Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Outline Last IPCC report : 2001 Last IPCC report :
|
|
|
- Bruce Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping gases ¾1896 Arrenhius calculates earth warming from gases Or «How do we go from a GreenHouse to and predicts future warming from doubling CO2 "On the Influence of Carbonic Acid in the Air upon the Temperature of the Ground" Philosophical Magazine 41, 237 (1896) - a changing climate» Introduction ¾1980s Ice core data (here from Vostok) reveal a large correlation between Temperature and Atmospheric Composition Introduction ¾1958 Keeling begins direct measurement of CO2 in atmosphere
2 Introduction 2001 Last IPCC report : An increasing body of observations gives a collective picture of a warming world and other changes in the climate system Introduction 2001 Last IPCC report : An increasing body of observations gives a collective picture of a warming world and other changes in the climate system Emissions of greenhouse gases ( ) due to human activities continue to alter the atmosphere in ways that are expected to affect the climate Introduction Outline 2001 Last IPCC report : An increasing body of observations gives a collective picture of a warming world and other changes in the climate system Emissions of greenhouse gases ( ) due to human activities continue to alter the atmosphere in ways that are expected to affect the climate There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities 1. Earth s radiative budget : The importance of the GreenHouse Effect 2. GHG : Species, Sources and Sinks, Recent evolution and projections 3. Response of Climate : observations, projections
3 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.1 Emission of radiation by a solid body or a gaz 1. Earth s radiative budget No spectral overlap between predicted spectra with temperatures similar to sun and earth Planck s Law : F 2 5 2πc hλ λ, T ) = ch kλt e 1 B ( / (monochromatic emissive power of a black body) Wien s Law : λ max ( T ) = 2897 /T Wavelength of maximum intensity with T Stefan-Boltzmann s Law : 4 F B = σt hot bodies radiate more energy than cold ones Peak at 15 µm Peak at 0.5 µm Observations 1. Earth s radiative budget Version 1 : Without any atmosphere S 0 αs 0 F e 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.2 Absorption of radiation by gases The mechanism of absorption differs depending on the the wavelength (1-α) S 0 = σ T e 4 S 0 = 342 W m -2 Albedo α = 0.3 Stephan-Boltzman Constant σ = W m -2 K -4 UltraViolet Molecule Dissociation InfraRed Molecule Vibration MicroWave Molecule Turning Te = 255 K! It is too cold
4 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.2 Absorption of radiation by gases Some greenhouse gases transmission spectra - di-atomic molecules (O2, N2) do not absorb IR radiation (no electric dipole moment) -Tri-atomic molecules (H2O, CO2, N2O, CH4, ) present different forms of vibration and thus absorb at different wavelength An example : the CO 2 molecule 4.2 µm 15 µm CO2 Absorption Spectrum : 2 absorbing bands at 4.2 micron (B mode) and 15.0 micron (C and D mode) 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.3 Greenhouse Principle Absorbing Spectrum : - almost complete in UV - very low in the visible and near IR - IR : mainly H2O except in the 7-15 micron band
5 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.3 Greenhouse Principle Radiation emitted to space 1. Earth s radiative budget Version 2 : With an atmosphere (only one layer here ) Altitude S 0 αs 0 τf e F a GHG F e F a Absorption - emission by gases Transparent atmosphere in SW Partially absorbing in IR Surface : (1-α) S 0 + F a = F e Top of the Atmosphere : F e -F a = τf e +F a Emission Temperature Surface Temperature Temperature Emitted Radiation from the surface 1. Earth s radiative budget 1.4 The Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Sinks : Mainly chemical processes - reaction with OH in troposphere (CH4, HFCs, HSFCs..) - photolysis in stratosphere and mesosphere (N2O, PCFs, CFCs, ) Greenhouse Gas Mean Concentration / Burden Repartition Radiative Properties (RF, GWP) Recent Evolution Sources (Natural and Artificial): Mainly at the surface IPCC, 2001
