The Industrial Revolution
|
|
|
- Sophie Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 The Industrial Revolution Biggest change in human lifestyles since the development of farming during the Neolithic Revolution!!! (New Stone Age) It will all begin with an Agricultural Revolution New ways of planting and growing crops were introduced during the 1700 s.
3 Crop rotation, the seed drill, and new fertilizers enable fewer farmers to produce far more food.
4 THE ENCLOSURE MOVEMENT Rich landowners bought land off village farmers and enclosed it with fences and/or hedges. Open land and common land was also sold and divided.
5 IMPACT OF THE AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION: Crop yields improved 300% Wealthy farmers control the land, many people lose farms and jobs A large part of the population begin to move to the cities in search of jobs (urbanization) The combination of an increased food supply and urbanization, a population explosion began, especially in cities
6 A POPULATION EXPLOSION IN ENGLAND There was more food produced using less farmers and less land! Food surplus Improved diets Better health Lower death rate Increased population Population Figures: 1750 approx. 5 million 1800 approx. 10 million 1850 approx. 20 million Growing cities
7 The Industrial Revolution begins in England Stable government and society Available resources (iron and coal) Supply of urban workers (urbanization) Many colonies, provide capital (money!) and resources as well as markets for products
8 Inventions Spur Technological Advances: Britain s textile (cloth) industry would be the first to be transformed. By 1800, several inventions had modernized the cotton industry John Kay Flying Samuel James Shuttle Crompton Hargreaves 1769 Spinning Spinning Richard Mule Jenny Arkwright 1787 Edmund Cartwright - Combined Water the features Frame Power Loom of the A shuttle sped back and forth on wheels. The flying shuttle, a A spinning wheel used to boat-shaped piece of wood to weave Used spinning water-power jenny and yarn. It allowed from the water a rapid which frame Run yarn by was attached, spinner streams to water-power. make to work to drive thread Sped 8 threads spinning that was up at a doubled stronger the work weaving. a weaver time. wheels. and finer. could do in a day.
9 1765 James Watt Steam Engine Need for a cheap, convenient source of power was met with the invention of the steam engine.
10 New energy sources were found that would help work new machines and inventions. A. Traditionally, and labor were used to do work. Wind human water animal B. and had been used to move wheels that would then move machine parts in mills. coal C. Then, was discovered to burn hotter and longer than wood and was used to create steam that would then be compressed in engines in order to move parts of machinery such as rotors or levers. D. Henry Bessemer discovered that coal could be used to heat mineral ore and remove the iron. Then he discovered that smelting coal and iron made. steel This became known as the. Bessemer process
11 An Energy Revolution Human/Animal power Water/Wind power Steam Power Electrical Power and Internal Combustion Engine
12 Key Industrial Resources: Early Industrial Revolution: Iron and Coal Iron: used to build machines, railroads. Late Industrial Revolution: Steel and Electricity Coal: burned to purify iron ore and produce steam.
13 New Production Methods Increased rate of production and made products less expensive!!! Interchangeable parts Assembly Line
14 Trains, steamships, automobiles, telegraphs, telephones all helped the world seem like a smaller place.
15 Steam Ship
16
17 Later Locomotives
18 Railroads spurred industrial growth by giving manufacturers a cheap way to transport material and finished products. Railroad boom created hundreds of thousands of new jobs for both railroad workers and miners. The railroads boosted England s agricultural and fishing industries, which could transport their products to distant cities. By making travel easier, railroads encouraged people to take distant city jobs.
