). 2. Determine the minimum required stairways width with a second-floor occupant load of 90: 90 occupants divided by 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) = 27 inches (686 mm) minimum; 27 inches (686 mm) divided by two stairways is 131/2 inches (343 mm); or Section prescribes that the width of an interior stairway cannot be less than 44 inches (1118 mm). Note that the stair width reduction in Section , Exception 1, is applicable only when the entire occupant load of a story is less than 50. The minimum clear width requirements are more restrictive and, therefore, the minimum required width for each stairway is 44 inches (1118 mm). The maximum capacity of a 44-inch (1118 mm) stairway is 44 inches divided by 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant = 146 occupants. Therefore, a floor level with two exit stairways could have 292 occupants before the capacity would control the stairway egress width. Using the exception for sprinklered buildings, a 44-inch (1118 mm) stairway divided by 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant = 220 occupants. Therefore, a floor level with two exit stairways could have 440 occupants before the capacity would control the stairway egress width. Keep in mind that accessible means of egress stairways in nonsprinklered buildings require a minimum clear width of 48 inches (1219 mm) between handrails. [B] Other egress components. The capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress components
5 other than stairways shall be calculated by multiplying the occupant load served by such component by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.2 inch (5.1 mm) per occupant. Exception: For other than Group H and I-2 occupancies, the capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress components other than stairways shall be calculated multiplying the occupant load served by such component by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.15 inch (3.8 mm) per occupant in buildings equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system installed in accordance with Section or and an emergency voice/alarm communication system in accordance with Section The capacity factor for other egress components (i.e., doors, gates, corridors, aisles, ramps) is less than stairways due to the slowdown of travel to negotiate the steps. When the required occupant capacity of an egress component is determined, multiplication by the results in the required clear width of the component in inches, based on capacity. Similarly, if the clear width of a component is known, division by the results in the permitted capacity of that component. Per the exception, other than in Group H or I-2, if the building is sprinklered and has an emergency voice/alarm communication system, the capacity factor for doors, corridors, aisles, etc., is permitted to be reduced to 0.15 inches (3.8 mm) per occupant. The 2009 edition of the code did not include the exception for sprinklered buildings; however, previous editions included similar allowances in a table. For example, two exit access doorways from a room with an occupant load of 300 would each have a required capacity of not less than 150. Based on the minimum required clear door width [32-inch
6 (813 mm) clear width per door divided by 0.2 inch (5.08 mm) per occupant = 160 occupants], two 32-inch (813 mm) clear width doors would meet both the minimum clear width (Section ) and the capacity requirements. Two exits from a space with an occupant load of 450 would each have a required capacity of not less than 225, necessitating more doors or larger door leaves. 0.2 inch (5.1 mm) per occupant in buildings equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system installed in accordance with Section or and an emergency voice/alarm communication system in accordance with Section The capacity factor for stairways is larger than other egress components due to the slowdown of travel to negotiate the steps. When the required occupant capacity of an egress component is determined, multiplication by the results in the required clear width of the component in inches, based on capacity. Similarly, if the clear width of a component is known, division by the results in the permitted capacity of that component. Per the exception, other than in Group H or I-2, if the building is sprinklered and has an emergency voice/alarm communication system, the capacity factor for stairways is permitted to be reduced to 0.2 inches (5.1 mm) per occupant. The 2009 edition of the code did not include the exception for sprinklered buildings; however, editions previous to 2009 included similar allowances in a table. The following illustrate typical calculations for stairways from a nonsprinklered, twostory, two-exit office building: 1. Determine the minimum required stairway width with a second-floor occupant load of 350: 350 occupants divided
7 by 0.3 inches = 105 inches (2667 mm) minimum; 105 inches divided by two stairways is 521/2 inches (1334 mm) minimum per stairway; or Section prescribes that the width of an interior stairway cannot be less than 44 inches (1118 mm). The capacity criteria are more restrictive and, therefore, the minimum required width for each stairway is 521/2 inches (1334 mm). 2. Determine the minimum required stairways width with a second-floor occupant load of 90: 90 occupants divided by 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) = 27 inches (686 mm) minimum; 27 inches (686 mm) divided by two stairways is 131/2 inches (343 mm); or Section prescribes that the width of an interior stairway cannot be less than 44 inches (1118 mm). Note that the stair width reduction in Section , Exception 1, is applicable only when the entire occupant load of a story is less than 50. The minimum clear width requirements are more restrictive and, therefore, the minimum required widthfor each stairway is 44 inches (1118 mm). The maximum capacity of a 44-inch (1118 mm)stairway is 44 inches divided by 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant = 146 occupants. Therefore, a floor level with two exit stairways could have 292 occupants before the capacity would control the stairway egress width. Using the exception for sprinklered buildings, a 44-inch (1118 mm) stairway divided by 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant = 220 occupants. Therefore, a floor level with two exit stairways could have 440 occupants before the capacity would control the stairway egress width. Keep in mind that accessible means of egress stairways in nonsprinklered buildings
8 require a minimum clear width of 48 inches (1219 mm) between handrails. [B] Other egress components. The capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress components other than stairways shall be calculated by multiplying the occupant load served by such component by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.2 inch (5.1 mm) per occupant. Exception: For other than Group H and I-2 occupancies, the capacity, in inches (mm), of means of egress components other than stairways shall be calculated multiplyingthe occupant load served by such component by a means of egress capacity factor of 0.15 inch (3.8 mm) per occupant in buildings equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system installed in accordance with Section or and an emergency voice/alarm communication system in accordance with Section The capacity factor for other egress components (i.e., doors, gates, corridors, aisles, ramps) is less than stairways due to the slowdown of travel to negotiate the steps. When the required occupant capacity of an egress component is determined, multiplication by the results in the required clear width of the component in inches, based on capacity. Similarly, if the clear width of a component is known, division by the results in the permitted capacity of that component. Per the exception, other than in Group H or I-2, if the building is sprinklered and has an emergency voice/alarm communication system, the capacity factor for doors, corridors, aisles, etc., is permitted to be reduced to 0.15 inches (3.8 mm) per occupant. The 2009 edition of the code did not include the exception for sprinklered buildings; however, previous editions included similar allowances in a table.
9 For example, two exit access doorways from a room with an occupant load of 300 would each have a required capacity of not less than 150. Based on the minimum required clear door width [32-inch (813 mm) clear width per door divided by 0.2 inch (5.08 mm) per occupant = 160 occupants], two 32-inch (813 mm) clear width doors would meet both the minimum clear width (Section ) and the capacity requirements. Two exits from a space with an occupant load of 450 would each have a required capacity of not less than 225, necessitating more doors or larger door leaves. Doors in any position shall not reduce the required width by more than one-half. Exceptions: 1. Surface-mounted latch release hardware shall be exempt from inclusion in the 7-inch maximum (178 mm) encroachment where: 1.1. The hardware is mounted to the side of the door facing away from the adjacent wall where the door is in the open position; and 1.2. The hardware is mounted not less than 34 inches (865 mm) nor more than 48 inches (1219 mm) above the finished floor. 2. The restrictions on door swing shall not apply to doors within individual dwelling units and sleeping units of Group R-2 occupancies and dwelling units of Group R-3 occupancies.
