8.0 Radioactive Waste
|
|
|
- Quentin Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8.0 Radioactive Waste 8.1 Solid Radioactive Waste Management Solid radioactive waste is disposed of by land burial at licensed, low-level radioactive waste facilities or by holding short-lived wastes for radioactive decay until their radiation levels are indistinguishable from background, and then disposing of them as ordinary waste. Because the availability of land burial sites is subject to political and technical limitations, and the space available for decaying short-lived wastes is limited, radioisotope users should make every effort to minimize the volume of radioactive wastes generated in their laboratories. All solid radioactive waste is packaged by users and then transferred to DRS personnel for treatment by decay-in-storage or other method of final disposal. As much as possible, wastes must be segregated according to isotopes. It is especially important to segregate dry wastes containing tritium (H-3) and carbon-14 (C-14) from other long-lived isotopes. Solid wastes should be collected, stored, and packaged in containers lined with plastic bags with a thickness of at least four mils of LDPE, clear or transparent yellow in color, and bearing the radiation hazard symbol. The containers must be labeled with the radiation hazard symbol and the words Caution Radioactive Material. Individual bags should be no greater than 30 gallons in volume. Laboratories are responsible for providing their own disposal containers and bags. No freestanding liquids, lead, sharps or animal carcasses/tissue shall be disposed of in solid wastes. If lead cannot be decontaminated, it should be packaged separately for collection. See section 8.3 for handling of radioactive sharps. MIXED WASTE CAUTION: Activities that generate wastes that are classified as both hazardous chemical wastes and radioactive wastes require special handling and incur high disposal costs. Mixed waste generation should be minimized to the extent practical. More information is provided in section 8.7 to follow. It is the responsibility of the laboratory personnel to comply with segregation, collection, packaging, and labeling requirements and to secure all wastes for removal from the laboratory. DRS will not handle any package that does not conform to the requirements of this section or which, in their opinion, may present a safety hazard to waste-handling personnel or members of the public. Containers/packages of waste that are not properly packaged and labeled must be promptly corrected. Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 18
2 Prior to pick-up by DRS, each container must have a completed Radioactive Waste tag attached to it. These tags are available from DRS. Appendix B gives instructions for completing these tags. When waste has been properly prepared, log on to DRS website at: and complete the online pickup request. 8.2 Liquid Scintillation Counting Vials, Glassware, and Plastic Containers Empty liquid scintillation counting vials that contained media with a concentration of C-14 or H-3 less than 0.05 micro-curie per milliliter (μci/ml) need not be decontaminated and should be disposed of with the regular, non-radioactive solid waste. Ensure that vials have been properly emptied and radioactive material labels have been removed or defaced. Used vials may be decontaminated by washing; alternatively, emptying and then discarding into the appropriate radioactive waste container is acceptable. Segregate wastes by radionuclide half-life (<=120 days and >120 days). Most glass items (e.g., test tubes, dishes) can be decontaminated by routine washing or an overnight soaking with an industrial-strength detergent and re-used. 8.3 Radioactive Sharps Radioactive sharps are hazardous items that require special precautions and handling. If the following items have come into contact with radioisotopes, dispose of them in containers specifically designed for sharps that bear a Caution Radioactive Material label listing isotope and date: Needles and syringes, Pasteur pipettes, Scalpels and razor blades, Microscope slides and coverslips, Glassware that cannot be decontaminated. Sharps containers are closable, puncture-resistant, leak-proof on the sides and bottoms, and are typically available in 1-quart, 2-gallon, and 8-gallon sizes. Most glassware, such as liquid scintillation vials and test tubes, is easily decontaminated as described in section 8.2 and should not be routinely discarded as sharps. When sharps containers are full and properly tagged, enter the appropriate information for pickup and disposal on DRS website at Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 19
3 8.4 Liquid Waste There are two main types of liquid radioactive wastes generated by research laboratories. The most common liquid waste is aqueous, in which the waste materials are dissolved in water. Such waste may be disposed of by dispersal into the sewage system if concentration limits are low enough. Designate and label a sink for this purpose. The ph range of any aqueous waste shall be adjusted to between 6.8 and 8.0. Aqueous wastes shall not exceed the following concentrations: Radionuclide Concentration (μci/ml) H-3 1 x 10-2 C-14 3 x 10-4 P-32 9 x 10-5 P-33 8 x 10-4 S-35 1 x 10-3 I x 10-5 I x 10-5 Other radionuclide concentration limits can be found in Title 10, Code of Federal Regulations, Part 20, Appendix B, Table 3. The other, less common form of liquid radioactive waste is composed of volatile, flammable, toxic or organic material that cannot be disposed of through the sewage system. Water insoluble organic solvents shall not be released into the sewage system under any circumstances. (Toluene and xylene-based liquid scintillation cocktails and some HPLC fluids fall into this category. Users are advised to use water-soluble fluids whenever possible). Nonaqueous waste shall be free of all filterable solids. For filtering liquid scintillation waste, a 60- mesh metal screen is recommended. Organic, water-insoluble liquid waste is then collected by DRS personnel for disposal. Non-aqueous waste shall be stored in spill-proof, unbreakable plastic containers of either six or ten liter capacities. Liquid wastes that do not fit into the above categories must be treated on a case-by-case basis. See also Section 8.7 Mixed Wastes CAUTION: Problems involving chemical reactions between mixtures of liquid wastes may occur. Disposing of cyanides in acidic liquid waste will produce hydrogen cyanide, a very toxic gas. Special care must be taken when disposing of tissue that has been digested in nitric acid, as oxides of nitrogen may be formed that could cause the waste container to explode. The PI must ensure that chemical reactions will not occur in liquid waste containers. Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 20
4 Improperly prepared or packaged radioactive waste that during movement or handling will pose an unacceptable hazard to workers, other members of the campus community, or the public must be immediately corrected before pick-up by DRS personnel can occur. Improperly packaged radioactive waste must not be left uncorrected. Prior to pick-up by DRS, each container must have a completed Radioactive Waste tag attached to it. These tags are available from DRS. Appendix B gives instructions for completing these tags. When waste has been properly prepared, logon to DRS website at: and complete the online pickup request. 8.5 Animal Carcasses Radioactive material used in animals must be handled on a case-by-case basis. PIs planning to administer radioactive material to animals should contact DRS for guidance concerning the disposal of carcasses. Animal tissues containing 0.05 µci or less of H-3, C-14, or I-125 per gram of animal tissue averaged over the weight of the entire animal can be disposed of as if it were not radioactive. However, animal tissue in which radioactive materials have been introduced shall not be disposed in a manner that would permit its use either as food for humans or as animal feed, such as rendering. 8.6 Unacceptable Methods of Radioactive Waste Disposal No freestanding liquids, lead, sharps, or animal carcasses/tissue may be disposed of in solid wastes. Under no circumstances shall personnel bury radioactive waste in the soil. Under no circumstances shall non-aqueous radioactive waste be released into the sewage system. Aqueous radioactive liquids in excess of the concentrations specified in Section 8.4 shall not be released into the sewage system. The liquid must either be held for decay or turned into dry waste and packaged appropriately. Carcasses or animal tissues in which radioactive materials have been introduced shall not be disposed of by rendering (a manner that would permit its use either as food for humans or as animal feed). Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 21
