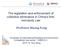
Introduction. S 1 Net welfare loss P 1 Q 0 Q 1. An Illustration of Welfare Losses and Distribution Distortions caused by Administrative Monopoly.
|
|
|
- Dennis Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction An administrative monopoly is a business monopoly granted by the administrative departments of the government to business agents enterprises or profit-making administrative entities. These monopolies are often granted through the issuance of administrative documents such as regulations, statutes, or guidelines. Administrative monopolies are often characterized by barriers to market entry and price regulations that are issued by administrative departments, establishing stronger or weaker economic monopolies. Granting monopoly powers to an enterprise is an important economic decision that represents a shift in the basic economic system (the socialist market economy ). Under the Law of Legislation, monopolies shall be established by the legislature. According to the principle of law reservation, monopolies established without the approval of the legislature pose great constraints to potential competitors economic freedom and consumers freedom of choice. In practice, most administrative monopolies in China are established by formal regulations issued by administrative departments, regulations that the departments themselves authorize. The monopoly powers established by the administrative bodies are unconstitutional and, therefore, illegal. Broadly speaking, administrative departments abuse their authority over drafting legislative acts to establish monopoly powers in favor of certain enterprises. This is made possible by a weak legislature, granting these departments their own kind of administrative monopoly in the regulatory process. Since the beginning of reform and opening up, China s constitution has been amended several times. There have been great changes made to its fundamental principles, such as xxiii
2 xxiv Introduction the introduction of the socialist market economy, and the guiding principle that the state encourages, supports and guides the development of the non-public economy. Laws that allow for the creation of administrative monopolies are incompatible with China s constitution. Almost all of the main industries subject to administrative monopoly that are discussed in this study evolved out of the completely planned economy. After years of reform to the fiscal system, the central government s main sources of revenue come from taxable income. The central government has incentives to push forward reforms for stateowned enterprises (SOEs), but no incentives to break the monopolies held by these enterprises. On the contrary, granting administrative monopolies as preferential policies to SOEs could be a way to reduce the financial burden on SOEs. With the success of China s economic reforms, huge domestic markets have emerged, which in turn highlighted the value of monopolies over these markets. Because the enterprises with monopoly powers do not need to hand over their profits, and there are no ceilings on the level of wages and bonuses, the enterprises keep all the profit derived from the existence of administrative monopolies. As interest groups, they have a strong incentive to attempt an expansion of their administrative monopolies. In-house lobbying refers to the lobbying of administrative officials done by high-level management at SOEs in order to secure administrative monopolies. One reason for this is the revolving door linking administrators and SOE managers, with SOE managers frequently serving stints in administrative positions and vice versa. This is an indirect yet important indicator of administrative monopolization, and this phenomenon appeared in several industries dealt with in this book. In-house lobbying works because of the existence of departmental legislation, the manipulation or creation of legislation by government administrators. Departmental legislation exists because of the lack of sufficient supervision over administrative departments in the current political structure, leading to an abuse of power that both directly and indirectly affects legislation. Broadly speaking, departmental legislation also refers to the fact that in carrying out administrative duties, departments are in effect creating or amending legislation.
3 Introduction xxv Administrative monopolies are created by setting barriers to entering an industry and by regulating prices. Price regulations can be further subdivided into (1) regulations over sales prices by monopolists; and (2) regulations over purchase prices for monopolists. The holders of administrative monopolies can, therefore, obtain resources and other inputs at large discounts or even for free. As long as there are institutional barriers to entry, even if other market conditions allow for fair competition, under a certain level of demand, administrative monopolies can also lead to high prices, low production, and welfare losses. When barriers to entry drive up prices, they unfairly convert consumer surplus into corporate profits, and in the process further distort income distribution. If the resources that become monopoly profits were used in exchanges dictated by the market, they would go toward the creation of other goods and services. The value of these goods and services (with consumer surplus added in) is the opportunity loss caused by administrative monopolies, along with the social welfare losses from distortions to income distribution. Regulation over purchase prices (with factor prices being low or zero) is a serious distortion of income distribution. It unfairly transfers huge amounts of wealth originally belonging to the state or other economic agents to SOEs. We assume that the rents for resources not paid or underpaid for by monopoly enterprises are used to occupy other production factors (such as labor, land, and capital), and that they could be put to more productive use if activities were determined by market forces. The value of such products (with consumer surplus added in) is the opportunity cost caused by the distortion of distribution. In the end, these lead to a decrease in aggregate social welfare. Administrative monopolies transfer wealth, in the form of money, from consumers to the companies that enjoy a monopoly, including their management and staff. These companies do not use these monetary resources to produce the corresponding amount of goods or services. From a macro social perspective, there now exists a greater supply of money chasing a relatively low amount of goods, a process that inevitably leads to inflation. In recent years, adjusting the deposit reserve requirements instead of interest rates has become the primary means of implementing monetary
4 xxvi Introduction policy. The deposit reserve requirement is frequently adjusted, changing up to ten times a year. The total range of adjustments has been 14%, with the highest rate being 21.5%. From the perspective of banks, adjusting the deposit reserve requirements and adjusting interest rates are very different. This is particularly true when implementing tightening policies where raising the deposit reserve requirements allows banks to avoid the huge costs of raising interest rates. Given the government s central role in the creation of administrative monopolies, the losses generated are three-fold. Not only do administrative monopolies lower economic efficiency and violate principles of social justice, but in the formation, maintenance, and strengthening of administrative monopolies, the credibility and authority of the administrators themselves is seriously weakened. This means that SOEs and the control they have over the national economy does not constitute the often-touted basis of rule for the government; it is instead a threat to that very rule. Following is a figure showing welfare loss and distribution distortions caused by administrative monopoly: D Welfare transfer and welfare loss caused by regulated (monopoly) sales prices S 1 Net welfare loss P 1 P 0 S 0 C Q( M 0, P0) Q 0 Q 1 Welfare transfer and welfare loss caused by buyers regulated (monopoly) purchase prices An Illustration of Welfare Losses and Distribution Distortions caused by Administrative Monopoly.
5 Introduction xxvii The dark grey triangle in the figure is the net loss of social welfare caused by administrative monopolies; we call it Social Welfare Loss I. The light grey part in the figure is distribution distortion caused by monopoly (regulated) sales prices; we call it Social Welfare Loss II. The grey part in the figure is the distribution distortion caused by buyers monopoly (regulated) purchase prices (with some costs approaching zero); we call it Social Welfare Loss III. Estimation of social welfare loss I: The net social welfare losses caused by the administrative monopoly granted to China Telecom, China Mobile, and China Unicom from totaled approximately RMB 84.6 billion. Total social welfare losses throughout the telecom industry during the same period were up to RMB billion, and the corresponding losses in the oil industry total around RMB trillion. Estimation of social welfare loss II (i.e. the profits derived from monopoly pricing): The annual rents accrued from administrative monopolies in the telecommunications industry average approximately RMB 31.3 billion per year. This amount is equal to the decrease in consumer surplus. The monopoly profits brought about by high prices in the oil industry total around RMB billion. The monopoly profits in the salt industry are as high as RMB 17.7 billion per year. These are direct losses for consumers and also amount to social welfare losses. Estimation of social welfare loss III: From 2001 to 2010, PetroChina underpaid by RMB billion on rental costs for industrial-use land. On land used for gas stations, PetroChina and Sinopec collectively underpaid by RMB billion, and the two underpaid RMB billion in royalties. Collectively, the Big Three in the oil industry underpaid on finance costs by RMB billion, with all of these underpayments contributing to social welfare losses. In most market economies, the average difference between deposit rates and interest rates on loans is around 1 2%. In China, the difference between one-year loan rates and deposit rates has averaged 3.06% in recent years. This is achieved by pushing deposit rates down to 1.5%. With total national deposits averaging RMB trillion in 2011, estimates of the losses to individuals and institutions total RMB trillion, equal to 2.6% of GDP in that year.