10
11 Projections or restrictions in the required width can impede and restrict occupant travel, causing egress to occur less efficiently than expected. The swinging of a door, such as from a room into a corridor, and any handrails along the route are permitted projections. Historically this section has looked at doors on one wall at a time. Doors located across the hall from one another are not considered additive when considering protrusion limits. Doors would not typically be opened to the full extent at exactly the same moment, nor can they remain open at 90 degrees and totally blocking the hall because of the maximum limitation of 7 inches (178 mm) when fully open (typically approaching 180 degrees). Regarding door encroachment there are two tests. The arc created by the doors outside edge cannot project into more than one-half of the required corridor width. When opened to its fullest extent, the door cannot project more than 7 inches (178 mm) into the required width, which is the dimension of the leaf thickness excluding the hardware as shown in Figure Door hardware encroachment is addressed separately in Exception 1. These projections are permitted because they are considered to be temporary and do not significantly impede the flow. Occupants will compensate for the projection by a reduction in the natural cushion they retain between themselves and a boundary, known as the edge effect.
12
13 Per Exception 2, the door swing restrictions do not apply within dwelling units since the occupant load is very low. Based on the intent of this section, other situations that could be approved by the official having jurisdiction would be situations where the opening door would not block the egress, such as the door at the end of a corridor, or the room was not typically occupied, such as a janitor s closet. The provision in Exception 1 indicates that hardware facing the corridor when the door is fully open need not be considered when determining the allowable door encroachment into a corridor of 7 inches (178 mm) maximum. The allowance is applicable provided the hardware is mounted within height range of 34 inches to 48 inches (865 to 1220 mm) which is consistent with the range for means of egress door hardware height as established in Section Where hardware extends across a door, such as panic hardware, the 4-inch (102 mm) projection in the door opening is addressed in Section [B] Other projections. Handrail projections shall be in accordance with the provisions of Section Other nonstructural projections such as trim and similar decorative features shall be permitted to project into the required width a maximum of 11/2 inches (38 mm) on each side. Handrails are not required along corridors, level aisles, exit passageways and exit corridors; however, if provided, Section would be applicable. Handrails are sometimes provided along the hallways in hospitals or nursing homes to aid the residents. Bumper guards along the walls are not handrails. Items such as baseboards, chair rails, pilasters, etc., are limited to protruding over the required width of the corridor a maximum of 11 /2
14 inches (38 mm); however, once again, Section would be applicable when the corridor was wider than required. [B] Protruding objects. Protruding objects shall comply with the applicable requirements of Section This section is a reminder that protruding objects are applicable when looking at encroachments into a confined path of travel. The difference, however, is that door and other projections are applied to the required minimum width, while protruding object provisions apply to paths of travel even when wider than required. Next Month: SECTION 1006 MEANS OF EGRESS ILLUMINATION - Page 471. The International Code, a membership association dedicated to building safety and fire prevention, develops the codes used to construct residential and commercial buildings, including homes and schools. Most U.S. cities, counties and states that adopt codes choose the International Codes developed by the International Code.
15 The Center for Campus Fire Safety
ICC CODE CORNER 2012 IFC Code & Commentary
 Chapter 10: Means of Egress General Comments The general criteria set forth in Chapter 10 regulating the design of the means of egress are established as the primary method for protection of people in
Chapter 10: Means of Egress General Comments The general criteria set forth in Chapter 10 regulating the design of the means of egress are established as the primary method for protection of people in
2015 International Fire Code
 1001, 1001.1, 1001.2, 1002, [BE] 1002.1, 1003, [BE] 1003.1, [BE] 1003.2, [BE] 1003.3, [BE] 1003.3.1, [BE] 1003.3.2, [BE] 1003.3.3, [BE] 1003.3.4, [BE] 1003.4, [BE] 1003.5, [BE] 1003.6, [BE] 1003.7, 1004,
1001, 1001.1, 1001.2, 1002, [BE] 1002.1, 1003, [BE] 1003.1, [BE] 1003.2, [BE] 1003.3, [BE] 1003.3.1, [BE] 1003.3.2, [BE] 1003.3.3, [BE] 1003.3.4, [BE] 1003.4, [BE] 1003.5, [BE] 1003.6, [BE] 1003.7, 1004,
Work Group Item Stairways serving an occupant load of less than 50 shall have a width of not less than 36 inches (914 mm).
 IBC-12/13 1009.1, 1009.4, 1009.7.2, 1009.7.4, 1009.8, 1009.10, 1009.15 (IFC [B] 1009.1, 1009.4, 1009.7.2, 1009.7.4, 1009.8, 1009.10, 1009.15) Proponent: S. Bajnai, Chesterfield County, VA, ICC Building
IBC-12/13 1009.1, 1009.4, 1009.7.2, 1009.7.4, 1009.8, 1009.10, 1009.15 (IFC [B] 1009.1, 1009.4, 1009.7.2, 1009.7.4, 1009.8, 1009.10, 1009.15) Proponent: S. Bajnai, Chesterfield County, VA, ICC Building
APPLICATION NUMBER:, TAX MAP KEY: STREET ADDRESS:, PRPOJECT: APPLICANT:, PHONE NO: MAILING ADDRESS:, FAX NO:
 COUNTY OF KAUAI BUILDING DIVISION, DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS 4444 RICE STREET, SUITE 175, LIHUE, HAWAII 96766 Telephone: (808) 241-6655 Fax Number: (808) 241-6806 BUILDING CODE COMMERCIAL CHECKLIST APPLICATION
COUNTY OF KAUAI BUILDING DIVISION, DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC WORKS 4444 RICE STREET, SUITE 175, LIHUE, HAWAII 96766 Telephone: (808) 241-6655 Fax Number: (808) 241-6806 BUILDING CODE COMMERCIAL CHECKLIST APPLICATION
2009 IBC Section 1024 Approved Luminous Egress Path Markings
 2009 IBC Section 1024 Approved Luminous Egress Path Markings Where Required Buildings of Groups A (Assembly), B (Business), E (Education), I (Institutional), M (Mercantile) and R-1 (Residential transient
2009 IBC Section 1024 Approved Luminous Egress Path Markings Where Required Buildings of Groups A (Assembly), B (Business), E (Education), I (Institutional), M (Mercantile) and R-1 (Residential transient
2015 IBC Accessible Means of Egress
 2015 IBC Accessible Means of Egress Based on the 2015 International Building Code Description Upon completion, the participant will be able to apply the accessible means of egress provisions of Section
2015 IBC Accessible Means of Egress Based on the 2015 International Building Code Description Upon completion, the participant will be able to apply the accessible means of egress provisions of Section
Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction
 Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction Accessibility Training Course Florida Building Commission Introduction Course will review the Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction as
Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction Accessibility Training Course Florida Building Commission Introduction Course will review the Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction as
2012 IBC Assembly Means of Egress. Based on the 2012 International Building Code