19
20
21 Factory Work and Urban Factory work: Slums repetitive, boring, very dangerous hour days no job protection or compensation no minimum wage no child labor laws Women and children paid far less than men
22 Children At Work
23 Girl at Weaving Machine in Textile Mill
24 View Of Spinning Room
25 Textile Factory Workers in England looms 150, 000 workers , 000 looms 200, 000 workers , 000 looms Over 1 million workers
26 Coal Mining in Britain: ton of coal 50, 000 miners tons 200, 000 miners million tons 500, 000 miners million tons 1, 200, 000 miners
27 Children in Coal Mines
28
29 Living Conditions in Industrial Cities: People migrated to cities looking for work, especially unemployed farmers due to the Enclosure Acts (Urbanization) Cities became more common and far more populated Cities were dirty and dangerous. There was a lack of sanitation laws, no fire or police departments, no running water
30 City Life for the Working Class
31
32
33 ADVANCES IN SCIENCE AND MEDICINE: Antiseptics (kill germs, disinfects) Anesthesia (stops pain) Pasteurization (wine, juice, milk) Vaccinations (prevents virus based illnesses) These discoveries, along with increased food production, lead to an increase in life expectancy
34 Advances in scientific knowledge Louis Pasteur Discover of Germs = sanitary regulations Albert Einstein Theory of Relativity Charles Darwin Theory of Evolution Survival of the Fittest Sigmund Freud Theories of the human subconscious
35 RESULTS OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Change in Social Structure Capitalist Upper Class: - used their money to buy and build factories and run large businesses New Middle Class: - Professionals, investors, merchants-they were financially stable, educated, and they wanted to become upper class The New Working Class: - Lowly, unskilled, mechanical, poor, uneducated
36
37 RESULTS CONTINUED Labor movements: Goal was to provide better wages and working conditions for working class Workers organized into labor unions and threatened to strike Eventually, laws limiting child labor, shorter working hours, and safer working conditions were introduced
38 New Ideas About Society Capitalism: private ownership of property and the means of production, emphasis on making profit (Laissez Faire) Socialism: people as a whole (society) own property and businesses Communism: form of socialism that believed class struggle was unavoidable
39 Karl Marx Saw history as a continuing class struggle between the wealthy mid and upper classes and the working lower classes. (the Have s vs. the Have Not's) Marx wrote Communist Manifesto in predicted an international proletariat (working class) revolution. Marx failed to foresee the improved standard of living for workers, he also underestimated the power of nationalism. Marx disliked Capitalism because the Rich get Richer and the Poor get Poorer!
Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society?
 Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society? The Industrial Revolution Begins in Britain Inventions Spur Industrialization Improvements in Transportation The Railway Age Begins
Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society? The Industrial Revolution Begins in Britain Inventions Spur Industrialization Improvements in Transportation The Railway Age Begins
The Industrial Revolution. Cizj5c
 The Industrial Revolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5d Cizj5c What was the Industrial Revolution? a shift from an agricultural (farming) economy to one based on industry (manufacturing) Agricultural
The Industrial Revolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5d Cizj5c What was the Industrial Revolution? a shift from an agricultural (farming) economy to one based on industry (manufacturing) Agricultural
##X. During the Agricultural Revolution, farmers in Europe developed a new farming method called the Crop Rotation System.##
 History Question Bank F.2 (Set C) True / False The Industrial Revolution first began in the West in the early 19 th century. ##X. The Industrial Revolution first began in the mid-18 th century.## Before
History Question Bank F.2 (Set C) True / False The Industrial Revolution first began in the West in the early 19 th century. ##X. The Industrial Revolution first began in the mid-18 th century.## Before
The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution
 The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution What was the Agrarian Revolution? An increase in food production from a change in the methods of farming. Enclosure Movement Taking over and fencing off land that
The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution What was the Agrarian Revolution? An increase in food production from a change in the methods of farming. Enclosure Movement Taking over and fencing off land that
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines
 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines mass-produced products which lowered costs, increased profits,
In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines mass-produced products which lowered costs, increased profits,
The Industrial Revolution. Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization.
 The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3:
 Essential Question: What caused an Industrial Revolution in England in the 1800s? World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3: Industrial Revolution notes Unit 10 Test: Tuesday, March 5 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial
Essential Question: What caused an Industrial Revolution in England in the 1800s? World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3: Industrial Revolution notes Unit 10 Test: Tuesday, March 5 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Industrial Revolution. Great Britain: How and Why It Happened
 Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
All of this was about to change. Industrialization was coming!!
 England in 1700: Was a rural, agricultural society. Most people lived on farms. They grew their own food, made their own clothing and worked hard Most people were poor and, if harvest failed, they risked
England in 1700: Was a rural, agricultural society. Most people lived on farms. They grew their own food, made their own clothing and worked hard Most people were poor and, if harvest failed, they risked
T H E I N D U S T R I A L R E V O L U T I O N
 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
World History Review for AP Human Geography
 World History Review for AP Human Geography Age of European Discovery, Exploration, and Colonization The geographical knowledge acquired was crucial to the expansion of European political and economic
World History Review for AP Human Geography Age of European Discovery, Exploration, and Colonization The geographical knowledge acquired was crucial to the expansion of European political and economic
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
The Industrial Revolution Begins ( )
 World History: Connection to Today Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution Begins (1750
World History: Connection to Today Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution Begins (1750
1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance
 Ultimate Review 1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance of natural resources and large population
Ultimate Review 1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance of natural resources and large population
Industrial Revolution
 Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Causes Agricultural Revolution ENCLOSURES Forced small farmers off land to create large farms Done to INCREASE PRODUCTION as population increased Forced small
Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Causes Agricultural Revolution ENCLOSURES Forced small farmers off land to create large farms Done to INCREASE PRODUCTION as population increased Forced small
DBQ 12: THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: BEGINNINGS
 Document 1 This map shows the resources and canals of England in the eighteenth century. Canals began in 1756 England resources and canals circa 1700 Cotton Lead Tin Lead According to the map, what resources
Document 1 This map shows the resources and canals of England in the eighteenth century. Canals began in 1756 England resources and canals circa 1700 Cotton Lead Tin Lead According to the map, what resources
16: Students should explain how the industrial Revolution transformed the British economy
 16: Students should explain how the industrial Revolution transformed the British economy Industrial Revolution Overview For thousands of years following the Neolithic Revolution & rise of civilization,
16: Students should explain how the industrial Revolution transformed the British economy Industrial Revolution Overview For thousands of years following the Neolithic Revolution & rise of civilization,
The Industrial Revolution ( )
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION The industrial revolution was another of those extraordinary jumps forward in the story of civilization. Stephen Gardiner https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5dcizj5c John Green Crash
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION The industrial revolution was another of those extraordinary jumps forward in the story of civilization. Stephen Gardiner https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5dcizj5c John Green Crash
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION LEARNING GOAL 1: DESCRIBE THE CAUSES OF INDUSTRIALIZATION AND EXPLAIN THE ROLE TECHNOLOGY PLAYED IN INDUSTRIALIZATION.