6 xxviii Introduction The persistent difficulty in buying train tickets in China indicates a general supply shortage for ordinary (non-high-speed) tickets. Judging from the constant traffic jams on the Beijing Tibet Expressway (some reaching 100 km and lasting for ten days) and the Qingdao Yinchuan Expressway caused by a glut of freight trucks, there appears to be a general shortage of railway freight capacity. At the same time, the already constructed high-speed railway lines are largely underutilized relative to optimal passenger levels. This suggests a severe misallocation of investment between high-speed and conventional railways. Reports estimate that in order for the utility-to-cost ratio of high-speed railway to equal that of regular railways, the high-speed line requires 129 daily departures. As we know, the busiest Beijing Shanghai highspeed line has only daily departures. This means that the decrease in construction of normal railways in favor of high-speed lines will lead to net social welfare losses. In accordance with relevant data, the welfare losses caused by the misallocated resources between high-speed and conventional railway is approximately RMB 53.3 billion per year. The net social welfare losses due to administrative monopolies in 2010 (including losses from misallocated railway spending) were equal to RMB 1.91 trillion. The combined losses due to monopoly sales pricing (social welfare loss II) and monopoly purchase prices on inputs equal RMB 1.62 trillion. Social welfare loss II is equal to the quantity of money that lacks corresponding goods and services, and thus inevitably brings about inflation pressure. Specifically, it will cause inflation to rise by 2.4%, equivalent to 78.7% of the rise in the retail goods price index for that year. In terms of adjusting deposit reserve requirements as an alternative to adjusting interest rates, we look at the June 20, 2011 decision by the People s Bank of China (PBOC) to raise deposit reserve requirements by 0.5%. The equivalent interest rate change would be 0.375%, but the decision to adjust deposit reserve requirements saved banks RMB billion in interest payments. The PBOC raised reserve requirements six times in 2011, each time by 0.5%. That is, equivalent to reducing the interest payments of banks and their main borrowers by RMB trillion.
7 Introduction xxix Although there are some shortcomings in the current Anti-Unfair Competition Law ( ) and Anti-Monopoly Law ( ), the laws do articulate legal constraints on the exercise of administrative monopolies. The monopoly behaviors defined in the Anti- Monopoly Law include achieving monopoly agreements between business agents, abusing monopoly positions, and concentrating firms for purpose of limiting or excluding competitors. There is even a particular chapter in the law to forbid the abuse of administrative powers to exclude and to limit competition. Administrative departments should avoid legislating through the preparation of drafts, especially when drafts of bills pertain to specific monopolies. At a bare minimum, these types of legislation should be drafted by neutral agents authorized by the legislature. Moreover, the legislature should organize committees of experts to review drafts for the establishment of monopolies in specific industries. Furthermore, the establishment of a specific monopoly should be treated as an isolated event. The legislature should avoid the creation of monopolies by reference to broad categories such as the often-cited economic lifeline of the country. Administrative departments do not have the power to establish specific monopolies. Any monopoly established by administrative departments through regulations or statutes is illegal. Rules should be established that exclude related administrative departments from the drafting of implementation details or regulations. Alternatively, the review of drafted implementation rules of specific laws could be strengthened to prevent the adding of articles related to the establishment or expansion of specific monopolies. The power of administrative departments to regulate prices should only come with authorization by the legislature. When an administrative department uses its price-regulating power, it should abide by the Price Law ( ), and must first go through fair hearings. In particular, it should differentiate between the adjustment of interest rates by the PBOC to implement monetary policy and the interest rates of commercial banks. The PBOC should avoid the regulation of commercial bank interest rates in the name of implementing monetary policy. The constitutional powers to govern the state-owned sector of the public economy could be used to more effectively monitor and
8 xxx Introduction constrain the management of SOEs. Because public resources and assets should be owned by all people, the supervision of these resources and assets should be strengthened. It must be assured that these assets do not flow into the hands of the managers who operate SOEs. Given the difficulties in effective public oversight of these resources and assets, this responsibility for supervision should be emphasized in the constitution, and established by corresponding institutions and rules in laws. The Standing Committee of the National People s Congress, as a specialized constitutional supervisory authority, can and should review and terminate unconstitutionally established administrative monopolies. At the same time, based on the provisions of existing constitutional law, the Law of Legislation ( ) empowers authorities (mainly the Standing Committee of the National People s Congress and the State Council) to terminate or revoke existing administrative documents that establish administrative monopolies. Proposals for judicial reforms to break administrative monopolies include: First, allow plaintiffs (not limited just to companies) to directly sue the companies suspected of holding an administrative monopoly. In addition, expand the rights of the plaintiff to include not merely suing for civil liabilities, but also requesting the court to review the legality of the monopoly itself. Second, amend the relevant legislation so that courts have substantive power to review the cases of administrative monopoly and to dispose of the monopoly status. Third, reinvigorate existing anti-trust administrative enforcement mechanisms. The keys are to consolidate institutions and functions, improve authority (for example, not relying on recommendations to the superior authority ), and strengthen the legitimacy of the process by ensuring a fair, transparent, and participatory process, rather than relying on internal operations. Fourth, establish a system for publicly prosecuting administrative monopolies.
9 Introduction xxxi Below are listed recommendations for breaking administrative monopolies at the administrative level: Note: First, directly encourage enterprises, including private enterprises and SOEs, to enter the sectors where there is an absence of legal provisions of monopolies. For instance, in the oil industry there are only administrative documents, but no legal restrictions to entry. Any administrative departments that impede enterprises from entering these fields should be subject to administrative penalties. Second, abolish and prohibit administrative departments from granting monopolies to themselves (or industrial associations controlled by them) by way of executive orders. Third, require the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Land Resource, and other related departments to set up specialized agencies to verify the number of public natural resources (including land and mining licenses) occupied by enterprises, and charge rents at market prices to companies that utilize these resources. Fourth, require the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC) of the State Council to set a reasonable wage ceiling on SOE employees based on average wages in society, and punish those who earn above these limits. Fifth, request that the Ministry of Finance establish specialized agencies to monitor SOEs (particularly central SOEs), give recommendations to the State Council on the distribution of profits, strictly implement the remittance of profits, and supervise the use of profits reinvested in the companies. Lastly, in the long run, promote the withdrawal of SOEs from profitmaking areas. In this book, the word monopoly will be used to refer to a range of monopoly, duopoly and oligopoly dynamics, with the scope of market concentration ranging along that spectrum. In this book, all Chinese names will be written according to the Chinese convention of placing the surname before the given name.
