Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS
|
|
|
- Harry Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical grassland) desert chaparral temperate grassland temperate deciduous forest coniferous forest (taiga) tundra alpine ( high mountains and polar ice )
2 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 37 COMMUNITIES AND ECOSYSTEMS 1. ecological niche: fundamental niche vs. realized niche competition 2. energy pyramid, trophic levels, food chains, food webs 3. producers, herbivores, carnivores, consumers, decomposers 4. 10% rule 5. energy flows and matter cycles 6. cycles in the environment: energy carbon phosphorus nitrogen water 7. species diversity 8. succession: primary succession vs. secondary succession lake succession pioneer species vs. climax community
3 Honors Biology Chapter 34 Word Roots THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS a- = without; bio- = life (abiotic factor: the non-living chemical and physical components of an ecosystem) -photo = light (aphotic zone: the region of an aquatic ecosystem beneath the photic zone, where light does not penetrate sufficiently for photosynthesis to occur) bio- = life (biome: a defined area of ecologically similar communities of organisms; biosphere: the part of the Earth inhabited by life; biotic factor: a living component of an ecosystem) bentho- = the depths of the sea (benthic realm: a seafloor, or the bottom of a freshwater lake, pond, river, or stream) estuar- = the sea (estuary: the area where a freshwater stream or river merges with the ocean) inter- = between (intertidal zone: the shallow zone of the ocean where land meets water) pelag- = the sea (pelagic realm: all of the open-water areas of an ocean, excluding the intertidal zone) perman- = remaining (permafrost: a permanently frozen stratum below the arctic tundra) -photo = light (photic zone: the region of an aquatic ecosystem where light penetrates and photosynthesis occurs) phyto- = a plant (phytoplankton: algae and photosynthetic bacteria that drift passively in aquatic environments) zoo- = animal (zooplankton: animals [heterotrophs] that drift freely in aquatic environments)
4 Honors Biology Chapter 37 Word Roots COMMUNITIES AND ECOSYSTEMS a- = without; bio- = life (abiotic reservoir: a part of an ecosystem where a chemical, such as carbon or nitrogen, accumulates or is stockpiled outside of living organisms) geo- = Earth (biogeochemical cycle: any of the various chemical circuits that involve both biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem) de- = from, down, out (decomposer: prokaryotes and fungi that secrete enzymes that digest organic material and break it down into inorganic forms) detrit- = wear off (detritus: dead organic matter); -vora = eat (detritivore: an organism that consumes organic wastes and dead organisms) herb- = grass; -vora = eat (herbivory: the consumption of plant material by an animal) quatr- = four (quaternary consumer: an organism that eats tertiary consumers; the fourth step on the food chain) terti- = three (tertiary consumer: an organism that eats secondary consumers; the third step on the food chain)
5 PROPERTY OF: HONORS BIOLOGY UNIT 5 CHAPTERS 34 & 37 NOTES THE BIOSPHERE & ECOSYSTEMS Terrestrial Ecosystems - temperate = mild temperatures, different seasons - tropical = hot, long summers; near the equator - deciduous = trees that lose their leaves in the fall - coniferous = trees that do not lose their leaves in the fall (evergreen) - TROPICAL RAIN FOREST climate: hot and rainy precipitation: 100 inches per year location: South America, Africa, India - SAVANNAH (TROPICAL GRASSLAND) climate: hot, alternating wet/dry seasons precipitation: inches per year location: South America, Africa - DESERT climate: very dry and hot precipitation: 8 inches per year location: Africa, Asia, southwestern US, Australia, Middle East - TEMPERATE GRASSLAND climate: dry, hot summers and cold winters precipitation: 5-25 inches per year location: midwestern US, Russia, Europe, Australia - CHAPARRAL climate: dry, hot summers and mild winters precipitation: inches per year location: coastal areas near the Mediterranean Sea, California, South Africa - TEMPERATE DECIDUOUS FOREST climate: warm summers and cold winters precipitation: inches per year location: Europe, US east of the Mississippi River - CONIFEROUS FOREST (TAIGA) climate: long, cold winters and short, cool summers precipitation: inches per year location: Canada, northern Europe, Russia - TUNDRA climate: long, cold winters and short, cool summers precipitation: 10 inches per year location: northern Canada, Siberia - ALPINE climate: long, cold winters and short, cool summers precipitation: inches per year location: North/South Poles, mountain tops