6 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2.1 Useful definitions Life time : Atmospheric burden divided by mean global sink for a gas in steady state. Characterizes time to turn over atmospheric burden once. Radiative Forcing (RF): Change in net radiative flux at the tropopause due to a perturbation of the climate system (e.g. GHG concentrations) after allowing for stratospheric temperatures to readjust to radiative equilibrium, but with surface and tropospheric temperatures held fixed at the unperturbed values GWP (Global Warming Potential) : ratio of the time-integrated forcing from the instantaneous release of 1 kg of trace substance relative to 1 kg of a reference gas (usually CO2). GWP is function of the radiative properties and life time of the considered gas but also of the time period considered. 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Gas 2.2 Main Greenhouse gases (Pre-Industrial) LifeTime Concentration (ppm) H 2 O few days CO yr Ozone O 3 variable Methane CH yrs Oxide Nitreux N 2 O yrs Natural Greenhouse Effect (W/m2) Climate Sensitivity : Perturbation to equilibrium surface temperature Ts is related to radiative forcing by Ts = λ RF Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2.2 Main Greenhouse gases (from pre-industrial to today) - Hydrofluorocarbons - Chlorofluorocarbons - Increase from 1750 CO 2 : +31 % CH 4 : +151 % N 2 O : +17 % O 3 trop. : +36 % IPCC, 2001
7 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Global Warming Potential Lifetime Global Warming Potential (Time Horizon in Years) GAS (years) 20 yrs 100 yrs 500 Carbon Dioxide CO Methane CH Nitrous Oxide N 2 O CHLOROFLUOROCARBONS CFC CFC CFC HYDROFLUOROCARBONS HFC-23 CHF HFC-32 CH 2 F HFC-41 CH 3 F HFC-125 CHF 2 CF HFC-134 CHF 2 CHF HFC-143 CHF 2 CH 2 F HFC-152 CH 2 FCH 2 F HFC-161 CH 3 CH 2 F HFC-227 CF 3 CHFCF Main Greenhouse gases IPCC (2001) classifies the different GHGs in -CO2 - non-co2 Kyoto Gases - CH4 -N2O - HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons) - PFCs (perfluorocarbons) and SF6 (sulphur hexafluoride) - Montreal Protocole Gases CFCs, halons - Tropospheric O3 - Non-direct GHGs -CO -NOx.. Contribution to Anthropogenic Greenhouse effect 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2.3 Example : CH4 cycle Second GHG in terms of contribution to anthropogenic grenhouse effect But also Controls amount of OH (hydroxyl) in the troposphere Affects concentrations of water vapor and O 3 (ozone) in the stratosphere and plays a key-role in conversion of reactive Cl to less reactive HCl in stratosphere But large uncertainties on H2O forcing. IPCC, 2001
8 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2.3 Example : CH4 cycle (From 750 ppb to 1745 ppb in 1998) 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2.3 Example : CH4 cycle Natural Sources (~200 TgC/yr) : Anthropogenic Sources (~ 400 TgC/yr) : Sinks (~576 TgC/yr) : Soils Tropospheric OH Stratospheric Loss Wetlands Wild ruminants Termites Agriculture (Rice) Ruminants Waste treatment FF burning Biomass burning Ocean Hydrates 2. Greenhouse Gases (GHG) 2. Greenhouse Gases 2.3 Example : CH4 cycle - Life time : t = 8.4 yr (IPCC, 2001) with a burden of 4850 TgCH4 ansd a sink of 576 TgCH4/yr But complex feedback on OH concentration. 2.4 Projections under different scenarios - Some sources poorly constrained and potential feedbacks of GW on some of those sources (hydrates?) IPCC 2001
9 3. Response of Climate? 3.1 Recent observations (from IPCC 2001) - Sea surface temperature : + 0,8ºC (± 0,2) from begining of XXth century 3.1 Observations 3.2 A Cause-Effect relationship? 3.3 Projections - Confirmed by others instruments (balloons, satellites..) Recent Warming compared to past 1000 y reconstruction But Warming is not uniform in time and space
10 World Mountain Glaciers Sea Level evolution - from maregraphs Le glacier d Argentière (Alpes) - mechanisms : water thermal expansion + contribution from greenland melting Precipitations Number of frost days and Heat Wave duration (IPCC, 2001) Frost Days Heat Waves - Mid to high latitudes from N.H. : increase (+0,5/1%/decade) - sub-tropics (10N-30N) : decrease (-0.3%/decade)
11 An increasing body of observations gives a collective picture of a warming world and other changes in the climate system 3.2 A cause-effect relationship? Historical Radiative Forcing IPCC,2001 Climate Models U + 2Ω U =. t There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over the last 50 years is attributable to human activities - from climate models - New detection techniques
12 3.3 Projections Temperature Change ( C) IPCC, 2001 And a new glaciation very unlikely
13
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
The next 2 weeks. Reading: IPCC (2007), Chap 7 (sections 7.4 and 7.5)
 PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic. Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR. with a focus on Atmospheric Chemistry
 FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming.
 Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Other GHGs. IPCC Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Other GHGs IPCC Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis 1 Atmospheric Chemistry and other long-lived GHG during the industrial period 1750-2000 The radiative forcing of climate during the period
Other GHGs IPCC Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis 1 Atmospheric Chemistry and other long-lived GHG during the industrial period 1750-2000 The radiative forcing of climate during the period
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
climate change Contents CO 2 (ppm)
 climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 : ocean acidification 5. OtherGreenhouse
climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 : ocean acidification 5. OtherGreenhouse
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge
 ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition
 TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition There s one more thing to correct in our the depiction of incoming Solar....... the atmosphere is NOT totally TRANSPARENT to INCOMING Solar
TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition There s one more thing to correct in our the depiction of incoming Solar....... the atmosphere is NOT totally TRANSPARENT to INCOMING Solar
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance
 GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance Dr. John Abatzoglou Spring 2011 Lecture Goals (1) Understand the global balance of energy and associated fluxes of energy and energy types (2) Qualita@ve and quan@ta@ve
GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance Dr. John Abatzoglou Spring 2011 Lecture Goals (1) Understand the global balance of energy and associated fluxes of energy and energy types (2) Qualita@ve and quan@ta@ve
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chemistry 471/671. Global Climate Change
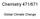 Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
GLOBAL WARMING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12
 GLOBAL WARMING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12 Previous lecture Radiation budget review Driving factors Albedo Solar forcing Greenhouse gases Feedbacks The climate machine
GLOBAL WARMING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12 Previous lecture Radiation budget review Driving factors Albedo Solar forcing Greenhouse gases Feedbacks The climate machine
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1
 OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds.
 Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Environmental Impacts of. Energy Production
 CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
Project report on. Climate Change and Carbon Emission
 Project report on Climate Change and Carbon Emission Introduction Climate is not the same as weather, but rather, its meteorological elements include precipitation, temperature, humidity, sunshine, wind
Project report on Climate Change and Carbon Emission Introduction Climate is not the same as weather, but rather, its meteorological elements include precipitation, temperature, humidity, sunshine, wind
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Energy and the Earth. Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation.
 S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
Global Climatic Change. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
 Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
1.1 The Greenhouse Effect
 1.1 The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere s Role on the Greenhouse Effect Energy flows, expressed in W/m 2 with or without greenhouse gases (GHG) 342 17 342 17 235 235 235-19 C 67 168 +14 C Source: after
1.1 The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere s Role on the Greenhouse Effect Energy flows, expressed in W/m 2 with or without greenhouse gases (GHG) 342 17 342 17 235 235 235-19 C 67 168 +14 C Source: after
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Global Warming Science Solar Radiation
 SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained?