5 8.7 Mixed Wastes Mixed wastes are defined as wastes that contain radioactive materials and a hazardous waste. These types of wastes require special handling. Researchers are encouraged to minimize the generation of mixed wastes because of the high disposal costs. For example, radioactive wastes that contain any of the following must be handled as a mixed waste (this list is not exhaustive, be alert for additional hazardous components that may be in your waste): Solvents (e.g., methanol, methylene chloride, acetone) Flammable chemicals Nitrates Sulfides Cyanides Aqueous solutions with ph < 2 or > 12.5* Arsenic Barium Cadmium Chromium Lead Mercury Selenium Silver Endrin Lindane Methoxychlor Toxaphene 2,4-D 2,4,5 TP (Silvex) Benzene *If ph is the only item on this list that makes the item a mixed waste, it can be neutralized and handled as Rad Waste. Carbon Tetrachloride Chlordane Chlorobenzene Chloroform O-Cresol M-Cresol P-Cresol 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 1,1,-Dichloroethylene 2,4-Dinitrotoluene Heptachlor Hexachlorobenzene Hexachlorobutadiene Hexachloroethane Methyl Ethyl Ketone Nitrobenzene PCBs Pentachlorophenol Pyridine Tetrachloroethylene Trichloroethylene 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol Vinyl Chloride If the waste contains I-125, P-32, P-33, S-35, Fe-59, or other short half-life (<90 days) radioisotopes in addition to anything listed above, the waste should be retained by the generator until it is adequately decayed (typically 10 half-lives) so that it no longer qualifies as a regulated radioactive waste. The waste can then be classified as chemical waste and a chemical waste pick-up can be initiated at: Remember to ensure that shielding (as needed) and proper containment is in place in the laboratory during the time the waste is retained in the laboratory while decaying. Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 22
6 If the waste contains C-14 or H-3 isotopes in addition to anything listed above, the following procedures should be followed: 8.8 Radioactive Mixed Waste - Generator Responsibilities 1. Initiate a chemical/mixed waste request at: 2. A copy from the liquid scintillation printout for the particular waste should be submitted to the DRS personnel picking up the waste. A calculation of the isotopic concentration (in μci/ml) and total activity (μci) for the waste is required. If there are multiple wastes, a copy of the printout with calculations should be submitted for each waste. DRS personnel are responsible for the pickup and disposal of mixed wastes from campus laboratories. Appendix A: Responsibilities for Radiation Safety The U of I strives to maintain a safe and healthy working and learning environment for faculty, staff, students, and visitors. The cooperation of the entire campus community is needed to realize this goal. This is particularly true of research and teaching that involves radiation sources, where the Campus Radiation and Laser Safety Committee, and radiation safety officer (RSO), principal investigators (PIs) and department heads, and laboratory workers share the responsibility for creating and maintaining a safe workplace. Radiation and Laser Safety Committee Responsibilities The Radiation and Laser Safety Committee advises the Chancellor through the Vice Chancellor for Research and the Division of Research Safety (DRS) on matters related to the campus Radiation Safety Program. The Committee is composed of academic staff and faculty members representing various areas of research and teaching, and members who represent the campus administration including the campus RSO. The chancellor delegates authority to the committee to oversee the use of radiation sources throughout the campus. The committee has the authority to permit, deny, or revoke authorization for individuals to obtain and use radiation sources at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The responsibilities of the Radiation and Laser Safety Committee include the following: Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 23
7 1. Review proposals for unusually hazardous uses of radiation sources as deemed by the RSO, and establish criteria for equipment and procedures to ensure employee, student, and public safety. 2. Review cases that involve repeated infractions of the rules and regulations for protection against radiation, including lasers. 3. Review accidents that may involve exposure or serious economic loss and other cases for which reports to outside regulatory authorities are required. 4. Review public relation problems that involve radiation sources and lasers. 5. Review appeals from radiation users and modify rules or the decisions of DRS personnel where necessary. 6. Meet formally as often as necessary, but at least four times per year, to review the campus radiation safety program with DRS personnel. 7. Recommend the establishment or modification of campus radiation and laser safety policies. 8. Work with DRS to effectively use electronic communication to keep committee members abreast of unusual events between committee meetings. 9. Review communications between DRS and government agencies that affect the campus radiation safety program and the campus radioactive materials license. Division of Research Safety and Radiation Safety Officer Responsibilities 1. Provide advice and assistance to all concerned on all aspects of radiation safety. 2. Approve proposals for procurement, use and transfer of radiation sources except proposals involving unfamiliar or extreme hazards that DRS judges as requiring review by the Committee. 3. Receive and monitor all shipments of radioactive materials, deliver acceptable incoming shipments to the consignee, and ensure that outgoing shipments conform to shipping regulations. 4. Maintain permanent records of receipt, use, transfer, and disposal of radioactive materials. 5. Supervise and assist in disposal of radioactive wastes. Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 24
8 6. Assign personnel monitoring devices (e.g., film badges, dosimeters) when necessary, give instructions in their use, and maintain personnel monitoring records. 7. Check radiation monitoring and survey instruments for proper operation and calibrate as often as necessary. 8. Assist in designing and selecting equipment, shielding, and facilities and in the formulating operating procedures for new or modifying existing installations or buildings. 9. Calculate the levels of radiation intensity, time limits of personnel exposure, and minimum working distance around accelerators, reactors, X-ray machines, and other intense radiation sources. 10. Perform and keep records of leak tests on sealed sources. 11. Make and keep records of systematic surveys in areas where the presence of radiation or contamination of surfaces, air, or water is suspected, and notify the area supervisor of the results. In some cases this may require detailed monitoring of an operation from beginning to end by a DRS member. 12. Report hazardous radiological conditions promptly to the individual responsible and, when necessary, to the immediate supervisor and the Radiation and Laser Safety Committee. 13. Supervise and assist in decontamination of all but minor spills. 14. Schedule routine medical examinations in accordance with established policy; help establish criteria, and make arrangements for such examinations as may be required in emergency situations. 15. Enforce all written directives of the committee. 16. Stop any operation or deny access of any individual to radiation sources in the interest of safety. Such action must be reported verbally and in writing to the committee as soon as possible. 17. Grant exemptions to the rules (or impose more stringent restrictions) in emergency situations when, in the judgment of DRS, such action is necessary to reduce risk of serious injury or economic loss. Such actions must be reported verbally and in writing to the committee as soon as possible. 18. Maintain files of federal, state, and local licenses and registrations concerned with radiation sources and initiate applications for renewals and/or amendments of same. 19. Determine whether a radiation incident requires a report to any governing body and prepare such reports for the approval of the committee. Exception: If an immediate report is Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 25
9 required, the campus radiation safety officer shall (with knowledge and approval of the chairman if possible) file such report with the appropriate authorities and shall provide copies to the committee. 20. Be familiar with the federal, state, and local laws relating to radiation and be aware of changes in such laws as they occur. Inform the committee when such changes make modifications of policy desirable and institute necessary changes in the radiation safety program. Radiation Safety Manual Revision Date: September 2016 Page 26
Radiation Safety Manual. Emergency reference information: METCAD Radiation Safety Spills or fires... page 10
 Radiation Safety Manual Emergency reference information: METCAD....911 Radiation Safety.217-333-2755 Spills or fires.... page 10 Revised: September 2016 Radiation Safety Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction...
Radiation Safety Manual Emergency reference information: METCAD....911 Radiation Safety.217-333-2755 Spills or fires.... page 10 Revised: September 2016 Radiation Safety Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction...
