People and the Temperate Region n /-» _ r»» i r. i,,.._ ^^ fen and the Biosphere Program 1991
|
|
|
- Austen Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Department of State People and the Temperate Region n /-» _ r»» i r. i,,.._ ^^ fen and the Biosphere Program 1991 United States Man and the Biosphere Program
2 Nitrogen Transformation Processes in Selected Forest Ecosystems of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park Wayne T. Swank The Southern Appalachian Biosphere Reserve Cluster was established to provide a basis for research on the structure, function, and dynamics of selected forest ecosystems and to enhance the understanding of natural processes and people's impacts upon them, with subsequent applications toward the formulation of better land management policies. Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory and the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, two biosphere reserves, are the sites for the development of this program. compartments of old-growth and aggrading forest stands in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Compare the rates of these nitrogen transformation processes in forests disturbed by wild pig rooting (Figure 1) with the rates from undisturbed forests, and measure the impacts of NO 3 concentrations in the soil and stream water draining these forests. Objectives Watershed studies at both biosphere reserve sites have shown that concentrations of nitrate-nitrogen (NO 3 -N) are highly variable in streamflows from old-growth, aggrading, and disturbed deciduous forest ecosystems. At the Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory, for example, logging and other disturbances produce elevated NO -N concentrations compared to aggrading forests; while in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, NO 3 -N concentrations are higher in streams of old-growth compared to aggrading forests. Other studies at the Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory indicate enhanced microbial activity in the forest floor and soil following disturbances, increasing soil NO 3 available for leaching to streams. However, similar nitrogen transformation data have been unavailable for the Great Smoky Mountains National Park and, consequently, this study was designed to address the following objectives: Quantify the rates of free-living nitrogen fixation, potential mineralization, and potential nitrification in the forest floor and soil FIGURE 1. Intensive wild pig rooting alters the nitrogen transformation processes in the deciduous forests of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. 11
3 Approach Four existing experimential sites located in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park were utilized in this study. The old-growth forest site, located on the Camel Hump Creek watershed, is dominated by a virgin stand of Tsuga, Aesculus, Tilia, and Betula species. Husky Branch watershed, selected as the aggrading forest, is dominated by an 80- year-old Liriodendron stand in association with Betula and Prunus species. These two watersheds are each about 650 hectares in size, oriented toward the northeast, and underlain by sandstone bedrock. The two sites selected to study the disturbance by wild pig rooting were the Double Spring Gap watershed, an area that has been rooted intensively for 15 years, and the Garretts Gap watershed, which had not been occupied by wild pigs. Each watershed, 0.2-hectare in size, is drained by intermittent streams. The forest cover, which is similar on both study sites, is comprised primarily of Fagus with Acer and Betula the predominant associated taxa. Samples of partially decomposed forest floor litter (the O 2 layer), and A horizon (0-10 centimeter depth) and B horizon (20-30 centimeter depth) soil compartments were collected seasonally in six sample periods for assays of nitrogen transformation. 12 For the old-growth and aggrading forest sites, on each sample date, six samples were taken for each soil horizon from plots located at approximately the same elevation and exposure on each watershed. For the two sites used to study wild pig rooting, five samples were obtained in the same manner. Nitrogen mineralization and nitrification potentials were measured as changes in total mineral nitrogen and NO 3, respectively, during 33- day aerobic incubations in the laboratory. Uniform temperature and moisture conditions were maintained throughout the incubation period. Nitrogen fixation potentials of free-living bacteria in the sampled horizons were measured on field-moist samples in the laboratory with the C 2 H 2 -reduction assay. Streams draining the rooted and unrooted sites were gauged with H- flumes. Samples of runoff were collected proportionally to the flow with a Coshocton wheel. Four pairs of porous cup lysimeters were installed on each watershed site at depths of 30 and 100 centimeters to collect soil water for chemical analyses. Major Findings Among the major findings of this study were: Potential nitrogen mineralization rates were highest in the forest floors on all study sites and declined with an increase in soil depth (Figure 2). In the comparison of old-growth and aggrading forests, potential mineralization was 20 to 30 percent higher in the forest floor and soil layers in the old-growth forest, although the differences were not statistically significant. For the rooted and unrooted comparison, the mineralization potential was lower in the O layer of the sites rooted by wild pigs (Figure 2). Percent of nitrogen also was significantly lower in this layer in comparison to the unrooted site. Conversely, the mineralization rates were about 20 percent higher in the A and B soil horizons on the rooted sites, but these differences were not statistically different.