Nature of Administrative Monopolies
 Chapter 1 Nature of Administrative Monopolies 1. Definition of Administrative Monopoly We usually divide monopolies into market monopolies and artificial monopolies. Market monopoly involves market powers
Chapter 1 Nature of Administrative Monopolies 1. Definition of Administrative Monopoly We usually divide monopolies into market monopolies and artificial monopolies. Market monopoly involves market powers
Economics. E.1.4 Describe how people respond predictably to positive and negative incentives.
 Standard 1: Scarcity and Economic Reasoning Students will understand that productive resources are limited; therefore, people cannot have all the goods and services they want. As a result, they must choose
Standard 1: Scarcity and Economic Reasoning Students will understand that productive resources are limited; therefore, people cannot have all the goods and services they want. As a result, they must choose
Introduction. Definitions
 Introduction Public-Private Partnerships, (PPP s or P3 s), and initiatives and legislation supporting them, are a prominent trend in State and Federal government. They are often supported by Big Government
Introduction Public-Private Partnerships, (PPP s or P3 s), and initiatives and legislation supporting them, are a prominent trend in State and Federal government. They are often supported by Big Government
Economics Challenge Online State Qualification Practice Test. 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from
 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
English - Or. English DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS COMPETITION COMMITTEE
 Unclassified DAF/COMP/WD(2015)53 DAF/COMP/WD(2015)53 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 11-Jun-2015 English
Unclassified DAF/COMP/WD(2015)53 DAF/COMP/WD(2015)53 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 11-Jun-2015 English
Strengthening Public Affairs through Project Financing of the Franchise Contract Foreign Intervention
 International Integration for Regional Public Management (ICPM 2014) Strengthening Public Affairs through Project Financing of the Franchise Contract Foreign Intervention Guo Xinyu1 School of Public Management,
International Integration for Regional Public Management (ICPM 2014) Strengthening Public Affairs through Project Financing of the Franchise Contract Foreign Intervention Guo Xinyu1 School of Public Management,
Regulating Public Utility Performance The Law of Market Structure, Pricing and Jurisdiction Scott Hempling
 Regulating Public Utility Performance The Law of Market Structure, Pricing and Jurisdiction Scott Hempling Regulatory Law: Purposes, Power, Rights and Responsibilities Market Structure: From Monopolies
Regulating Public Utility Performance The Law of Market Structure, Pricing and Jurisdiction Scott Hempling Regulatory Law: Purposes, Power, Rights and Responsibilities Market Structure: From Monopolies
Countermeasures for Regulating Income Distribution in Monopoly Industries of China
 Countermeasures for Regulating Income Distribution in Monopoly Industries of China Pan Shengwen Economics and Business Administration Academy in Central China Normal University, Wuhan, Hubei, China panwen69@126.com
Countermeasures for Regulating Income Distribution in Monopoly Industries of China Pan Shengwen Economics and Business Administration Academy in Central China Normal University, Wuhan, Hubei, China panwen69@126.com
City of Colorado Springs Code of Ethics
 City of Colorado Springs Code of Ethics CITY OF COLORADO SPRINGS, COLORADO CODE OF ETHICS As found in Chapter 1, Article 3 of the City Code 1.3.101: LEGISLATIVE PURPOSE: A. There is hereby adopted by the
City of Colorado Springs Code of Ethics CITY OF COLORADO SPRINGS, COLORADO CODE OF ETHICS As found in Chapter 1, Article 3 of the City Code 1.3.101: LEGISLATIVE PURPOSE: A. There is hereby adopted by the
Challenges and Opportunities: Reform of China s Public Administration in the New Era
 REFORM Asian Review OF of CHINA S Public Administration, PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION Vol. XIII, No. 1 (January-June 2001) 1 Challenges and Opportunities: Reform of China s Public Administration in the New Era
REFORM Asian Review OF of CHINA S Public Administration, PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION Vol. XIII, No. 1 (January-June 2001) 1 Challenges and Opportunities: Reform of China s Public Administration in the New Era
The Fundamentals of Economic Management and Governance in the Drive for Economic Transformation. Omotunde E. G. Johnson
 The Fundamentals of Economic Management and Governance in the Drive for Economic Transformation Omotunde E. G. Johnson Outline Introduction: The Fundamental Problem and the Challenges Economic Growth:
The Fundamentals of Economic Management and Governance in the Drive for Economic Transformation Omotunde E. G. Johnson Outline Introduction: The Fundamental Problem and the Challenges Economic Growth:
PRYSMIAN GROUP ETHICAL CODE
 PRYSMIAN GROUP ETHICAL CODE the Prysmian ethical code Ethical Code Introduction pag. 1 Articles: Article 1 Article 2 Article 3 Article 4 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 10 Article
PRYSMIAN GROUP ETHICAL CODE the Prysmian ethical code Ethical Code Introduction pag. 1 Articles: Article 1 Article 2 Article 3 Article 4 Article 5 Article 6 Article 7 Article 8 Article 9 Article 10 Article
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By
 Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
China s Perspective in Administrative Reform
 2008/ACT/SYM/013 Session: 3 China s Perspective in Administrative Reform Submitted by: China International Symposium on Anti-Corruption and Administrative Reform Hanoi, Viet Nam 25-26 June 2008 China s
2008/ACT/SYM/013 Session: 3 China s Perspective in Administrative Reform Submitted by: China International Symposium on Anti-Corruption and Administrative Reform Hanoi, Viet Nam 25-26 June 2008 China s
Reform,Opening up & China s Economic Growth
 Reform,Opening up & China s Economic Growth November 16, 2009 1 Overview of China s Economic Growth 2 Land reform and China s Agriculture Industry 3 Monopoly and Anti-trust: Case in China Telecom Market
Reform,Opening up & China s Economic Growth November 16, 2009 1 Overview of China s Economic Growth 2 Land reform and China s Agriculture Industry 3 Monopoly and Anti-trust: Case in China Telecom Market
Independent Regulators Group Rail. IRG Rail
 IRG-Rail (15) 6 Independent Regulators Group Rail IRG Rail Position Paper on the new proposals concerning governance and the award of public service contracts with a strong focus on the role of the regulatory
IRG-Rail (15) 6 Independent Regulators Group Rail IRG Rail Position Paper on the new proposals concerning governance and the award of public service contracts with a strong focus on the role of the regulatory
Business. Management 113. Complete
 Business Management 113 Complete 1 CHAPTER 1:Business Environment BUSINESS: A DEFINITION BUSINESS: The organised effort of individuals to produce and sell, for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy
Business Management 113 Complete 1 CHAPTER 1:Business Environment BUSINESS: A DEFINITION BUSINESS: The organised effort of individuals to produce and sell, for a profit, the goods and services that satisfy
Re: Draft Anti-Pricing Monopoly Regulation
 DRAFT 8/31/09 BY EMAIL xueq@ndrc.gov.cn AND FEDEX Department of Price Supervision No. 38 Yuetan Nanjie Beijing 100824 China Dear Sir/Madam: Re: Draft Anti-Pricing Monopoly Regulation The Section of International
DRAFT 8/31/09 BY EMAIL xueq@ndrc.gov.cn AND FEDEX Department of Price Supervision No. 38 Yuetan Nanjie Beijing 100824 China Dear Sir/Madam: Re: Draft Anti-Pricing Monopoly Regulation The Section of International
New Review System Milestone for Fair Market Competition. Michael Gu/ Sun Sihui 1
 New Review System Milestone for Fair Market Competition Michael Gu/ Sun Sihui 1 Introduction On June 1 2016 the State Council published its Opinions on Establishing a Fair Competition Review System in
New Review System Milestone for Fair Market Competition Michael Gu/ Sun Sihui 1 Introduction On June 1 2016 the State Council published its Opinions on Establishing a Fair Competition Review System in
CHINESE ENFORCEMENT AGAINST ABUSES OF DOMINANCE RAMPS UP