University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Radiation Safety Manual
 University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Radiation Safety Manual Emergency reference information: MetCAD....9-911 Radiation Safety..3-2755 Spills or fires.. page 10 Revised: April 2014 Radiation Safety
University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Radiation Safety Manual Emergency reference information: MetCAD....9-911 Radiation Safety..3-2755 Spills or fires.. page 10 Revised: April 2014 Radiation Safety
Hazardous Waste Initial Training
 Hazardous Waste Initial Training Hazardous Waste Disposal Types of Waste Chemical Waste Radioactive Waste Biohazardous Waste/Medical Waste Pathological Waste Refer to the Waste Disposal Guide Typical Wastes
Hazardous Waste Initial Training Hazardous Waste Disposal Types of Waste Chemical Waste Radioactive Waste Biohazardous Waste/Medical Waste Pathological Waste Refer to the Waste Disposal Guide Typical Wastes
Hazardous Waste Section. Hazardous Waste Determinations
 Hazardous Waste Section Hazardous Waste Determinations RCRA Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 (RCRA) Gave EPA the authority to regulate hazardous waste from cradle to grave Hazardous and
Hazardous Waste Section Hazardous Waste Determinations RCRA Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976 (RCRA) Gave EPA the authority to regulate hazardous waste from cradle to grave Hazardous and
Facilities Management
 Facilities Management Policy Number: 700.14 Title: Hazardous Waste Management Plan Implementation Date: November 2008 Last Audit: April 27, 2016 Last Revised: April 27, 2016 Introduction East Tennessee
Facilities Management Policy Number: 700.14 Title: Hazardous Waste Management Plan Implementation Date: November 2008 Last Audit: April 27, 2016 Last Revised: April 27, 2016 Introduction East Tennessee
PROGRAM FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND DISPOSAL OF RADIOACTIVE WASTE
 RADIATION SAFETY DEPARTMENT West Virginia University Health Sciences Center WVU Hospitals Jefferson Memorial Hospital G-139 Health Sciences Center PO Box 9006 Morgantown, WV 26506-9006 Phone: 304-293-3413
RADIATION SAFETY DEPARTMENT West Virginia University Health Sciences Center WVU Hospitals Jefferson Memorial Hospital G-139 Health Sciences Center PO Box 9006 Morgantown, WV 26506-9006 Phone: 304-293-3413
Safety Best Practices Manual
 CHAPTER 13 Hazardous Waste POLICY This section establishes minimum requirements for the disposal of hazardous wastes to ensure compliance with federal, state, and local regulations concerning hazardous
CHAPTER 13 Hazardous Waste POLICY This section establishes minimum requirements for the disposal of hazardous wastes to ensure compliance with federal, state, and local regulations concerning hazardous
Waste Awareness at Kansas State University. Division of Public Safety Dept. of Environmental Health & Safety
 Waste Awareness at Kansas State University Division of Public Safety Dept. of Environmental Health & Safety Hazardous Materials (not waste) v Usable chemicals v Must be labeled at all times with the name
Waste Awareness at Kansas State University Division of Public Safety Dept. of Environmental Health & Safety Hazardous Materials (not waste) v Usable chemicals v Must be labeled at all times with the name
V. Waste Identification
 V. Waste Identification The first step in the management of hazardous waste is to determine whether a material is a waste. A waste is generally defined as a material, which is discarded, including materials
V. Waste Identification The first step in the management of hazardous waste is to determine whether a material is a waste. A waste is generally defined as a material, which is discarded, including materials
Swette Center for Environmental Biotechnology Radiation Safety Policy
 Reviewed: BR date RKB date CIT date Swette Center for Environmental Biotechnology Radiation Safety Policy Scope, Application and Purpose: The purpose of the Center for Environmental Biotechnology Radiation
Reviewed: BR date RKB date CIT date Swette Center for Environmental Biotechnology Radiation Safety Policy Scope, Application and Purpose: The purpose of the Center for Environmental Biotechnology Radiation
Waste Awareness at Kansas State University. Department of Environmental Health & Safety
 Waste Awareness at Kansas State University Department of Environmental Health & Safety Hazardous Materials (not waste) Usable chemicals Requirements fall under KDOL Must be labeled at all times with the
Waste Awareness at Kansas State University Department of Environmental Health & Safety Hazardous Materials (not waste) Usable chemicals Requirements fall under KDOL Must be labeled at all times with the
RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT PLAN
 RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT PLAN Copies of this plan will be made available to all members of the campus community with the potential to generate radioactive waste. Contents I. Purpose II. Regulatory
RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT PLAN Copies of this plan will be made available to all members of the campus community with the potential to generate radioactive waste. Contents I. Purpose II. Regulatory
2/07. PROCEDURE for DISPOSAL of RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS
 2/07 CORNELL UNIVERSITY PROCEDURE for DISPOSAL of RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS This procedure has been developed to ensure the safety of those individuals who handle radioactive waste and to comply with University,
2/07 CORNELL UNIVERSITY PROCEDURE for DISPOSAL of RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS This procedure has been developed to ensure the safety of those individuals who handle radioactive waste and to comply with University,
Radiation Safety Manual
 University of California, Merced Environment, Health and Safety Radiation Safety Manual Approved by: Signature: Title: Date: TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. ORGANIZATION AND RESPONSIBILITIES 1.1 POLICY 1.2 RADIATION
University of California, Merced Environment, Health and Safety Radiation Safety Manual Approved by: Signature: Title: Date: TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. ORGANIZATION AND RESPONSIBILITIES 1.1 POLICY 1.2 RADIATION
By: Georgia Institute of Technology
 Date: / / Page 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE 2.0 SCOPE To describe the handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive waste and the documentation requirements of these activities. This procedure applies to all radioactive
Date: / / Page 1 of 7 1.0 PURPOSE 2.0 SCOPE To describe the handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive waste and the documentation requirements of these activities. This procedure applies to all radioactive
Radiation Safety Policy & Procedures
 Radiation Safety Policy & Procedures Emergency Numbers RADIATION SAFETY OFFICER, RAMIN VAKILI... FIRE, POLICE, AND AMBULANCE...- CAMPUSE SECURITY... TABLE OF CONTENTS. PREAMBLE.... SCOPE.... POLICY....
Radiation Safety Policy & Procedures Emergency Numbers RADIATION SAFETY OFFICER, RAMIN VAKILI... FIRE, POLICE, AND AMBULANCE...- CAMPUSE SECURITY... TABLE OF CONTENTS. PREAMBLE.... SCOPE.... POLICY....
APPENDIX A NON-ASBESTOS SPECIAL WASTE PROFILE FORM
 APPENDIX A NON-ASBESTOS SPECIAL WASTE PROFILE FORM Materials Management Facility 23400 NYS Rt. 177, Rodman, NY 13682 Phone: (315)661-3230 Fax (315)661-3231 DEC Permit # 6-2252-00006/00007 Directions Complete
APPENDIX A NON-ASBESTOS SPECIAL WASTE PROFILE FORM Materials Management Facility 23400 NYS Rt. 177, Rodman, NY 13682 Phone: (315)661-3230 Fax (315)661-3231 DEC Permit # 6-2252-00006/00007 Directions Complete
Midwest Analytical Services, Inc. "Where industry comes for answers." PRICE LIST 2009
 PRICE LIST 2009 Midwest Analytical Services, Inc. (MAS) takes pride in its commitment to provide reliable and valid analytical data to customers. Our staff at MAS is active in a comprehensive QA/QC program
PRICE LIST 2009 Midwest Analytical Services, Inc. (MAS) takes pride in its commitment to provide reliable and valid analytical data to customers. Our staff at MAS is active in a comprehensive QA/QC program
Medical, Pathological and Low-level Radioactive Waste Management Plan for Incinerator Revised 3-08
 Background Medical, Pathological and Low-level Radioactive Waste Management Plan for Incinerator Revised 3-08 Many WSU laboratories and departments generate medical waste (contaminated solids), pathological
Background Medical, Pathological and Low-level Radioactive Waste Management Plan for Incinerator Revised 3-08 Many WSU laboratories and departments generate medical waste (contaminated solids), pathological
For ethidium bromide waste that is generated at Harvard, each waste stream is to be managed or accumulated as described below.