4 mg N/kg/ 33 days 500 Potential Mineralization significantly lower in the O 2 layer on the rooted site, although they tended to be higher in the soil horizons in comparison to the unrooted site Old Growth B 02 Soil Horizon Aggrading \~\ Rooted FIGURE 2. Potential nitrogen mineralization rates on the forest floor of all study sites declined in relation to soil depth. mg NOs- N/kg/ 33 days II02 Old Growth Potential Nitrification B 02 ni Unrooted Soil Horizon Aggrading CH Rooted Unrooted FIGURE 3. Potential nitrification rates on the forest floors in all study sites declined in relation to soil depth. Potential nitrification rates (that is, the oxidation of ammonium to nitrate) also were highest in the forest floor on all study sites and declined with soil depth (Figure 3). These rates were not statistically different on the old-growth and aggrading forest sites, but they tended to be higher in several compartments of the old-growth stand. Rates of nitrification were Nitrogen fixation potentials were higher in the O layer in the aggrading forest, but lower than the rates for the two soil compartments in the old-growth forest. There were no significant differences in nitrogen fixation between the rooted and unrooted stands. Soil water concentrations of NO 3 -N at 30 and 100 centimeters were higher in the rooted forest. Nitratenitrogen concentrations in the stream water of the rooted sites were greater than those that were found at the unrooted site. These concentrations showed a trend that was parallel to that of the soil water. Implications The results of this initial study of nitrogen transformations in selected forest ecosystems of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park generally parallel the findings at the Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory and other eastern temperate forest ecosystems. Specifically, these results indicate the following: Higher rates of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in old-growth forests in comparison to aggrading forests appear to contribute to higher NO 3 concentrations in the streams draining the old-growth forests. Other processes of nitrogen cycling not measured in this study, such as vegetative uptake and incorporation of nitrogen into the old-growth stands, are thought to account for part of the observed differences in the levels of NO 3 in the streams. The high NO 3 losses from old-growth forest stands, therefore, should be interpreted as a natural consequence of stand maturation rather than an external influence of people. 13
5 Disturbance, as represented by the intensive wild pig rooting of deciduous forests in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, alters the nitrogen transformation processes in the forest floor and soil compartments. Observed increases in NO 3 concentrations in the soil and stream water of the rooted forest could be partly the net effect of nitrogen microbial processes, and partly a response to reduced nitrogen uptake and recycling due to the elimination of the herbaceous vegetative layer by the rooting activity. In combination with other studies of wild pig rooting in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, such a disturbance is considered to have negative impacts on the deciduous forest. 14
D.W. Johnson and W.W. Miller
 Revised Work Plan: Spatial variability in the KREW watersheds: Effects on nutrient cycling and water quality D.W. Johnson and W.W. Miller Natural Resources and Environmental Science University of Nevada,
Revised Work Plan: Spatial variability in the KREW watersheds: Effects on nutrient cycling and water quality D.W. Johnson and W.W. Miller Natural Resources and Environmental Science University of Nevada,
EFFECTS OF ACID PRECIPITATION ON NUTRIENT CYCLING PROCESSES AND WATER QUALITY IN FOREST ECOSYSTEMS OF SOUTHERN APPALACHIAN AND PIEDMONT WATERSHEDS
 EFFECTS OF ACID PRECIPITATION ON NUTRIENT CYCLING PROCESSES AND WATER QUALITY IN FOREST ECOSYSTEMS OF SOUTHERN APPALACHIAN AND PIEDMONT WATERSHEDS Task Group Project Code: E1-6.3 and F10-20 Wayne T. Swank,
EFFECTS OF ACID PRECIPITATION ON NUTRIENT CYCLING PROCESSES AND WATER QUALITY IN FOREST ECOSYSTEMS OF SOUTHERN APPALACHIAN AND PIEDMONT WATERSHEDS Task Group Project Code: E1-6.3 and F10-20 Wayne T. Swank,
Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Intro
 Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function
 Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
The Carbon Cycle. Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 DATE: NAME: CLASS:
 CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
 E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
Consequences of Nitrogen Deposition to Rocky Mountain National Park
 Consequences of Nitrogen Deposition to Rocky Mountain National Park Jill S. Baron, US Geological Survey M.Hartman, D.S.Ojima, K. Nydick, H.M. Rueth B.Moraska Lafrancois, A.P. Wolfe, J. Botte, W.D. Bowman
Consequences of Nitrogen Deposition to Rocky Mountain National Park Jill S. Baron, US Geological Survey M.Hartman, D.S.Ojima, K. Nydick, H.M. Rueth B.Moraska Lafrancois, A.P. Wolfe, J. Botte, W.D. Bowman
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycles in Nature Standard 1 Objective 2:
 Cycles in Nature Standard 1 Objective 2: Explain relationships between matter cycles and Energy a) use diagrams to trace the movement of matter through a cycle b) Explain how water is a limiting factor
Cycles in Nature Standard 1 Objective 2: Explain relationships between matter cycles and Energy a) use diagrams to trace the movement of matter through a cycle b) Explain how water is a limiting factor
Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical, & biological processes
 OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles
 The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
Introduction. Wetland System. A Wetland Scene at Lorne C. Henderson Conservation Area near Petrolia
 Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
New Practices for Nutrient Reduction: STRIPs and Saturated Buffers. Matthew Helmers and Tom Isenhart Iowa State University
 New Practices for Nutrient Reduction: STRIPs and Saturated Buffers Matthew Helmers and Tom Isenhart Iowa State University Situation Increasing concern for local and regional waters Substantial demand for
New Practices for Nutrient Reduction: STRIPs and Saturated Buffers Matthew Helmers and Tom Isenhart Iowa State University Situation Increasing concern for local and regional waters Substantial demand for
Exploring Coupled Dynamic Biogeochemical and Vegetation Models in Temperate Forest Ecosystems of the Eastern United States
 Exploring Coupled Dynamic Biogeochemical and Vegetation Models in Temperate Forest Ecosystems of the Eastern United States Todd McDonnell E&S Environmental Chemistry Salim Belyazid - Luc Bonten - Chris
Exploring Coupled Dynamic Biogeochemical and Vegetation Models in Temperate Forest Ecosystems of the Eastern United States Todd McDonnell E&S Environmental Chemistry Salim Belyazid - Luc Bonten - Chris
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture
 Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
Managing Soils for Improved Pasture Jonathan Deenik, PhD Department of Tropical Plant and Soil Sciences University of Hawaii Rota Grazing and Livestock Management Workshop June 10-12, 12, 2010 1 Water
EFFECTS OF COMMERCIAL CLEARCUTTING ON NUTRIEN^LoSls IN APPALACHIAN FORESTS SUMMARY
 EFFECTS OF COMMERCIAL CLEARCUTTING ON NUTRIEN^LoSls IN APPALACHIAN FORESTS V SUMMARY m ' U ' WAYNE T. SWANK, PROJECT LEADER COWEETA HYDROLOGIC LABORATORY OTTO, NORTH CAROLINA Much research has been conducted
EFFECTS OF COMMERCIAL CLEARCUTTING ON NUTRIEN^LoSls IN APPALACHIAN FORESTS V SUMMARY m ' U ' WAYNE T. SWANK, PROJECT LEADER COWEETA HYDROLOGIC LABORATORY OTTO, NORTH CAROLINA Much research has been conducted
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
Stemflow nutrient inputs to soil in a successional hardwood forest
 Plant and Soil 4: 249-254, 992. (E) 992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. PLSO 963 Stemflow nutrient inputs to soil in a successional hardwood forest CHRISTOPHER S. POTTER Biology
Plant and Soil 4: 249-254, 992. (E) 992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. PLSO 963 Stemflow nutrient inputs to soil in a successional hardwood forest CHRISTOPHER S. POTTER Biology
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems. Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid?
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Reading Questions
 APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
Grapes, Wine, Balance and Soil Health. George W. Bird, Professor Department of Entomology Michigan State University
 Grapes, Wine, Balance and Soil Health George W. Bird, Professor Department of Entomology Michigan State University Presentation Overview Balance: How it Works Soil Biology in Action Soil Health Indicators
Grapes, Wine, Balance and Soil Health George W. Bird, Professor Department of Entomology Michigan State University Presentation Overview Balance: How it Works Soil Biology in Action Soil Health Indicators
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Effects of Prescribed Burning on Stream Water Quantity, Quality, and fuel loads in a Small Piedmont Watershed in North Carolina
 Effects of Prescribed Burning on Stream Water Quantity, Quality, and fuel loads in a Small Piedmont Watershed in North Carolina Matthew Haunsperger Johnny Boggs, Ge Sun, Michael Gavazzi USDA Forest Service
Effects of Prescribed Burning on Stream Water Quantity, Quality, and fuel loads in a Small Piedmont Watershed in North Carolina Matthew Haunsperger Johnny Boggs, Ge Sun, Michael Gavazzi USDA Forest Service
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Scientific insights on emerging groundwater concerns in Prince Edward Island Atlantic Agrology Workshop, Stanley Bridge Resort, PEI 21 July 2014
 Scientific insights on emerging groundwater concerns in Prince Edward Island Atlantic Agrology Workshop, Stanley Bridge Resort, PEI 21 July 2014 Yefang Jiang Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Yefang.jiang@agr.gc.ca
Scientific insights on emerging groundwater concerns in Prince Edward Island Atlantic Agrology Workshop, Stanley Bridge Resort, PEI 21 July 2014 Yefang Jiang Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Yefang.jiang@agr.gc.ca
Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences. 3-8 Research Introduction Affected Environment
 3-8 Research Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3-8.1 Introduction The following section provides information to assess the consequences on the information able to be developed and analyzed
3-8 Research Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3-8.1 Introduction The following section provides information to assess the consequences on the information able to be developed and analyzed
Cycles of Matter. Slide 1 of 33. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
The nitrate contamination concern
 Section A The nitrate contamination concern In 1974, the U.S. Congress passed the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). This law required the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to determine the level of contaminants
