Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells
|
|
|
- Lesley Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 61 Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Victor Prajapati. Department ofmicroelectronic Engineering, 82 Lomb Memorial Dr., Rochester, NY Abstract Fully processed CMOS Si wafers were reclaimed to make solar cells, while ensuring an acceptable efficiency loss of 15%. This project successfully developed a wafer reclaim process coupled with a solar cell fabrication process. The optimum efficiency obtained was 12.4% using prime wafers and surface texturing, while comparably processed reclaimed wafers were able to achieve 1.5% efficiency. I. INTRODUCTION Demand for electricity is increasing at an exponential rate, our consumption of coal is harmful to the environment and solar cells seem to be a promising alternative. One key factor for future implementation of solar cells is cost per watt, reclaiming scrapped silicon wafers into solar cells may be a viable option. This project is aimed towards the use of reclaimed silicon wafers for reducing cost while ensuring acceptable efficiencies. Fully processed CMOS Si wafers were reclaimed to make solar cells. The reclaim process removes l~im of the top surface by grinding, this was done to ensure all deposited and diffused layers have been removed. After the front grind process, wafers were polished using chemical mechanical polishing (CMP), followed by a clean using wet processes. II. THEORY A. Wafer Reclaim Wafers that have undergone CMOS processing may have many deposited layers as well as diffused layers that need to be removed before subsequent processing. liim of the top surface ensures the removal of all deposited and diffused layers. The wafers were than polished in order to be of the same surface roughness of prime wafers, this step may be skipped in future work. Once polished, a modified RCA clean was used to ensure the removal of contaminants. A modified SC2 is used initially to remove metal contaminates. The higher concentration of hydrochloric acid etches off iesidual metals that may have adhered to the substrate during the wafer grind process. The SC 1 bath is used to ensure the removal of organic contaminants, the wafers are then etched in HF to remove the native oxide. Once the native oxide is removed a subsequent metal contaminant clean is utilized to further ensure the removal of metals. Between cleans is an assumed 5mm DI water rinse clean undergone at room temperature. Fig. 1 shows the entire clean process. 3mL H2 7m1 H22 4m1 HCI, ~,-,. 4SOOmLH2O 7mLH1O2 3mLNH4OH ~ mlh2o lomi.kf, 45mL H2 7m1 H21 3mLHCI Figure 1 Wafer Cleaning Process B. Solar Cell Figure 2 shows a typical solar cell with an n-type emitter on a p-type wafer. An if the hv of the incoming light is greater than the bandgap of silicon, an electron hole pair is generated. A fraction of the generated electron hole pairs are collected by the depletion region and internal electric field. If the carriers are not recombined, they are collected by the metal fingers and grid. t4 Metal,~ e 2 Typical~..olar CL..~, V. Prajapati Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Page 61
2 62 VL Figure 3 Solar Cell Circuit Diagram Figure 3 shows a single diode with simulated parasitic series and shunt resistances. To obtain the maximum amount of power from the solar generated current (IR) to the load, the series resistances should be minimized and the shunt resistance should be maximized. Two key parameters when considering solar cells are the short circuit current and the open circuit voltage, these parameters are highly dependant on series and shunt resistances as shown in equation 1 and equation 2. voc = nkt~[ir+lv~] q 4 Equation 2 Solar cell open circuit voltage Figure 4 Experiment 1 Cross-.~.~. Figure 4 shows the cross-section of the devices fabricated in experiment 1, the substrate chosen was an n-type wafer with a p-type emitter due to its abundance at RIT. It is ideal to use a p-type substrate with an n-type emitter for enhanced minority carrier mobility and future work can be to do so. The thick field oxide is used as an implant block for the spin on dopant used to diffuse, the n+ region is used as a back surface field to sweep holes back into the depletion region to be collected. I ~~ 3W1~7~ ~2H~ A. Experimenti III. EXPERIMENTS The goal of the first experiment was to fabricate working solar cells using different simulated diffusion profiles as well as oxide thicknesses. Table 1 shows all the treatment combinations X~ OXIDE INTEGRATED AVERAGE CONDITION (nm) (nm) DOSE DOPING 9 C FOR 2OMIN 1 C FOR 2OMIN 11 C FOR 2OMIN TABLE I OnT A TA ( TAT A On LI IT * PUn VALUES 25/5 167/ /25 1/2 TLM Stwcture Test tliodes >.. I Figure 5 Metal finger mask design The top metal finger grid design was also varied for all experiments to detei-mine what the optimum spacing between fingers and the optimum metal thickness is. Figure 5 shows this top level metal mask, which also includes TLM structures and test diodes to be able to extract contact resistance and diode idealities. The nomenclature for the mask is line width! spacing and all numbers are in microns. B. Experiment II E E Using the optimum diffusion profile found m experiment 1, E E+16 fully processed CMOS wafers were reclaimed and were E E+16 processed into solar cells. Using the tools and process parameters shown in figure 6 coupled with the wet processes shown in figure 1, reclaimed wafers had 1 OOum of their top layer removed were chemical-mechanically polished and then wet cleaned. V. Prajapati Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Page 62
3 I Buehler Eromet IV Wafer PlaMn5peed~ ~C) RPM Pcevvurov 4p~ I Removal Ra~ov i~ um!mmn Gth~der CMOS cw~er~ j Strassbauçjh CMP Tool Platen Speeth 5RPM Prevaurpe P pal Slurry DrIp Ruben 1 clrop/aec ~TIr.5 ~4 63 4nm Ox Exp 4nm Simulated 1 O.8_... ~.3.6~ ~.2 t.4t.1.2 C. Experiment III Experiment III s goal was to increase efficiency by increasing the surface area of the solar cell and also attempting to reduce reflection loss. This was done by surface texturing as seen in figure Figure 9 4nm Oxide spectral response and simulated 1.8 m.6 ~.4.2 Inverted pyramids by KOR etching in the configuration shown in figure 7 were achieved as well as top and back surface fields for enhanced carrier collection. A. Experiment I.5 Figure 7 Cross-section of modified PERL design[1] IV. RESULTS loonm Ox Spectral Response Wavelength(nm) Figure 8 loonm Oxide spectral response and simulated I:.2.4 t~.1.2 z E V., C U Figure 1 SOOnm Oxide spectral response and simulated.6.5 ~.4 ~.3. 5nm Oxide ~ 4nm Oxide loonm Oxide Figure 11 Experiment 1 Spectral Response V. Prajapati Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Page 63