 CHINESE ENFORCEMENT AGAINST ABUSES OF DOMINANCE RAMPS UP Peter Wang, Yizhe Zhang & Sébastien Evrard Jones Day Copyright 2012 Competition Policy International, Inc. For more articles and information, visit
CHINESE ENFORCEMENT AGAINST ABUSES OF DOMINANCE RAMPS UP Peter Wang, Yizhe Zhang & Sébastien Evrard Jones Day Copyright 2012 Competition Policy International, Inc. For more articles and information, visit
Law of the People s Republic of China on Administration of Foreign NGOs' Activities within China
 In-house translation prepared by Law of the People s Republic of China on Administration of Foreign NGOs' Activities within China CONTENTS Chapter 1. General Provisions Chapter 2. Registration and Filing
In-house translation prepared by Law of the People s Republic of China on Administration of Foreign NGOs' Activities within China CONTENTS Chapter 1. General Provisions Chapter 2. Registration and Filing
Concslusions on Iceland
 Concslusions on Iceland (extract from the Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council "Enlargement Strategy and Main Challenges 2012-2013", COM(2012)600 final) Iceland
Concslusions on Iceland (extract from the Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council "Enlargement Strategy and Main Challenges 2012-2013", COM(2012)600 final) Iceland
Competition Law & Policy in India
 Competition Law & Policy in India Prepared by Competition Commission of India June 2004 Competition Is a situation in a market in which firms or sellers independently strive for the buyers patronage in
Competition Law & Policy in India Prepared by Competition Commission of India June 2004 Competition Is a situation in a market in which firms or sellers independently strive for the buyers patronage in
European System of Financial Supervisors (ESFS): Frequently Asked Questions (see IP/09/1347 and MEMO/09/405)
 MEMO/09/404 Brussels, 23 September 2009 European System of Financial Supervisors (ESFS): Frequently Asked Questions (see IP/09/1347 and MEMO/09/405) Why are the new European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs)
MEMO/09/404 Brussels, 23 September 2009 European System of Financial Supervisors (ESFS): Frequently Asked Questions (see IP/09/1347 and MEMO/09/405) Why are the new European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs)
Central Bank Governance. 30 November 2010 Oliver Loch 1
 Central Bank Governance 1 Agenda 1 Corporate Governance of state owned enterprises 2 Key aspects in Central Bank Governance and framework at the Bundesbank 3 Independence and Governance Agenda 1 Corporate
Central Bank Governance 1 Agenda 1 Corporate Governance of state owned enterprises 2 Key aspects in Central Bank Governance and framework at the Bundesbank 3 Independence and Governance Agenda 1 Corporate
PUBLIC AUTHORITY BOARD MEMBER DUTIES Anita Laremont, SVP - Legal & General Counsel Empire State Development Corporation December 2005
 PUBLIC AUTHORITY BOARD MEMBER DUTIES Anita Laremont, SVP - Legal & General Counsel Empire State Development Corporation December 2005 I. The duties and legal responsibilities of board of director members
PUBLIC AUTHORITY BOARD MEMBER DUTIES Anita Laremont, SVP - Legal & General Counsel Empire State Development Corporation December 2005 I. The duties and legal responsibilities of board of director members
Louisiana Society for Human Resource Management
 Louisiana Society for Human Resource Management 2017 Regular Session Bills of Interest The following are summaries of bills pending before the Louisiana Legislature during the 2017 Regular Session, and
Louisiana Society for Human Resource Management 2017 Regular Session Bills of Interest The following are summaries of bills pending before the Louisiana Legislature during the 2017 Regular Session, and
Principles of Economics. January 2018
 Principles of Economics January 2018 Monopoly Contents Market structures 14 Monopoly 15 Monopolistic competition 16 Oligopoly Principles of Economics January 2018 2 / 39 Monopoly Market power In a competitive
Principles of Economics January 2018 Monopoly Contents Market structures 14 Monopoly 15 Monopolistic competition 16 Oligopoly Principles of Economics January 2018 2 / 39 Monopoly Market power In a competitive
PROVISIONS IN THE ANTI-MONOPOLY LAW OF PRC ON ABUSE OF ADMINISTRATIVE POWERS TO ELIMINATE OR RESTRICT COMPETITION AND RELATED LAW ENFORCEMENT PRACTICE
 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会 National Development and Reform Commission PROVISIONS IN THE ANTI-MONOPOLY LAW OF PRC ON ABUSE OF ADMINISTRATIVE POWERS TO ELIMINATE OR RESTRICT COMPETITION AND RELATED LAW ENFORCEMENT
中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会 National Development and Reform Commission PROVISIONS IN THE ANTI-MONOPOLY LAW OF PRC ON ABUSE OF ADMINISTRATIVE POWERS TO ELIMINATE OR RESTRICT COMPETITION AND RELATED LAW ENFORCEMENT
13 C H A P T E R O U T L I N E
 PEARSON PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2of 37 PART III MARKET IMPERFECTIONS AND THE ROLE OF GOVERNMENT Monopoly
PEARSON PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2of 37 PART III MARKET IMPERFECTIONS AND THE ROLE OF GOVERNMENT Monopoly
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 28. Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy
 Chapter 28 Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy Introduction The term sticker shock has come into widespread use to describe a consumer s surprise and dismay about higher-than-anticipated
Chapter 28 Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy Introduction The term sticker shock has come into widespread use to describe a consumer s surprise and dismay about higher-than-anticipated
TELECOMMUNICATIONS LIBERALISATION IN THE BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS LIBERALISATION IN THE BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS 10 January 2007 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 The British Virgin Islands Government (BVIG) has decided that it wishes to introduce competition in
TELECOMMUNICATIONS LIBERALISATION IN THE BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS 10 January 2007 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 The British Virgin Islands Government (BVIG) has decided that it wishes to introduce competition in
EOCT Test Semester 2 final
 EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
Is China s growth sustainable? Chang Ka Mun Managing Director Li & Fung Development (China) Limited CNAPS Advisory Council, 28 November 2007
 Is China s growth sustainable? Chang Ka Mun Managing Director Li & Fung Development (China) Limited CNAPS Advisory Council, 28 November 2007 Recent developments of Chinese economy (1) High growth rate
Is China s growth sustainable? Chang Ka Mun Managing Director Li & Fung Development (China) Limited CNAPS Advisory Council, 28 November 2007 Recent developments of Chinese economy (1) High growth rate
PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER. PEARSON Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft
 PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER PEARSON Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2 of 25 PART III MARKET IMPERFECTIONS AND THE ROLE OF GOVERNMENT Monopoly
PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER PEARSON Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2 of 25 PART III MARKET IMPERFECTIONS AND THE ROLE OF GOVERNMENT Monopoly
A Correlation of. To the Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies Table of Contents E.1... 3 E.2... 6 E.3... 7 E.4... 11 E.5... 15 E.6... 19 E.7... 24 E.8... 26 E.9... 28
A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies Table of Contents E.1... 3 E.2... 6 E.3... 7 E.4... 11 E.5... 15 E.6... 19 E.7... 24 E.8... 26 E.9... 28
Third Party Environmental Governance of Chemical Industrial Pollution
 613 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERINGTRANSACTIONS VOL. 62, 2017 Guest Editors: Fei Song,Haibo Wang, Fang He Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN978-88-95608-60-0; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian Association
613 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERINGTRANSACTIONS VOL. 62, 2017 Guest Editors: Fei Song,Haibo Wang, Fang He Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN978-88-95608-60-0; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian Association
Code of Conduct SAMSUNG SDI Co., Ltd.