Section A The nitrate contamination concern In 1974, the U.S. Congress passed the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). This law required the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to determine the level of contaminants
NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT PLAN FIELD MONITORING 1. Bradford D. Brown ABSTRACT
 NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT PLAN FIELD MONITORING 1 Bradford D. Brown ABSTRACT Nutrient Management Plan Field Monitoring enables producers to evaluate the effectiveness of their Nutrient Management Plan implementation
NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT PLAN FIELD MONITORING 1 Bradford D. Brown ABSTRACT Nutrient Management Plan Field Monitoring enables producers to evaluate the effectiveness of their Nutrient Management Plan implementation
The national-level nutrient loading estimation tool for Finland: Watershed Simulation and Forecasting System WSFS-Vemala
 The national-level nutrient loading estimation tool for Finland: Watershed Simulation and Forecasting System WSFS-Vemala Markus Huttunen, Finnish Environment Institute SYKE, HELCOM workshop on transboundary
The national-level nutrient loading estimation tool for Finland: Watershed Simulation and Forecasting System WSFS-Vemala Markus Huttunen, Finnish Environment Institute SYKE, HELCOM workshop on transboundary
Accumulation of carbon and nitrogen in Swedish forest soils over stand age
 Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Department of Soil and Environment Accumulation of carbon and nitrogen in Swedish forest soils over stand age Petros Georgiadis Master s Thesis in Environmental
Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Department of Soil and Environment Accumulation of carbon and nitrogen in Swedish forest soils over stand age Petros Georgiadis Master s Thesis in Environmental
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry. Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology
 Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology 1 Terms Bole Ecology Ecosystem Forest ecology Hardening-off Hardiness Material cycle Mycorrhizae Overstory Photoperiod Stratification
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology 1 Terms Bole Ecology Ecosystem Forest ecology Hardening-off Hardiness Material cycle Mycorrhizae Overstory Photoperiod Stratification
Biomass and production of southern Appalachian cove forests reexamined
 760 Biomass and production of southern Appalachian cove forests reexamined R. T. B USING[ North Carolina Botanical Garden, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3375, U S.A. E.E.C. CLEnscit
760 Biomass and production of southern Appalachian cove forests reexamined R. T. B USING[ North Carolina Botanical Garden, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3375, U S.A. E.E.C. CLEnscit
LOWER WATER TEMPERATURES WITHIN A STREAMSIDE BUFFER STRIP
 L USDA Forest Service Research Note SE- 193 April 1973 LOWER WATER TEMPERATURES WITHIN A STREAMSIDE BUFFER STRIP Abstract. --The removal of streamside vegetation increases the water temperature in mountain
L USDA Forest Service Research Note SE- 193 April 1973 LOWER WATER TEMPERATURES WITHIN A STREAMSIDE BUFFER STRIP Abstract. --The removal of streamside vegetation increases the water temperature in mountain
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
Vadose Zone Monitoring of Fields Irrigated with Recycled Processing and Municipal Wastewaters.
 Vadose Zone Monitoring of Fields Irrigated with Recycled Processing and Municipal Wastewaters. Diganta D. Adhikari *, Dave Goorahoo, and Florence Cassel S. Center for Irrigation Technology, California
Vadose Zone Monitoring of Fields Irrigated with Recycled Processing and Municipal Wastewaters. Diganta D. Adhikari *, Dave Goorahoo, and Florence Cassel S. Center for Irrigation Technology, California
Iowa Senate Natural Resources Committee February 3, 2015
 Iowa Senate Natural Resources Committee February 3, 2015 Dr. Matthew Helmers Dean s Professor, College of Agriculture & Life Sciences Professor, Department of Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering mhelmers@iastate.edu,
Iowa Senate Natural Resources Committee February 3, 2015 Dr. Matthew Helmers Dean s Professor, College of Agriculture & Life Sciences Professor, Department of Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering mhelmers@iastate.edu,
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Curve Numbers for Nine Mountainous Eastern United States Watersheds: Seasonal Variation and Forest Cutting
 Curve Numbers for Nine Mountainous Eastern United States Watersheds: Seasonal Variation and Forest Cutting Negussie H. Tedela 1 ; Steven C. McCutcheon, P.E., M.ASCE 2 ; John L. Campbell 3 ; Wayne T. Swank
Curve Numbers for Nine Mountainous Eastern United States Watersheds: Seasonal Variation and Forest Cutting Negussie H. Tedela 1 ; Steven C. McCutcheon, P.E., M.ASCE 2 ; John L. Campbell 3 ; Wayne T. Swank
Transactions. American Geophysical Union Volume 28, Number 1 February 1947
 Transactions. American Geophysical Union Volume 28, Number 1 February 1947 EFFECT OF REMOVAL OF STREAM-BANK VEGETATION UPON WATER YIELD Earl G. Dunford and P. W. Fletcher Abstract--This is a preliminary
Transactions. American Geophysical Union Volume 28, Number 1 February 1947 EFFECT OF REMOVAL OF STREAM-BANK VEGETATION UPON WATER YIELD Earl G. Dunford and P. W. Fletcher Abstract--This is a preliminary
Climate and Biodiversity