4 Voltage C. Experiment III 4 I:: ~-~ 4oa~rn~i øxl4e ~*~5o~im oxide ~ ijigt~ni~ o~id~.~. - image of textured fabricated solar cell Figure 12 Solar cell IV characteristic B. Experiment II * loonm Oxide.6,5 ~.4 loonm Reclaim F 1.3 t Figure 13 Reclaim wafer spectral response z C C) C SEM image of textured fabricated solar cell -.4. ~1nm Reclaimed ~ 1nm Figure 14 Reclaim wafer IV characteristic V. Prajapati Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Page 64
5 n.3 U.2.1 Structured Structured Reclaim Figure 166 Reclaimed textured cell spectral response TABLE 2 SOLAR CELL RESULTS Jsc VC FILL 1 (%) (majcm2) (V) FACTOR (%) 5nm Oxide nm Oxide loonmoxide loonm Ox. Reclaim Surface Texturing Surface Text. Reclaim wafer and wet etch the gettered sites preferentially and under a scanning electron microscope it will be easy to see where the gettered sites are located. As expected the generated current for the reclaim wafers is not as high as the current generated by the prime wafers. This is can be attributed to a lower carrier lifetime, the carriers are being recombined before they are collected by the metal finger scheme. Figure 15A-C show the fabricated textured cell s crosssection which is similar to the simulated desired cross-section shown in figure 7. The pyramid mask design was 3jimX3~m squares, but after undercutting they were fabricated at 37.5.irnX37.5~im squares as shown in the scanning electron microscope pictures. This increased the surface area of the device by 5%, although the irradiance through the increased surface area is constant. Another advantage of the inverted pyramid design is its decrease in reflection as shown in figure 2. A measurement that can be taken as future work is scatterometry measurements, by shinning light incident to the sample and collecting reflected light at various angles, an experimental reflection value can be obtained by adding all of the individual angle s reflection measurement. Figure 16 shows the reclaim wafer performance as compared to a prime wafers performance, and as expected the reclaim wafer has a decrease in spectral response as shown in table 2 as well. VI. CONCLUSION The goal of developing a process to reclaim wafers into solar cells has successfully completed. An acceptable efficiency loss of 15% has been demonstrated comparing prime and reclaimed silicon as shown in table 2. This experiment has shown that using reclaimed silicon can be a viable option to meet the future electricity demands. ACKNOWLEDGMENT V. DISCUSSION Figures 8-1 show the spectral response plotted with the simulated. Figure 8 shows the 1 OOnm oxide device performance not being hindered by its reflection loss, where as the other figures 9 and 1 show significant device performance decreases at the reflection peaks or the valleys. These were proof of concept measurements to accurately indicate that reflection was truly hindering the performance of the device and using an optimum oxide thickness increases device performance. This conclusion is clearly shown in figure 11 where the spectral response of all three devices are plotted together. It shows that the loonm oxide has the best device performance, which is also reflected in figure 12 s current-voltage characteristic. The loonm device generates more current as expected from its spectral response. Experiment II s results are shown in figures 13 and 14, where it could be shown that the reclaim wafer has a shifted spectral response and does not perform as well as the prime wafer. At 6nm the reclaim wafer has a decrease in response as shown in figure 13, this may be attributed to gettered sites in the CMOS process the reclaim wafers had undergone previously. In future work, it is possible to cleave the reclaim The author would like to acknowledge all of those who have helped along the way, including, but not limited to SMFL, NPRL and 1iE. If it weren t for the people around us, we would be nothing. REFERENCES [1] N. Savage. (1999, December). Photovoltaics: Small and efficient wins the race Laser Focus World [Online] Available: V. Prajapati Reclaimed Silicon Solar Cells Page 65
HOMEWORK 4 and 5. March 15, Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook:
 HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
HOMEWORK 4 and 5 March 15, 2009 Homework is due on Monday March 30, 2009 in Class. Chapter 7 Answer the following questions from the Course Textbook: 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6*, 7.7, 7.9*, 7.10*, 7.16, 7.17*,
ET3034TUx High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells
 ET3034TUx - 4.4 - High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells In the previous block we have discussed various technological aspects on crystalline silicon wafer based PV technology. In this
ET3034TUx - 4.4 - High efficiency concepts of c- Si wafer based solar cells In the previous block we have discussed various technological aspects on crystalline silicon wafer based PV technology. In this
Isolation Technology. Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Isolation Technology Dr. Lynn Fuller Motorola Professor 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041
IBM Research Report. Low-cost, High Efficiency Solar Cells on Scrapped CMOS Silicon
 RC24941 (W1001-102) January 29, 2010 Materials Science IBM Research Report Low-cost, High Efficiency Solar Cells on Scrapped CMOS Silicon Joel P. de Souza, Daniel Inns*, Katherine L. Saenger, Harold J.
RC24941 (W1001-102) January 29, 2010 Materials Science IBM Research Report Low-cost, High Efficiency Solar Cells on Scrapped CMOS Silicon Joel P. de Souza, Daniel Inns*, Katherine L. Saenger, Harold J.