 Code of Conduct 2010. 12. SAMSUNG SDI Co., Ltd. 1 IMPORTANT NOTICE SAMSUNG SDI RECOGNIZES THAT VARIOUS COUNTRIES MAY HAVE LAWS AND REGULATIONS THAT ESTABLISH DIFFERENT REQUIREMENTS FOR CORPORATE INTERGRITY.
Code of Conduct 2010. 12. SAMSUNG SDI Co., Ltd. 1 IMPORTANT NOTICE SAMSUNG SDI RECOGNIZES THAT VARIOUS COUNTRIES MAY HAVE LAWS AND REGULATIONS THAT ESTABLISH DIFFERENT REQUIREMENTS FOR CORPORATE INTERGRITY.
INTERFACE BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITIES, COMPETITION REGULATIONS AND OTHER REGULATORY FRAMEWORKS AND INSTITUTIONS IN INFRASTRUCTURE SERVICES
 MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON SERVICES, DEVELOPMENT AND TRADE: THE REGULATORY AND INSTITUTIONAL DIMENSION Geneva, 17-19 March 2010 INTERFACE BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITIES, COMPETITION REGULATIONS AND
MULTI-YEAR EXPERT MEETING ON SERVICES, DEVELOPMENT AND TRADE: THE REGULATORY AND INSTITUTIONAL DIMENSION Geneva, 17-19 March 2010 INTERFACE BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITIES, COMPETITION REGULATIONS AND
Price Maintenance & Vertical Restraints. KING & WOOD MALLESONS
 Price Maintenance & Vertical Restraints KING & WOOD MALLESONS 2015 www.kwm.com Overview of the Legal Basis and the Regulators Anti-monopoly Law ( AML ) Monopoly agreements Abuse of dominance Concentrations
Price Maintenance & Vertical Restraints KING & WOOD MALLESONS 2015 www.kwm.com Overview of the Legal Basis and the Regulators Anti-monopoly Law ( AML ) Monopoly agreements Abuse of dominance Concentrations
LAW ON PUBLIC ENTERPRISES Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia no. 38/96; 9/97
 LAW ON PUBLIC ENTERPRISES Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia no. 38/96; 9/97 GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 The public enterprises are established for the purpose of carrying out economic activities
LAW ON PUBLIC ENTERPRISES Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia no. 38/96; 9/97 GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 The public enterprises are established for the purpose of carrying out economic activities
THEMATIC COMPILATION OF RELEVANT INFORMATION SUBMITTED BY ARMENIA ARTICLE 10 UNCAC PUBLIC REPORTING
 THEMATIC COMPILATION OF RELEVANT INFORMATION SUBMITTED BY ARMENIA ARTICLE 10 UNCAC PUBLIC REPORTING ARMENIA (SEVENTH MEETING) RA Law on freedom of information regulates the relations concerning freedom
THEMATIC COMPILATION OF RELEVANT INFORMATION SUBMITTED BY ARMENIA ARTICLE 10 UNCAC PUBLIC REPORTING ARMENIA (SEVENTH MEETING) RA Law on freedom of information regulates the relations concerning freedom
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 28. Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy
 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 28 Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy All rights reserved. Introduction The term sticker shock has come into widespread use to describe
Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 28 Regulation and Antitrust Policy in a Globalized Economy All rights reserved. Introduction The term sticker shock has come into widespread use to describe
Corporate Governance Policy of The Japan Steel Works, Ltd.
 Corporate Governance Policy of The Japan Steel Works, Ltd. Established: November 18, 2015 Amendment: June 24, 2016 Chapter 1. General Provisions 1. Purpose The purpose of this document is to prescribe
Corporate Governance Policy of The Japan Steel Works, Ltd. Established: November 18, 2015 Amendment: June 24, 2016 Chapter 1. General Provisions 1. Purpose The purpose of this document is to prescribe
LAW OF MONGOLIA ON PROHIBITING UNFAIR COMPETITION
 LAW OF MONGOLIA ON PROHIBITING UNFAIR COMPETITION (Unofficial Translation, 19/9/94) Chapter One General Basis Article 1. The Purpose of the Law The purpose of the Law is to regulate relations connected
LAW OF MONGOLIA ON PROHIBITING UNFAIR COMPETITION (Unofficial Translation, 19/9/94) Chapter One General Basis Article 1. The Purpose of the Law The purpose of the Law is to regulate relations connected
Chapter 1: Managers and Economics
 Economics for Managers by Paul Farnham Chapter 1: Managers and Economics 1.1 The best time for a managerial angle on life 1.2 What happened on the global markets in the last year? Governments designing
Economics for Managers by Paul Farnham Chapter 1: Managers and Economics 1.1 The best time for a managerial angle on life 1.2 What happened on the global markets in the last year? Governments designing
Electricity Power System Planning
 Chapter 1 Section 1.05 Ministry of Energy Electricity Power System Planning Follow-Up on VFM Section 3.05, 2015 Annual Report Chapter 1 Follow-Up Section 1.05 RECOMMENDATION STATUS OVERVIEW # of Status
Chapter 1 Section 1.05 Ministry of Energy Electricity Power System Planning Follow-Up on VFM Section 3.05, 2015 Annual Report Chapter 1 Follow-Up Section 1.05 RECOMMENDATION STATUS OVERVIEW # of Status
Research on Mixed Ownership Economy Development in Hubei Province
 International Conference on Social Science and Technology Education (ICSSTE 2015) Research on Mixed Ownership Economy Development in Hubei Province Li Xiuping Wuhan Donghu University, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
International Conference on Social Science and Technology Education (ICSSTE 2015) Research on Mixed Ownership Economy Development in Hubei Province Li Xiuping Wuhan Donghu University, Wuhan, Hubei, China,
The Application of Consumer Interests in China's Anti-monopoly Law Enforcement: Take the Cases of Industry and Commerce Bureau as an Example
 2018 International Conference on E-commerce and Contemporary Economic Development (ECED 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-552-0 The Application of Consumer Interests in China's Anti-monopoly Law Enforcement: Take
2018 International Conference on E-commerce and Contemporary Economic Development (ECED 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-552-0 The Application of Consumer Interests in China's Anti-monopoly Law Enforcement: Take
OECD Global Forum on Competition
 For Official Use CCNM/GF/COMP/WD(2004)21 CCNM/GF/COMP/WD(2004)21 For Official Use Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 02-Feb-2004
For Official Use CCNM/GF/COMP/WD(2004)21 CCNM/GF/COMP/WD(2004)21 For Official Use Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 02-Feb-2004
Global Forum on Competition
 Unclassified Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 27-Oct-2015 English - Or. English DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL
Unclassified Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 27-Oct-2015 English - Or. English DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL
Conclusions on Iceland
 Conclusions on Iceland (extract from the Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council "Enlargement Strategy and Main Challenges 2011-2012", COM(2011)666 final) Iceland continues
Conclusions on Iceland (extract from the Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council "Enlargement Strategy and Main Challenges 2011-2012", COM(2011)666 final) Iceland continues
July 2017 AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW
 July 2017 AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW AMENDMENTS TO THE DECREE OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF AZERBAIJAN "ON CERTAIN ISSUES OF MORTGAGE LENDING IN THE REPUBLIC OF AZERBAIJAN" On July 13, 2017,
July 2017 AZERBAIJAN ECONOMIC REFORMS REVIEW AMENDMENTS TO THE DECREE OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF AZERBAIJAN "ON CERTAIN ISSUES OF MORTGAGE LENDING IN THE REPUBLIC OF AZERBAIJAN" On July 13, 2017,
The Exploration of Implementation of Emissions Trading System in China 1
 J. Service Science & Management, 2009, 2: 270-275 doi:10.4236/jssm.2009.24032 Published Online December 2009 (www.scirp.org/journal/jssm) The Exploration of Implementation of Emissions Trading System in
J. Service Science & Management, 2009, 2: 270-275 doi:10.4236/jssm.2009.24032 Published Online December 2009 (www.scirp.org/journal/jssm) The Exploration of Implementation of Emissions Trading System in