 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION LEARNING GOAL 1: DESCRIBE THE CAUSES OF INDUSTRIALIZATION AND EXPLAIN THE ROLE TECHNOLOGY PLAYED IN INDUSTRIALIZATION. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 WHAT WAS THE INDUSTRIAL
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION LEARNING GOAL 1: DESCRIBE THE CAUSES OF INDUSTRIALIZATION AND EXPLAIN THE ROLE TECHNOLOGY PLAYED IN INDUSTRIALIZATION. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 WHAT WAS THE INDUSTRIAL
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution An Overview 1700-1900 CSCOPE World History Production Before The Industrial Revolution: Food All goods were made by hand or grown on the farm. Farmers grew just enough food to
The Industrial Revolution An Overview 1700-1900 CSCOPE World History Production Before The Industrial Revolution: Food All goods were made by hand or grown on the farm. Farmers grew just enough food to
9. Describe the factors available to Britain which promoted the success of the Industrial Revolution:
 Social Studies 9 Unit 6 Worksheet Chapter 5, Part 1. 1. Not all are violent. Some come as the result of and new ways of doing things. After the, the methods of growing foods, manufacturing and goods completely
Social Studies 9 Unit 6 Worksheet Chapter 5, Part 1. 1. Not all are violent. Some come as the result of and new ways of doing things. After the, the methods of growing foods, manufacturing and goods completely
The Industrial Revolution in Britain. AP World History
 The Industrial Revolution in Britain AP World History Today s main idea: What does it mean for a country to experience an Industrial Revolution? Why was Britain the first? Industrialization fundamentally
The Industrial Revolution in Britain AP World History Today s main idea: What does it mean for a country to experience an Industrial Revolution? Why was Britain the first? Industrialization fundamentally
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION CH. 9.1 THE BEGINNINGS OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Objectives 1. List two reasons why Industrialization began in England. 2. List one invention created to speed up industry. 3. List four
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION CH. 9.1 THE BEGINNINGS OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Objectives 1. List two reasons why Industrialization began in England. 2. List one invention created to speed up industry. 3. List four
Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1
 Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. New technology produced the Industrial Revolution. The Growth of Industry Main Idea:
Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. New technology produced the Industrial Revolution. The Growth of Industry Main Idea:
What was the Industrial Revolution?
 . What was the Industrial Revolution?! The Industrial Revolution was a fundamental change in the way goods were produced, from human labor to machines! The more efficient means of production and subsequent
. What was the Industrial Revolution?! The Industrial Revolution was a fundamental change in the way goods were produced, from human labor to machines! The more efficient means of production and subsequent
ECON European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett. Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.
 ECON 30733 European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to lecture, which change in agriculture will lead
ECON 30733 European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to lecture, which change in agriculture will lead
Careers Note Sheet and Timeline. Agrarian Trades a trade involving farming or natural resources:
 1700 s Careers Note Sheet and Timeline Artisan Trades a skilled trade, a job requiring the creation of a product Blacksmith Silversmith Wheelwright Cooper Carpenter Cabinetmaker Milliner Printer Shoemaker
1700 s Careers Note Sheet and Timeline Artisan Trades a skilled trade, a job requiring the creation of a product Blacksmith Silversmith Wheelwright Cooper Carpenter Cabinetmaker Milliner Printer Shoemaker
Why did the Industrial Rev. begin in New England? Define Capitalism- Define Free Enterprise-
 Warm Up 1/14 What city on the east coast were the British successful at attacking? What city on the east coast were they unsuccessful at attacking? What did the British decide after they lost at the Battle
Warm Up 1/14 What city on the east coast were the British successful at attacking? What city on the east coast were they unsuccessful at attacking? What did the British decide after they lost at the Battle
Industrialization. From Farm to Factories: Urbanization Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system?