2. High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells
 2 High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells Students: Karthick Murukesan, Sandeep S S, Meenakshi Bhaisare, Bandana Singha, Kalaivani S and Ketan Warikoo Faculty members: Anil Kottantharayil, B M Arora,
2 High Efficiency Crystalline Si Solar Cells Students: Karthick Murukesan, Sandeep S S, Meenakshi Bhaisare, Bandana Singha, Kalaivani S and Ketan Warikoo Faculty members: Anil Kottantharayil, B M Arora,
MEMS Surface Fabrication
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING MEMS Surface Fabrication Dr. Lynn Fuller webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering Rochester Institute
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING MEMS Surface Fabrication Dr. Lynn Fuller webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee Electrical and Microelectronic Engineering Rochester Institute
TWO-DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF EWT MULTICRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS AND COMPARISON WITH THE IBC SOLAR CELL
 TWO-DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF EWT MULTICRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS AND COMPARISON WITH THE IBC SOLAR CELL Mohamed M. Hilali, Peter Hacke, and James M. Gee Advent Solar, Inc. 8 Bradbury Drive S.E, Suite,
TWO-DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF EWT MULTICRYSTALLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS AND COMPARISON WITH THE IBC SOLAR CELL Mohamed M. Hilali, Peter Hacke, and James M. Gee Advent Solar, Inc. 8 Bradbury Drive S.E, Suite,
162 Solar Energy. front contact (metal grid) serial connections (to the back contact of the next cell) p-type wafer back contact
 162 Solar Energy serial connections (to the back contact of the next cell) front contact (metal grid) antireflective coating n + -type emitter p + -type layer p-type wafer back contact 200 μm Figure 12.8:
162 Solar Energy serial connections (to the back contact of the next cell) front contact (metal grid) antireflective coating n + -type emitter p + -type layer p-type wafer back contact 200 μm Figure 12.8:
EE 143 FINAL EXAM NAME C. Nguyen May 10, Signature:
 INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
INSTRUCTIONS Read all of the instructions and all of the questions before beginning the exam. There are 5 problems on this Final Exam, totaling 143 points. The tentative credit for each part is given to
Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell. Jennifer Felder
 SLAC-TN-12-021 Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell Jennifer Felder Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Carolina State University SLAC National
SLAC-TN-12-021 Design & Fabrication of a High-Voltage Photovoltaic Cell Jennifer Felder Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) North Carolina State University SLAC National
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 19: CMOS Fabrication Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Miller Effect Interconnect
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 19: CMOS Fabrication Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Miller Effect Interconnect
Inductive Coupled Plasma (ICP) Textures as Alternative for Wet Chemical Etching in Solar Cell Fabrication
 Inductive Coupled Plasma (ICP) Textures as Alternative for Wet Chemical Etching in Solar Cell Fabrication 1 Motivation 2 Experimental setup 3 ICP textures as alternative technique 3.1 Surface morphology
Inductive Coupled Plasma (ICP) Textures as Alternative for Wet Chemical Etching in Solar Cell Fabrication 1 Motivation 2 Experimental setup 3 ICP textures as alternative technique 3.1 Surface morphology
Cleanroom, Wafer Clean and Gettering
 Principles of Micro- and Nanofabrication for Electronic and Photonic Devices Cleanroom, Wafer Clean and Gettering Xing Sheng 盛兴 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University xingsheng@tsinghua.edu.cn
Principles of Micro- and Nanofabrication for Electronic and Photonic Devices Cleanroom, Wafer Clean and Gettering Xing Sheng 盛兴 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University xingsheng@tsinghua.edu.cn
Chapter 2 Problems. The CMOS technology we need to realize is shown below, from Figure 1-34 in the text. S P + N P + N WELL P +
 Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
Chapter 2 roblems 2.1 Sketch a process flow that would result in the structure shown in Figure 1-34 by drawing a series of drawings similar to those in this chapter. You only need to describe the flow
A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process
 Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
Chapter 3 A Novel Low Temperature Self-Aligned Field Induced Drain Polycrystalline Silicon Thin Film Transistor by Using Selective Side-Etching Process 3.1 Introduction Low-temperature poly-si (LTPS) TFTs
9/4/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter II CMOS Manufacturing Process 1 Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 p-well poly n-well SiO 2 n+ p-epi p+ p+ 2 Schematic Layout
Implant Metrology for Bonded SOI Wafers Using a Surface Photo-Voltage Technique
 Implant Metrology for Bonded SOI Wafers Using a Surface Photo-Voltage Technique Adam Bertuch a, Wesley Smith a, Ken Steeples a, Robert Standley b, Anca Stefanescu b, and Ron Johnson c a QC Solutions Inc.,
Implant Metrology for Bonded SOI Wafers Using a Surface Photo-Voltage Technique Adam Bertuch a, Wesley Smith a, Ken Steeples a, Robert Standley b, Anca Stefanescu b, and Ron Johnson c a QC Solutions Inc.,
EE 432 CyMOS process PWELL Photolithography and Diffusion Feb. 23th 2017
 1 EE 432 CyMOS process PWELL Photolithography and Diffusion Feb. 23th 2017 Group III Jake Asmus (Leader) John Guss Shengliang Liu Xin Chen Lab instructor Matt Weinstein 2 Overview With the field oxide
1 EE 432 CyMOS process PWELL Photolithography and Diffusion Feb. 23th 2017 Group III Jake Asmus (Leader) John Guss Shengliang Liu Xin Chen Lab instructor Matt Weinstein 2 Overview With the field oxide
Presented at the 28th European PV Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, 30 Sept October 2013, Paris, France
 A NOVEL APPROACH TO HIGH PERFORMANCE AND COST EFFECTIVE SURFACE CLEANING FOR HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR CELLS A. Moldovan 1A, M. Zimmer 1, J.Rentsch 1, B.Ferstl 2, S.Rajagopalan 2, S.Thate 2, J.Hoogboom 2,
A NOVEL APPROACH TO HIGH PERFORMANCE AND COST EFFECTIVE SURFACE CLEANING FOR HIGH EFFICIENCY SOLAR CELLS A. Moldovan 1A, M. Zimmer 1, J.Rentsch 1, B.Ferstl 2, S.Rajagopalan 2, S.Thate 2, J.Hoogboom 2,
PASHA: A NEW INDUSTRIAL PROCESS TECHNOLOGY ENABLING HIGH EFFICIENCIES ON THIN AND LARGE MC-SI WAFERS
 PASHA: A NEW INDUSTRIAL PROCESS TECHNOLOGY ENABLING HIGH EFFICIENCIES ON THIN AND LARGE MC-SI WAFERS Ingrid Romijn, Ilkay Cesar, Martien Koppes, Eric Kossen and Arthur Weeber ECN Solar Energy, P.O. Box
PASHA: A NEW INDUSTRIAL PROCESS TECHNOLOGY ENABLING HIGH EFFICIENCIES ON THIN AND LARGE MC-SI WAFERS Ingrid Romijn, Ilkay Cesar, Martien Koppes, Eric Kossen and Arthur Weeber ECN Solar Energy, P.O. Box