 2012 IBC Assembly Means of Egress Based on the 2012 International Building Code Overview This seminar deals with those means of egress provisions of the IBC that are intended to address the concerns related
2012 IBC Assembly Means of Egress Based on the 2012 International Building Code Overview This seminar deals with those means of egress provisions of the IBC that are intended to address the concerns related
PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD
 CHAPTER 3 PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD [B] SECTION 301 GENERAL 301.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall control the alteration, repair, addition and change of occupancy of existing structures,
CHAPTER 3 PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD [B] SECTION 301 GENERAL 301.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall control the alteration, repair, addition and change of occupancy of existing structures,
PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD
 CHAPTER PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD 3 SECTION 301 GENERAL 301.2 Building materials. Building materials shall comply with the requirements of this section. 301.2.1 Existing materials. Materials already
CHAPTER PRESCRIPTIVE COMPLIANCE METHOD 3 SECTION 301 GENERAL 301.2 Building materials. Building materials shall comply with the requirements of this section. 301.2.1 Existing materials. Materials already
EGRESS CHAPTER ,500 3 Over 2,500 4 OCCUPANT LOAD REQUIRED MEANS OF EGRESS
 CHAPTER 4 EGRESS SECTION 401 GENERAL 401.1 General. The means of egress for new bleachers, folding and telescopic seating, and grandstands shall comply with this chapter. SECTION 402 TRAVEL 402.1 Exit
CHAPTER 4 EGRESS SECTION 401 GENERAL 401.1 General. The means of egress for new bleachers, folding and telescopic seating, and grandstands shall comply with this chapter. SECTION 402 TRAVEL 402.1 Exit
The Building Codes A.R.E. Building Design and Construction Exam Prep
 Know Thy Codes! The Building Codes Building Codes The Code of Hammurabi 4000bc Developed 19 th and 20 th c. Codes define what you can and can t do Allowable area and height based on degree of danger Fire
Know Thy Codes! The Building Codes Building Codes The Code of Hammurabi 4000bc Developed 19 th and 20 th c. Codes define what you can and can t do Allowable area and height based on degree of danger Fire
Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction
 Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction Accessibility Training Course Florida Building Commission 1 Introduction Course will review the Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction
Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction Accessibility Training Course Florida Building Commission 1 Introduction Course will review the Florida Accessibility Code for Building Construction
Universal Design Standards
 Universal Design Standards For applications submitted and approved after April 16, 2007 Introduction to Universal Design Universal design is a building concept that incorporates products, general design
Universal Design Standards For applications submitted and approved after April 16, 2007 Introduction to Universal Design Universal design is a building concept that incorporates products, general design
2012 IBC Exit Systems
 Accreditation Based on the 2012 International Building Code The International Code Council has been accredited as an Authorized Provider by the International Association for Continuing Education and Training
Accreditation Based on the 2012 International Building Code The International Code Council has been accredited as an Authorized Provider by the International Association for Continuing Education and Training
2007 Title 24 Accessibility Code Updates and ADA Issues
 2007 Title 24 Accessibility Code Updates and ADA Issues C.A.S.H. Workshop June 2007 Introduction Update on ADA Certification of the California Building Code Overview of significant changes to accessibility
2007 Title 24 Accessibility Code Updates and ADA Issues C.A.S.H. Workshop June 2007 Introduction Update on ADA Certification of the California Building Code Overview of significant changes to accessibility
BRADYGLO EMERGENCY EGRESS MARKING HANDBOOK
 BRADYGLO EMERGENCY EGRESS MARKING HANDBOOK BRADYGLO EMERGENCY EGRESS MARKING HANDBOOK Table of Contents Introduction to Code Changes...2 2009 International Building Code and International Fire Code...3
BRADYGLO EMERGENCY EGRESS MARKING HANDBOOK BRADYGLO EMERGENCY EGRESS MARKING HANDBOOK Table of Contents Introduction to Code Changes...2 2009 International Building Code and International Fire Code...3
E2-09/ (IFC [B] )
![E2-09/ (IFC [B] ) E2-09/ (IFC [B] )](/thumbs/78/77541898.jpg) Code Technology Committee 2010 Final Action Agenda The following are code changes and public comments to be considered at the 2010 Dallas Final Action Hearings that are related to the CTC Area of Study
Code Technology Committee 2010 Final Action Agenda The following are code changes and public comments to be considered at the 2010 Dallas Final Action Hearings that are related to the CTC Area of Study
EXIT ACCESS RAMP. An interior ramp that is not a required interior exit ramp.
 Coordination with language throughout code 10/05/2011 Stair vs. stairway Repetitive language with stairways and ramps Including ramps when applicable The locations for stair, stairway and ramp as used
Coordination with language throughout code 10/05/2011 Stair vs. stairway Repetitive language with stairways and ramps Including ramps when applicable The locations for stair, stairway and ramp as used
Comparison of the life safety elements of the 1997 UBC and the IBC 2000.
 Comparison of the life safety elements of the 1997 UBC and the IBC 2000. Introduction The Building Performance Research Institute s mission is primarily one of education on building safety and performance.
Comparison of the life safety elements of the 1997 UBC and the IBC 2000. Introduction The Building Performance Research Institute s mission is primarily one of education on building safety and performance.
CITY OF LOS ANGELES Department of Building and Safety Disabled Access Section RESIDENTIAL ACCESSIBILITY PLAN REVIEW LIST
 GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PERMIT APPLICATION # PLAN CHECK NO JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE DATE NOTE: Numbers in the parenthesis ( ) refer to sections of the 2014 edition of the Los Angeles
GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PERMIT APPLICATION # PLAN CHECK NO JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE DATE NOTE: Numbers in the parenthesis ( ) refer to sections of the 2014 edition of the Los Angeles
Applying the Building Code During Design
 Applying the Building Code During Design A Step-By-Step Process AIA Learning Units The Salt Lake City CSI Chapter is a Registered Provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education
Applying the Building Code During Design A Step-By-Step Process AIA Learning Units The Salt Lake City CSI Chapter is a Registered Provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education
2015 IBC Exit Systems
 Objectives 2015 IBC Exit Systems Based on the 2015 International Building Code Upon completion, participants will be better able to: Determine those means of egress components that are defined as exits
Objectives 2015 IBC Exit Systems Based on the 2015 International Building Code Upon completion, participants will be better able to: Determine those means of egress components that are defined as exits
Stairs have many potential violations this Newsletter is Part 1 of two parts.