AMETEK, Inc. Code of Ethics and Business Conduct
 AMETEK, Inc. Code of Ethics and Business Conduct Code of Ethics and Business Conduct A Message from the Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer Dear AMETEK Colleague: AMETEK has been in business
AMETEK, Inc. Code of Ethics and Business Conduct Code of Ethics and Business Conduct A Message from the Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer Dear AMETEK Colleague: AMETEK has been in business
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITY AND REGULATORY AUTHORITY REGARDING THE POWER TO REGULATE ABUSE OF MARKET DOMINANCE
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITY AND REGULATORY AUTHORITY REGARDING THE POWER TO REGULATE ABUSE OF MARKET DOMINANCE Contribution by the REPUBLIC OF KOREA Submitted to UNCTAD's Seventh Session
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN COMPETITION AUTHORITY AND REGULATORY AUTHORITY REGARDING THE POWER TO REGULATE ABUSE OF MARKET DOMINANCE Contribution by the REPUBLIC OF KOREA Submitted to UNCTAD's Seventh Session
Adopted by the State Duma on July 15, 1998 Approved by the Federation Council on July 17, 1998
 FEDERAL LAW NO. 39-FZ OF FEBRUARY 25, 1999 ON INVESTMENT ACTIVITY IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION PURSUED IN THE FORM OF CAPITAL INVESTMENTS (with the Amendments and Additions of January 2, 2000) Adopted by
FEDERAL LAW NO. 39-FZ OF FEBRUARY 25, 1999 ON INVESTMENT ACTIVITY IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION PURSUED IN THE FORM OF CAPITAL INVESTMENTS (with the Amendments and Additions of January 2, 2000) Adopted by
Chapter 3. Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary Business
 Chapter 3 Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary Business Learning Objectives 1 Discuss microeconomics and explain the forces of demand and supply. 4 Discuss managing the economy s performance. 2 Describe
Chapter 3 Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary Business Learning Objectives 1 Discuss microeconomics and explain the forces of demand and supply. 4 Discuss managing the economy s performance. 2 Describe
The Analysis of Marketing Strategy of Jianzhijia Chain Drugstore
 The Analysis of Marketing Strategy of Jianzhijia Chain Drugstore YU CHEN 1 Abstract The aim of this paper is to comprehensively use tools and principles of strategic planning so as to analyze and develop
The Analysis of Marketing Strategy of Jianzhijia Chain Drugstore YU CHEN 1 Abstract The aim of this paper is to comprehensively use tools and principles of strategic planning so as to analyze and develop
DECREE ON TRADE COMPETITION
 Lao People's Democratic Republic Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity The Prime Minister Office No. 15 /PMO Vientiane, dated 04/02/2004 DECREE ON TRADE COMPETITION Based upon the Law regarding
Lao People's Democratic Republic Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity The Prime Minister Office No. 15 /PMO Vientiane, dated 04/02/2004 DECREE ON TRADE COMPETITION Based upon the Law regarding
Liberalization, Investment, and Regulation: The Key Factors for the Development of the Electronic Communications Market
 Liberalization, Investment, and Regulation: The Key Factors for the Development of the Electronic Communications Market Jonida Gjika, PhD Electronic Communications and Postal Authority of Albania doi:
Liberalization, Investment, and Regulation: The Key Factors for the Development of the Electronic Communications Market Jonida Gjika, PhD Electronic Communications and Postal Authority of Albania doi:
Agency Name: Office of Competition and Consumer Protection, Poland Date: December 16, 2008 Tying & Bundled Discounting
 Agency Name: Office of Competition and Consumer Protection, Poland Date: December 16, 2008 Tying & Bundled Discounting This part of the questionnaire seeks information on ICN members analysis and treatment
Agency Name: Office of Competition and Consumer Protection, Poland Date: December 16, 2008 Tying & Bundled Discounting This part of the questionnaire seeks information on ICN members analysis and treatment
Competitive Neutrality Project UNCTAD RPP Meeting July Project leader: Deborah Healey
 Competitive Neutrality Project UNCTAD RPP Meeting July 7 2013 Project leader: Deborah Healey The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of UNCTAD What is competitive
Competitive Neutrality Project UNCTAD RPP Meeting July 7 2013 Project leader: Deborah Healey The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of UNCTAD What is competitive
Audit Law of the People's Republic of China. (Adopted at the Ninth Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National
 Audit Law of the People's Republic of China (Adopted at the Ninth Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on August 31, l994 and amended in accordance with the Decision
Audit Law of the People's Republic of China (Adopted at the Ninth Meeting of the Standing Committee of the Eighth National People's Congress on August 31, l994 and amended in accordance with the Decision
US-China Business Council Comments on Antimonopoly Law Amendment Questionnaire
 US-China Business Council Comments on Antimonopoly Law Amendment Questionnaire The US-China Business Council (USCBC) and its member companies appreciate the opportunity to participate in the consultation
US-China Business Council Comments on Antimonopoly Law Amendment Questionnaire The US-China Business Council (USCBC) and its member companies appreciate the opportunity to participate in the consultation
The legislation and enforcement of collective dominance in China s Antimonopoly
 The legislation and enforcement of collective dominance in China s Antimonopoly Law Professor Huang Yong University of International Business and Economics Competition law center(uibeclc) 2013.10 Kun Ming
The legislation and enforcement of collective dominance in China s Antimonopoly Law Professor Huang Yong University of International Business and Economics Competition law center(uibeclc) 2013.10 Kun Ming
Exploring the World of Business and Economics
 Chapter 1 Exploring the World of Business and Economics 1 Discuss what you must do to be successful in the world of business. 2 Define business and identify potential risks and rewards. 3 Define economics
Chapter 1 Exploring the World of Business and Economics 1 Discuss what you must do to be successful in the world of business. 2 Define business and identify potential risks and rewards. 3 Define economics
Merger Review in the United States and the European Union. Jeffrey I. Shinder Constantine & Partners
 Merger Review in the United States and the European Union Jeffrey I. Shinder Constantine & Partners What is Antitrust? Fairness Law Protect smaller firms from larger firms Disperse business power Distribute
Merger Review in the United States and the European Union Jeffrey I. Shinder Constantine & Partners What is Antitrust? Fairness Law Protect smaller firms from larger firms Disperse business power Distribute
1.5 Nov 98 a. Explain the term natural monopolies and why are they considered a danger if left unregulated. [10] b. (not in 2013 syllabus)
![1.5 Nov 98 a. Explain the term natural monopolies and why are they considered a danger if left unregulated. [10] b. (not in 2013 syllabus) 1.5 Nov 98 a. Explain the term natural monopolies and why are they considered a danger if left unregulated. [10] b. (not in 2013 syllabus)](/thumbs/72/66862943.jpg) Higher Level Essays Microeconomics only 1.5 (old syllabus specimen) a. Explain the main features of an oligopolistic market. [10] b. Discuss whether oligopolies work in favor of, or against the interest
Higher Level Essays Microeconomics only 1.5 (old syllabus specimen) a. Explain the main features of an oligopolistic market. [10] b. Discuss whether oligopolies work in favor of, or against the interest
Definition - Markets and Dominance Control
 1 Definition - Markets and Dominance Control 2 Markets and dominance DEFINITION: MARKET: A medium that allows buyers and sellers of a specific good or service to interact in order to facilitate an exchange.