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
Chemical Testing of Drinking Water
 Chemical Testing of Drinking Water Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity. Water Chemistry Grade Level: all Duration: 50 minutes Setting: lab or classroom Summary: Students will conduct chemistry
Chemical Testing of Drinking Water Adapted from: An original Creek Connections activity. Water Chemistry Grade Level: all Duration: 50 minutes Setting: lab or classroom Summary: Students will conduct chemistry
OTBA. THEME: Forests - Friends for Life
 OTBA THEME: Forests - Friends for Life The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area
OTBA THEME: Forests - Friends for Life The forest is a complex ecosystem consisting mainly of trees that have formed a buffer for the earth to protect life forms. The trees which make up the main area
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lecture 4. Forests of the world (II)
 Lecture 4 Forests of the world (II) The Worlds Major Forest Biomes Near Vancouver Temperate Forest Biome These forests mainly occupy the temperate latitudes of the northern hemisphere. They comprise a
Lecture 4 Forests of the world (II) The Worlds Major Forest Biomes Near Vancouver Temperate Forest Biome These forests mainly occupy the temperate latitudes of the northern hemisphere. They comprise a
Phosphorus Dynamics and Mitigation in Soils
 Phosphorus Dynamics and Mitigation in Soils Umass Extension - Managing Phosphorus in Organic Residuals Applied to Soils: Composts, Biosolids, Manures and Others November 2, 2016 - Marlborough, MA Jennifer
Phosphorus Dynamics and Mitigation in Soils Umass Extension - Managing Phosphorus in Organic Residuals Applied to Soils: Composts, Biosolids, Manures and Others November 2, 2016 - Marlborough, MA Jennifer
Stand age related differences in non-co 2 soil atmosphere GHG-exchange in wet temperate Eucalyptus forests of SE Australia
 Benedikt Fest b.fest@pgrad.unimelb.edu.au Stand age related differences in non-co 2 soil atmosphere GHG-exchange in wet temperate Eucalyptus forests of SE Australia Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research
Benedikt Fest b.fest@pgrad.unimelb.edu.au Stand age related differences in non-co 2 soil atmosphere GHG-exchange in wet temperate Eucalyptus forests of SE Australia Table of Content 1. Background 2. Research
Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers
 Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
Symposium no. 65 Paper no. 246 Presentation: poster Changes of greenhouse gases emission from agricultural soils under the influence of mineral fertilizers KOZLOV A.E., STEPANOV A. and MANUCHAROVA N. Moscow
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Status on Land Use Change and Forestry Sector in Myanmar
 Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Status on Land Use Change and Forestry Sector in Myanmar CHO CHO WIN ASSISTANT RESEARCH OFFICER FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE YEZIN, MYANMAR International Workshop on Air Quality in Asia-Impacts
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Status on Land Use Change and Forestry Sector in Myanmar CHO CHO WIN ASSISTANT RESEARCH OFFICER FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE YEZIN, MYANMAR International Workshop on Air Quality in Asia-Impacts
SUCCESSION AND STABILITY
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 20 SUCCESSION AND STABILITY Community changes during succession include increases in species diversity and changes in species composition Ecosystem changes during succession include
Chapter Concepts Chapter 20 SUCCESSION AND STABILITY Community changes during succession include increases in species diversity and changes in species composition Ecosystem changes during succession include
Performance Standards for Target Hydrology
 Performance Standards for Target Hydrology Steve Eggers Senior Ecologist Regulatory Branch St. Paul District December 10, 2015 US Army Corps of Engineers Introduction Target Hydrology: the hydrology necessary
Performance Standards for Target Hydrology Steve Eggers Senior Ecologist Regulatory Branch St. Paul District December 10, 2015 US Army Corps of Engineers Introduction Target Hydrology: the hydrology necessary
Reduced N in precipitation as N source for boreal bryophytes
 Reduced N in precipitation as N source for boreal bryophytes Annika Nordin and Åsa Forsum Umeå Plant Science Centre Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Reduced N in precipitation as N source for
Reduced N in precipitation as N source for boreal bryophytes Annika Nordin and Åsa Forsum Umeå Plant Science Centre Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Reduced N in precipitation as N source for
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology 1 Keystone Anchors Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere. o Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem,
Principles of Ecology 1 Keystone Anchors Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere. o Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem,
Interpreting Nitrate Concentration in Tile Drainage Water
 Agronomy Guide AY-318-W SOILS (TILLAGE) Sylvie Brouder, Brenda Hofmann, Eileen Kladivko, Ron Turco, Andrea Bongen, Purdue University Department of Agronomy; Jane Frankenberger, Purdue University Department
Agronomy Guide AY-318-W SOILS (TILLAGE) Sylvie Brouder, Brenda Hofmann, Eileen Kladivko, Ron Turco, Andrea Bongen, Purdue University Department of Agronomy; Jane Frankenberger, Purdue University Department