CMOS Technology. Flow varies with process types & company. Start with substrate selection. N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI
 CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
CMOS Technology Flow varies with process types & company N-Well CMOS Twin-Well CMOS STI Start with substrate selection Type: n or p Doping level, resistivity Orientation, 100, or 101, etc Other parameters
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells
 Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Low-cost, deterministic quasi-periodic photonic structures for light trapping in thin film silicon solar cells The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Doping and Oxidation
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping and Oxidation Franssila: Chapters 13,14, 15 Peter Hadley Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Doping Add donors
Localized laser doped contacts for silicon solar cells: characterization and efficiency potential
 Localized laser doped contacts for silicon solar cells: characterization and efficiency potential Andreas Fell, Evan Franklin, Daniel Walter, Klaus Weber SPREE Seminar Sydney, 21/08/2014 2 Outline What
Localized laser doped contacts for silicon solar cells: characterization and efficiency potential Andreas Fell, Evan Franklin, Daniel Walter, Klaus Weber SPREE Seminar Sydney, 21/08/2014 2 Outline What
Lei Zhao, Chunlan Zhou, Hailing Li, Hongwei Diao, and Wenjing Wang
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 48, NO. 3 June 2010 Characterization on the Passivation Stability of HF Aqueous Solution Treated Silicon Surfaces for HIT Solar Cell Application by the Effective Minority
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 48, NO. 3 June 2010 Characterization on the Passivation Stability of HF Aqueous Solution Treated Silicon Surfaces for HIT Solar Cell Application by the Effective Minority
Electroless Silver Plating as a Tool for Enhancement of Efficiency of Standard Industrial Solar Cells
 Electroless Silver Plating as a Tool for Enhancement of Efficiency of Standard Industrial Solar Cells Outline Short introduction to ISC Konstanz Plating on standard industrial solar cells Electroless Ag-plating
Electroless Silver Plating as a Tool for Enhancement of Efficiency of Standard Industrial Solar Cells Outline Short introduction to ISC Konstanz Plating on standard industrial solar cells Electroless Ag-plating
Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester,
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Bulk MEMS Fabrication Details Dr. Lynn Fuller, Casey Gonta, Patsy Cadareanu Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester,
Czochralski Crystal Growth
 Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
Czochralski Crystal Growth Crystal Pulling Crystal Ingots Shaping and Polishing 300 mm wafer 1 2 Advantage of larger diameter wafers Wafer area larger Chip area larger 3 4 Large-Diameter Wafer Handling
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005
 3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
3.155J / 6.152J Micro/Nano Processing Technology TAKE-HOME QUIZ FALL TERM 2005 1) This is an open book, take-home quiz. You are not to consult with other class members or anyone else. You may discuss the
Review of CMOS Processing Technology
 - Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
- Scaling and Integration Moore s Law Unit processes Thin Film Deposition Etching Ion Implantation Photolithography Chemical Mechanical Polishing 1. Thin Film Deposition Layer of materials ranging from
CRYSATLLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS IN MANUFACUTRING TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS BACKGROUND AND BASE MATERIAL
 CRYSATLLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS IN MANUFACUTRING TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS BACKGROUND AND BASE MATERIAL ABSTRACT Kazimierz Drabczyk Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science, Polish Academy of Sciences 25
CRYSATLLINE SILICON SOLAR CELLS IN MANUFACUTRING TECHNOLOGY ASPECTS BACKGROUND AND BASE MATERIAL ABSTRACT Kazimierz Drabczyk Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science, Polish Academy of Sciences 25
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts
 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. Oxide Thickness µm 0. µm 0 nm nm Thermally Grown Oxides
N-PERT BACK JUNCTION SOLAR CELLS: AN OPTION FOR THE NEXT INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGY GENERATION?
 N-PERT BACK JUNCTION SOLAR CELLS: AN OPTION FOR THE NEXT INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGY GENERATION? Bianca Lim *, Till Brendemühl, Miriam Berger, Anja Christ, Thorsten Dullweber Institute for Solar Energy Research
N-PERT BACK JUNCTION SOLAR CELLS: AN OPTION FOR THE NEXT INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGY GENERATION? Bianca Lim *, Till Brendemühl, Miriam Berger, Anja Christ, Thorsten Dullweber Institute for Solar Energy Research
COMPATIBILITY OF THE ALTERNATIVE SEED LAYER (ASL) PROCESS WITH MONO- Si AND POLY-Si SUBSTRATES PATTERNED BY LASER OR WET ETCHING
 COMPATIBILITY OF THE ALTERNATIVE SEED LAYER (ASL) PROCESS WITH MONO- Si AND POLY-Si SUBSTRATES PATTERNED BY LASER OR WET ETCHING Lynne Michaelson 1, Anh Viet Nguyen 2, Krystal Munoz 1, Jonathan C. Wang
COMPATIBILITY OF THE ALTERNATIVE SEED LAYER (ASL) PROCESS WITH MONO- Si AND POLY-Si SUBSTRATES PATTERNED BY LASER OR WET ETCHING Lynne Michaelson 1, Anh Viet Nguyen 2, Krystal Munoz 1, Jonathan C. Wang
INDUSTRIALLY FEASIBLE >19% EFFICIENCY IBC CELLS FOR PILOT LINE PROCESSING
 INDUSTRIALLY FEASIBLE >19% EFFICIENCY IBC CELLS FOR PILOT LINE PROCESSING F. J. Castaño 1, D. Morecroft 1, M. Cascant 1, H. Yuste 1, M.W.P.E. Lamers 2, A.A. Mewe 2, I.G. Romijn 2, E.E. Bende 2, Y. Komatsu
INDUSTRIALLY FEASIBLE >19% EFFICIENCY IBC CELLS FOR PILOT LINE PROCESSING F. J. Castaño 1, D. Morecroft 1, M. Cascant 1, H. Yuste 1, M.W.P.E. Lamers 2, A.A. Mewe 2, I.G. Romijn 2, E.E. Bende 2, Y. Komatsu
Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon
 Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Fabrication and Layout
 Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
Fabrication and Layout Kenneth Yun UC San Diego Adapted from EE271 notes, Stanford University Overview Semiconductor properties How chips are made Design rules for layout Reading Fabrication: W&E 3.1,
Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Wafer Cleaning and Oxide Growth Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/~lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
CMOS Fabrication. Dr. Bassam Jamil. Adopted from slides of the textbook
 CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
CMOS Fabrication Dr. Bassam Jamil Adopted from slides of the textbook CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different
An advantage of thin-film silicon solar cells is that they can be deposited on glass substrates and flexible substrates.
