Climate Change. Some solar radiation is reflected by Earth and the atmosphere. Earth s Surface
|
|
|
- Evelyn Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back into space, especially by bright surfaces such as ice and clouds, and the rest is absorbed by the surface and the atmosphere. Much of this absorbed solar energy is re-emitted as heat (longwave or infrared radiation). The atmosphere in turn absorbs and re-radiates heat, some of which escapes to space. Any disturbance to this balance of incoming and outgoing energy will affect the climate. For example, small changes in the output of energy from the Sun will affect this balance directly. If all heat energy emitted from the surface passed through the atmosphere directly into space, Earth s average surface temperature would be tens of degrees colder than today. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, act to make the surface much warmer than this, because they absorb and emit heat energy in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth s surface and lower atmosphere warm [Figure B1]. Without this greenhouse effect, life as we know it could not have evolved on our planet. Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere makes it even more effective at preventing heat from escaping into space. When the energy leaving is less than the energy entering, Earth warms until a new balance is established. figure b1. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb heat energy and emit it in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth s surface and lower atmosphere warm. Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth s surface and lower atmosphere even warmer. Image based on a figure from US EPA. THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT Some solar radiation is reflected by Earth and the atmosphere Earth s Surface Some of the infrared radiation passes through the atmosphere. Some is absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-emitted in all directions by the atmosphere. The effect of this is to warm Earth s Atmosphere surface and the lower atmosphere. Some radiation is absorbed by Earth s surface and warms it Infrared radiation is emitted by Earth s surface Evidence & Causes B1
2 Greenhouse gases emitted by human activities alter Earth s energy balance and thus its climate. Humans also affect climate by changing the nature of the land surfaces (for example by clearing forests for farming) and through the emission of pollutants that affect the amount and type of particles in the atmosphere. Scientists have determined that, when all human and natural factors are considered, Earth s climate balance has been altered towards warming, with the biggest contributor being increases in. Human activities have added greenhouse gases to the atmosphere The atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide have increased significantly since the Industrial Revolution began. In the case of carbon dioxide, the average concentration measured at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii has risen from 316 parts per million (ppm) 1 in 1959 (the first full year of data available) to 396 ppm in 2013 [Figure B2]. The same rates of increase have since been recorded at numerous other stations worldwide. Since pre-industrial times, the atmospheric concentration of has increased by 40%, methane has increased by about 150%, and nitrous oxide has increased by roughly 20%. More than half of the increase in has occurred since Increases in all three gases contribute to warming of Earth, with the increase in playing the largest role. See page B3 to learn about the sources of human emitted greenhouse gases. Scientists have examined greenhouse gases in the context of the past. Analysis of air trapped inside ice that has been accumulating over time in Antarctica shows that the 1 that is, for every million molecules in the air, 316 of them were Figure B2. Measurements of atmospheric since 1958 from the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii (black) and from the South Pole (red) show a steady annual increase in atmospheric concentration. (The measurements are made at remote places like those because they are not greatly influenced by local processes, so therefore are representative of the background atmosphere.) The small up and down saw-tooth pattern reflects seasonal changes in the release and uptake of by plants. Source: Scripps Program / ppm Year B2
3 concentration began to increase significantly in the 19 th century [Figure B3], after staying in the range of 260 to 280 ppm for the previous 10,000 years. Ice core records extending back 800,000 years show that during that time, concentrations remained within the range of 170 to 300 ppm throughout many ice age cycles see page B4 to learn about the ice ages and no concentration above 300 ppm is seen in ice core records until the past 200 years. / ppm Atmospheric measurements (ML) Law Dome Figure B3. variations during the past 1,000 years, obtained from analysis of air trapped in an ice core extracted from Antarctica (red squares), show a sharp rise in atmospheric starting in the late 19 th century. Modern atmospheric measurements from Mauna Loa are superimposed in blue. Source: figure by Eric Wolff, data from Etheridge et al., 1996; MacFarling Meure et al., Year Learn about the sources of human-emitted greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide ( ) has both natural and human sources, but levels are increasing primarily because of the combustion of fossil fuels, cement production, deforestation (which reduces the taken up by trees and increases the released by decomposition of the detritus), and other land use changes. Increases in are the single largest contributor to global warming. Methane (CH 4 ) has both human and natural sources, and levels have risen significantly since pre-industrial times due to human activities such as raising livestock, growing paddy rice, filling landfills, and using natural gas (which is mostly CH 4, some of which may be released when it is extracted, transported, and used). Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) concentrations have risen primarily because of agricultural activities such as the use of nitrogen-based fertilisers and land use changes. Halocarbons, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), are chemicals used as refrigerants and fire retardants. In addition to being potent greenhouse gases, CFCs also damage the ozone layer. The production of most CFCs has now been banned, so their impact is starting to decline. However, many CFC replacements are also potent greenhouse gases and their concentrations and the concentrations of other halocarbons continue to increase. Evidence & Causes B3
4 Measurements of the forms (isotopes) of carbon in the modern atmosphere show a clear fingerprint of the addition of old carbon (depleted in natural radioactive 14 C) coming from the combustion of fossil fuels (as opposed to newer carbon coming from living systems). In addition, it is known that human activities (excluding land-use changes) currently emit an estimated 10 billion tonnes of carbon each year, mostly by burning fossil fuels, which is more than enough to explain the observed increase in concentration. These and other lines of evidence point conclusively to the fact that the elevated concentration in our atmosphere is the result of human activities. Climate records show a warming trend Estimating global average surface air temperature increase requires careful analysis of millions of measurements from around the world, including from land stations, ships, and satellites. Despite the many complications of synthesising such data, multiple independent teams have concluded separately and unanimously that global average surface air temperature has risen by about 0.8 C (1.4 F) since 1900 [Figure B4]. Although the record shows several pauses and accelerations in the increasing trend, each of the last three decades has been warmer than any other decade in the instrumental record since Going further back in time before accurate thermometers were widely available, temperatures can be reconstructed using climate-sensitive indicators ( proxies ) Learn about the ice ages Detailed analyses of ocean sediments, ice cores, and other data show that for at least the last 2.6 million years, Earth has gone through extended periods when temperatures were much lower than today and thick blankets of ice covered large areas of the Northern Hemisphere. These long cold spells, lasting in the most recent cycles for around 100,000 years, were interrupted by shorter warm interglacial periods, including the past 10,000 years. Through a combination of theory, observations, and modelling, scientists have deduced that the ice ages * are triggered by recurring variations in Earth s orbit that primarily alter the regional and seasonal distribution of solar energy reaching Earth. These relatively small changes in solar energy are reinforced over thousands of years by gradual changes in Earth s ice cover (the cryosphere), especially over the Northern Hemisphere, and in atmospheric composition, eventually leading to large changes in global temperature. The average global temperature change during an ice-age cycle is estimated as 5 C ± 1 C (9 F ± 2 F). *Note that in geological terms Earth has been in an ice age ever since the Antarctic Ice Sheet last formed about 36 million years ago. However, in this document we have used the term in its more colloquial usage indicating the regular occurrence of extensive ice sheets over North America and northern Eurasia. B4
5 in materials such as tree rings, ice cores, and marine sediments. Comparisons of the thermometer record with these proxy measurements suggest that the time since the early 1980s has been the warmest 30-year period in at least eight centuries, and that global temperature is rising towards peak temperatures last seen 5,000 to 10,000 years ago in the warmest part of our current interglacial period. Many other impacts associated with the warming trend have become evident in recent years. Arctic summer sea ice cover has shrunk dramatically. The heat content of the ocean has increased. Global average sea level has risen by approximately 20 cm (8 inches) since 1901, due both to the expansion of warmer ocean water and to the addition of melt waters from glaciers and ice sheets on land. Warming and precipitation changes are altering the geographical ranges of many plant and animal species and the timing of their life cycles. In addition to the effects on climate, some of the excess in the atmosphere is being taken up by the ocean, changing its chemical composition (causing ocean acidification). Figure B4. Earth s global average surface temperature has risen as shown in this plot of combined land and ocean measurements from 1850 to 2012, derived from three independent analyses of the available data sets. The top panel shows annual average values from the three analyses, and the bottom panel shows decadal average values, including the uncertainty range (grey bars) for the black (HadCRUT4) dataset. The temperature changes are relative to the global average surface temperature, averaged from Source: IPCC AR5, data from the HadCRUT4 dataset (black), UK Met Office Hadley Centre, the NCDC MLOST dataset (orange), US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the NASA GISS dataset (blue), US National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Evidence & Causes B5