 Industrialization From Farm to Factories: Urbanization Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system? Problem How do you maximize the land around you? Solution How do you increase
Industrialization From Farm to Factories: Urbanization Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system? Problem How do you maximize the land around you? Solution How do you increase
Unit 7 Expansion of Europe
 Unit 7 Expansion of Europe I. Agricultural Revolution (17 th & 18 th Century) A. Before 1. Peasants and artisans life were same as Middle Ages a. Most people battles hunger and lacked sufficient clothing
Unit 7 Expansion of Europe I. Agricultural Revolution (17 th & 18 th Century) A. Before 1. Peasants and artisans life were same as Middle Ages a. Most people battles hunger and lacked sufficient clothing
Part 1: The Age of Industrialism and Industry. Was the rise of industry good for the US?
 Part 1: The Age of Industrialism and Industry Was the rise of industry good for the US? New Inventions & Technologies Capitalists provide financial backing for scientific research new inventions funds
Part 1: The Age of Industrialism and Industry Was the rise of industry good for the US? New Inventions & Technologies Capitalists provide financial backing for scientific research new inventions funds
Upcoming Assignments. (Storck): CCoT Essay due Monday, May 2 Ch. 16 & Ch. 17 Reading Guides due Monday, May 9
 Upcoming Assignments (Storck): CCoT Essay due Monday, May 2 Ch. 16 & Ch. 17 Reading Guides due Monday, May 9 1750-1914 Modern era of history. It s very connected! The Industrial Revolution AP World History
Upcoming Assignments (Storck): CCoT Essay due Monday, May 2 Ch. 16 & Ch. 17 Reading Guides due Monday, May 9 1750-1914 Modern era of history. It s very connected! The Industrial Revolution AP World History
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion
 I. Create an episode map on westward expansion A. What is a market?? What do people do at markets?? What is an example of a market?? What are some markets that we use frequently?? I. The Industrial Revolution
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion A. What is a market?? What do people do at markets?? What is an example of a market?? What are some markets that we use frequently?? I. The Industrial Revolution
THE RISE OF INDUSTRIALIZATION
 THE RISE OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Day 1 Goals Define Key terms Related to Industrialization Understand what is needed for industrialization to occur. Understand what the experiences of workers was during the
THE RISE OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Day 1 Goals Define Key terms Related to Industrialization Understand what is needed for industrialization to occur. Understand what the experiences of workers was during the
The Market Revolution. The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages
 The Market Revolution The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages 274-279. U.S. Markets Expand Early 19 th Century Workers produce own goods Farms self-sufficient Trade surplus at local markets Purchase luxuries
The Market Revolution The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages 274-279. U.S. Markets Expand Early 19 th Century Workers produce own goods Farms self-sufficient Trade surplus at local markets Purchase luxuries
Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation
 1865-1914 Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation 1865-1914 Manufacturing areas were created near
1865-1914 Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation 1865-1914 Manufacturing areas were created near
INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT
 CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRY INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT The recent success of Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and other Asian countries is a dramatic change from the historic dominance of world industry by Western countries.
CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRY INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT The recent success of Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and other Asian countries is a dramatic change from the historic dominance of world industry by Western countries.
The Industrial Revolution (Part I)
 Unit Three: Modern Europe (1800-1914) Chp. 7 The Birth of Modern Industrial Society Introduction: The Industrial Revolution (Part I) The Industrial Revolution was a long, slow process in which production
Unit Three: Modern Europe (1800-1914) Chp. 7 The Birth of Modern Industrial Society Introduction: The Industrial Revolution (Part I) The Industrial Revolution was a long, slow process in which production
Chapter 22. The Early Industrial Revolution,
 Chapter 22 The Early Industrial Revolution, 1760-1851 23 1 Essential Question: What was so revolutionary about the Industrial Revolution? 23 2 Key Terms Industrial Revolution agricultural revolution mass
Chapter 22 The Early Industrial Revolution, 1760-1851 23 1 Essential Question: What was so revolutionary about the Industrial Revolution? 23 2 Key Terms Industrial Revolution agricultural revolution mass
Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes
 Name: Date: Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes The Industrial Revolution Begins 1. 1700 s most people were farmers making cloth, tools, furniture by 2. 1800 s people began making cloth and other goods
Name: Date: Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes The Industrial Revolution Begins 1. 1700 s most people were farmers making cloth, tools, furniture by 2. 1800 s people began making cloth and other goods
Learning Goal: I will understand the economic differences between the North and South in the years leading up to the Civil War.