 ET3034TUx - 5.2.1 - Thin film silicon PV technology 1 Last week we have discussed the dominant PV technology in the current market, the PV technology based on c-si wafers. Now we will discuss a different
ET3034TUx - 5.2.1 - Thin film silicon PV technology 1 Last week we have discussed the dominant PV technology in the current market, the PV technology based on c-si wafers. Now we will discuss a different
Department of Electrical Engineering. Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 3 Fabrication of CMOS Integrated Circuits Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Background Outline The CMOS Process Flow Design Rules Latchup
Chapter 3 Fabrication of CMOS Integrated Circuits Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Background Outline The CMOS Process Flow Design Rules Latchup
Lecture 6. Monocrystalline Solar Cells
 Lecture 6 Monocrystalline Solar Cells References: 1. Physics of Solar Cells. Jenny Nelson. Imperial College Press, 2003. 2. Photovoltaic Materials, Series on Properties of Semiconductor Materials, Vol.1,
Lecture 6 Monocrystalline Solar Cells References: 1. Physics of Solar Cells. Jenny Nelson. Imperial College Press, 2003. 2. Photovoltaic Materials, Series on Properties of Semiconductor Materials, Vol.1,
Overview of CMP for TSV Applications. Robert L. Rhoades, Ph.D. Presentation for AVS Joint Meeting June 2013 San Jose, CA
 Overview of CMP for TSV Applications Robert L. Rhoades, Ph.D. Presentation for AVS Joint Meeting June 2013 San Jose, CA Outline TSV s and the Role of CMP TSV Pattern and Fill TSV Reveal (non-selective)
Overview of CMP for TSV Applications Robert L. Rhoades, Ph.D. Presentation for AVS Joint Meeting June 2013 San Jose, CA Outline TSV s and the Role of CMP TSV Pattern and Fill TSV Reveal (non-selective)
Solar Spectrum. -Black body radiation. Light bulb 3000 K Red->Yellow->White Surface of Sun 6000 K
 Solar Spectrum 1 Solar Spectrum -Black body radiation Light bulb 3000 K Red->Yellow->White Surface of Sun 6000 K 2 Solar Spectrum -Black body radiation Light bulb 3000 K Red->Yellow->White Surface of Sun
Solar Spectrum 1 Solar Spectrum -Black body radiation Light bulb 3000 K Red->Yellow->White Surface of Sun 6000 K 2 Solar Spectrum -Black body radiation Light bulb 3000 K Red->Yellow->White Surface of Sun
REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY
 REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY Meijun Lu 1,2, Ujjwal Das 1, Stuart Bowden 1, and Robert Birkmire 1,2 1 Institute of Energy
REAR SURFACE PASSIVATION OF INTERDIGITATED BACK CONTACT SILICON HETEROJUNCTION SOLAR CELL AND 2D SIMULATION STUDY Meijun Lu 1,2, Ujjwal Das 1, Stuart Bowden 1, and Robert Birkmire 1,2 1 Institute of Energy
A Novel Buried-Emitter Photovoltaic Cell for High Efficiency Energy Conversion
 A Novel Buried-Emitter Photovoltaic Cell for High Efficiency Energy Conversion by Roohollah Samadzadeh Tarighat A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
A Novel Buried-Emitter Photovoltaic Cell for High Efficiency Energy Conversion by Roohollah Samadzadeh Tarighat A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement
HIGH EFFICIENCY INDUSTRIAL SCREEN PRINTED N-TYPE SOLAR CELLS WITH FRONT BORON EMITTER
 HIGH EFFICIENCY INDUSTRIAL SCREEN PRINTED N-TYPE SOLAR CELLS WITH FRONT BORON EMITTER V.D. Mihailetchi 1, Y. Komatsu 1, G. Coletti 1, R. Kvande 2, L. Arnberg 2, C. Knopf 3, K. Wambach 3, L.J. Geerligs
HIGH EFFICIENCY INDUSTRIAL SCREEN PRINTED N-TYPE SOLAR CELLS WITH FRONT BORON EMITTER V.D. Mihailetchi 1, Y. Komatsu 1, G. Coletti 1, R. Kvande 2, L. Arnberg 2, C. Knopf 3, K. Wambach 3, L.J. Geerligs
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Layout, Fabrication, and Elementary Logic Design CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each
Manufacturing Process
 CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten SiO n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V DD
CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process 1 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi AlCu Tungsten SiO n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V DD
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO 2 (glass) Major factor in making
 Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
Thermal Oxidation and Growth of Insulators (Chapter 3 - Jaeger 3) Key advantage of Si: Oxidation of Si into SiO (glass) Major factor in making Silicon the main semiconductor Grown at high temperature in
EE THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6. Basic Concepts
 EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
EE 22 FALL 999-00 THERMAL OXIDATION - Chapter 6 Basic Concepts SiO 2 and the Si/SiO 2 interface are the principal reasons for silicon s dominance in the IC industry. SiO 2 : Easily selectively etched using
FABRICATION of MOSFETs
 FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
FABRICATION of MOSFETs CMOS fabrication sequence -p-type silicon substrate wafer -creation of n-well regions for pmos transistors, -impurity implantation into the substrate. -thick oxide is grown in the
PHYSICSOF SOLARCELLS. Jenny Nelson. Imperial College, UK. Imperial College Press ICP
 im- PHYSICSOF SOLARCELLS Jenny Nelson Imperial College, UK ICP Imperial College Press Contents Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Photons In, Electrons Out: The Photovoltaic Effect 1 1.2. Brief History
im- PHYSICSOF SOLARCELLS Jenny Nelson Imperial College, UK ICP Imperial College Press Contents Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1. Photons In, Electrons Out: The Photovoltaic Effect 1 1.2. Brief History
UT Austin, ECE Department VLSI Design 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout Rules
 2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
2. CMOS Fabrication, Layout, Design Rules Last module: Introduction to the course How a transistor works CMOS transistors This module: CMOS Fabrication Design Rules CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are
CMOS Manufacturing Process
 CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V
CMOS Manufacturing Process CMOS Process A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process Circuit Under Design V
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
MRS Fall Meeting, Boston, USA, 28 November 2 December 2011
 Examination of the properties of the interface of a-sin x :H/Si in crystalline silicon solar cells and its effect on cell efficiency Machteld W.P.E. Lamers 1, Keith Butler 2, Ingrid G. Romijn 1, John Harding
Examination of the properties of the interface of a-sin x :H/Si in crystalline silicon solar cells and its effect on cell efficiency Machteld W.P.E. Lamers 1, Keith Butler 2, Ingrid G. Romijn 1, John Harding