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology Ecology Study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environments Living things are affected by nonliving and living parts of the environment Abiotic factors:
Principles of Ecology Ecology Study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environments Living things are affected by nonliving and living parts of the environment Abiotic factors:
Water Quality Conditions & Management on Rangelands
 Water Quality Conditions & Management on Rangelands Ken Tate, Leslie Roche, and Rob Atwill UC Davis and UC Cooperative Extension Grazing Workshop Mariposa County UCCE March 2014 CA Rangelands Safe Water
Water Quality Conditions & Management on Rangelands Ken Tate, Leslie Roche, and Rob Atwill UC Davis and UC Cooperative Extension Grazing Workshop Mariposa County UCCE March 2014 CA Rangelands Safe Water
Ecosystem Succession and Nutrient Retention: A Hypothesis
 Ecosystem Succession and Nutrient Retention: A Hypothesis Peter M. Vitousek and William A. Reiners Twenty-four broad hypotheses for trends associated with successional development of ecosystems were presented
Ecosystem Succession and Nutrient Retention: A Hypothesis Peter M. Vitousek and William A. Reiners Twenty-four broad hypotheses for trends associated with successional development of ecosystems were presented
Substrates for Plants Grown in BIG CONTAINERS? Ted Bilderback Nursery Crops Extension Specialist
 Substrates for Plants Grown in BIG CONTAINERS? Ted Bilderback Nursery Crops Extension Specialist There are no one size fits all potting mix recipes for growing nursery crops in large containers. Pine bark
Substrates for Plants Grown in BIG CONTAINERS? Ted Bilderback Nursery Crops Extension Specialist There are no one size fits all potting mix recipes for growing nursery crops in large containers. Pine bark
CONCEPTS & SYNTHESIS
 CONCEPTS & SYNTHESIS EMPHASIZING NEW IDEAS TO STIMULATE RESEARCH IN ECOLOGY Ecological Monographs, 75(2), 2005, pp. 139 157 2005 by the Ecological Society of America CONTROLS ON NITROGEN CYCLING IN TERRESTRIAL
CONCEPTS & SYNTHESIS EMPHASIZING NEW IDEAS TO STIMULATE RESEARCH IN ECOLOGY Ecological Monographs, 75(2), 2005, pp. 139 157 2005 by the Ecological Society of America CONTROLS ON NITROGEN CYCLING IN TERRESTRIAL
2003 AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2003 AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE SECTION II Time 90 minutes 4 Questions Directions: Answer all four questions, which are weighted equally; the suggested time
2003 AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE SECTION II Time 90 minutes 4 Questions Directions: Answer all four questions, which are weighted equally; the suggested time
3 3 Cycles of Matter. EOC Review
 EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
Food web Diagram that shows how food chains are linked together in a complex feeding relationship
 Energy Flow Food web Diagram that shows how food chains are linked together in a complex feeding relationship The food web has a number of advantages over a food chains including: More than one producer
Energy Flow Food web Diagram that shows how food chains are linked together in a complex feeding relationship The food web has a number of advantages over a food chains including: More than one producer
Agricultural/Rural Riparian Buffer Analysis
 Agricultural/Rural Riparian Buffer Analysis December 2014 Executive Summary The Agricultural/Rural Riparian Buffer Analysis was developed from a 2014 analysis of current requirements for the riparian areas
Agricultural/Rural Riparian Buffer Analysis December 2014 Executive Summary The Agricultural/Rural Riparian Buffer Analysis was developed from a 2014 analysis of current requirements for the riparian areas
NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT
 NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT Please pick up Syllabus, Reading Material & Today s Lab on the Table in the Front Dick Schultz Instructor Sara Berges Teaching Assistant January 13, 2009 1. Conduct Get
NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT Please pick up Syllabus, Reading Material & Today s Lab on the Table in the Front Dick Schultz Instructor Sara Berges Teaching Assistant January 13, 2009 1. Conduct Get
ENGINEERED FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE GROWTH. IgniteS HEALTHIER SOILS STRONGER PLANTS HIGHER YIELDS
 ENGINEERED FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE GROWTH IgniteS HEALTHIER SOILS STRONGER PLANTS HIGHER YIELDS Start Strong... To finish on top you need a strong start is formulated to get your crops out of the gate early
ENGINEERED FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE GROWTH IgniteS HEALTHIER SOILS STRONGER PLANTS HIGHER YIELDS Start Strong... To finish on top you need a strong start is formulated to get your crops out of the gate early
7.014 Lecture 20: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 2007
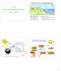 Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Pollutants Transformation and Removal within Constructed Wetlands Hybrid Systems
 Pollutants Transformation and Removal within Constructed Wetlands Hybrid Systems T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. C. Chuang 1, C. H. Ju 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung
Pollutants Transformation and Removal within Constructed Wetlands Hybrid Systems T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. C. Chuang 1, C. H. Ju 1 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung
Vegetation Management and Water Yield: Silver Bullet or a Pipe Dream?