 HOOK HOOK What conclusions can you make about the impact of the railway development in the U.S.? What impact will this make on the nation before and during the Civil War? North and South Benchmark: SS.8.A.4.10
HOOK HOOK What conclusions can you make about the impact of the railway development in the U.S.? What impact will this make on the nation before and during the Civil War? North and South Benchmark: SS.8.A.4.10
Big Business and Labor:
 Big Business and Labor: "God gave me money", and he did not apologize for it. He felt at ease and righteous following John Wesley s dictum, "gain all you can, save all you can, and give all you can. -John
Big Business and Labor: "God gave me money", and he did not apologize for it. He felt at ease and righteous following John Wesley s dictum, "gain all you can, save all you can, and give all you can. -John
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!
 1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
Industrialism in America. Building the American Powerhouse
 Industrialism in America Building the American Powerhouse The Brooklyn Bridge - 1883 Significance: a symbol of America s transition from a rural to an industrial nation. Impact of Industry On different
Industrialism in America Building the American Powerhouse The Brooklyn Bridge - 1883 Significance: a symbol of America s transition from a rural to an industrial nation. Impact of Industry On different
MIDTERM 1 VERSION #2
 Gregory Clark Econ 110B, Winter 2001 MIDTERM 1 VERSION #2 A total of 100 points are possible. Last Name: First Name: Your Student ID Number: - - Part A: Multiple Choice Questions (25 questions, each of
Gregory Clark Econ 110B, Winter 2001 MIDTERM 1 VERSION #2 A total of 100 points are possible. Last Name: First Name: Your Student ID Number: - - Part A: Multiple Choice Questions (25 questions, each of
What is an Economic System?
 Economic Systems What is an Economic System? Economic system: how society uses resources to satisfy people s wants Seeks to answer the three economic questions: What to produce? How to produce it? For
Economic Systems What is an Economic System? Economic system: how society uses resources to satisfy people s wants Seeks to answer the three economic questions: What to produce? How to produce it? For
Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, CE
 Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, 1750-1914 CE 6 Major Changes Population Growth Energy Communication and Transportation Industry Liberalism Imperialism 1: Population
Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, 1750-1914 CE 6 Major Changes Population Growth Energy Communication and Transportation Industry Liberalism Imperialism 1: Population
Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important
 Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important effect of this new canal? How did the original Erie Canal
Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important effect of this new canal? How did the original Erie Canal
The Urban Game. Aim: How did industrialization reshape the English countryside?
 The Urban Game Aim: How did industrialization reshape the English countryside? You will need: Blank legal sized-paper Pencil with eraser Background Material reading Change over Time chart Drawing guide
The Urban Game Aim: How did industrialization reshape the English countryside? You will need: Blank legal sized-paper Pencil with eraser Background Material reading Change over Time chart Drawing guide
Urbanization and Industrialization
 Urbanization and Industrialization You will create your own village and see the development of urbanization and industrialization during the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. Over several rounds,
Urbanization and Industrialization You will create your own village and see the development of urbanization and industrialization during the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. Over several rounds,
Key Issue 1: Where is Industry Distributed?
 Revised 2017 NAME: PERIOD: Rubenstein: The Cultural Landscape (12 th edition) Chapter Eleven Industry and Energy (pages 382 thru 429) This is the primary means by which you will be taking notes this year
Revised 2017 NAME: PERIOD: Rubenstein: The Cultural Landscape (12 th edition) Chapter Eleven Industry and Energy (pages 382 thru 429) This is the primary means by which you will be taking notes this year
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion
 I. Create an episode map on westward expansion I. The Industrial Revolution led to an increased production by machines instead of humans or animals. A. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion I. The Industrial Revolution led to an increased production by machines instead of humans or animals. A. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain
Urbanization Mapping Activity,
 Urbanization Mapping Activity, 1746 1850 Organization & Materials: Everyone will need a pencil. Get into groups of 3. Each group will need newsprint. Directions: Read each of the following slides & add
Urbanization Mapping Activity, 1746 1850 Organization & Materials: Everyone will need a pencil. Get into groups of 3. Each group will need newsprint. Directions: Read each of the following slides & add
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy
 Chapter 11 Lecture Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Tim Scharks Green River College Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why
Chapter 11 Lecture Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Tim Scharks Green River College Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy
 Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why Do Industries Face Resource Challenges? 4. Why Are
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why Do Industries Face Resource Challenges? 4. Why Are
Industrialization. From Farm to Factories: Urbanization. Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system?