LBIC investigations of the lifetime degradation by extended defects in multicrystalline solar silicon
 LBIC investigations of the lifetime degradation by extended defects in multicrystalline solar silicon Markus Rinio 1, Hans Joachim Möller 1 and Martina Werner 2, 1 Institute for Experimental Physics, TU
LBIC investigations of the lifetime degradation by extended defects in multicrystalline solar silicon Markus Rinio 1, Hans Joachim Möller 1 and Martina Werner 2, 1 Institute for Experimental Physics, TU
Process Development for Porous Silicon Light-Emitting Devices
 Process Development for Porous Silicon Light-mitting Devices Jason Benz Advisor: K. Hirschman Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623 Absfract - The primary focus of this project was to continue
Process Development for Porous Silicon Light-mitting Devices Jason Benz Advisor: K. Hirschman Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623 Absfract - The primary focus of this project was to continue
BIFACIAL SOLAR CELLS WITH BORON BACK SURFACE FIELD
 BIFACIAL SOLAR CELLS WITH BORON BACK SURFACE FIELD C. Duran 1, T. Buck 1, R. Kopecek 1, J. Libal 2, F. Traverso 2 1 International Solar Energy Research Center - ISC - Konstanz, Rudolf-Diesel-Str. 15, D-78467
BIFACIAL SOLAR CELLS WITH BORON BACK SURFACE FIELD C. Duran 1, T. Buck 1, R. Kopecek 1, J. Libal 2, F. Traverso 2 1 International Solar Energy Research Center - ISC - Konstanz, Rudolf-Diesel-Str. 15, D-78467
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very
 Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very high voltages (10-600 KeV) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
Ion Implantation Most modern devices doped using ion implanters Ionize gas sources (single +, 2+ or 3+ ionization) Accelerate dopant ions to very high voltages (10-600 KeV) Use analyzer to selection charge/mass
EE 143 MICROFABRICATION TECHNOLOGY FALL 2014 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #9
 Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
Issued: Tuesday, Nov. 11, 2014 PROLEM SET #9 Due: Wednesday, Nov. 19, 2010, 8:00 a.m. in the EE 143 homework box near 140 Cory 1. The following pages comprise an actual pwell CMOS process flow with poly-to-poly
CMOS FABRICATION. n WELL PROCESS
 CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
CMOS FABRICATION n WELL PROCESS Step 1: Si Substrate Start with p- type substrate p substrate Step 2: Oxidation Exposing to high-purity oxygen and hydrogen at approx. 1000 o C in oxidation furnace SiO
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
 INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
INTEGRATED-CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY 0. Silicon crystal growth and wafer preparation 1. Processing Steps 1.1. Photolitography 1.2. Oxidation 1.3. Layer Deposition 1.4. Etching 1.5. Diffusion 1.6 Backend: assembly,
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
VLSI INTRODUCTION P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents UNIT I INTRODUCTION: Introduction to IC Technology MOS, PMOS, NMOS, CMOS & BiCMOS technologies. BASIC ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES : Basic Electrical
Report 1. B. Starting Wafer Specs Number: 10 Total, 6 Device and 4 Test wafers
 Aaron Pederson EE 432 Lab Dr. Meng Lu netid: abp250 Lab instructor: Yunfei Zhao Report 1 A. Overview The goal of this lab is to go through the semiconductor fabrication process from start to finish. This
Aaron Pederson EE 432 Lab Dr. Meng Lu netid: abp250 Lab instructor: Yunfei Zhao Report 1 A. Overview The goal of this lab is to go through the semiconductor fabrication process from start to finish. This
Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 44, No. 6, June 2004, pp. 1581 1586 Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing Ji Youn Lee Photovoltaics R&D Center, Sung Jin
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 44, No. 6, June 2004, pp. 1581 1586 Boron Back Surface Field Using Spin-On Dopants by Rapid Thermal Processing Ji Youn Lee Photovoltaics R&D Center, Sung Jin
VLSI. Lecture 1. Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University. Based on slides of David Money Harris
 VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
VLSI Lecture 1 Jaeyong Chung System-on-Chips (SoC) Laboratory Incheon National University Based on slides of David Money Harris Goals of This Course Learn the principles of VLSI design Learn to design
Impact of Si Surface Topography on the Glass Layer Resulting from Screen Printed Ag-Paste Solar Cell Contacts
 Impact of Si Surface Topography on the Glass Layer Resulting from Screen Printed Ag-Paste Solar Cell Contacts Enrique Cabrera 1, Sara Olibet 1, Dominik Rudolph 1, Joachim Glatz-Reichenbach 1, Radovan Kopecek
Impact of Si Surface Topography on the Glass Layer Resulting from Screen Printed Ag-Paste Solar Cell Contacts Enrique Cabrera 1, Sara Olibet 1, Dominik Rudolph 1, Joachim Glatz-Reichenbach 1, Radovan Kopecek
Microelettronica. Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication. 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica
 Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Microelettronica Planar Technology for Silicon Integrated Circuits Fabrication 26/02/2017 A. Neviani - Microelettronica Introduction Simplified crosssection of an nmosfet and a pmosfet Simplified crosssection
Properties of Inverse Opal Photonic Crystals Grown By Atomic Layer Deposition
 Properties of Inverse Opal Photonic Crystals Grown By Atomic Layer Deposition J.S. King 1, C. W. Neff 1, W. Park 2, D. Morton 3, E. Forsythe 3, S. Blomquist 3, and C. J. Summers 1 (1) School of Materials
Properties of Inverse Opal Photonic Crystals Grown By Atomic Layer Deposition J.S. King 1, C. W. Neff 1, W. Park 2, D. Morton 3, E. Forsythe 3, S. Blomquist 3, and C. J. Summers 1 (1) School of Materials
Comparison of PV Efficiency Using Different Types of Steam for Wet Thermal Oxidation
 Comparison of PV Efficiency Using Different Types of Steam for Wet Thermal Oxidation Jeffrey Spiegelman 1 Jan Benick 2 1 RASIRC 2 Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) PRINT this article
Comparison of PV Efficiency Using Different Types of Steam for Wet Thermal Oxidation Jeffrey Spiegelman 1 Jan Benick 2 1 RASIRC 2 Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) PRINT this article
Nickel Silicide Contact for Copper. Plated Silicon Solar Cells. Harsh Narendrakumar Jain
 Nickel Silicide Contact for Copper Plated Silicon Solar Cells by Harsh Narendrakumar Jain A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved July 2016
Nickel Silicide Contact for Copper Plated Silicon Solar Cells by Harsh Narendrakumar Jain A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved July 2016