 How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since Estimated global mean temperature
 1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall
 More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2
 Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission
 Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reshmi Banerjee Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, W.B., India ABSTRACT: Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called
Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reshmi Banerjee Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, W.B., India ABSTRACT: Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014
 Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
Basics of greenhouse gases and climate change
 Basics of greenhouse gases and climate change Facts and theories We need to distinguish between what we know (facts), and what we think will happen (theories). In the subject of greenhouse gases and global
Basics of greenhouse gases and climate change Facts and theories We need to distinguish between what we know (facts), and what we think will happen (theories). In the subject of greenhouse gases and global
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Chapter 11: Atmosphere
 To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
The Science of Global Warming
 The Science of Global Warming Global Warming can be understood qualitatively using the two concepts: Energy Balance Feedback Loops Two important Definitions Greenhouse effect: natural, beneficial consequence
The Science of Global Warming Global Warming can be understood qualitatively using the two concepts: Energy Balance Feedback Loops Two important Definitions Greenhouse effect: natural, beneficial consequence
ATMOSPHERE CHEMISTRY
 ATMOSPHERE CHEMISTRY Lecture No.: 6 Slide No. 1 Organisation of study Lecturer: Marek Staf, MSc., Ph.D., phone: +420 220 444 458 e-mail:, web: building A, Dept. 216, door No.162 e-learning: Scale of subject:
ATMOSPHERE CHEMISTRY Lecture No.: 6 Slide No. 1 Organisation of study Lecturer: Marek Staf, MSc., Ph.D., phone: +420 220 444 458 e-mail:, web: building A, Dept. 216, door No.162 e-learning: Scale of subject:
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Climate Change. Black-Body Radiation. Factors that affect how an object absorbs, emits (radiates), and reflects EM radiation incident on them:
 Climate Change Black-Body Radiation Factors that affect how an object absorbs, emits (radiates), and reflects EM radiation incident on them: 1) Nature of the surface: material, shape, texture, etc. 2)
Climate Change Black-Body Radiation Factors that affect how an object absorbs, emits (radiates), and reflects EM radiation incident on them: 1) Nature of the surface: material, shape, texture, etc. 2)
ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE -- 2013 1. Y (visible) 2. Z (infrared) 3. X (ultraviolet) 4. d (the absorption is occurring almost entirely in the infrared (LW) part
ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE -- 2013 1. Y (visible) 2. Z (infrared) 3. X (ultraviolet) 4. d (the absorption is occurring almost entirely in the infrared (LW) part
Climate Change Vocabulary Global Challenges for the 21 st Century Tony Del Vecchio, M.Ed. Atmosphere
 Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
The science of the Kyoto protocol
 The science of the Kyoto protocol Vicky Pope Hadley Centre with lots of help from Climate Chemistry and Ecosystem group ECMWF seminar September 2005 Page 1 Outline Kyoto protocol Observations relevant
The science of the Kyoto protocol Vicky Pope Hadley Centre with lots of help from Climate Chemistry and Ecosystem group ECMWF seminar September 2005 Page 1 Outline Kyoto protocol Observations relevant
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate
 Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633. Ross Salawitch
 Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Note: An entry for CHEM 433 has appeared on Testudo
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Note: An entry for CHEM 433 has appeared on Testudo
The Chemistry of Carbon and Global Warming Potentials Dr. Erik Krogh, Department of Chemistry; Local 2307
 The Chemistry of Carbon and Global Warming Potentials Dr. Erik Krogh, Department of Chemistry; erik.krogh@viu.ca; Local 2307 Biogeochemical Cycling - Where on Earth is all the carbon and what s it doing
The Chemistry of Carbon and Global Warming Potentials Dr. Erik Krogh, Department of Chemistry; erik.krogh@viu.ca; Local 2307 Biogeochemical Cycling - Where on Earth is all the carbon and what s it doing
AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Revision 1: 20 Feb 2013 Page 1 of 6 AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Problem Set #2 (150 points total) Due: Thurs, 21 Feb 2013 (start of class) Late penalty: 10 points per
Revision 1: 20 Feb 2013 Page 1 of 6 AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Problem Set #2 (150 points total) Due: Thurs, 21 Feb 2013 (start of class) Late penalty: 10 points per
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32)
 Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009
 Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
Global Climate Change. The sky is falling! The sky is falling!
 Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department
 Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming
 1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
The Greenhouse Effect
 Name: Date: The Greenhouse Effect This document provides an overview of the earth's atmospheric "greenhouse effect" by briefly exploring the atmospheres of nearby planets and discussing our atmosphere's
Name: Date: The Greenhouse Effect This document provides an overview of the earth's atmospheric "greenhouse effect" by briefly exploring the atmospheres of nearby planets and discussing our atmosphere's
GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere
 GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere Global Atmo Energy Balance In a stable climate, Solar Energy IN = IR Energy OUT IR Out Ahrens, Fig. 2.14 Solar in The Natural Greenhouse Effect: clear sky O 3 8% CH 4
GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere Global Atmo Energy Balance In a stable climate, Solar Energy IN = IR Energy OUT IR Out Ahrens, Fig. 2.14 Solar in The Natural Greenhouse Effect: clear sky O 3 8% CH 4
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Chapter 2. Climate Change: Scientific Basis
 a. The Greenhouse Effect Chapter 2 Climate Change: Scientific Basis Climate scientists have clearly established that: The Earth s atmosphere is like a greenhouse, reflecting some of the sun s harmful rays
a. The Greenhouse Effect Chapter 2 Climate Change: Scientific Basis Climate scientists have clearly established that: The Earth s atmosphere is like a greenhouse, reflecting some of the sun s harmful rays
3/5/2012. Study Questions. Global Warming. Weather: daily temperature and moisture conditions Climate: long-term weather patterns
 Study Questions Global Warming 1. Explain what is meant by the term Greenhouse effect. 2. List 3 indications that global climate is currently increasing. 3. Describe 3 possible consequences of global warming.