 Industrialization From Farm to Factories: Urbanization Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system? Problem How do you maximize the land around you? Solution How do you increase
Industrialization From Farm to Factories: Urbanization Context: What was the situation in England with the open field system? Problem How do you maximize the land around you? Solution How do you increase
THE MARKET REVOLUTION AND AMERICA S REGIONAL IDENTITY ( )
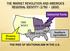 REGIONAL IDENTITY (1790 1850) Industrial North Western Frontier Southern Agriculture THE RISE OF SECTIONALISM IN THE U.S. The Role of Transportation (1806 1853) Native resistance slowed, but did not stop
REGIONAL IDENTITY (1790 1850) Industrial North Western Frontier Southern Agriculture THE RISE OF SECTIONALISM IN THE U.S. The Role of Transportation (1806 1853) Native resistance slowed, but did not stop
The Secret of Capitalist Exploitation
 The Secret of Capitalist Exploitation Day in and day out, in plants and factories all over this country, workers talk about A fair day s wages for a fair day s work. This has been one of the main mottos
The Secret of Capitalist Exploitation Day in and day out, in plants and factories all over this country, workers talk about A fair day s wages for a fair day s work. This has been one of the main mottos
AN OHIO WATER MILL. Learning Objective. Video Synopsis. Teacher Background
 Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
The Model T Takes Off
 UNIT 5 WEEK 3 Read the article The Model T Takes Off before answering Numbers 1 through 5. The Model T Takes Off The invention of the automobile in the late 19th century was one of the greatest technological
UNIT 5 WEEK 3 Read the article The Model T Takes Off before answering Numbers 1 through 5. The Model T Takes Off The invention of the automobile in the late 19th century was one of the greatest technological
Chapter 11 Industry and Manufacturing
 AP Human Geography Chapter 11 Industry and Manufacturing Key Issues Where is industry distributed? Why are situation and site factors important? Why does industry cause pollution? Why are situation and
AP Human Geography Chapter 11 Industry and Manufacturing Key Issues Where is industry distributed? Why are situation and site factors important? Why does industry cause pollution? Why are situation and
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products.
 Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution
 Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution Goods and products were made in numerous places Most interesting relationship was Britain & India (their colony) India s products became
Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution Goods and products were made in numerous places Most interesting relationship was Britain & India (their colony) India s products became
Natural Resources. A. Soil (Arable land is land that can be farmed) B. Water C. Plants such as trees or even food crops D. Animals E. The Sun F.
 Economic Geography Natural Resources A natural resource is anything from nature that can be of value to humans. Renewable resources are natural resources that can replenish themselves with proper management
Economic Geography Natural Resources A natural resource is anything from nature that can be of value to humans. Renewable resources are natural resources that can replenish themselves with proper management
1. Draw a river across your paper connecting east to west the river should be 1 inch wide 2. Draw a wooden bridge across the river 3.
 Urban game Pre game set up 1. Draw a river across your paper connecting east to west the river should be 1 inch wide 2. Draw a wooden bridge across the river 3. Draw 4 roads originating from each direction
Urban game Pre game set up 1. Draw a river across your paper connecting east to west the river should be 1 inch wide 2. Draw a wooden bridge across the river 3. Draw 4 roads originating from each direction
A. Abundance of natural resources (oil, timber, iron, gold, cattle, copper)
 History 271 Devine Spring 2015 INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE LATE NINETEENTH CENTURY An Incredible Economic Expansion 1860-1900 $3 billion in manufactures (1869) $13 billion (1900) Iron ore production quadruples
History 271 Devine Spring 2015 INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE LATE NINETEENTH CENTURY An Incredible Economic Expansion 1860-1900 $3 billion in manufactures (1869) $13 billion (1900) Iron ore production quadruples
The Industrial Revolution. The Big History of our Planet Threshold 8
 The Industrial Revolution The Big History of our Planet Threshold 8 This lecture: The Industrial Revolution The moment of breakthrough: From c. 1800, growth/innovation took off: 1. Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution The Big History of our Planet Threshold 8 This lecture: The Industrial Revolution The moment of breakthrough: From c. 1800, growth/innovation took off: 1. Industrial Revolution
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 7 th Grade Technology Unit of Study Unit 5 Change Unit Title Industrial Revolution & Society s Response Power Pacing
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 7 th Grade Technology Unit of Study Unit 5 Change Unit Title Industrial Revolution & Society s Response Power Pacing
Name: Group: 404- Date: Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization
 Name: Group: 404- Date: Notes 1.6 Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization Pages that correspond to this presentation: The First Phase of Industrialization:
Name: Group: 404- Date: Notes 1.6 Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization Pages that correspond to this presentation: The First Phase of Industrialization:
Industrialization Practice Test
 Class: Date: Industrialization Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What contribution did Henry Bessemer make to the steel industry?
Class: Date: Industrialization Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What contribution did Henry Bessemer make to the steel industry?