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals. Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi
 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8588,
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells With Two Different Metals Toshiyuki Sameshima*, Kazuya Kogure, and Masahiko Hasumi Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2-24-16 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8588,
CMOS Manufacturing process. Design rule set
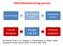 CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
CMOS Manufacturing process Circuit design Set of optical masks Fabrication process Circuit designer Design rule set Process engineer All material: Chap. 2 of J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic, Digital
This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes.
 IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
IC Fabrication B B.1 Introduction This Appendix discusses the main IC fabrication processes. B.2 NMOS fabrication NMOS transistors are formed in a p-type substrate. The NMOS fabrication process requires
Modeling of Local Oxidation Processes
 Introduction Isolation Processes in the VLSI Technology Main Aspects of LOCOS simulation Athena Oxidation Models Several Examples of LOCOS structures Calibration of LOCOS effects using VWF Field Oxide
Introduction Isolation Processes in the VLSI Technology Main Aspects of LOCOS simulation Athena Oxidation Models Several Examples of LOCOS structures Calibration of LOCOS effects using VWF Field Oxide
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 55 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 55 (2014 ) 287 294 4th International Conference on Silicon Photovoltaics, SiliconPV 2014 Codiffused bifacial n-type solar cells (CoBiN)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 55 (2014 ) 287 294 4th International Conference on Silicon Photovoltaics, SiliconPV 2014 Codiffused bifacial n-type solar cells (CoBiN)
Manufacturing Process
 Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
Manufacturing Process 1 CMOS Process 2 A Modern CMOS Process gate-oxide TiSi 2 AlCu Tungsten SiO 2 n+ p-well p-epi poly n-well p+ SiO 2 p+ Dual-Well Trench-Isolated CMOS Process 3 Single-crystal ingot
MOS Front-End. Field effect transistor
 MOS Front-End Back-end Transistor Contact Front-end p-well STI n-well Front-end-of-line includes substrate, isolation, wells, transistor, silicide Field effect transistor MOSFET: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
MOS Front-End Back-end Transistor Contact Front-end p-well STI n-well Front-end-of-line includes substrate, isolation, wells, transistor, silicide Field effect transistor MOSFET: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Tuesday, September 04, 2012 Lecture 01
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2012 Tuesday, September 04, 2012 Lecture 01 1 Instructor: Jing Bai Contact Email: jingbai@d.umn.edu, hone: (218)726-8606, Office: MWAH 255 Webpage:
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2012 Tuesday, September 04, 2012 Lecture 01 1 Instructor: Jing Bai Contact Email: jingbai@d.umn.edu, hone: (218)726-8606, Office: MWAH 255 Webpage:
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions. Stuart Bowden BAPVC January Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12,
 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 2011 Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12, 2011 1 Stuart Bowden Co-Director of Solar Power Labs at ASU Work relevant to BAPVC: Pilot
Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells Future Directions Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 2011 Stuart Bowden BAPVC January 12, 2011 1 Stuart Bowden Co-Director of Solar Power Labs at ASU Work relevant to BAPVC: Pilot
Total Points = 110 possible (graded out of 100)
 Lab Report 1 Table of Contents 1. Profiles & Layout (9 Points) 2. Process Procedures (20 points) 3. Calculations (36 Points) 4. Questions (35 Points) 5. Bonus Questions (10 Points) Total Points = 110 possible
Lab Report 1 Table of Contents 1. Profiles & Layout (9 Points) 2. Process Procedures (20 points) 3. Calculations (36 Points) 4. Questions (35 Points) 5. Bonus Questions (10 Points) Total Points = 110 possible
Chapter 4. UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication. Oxidation
 Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
Chapter 4 UEEP2613 Microelectronic Fabrication Oxidation Prepared by Dr. Lim Soo King 24 Jun 2012 Chapter 4...113 Oxidation...113 4.0 Introduction... 113 4.1 Chemistry of Silicon Dioxide Formation... 115
PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS
 Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Contents: VI Sem ECE 06EC63: Analog and Mixed Mode VLSI Design PROCESS FLOW AN INSIGHT INTO CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS 1. Introduction 2. CMOS Fabrication 3. Simplified View of Fabrication Process 3.1 Alternative
Lecture 5. SOI Micromachining. SOI MUMPs. SOI Micromachining. Silicon-on-Insulator Microstructures. Agenda:
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 2005) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie SOI Micromachining Agenda: SOI Micromachining SOI MUMPs Multi-level structures Lecture 5 Silicon-on-Insulator Microstructures Single-crystal
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 2005) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie SOI Micromachining Agenda: SOI Micromachining SOI MUMPs Multi-level structures Lecture 5 Silicon-on-Insulator Microstructures Single-crystal
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003
 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note June 1983 Revised March 2003 High-Speed CMOS (MM74HC) Processing The MM74HC logic family achieves its high speed by utilizing microcmos Technology. This is a 3.5
Research Article Silicon Nitride Film by Inline PECVD for Black Silicon Solar Cells
 Photoenergy Volume 2012, Article ID 971093, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/971093 Research Article Silicon Nitride Film by Inline PECVD for Black Silicon Solar Cells Bangwu Liu, Sihua Zhong, Jinhu Liu, Yang
Photoenergy Volume 2012, Article ID 971093, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/971093 Research Article Silicon Nitride Film by Inline PECVD for Black Silicon Solar Cells Bangwu Liu, Sihua Zhong, Jinhu Liu, Yang
DESIGN AND OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF III- V SOLAR CELLS
 DESIGN AND OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF III- V SOLAR CELLS ANTHONY MELECO CAPSTONE ADVISER: DR. IAN SELLERS TABLE OF CONTENTS Abstract... 3 Introduction... 3 Procedure... 4 Photomask... 4 Modeling... 5 IV curve...