6 Many complex processes shape our climate Based just on the physics of the amount of energy that absorbs and emits, a doubling of atmospheric concentration from pre-industrial levels (up to about 560 ppm) would, by itself, cause a global average temperature increase of about 1 C (1.8 F). In the overall climate system, however, things are more complex; warming leads to further effects (feedbacks) that either amplify or diminish the initial warming. The most important feedbacks involve various forms of water. A warmer atmosphere generally contains more water vapour. Water vapour is a potent greenhouse gas, thus causing more warming; its short lifetime in the atmosphere keeps its increase largely in step with warming. Thus, water vapour is treated as an amplifier, and not a driver, of climate change. Higher temperatures in the polar regions melt sea ice and reduce seasonal snow cover, exposing a darker ocean and land surface that can absorb more heat, causing further warming. Another important but uncertain feedback concerns changes in clouds. Warming and increases in water vapour together may cause cloud cover to increase or decrease which can either amplify or dampen temperature change depending on the changes in the horizontal extent, altitude, and properties of clouds. The latest assessment of the science indicates that the overall net global effect of cloud changes is likely to be to amplify warming. The ocean moderates climate change. The ocean is a huge heat reservoir, but it is difficult to heat its full depth because warm water tends to stay near the surface. The rate at which heat is transferred to the deep ocean is therefore slow; it varies from year to year and from decade to decade, and helps to determine the pace of warming at the surface. Observations of the sub-surface ocean are limited prior to about 1970, but since then, warming of the upper 700 m (2,300 feet) is readily apparent. There is also evidence of deeper warming. Surface temperatures and rainfall in most regions vary greatly from the global average because of geographical location, in particular latitude and continental position. Both the average values of temperature, rainfall, and their extremes (which generally have the largest impacts on natural systems and human infrastructure), are also strongly affected by local patterns of winds. Estimating the effects of feedback processes, the pace of the warming, and regional climate change requires the use of mathematical models of the atmosphere, ocean, land, and ice (the cryosphere) built upon established laws of physics and the latest understanding of the physical, chemical and biological processes affecting climate, and run on powerful computers. Models vary in their projections of how much additional warming to expect (depending on the type of model and on assumptions used in simulating certain climate processes, particularly cloud formation and ocean mixing), but all such models agree that the overall net effect of feedbacks is to amplify warming. B6
7 Human activities are changing the climate Rigorous analysis of all data and lines of evidence shows that most of the observed global warming over the past 50 years or so cannot be explained by natural causes and instead requires a significant role for the influence of human activities. In order to discern the human influence on climate, scientists must consider many natural variations that affect temperature, precipitation, and other aspects of climate from local to global scale, on timescales from days to decades and longer. One natural variation is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), an irregular alternation between warming and cooling (lasting about two to seven years) in the equatorial Pacific Ocean that causes significant year-to-year regional and global shifts in temperature and rainfall patterns. Volcanic eruptions also alter climate, in part increasing the amount of small (aerosol) particles in the stratosphere that reflect or absorb sunlight, leading to a short-term surface cooling lasting typically about two to three years. Over hundreds of thousands of years, slow, recurring variations in Earth s orbit around the Sun, which alter the distribution of solar energy received by Earth, have been enough to trigger the ice age cycles of the past 800,000 years. Fingerprinting is a powerful way of studying the causes of climate change. Different influences on climate lead to different patterns seen in climate records. This becomes obvious when scientists probe beyond changes in the average temperature of the planet and look more closely at geographical and temporal patterns of climate change. For example, an increase in the Sun s energy output will lead to a very different pattern of temperature change (across Earth s surface and vertically in the atmosphere) compared to that induced by an increase in concentration. Observed atmospheric temperature changes show a fingerprint much Learn more about other human causes of climate change In addition to emitting greenhouse gases, human activities have also altered Earth s energy balance through, for example: Changes in land use. Changes in the way people use land for example, for forests, farms, or cities can lead to both warming and cooling effects locally by changing the reflectivity of Earth s surfaces (affecting how much sunlight is sent back into space) and by changing how wet a region is. Emissions of pollutants (other than greenhouse gases). Some industrial and agricultural processes emit pollutants that produce aerosols (small droplets or particles suspended in the atmosphere). Most aerosols cool Earth by reflecting sunlight back to space. Some aerosols also affect the formation of clouds, which can have a warming or cooling effect depending on their type and location. Black carbon particles (or soot ) produced when fossil fuels or vegetation are burned, generally have a warming effect because they absorb incoming solar radiation. Evidence & Causes B7