 Stairs have many potential violations this Newsletter is Part 1 of two parts. Violation 1 : Risers do not meet requirements: riser heights too high/low; too much variation between riser heights; risers
Stairs have many potential violations this Newsletter is Part 1 of two parts. Violation 1 : Risers do not meet requirements: riser heights too high/low; too much variation between riser heights; risers
City of Des Moines. Permit and Development Center 602 Robert D Ray Drive Des Moines, IA Phone: Fax:
 City of Des Moines Permit and Development Center 602 Robert D Ray Drive Des Moines, IA 50309 Phone: 515-283-4200 Fax: 515-283-4270 This Code Analysis Form must be completed and returned with the Building
City of Des Moines Permit and Development Center 602 Robert D Ray Drive Des Moines, IA 50309 Phone: 515-283-4200 Fax: 515-283-4270 This Code Analysis Form must be completed and returned with the Building
INTERIOR FINISHES CHAPTER 8
 CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.2 Interior wall and
CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.2 Interior wall and
FBC 5 th Edition. General. Update to the Florida Building and Residential Codes Updates to the Florida Building and Residential Codes
 Updates to the Florida Building and presented by T. Eric Stafford T. Eric Stafford & Associates, LLC This material is protected and the property of T. Eric Stafford & Associates, LLC and cannot be reproduced
Updates to the Florida Building and presented by T. Eric Stafford T. Eric Stafford & Associates, LLC This material is protected and the property of T. Eric Stafford & Associates, LLC and cannot be reproduced
A117.1 Chapter 3 Building Blocks
 Study Session 3 A117.1 Chapter 3 Building Blocks OBJECTIVE: To obtain an understanding of the fundamental accessibility requirements related to floor surfaces, changes in level, turning space, clear floor
Study Session 3 A117.1 Chapter 3 Building Blocks OBJECTIVE: To obtain an understanding of the fundamental accessibility requirements related to floor surfaces, changes in level, turning space, clear floor
ELEVATORS, LULAS AND PLATFORM LIFTS
 ELEVATORS City of Los Angeles Plan Check No: 1. Elevators provided for passengers shall comply with 11B-407 Elevators. Where multiple elevators are provided, each elevator shall comply with 11B-407 Elevators;
ELEVATORS City of Los Angeles Plan Check No: 1. Elevators provided for passengers shall comply with 11B-407 Elevators. Where multiple elevators are provided, each elevator shall comply with 11B-407 Elevators;
Accessible Means Of Egress
 Accessible Means Of Egress 2 New ADA Standards DOJ s 2010 standards (mandatory as of March 15) Based on the Board s ADA-ABA Guidelines (2004) 3 Standards Department of Transportation s ADA Standards Federal
Accessible Means Of Egress 2 New ADA Standards DOJ s 2010 standards (mandatory as of March 15) Based on the Board s ADA-ABA Guidelines (2004) 3 Standards Department of Transportation s ADA Standards Federal
First Revision No NFPA [ Section No ]
![First Revision No NFPA [ Section No ] First Revision No NFPA [ Section No ]](/thumbs/72/67132364.jpg) National Fire Protection Association Report of 13 http://submittals.nfpa.org/terraviewweb/contentfetcher?commentpara... 10/28/2015 10:35 AM First Revision No. 5501-NFPA 5000-2015 [ Section No. 3.3.220.4
National Fire Protection Association Report of 13 http://submittals.nfpa.org/terraviewweb/contentfetcher?commentpara... 10/28/2015 10:35 AM First Revision No. 5501-NFPA 5000-2015 [ Section No. 3.3.220.4
WINDOW AND DOOR REPLACEMENT SAMPLE PLAN
 To aid in communication between yourself, the inspectors, and the plans examiners, we have prepared this sample plan to assist in the preparations of your plan for window and door replacement. Follow the
To aid in communication between yourself, the inspectors, and the plans examiners, we have prepared this sample plan to assist in the preparations of your plan for window and door replacement. Follow the
WON-DOOR CORPORATION Won-Door FireGuard Applications
 WON-DOOR CORPORATION Won-Door FireGuard Applications A Code Analysis WON-DOOR CORPORATION Won-Door FireGuard Applications A Code Analysis THE INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE is widely recognized in the United
WON-DOOR CORPORATION Won-Door FireGuard Applications A Code Analysis WON-DOOR CORPORATION Won-Door FireGuard Applications A Code Analysis THE INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE is widely recognized in the United
Code Requirements for Existing Buildings. R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617)
 Code Requirements for Existing Buildings R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617) 523-8227 www.rwsullivan.com R.W. Sullivan Engineering (RWS) was established in 1945 and currently
Code Requirements for Existing Buildings R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617) 523-8227 www.rwsullivan.com R.W. Sullivan Engineering (RWS) was established in 1945 and currently
INTERIOR FINISHES CHAPTER 8
 CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.1.1 Interior finishes.
CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.1.1 Interior finishes.
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING REQUIREMENTS
 RESIDENTIAL BUILDING REQUIREMENTS Residential Building Requirements This is an informational booklet with some of the general residential construction requirements taken from the codes adopted by Campbell
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING REQUIREMENTS Residential Building Requirements This is an informational booklet with some of the general residential construction requirements taken from the codes adopted by Campbell
CITY OF DANA POINT. COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT, BUILDING AND SAFETY Golden Lantern, Suite 209 Dana Point, CA
 CITY OF DANA POINT COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT, BUILDING AND SAFETY 33282 Golden Lantern, Suite 209 Dana Point, CA 92629 949 248-3594 www.danapoint.org B005 COM STRUCT 2016 CALIFORNIA CODES CODE CYCLE 01/01/2017
CITY OF DANA POINT COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT, BUILDING AND SAFETY 33282 Golden Lantern, Suite 209 Dana Point, CA 92629 949 248-3594 www.danapoint.org B005 COM STRUCT 2016 CALIFORNIA CODES CODE CYCLE 01/01/2017
STAIRWAYS, HANDRAILS, AND GUARDRAILS (RESIDENTIAL)
 01/25/08 STAIRWAYS, HANDRAILS, AND GUARDRAILS (RESIDENTIAL) City of Austin International Residential Code: 500 Fourth Avenue NE R314.1 Width. Stairways shall not be less than 36 in clear width at all points
01/25/08 STAIRWAYS, HANDRAILS, AND GUARDRAILS (RESIDENTIAL) City of Austin International Residential Code: 500 Fourth Avenue NE R314.1 Width. Stairways shall not be less than 36 in clear width at all points
WHO IS THIS COURSE FOR?