 LABORATORY CHEMICAL WASTE FAQS ETHIDIUM BROMIDE 1. Q - How should I manage and dispose of ethidium bromide waste? Answer - Ethidium bromide is a mutagen that requires special storage, handling, and disposal
LABORATORY CHEMICAL WASTE FAQS ETHIDIUM BROMIDE 1. Q - How should I manage and dispose of ethidium bromide waste? Answer - Ethidium bromide is a mutagen that requires special storage, handling, and disposal
THE UNIVERSITY OF TULSA RADIATION SAFETY PROGRAM. Table of Contents
 v6.13.2013 THE UNIVERSITY OF TULSA RADIATION SAFETY PROGRAM Table of Contents I. PURPOSE OF THE RADIATION SAFETY PROGRAM II. III. IV. DEFINITIONS SCOPE OF THE PROGRAM DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY AND RESPONSIBILITY
v6.13.2013 THE UNIVERSITY OF TULSA RADIATION SAFETY PROGRAM Table of Contents I. PURPOSE OF THE RADIATION SAFETY PROGRAM II. III. IV. DEFINITIONS SCOPE OF THE PROGRAM DELEGATION OF AUTHORITY AND RESPONSIBILITY
LABORATORY WASTE DISPOSAL GUIDE
 LABORATORY WASTE DISPOSAL GUIDE Purpose This guide will help lab members properly identify and manage hazardous waste in their laboratory. Identifying the types of waste generated is crucial to handling
LABORATORY WASTE DISPOSAL GUIDE Purpose This guide will help lab members properly identify and manage hazardous waste in their laboratory. Identifying the types of waste generated is crucial to handling
OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY RADIATION SAFETY OPERATING PROCEDURE 1801 RADIOACTIVE WASTE HANDLING & STORAGE
 OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY RADIATION SAFETY OPERATING PROCEDURE 1801 RADIOACTIVE WASTE HANDLING & STORAGE I. PURPOSE: To describe the manner in which radioactive waste shall be stored and/or disposed
OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY RADIATION SAFETY OPERATING PROCEDURE 1801 RADIOACTIVE WASTE HANDLING & STORAGE I. PURPOSE: To describe the manner in which radioactive waste shall be stored and/or disposed
Waste Management Plan
 Waste Management Plan for Stevens Institute of Technology Castle Point on Hudson Hoboken, New Jersey 07030-5991 Prepared By: Tetra Tech EC 1000 The American Road Morris Plains, New Jersey 07950 March 25,
Waste Management Plan for Stevens Institute of Technology Castle Point on Hudson Hoboken, New Jersey 07030-5991 Prepared By: Tetra Tech EC 1000 The American Road Morris Plains, New Jersey 07950 March 25,
Radioactive Material User Annual Refresher Training. Created by SU Environmental Health & Safety Services
 Created by SU Environmental Health & Safety Services Syracuse University Office of Human Resources 2015 Welcome to Syracuse University s On-Line Radioactive Material User Refresher Training. This Refresher
Created by SU Environmental Health & Safety Services Syracuse University Office of Human Resources 2015 Welcome to Syracuse University s On-Line Radioactive Material User Refresher Training. This Refresher
EK-35 Environmental Message February 2001
 EK-35 Environmental Message February 2001 EK-35 is a specially formulated intense use, continuous life dust control agent. Highly refined synthetic fluids enhanced with natural rosins are used in the formulation
EK-35 Environmental Message February 2001 EK-35 is a specially formulated intense use, continuous life dust control agent. Highly refined synthetic fluids enhanced with natural rosins are used in the formulation
Hazardous Waste Awareness Training
 Hazardous Waste Awareness Training Who We Are Occupational & Research Safety Radiation Safety Fire Safety Biosafety/Sanitation Hazardous Materials/Waste Environmental Compliance www.ksu.edu/safety @KSUSafety
Hazardous Waste Awareness Training Who We Are Occupational & Research Safety Radiation Safety Fire Safety Biosafety/Sanitation Hazardous Materials/Waste Environmental Compliance www.ksu.edu/safety @KSUSafety
Radioactive Waste Radiation Safety Orientation Open Source Booklet 7 (June 1, 2018)
 Radioactive Waste Radiation Safety Orientation Open Source Booklet 7 (June 1, 2018) For more information, refer to the Radiation Safety Manual, 2017 RSP-3 and the Quick Step for waste in the radiation
Radioactive Waste Radiation Safety Orientation Open Source Booklet 7 (June 1, 2018) For more information, refer to the Radiation Safety Manual, 2017 RSP-3 and the Quick Step for waste in the radiation
BALL STATE UNIVERSITY RADIATION PROTECTION PROCEDURES* USER S GUIDE
 BALL STATE UNIVERSITY RADIATION PROTECTION PROCEDURES* USER S GUIDE At Ball State University, there are two categories of material users. Authorized Users and Supervised Users. Authorized Users must have
BALL STATE UNIVERSITY RADIATION PROTECTION PROCEDURES* USER S GUIDE At Ball State University, there are two categories of material users. Authorized Users and Supervised Users. Authorized Users must have
Delaware State University
 Delaware State University University Area Responsible: Risk and Safety Management Policy Number and Name: 7-22: Laboratories Closeout Approval Date: 7/28/11 Reviewed: 7/26/2013 Revisions: 8/13/2013 Related
Delaware State University University Area Responsible: Risk and Safety Management Policy Number and Name: 7-22: Laboratories Closeout Approval Date: 7/28/11 Reviewed: 7/26/2013 Revisions: 8/13/2013 Related
BURLINGTON COUNTY DEPARTMENT OF SOLID WASTE WASTE CLASSIFICATION REQUEST FORM AND INSTRUCTIONS
 BURLINGTON COUNTY DEPARTMENT OF SOLID WASTE WASTE CLASSIFICATION REQUEST FORM AND INSTRUCTIONS Burlington County owns and operates a Resource Recovery Complex which includes, among other facilities, a
BURLINGTON COUNTY DEPARTMENT OF SOLID WASTE WASTE CLASSIFICATION REQUEST FORM AND INSTRUCTIONS Burlington County owns and operates a Resource Recovery Complex which includes, among other facilities, a
RADIOISOTOPE ACQUISITION AND DISPOSITION
 RADIOISOTOPE ACQUISITION AND DISPOSITION PURPOSE This procedure specifies measures for the control of radioactive materials from initial acquisition to final disposition. It describes the prerequisites
RADIOISOTOPE ACQUISITION AND DISPOSITION PURPOSE This procedure specifies measures for the control of radioactive materials from initial acquisition to final disposition. It describes the prerequisites
Hazardous Waste Manual. Version
 Hazardous Waste Manual Version 2019.2.3 Record of Revisions Revision No. Date Revision Description Original Document 2.0 09/2013 Significant revisions to hazardous waste pickup procedures and hazardous
Hazardous Waste Manual Version 2019.2.3 Record of Revisions Revision No. Date Revision Description Original Document 2.0 09/2013 Significant revisions to hazardous waste pickup procedures and hazardous
Radiation Protection Manual. Minnesota State University, Mankato
 Radiation Protection Manual Minnesota State University, Mankato 2015 Statement of Commitment The University is committed to maintaining radiation exposures to faculty, staff, students and the public, resulting
Radiation Protection Manual Minnesota State University, Mankato 2015 Statement of Commitment The University is committed to maintaining radiation exposures to faculty, staff, students and the public, resulting
Radiation Protection Manual. Minnesota State University, Mankato
 Radiation Protection Manual Minnesota State University, Mankato 2015 Statement of Commitment The University is committed to maintaining radiation exposures to faculty, staff, students and the public, resulting
Radiation Protection Manual Minnesota State University, Mankato 2015 Statement of Commitment The University is committed to maintaining radiation exposures to faculty, staff, students and the public, resulting
RSP-2 Page 1 of 12. Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection Committee
 Radiation Safety Manual Title: Number: Radiation Safety Program Administrative Structure and Permit Process Page 1 of 12 Issued by: Approved by: Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection Committee
Radiation Safety Manual Title: Number: Radiation Safety Program Administrative Structure and Permit Process Page 1 of 12 Issued by: Approved by: Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection Committee