8 closer to that of a long-term increase than to that of a fluctuating Sun alone. Scientists routinely test whether purely natural changes in the Sun, volcanic activity, or internal climate variability could plausibly explain the patterns of change they have observed in many different aspects of the climate system. These analyses have shown that the observed climate changes of the past several decades cannot be explained just by natural factors. Figure B5. The amount and rate of warming expected for the 21 st century depends on the total amount of greenhouse gases that humankind emits. Models project the temperature increase for a business-as-usual emissions scenario (in red) and aggressive emission reductions, falling close to zero 50 years from now (in blue). Black is the modelled estimate of past warming. Each solid line represents the average of different model runs using the same emissions scenario, and the shaded areas provide a measure of the spread (one standard deviation) between the temperature changes projected by the different models. All data are relative to a reference period (set to zero) of Source: IPCC AR5 How will climate change in the future? Scientists have made major advances in the observations, theory, and modelling of Earth s climate system; and these advances have enabled them to project future climate change with increasing confidence. Nevertheless, several major issues make it impossible to give precise estimates of how global or regional temperature trends will evolve decade by decade into the future. Firstly, we cannot predict how much human activities will emit, as this depends on factors such as how the global economy develops and how society s production and consumption of energy changes in the coming decades. Secondly, with current understanding of the complexities of how climate feedbacks operate, there is a range of possible outcomes, even for a particular scenario of emissions. Finally, over timescales of a decade or so, natural variability can modulate the effects of an underlying trend in temperature. Taken together, all model projections indicate that Earth will continue to warm considerably more over the next few decades to centuries. If there were no technological or policy changes to reduce emission trends from their current trajectory, then further warming of 2.6 to 4.8 C (4.7 to 8.6 F) in addition to that which has already occurred would be expected during the 21 st century [Figure B5]. Projecting what those ranges will mean for the climate experienced at any particular location is a challenging scientific problem, but estimates are continuing to improve as regional and local-scale models advance. ( o C) Global average surface temperature change Historical Aggressive emissions reductions Business as usual emissions B8
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study
 Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals. October 2011
 1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
Physics 100 Lecture 17. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018
 1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change
 Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Chapter 19: Global Change
 1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
What is climate change? - BBC News
 What is climate change? - BBC News Media caption Why we should care about climate change? In December, of cials from across the world will gather in Paris, France, to try to hammer out a deal to tackle
What is climate change? - BBC News Media caption Why we should care about climate change? In December, of cials from across the world will gather in Paris, France, to try to hammer out a deal to tackle
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank
 How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature
 LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change Date: 17 April 2018 I. Early Earth was more similar to present-day Venus o very high amounts of carbon dioxide
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change Date: 17 April 2018 I. Early Earth was more similar to present-day Venus o very high amounts of carbon dioxide
Concentrations of several of these greenhouse gases (CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O and CFCs) have increased dramatically in the last hundred years due to human
 Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System
 1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
Feedback loops modify atmospheric processes
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Earth s Dynamic Climate
 UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
Changing? What Is Climate and How Is It. You have probably seen or heard
 What Is Climate and How Is It Changing? Photo by Jesse Stanley Student Reading 1 Exit Glacier in Alaska has receded significantly in the last century. Photo by Jesse Stanley You have probably seen or heard
What Is Climate and How Is It Changing? Photo by Jesse Stanley Student Reading 1 Exit Glacier in Alaska has receded significantly in the last century. Photo by Jesse Stanley You have probably seen or heard
Global Warming. By William K. Tong. Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College
 Global Warming By William K. Tong Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College What Is Global Warming? According to the National Academy of Sciences, the Earth's surface temperature has risen
Global Warming By William K. Tong Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College What Is Global Warming? According to the National Academy of Sciences, the Earth's surface temperature has risen
Figure 1 - Global Temperatures - A plot from the EarthScience Centre at
 GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Contents. Permafrost Global Warming: An Introduction...4. Earth Is Getting Hotter...6. Green Homes The Greenhouse Effect...