 INTRODUCTION INSTRUCTIONS - READ ME FIRST BEFORE THE COURSE STARTS, WORK ON YOUR OWN AND COMPLETE ALL OF THE EXERCISES. If you come unprepared, you will have a difficult time to keep up with the pace of
INTRODUCTION INSTRUCTIONS - READ ME FIRST BEFORE THE COURSE STARTS, WORK ON YOUR OWN AND COMPLETE ALL OF THE EXERCISES. If you come unprepared, you will have a difficult time to keep up with the pace of
INTERIOR FINISHES CHAPTER 8
 CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.2 Interior wall and
CHAPTER 8 INTERIOR FINISHES SECTION 801 GENERAL 801.1 Scope. Provisions of this chapter shall govern the use of materials used as interior finishes, trim and decorative materials. 801.2 Interior wall and
780 CMR CHAPTER 34 EXISTING BUILDINGS STRUCTURES
 780 CMR CHAPTER 34 EXISTING BUILDINGS STRUCTURES SECTION 3401 GENERAL 3401.1 Scope. Chapter 34 of the International Building Code 2009 is deleted in its entirety. The provisions of the International Existing
780 CMR CHAPTER 34 EXISTING BUILDINGS STRUCTURES SECTION 3401 GENERAL 3401.1 Scope. Chapter 34 of the International Building Code 2009 is deleted in its entirety. The provisions of the International Existing
2003 International Residential Building Code
 2003 International Residential Building Code Section R305 Ceiling Height Habitable rooms, hallways, corridors, bathrooms, toilet rooms, laundry rooms and basements shall have a ceiling height of not less
2003 International Residential Building Code Section R305 Ceiling Height Habitable rooms, hallways, corridors, bathrooms, toilet rooms, laundry rooms and basements shall have a ceiling height of not less
HERMIT S REST GRAND CANYON NATIONAL PARK BUILDING CODE REVIEW
 HERMIT S REST GRAND CANYON NATIONAL PARK BUILDING CODE REVIEW 27 September 2007 prepared by: J. CHRIS EVANS ARCHITECT 3220 E. Terra Alta Blvd. No. 9 Tucson, Arizona 85716 520.319.8835 evansarch@hotmail.com
HERMIT S REST GRAND CANYON NATIONAL PARK BUILDING CODE REVIEW 27 September 2007 prepared by: J. CHRIS EVANS ARCHITECT 3220 E. Terra Alta Blvd. No. 9 Tucson, Arizona 85716 520.319.8835 evansarch@hotmail.com
IWF Safety Guidelines
 2018 The purpose for the display rules and height restrictions is to provide visibility to all exhibitors. At the same time, these regulations should maintain the inherent benefits of differing exhibit
2018 The purpose for the display rules and height restrictions is to provide visibility to all exhibitors. At the same time, these regulations should maintain the inherent benefits of differing exhibit
2007/2008 INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE Means of Egress Code Development Committee
 2007/2008 INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE Means of Egress Code Development Committee Dave Frable - Chair Senior Fire Protection Engineer U.S. General Services Administration, Public Building Services Geneva,
2007/2008 INTERNATIONAL BUILDING CODE Means of Egress Code Development Committee Dave Frable - Chair Senior Fire Protection Engineer U.S. General Services Administration, Public Building Services Geneva,
Minnesota Healthcare Engineers Association, Fall Conference. Bob Dehler, P.E. Engineering Program Manager September 14, 2017
 Minnesota Healthcare Engineers Association, Fall Conference Bob Dehler, P.E. Engineering Program Manager September 14, 2017 Categories of Rehabilitation Work in Healthcare Facilities Bob Dehler, P.E. robert.dehler@state.mn.us
Minnesota Healthcare Engineers Association, Fall Conference Bob Dehler, P.E. Engineering Program Manager September 14, 2017 Categories of Rehabilitation Work in Healthcare Facilities Bob Dehler, P.E. robert.dehler@state.mn.us
Excerpts from: International Residential Code 2009
 LUMBER & MILLWORK Excerpts from: International Residential Code 2009 R310.1 Emergency escape and rescue required. Basements, habitable attics and every sleeping room shall have at least one operable emergency
LUMBER & MILLWORK Excerpts from: International Residential Code 2009 R310.1 Emergency escape and rescue required. Basements, habitable attics and every sleeping room shall have at least one operable emergency
Code Requirements for Existing Buildings. R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617)
 Code Requirements for Existing Buildings R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617) 523-8227 www.rwsullivan.com R.W. Sullivan Engineering (RWS) was established in 1945 and currently
Code Requirements for Existing Buildings R. W. Sullivan, Inc. 529 Main St., Suite 203 Charlestown, MA (617) 523-8227 www.rwsullivan.com R.W. Sullivan Engineering (RWS) was established in 1945 and currently
What is a Won-Door FireGuard Door?
 What is a Won-Door FireGuard Door?. A horizontal sliding accordion fire door that meets all IBC requirements for use in a means of egress and has fire ratings up to 3 hours. A Reference Guide to special
What is a Won-Door FireGuard Door?. A horizontal sliding accordion fire door that meets all IBC requirements for use in a means of egress and has fire ratings up to 3 hours. A Reference Guide to special
Chapter 11. Dwelling Units and Sleeping Units
 1101 General Chapter 11. Dwelling Units and Sleeping Units 1101.1 Scoping. Dwelling units and sleeping units required by the scoping provisions adopted by the administrative authority to be Accessible
1101 General Chapter 11. Dwelling Units and Sleeping Units 1101.1 Scoping. Dwelling units and sleeping units required by the scoping provisions adopted by the administrative authority to be Accessible
CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY UPDATE
 CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY UPDATE No. 78, September 2011 Building Egress Using Photoluminescent Markings by Noureddine Benichou and Guylene Proulx The use of photoluminescent material systems in buildings
CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY UPDATE No. 78, September 2011 Building Egress Using Photoluminescent Markings by Noureddine Benichou and Guylene Proulx The use of photoluminescent material systems in buildings
COMMUNITY RISK REDUCTION BUREAU MANUAL CODE REQUREMENTS TEMPORARY TENTS AND MEMBRANE STRUCTURES EFFECTIVE: APRIL 1, 2016 AUTHORIZED: R.
 COMMUNITY RISK REDUCTION BUREAU MANUAL CODE REQUREMENTS 423.7 TEMPORARY TENTS AND MEMBRANE STRUCTURES EFFECTIVE: APRIL 1, 2016 AUTHORIZED: R. Pearce SCOPE This policy applies to temporary tents, air-supported,
COMMUNITY RISK REDUCTION BUREAU MANUAL CODE REQUREMENTS 423.7 TEMPORARY TENTS AND MEMBRANE STRUCTURES EFFECTIVE: APRIL 1, 2016 AUTHORIZED: R. Pearce SCOPE This policy applies to temporary tents, air-supported,
Analysis of Changes for the 5 th Edition (2014) of the Florida Codes
 Analysis of Changes for the 5 th Edition (2014) of the Florida Codes Changes to the Florida Building Code, Existing Building This Analysis of Changes for the 5 th Edition (2014) of the Florida Codes is
Analysis of Changes for the 5 th Edition (2014) of the Florida Codes Changes to the Florida Building Code, Existing Building This Analysis of Changes for the 5 th Edition (2014) of the Florida Codes is
Building Codes and Ordinances ARC 227
 Building Codes and Ordinances ARC 227 Week 6 Fire Resistive Construction 03.02.10 Instructor: Rick Staub, AIA Email: staub@pointonearchitects.com Phone: 860-434-7707 Fire Resistive Construction Passive
Building Codes and Ordinances ARC 227 Week 6 Fire Resistive Construction 03.02.10 Instructor: Rick Staub, AIA Email: staub@pointonearchitects.com Phone: 860-434-7707 Fire Resistive Construction Passive
Visual Interpretation Of The
 Visual Interpretation Of The N T E R N A T I O N A L E S I D E N T I A L O D E 2006 IRC NEW JERSEY EDITION RESIDENTIAL BUILDING CODE SECTION R314 STAIRWAYS R314.1 Width. Stairways shall not be less than
Visual Interpretation Of The N T E R N A T I O N A L E S I D E N T I A L O D E 2006 IRC NEW JERSEY EDITION RESIDENTIAL BUILDING CODE SECTION R314 STAIRWAYS R314.1 Width. Stairways shall not be less than
2018 APPENDIX B BUILDING CODE SUMMARY FOR ALL COMMERCIAL PROJECTS (EXCEPT 1 AND 2-FAMILY DWELLINGS AND TOWNHOUSES)
 2018 APPENDIX B BUILDING CODE SUMMARY FOR ALL COMMERCIAL PROJECTS (EXCEPT 1 AND 2-FAMILY DWELLINGS AND TOWNHOUSES) (Reproduce the following data on the building plans sheet 1 or 2) Name of Project: Address:
2018 APPENDIX B BUILDING CODE SUMMARY FOR ALL COMMERCIAL PROJECTS (EXCEPT 1 AND 2-FAMILY DWELLINGS AND TOWNHOUSES) (Reproduce the following data on the building plans sheet 1 or 2) Name of Project: Address:
DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS CONSUMER AND INDUSTRY SERVICES DIRECTOR S OFFICE BUREAU OF SAFETY AND REGULATION
 DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS CONSUMER AND INDUSTRY SERVICES DIRECTOR S OFFICE BUREAU OF SAFETY AND REGULATION GENERAL INDUSTRY SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARD GENERAL INDUSTRY SAFETY STANDARDS
DEPARTMENT OF LICENSING AND REGULATORY AFFAIRS CONSUMER AND INDUSTRY SERVICES DIRECTOR S OFFICE BUREAU OF SAFETY AND REGULATION GENERAL INDUSTRY SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARD GENERAL INDUSTRY SAFETY STANDARDS
Overview of Revised School Regulation
 Office of the State Fire Marshal Overview of Revised School Regulation By: Timothee Rodrique Director, OSFM October, 2003 Training Effective Fire Prevention through Public Education Introduction! Purpose
Office of the State Fire Marshal Overview of Revised School Regulation By: Timothee Rodrique Director, OSFM October, 2003 Training Effective Fire Prevention through Public Education Introduction! Purpose