 Vegetation Management and Water Yield: Silver Bullet or a Pipe Dream? Lee H. MacDonald rofessor Emeritus and Senior Research Scientist Watershed Science/NREL Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO
Vegetation Management and Water Yield: Silver Bullet or a Pipe Dream? Lee H. MacDonald rofessor Emeritus and Senior Research Scientist Watershed Science/NREL Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO
Fertilizer Management for Plant Health and Environmental Water Quality Protection
 Fertilizer Management for Plant Health and Environmental Water Quality Protection Florida and California are different but we share some problems, and solutions Nitrogen and phosphorus management for horticultural
Fertilizer Management for Plant Health and Environmental Water Quality Protection Florida and California are different but we share some problems, and solutions Nitrogen and phosphorus management for horticultural
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
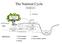 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
FOREST INVESTMENT ACCOUNT FOREST SCIENCE PROGRAM
 FOREST INVESTMENT ACCOUNT FOREST SCIENCE PROGRAM Project Y051293 HYDROLOGIC DECISION MAKING TOOLS FOR SUSTAINABLE FOREST MANAGEMENT IN RAIN DOMINATED COASTAL BC WATERSHEDS Background Summary: Forest Recovery
FOREST INVESTMENT ACCOUNT FOREST SCIENCE PROGRAM Project Y051293 HYDROLOGIC DECISION MAKING TOOLS FOR SUSTAINABLE FOREST MANAGEMENT IN RAIN DOMINATED COASTAL BC WATERSHEDS Background Summary: Forest Recovery
The Law of Conservation of Matter. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away
 Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Watershed Characterization, Monitoring and Measurements
 Watershed Characterization, Monitoring and Measurements Intent - highlight key approaches to watershed monitoring using the Fair Hill Study watershed as an example Watershed characterization and monitoring
Watershed Characterization, Monitoring and Measurements Intent - highlight key approaches to watershed monitoring using the Fair Hill Study watershed as an example Watershed characterization and monitoring
Forest Biomes. Chapter 9
 Forest Biomes Chapter 9 9.1 Objectives ~Describe the characteristics of the coniferous forest. ~Explain adaptations that enable organisms to survive in coniferous forests. 9.1 Coniferous Forests Coniferous
Forest Biomes Chapter 9 9.1 Objectives ~Describe the characteristics of the coniferous forest. ~Explain adaptations that enable organisms to survive in coniferous forests. 9.1 Coniferous Forests Coniferous
Chapter 54. Ecosystems. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
Denitrification - eutrophication
 Figure 58.7 Temp normally fluctuates Humans are forcing climate change The Nitrogen Cycle Most Nitrogen gas (N 2 ) (78 %) is in the atmosphere Can plants and animals use this directly? How then? Nitrogen
Figure 58.7 Temp normally fluctuates Humans are forcing climate change The Nitrogen Cycle Most Nitrogen gas (N 2 ) (78 %) is in the atmosphere Can plants and animals use this directly? How then? Nitrogen
Repeated disturbance in the Southern Yucatan: Biogeochemical and hydrological feedbacks on carbon and phosphorus cycling
 Repeated disturbance in the Southern Yucatan: Biogeochemical and hydrological feedbacks on carbon and phosphorus cycling Deborah Lawrence, Paolo D Odorico, Marcia DeLonge, Lucy Diekmann, Rishiraj Das,
Repeated disturbance in the Southern Yucatan: Biogeochemical and hydrological feedbacks on carbon and phosphorus cycling Deborah Lawrence, Paolo D Odorico, Marcia DeLonge, Lucy Diekmann, Rishiraj Das,
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE. nutrients: aka.
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
Objective 1: Manage the demonstration site using common agricultural practices and monitor runoff quantity and quality.