Rags and Absorbents Disposal
 Rags and Absorbents Disposal University of Tennessee Safety Guide EC-023 Document Contact: EHS-Environmental Compliance Date effective: March 14, 2017 Revision Date: March 14, 2017 Purpose The purpose
Rags and Absorbents Disposal University of Tennessee Safety Guide EC-023 Document Contact: EHS-Environmental Compliance Date effective: March 14, 2017 Revision Date: March 14, 2017 Purpose The purpose
LABORATORY WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES
 LABORATORY WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES Sylvia Wanjiru Kamau INTERNATIONAL LIVESTOCK RESEARCH INSTITUTE LABORATORY MANAGEMENT AND EQUIPMENT OPERATIONS WORKSHOP. 17 TH -21 ST JUNE 2012 TRAINING OBJECTIVES
LABORATORY WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAMMES Sylvia Wanjiru Kamau INTERNATIONAL LIVESTOCK RESEARCH INSTITUTE LABORATORY MANAGEMENT AND EQUIPMENT OPERATIONS WORKSHOP. 17 TH -21 ST JUNE 2012 TRAINING OBJECTIVES
Date June 2, 2006 Page 1 of 5. Approved By
 Date June 2, 2006 Page 1 of 5 Reviewed By Lisa Arceneaux Approved By 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to provide a viable method of waste management of radioactive waste when the half-life of
Date June 2, 2006 Page 1 of 5 Reviewed By Lisa Arceneaux Approved By 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to provide a viable method of waste management of radioactive waste when the half-life of
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Environmental Health & Safety Department Radiation Safety Division
 Page 1 of 6 The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Environmental Health & Safety Department Radiation Safety Division RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL AUTHORIZATION INITIAL APPLICATION AMENDENT
Page 1 of 6 The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Environmental Health & Safety Department Radiation Safety Division RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL AUTHORIZATION INITIAL APPLICATION AMENDENT
University of Richmond Radiation Safety Manual
 University of Richmond Radiation Safety Manual Office of Safety Services and Risk Management Revised: October 2017 i TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Purpose....1 B. Responsibility 1. Radiation Safety Committee.......1
University of Richmond Radiation Safety Manual Office of Safety Services and Risk Management Revised: October 2017 i TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Purpose....1 B. Responsibility 1. Radiation Safety Committee.......1
Environmental Health and Safety at Alfred University. Identifying A Hazardous Waste
 Environmental Health and Safety at Alfred University Identifying A Hazardous Waste What is a Hazardous Waste? A waste is basically any discarded material. By law hazardous waste is defined as a waste,
Environmental Health and Safety at Alfred University Identifying A Hazardous Waste What is a Hazardous Waste? A waste is basically any discarded material. By law hazardous waste is defined as a waste,
Standard Operating Procedure. Handling of Radioactive Material. PC-SOP-IM-005-v02
 Standard Operating Procedure Handling of Radioactive Material Revision History Version Reason for Revision Date 01 New SOP August/21/2013 02 Review and update February/12/2015 Summary The content of this
Standard Operating Procedure Handling of Radioactive Material Revision History Version Reason for Revision Date 01 New SOP August/21/2013 02 Review and update February/12/2015 Summary The content of this
Code of Federal Regulations
 This definition was taken from the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations on 5/6/13. Title 40 - Protection of Environment Volume: 27 Date: 2012-07-01 Original Date: 2012-07-01 Code of Federal Regulations
This definition was taken from the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations on 5/6/13. Title 40 - Protection of Environment Volume: 27 Date: 2012-07-01 Original Date: 2012-07-01 Code of Federal Regulations
Waterfront Substation
 Waterfront Substation July 8, 2015 Project Milestones 2 Waterfront Substation The Southeast and Southwest region of the District of Columbia is experiencing residential, commercial, and retail growth.
Waterfront Substation July 8, 2015 Project Milestones 2 Waterfront Substation The Southeast and Southwest region of the District of Columbia is experiencing residential, commercial, and retail growth.
WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDE. Creighton University Environmental Health and Safety
 WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Creighton University Environmental Health and Safety www.creighton.edu/ehs 402 546 6400 Overview With over 150 teaching and research labs, as well as other areas such as fine arts
WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Creighton University Environmental Health and Safety www.creighton.edu/ehs 402 546 6400 Overview With over 150 teaching and research labs, as well as other areas such as fine arts
LABORATORY CLOSURE AND DECOMMISSIONING POLICY
 LABORATORY CLOSURE AND DECOMMISSIONING POLICY Yale University is committed to the health and safety of its students, faculty, staff and visitors as well as the surrounding community and environment in
LABORATORY CLOSURE AND DECOMMISSIONING POLICY Yale University is committed to the health and safety of its students, faculty, staff and visitors as well as the surrounding community and environment in
SARATOGA SPRING WATER COMPANY 11 Geyser Road, Saratoga Springs, New York Phone: , Fax: , Web:
 Bottler s Name: Saratoga Spring Water Company BOTTLED WATER REPORT Address: 11 Geyser Road, Saratoga Springs, NY, 12866 Telephone Number: 518-584-6363 Source(s): Spring Water Sweet Water Spring Saratoga
Bottler s Name: Saratoga Spring Water Company BOTTLED WATER REPORT Address: 11 Geyser Road, Saratoga Springs, NY, 12866 Telephone Number: 518-584-6363 Source(s): Spring Water Sweet Water Spring Saratoga
Laboratory Close-Out Guidelines
 Office of Laboratory Safety 2300 I Street, NW Ross Hall, Suite B- 05 Washington, DC 20037 t. 202-994- 8258 I labsafety@gwu.edu Guidelines The Principal Investigator (PI) is responsible for leaving laboratories
Office of Laboratory Safety 2300 I Street, NW Ross Hall, Suite B- 05 Washington, DC 20037 t. 202-994- 8258 I labsafety@gwu.edu Guidelines The Principal Investigator (PI) is responsible for leaving laboratories
WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN
 July 15, 2015 WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN Table of Contents General.. 1 Responsibilities. 1 Program Development... 2 References... 2 Management Procedures
July 15, 2015 WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN Table of Contents General.. 1 Responsibilities. 1 Program Development... 2 References... 2 Management Procedures
HEALTH PHYSICS Emergency Procedures and Levels of Action
 HEALTH PHYSICS Emergency Procedures and Levels of Action AREAS OF RESPONSIBILITY: 1. Personnel Monitoring: Film badges, ring dosimeters, and other types of personnel monitors are available to persons working
HEALTH PHYSICS Emergency Procedures and Levels of Action AREAS OF RESPONSIBILITY: 1. Personnel Monitoring: Film badges, ring dosimeters, and other types of personnel monitors are available to persons working
WASTE ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA
 KIRBY CANYON RECYCLING & DISPOSAL FACILITY WASTE ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA Kirby Canyon Recycling & Disposal Facility Highway 101 at Coyote Creek Golf Drive Exit 910 Coyote Creek Golf Drive Morgan Hill, CA 95037
KIRBY CANYON RECYCLING & DISPOSAL FACILITY WASTE ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA Kirby Canyon Recycling & Disposal Facility Highway 101 at Coyote Creek Golf Drive Exit 910 Coyote Creek Golf Drive Morgan Hill, CA 95037
Marquette University Effective: 5/21/06 Hazardous Waste Management Program Updated: 03/11/09 Updated: 05/06/09 Revision No.