Q. Do residential and historical buildings that are going to be protected with sprinklers need to conduct an LSE?
 TECHNICAL AND CODE INTERPRETATION QUESTIONS: Q. For evaluation and scoring purposes, the Rules distinguish between Residential and Commercial occupancies. In terms of the referenced sections of the Chicago
TECHNICAL AND CODE INTERPRETATION QUESTIONS: Q. For evaluation and scoring purposes, the Rules distinguish between Residential and Commercial occupancies. In terms of the referenced sections of the Chicago
Workplaces must be kept clean, orderly, and sanitary. Workroom floors must be maintained as clean and dry as possible.
 Section C.19 University of South Carolina Safety Program Guide WALKING AND WORKING SURFACES Introduction Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) CFR 1910 Subpart D Walking and Working Surfaces
Section C.19 University of South Carolina Safety Program Guide WALKING AND WORKING SURFACES Introduction Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) CFR 1910 Subpart D Walking and Working Surfaces
COMMERCIAL PLAN REVIEW FOR CODE COMPLIANCE
 3800 Laverne Avenue Lake Elmo, Minnesota 55042 (651) 747-3900 Fax (651)747-3901 COMMERCIAL PLAN REVIEW FOR CODE COMPLIANCE Introduction Site Address: Facility Name: Project Contact(s): (Name/address/phone/fax
3800 Laverne Avenue Lake Elmo, Minnesota 55042 (651) 747-3900 Fax (651)747-3901 COMMERCIAL PLAN REVIEW FOR CODE COMPLIANCE Introduction Site Address: Facility Name: Project Contact(s): (Name/address/phone/fax
Chapter 4-16 SPECIAL DESIGN STANDARDS FOR TYPE V CONSTRUCTION
 Chapter 4-16 SPECIAL DESIGN STANDARDS FOR TYPE V CONSTRUCTION Sections: 4-16-01 PURPOSE 4-16-02 APPLICABLE AREA 4-16-03 CONSTRUCTION AND OCCUPANCY 4-16-04 UPPER BUILDING AREA, HEIGHT, NUMBER OF STORIES
Chapter 4-16 SPECIAL DESIGN STANDARDS FOR TYPE V CONSTRUCTION Sections: 4-16-01 PURPOSE 4-16-02 APPLICABLE AREA 4-16-03 CONSTRUCTION AND OCCUPANCY 4-16-04 UPPER BUILDING AREA, HEIGHT, NUMBER OF STORIES
LINCOLN COUNTY REQUIRED INSPECTIONS (Last updated August 23, 2017)
 LINCOLN COUNTY REQUIRED INSPECTIONS (Last updated August 23, 2017) It is the responsibility of the permit applicant to notify the building inspector when the work is ready for inspection. To request an
LINCOLN COUNTY REQUIRED INSPECTIONS (Last updated August 23, 2017) It is the responsibility of the permit applicant to notify the building inspector when the work is ready for inspection. To request an
Priority 2 Access to Goods & Services
 Based on the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design Project Building Location Date Surveyors Contact Information The layout of the building should allow people with disabilities to obtain goods and services
Based on the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design Project Building Location Date Surveyors Contact Information The layout of the building should allow people with disabilities to obtain goods and services
PROGRAM OVERVIEW WALKING/WORKING SURFACE INDUSTRIAL SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR
 PROGRAM OVERVIEW WALKING/WORKING SURFACE INDUSTRIAL SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.21-23 INTRODUCTION: Thousands of workers are injured every year due to slips, trips, or falls
PROGRAM OVERVIEW WALKING/WORKING SURFACE INDUSTRIAL SAFETY PROGRAM REGULATORY STANDARD: OSHA - 29 CFR 1910.21-23 INTRODUCTION: Thousands of workers are injured every year due to slips, trips, or falls
CHAPTER 26 PLASTIC SECTION BC 2601 SECTION BC 2603 GENERAL FOAM PLASTIC INSULATION
 CHAPTER 26 PLASTIC SECTION BC 2601 GENERAL 2601.1 Scope. These provisions shall govern the materials, design, application, construction and installation of foam plastic, foam plastic insulation, plastic
CHAPTER 26 PLASTIC SECTION BC 2601 GENERAL 2601.1 Scope. These provisions shall govern the materials, design, application, construction and installation of foam plastic, foam plastic insulation, plastic
Model Safety Program
 Model Safety Program DATE: SUBJECT: Walking/Working Surface Safety Program (Industrial). REGULATORY STATUTES: OSHA 29 CFR 1910.21 23 RESPONSIBILITY: The company Safety Officer is. He/she is solely responsible
Model Safety Program DATE: SUBJECT: Walking/Working Surface Safety Program (Industrial). REGULATORY STATUTES: OSHA 29 CFR 1910.21 23 RESPONSIBILITY: The company Safety Officer is. He/she is solely responsible
IBC Significant Changes Summary Tier I
 2009-2015 IBC Significant Changes Summary Tier I 503 General Building Height & Area Limitations Methods for determining allowable heights and areas have been dramatically revised and reformatted to improve
2009-2015 IBC Significant Changes Summary Tier I 503 General Building Height & Area Limitations Methods for determining allowable heights and areas have been dramatically revised and reformatted to improve
Accessibility Guidelines for Buildings and Facilities (ADAAG) The American with Disabilities Act
 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Municipality of Trent Hills would like to thank and recognize the City of London for creating the original document on which these design standards have been based the City of London
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Municipality of Trent Hills would like to thank and recognize the City of London for creating the original document on which these design standards have been based the City of London
BUILDING CODE VARIANCE
 BUILDING CODE VARIANCE April 2009 06-BCV-011-R1 Page 1 of 8 DISCUSSION MULTI-LEVEL STORAGE RACKING SYSTEMS The Alberta Building Code 2006 contains no specific requirements for multi-level storage racking
BUILDING CODE VARIANCE April 2009 06-BCV-011-R1 Page 1 of 8 DISCUSSION MULTI-LEVEL STORAGE RACKING SYSTEMS The Alberta Building Code 2006 contains no specific requirements for multi-level storage racking
Minnesota Health Care Engineers Association
 Minnesota Health Care Engineers Association Life Safety Code Potpourri Friday, May 1, 2015 Presenter: Bob Dehler, P.E., Engineering Program Manager, Minnesota Department of Health Minnesota Department
Minnesota Health Care Engineers Association Life Safety Code Potpourri Friday, May 1, 2015 Presenter: Bob Dehler, P.E., Engineering Program Manager, Minnesota Department of Health Minnesota Department
1. Frozen food warehouses used solely for storage of Class I and II commodities where protected by an approved automatic sprinkler system.