1 Definition - Markets and Dominance Control 2 Markets and dominance DEFINITION: MARKET: A medium that allows buyers and sellers of a specific good or service to interact in order to facilitate an exchange.
ABUSE OF DOMINANCE. John Pheasant Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014
 ABUSE OF DOMINANCE Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014 2 The Competition Laws Cartels Abuse of dominance Control of mergers 3 Competition Policy Goals The Protection of: Competitive
ABUSE OF DOMINANCE Lecture to National Law University, Jodhpur 24 January 2014 2 The Competition Laws Cartels Abuse of dominance Control of mergers 3 Competition Policy Goals The Protection of: Competitive
English - Or. English DIRECTORATE FOR FINANCIAL AND ENTERPRISE AFFAIRS COMPETITION COMMITTEE
 Unclassified DAF/COMP/WD(2014)97 DAF/COMP/WD(2014)97 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 08-Dec-2014 English
Unclassified DAF/COMP/WD(2014)97 DAF/COMP/WD(2014)97 Unclassified Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 08-Dec-2014 English
Salt Lake Community College Policies and Procedures
 COLLEGE PROCUREMENT POLICY Board of Trustees Approval: 04/12/2017 POLICY 10.01 Page 1 of 1 I. POLICY All products and services purchased by the College shall be procured in compliance with applicable statutes,
COLLEGE PROCUREMENT POLICY Board of Trustees Approval: 04/12/2017 POLICY 10.01 Page 1 of 1 I. POLICY All products and services purchased by the College shall be procured in compliance with applicable statutes,
The Anti-monopoly Commission of the State Council. Anti-monopoly Guideline on Abuse of Intellectual Property Rights.
 The Anti-monopoly Commission of the State Council Anti-monopoly Guideline on Abuse of Intellectual Property Rights (Exposure Draft) (December 31, 2015) Preamble Anti-monopoly and intellectual property
The Anti-monopoly Commission of the State Council Anti-monopoly Guideline on Abuse of Intellectual Property Rights (Exposure Draft) (December 31, 2015) Preamble Anti-monopoly and intellectual property
2011 APEC ECONOMIC POLICY R EPORT 69. Indonesia
 2011 APEC ECONOMIC POLICY R EPORT 69 Indonesia 1. In which areas of structural reforms have the most significant progress been made in your economy in the past five years? Please describe in what way you
2011 APEC ECONOMIC POLICY R EPORT 69 Indonesia 1. In which areas of structural reforms have the most significant progress been made in your economy in the past five years? Please describe in what way you
Pubic Monopolies, Concessions and Competition Law and Policies
 Intergovernmental Group of Experts on Competition Law and Policy Geneva, 7-9 July 2009 Pubic Monopolies, Concessions and Competition Law and Policies By European Communities The views expressed are those
Intergovernmental Group of Experts on Competition Law and Policy Geneva, 7-9 July 2009 Pubic Monopolies, Concessions and Competition Law and Policies By European Communities The views expressed are those
Micro Economics Review
 Micro Economics Review 1. Intro to Economics a. What is Economics? i. Scarcity and the factors of production 1. Explain why scarcity and choice are basic problems of economics 2. Identify the factors of
Micro Economics Review 1. Intro to Economics a. What is Economics? i. Scarcity and the factors of production 1. Explain why scarcity and choice are basic problems of economics 2. Identify the factors of
Introduction to Agricultural Economics Agricultural Economics 105 Spring 2012 Second Hour Exam Version 1
 Name Introduction to Agricultural Economics Agricultural Economics 105 Spring 2012 Second Hour Exam Version 1 There is only ONE correct answer per multiple choice question. Please put your answer on the
Name Introduction to Agricultural Economics Agricultural Economics 105 Spring 2012 Second Hour Exam Version 1 There is only ONE correct answer per multiple choice question. Please put your answer on the
Chapter One (cont ) Economics is defined as: The science that studies the choices people make in a world of scarcity
 Economics Review Chapter One Wants exceed resources to fill wants Therefore scarcity exists Therefore we must make choices Every time we make a choice, we leave behind an opportunity cost, the most likely
Economics Review Chapter One Wants exceed resources to fill wants Therefore scarcity exists Therefore we must make choices Every time we make a choice, we leave behind an opportunity cost, the most likely
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name
 CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
Critical Success Factors of Collaboration for Public Service
 Critical Success Factors of Collaboration for Public Service Different factors affect the performance of these collaboration projects. These factors are related either to the project's macro, meso or micro
Critical Success Factors of Collaboration for Public Service Different factors affect the performance of these collaboration projects. These factors are related either to the project's macro, meso or micro
Unit 3: Business Environment
 Unit 3: Business Environment Name: Date: / / Meaning The term business environment means the sum total of all individuals, institutions and other forces that are outside the control of a business enterprise
Unit 3: Business Environment Name: Date: / / Meaning The term business environment means the sum total of all individuals, institutions and other forces that are outside the control of a business enterprise
Republic of Bulgaria NATIONAL ANTI-CORRUPTION STRATEGY
 Republic of Bulgaria NATIONAL ANTI-CORRUPTION STRATEGY In the last years corruption has become a global threat not only for the economic development of the countries themselves and their international
Republic of Bulgaria NATIONAL ANTI-CORRUPTION STRATEGY In the last years corruption has become a global threat not only for the economic development of the countries themselves and their international
The Role of Planning in China's Market Economy
 Journal of Chinese Economic and Business Studies ISSN: 1476-5284 (Print) 1476-5292 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/rcea20 The Role of Planning in China's Market Economy Gregory
Journal of Chinese Economic and Business Studies ISSN: 1476-5284 (Print) 1476-5292 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/rcea20 The Role of Planning in China's Market Economy Gregory
SUNRISE TELECOM CODE OF BUSINESS CONDUCT AND ETHICS Overview Sunrise Telecom is committed to its customers, partners, employees and stockholders.