6 Aquatic Biomes - photic zone = contains light (upper layers) - aphotic zone = does not contain light (lower layers) - little temperature variation (unlike land biomes) - categorized by light intensity, oxygen and carbon dioxide availability, and nutrient availability Niche - niche = an organism s role in the environment - niche can include: climate, when it feeds, when it mates, diet, sleep pattern, etc. - fundamental niche = the theoretical niche in which the organism has access to everything it needs - realized niche = the actual niche based on the fact that certain resources may not be available (due to competition) - no two organisms can occupy the same realized niche - competition occurs when two organisms try to occupy the same niche Energy in the Environment - energy pyramid: producer à herbivore à primary carnivore à secondary carnivore à tertiary carnivore -- OR -- producers à 1 consumer à 2 consumer à 3 consumer à 4 (quaternary) consumer - bottom of pyramid: most amount of energy, greater # of organisms - top of pyramid: least amount of energy, least # of organisms - sun = original source of energy for any food chain - producer = organism that produces its own food (autotroph) - consumer = organism that cannot produce its own food (heterotroph) - decomposers = organisms that break down dead material, feed at every trophic level (except plants) - trophic level = each level on the pyramid or food chain - top carnivores are often (but not always) larger and produce fewer offspring - there are usually fewer organisms as you move up the food chain Ten Percent Rule - 10% rule = at least 90% of the energy is lost moving up each trophic level - as you move up the pyramid, there is less energy available - energy is lost due to daily functions (EX: cellular respiration, feces, heat energy) - EX: 1 à 2 the energy goes from 1 to 2 #2 consumes #1 - EX: chicken feed à chicken à Carlos à Lion à Jenny 4000 cal 400 cal 40 cal 4 cal 0.4 cal - Why are food chains usually limited to 4 or 5 trophic levels?
7 Succession - a regular pattern of changes over time of the species in an ecosystem - pioneer species: the first species to colonize an area - climax community: the final, stable community in an ecosystem - Succession starts with bare land. - Primary succession starts with bare land and rock (no soil). - Secondary succession starts after a forest experiences a disruption, such as a forest fire. Soil is already present. - Lake succession starts with a lake that dries up, fills with soil, and becomes flat land. Hypothetical Example of Succession EX: A forest burns down. 1 month = weeds, insects, rats 1 year = grass, insects, large rodents 5 years = shrubs, saplings, small birds, rabbits, squirrels 20 years = small trees, squirrels, deer, hawk 200 years = large forest, bears, fox, all trophic levels (complete food chain) Pioneer Species - small animals - mate earlier in life - more offspring - less stable (cannot easily adapt to changes) - missing some trophic levels (top levels of food chain are absent) Climax Community - larger animals - mates later in life - less offspring - more stable (can easily adapt to changes) - contains all trophic levels (from producers to top carnivores)
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ecosystems. 6.L.2.2 Explain how plants respond to external stimuli (including dormancy and forms of tropism) to enhance survival in an environment.
 Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive?
 Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
Biology Chapter Two. Principles of Ecology
 Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Ecology Review. Name: Date: Period:
 Ecology Review Name: Date: Period: 1. Define the terms ecology and ecosystem. Ecology - The study of the interactions among organisms and their environment Ecosystem - collection of all the organisms that
Ecology Review Name: Date: Period: 1. Define the terms ecology and ecosystem. Ecology - The study of the interactions among organisms and their environment Ecosystem - collection of all the organisms that
What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae
 What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae What is an autotroph? A producer/ plant or plant relative that can make its own food How do producers make their own food? photosynthesis What is
What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae What is an autotroph? A producer/ plant or plant relative that can make its own food How do producers make their own food? photosynthesis What is
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecosystems on land are grouped into biomes primarily based on the plant communities within them.