 Draft curtains are typically used in warehouses, aircraft hangars and large industrial plants to contain or channel smoke that rises to the ceiling in a fire. They can keep the smoke from rolling across
Draft curtains are typically used in warehouses, aircraft hangars and large industrial plants to contain or channel smoke that rises to the ceiling in a fire. They can keep the smoke from rolling across
Introduction. Products conforming with a European Council Directive. CE marked construction products. Other regulations
 Introduction This Technical Booklet has been prepared by the Department of Finance and Personnel and provides for certain methods and standards of building which, if followed, will satisfy the requirements
Introduction This Technical Booklet has been prepared by the Department of Finance and Personnel and provides for certain methods and standards of building which, if followed, will satisfy the requirements
Module 8: Ontario Building Code Fire and Spatial Separations
 Ontario Building Code (OBC) 1. Fire Separations 2. Fire Resistance Ratings By Classification 3. Fire Resistance Ratings By Adjacent Use 4. Fire Resistance Ratings By Specific Space 5. Fire Resistance Ratings
Ontario Building Code (OBC) 1. Fire Separations 2. Fire Resistance Ratings By Classification 3. Fire Resistance Ratings By Adjacent Use 4. Fire Resistance Ratings By Specific Space 5. Fire Resistance Ratings
ARTICLE 4 SUPPLEMENTARY PROVISIONS
 ARTICLE 4 SUPPLEMENTARY PROVISIONS Section 4-10 1. Permitted Uses and Conditional Uses Permitted uses and uses permitted by special review may be located in the same building Section 4-102. District Boundaries
ARTICLE 4 SUPPLEMENTARY PROVISIONS Section 4-10 1. Permitted Uses and Conditional Uses Permitted uses and uses permitted by special review may be located in the same building Section 4-102. District Boundaries
DSA Access Compliance Official Comments (Checklists) Checklists
 DSA Access Compliance Official Comments (Checklists) Checklists California Department of General Services Division of the State Architect Checklists DSA 2011 CALIFORNIA ACCESS COMPLIANCE REFERENCE MANUAL
DSA Access Compliance Official Comments (Checklists) Checklists California Department of General Services Division of the State Architect Checklists DSA 2011 CALIFORNIA ACCESS COMPLIANCE REFERENCE MANUAL
GENERAL BUILDING HEIGHTS AND AREAS
 CHPTER GENERL BUILDING HEIGHT ND RE ECTION 0 GENERL 0. cope. The provisions of this chapter control the height and area of structures hereafter erected and additions to existing structures. [F] 0. ddress
CHPTER GENERL BUILDING HEIGHT ND RE ECTION 0 GENERL 0. cope. The provisions of this chapter control the height and area of structures hereafter erected and additions to existing structures. [F] 0. ddress
Baseline Hillside Ordinance Correction Sheet (Ordinance No. 184,802 Effective 3/17/17)
 Baseline Hillside Ordinance Correction Sheet (Ordinance No. 184,802 Effective 3/17/17) Plan Check #: Permit App. #: Job Address: Zone: Maximum Allowed RFA: Plan Check Engineer: Phone: Fax: (E-mail: firstname.lastname@lacity.org)
Baseline Hillside Ordinance Correction Sheet (Ordinance No. 184,802 Effective 3/17/17) Plan Check #: Permit App. #: Job Address: Zone: Maximum Allowed RFA: Plan Check Engineer: Phone: Fax: (E-mail: firstname.lastname@lacity.org)
Report on First Revisions with Statement June 2014 NFPA 5000
 5000 FR704 BLD-BSY (Chapter 12) Recommendation: 54.5 Elevator Machine/Control Rooms and Machinery/Control Spaces. Elevator machine/control rooms and machinery/control spaces that contain solid-state equipment
5000 FR704 BLD-BSY (Chapter 12) Recommendation: 54.5 Elevator Machine/Control Rooms and Machinery/Control Spaces. Elevator machine/control rooms and machinery/control spaces that contain solid-state equipment
EXERCISE 2. Codes Course Supplement California Building Code International Building Code
 EXERCISE 2 SECTION 3 01 GENERA L 301.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall control the classification of all buildings and structures as to use and occupancy. SECTION 30 2 CLASSIFICA TION 302.1
EXERCISE 2 SECTION 3 01 GENERA L 301.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall control the classification of all buildings and structures as to use and occupancy. SECTION 30 2 CLASSIFICA TION 302.1
Corridor Residential Traditional District Regulations City of St. Petersburg City Code Chapter 16, Land Development Regulations
 Section 16.20.060 - Corridor Residential Traditional Districts ( CRT ) Typical Buildings in the CRT District Sections: 16.20.060.1 Composition of Traditional Residential Corridors 16.20.060.2 Purpose and
Section 16.20.060 - Corridor Residential Traditional Districts ( CRT ) Typical Buildings in the CRT District Sections: 16.20.060.1 Composition of Traditional Residential Corridors 16.20.060.2 Purpose and
The Uniform Building and Accessibility Standards Regulations
 UNIFORM BUILDING AND 1 The Uniform Building and Accessibility Standards Regulations being Chapter U-1.2 Reg 5 (effective April 10, 1992) as amended by Saskatchewan Regulations 102/92, 81/93, 35/94, 23/98
UNIFORM BUILDING AND 1 The Uniform Building and Accessibility Standards Regulations being Chapter U-1.2 Reg 5 (effective April 10, 1992) as amended by Saskatchewan Regulations 102/92, 81/93, 35/94, 23/98
International Code Council
 Page 1 of 21 International Code Council ICC 300-2012 edition Committee Actions Report For Committee Actions taken at the November 24 th and December 14 th, 2010 meetings Page 2 of 21 IS-BLE1-10/11 ICC
Page 1 of 21 International Code Council ICC 300-2012 edition Committee Actions Report For Committee Actions taken at the November 24 th and December 14 th, 2010 meetings Page 2 of 21 IS-BLE1-10/11 ICC
UBC. (1997 Edition) (p.1-116) 2-hr. shaft required for
 Protection of Shaft Enclosures (Exit Stairs) Protection of Shaft Enclosures (Other Shafts) Comparison on Fire Safety Provisions* (Revised 2/28/03) (S) = Small difference in fire protection, (M) = Moderate
Protection of Shaft Enclosures (Exit Stairs) Protection of Shaft Enclosures (Other Shafts) Comparison on Fire Safety Provisions* (Revised 2/28/03) (S) = Small difference in fire protection, (M) = Moderate
CITY OF CALABASAS RESIDENTIAL PLAN REQUIREMENTS 1 OF 5 8/2017 PLAN INFORMATION
 1 PLAN INFORMATION Residential plans must be legible and capable of digital scanning. All sheets shall be the same size and distinctly labeled with a sheet title and number. The minimum dimension of the
1 PLAN INFORMATION Residential plans must be legible and capable of digital scanning. All sheets shall be the same size and distinctly labeled with a sheet title and number. The minimum dimension of the
GENERAL BUILDING HEIGHTS AND AREAS
 CHPTER GENERL BUILDING HEIGHT ND RE ECTION 0 GENERL 0. cope. The provisions of this chapter control the height and area of structures hereafter erected and additions to existing structures. [F] 0. ddress
CHPTER GENERL BUILDING HEIGHT ND RE ECTION 0 GENERL 0. cope. The provisions of this chapter control the height and area of structures hereafter erected and additions to existing structures. [F] 0. ddress
Floor Plan. *The floor plan represents a section view of a residence which has had an imaginary cut made approximately 4 feet above the floor line.