 Page: 1 MARQUETTE UNIVERSITY HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE... 3 2. RESPONSIBILITIES... 3 2.1 ADMINISTRATION... 3 2.2 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS... 3 2.3 FACULTY AND STAFF...
Page: 1 MARQUETTE UNIVERSITY HAZARDOUS WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Table of Contents 1. PURPOSE... 3 2. RESPONSIBILITIES... 3 2.1 ADMINISTRATION... 3 2.2 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATORS... 3 2.3 FACULTY AND STAFF...
Laboratory Safety Reminders
 Laboratory Safety Reminders July 2012 Mount Holyoke College Environmental Health and Safety Safe Use of Radioactive Materials in MHC Research Labs Research Protocols A Radioactive Materials (RAM) use Protocol
Laboratory Safety Reminders July 2012 Mount Holyoke College Environmental Health and Safety Safe Use of Radioactive Materials in MHC Research Labs Research Protocols A Radioactive Materials (RAM) use Protocol
Inorganic Chemicals (IOCs)
 Burlington WA Corporate Office 1620 S Walnut St - 98233 800.755.9295 $ 360.757.1400 Bellingham WA Microbiology 805 Orchard Dr Ste 4-98225 360.671.0688 Portland OR Microbiology/Chemistry 9150 SW Pioneer
Burlington WA Corporate Office 1620 S Walnut St - 98233 800.755.9295 $ 360.757.1400 Bellingham WA Microbiology 805 Orchard Dr Ste 4-98225 360.671.0688 Portland OR Microbiology/Chemistry 9150 SW Pioneer
Western Michigan University
 Western Michigan University Radiation Safety Source Inventory and Control Program Purpose A. To ensure all Western Michigan University licensed material and radiation producing machines are controlled
Western Michigan University Radiation Safety Source Inventory and Control Program Purpose A. To ensure all Western Michigan University licensed material and radiation producing machines are controlled
Waterfront Substation
 Waterfront Substation July 8, 2015 Project Milestones I Pepco Holdinqs Inc 2 Waterfront Substation The Southeast and Southwest region of the District of Columbia is experiencing residential, commercial,
Waterfront Substation July 8, 2015 Project Milestones I Pepco Holdinqs Inc 2 Waterfront Substation The Southeast and Southwest region of the District of Columbia is experiencing residential, commercial,
CHEMICALS GENERALLY ACCEPTABLE FOR SANITARY SEWER DISPOSAL SANITARY SEWER DISPOSAL OF LABORATORY CHEMICALS. Introduction
 Harvey Ingham 30 2804 Forest Ave Des Moines, IA50311 515-271-3804 ehs@drake.edu www.drake.edu/ehs CHEMICALS GENERALLY ACCEPTABLE FOR SANITARY SEWER DISPOSAL Introduction Some chemicals that are water soluble
Harvey Ingham 30 2804 Forest Ave Des Moines, IA50311 515-271-3804 ehs@drake.edu www.drake.edu/ehs CHEMICALS GENERALLY ACCEPTABLE FOR SANITARY SEWER DISPOSAL Introduction Some chemicals that are water soluble
Lewis & Clark Policy and Procedure
 Lewis & Clark Policy and Procedure Subject: Hazardous Waste Program Policy No.: Division: Business and Finance Department: Facilities Services Original Effective Date: March 29, 1994 Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
Lewis & Clark Policy and Procedure Subject: Hazardous Waste Program Policy No.: Division: Business and Finance Department: Facilities Services Original Effective Date: March 29, 1994 Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
MIXED WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM. UNIVERSITY RISK MANAGEMENT Radiation Safety 19 Hagood Avenue, Suite 301 Charleston SC
 MIXED WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM UNIVERSITY RISK MANAGEMENT Radiation Safety 19 Hagood Avenue, Suite 301 Charleston SC 29425 843-792-4255 Revised: January 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 DEFINITION...
MIXED WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM UNIVERSITY RISK MANAGEMENT Radiation Safety 19 Hagood Avenue, Suite 301 Charleston SC 29425 843-792-4255 Revised: January 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 DEFINITION...
Water Analysis Report (2017)
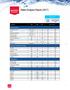 Analysis Report (2017) Type Physical Quality Alkalinity as CaCO3 mg/l CaCO3 5 NR 0.52 9.69 Color Color unit 5 15 ND ND Specific Conductance umhos/cm 0.1 NR 3.95 45.79 Hardness, Total mg/l CaCO3 2 NR ND
Analysis Report (2017) Type Physical Quality Alkalinity as CaCO3 mg/l CaCO3 5 NR 0.52 9.69 Color Color unit 5 15 ND ND Specific Conductance umhos/cm 0.1 NR 3.95 45.79 Hardness, Total mg/l CaCO3 2 NR ND
Tufts University Radiation Safety Committee Policies and Procedures Manual
 Tufts University Radiation Safety Committee Policies and Procedures Manual Revised 3/27/13 Table of Contents 1. Purpose 2. Administration and Delegation of Authority 3. Organization and Responsibility
Tufts University Radiation Safety Committee Policies and Procedures Manual Revised 3/27/13 Table of Contents 1. Purpose 2. Administration and Delegation of Authority 3. Organization and Responsibility
Policy & Procedure Manual
 Environmental Health & Safety Policy & Procedure Manual Title: 1. Purpose: To establish policies, work practices, and systematic procedures for the handling, packaging, collection, treatment, and disposal
Environmental Health & Safety Policy & Procedure Manual Title: 1. Purpose: To establish policies, work practices, and systematic procedures for the handling, packaging, collection, treatment, and disposal
Chapter 7 Transportation of Radioactive Material
 Chapter 7 Transportation of Radioactive Material Radioactive material that is possessed by UIC must be transported in a safe and legal manner. This chapter explains the requirements for transportation
Chapter 7 Transportation of Radioactive Material Radioactive material that is possessed by UIC must be transported in a safe and legal manner. This chapter explains the requirements for transportation
Biomedical Waste Management Guide
 Biomedical Waste Management Guide Yale University Office of Environmental Health & Safety 135 College Street, Suite 100, New Haven, CT 06510 Updated April 2017 Telephone: 203-785-3550 / Fax: 203-785-7588
Biomedical Waste Management Guide Yale University Office of Environmental Health & Safety 135 College Street, Suite 100, New Haven, CT 06510 Updated April 2017 Telephone: 203-785-3550 / Fax: 203-785-7588
Radiation Safety Committee Control Functions and Administrative Procedures
 and Administrative Procedures A) Rationale, Functions and Composition (University Regulation 1-2, section 3.J.) 1) Rationale The University, operating under a type A broad scope byproduct (radioactive
and Administrative Procedures A) Rationale, Functions and Composition (University Regulation 1-2, section 3.J.) 1) Rationale The University, operating under a type A broad scope byproduct (radioactive
Industrial and Hazardous Waste: Rules and Regulations for Small-Quantity Generators
 Texas Commission on Environmental Quality RG-234 (Rev. 7/09) Industrial and Hazardous Waste: Rules and Regulations for Small-Quantity Generators Small Business and Environmental Assistance Division Texas
Texas Commission on Environmental Quality RG-234 (Rev. 7/09) Industrial and Hazardous Waste: Rules and Regulations for Small-Quantity Generators Small Business and Environmental Assistance Division Texas
University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, Massachusetts
 University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, Massachusetts March 2007 Revision In the event of a Radiation Emergency: Call the Radiation Safety Office: (978) 934-3372 (978) 934-3373 If unavailable or after
University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, Massachusetts March 2007 Revision In the event of a Radiation Emergency: Call the Radiation Safety Office: (978) 934-3372 (978) 934-3373 If unavailable or after