 Section 2: Ecosystems on land are grouped into biomes primarily based on the plant communities within them. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How is latitude
Section 2: Ecosystems on land are grouped into biomes primarily based on the plant communities within them. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How is latitude
1. Global Climate. Latitude and Sunlight Intensity 12/4/2014. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere. 1.
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
8/7/18. UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
What is Ecology? Includes land, air, and water as well as life. Living organisms are NOT distributed uniformly throughout the biosphere.
 Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology: Chapters Worksheet
 Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
The Law of Conservation of Matter. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away
 Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Ecosystems. Trophic relationships determine the routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems.
 AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
Chapter 21. Table of Contents. Objectives. Earth s Major Biomes. The Major Biomes. Tundra. Tundra. Identify the eight major biomes.
 Ecosystems Table of Contents Objectives Identify the eight major biomes. Compare tundra with taiga. Compare the different kinds of forests. Compare the different kinds of grasslands. Describe the adaptations
Ecosystems Table of Contents Objectives Identify the eight major biomes. Compare tundra with taiga. Compare the different kinds of forests. Compare the different kinds of grasslands. Describe the adaptations
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline
 Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Chapter 4. Ecosystems and Communities
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities I. The Role of Climate 4-1 A. Weather = Day to day conditions of Earth s atmosphere in a particular place and time B. Climate = Average year after year conditions of
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities I. The Role of Climate 4-1 A. Weather = Day to day conditions of Earth s atmosphere in a particular place and time B. Climate = Average year after year conditions of
Warm Up. What process do plants use to make sugar? What is chemosynthesis? What is transpiration?
 Warm Up What process do plants use to make sugar? What is chemosynthesis? What is transpiration? Check your answers: What process do plants use to make sugar? photosynthesis What is chemosynthesis? Organisms
Warm Up What process do plants use to make sugar? What is chemosynthesis? What is transpiration? Check your answers: What process do plants use to make sugar? photosynthesis What is chemosynthesis? Organisms
A Food Web. Basic Concepts. Master 1. Use with Chapter 2, Section 2.2. Second-order. heterotrophs. heterotrophs. First-order. Autotrophs.
 Master 1 A Food Web Rabbits Grass Mountain lions Snakes Mice Seed-eating birds Shrubs Hawks Second-order heterotrophs Deer First-order heterotrophs Autotrophs Trees Decomposers BASIC CONCEPTS TRANSPARENCY
Master 1 A Food Web Rabbits Grass Mountain lions Snakes Mice Seed-eating birds Shrubs Hawks Second-order heterotrophs Deer First-order heterotrophs Autotrophs Trees Decomposers BASIC CONCEPTS TRANSPARENCY
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Mid-Unit Practice Review for Assessment
 Mid-Unit Practice Review for Assessment Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. Mountains are
Mid-Unit Practice Review for Assessment Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. Mountains are
6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment.