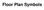 Floor Plan Symbols Floor Plan *The floor plan represents a section view of a residence which has had an imaginary cut made approximately 4 feet above the floor line. *Residential floor plans are generally
Floor Plan Symbols Floor Plan *The floor plan represents a section view of a residence which has had an imaginary cut made approximately 4 feet above the floor line. *Residential floor plans are generally
FIRE AND SMOKE PROTECTION FEATURES
 CHAPTER 7 FIRE AND SMOKE PROTECTION FEATURES SECTION 70 GENERAL 70. Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall govern the materials, systems and assemblies used for structural fire resistance and fire-resistance-rated
CHAPTER 7 FIRE AND SMOKE PROTECTION FEATURES SECTION 70 GENERAL 70. Scope. The provisions of this chapter shall govern the materials, systems and assemblies used for structural fire resistance and fire-resistance-rated
INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE 2015 Edition
 WASHINGTON STATE BUILDING CODE CHAPTER 51-51 WAC INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE 2015 Edition Washington State Building Code Council Copies of the State Building Codes and complete copies of the 2015 International
WASHINGTON STATE BUILDING CODE CHAPTER 51-51 WAC INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE 2015 Edition Washington State Building Code Council Copies of the State Building Codes and complete copies of the 2015 International
Plan Check No. A. GROUP M OCCUPANCIES. NOTE: General sales, display and office areas together with toilet rooms shall be made accessible. (1110B.1.
 Plan Check No. A. GROUP M OCCUPANCIES NOTE: General sales, display and office areas together with toilet rooms shall be made accessible. (1110B.1.1) 1. Sales employee workstations shall be located on accessible
Plan Check No. A. GROUP M OCCUPANCIES NOTE: General sales, display and office areas together with toilet rooms shall be made accessible. (1110B.1.1) 1. Sales employee workstations shall be located on accessible
BUILDING CODE COMMISSION
 Ruling No. 01-22-815 Application # 2001-14 BUILDING CODE COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF Subsection 24 (1) of the Building Code Act, 1992. AND IN THE MATTER OF Articles 3.3.1.8. and 3.4.3.6. of Regulation
Ruling No. 01-22-815 Application # 2001-14 BUILDING CODE COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF Subsection 24 (1) of the Building Code Act, 1992. AND IN THE MATTER OF Articles 3.3.1.8. and 3.4.3.6. of Regulation
WOOD USE IN NONCOMBUSTIBLE BUILDINGS
 INTRODUCTION The National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 1 requires that some buildings be of noncombustible construction under its prescriptive requirements. Its use in certain types of buildings such
INTRODUCTION The National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) 1 requires that some buildings be of noncombustible construction under its prescriptive requirements. Its use in certain types of buildings such
ATI Evaluation Service A Division of Architectural Testing Certification Services
 ATI Evaluation Service A Division of Architectural Testing Certification Services Subject to Renewal: 04/08/2014 Issued: 04/08/2013 Visit www.ati-es.com for current status Revision: 11/11/2013 Page 1 of
ATI Evaluation Service A Division of Architectural Testing Certification Services Subject to Renewal: 04/08/2014 Issued: 04/08/2013 Visit www.ati-es.com for current status Revision: 11/11/2013 Page 1 of
BUILDING CODE COMMISSION
 Ruling No. 02-38-893 Application No. 2002-33 BUILDING CODE COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF Subsection 24(1) of the Building Code Act, S.O. 1992, c. 23, as amended. AND IN THE MATTER OF Clause 3.3.4.4.(1)(a)
Ruling No. 02-38-893 Application No. 2002-33 BUILDING CODE COMMISSION IN THE MATTER OF Subsection 24(1) of the Building Code Act, S.O. 1992, c. 23, as amended. AND IN THE MATTER OF Clause 3.3.4.4.(1)(a)
Section Subparts T. Cleveland State University Work Zone Safety and Efficiency Transportation Center. Demolition
 Demolition 1926.252(a) Whenever materials are dropped more than 20 feet to any point lying outside the exterior walls of the building, an enclosed chute of wood, or equivalent material, shall be used.
Demolition 1926.252(a) Whenever materials are dropped more than 20 feet to any point lying outside the exterior walls of the building, an enclosed chute of wood, or equivalent material, shall be used.
PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED
 Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-03-13-05 Ontario CODE REFERENCE: Div. B 3.13.4.5. DESCRIPTION OF THE PROPOSED
Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-03-13-05 Ontario CODE REFERENCE: Div. B 3.13.4.5. DESCRIPTION OF THE PROPOSED
2015 IBC Update. Copyright 2014 International Code Council #1000PDF15 1
 Goal 2015 IBC Update Based on the International Building Code (IBC ) The goal is to familiarize building officials, fire officials, plans examiners, inspectors, design professionals, contractors, and others
Goal 2015 IBC Update Based on the International Building Code (IBC ) The goal is to familiarize building officials, fire officials, plans examiners, inspectors, design professionals, contractors, and others
TENTS AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 31 TENTS AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES SECTION 3101 GENERAL 3101.1 Scope. Tents and membrane structures shall comply with this chapter. The provisions of Section 3103 are applicable only to temporary
CHAPTER 31 TENTS AND OTHER MEMBRANE STRUCTURES SECTION 3101 GENERAL 3101.1 Scope. Tents and membrane structures shall comply with this chapter. The provisions of Section 3103 are applicable only to temporary