DESIGN AND OPERATING PRINCIPLES OF III- V SOLAR CELLS ANTHONY MELECO CAPSTONE ADVISER: DR. IAN SELLERS TABLE OF CONTENTS Abstract... 3 Introduction... 3 Procedure... 4 Photomask... 4 Modeling... 5 IV curve...
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 MOSFET I Metal gate vs self-aligned poly gate So far, we have discussed about
Choi, Jun-Hyuk Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials
 The 11 th US-Korea Nanosymposium Choi, Jun-Hyuk 2014. 09. 29 Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials About KIMM Nano-research Bldg Clean RM Five Research Divisions; 1. Advanced Manufacturing Sys. 2. Extreme
The 11 th US-Korea Nanosymposium Choi, Jun-Hyuk 2014. 09. 29 Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials About KIMM Nano-research Bldg Clean RM Five Research Divisions; 1. Advanced Manufacturing Sys. 2. Extreme
Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Photoresist Coat, Expose and Develop Laboratory Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://www.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604
Supporting Information: Model Based Design of a Microfluidic. Mixer Driven by Induced Charge Electroosmosis
 Supporting Information: Model Based Design of a Microfluidic Mixer Driven by Induced Charge Electroosmosis Cindy K. Harnett, Yehya M. Senousy, Katherine A. Dunphy-Guzman #, Jeremy Templeton * and Michael
Supporting Information: Model Based Design of a Microfluidic Mixer Driven by Induced Charge Electroosmosis Cindy K. Harnett, Yehya M. Senousy, Katherine A. Dunphy-Guzman #, Jeremy Templeton * and Michael
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 02 MOS Transistors - I Hello and welcome to today
CS/ECE 5710/6710. N-type Transistor. N-type from the top. Diffusion Mask. Polysilicon Mask. CMOS Processing
 CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
CS/ECE 5710/6710 CMOS Processing Addison-Wesley N-type Transistor D G +Vgs + Vds S N-type from the top i electrons - Diffusion Mask Mask for just the diffused regions Top view shows patterns that make
Anodic Aluminium Oxide for Passivation in Silicon Solar Cells
 Anodic Aluminium Oxide for Passivation in Silicon Solar Cells School of Photovoltaic & Renewable Energy Engineering Zhong Lu Supervisor: Alison Lennon May. 2015 Co-supervisor: Stuart Wenham Outline Introduction
Anodic Aluminium Oxide for Passivation in Silicon Solar Cells School of Photovoltaic & Renewable Energy Engineering Zhong Lu Supervisor: Alison Lennon May. 2015 Co-supervisor: Stuart Wenham Outline Introduction
THREE TERMINAL SI-SI:GE MONOLITIC TANDEM SOLAR CELLS. Lu Wang
 THREE TERMINAL SI-SI:GE MONOLITIC TANDEM SOLAR CELLS by Lu Wang A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
THREE TERMINAL SI-SI:GE MONOLITIC TANDEM SOLAR CELLS by Lu Wang A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Investigation on the Impact of Metallic Surface Contaminations on Minority Carrier Lifetime of a-si:h Passivated Crystalline Silicon
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 8 (2011) 6 288 293 1 5 SiliconPV: 17-20 April 2011, Freiburg, Germany Investigation on the Impact of Metallic Surface Contaminations on Minority
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 8 (2011) 6 288 293 1 5 SiliconPV: 17-20 April 2011, Freiburg, Germany Investigation on the Impact of Metallic Surface Contaminations on Minority
Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing
 Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing D. Lysáček, L. Válek ON SEMICONDUCTOR CZECH REPUBLIC, Rožnov p. R., david.lysacek@onsemi.com Abstract The structure
Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing D. Lysáček, L. Válek ON SEMICONDUCTOR CZECH REPUBLIC, Rožnov p. R., david.lysacek@onsemi.com Abstract The structure
Characteristics of Heat-Annealed Silicon Homojunction Infrared Photodetector Fabricated by Plasma-Assisted Technique
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 345 35 Characteristics of Heat-Annealed Silicon Homojunction Infrared Photodetector Fabricated by Plasma-Assisted Technique Oday A. HAMMADI * Department of Physics,
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 345 35 Characteristics of Heat-Annealed Silicon Homojunction Infrared Photodetector Fabricated by Plasma-Assisted Technique Oday A. HAMMADI * Department of Physics,