 Contents Global Warming: An Introduction...4 Earth Is Getting Hotter...6 The Greenhouse Effect...8 Greenhouse Gases...10 Ozone Layer Depletion...12 The Carbon Cycle...14 The Kyoto Protocol...16 Climate
Contents Global Warming: An Introduction...4 Earth Is Getting Hotter...6 The Greenhouse Effect...8 Greenhouse Gases...10 Ozone Layer Depletion...12 The Carbon Cycle...14 The Kyoto Protocol...16 Climate
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE
 1 GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE From About Transportation and Climate Change (Source; Volpe center for Climate Change and Environmental forecasting, http://climate.volpe.dot.gov/trans.html Greenhouse effect has
1 GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE From About Transportation and Climate Change (Source; Volpe center for Climate Change and Environmental forecasting, http://climate.volpe.dot.gov/trans.html Greenhouse effect has
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Climate Change Science: What We Know
 Climate Change Science: What We Know by Lydia Olander, Rob Jackson, Gabi Hegerl, and Nicole St.Clair March 2007 What We Know 1. Scientists first described how accumulating carbon dioxide levels would raise
Climate Change Science: What We Know by Lydia Olander, Rob Jackson, Gabi Hegerl, and Nicole St.Clair March 2007 What We Know 1. Scientists first described how accumulating carbon dioxide levels would raise
TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century
 TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of
TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of
Global Warming Science Solar Radiation
 SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
The instrumental record goes back to about A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern
 The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Lecture 27: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change
 Lecture 27: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
Lecture 27: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
Global Warming and Climate Change
 Global Warming and Climate Change 1800s: Scientists knew that: If the earth were a bare, airless rock, the surface would be much colder than it actually is. Why? Tens of thousands of years ago, thick layers
Global Warming and Climate Change 1800s: Scientists knew that: If the earth were a bare, airless rock, the surface would be much colder than it actually is. Why? Tens of thousands of years ago, thick layers
Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change
 FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
Climate Change. (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88
 Climate Change An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88 The following is an Information Statement intended to
Climate Change An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88 The following is an Information Statement intended to
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge
 ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
Name: Class: Date: 6. Most air pollution is produced by a. thermal inversions. c. ozone layer depletion. b. fuel burning. d. volcanic eruptions.
 Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I
 Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Energy and the Earth. Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation.
 S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1. Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE
 Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Chapter Overview. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Change
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Global Warming & Climate Change Review Learning Target 1
 Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
Why is carbon dioxide so important? Examining the evidence
 Why is carbon dioxide so important? Examining the evidence In the light of new evidence and taking into account the remaining uncertainties, most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely
Why is carbon dioxide so important? Examining the evidence In the light of new evidence and taking into account the remaining uncertainties, most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist
 Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ
 Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
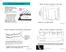 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Climate Change state of the science
 Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING
 Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity
 Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change
 Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming
 1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Earth's Atmosphere. Atmospheric Layers. Atmospheric Layers
 Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
IPCC 5 th Assessment Report
 The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It
 Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Slide 1 of 30
 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 1 of 30 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Researchers are gathering data to monitor and evaluate the effects of human activities on important systems in the biosphere.