Study Questions Global Warming 1. Explain what is meant by the term Greenhouse effect. 2. List 3 indications that global climate is currently increasing. 3. Describe 3 possible consequences of global warming.
Global Warming Potentials in AR4. V. Ramaswamy. NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University
 Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Drivers of Climate Change
 .3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
.3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
Chapter 19: Global Change
 1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
GE 2211 Environmental Science and Engineering Unit IV Global Warming. M. Subramanian
 GE 2211 Environmental Science and Engineering Unit IV Global Warming M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
GE 2211 Environmental Science and Engineering Unit IV Global Warming M. Subramanian Assistant Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change
 Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Anthropogenic Global Warming. Be aware, be concerned and. start acting. - it is real
 Anthropogenic Global Warming - it is real Be aware, be concerned and start acting Ben Rose Sustainability Consultant, Nov 2009 email:biroses@westnet.com.au AIMING FOR CARBON NEUTRAL -THE 4 C S 1. CO2e
Anthropogenic Global Warming - it is real Be aware, be concerned and start acting Ben Rose Sustainability Consultant, Nov 2009 email:biroses@westnet.com.au AIMING FOR CARBON NEUTRAL -THE 4 C S 1. CO2e
Atmospheric Methane Distribution and Trends: Impacts on Climate and Ozone Air Quality
 Atmospheric Methane Distribution and Trends: Impacts on Climate and Ozone Air Quality Arlene M. Fiore Larry Horowitz (NOAA/GFDL) Jason West (Princeton) Ed Dlugokencky (NOAA/GMD) Earth, Atmospheric, and
Atmospheric Methane Distribution and Trends: Impacts on Climate and Ozone Air Quality Arlene M. Fiore Larry Horowitz (NOAA/GFDL) Jason West (Princeton) Ed Dlugokencky (NOAA/GMD) Earth, Atmospheric, and
ASTRONOMY 161. Introduction to Solar System Astronomy. Class 16
 ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
Chapter 8 The chemistry of global climate
 Chapter 8 The chemistry of global climate The focus of this chapter is to examine the ways in which global climate is infl uenced by the composition and chemistry of the atmosphere. This will be done by:
Chapter 8 The chemistry of global climate The focus of this chapter is to examine the ways in which global climate is infl uenced by the composition and chemistry of the atmosphere. This will be done by:
Introduction to Climate Change: the UNFCCC and the Kyoto Protocol
 Introduction to Climate Change: the UNFCCC and the Kyoto Protocol Colin Mattis National Climate Change Office Ministry of Forestry, Fisheries and Sustainable Development Overview What is Climate Change
Introduction to Climate Change: the UNFCCC and the Kyoto Protocol Colin Mattis National Climate Change Office Ministry of Forestry, Fisheries and Sustainable Development Overview What is Climate Change
The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic
 C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change
 Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas?