Working in an Industrial World
 Working in an Industrial World What was it like to work in an industrial setting? Before the Industrial Revolution in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, people worked out of their homes
Working in an Industrial World What was it like to work in an industrial setting? Before the Industrial Revolution in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, people worked out of their homes
Opinion: Workers need to prepare for changing technology on the job
 Opinion: Workers need to prepare for changing technology on the job By Project Syndicate, adapted by Newsela staff on 11.24.15 Word Count 718 Automated robots build a 2015 Chrysler 200 at the Sterling
Opinion: Workers need to prepare for changing technology on the job By Project Syndicate, adapted by Newsela staff on 11.24.15 Word Count 718 Automated robots build a 2015 Chrysler 200 at the Sterling
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 21 ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 21 Politics and Prosperity (1920 1929) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights reserved.
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 21 Politics and Prosperity (1920 1929) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights reserved.
MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
 1 MANUFACTURING PROCESSES - AMEM 201 Lecture 1: DR. SOTIRIS L. OMIROU The Manufacturing is a DRIVING FORCE for any economy We are living in an environment that is created and reshaped by manufacturing
1 MANUFACTURING PROCESSES - AMEM 201 Lecture 1: DR. SOTIRIS L. OMIROU The Manufacturing is a DRIVING FORCE for any economy We are living in an environment that is created and reshaped by manufacturing
Unit 1: Fundamental Concepts. Types of Economic Systems. Types of Economic Systems
 Unit 1: Fundamental Concepts 1-2 Economic Systems 1 Ch. 2 Types of Economic Systems An economic system is the way in which a society uses its resources to satisfy its people s unlimited wants. An economic
Unit 1: Fundamental Concepts 1-2 Economic Systems 1 Ch. 2 Types of Economic Systems An economic system is the way in which a society uses its resources to satisfy its people s unlimited wants. An economic
Ch. 1 Prehistory Test
 Name: Date: 1. In which order did the occupations listed below most likely develop in human history? (A) farmers (B) traders (C) nomadic herders (D) hunters and gatherers A. A,B,C,D B. B,D,A,C C. C,A,B,D
Name: Date: 1. In which order did the occupations listed below most likely develop in human history? (A) farmers (B) traders (C) nomadic herders (D) hunters and gatherers A. A,B,C,D B. B,D,A,C C. C,A,B,D
Activity: The Urban Game. Simulating the Impact of the Industrial Revolution. Lauren Webb {a social studies life}
 Activity: The Urban Game Simulating the Impact of the Industrial Revolution Lauren Webb. 2015. {a social studies life} Unit: Industrialization Pivotal Questions (during/after activity) 1) Explain the changes
Activity: The Urban Game Simulating the Impact of the Industrial Revolution Lauren Webb. 2015. {a social studies life} Unit: Industrialization Pivotal Questions (during/after activity) 1) Explain the changes
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS? INDUSTRIAL LOCATION Situation factors Location near inputs Location near markets Transport choices Site factors Land Labor Capital
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS? INDUSTRIAL LOCATION Situation factors Location near inputs Location near markets Transport choices Site factors Land Labor Capital
1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepreneurship technology
 Intro to Economics Review Name Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepreneurship technology 2. Describe a situation and then explain the opportunity
Intro to Economics Review Name Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepreneurship technology 2. Describe a situation and then explain the opportunity
Types of Economic Systems
 Name: Period: Types of Economic Systems What is an Economy? Economy: or exchange of goods and services by a group : things to be traded, bought, or sold : work done in exchange for payment : work force,
Name: Period: Types of Economic Systems What is an Economy? Economy: or exchange of goods and services by a group : things to be traded, bought, or sold : work done in exchange for payment : work force,
Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4)
 Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4) You re largely on your own for this chapter, but email me if you need help or have concerns. There are more questions than normal, but they re shorter
Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4) You re largely on your own for this chapter, but email me if you need help or have concerns. There are more questions than normal, but they re shorter
The Rise of Big Business. Chapter 14 Section 2 The Second Industrial Revolution Riddlebarger
 The Rise of Big Business Chapter 14 Section 2 The Second Industrial Revolution Riddlebarger Capitalism An economic system in which private businesses run most industries. Competition determines prices
The Rise of Big Business Chapter 14 Section 2 The Second Industrial Revolution Riddlebarger Capitalism An economic system in which private businesses run most industries. Competition determines prices
The Farming Industry of Texas After the Civil War. Suggested Instructional Activity: Bow Tie Strategy
 The Farming Industry of Texas After the Civil War Suggested Instructional Activity: Bow Tie Strategy Questions/prompts for students to consider as they read each document: What changes occurred in the
The Farming Industry of Texas After the Civil War Suggested Instructional Activity: Bow Tie Strategy Questions/prompts for students to consider as they read each document: What changes occurred in the
1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. 2. Describe a situation and then explain the opportunity cost of that action.