 Ecosystems 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from the
Ecosystems 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from the
Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter
 Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment
 Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment This includes both biotic and abiotic factors- biotic factors are living
Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment This includes both biotic and abiotic factors- biotic factors are living
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY. Interspecific Interactions. Ecosystems unit
 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
Ch. 4 Ecosystems. Biology I Loulousis
 Ch. 4 Ecosystems Biology I Loulousis Objectives 1.) Define ecology, ecosystem, and succession 2.) Identify and distinguish between the levels of organization in ecology 3.)Distinguish between primary and
Ch. 4 Ecosystems Biology I Loulousis Objectives 1.) Define ecology, ecosystem, and succession 2.) Identify and distinguish between the levels of organization in ecology 3.)Distinguish between primary and
Ecosystems. Chapter 55. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 55 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 55 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Chapter 4. Ecosystems
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Monday, May 16, 16
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Populations, Communities, and Ecosystems Ø Members of a species interact in groups called populations. Ø Populations of different species living and interacting in an area form
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Populations, Communities, and Ecosystems Ø Members of a species interact in groups called populations. Ø Populations of different species living and interacting in an area form
Ecology. Climate. Global Climate. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Studying organisms in their environment
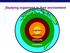 Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
Ecology. Study of interactions between organisms and their environment
 ECOLOGY UNIT Ecology Study of interactions between organisms and their environment Bio means Biotic Factors Bio means life Biotic Factors Biotic Factors Bio means life Biotic factors: Biotic Factors Bio
ECOLOGY UNIT Ecology Study of interactions between organisms and their environment Bio means Biotic Factors Bio means life Biotic Factors Biotic Factors Bio means life Biotic factors: Biotic Factors Bio
Ecological Levels of Organization
 This occurs when soil is permanently frozen These biomes have very little precipitation We live in this biome example This consists of all living and nonliving factors This consists of all populations
This occurs when soil is permanently frozen These biomes have very little precipitation We live in this biome example This consists of all living and nonliving factors This consists of all populations
Climates and Ecosystems
 Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Energy. Raw materials to make building blocks of life. From sun or chemicals. From food
 Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District
 Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Ecosystems & Biomes 1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems What are energy roles in ecosystems? What are energy roles in ecosystems? Producers An organism that can make its own food = AUTOTROPHS! Source of all the
Ecosystems & Biomes 1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems What are energy roles in ecosystems? What are energy roles in ecosystems? Producers An organism that can make its own food = AUTOTROPHS! Source of all the
Part IV Living World
 Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Ecosystem Ecology: Part 1. September 22, 2014 Mr. Alvarez
 Ecosystem Ecology: Part 1 September 22, 2014 Mr. Alvarez Ecosystems Ecosystem- a particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting biotic and abiotic components. Forest Ecosystem
Ecosystem Ecology: Part 1 September 22, 2014 Mr. Alvarez Ecosystems Ecosystem- a particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting biotic and abiotic components. Forest Ecosystem
ECOLOGY. Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements
 ECOLOGY Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements Living Non-Living Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors Circle of Life (clip from Lion King) Ecology the study of the relationships
ECOLOGY Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements Living Non-Living Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors Circle of Life (clip from Lion King) Ecology the study of the relationships
What determines a terrestrial. biome?
 BIOMES What determines a terrestrial Climate Temperature Precipitation Similarly adapted plants & animals Can vary depending on external forces- human disturbance Fire important to many Controls tree
BIOMES What determines a terrestrial Climate Temperature Precipitation Similarly adapted plants & animals Can vary depending on external forces- human disturbance Fire important to many Controls tree
CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1
 CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1 15.1 BIOSPHERE Part of Earth where life exists All of Earth s ecosystems Biota all living things in biosphere Abiotic factors NOT included Ex: water, air, rocks 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS
CH. 15 THE BIOSPHERE 1 15.1 BIOSPHERE Part of Earth where life exists All of Earth s ecosystems Biota all living things in biosphere Abiotic factors NOT included Ex: water, air, rocks 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Chapter 34. The Biosphere: An introduction to Earth s Diverse Environments
 Chapter 34 The Biosphere: An introduction to Earth s Diverse Environments PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009
Chapter 34 The Biosphere: An introduction to Earth s Diverse Environments PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009
What is Ecology? QGdH3QU
 Ecology What is Ecology? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgr- QGdH3QU Ecology The study of the interactions of different organisms (living things) between each other and with their environment (surroundings).
Ecology What is Ecology? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgr- QGdH3QU Ecology The study of the interactions of different organisms (living things) between each other and with their environment (surroundings).
Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided.
 Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Part A: Multiple Choice. (60%) Name: Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided. 1. Which describes a system that meets the needs of both present
Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Part A: Multiple Choice. (60%) Name: Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided. 1. Which describes a system that meets the needs of both present
Intro to Ecology. Chapter 18
 Intro to Ecology Chapter 18 Interdependence: A Key Theme in Ecology Ecology- study of the interactions of living organisms w/ one another and w/ their physical environment (soil, water,weather) Interdependence:
Intro to Ecology Chapter 18 Interdependence: A Key Theme in Ecology Ecology- study of the interactions of living organisms w/ one another and w/ their physical environment (soil, water,weather) Interdependence:
Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems
 Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems Part I Ecology Ecology Vocabulary Pioneer Organisms Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Succession Biotic Food web Autotroph Biomass
Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems Part I Ecology Ecology Vocabulary Pioneer Organisms Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Succession Biotic Food web Autotroph Biomass
Unit 3 - Ecology. Section 3 - Canada s Biomes and Climate Change. Watch: An Introduction to Biomes. Unit 3 - Ecology 1 / 19
 Unit 3 - Ecology Section 3 - Canada s Biomes and Climate Change Watch: An Introduction to Biomes Unit 3 - Ecology 1 / 19 Ecosystems can be grouped into larger categories called biomes. A biome is a collection
Unit 3 - Ecology Section 3 - Canada s Biomes and Climate Change Watch: An Introduction to Biomes Unit 3 - Ecology 1 / 19 Ecosystems can be grouped into larger categories called biomes. A biome is a collection
Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities
 Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities Section 4.1 The Role of Climate In Earth s atmosphere, temperature, precipitation, and other environmental factors combine to produce weather and climate. Weather is
Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities Section 4.1 The Role of Climate In Earth s atmosphere, temperature, precipitation, and other environmental factors combine to produce weather and climate. Weather is
COMMUNITIES & ECOSYSTEMS. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 COMMUNITIES & ECOSYSTEMS Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted COMMUNITIES & ECOSYSTEMS Ecosystem = groups of organisms living together
COMMUNITIES & ECOSYSTEMS Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted COMMUNITIES & ECOSYSTEMS Ecosystem = groups of organisms living together
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones
 3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
4/21/2013. Ecology. Ecology and the biosphere. Environments vary across the planet. Predictable air circulation patterns. Incidence of sunlight varies
 Ecology The study of the interactions of organisms with each other and with the environment Ecologists work at all levels of biology from molecules to biosphere Ecology and the biosphere Chapter 52 Environments
Ecology The study of the interactions of organisms with each other and with the environment Ecologists work at all levels of biology from molecules to biosphere Ecology and the biosphere Chapter 52 Environments
Studying organisms in their environment
 Ecosystems (Ch. 3) Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How does energy move through the
Ecosystems (Ch. 3) Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How does energy move through the
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 11 Living Systems
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem:
 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem: The vast majority of life on Earth depends on sunlight as its source of energy. Of all the radiant energy that reaches the earth, some of it penetrates the earth's atmosphere
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem: The vast majority of life on Earth depends on sunlight as its source of energy. Of all the radiant energy that reaches the earth, some of it penetrates the earth's atmosphere
9/23/2015 Question 1 Review Chapter 15 What biome do you live in? Biomes Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes.
 Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish Describe Sequence Interactions of Organisms and Their Environment Ecology Habitat
 Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Theme 7 Review: Ecology
 Theme 7 Review: Ecology 7.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 7.2: All biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities and ecosystems are affected by complex
Theme 7 Review: Ecology 7.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 7.2: All biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities and ecosystems are affected by complex
Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
BIOLOGY NOTES. Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment
 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 1: ECOLOGY SUBTOPIC : 12.1 Introduction to ecology. LEARNING OUTCOMES: Define basic terminologies in ecology. - niche, habitat, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere..
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 1: ECOLOGY SUBTOPIC : 12.1 Introduction to ecology. LEARNING OUTCOMES: Define basic terminologies in ecology. - niche, habitat, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere..