Sample Number: Type of Water: Collection Date and Time: Received Date and Time: Date Completed:
 Informational Water Quality Report Watercheck w/po Client: Ordered By: Aqua Falls Bottled Water 7606 Dayton Road Fairborn, OH 45324-1904 ATTN: Bob Kennedy Sample Number: Location: Type of Water: Collection
Informational Water Quality Report Watercheck w/po Client: Ordered By: Aqua Falls Bottled Water 7606 Dayton Road Fairborn, OH 45324-1904 ATTN: Bob Kennedy Sample Number: Location: Type of Water: Collection
Water Analysis Report (2018)
 Analysis Report (2018) Type Purified with Physical Quality Alkalinity in CaCO3 units mg/l 2 NR ND 10 63 Apparent Color ACU 3 15 ND ND ND Specific Conductance, 25 C umho/cm 2 1600 5 50 180 Total Hardness
Analysis Report (2018) Type Purified with Physical Quality Alkalinity in CaCO3 units mg/l 2 NR ND 10 63 Apparent Color ACU 3 15 ND ND ND Specific Conductance, 25 C umho/cm 2 1600 5 50 180 Total Hardness
WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN
 3 February, 2001 WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN 1. General 2. Responsibilities 3. Program Development 4. References 5. Management
3 February, 2001 WARTBURG COLLEGE ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS HAZARDOUS WASTE PLAN 1. General 2. Responsibilities 3. Program Development 4. References 5. Management
This is Chapter 6, part-two of the Radiation Safety Short Course: Radioisotope Laboratory Techniques. In this section we will review what Radiation
 This is Chapter 6, part-two of the Radiation Safety Short Course: Radioisotope Laboratory Techniques. In this section we will review what Radiation Safety personnel evaluate when completing the quarterly
This is Chapter 6, part-two of the Radiation Safety Short Course: Radioisotope Laboratory Techniques. In this section we will review what Radiation Safety personnel evaluate when completing the quarterly
Hazard Waste Management Training. This training is a one-time requirement for personnel generating waste at WCU
 Hazard Waste Management Training This training is a one-time requirement for personnel generating waste at WCU Hazard Waste Compliance WCU is classified as a hazardous waste generator by the U.S. Environmental
Hazard Waste Management Training This training is a one-time requirement for personnel generating waste at WCU Hazard Waste Compliance WCU is classified as a hazardous waste generator by the U.S. Environmental
Inorganic Analytes - Metals. Aluminum ND mg/l 0.2 EPA Secondary 0.1. Arsenic ND mg/l EPA Primary Barium ND mg/l 2 EPA Primary 0.
 Inorganic Analytes - Metals Aluminum ND mg/l 0.2 EPA Secondary 0.1 Arsenic ND mg/l 0.010 EPA Primary 0.005 Barium ND mg/l 2 EPA Primary 0.30 Cadmium ND mg/l 0.005 EPA Primary 0.002 Calcium 10.3 mg/l --
Inorganic Analytes - Metals Aluminum ND mg/l 0.2 EPA Secondary 0.1 Arsenic ND mg/l 0.010 EPA Primary 0.005 Barium ND mg/l 2 EPA Primary 0.30 Cadmium ND mg/l 0.005 EPA Primary 0.002 Calcium 10.3 mg/l --
CHAPTER 10 HAZARDOUS MATERIAL DISPOSAL 2.0 IDENTIFICATION OF REGULATED WASTES
 CHAPTER 10 HAZARDOUS MATERIAL DISPOSAL 2.0 IDENTIFICATION OF REGULATED WASTES 2.1 Chemical Wastes... 2 2.1.1 Ignitability... 2 2.1.2 Corrosivity... 2 2.1.3 Reactivity... 3 2.1.4 Toxicity... 3 2.1.5 Listed
CHAPTER 10 HAZARDOUS MATERIAL DISPOSAL 2.0 IDENTIFICATION OF REGULATED WASTES 2.1 Chemical Wastes... 2 2.1.1 Ignitability... 2 2.1.2 Corrosivity... 2 2.1.3 Reactivity... 3 2.1.4 Toxicity... 3 2.1.5 Listed
2015 Water Analysis Report for Purified Drinking Water
 2015 Water Analysis Report for Purified Drinking Water Substance Units MDL* MCL** Market Pantry Purifi ed Water Physical Quality Alkalinity as CaCO3 mg/l CaCO3 5 NR ND Color Color unit 5 15 ND Hardness,
2015 Water Analysis Report for Purified Drinking Water Substance Units MDL* MCL** Market Pantry Purifi ed Water Physical Quality Alkalinity as CaCO3 mg/l CaCO3 5 NR ND Color Color unit 5 15 ND Hardness,
2016 Water Quality Chart
 2016 Water Quality Chart The City of Water Department performs over 50,000 tests each year before, during, and after treatment. In addition, further tests are conducted at independent, certified laboratories.
2016 Water Quality Chart The City of Water Department performs over 50,000 tests each year before, during, and after treatment. In addition, further tests are conducted at independent, certified laboratories.
2015 Water Quality Chart
 2015 Water Quality Chart The City of Water Department performs over 50,000 tests each year before, during, and after treatment. In addition, further tests are conducted at independent, certified laboratories.
2015 Water Quality Chart The City of Water Department performs over 50,000 tests each year before, during, and after treatment. In addition, further tests are conducted at independent, certified laboratories.
Biological and Regulated Medical Waste Plan
 Biological and Regulated Medical Waste Plan TUFTS ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY OCTOBER 2016 Table of Contents I. Purpose... 3 II. Responsibilities... 3 III. Sink and sewer discharge of specific medical
Biological and Regulated Medical Waste Plan TUFTS ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH AND SAFETY OCTOBER 2016 Table of Contents I. Purpose... 3 II. Responsibilities... 3 III. Sink and sewer discharge of specific medical
Hazardous Waste Program Manual
 Hazardous Waste Program Manual Environmental Health, Safety and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Original January 2010 Revised February 2018 Contents I. Introduction...
Hazardous Waste Program Manual Environmental Health, Safety and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Original January 2010 Revised February 2018 Contents I. Introduction...
MANAGING HAZARDOUS WASTE AT WSU TRI-CITIES
 MANAGING HAZARDOUS WASTE AT WSU TRI-CITIES WHAT IS A HAZARDOUS WASTE? Most laboratory chemicals including mixtures and solutions Expired chemicals Pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers Paints, automotive
MANAGING HAZARDOUS WASTE AT WSU TRI-CITIES WHAT IS A HAZARDOUS WASTE? Most laboratory chemicals including mixtures and solutions Expired chemicals Pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers Paints, automotive
WHO NEEDS TO KNOW THIS PROGRAM All NYU employees that generate, handle or transport RMW should be familiar with this written program.
 Title: NYU Regulated Medical Waste Safety Written Program Effective Date: October 2002 Revision Date: April 14, 2017 Issuing Authority: Responsible Officer: VP, Facilities and Construction Management Director
Title: NYU Regulated Medical Waste Safety Written Program Effective Date: October 2002 Revision Date: April 14, 2017 Issuing Authority: Responsible Officer: VP, Facilities and Construction Management Director
1. What is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announcing?
 Fact Sheet: Announcement of the Results of EPA s Review of Existing Drinking Water Standards and Request for Public Comment 1. What is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announcing? The Agency is
Fact Sheet: Announcement of the Results of EPA s Review of Existing Drinking Water Standards and Request for Public Comment 1. What is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announcing? The Agency is
Radiation Safety Program Hunter College of the City University of New York
 Radiation Safety Program Hunter College of the City University of New York 1. Guidelines for All Users of Radioactive Materials This document presents the guidelines for all persons using radioactive materials.