 Intro to Economics Review Name _ Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. 2. Describe a situation and then explain the opportunity cost of that action. 3. List the four
Intro to Economics Review Name _ Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. 2. Describe a situation and then explain the opportunity cost of that action. 3. List the four
Code Name: Part 1: (71 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.)
 Code Name: Part 1: (71 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to class, what was the likely relationship between agricultural improvement and industrialization? a. Improvements
Code Name: Part 1: (71 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to class, what was the likely relationship between agricultural improvement and industrialization? a. Improvements
Alabama Moves Ahead. Chapter 8
 Alabama Moves Ahead Chapter 8 Lesson 1 Rights and Reforms The Bourbon Redeemers approved a constitution in 1875. Remember, they wanted to take away the right to vote from men who were poor and from African
Alabama Moves Ahead Chapter 8 Lesson 1 Rights and Reforms The Bourbon Redeemers approved a constitution in 1875. Remember, they wanted to take away the right to vote from men who were poor and from African
HISTORICALLY, agriculture meant the practice of
 The Development of Mechanical Technology in Agriculture HISTORICALLY, agriculture meant the practice of farming or growing animals and plants. Today, it is better defined as the science and art of growing
The Development of Mechanical Technology in Agriculture HISTORICALLY, agriculture meant the practice of farming or growing animals and plants. Today, it is better defined as the science and art of growing
1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepunuership human capital or technology
 Intro to Economics Review Name Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepunuership human capital or technology 2. Describe a situation and then
Intro to Economics Review Name Hour 1. List the five factors of production and give and example of each. land labor capital entrepunuership human capital or technology 2. Describe a situation and then
Manufacturing Technology
 Manufacturing Technology What is manufacturing technology? A manufacturing technology is a system of people, machines, and materials that mass-produce goods for the market. Automation is manufacturing
Manufacturing Technology What is manufacturing technology? A manufacturing technology is a system of people, machines, and materials that mass-produce goods for the market. Automation is manufacturing
Industrialization and Urbanization. Standard 5-3.4
 Industrialization and Urbanization Standard 5-3.4 Signs of Change 1 in 6 or 16% of people lived in cities by 1860 1 in 3 or 33% of people lived in cities by 1900 People were moving from farms to cities
Industrialization and Urbanization Standard 5-3.4 Signs of Change 1 in 6 or 16% of people lived in cities by 1860 1 in 3 or 33% of people lived in cities by 1900 People were moving from farms to cities
1. Define: Cottage Industry a business or manufacturing activity carried on in a person's home. Traditional Economy Less Developed Countries Weaving
 1. Define: Cottage Industry a business or manufacturing activity carried on in a person's home. Traditional Economy Less Developed Countries Weaving Tool/weapon building Pottery Crafts 1. Define: Life
1. Define: Cottage Industry a business or manufacturing activity carried on in a person's home. Traditional Economy Less Developed Countries Weaving Tool/weapon building Pottery Crafts 1. Define: Life
Agriculture and Society. Pa E & E Standards 4.4
 Agriculture and Society Pa E & E Standards 4.4 I. Background 1. Let s look at Agriculture in the U.S. and in Pennsylvania. 2. Agriculture in the U.S. has changed a lot in the last 200 years. In 1790, 95%
Agriculture and Society Pa E & E Standards 4.4 I. Background 1. Let s look at Agriculture in the U.S. and in Pennsylvania. 2. Agriculture in the U.S. has changed a lot in the last 200 years. In 1790, 95%
The gilded age ( )
 The gilded age (1870-1900) This unit will be divided into two major parts: 1. industrialization & the labor movement 2. The development of cities and city life Section one: Changes in the u.s. Gild To
The gilded age (1870-1900) This unit will be divided into two major parts: 1. industrialization & the labor movement 2. The development of cities and city life Section one: Changes in the u.s. Gild To
Come into tutoring to get the placard letters. Discussion questions at the end. Cotton Gin and Spinning Jenny
 Come into tutoring to get the placard letters. Discussion questions at the end. Cotton Gin and Spinning Jenny Textiles were the first product of the Industrial Revolution. Prior to the Industrial Revolution,
Come into tutoring to get the placard letters. Discussion questions at the end. Cotton Gin and Spinning Jenny Textiles were the first product of the Industrial Revolution. Prior to the Industrial Revolution,
Do Now: Why do you think the Industrial Revolution was referred to as a revolution?
 Do Now: Why do you think the Industrial Revolution was referred to as a revolution? The Industrial Revolution was the major shift of technological, socioeconomic and cultural conditions in the 1800s. 1
Do Now: Why do you think the Industrial Revolution was referred to as a revolution? The Industrial Revolution was the major shift of technological, socioeconomic and cultural conditions in the 1800s. 1