 Appendix B Objectives/Tasks Accomplishments By T. Trooien and J. Kjaersgaard, South Dakota State University. Objective 1: Manage the demonstration site using common agricultural practices and monitor runoff
Appendix B Objectives/Tasks Accomplishments By T. Trooien and J. Kjaersgaard, South Dakota State University. Objective 1: Manage the demonstration site using common agricultural practices and monitor runoff
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics. Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow
 Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow Let us consider ecosystems We have looked at the biosphere, and the biomes within the biosphere, the populations
Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow Let us consider ecosystems We have looked at the biosphere, and the biomes within the biosphere, the populations
Modeling the Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics Following Disturbance in Eastern U.S. Forests
 Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 2011 Modeling the Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics Following Disturbance in Eastern U.S. Forests Shree Ram Sharma Dangal Lehigh University Follow
Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 2011 Modeling the Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics Following Disturbance in Eastern U.S. Forests Shree Ram Sharma Dangal Lehigh University Follow
CEPUDER Peter (1), SHUKLA Manoj Kumar (1), LIEBHARD Peter (2), TULLER Markus (1)
 Scientific registration n : 1315 Symposium n : 14 Presentation : poster Optimizing soil fertility and plant nutrition to prevent groundwater pollution Prévenir la pollution de la nappe des sols en optimisant
Scientific registration n : 1315 Symposium n : 14 Presentation : poster Optimizing soil fertility and plant nutrition to prevent groundwater pollution Prévenir la pollution de la nappe des sols en optimisant
PRESCRIBED FIRE IN SOUTHWEST IDAHO
 2016 PRESCRIBED FIRE IN SOUTHWEST IDAHO In southwest Idaho, public land managers work to: address public health and safety concerns; treat insect and disease infestations; reduce the risk of severe wildfires
2016 PRESCRIBED FIRE IN SOUTHWEST IDAHO In southwest Idaho, public land managers work to: address public health and safety concerns; treat insect and disease infestations; reduce the risk of severe wildfires
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Nitrates are essential for plant growth
 THE NITROGEN CYCLE Nitrates are essential for plant growth Plant protein Root uptake Nitrate NO 3 Nitrates are recycled via microbes Animal protein Soil organic nitrogen Ammonification Ammonium NH 4 +
THE NITROGEN CYCLE Nitrates are essential for plant growth Plant protein Root uptake Nitrate NO 3 Nitrates are recycled via microbes Animal protein Soil organic nitrogen Ammonification Ammonium NH 4 +
White Pine Needle Damage Report
 Cameron D. McIntire Graduate Research Assistant cameron.d.mcintire@gmail.com White Pine Needle Damage Report In recent years, a complex of foliar fungal pathogens, known collectively as White Pine Needle
Cameron D. McIntire Graduate Research Assistant cameron.d.mcintire@gmail.com White Pine Needle Damage Report In recent years, a complex of foliar fungal pathogens, known collectively as White Pine Needle
Chapter 2 9/15/2015. Chapter 2. Penny Boat. 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production
 Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
Hydrology and Water Quality. Water. Water 9/13/2016. Molecular Water a great solvent. Molecular Water
 Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Go to and answer these questions: 1. Draw the carbon cycle:
 Name Date Hour Cycling WebQuest: Directions: Visit the following websites and answer the related questions. Your goal is to gain a better understanding of the carbon, nitrogen and water cycle and to understand
Name Date Hour Cycling WebQuest: Directions: Visit the following websites and answer the related questions. Your goal is to gain a better understanding of the carbon, nitrogen and water cycle and to understand
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES
 WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
Joint Research Centre (JRC)
 Joint Research Centre (JRC) Marco Pastori and Faycal Bouraoui IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra - Italy http://ies.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ http://www.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ CONTENT Introduction
Joint Research Centre (JRC) Marco Pastori and Faycal Bouraoui IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra - Italy http://ies.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ http://www.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ CONTENT Introduction
BIOLOGICAL NITRIFICATION INHIBITION (BNI) -POTENTIAL FOR REDUCING NITRIFICATION AND N 2O EMISSIONS FROM AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS. Guntur V.
 Session 1 BIOLOGICAL NITRIFICATION INHIBITION (BNI) -POTENTIAL FOR REDUCING NITRIFICATION AND N 2O EMISSIONS FROM AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS Guntur V. Subbarao Japan International Research Center for Agricultural
Session 1 BIOLOGICAL NITRIFICATION INHIBITION (BNI) -POTENTIAL FOR REDUCING NITRIFICATION AND N 2O EMISSIONS FROM AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS Guntur V. Subbarao Japan International Research Center for Agricultural
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: What Is an Ecosystem? In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. ecology 2. habitat 3. community 4. ecosystem
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: What Is an Ecosystem? In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. ecology 2. habitat 3. community 4. ecosystem
Retention of soluble organic nutrients by a forested ecosystem
 Biogeochemistry 61: 135 171, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Retention of soluble organic nutrients by a forested ecosystem R.G. QUALLS 1, *, B.L. HAINES 2, W.T. SWANK
Biogeochemistry 61: 135 171, 2002. 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Retention of soluble organic nutrients by a forested ecosystem R.G. QUALLS 1, *, B.L. HAINES 2, W.T. SWANK
Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish Describe Sequence Interactions of Organisms and Their Environment Ecology Habitat
 Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Comparison of Discharge Duration Curves from Two Adjacent Forested Catchments Effect of Forest Age and Dominant Tree Species
 J. Water Resource and Protection, 2010, 2, 742-750 doi:10.4236/jwarp.2010.28086 Published Online August 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Comparison of Discharge Duration Curves from Two Adjacent
J. Water Resource and Protection, 2010, 2, 742-750 doi:10.4236/jwarp.2010.28086 Published Online August 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) Comparison of Discharge Duration Curves from Two Adjacent