Radiation Safety Program Hunter College of the City University of New York 1. Guidelines for All Users of Radioactive Materials This document presents the guidelines for all persons using radioactive materials.
Infectious Waste Disposal Procedure 25 PA Code 284 Ursinus College Collegeville, PA 19426
 The purpose of the Infectious Waste Disposal procedure is to establish procedures for the safe handling and proper disposal of infectious waste generated at in accordance with regulation 25 PA Code Chapter
The purpose of the Infectious Waste Disposal procedure is to establish procedures for the safe handling and proper disposal of infectious waste generated at in accordance with regulation 25 PA Code Chapter
Radiation Safety Operating Procedure. Shipping and Transporting
 1.0 Statement All shipments of open source nuclear substances to and from Memorial University shall be handled as detailed in this procedure to ensure compliance with appropriate regulations and in a manner
1.0 Statement All shipments of open source nuclear substances to and from Memorial University shall be handled as detailed in this procedure to ensure compliance with appropriate regulations and in a manner
California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo. Radiation Safety Manual
 California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo Radiation Safety Manual November 2016 1. ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The purpose of the Radiation Safety Program is to assure
California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo Radiation Safety Manual November 2016 1. ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURES AND RESPONSIBILITIES The purpose of the Radiation Safety Program is to assure
UNIVERSITY OF RICHMOND REGULATED MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
 UNIVERSITY OF RICHMOND REGULATED MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES October 2016 Table of Contents Section Page I. Introduction.... 1 II. Characteristics of Regulated Medical Waste 1-2 III. Exclusions...2-3
UNIVERSITY OF RICHMOND REGULATED MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES October 2016 Table of Contents Section Page I. Introduction.... 1 II. Characteristics of Regulated Medical Waste 1-2 III. Exclusions...2-3
BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT POLICY
 BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT POLICY Managing biomedical waste in a safe and environmentally responsible manner is a key focus of the Environmental Compliance and Sustainability office. 1.0 PURPOSE In an
BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT POLICY Managing biomedical waste in a safe and environmentally responsible manner is a key focus of the Environmental Compliance and Sustainability office. 1.0 PURPOSE In an
2018 BOTTLED WATER QUALITY REPORT Starkey Spring Water. Treatment process: 25 um Filtration, 2 um Filtration, 0.5 um Filtration, UV Disinfection
 2018 BOTTLED WATER QUALITY REPORT Starkey Spring Water Bottler s Name: Starkey Water Address: 101 Council Avenue; Council,, ID 83612 Telephone Number: 855-910-4844 Source(s): Starkey Hot Spring Treatment
2018 BOTTLED WATER QUALITY REPORT Starkey Spring Water Bottler s Name: Starkey Water Address: 101 Council Avenue; Council,, ID 83612 Telephone Number: 855-910-4844 Source(s): Starkey Hot Spring Treatment
Radioactive Material Safety Manual
 Radioactive Material Safety Manual Radiation Safety Office URI Bay Campus 16 Reactor Road Narragansett, RI 02882 Phone: 401-874-2600 Fax: 401-874-9452 www.uri.edu/radiation 02/2015 Updated 07/2017 Table
Radioactive Material Safety Manual Radiation Safety Office URI Bay Campus 16 Reactor Road Narragansett, RI 02882 Phone: 401-874-2600 Fax: 401-874-9452 www.uri.edu/radiation 02/2015 Updated 07/2017 Table
Ontario Soil Standards (other than sediment) II (mg/kg) Potable Ground Water Non-Potable Ground Water. Industrial/ Commercial
 T3 Table 3 Soil quality benchmarks I Substance Ontario Soil Standards (other than sediment) II (mg/kg) Potable Ground Water Non-Potable Ground Water Canadian Environmental Quality Criteria and Guidelines
T3 Table 3 Soil quality benchmarks I Substance Ontario Soil Standards (other than sediment) II (mg/kg) Potable Ground Water Non-Potable Ground Water Canadian Environmental Quality Criteria and Guidelines
Animal cell and tissue culture. Lab 1
 Animal cell and tissue culture Lab 1 Tissue culture Laboratory Safety Outline Lab Safety Biohazards Biosafety Levels Biosafety Cabinets Decontamination Biological Waste Introduction A cell culture laboratory
Animal cell and tissue culture Lab 1 Tissue culture Laboratory Safety Outline Lab Safety Biohazards Biosafety Levels Biosafety Cabinets Decontamination Biological Waste Introduction A cell culture laboratory
Hazardous waste from non-specific sources.
 ACTION: Final DATE: 07/23/2010 9:11 AM 3745-51-31 1 3745-51-31 from non-specific sources. (A) The following table lists hazardous wastes from non-specific sources, along with industry and s and hazard
ACTION: Final DATE: 07/23/2010 9:11 AM 3745-51-31 1 3745-51-31 from non-specific sources. (A) The following table lists hazardous wastes from non-specific sources, along with industry and s and hazard
ARKANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY GOVERNING PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURES RADIATION SAFETY
 ARKANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY GOVERNING PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURES RADIATION SAFETY Number: S-008 Responsible Official: Provost Version: 01 Date: 8/26/2009 1.0 INTRODUCTION Arkansas State University (ASU) is
ARKANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY GOVERNING PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURES RADIATION SAFETY Number: S-008 Responsible Official: Provost Version: 01 Date: 8/26/2009 1.0 INTRODUCTION Arkansas State University (ASU) is
Environmental Health and Safety Equipment Release Form
 Environmental Health and Equipment Release Form Date: Location of Origin: Principal Investigator/Supervisor: Type of Equipment: Destination/Service Department: Service to Be Performed: Contaminated: Not
Environmental Health and Equipment Release Form Date: Location of Origin: Principal Investigator/Supervisor: Type of Equipment: Destination/Service Department: Service to Be Performed: Contaminated: Not
November, Contents
 Microbiology Minimum Standard November, 2013 Contents 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 More Information... 3 3 Using this Standard... 3 4 Standard Provisions... 3 4.1 Application to work with Infectious Agents...
Microbiology Minimum Standard November, 2013 Contents 1 Executive Summary... 3 2 More Information... 3 3 Using this Standard... 3 4 Standard Provisions... 3 4.1 Application to work with Infectious Agents...
City of Las Cruces, New Mexico INDUSTRIAL WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE AND PERMIT APPLICATION
 City of Las Cruces, New Mexico INDUSTRIAL WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE AND PERMIT APPLICATION A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1) Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) Code for Primary Activity: 2) Company Name: Mailing
City of Las Cruces, New Mexico INDUSTRIAL WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE AND PERMIT APPLICATION A. GENERAL INFORMATION 1) Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) Code for Primary Activity: 2) Company Name: Mailing
Trade Waste Approved Acceptance Criteria
 Trade Waste Approved Acceptance Criteria Trade waste discharged from land, at the point where it is sampled, must comply with the standards set out in this Schedule. 1. PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS 1.1. Temperature
Trade Waste Approved Acceptance Criteria Trade waste discharged from land, at the point where it is sampled, must comply with the standards set out in this Schedule. 1. PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS 1.1. Temperature
Appendix J. University of Alabama at Birmingham Medical Waste Management Plan
 University of Alabama at Birmingham Medical Waste Management Plan I. Definitions per the Alabama Department of Environmental Management Land Division 13-Solid Waste Program, Chapter 335-13-1, Medical Waste
University of Alabama at Birmingham Medical Waste Management Plan I. Definitions per the Alabama Department of Environmental Management Land Division 13-Solid Waste Program, Chapter 335-13-1, Medical Waste