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 1 of 30 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Researchers are gathering data to monitor and evaluate the effects of human activities on important systems in the biosphere.
11/15. Agenda. Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes
 Agenda 11/15 Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes Announcements -Test (11/20) -Notebook check (tomorrow) -Lab due (11.59pm, tomorrow) -No quiz tomorrow Criteria Table of contents labeled
Agenda 11/15 Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes Announcements -Test (11/20) -Notebook check (tomorrow) -Lab due (11.59pm, tomorrow) -No quiz tomorrow Criteria Table of contents labeled
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32)
 Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
State of the planetary life support system
 State of the planetary life support system "We're simply talking about the very life support system of this planet Joachim Hans Schellnhuber, Director of the Potsdam Climate Impacts Institute and Climate
State of the planetary life support system "We're simply talking about the very life support system of this planet Joachim Hans Schellnhuber, Director of the Potsdam Climate Impacts Institute and Climate
Global Climatic Change. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
 Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Atmosphere. The layer of gas surrounding the Earth
 Earth and Space Notes: Atmosphere Atmosphere The layer of gas surrounding the Earth Breakdown: Nitrogen (~79%) Oxygen (~21%) Argon, CO2, methane, ozone, water, nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, etc Gases
Earth and Space Notes: Atmosphere Atmosphere The layer of gas surrounding the Earth Breakdown: Nitrogen (~79%) Oxygen (~21%) Argon, CO2, methane, ozone, water, nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, etc Gases
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change
 Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
Draft Environmental Impact Statement
 The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings. Climate changes (1900 to 2000) due to human activity. Climate Variability and Climate Change
 Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years
 State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years 2012 Further developed from the past 20 year UNEP report Keeping Track of Our Changing Environment From Rio to Rio+20 (1992-2012) UNEP
State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years 2012 Further developed from the past 20 year UNEP report Keeping Track of Our Changing Environment From Rio to Rio+20 (1992-2012) UNEP
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN. Climate Disruption. Cengage Learning 2015
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
Earth Science & Society T. Perron
 Earth Science & Society T. Perron 12.001 The easiest way to introduce the relationship between Earth science and society is to point out that everything in our economy ultimately depends on the use and
Earth Science & Society T. Perron 12.001 The easiest way to introduce the relationship between Earth science and society is to point out that everything in our economy ultimately depends on the use and
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios
 Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Global warming. Models for global warming Sand analogy
 8.10 Global warming Assessment statements 8.6.1 Describe some possible models of global warming. 8.6. State what is meant by the enhanced greenhouse effect. 8.6.3 Identify the increased combustion of fossil
8.10 Global warming Assessment statements 8.6.1 Describe some possible models of global warming. 8.6. State what is meant by the enhanced greenhouse effect. 8.6.3 Identify the increased combustion of fossil
THE LONG TERM EVIDENCE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE
 THE LONG TERM EVIDENCE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE Robert B. Adams 11/12/13 A. INTRO A.1. Today I m going to talk about Climate Change and show you some of the evidence for the idea that the Earth s Climate may
THE LONG TERM EVIDENCE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE Robert B. Adams 11/12/13 A. INTRO A.1. Today I m going to talk about Climate Change and show you some of the evidence for the idea that the Earth s Climate may
Global Warming and Climate Change: State of the Science
 Freedman, F. and P. Zannetti. 2007. Global Warming and Climate Change: State of the Science. 1 Chapter 10 of Environmental Sciences and Environmental Computing. Vol. III (P. Zannetti, S. Elliott and D.
Freedman, F. and P. Zannetti. 2007. Global Warming and Climate Change: State of the Science. 1 Chapter 10 of Environmental Sciences and Environmental Computing. Vol. III (P. Zannetti, S. Elliott and D.
Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov.
 Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
Normal equatorial flow. Climate Variability. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources
 Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
B1 Biogeochemical Systems
 B1 Biogeochemical Systems Carbon Cycle What elements makes life possible? Carbon based life Key component of all known naturally occurring life on Earth Unique properties make it ideal for construction
B1 Biogeochemical Systems Carbon Cycle What elements makes life possible? Carbon based life Key component of all known naturally occurring life on Earth Unique properties make it ideal for construction
You Think the North is Cold! A Blanket Around Our World
 We know that climate change is being caused by the warming of our planet. But what causes this warming? Who or what is in control of the thermostat? This backgrounder provides the answers to these questions.
We know that climate change is being caused by the warming of our planet. But what causes this warming? Who or what is in control of the thermostat? This backgrounder provides the answers to these questions.
Basics of Sustainability. Climate Change
 Basics of Sustainability 2 Climate Change 1 Contents Page Aims. 2 Introduction. 3 Causes of Climate Change: Natural and Human Influences. 3 The Impacts of Climate Change.. 4 Mitigating Climate Change...
Basics of Sustainability 2 Climate Change 1 Contents Page Aims. 2 Introduction. 3 Causes of Climate Change: Natural and Human Influences. 3 The Impacts of Climate Change.. 4 Mitigating Climate Change...
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva
 Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer. Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June
 ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
GREENHOUSE GASES 3/14/2016. Water Vapor, CO 2, CFCs, Methane and NO x all absorb radiation Water vapor and CO 2 are the primary greenhouse gases
 GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained?
 How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34. Global Warming Part I
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34 Global Warming Part I Outline of three part global warming presentation What is the problem? How has the Earth s climate changed in recent years? Are these changes attributable
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34 Global Warming Part I Outline of three part global warming presentation What is the problem? How has the Earth s climate changed in recent years? Are these changes attributable
1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse.
 1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse. 5. A gradual increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide would warm Earth s because carbon dioxide is a A) poor reflector of ultraviolet radiation B) good reflector
1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse. 5. A gradual increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide would warm Earth s because carbon dioxide is a A) poor reflector of ultraviolet radiation B) good reflector
Greenhouse Effect. How we stay warm
 Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS FIRST -- The answers to the G-5 GROUP ACTIVITY on VOLCANISM & CLIMATE G-5 VOLCANISM & CLIMATE ACTIVITY #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted
A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS FIRST -- The answers to the G-5 GROUP ACTIVITY on VOLCANISM & CLIMATE G-5 VOLCANISM & CLIMATE ACTIVITY #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted
FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING. gogreen. Shop visit An Ekotribe Initiative
 FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING Shop Online @ www.thegreenecostore.com Definition The earth is a natural greenhouse and is kept warm by water vapors, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other gases in the atmosphere,
FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING Shop Online @ www.thegreenecostore.com Definition The earth is a natural greenhouse and is kept warm by water vapors, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other gases in the atmosphere,
Climate Change Questions, Condensed
 Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
The role of carbon dioxide in climate forcing from 1979 to 2004: introduction of the Annual Greenhouse Gas Index
 Tellus (2006), 58B, 614 619 Copyright C Blackwell Munksgaard, 2006 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved TELLUS The role of carbon dioxide in climate forcing from 1979 to 2004: introduction of the
Tellus (2006), 58B, 614 619 Copyright C Blackwell Munksgaard, 2006 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved TELLUS The role of carbon dioxide in climate forcing from 1979 to 2004: introduction of the
CHAPTER 19. Global Change
 CHAPTER 19 Global Change WALKING ON THIN ICE Polar bears play important role in North Pole ecosystem Food seals Important as food and fur for clothing source for indigenous people Problem temperatures
CHAPTER 19 Global Change WALKING ON THIN ICE Polar bears play important role in North Pole ecosystem Food seals Important as food and fur for clothing source for indigenous people Problem temperatures
Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since Estimated global mean temperature
 1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future Slide 2 of 30
 6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 2 of 30 Ozone Depletion What are two types of global change of concern to biologists? the ozone layer high in the atmosphere the global climate system 3 of 30 Ozone
6-4 Charting a Course for the Future 2 of 30 Ozone Depletion What are two types of global change of concern to biologists? the ozone layer high in the atmosphere the global climate system 3 of 30 Ozone