AP Biology. Ecosystems
 Ecosystems Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
Ecosystems Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
The Biosphere. GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
HU-205: Geography. Geography 04: Biogeochemical Cycles & Biosphere. Biomes. Global patterns in the biosphere
 HU-205: Geography Geography 04: Biogeochemical Cycles & Biosphere Biomes Global patterns in the biosphere Plant and animal types Similar distributions Soil Vegetation Climate Human impacts Population growth
HU-205: Geography Geography 04: Biogeochemical Cycles & Biosphere Biomes Global patterns in the biosphere Plant and animal types Similar distributions Soil Vegetation Climate Human impacts Population growth
Chapter 59 ~ The Biosphere How biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem
 I am the Lorax. I speak for the trees. I speak for the trees, for the trees have no tongues. Chapter 59 ~ The Biosphere How biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem QOD What strategies do different
I am the Lorax. I speak for the trees. I speak for the trees, for the trees have no tongues. Chapter 59 ~ The Biosphere How biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem QOD What strategies do different
Producers. living systems need energy to function. autotrophs. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
 Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
The Biosphere Chapter 3. What Is Ecology? Section 3-1
 The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
Slide 1 / All of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a. Population Community Biome Biosphere
 Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52 An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 52 An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
15.1. The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. The Biosphere CHAPTER 15 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 15.1 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. VOCABULARY biosphere hydrosphere geosphere biota atmosphere The biosphere is the
SECTION 15.1 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. VOCABULARY biosphere hydrosphere geosphere biota atmosphere The biosphere is the
Human Biology 100A Biome Images
 Human Biology 100A Biome Images Coastal Zone Kelp Forest (temperate latitudes) Instructor: Mark Eberle Oregon Coast Aquarium, Newport, Oregon (photographs by Megan Rohweder) Coral Reef (tropical latitudes)
Human Biology 100A Biome Images Coastal Zone Kelp Forest (temperate latitudes) Instructor: Mark Eberle Oregon Coast Aquarium, Newport, Oregon (photographs by Megan Rohweder) Coral Reef (tropical latitudes)
4/13/2015. The Biosphere
 The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships. KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment.
 13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. 13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships Ecologists study environments at different
13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. 13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships Ecologists study environments at different
This presentation was developed for a middle school/junior high science class. Through use of this presentation and their science book, students will
 This presentation was developed for a middle school/junior high science class. Through use of this presentation and their science book, students will be able to identify and name important characteristics
This presentation was developed for a middle school/junior high science class. Through use of this presentation and their science book, students will be able to identify and name important characteristics
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
What is an ecosystem?
 1 What is an ecosystem? System = regularly interacting and interdependent components forming a unified whole Ecosystem = an ecological system; = a community and its physical environment treated together
1 What is an ecosystem? System = regularly interacting and interdependent components forming a unified whole Ecosystem = an ecological system; = a community and its physical environment treated together
12. How could forest fire change populations in the ecosystem? Populations could be destroyed or have to relocate,
 Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment.
 Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3
 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface Contain about 50% of the world s known plant
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface Contain about 50% of the world s known plant
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
Chp Practice Test
 Name: Chp 3.1-3.3 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT a basic method used by ecologists to study
Name: Chp 3.1-3.3 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT a basic method used by ecologists to study
Ecology: Part 2. Biology Mrs. Bradbury
 Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Ecosystems- Matter and Energy. Ecosystems. Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chain linear flow chart of who eats whom. Ecosystems 9/30/2013
 Ecosystems- Matter and Energy Ecosystems 1 Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chain linear flow chart of who eats whom grass --> zebra --> lion --> vulture Food Webs expanded, more complete Trophic Levels
Ecosystems- Matter and Energy Ecosystems 1 Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chain linear flow chart of who eats whom grass --> zebra --> lion --> vulture Food Webs expanded, more complete Trophic Levels
Ecosystems. Physical Laws Law of Conservation of Energy - Energy can not be created or destroyed, only transformed. Chapter 55: Ecosystems. Fig. 55.
 Chapter 55: Ecosystems 1 Ecosystems consist of the living organisms in a community as well as the abiotic factors Microecosystem Two important considerations: Energy Flow Chemical cycling Fig. 55.1 2 Physical
Chapter 55: Ecosystems 1 Ecosystems consist of the living organisms in a community as well as the abiotic factors Microecosystem Two important considerations: Energy Flow Chemical cycling Fig. 55.1 2 Physical
Biology. Slide 1 of 41. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
Principles of Ecology Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-1)
 Paper No. : 12 Module : 29 Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-I) Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer: Prof. Neeta
Paper No. : 12 Module : 29 Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-I) Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer: Prof. Neeta