 SUNRISE TELECOM CODE OF BUSINESS CONDUCT AND ETHICS Overview Sunrise Telecom is committed to its customers, partners, employees and stockholders. Accordingly, we believe that operating with integrity is
SUNRISE TELECOM CODE OF BUSINESS CONDUCT AND ETHICS Overview Sunrise Telecom is committed to its customers, partners, employees and stockholders. Accordingly, we believe that operating with integrity is
CHAPTER 3. Economic system Market structure Consumer price index
 CHAPTER 3 Economic system Market structure Consumer price index ECONOMIC SYSTEM Definition: Institutions, laws, technology, tradition, ideas and attitude that mobilizing production, managing resources
CHAPTER 3 Economic system Market structure Consumer price index ECONOMIC SYSTEM Definition: Institutions, laws, technology, tradition, ideas and attitude that mobilizing production, managing resources
12) What determines the distribution of goods and services in a market economy?
 The Principles of Economics: EOCT Review 1) What is scarcity? How is scarcity different from shortages? 2) What are the three factors of production: 3) Define "labor" and give an example: 4) Define "land"
The Principles of Economics: EOCT Review 1) What is scarcity? How is scarcity different from shortages? 2) What are the three factors of production: 3) Define "labor" and give an example: 4) Define "land"
Florence October 29 November 2, 2014 LABOUR LAW COMMISSION OUTSOURCING, SUBCONTRACTING AND STAFF LEASING
 58 th UIA CONGRESS Florence October 29 November 2, 2014 LABOUR LAW COMMISSION Saturday, 1 November 2014 OUTSOURCING, SUBCONTRACTING AND STAFF LEASING Hervé Duval - KGA Avocats 44, avenue des Champs-Elysées
58 th UIA CONGRESS Florence October 29 November 2, 2014 LABOUR LAW COMMISSION Saturday, 1 November 2014 OUTSOURCING, SUBCONTRACTING AND STAFF LEASING Hervé Duval - KGA Avocats 44, avenue des Champs-Elysées
WORKSHOP ON COMMUNICATIONS REGULATION IN SOMALIA
 WORKSHOP ON COMMUNICATIONS REGULATION IN SOMALIA World Bank Group Offices, Nairobi Presenter: Dr. Monica Kerretts-Makau Policy & Regulatory Consultant WBG June 2015 POLICY AND REGULATION 2 Policy and regulatory
WORKSHOP ON COMMUNICATIONS REGULATION IN SOMALIA World Bank Group Offices, Nairobi Presenter: Dr. Monica Kerretts-Makau Policy & Regulatory Consultant WBG June 2015 POLICY AND REGULATION 2 Policy and regulatory
A Look into New Texas Conduct and Disclosure Requirements
 A Look into New Texas Conduct and Disclosure Requirements Introduction By Claudia Russell Transparency and ethics reform were very popular terms used by many during the 84 th Texas Legislature. In fact,
A Look into New Texas Conduct and Disclosure Requirements Introduction By Claudia Russell Transparency and ethics reform were very popular terms used by many during the 84 th Texas Legislature. In fact,
China s Administrative Reforms in the Economic Transition
 256 ASIAN REVIEW OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION China s Administrative Reforms in the Economic Transition WANG TONGXUN, Institute of Personnel and Talents Science People s Republic of China China s Administrative
256 ASIAN REVIEW OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION China s Administrative Reforms in the Economic Transition WANG TONGXUN, Institute of Personnel and Talents Science People s Republic of China China s Administrative
Class No. 14 (file 11): Regulation in
 Regulation Policy and Economics of Regulation Class No. 14 (file 11): Regulation in Transportation Industry Objectives of Today s Class (1)T To understand dthe theory behind dthe regulation in the taxi
Regulation Policy and Economics of Regulation Class No. 14 (file 11): Regulation in Transportation Industry Objectives of Today s Class (1)T To understand dthe theory behind dthe regulation in the taxi
This document has been provided by the International Center for Not-for-Profit Law (ICNL).
 This document has been provided by the International Center for Not-for-Profit Law (ICNL). ICNL is the leading source for information on the legal environment for civil society and public participation.
This document has been provided by the International Center for Not-for-Profit Law (ICNL). ICNL is the leading source for information on the legal environment for civil society and public participation.
Government and Industry: Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and Philip Young
 Chapter 15 Government and Industry: Challenges and Opportunities for Today's Managers Managerial Economics: Economic Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and
Chapter 15 Government and Industry: Challenges and Opportunities for Today's Managers Managerial Economics: Economic Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today s Decision Makers, 4/e By Paul Keat and
The Promulgation of the Law of the People's Republic of China. against Unfair Competition (Revised Draft for Review) and the
 The Promulgation of the Law of the People's Republic of China against Unfair Competition (Revised Draft for Review) and the Substantial Modification of the Commercial Bribery Related Terms I. Background
The Promulgation of the Law of the People's Republic of China against Unfair Competition (Revised Draft for Review) and the Substantial Modification of the Commercial Bribery Related Terms I. Background
Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems
 Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems 1. Why is there a need for an aggregate demand and aggregate supply model of the economy? Why can t the supply and demand model for a single product
Chapter 26 Answers to Short-Answer, Essays, and Problems 1. Why is there a need for an aggregate demand and aggregate supply model of the economy? Why can t the supply and demand model for a single product
Research Agenda for Competition Policy and Market Reforms
 Research Agenda for Competition Policy and Market Reforms Arvind Panagariya Columbia University New York NY 10027 NCAER Conference on Competition Policy, November 24, 2009 Definition Traded Goods Traded
Research Agenda for Competition Policy and Market Reforms Arvind Panagariya Columbia University New York NY 10027 NCAER Conference on Competition Policy, November 24, 2009 Definition Traded Goods Traded
What is an Effective and Independent Regulator: General Overview (1)
 What is an Effective and Independent Regulator: Daniel Leza Presented at the ITU Seminar on Establishing New Regulators in the Asian Pacific Region October 26-27, 2007 Vientiane, LAO P.D.R. ENSURING TELECOMMUNICATIONS
What is an Effective and Independent Regulator: Daniel Leza Presented at the ITU Seminar on Establishing New Regulators in the Asian Pacific Region October 26-27, 2007 Vientiane, LAO P.D.R. ENSURING TELECOMMUNICATIONS
Economics. East Poinsett County School District
 Economics East Poinsett County School District Economics: Third Quarter Strand: Economic Fundamentals Content Standard 1: Students shall examine scarcity and choice. EF.1.E.1 Explain the role scarcity
Economics East Poinsett County School District Economics: Third Quarter Strand: Economic Fundamentals Content Standard 1: Students shall examine scarcity and choice. EF.1.E.1 Explain the role scarcity
Executive Summary and Summary of Recommendations from RICA
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Executive Summary and Summary of Recommendations from RICA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Government
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Executive Summary and Summary of Recommendations from RICA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Government