 1 What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas? You may have stood in a greenhouse and felt the heat, but what do greenhouse gases have to do with greenhouses? A greenhouse gas is any gas that absorbs and re-emits
1 What Exactly is a Greenhouse Gas? You may have stood in a greenhouse and felt the heat, but what do greenhouse gases have to do with greenhouses? A greenhouse gas is any gas that absorbs and re-emits
Case 3:17-cv WHA Document Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5
 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 2 of 71 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity
Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 2 of 71 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Concentrations of several of these greenhouse gases (CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O and CFCs) have increased dramatically in the last hundred years due to human
 Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School
 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School of Geography and the Environment & Department of Physics
Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School of Geography and the Environment & Department of Physics
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013
 Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013 MRS 1 Due Tuesday The Earth s atmosphere has changed substantially over our planet s history First gases surrounding Earth were originally hydrogen and helium (during
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 2/28/2013 MRS 1 Due Tuesday The Earth s atmosphere has changed substantially over our planet s history First gases surrounding Earth were originally hydrogen and helium (during
Thursday Sep 25th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY! Topic # 6 Atmospheric Structure & Chemical Composition
 Thursday Sep 25th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY! Topic # 6 Atmospheric Structure & Chemical Composition Self Test 4 & RQ-4 on The Laws of Thermodynamics are now posted. The readings that will prepare you for
Thursday Sep 25th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY! Topic # 6 Atmospheric Structure & Chemical Composition Self Test 4 & RQ-4 on The Laws of Thermodynamics are now posted. The readings that will prepare you for
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Atmospheric chemistry Summary
 Atmospheric chemistry Summary Pontus Roldin Div. Nuclear Physics Department of Physics Lund University Summary 1 Chapman mechanism (1930) The Chapman mechanism for stratospheric ozone (1) O 2 + hn O +
Atmospheric chemistry Summary Pontus Roldin Div. Nuclear Physics Department of Physics Lund University Summary 1 Chapman mechanism (1930) The Chapman mechanism for stratospheric ozone (1) O 2 + hn O +
Figure 1 - Global Temperatures - A plot from the EarthScience Centre at
 GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
Fact sheet 18 June Selecting and Using GWP values for Refrigerants
 Selecting and Using GWP values for Refrigerants Summary and Recommendations Refrigerant GWP values have been revised with each new IPCC Assessment Report. Regulations and guidance for the use of GWP values
Selecting and Using GWP values for Refrigerants Summary and Recommendations Refrigerant GWP values have been revised with each new IPCC Assessment Report. Regulations and guidance for the use of GWP values
Florida Atlantic University Environmental Issues in Atmospheric and Earth Science Second Midterm Examination Key
 ESC3704 Name 56 points March 20, 2012 24 students took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic
ESC3704 Name 56 points March 20, 2012 24 students took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test
 Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate. Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK
 Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle
 Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Dr. Shelley Kauffman Albright College
 Dr. Shelley Kauffman Albright College skauffman@albright.edu HS-ESS2-4.Use a model to describe how variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth s systems result in changes in climate. [Clarification
Dr. Shelley Kauffman Albright College skauffman@albright.edu HS-ESS2-4.Use a model to describe how variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth s systems result in changes in climate. [Clarification
Carbon Management 101
 Carbon Management 101 West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum January 12, 2009 Clinton S. Boyd, PHD Sustainable Research Group Decarbonization The systematic reduction of the carbon intensity* of emissions
Carbon Management 101 West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum January 12, 2009 Clinton S. Boyd, PHD Sustainable Research Group Decarbonization The systematic reduction of the carbon intensity* of emissions
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality
 Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Notes: Ross, Allison & Tim co-teach this
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Notes: Ross, Allison & Tim co-teach this
Global Warming is unequivocal
 Global Warming is unequivocal The recent Kevin IPCC E Trenberth report has clearly stated that Warming NCAR of the climate system is unequivocal and it is very likely caused by human activities. Moreover,
Global Warming is unequivocal The recent Kevin IPCC E Trenberth report has clearly stated that Warming NCAR of the climate system is unequivocal and it is very likely caused by human activities. Moreover,
Atmospheric chemistry Summary Presented by Pontus Roldin Material from Erik Swietlicki Avd. för Kärnfysik Fysiska institutionen Lunds universitet
 Atmospheric chemistry Summary Presented by Pontus Roldin Material from Erik Swietlicki Avd. för Kärnfysik Fysiska institutionen Lunds universitet Summary 1 Chapman mechanism (1930) The Chapman mechanism
Atmospheric chemistry Summary Presented by Pontus Roldin Material from Erik Swietlicki Avd. för Kärnfysik Fysiska institutionen Lunds universitet Summary 1 Chapman mechanism (1930) The Chapman mechanism
Klimaänderung. Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen
 Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
