it is transmitted easily over distance, through electricity cables it can be used in many ways, for example electric lamps, heaters, motors etc
|
|
|
- Annice Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM Science Generating electricity Electricity is a convenient source of energy and can be generated in a number of different ways. You will need to weigh up the advantages and disadvantages of other ways of producing energy, such as the use of nuclear power stations. Electricity Coal, oil and natural gas are primary energy sources. Electricity is a secondary energy source because we use primary energy sources to produce it. These primary sources can be non-renewable or renewable. Electricity itself is neither non-renewable nor renewable. Electricity is convenient because: it is transmitted easily over distance, through electricity cables it can be used in many ways, for example electric lamps, heaters, motors etc Process of using electrical energy Generating electricity Generators are the devices that transfer kinetic energy into
2 2 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM electrical energy. Turning generators directly Generators can be turned directly, for example, by: wind turbines hydroelectric turbines wave and tidal turbines When electricity is generated using wave, wind, tidal or hydroelectric power (HEP) there are two steps: The turbine turns a generator. Electricity is produced. Turning generators indirectly Generators can be turned indirectly using fossil or nuclear fuels. The heat from the fuel boils water to make steam, which expands and pushes against the blades of a turbine. The spinning turbine then turns the generator. These are the steps by which electricity is generated from fossil fuels: 1. Heat is released from fuel and boils the water to make
3 3 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM steam. 2. The steam turns the turbine. 3. The turbine turns a generator and electricity is produced. 4. The electricity goes to the transformers to produce the correct voltage. Efficiency of energy transfer "Wasted" energy Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transferred from one form to another, or moved. Energy that is "wasted", like the heat energy from an electric lamp, does not disappear. Instead, it is transferred to its surroundings and spreads out so much that it becomes difficult to do anything useful with it. Electric lamps Ordinary electric lamps contain a thin metal filament that glows when electricity passes through it. However, most of the electrical energy is transferred as heat rather than light energy. This is the Sankey diagram for a typical filament lamp. Sankey diagram for a filament lamp Modern energy-saving lamps work in a different way. They
4 4 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM transfer a greater proportion of electrical energy as light energy. This is the Sankey diagram for a typical energy-saving lamp. Sankey diagram for a typical energy-saving lamp From the diagram, you can see that much less electrical energy is transferred, or "wasted", as heat energy. Calculating efficiency The efficiency of a device such as a lamp can be calculated using this equation: efficiency = (useful energy transferred energy supplied) 100 The efficiency of the filament lamp is = 10%. This means that 10% of the electrical energy supplied is transferred as light energy. 90% is transferred as heat energy. The efficiency of the energy-saving lamp is = 75%. This means that 75% of the electrical energy supplied is transferred as light energy. 25% is transferred as heat energy. Note that the efficiency of a device will always be less than 100%.
5 5 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM Efficiency of power stations The energy produced by burning fuel is transferred as heat and stored in water as steam. The energy in steam is transferred to movement in a turbine, then to electrical energy in the turbine. Energy is lost to the environment at each stage. Here is a Sankey diagram to show these losses. Sankey diagram Note that only about a third of the energy stored in the fuel was transferred as electrical energy to customers. Different kinds of energy sources Renewable energy sources Our renewable energy resources will never run out. Their supply is not limited. There are no fuel costs either. And they typically generate far less pollution than fossil fuels. Renewable energy resources include: wind energy water energy, such as wave machines, tidal barrages and
6 6 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM hydroelectric power geothermal energy solar energy biomass energy, for example energy released from wood Wind farms are noisy and may spoil the view of people who live near them. The amount of electricity generated depends on the strength of the wind. If there is no wind, there is no electricity. A wind turbine Non-renewable energy sources There is a limited supply of non-renewable energy resources, which will eventually run out. They include: fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas nuclear fuels, such as uranium Fossil fuels release carbon dioxide when they burn, which adds to the greenhouse effect and increases global warming. Of the three fossil fuels, coal produces the most carbon dioxide, for a given amount of energy released, while natural gas generates the least. The fuel for nuclear power stations is relatively cheap. But the power stations themselves are expensive to build. It is also very expensive to dismantle old nuclear power stations or store radioactive waste, which is a dangerous health hazard. Nuclear power stations The main nuclear fuels are uranium and plutonium, both of which are radioactive metals. Nuclear fuels are not burned to
7 7 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM release energy. Instead, heat is released from changes in the nucleus. Just as with power stations burning fossil fuels, the heat energy is used to boil water. The kinetic energy in the expanding steam spins turbines, which drive generators to produce electricity Advantages Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear fuels do not produce carbon dioxide. Disadvantages Like fossil fuels, nuclear fuels are non-renewable energy resources. And if there is an accident, large amounts of radioactive material could be released into the environment. In addition, nuclear waste remains radioactive and is hazardous to health for thousands of years. It must be stored safely. Nuclear waste is given different categories. Nuclear waste categories Category Examples Disposal Low level Intermediate level Contaminated equipment, materials and protective clothing Components from nuclear reactors, radioactive sources used in medicine or research They are put in drums and surrounded by concrete, and put into clay lined landfill sites. They are mixed with concrete, then put in a stainless steel drum in a purpose-built store.
8 8 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM Category Examples Disposal High level Used nuclear fuel and chemicals from reprocessing fuels They are stored underwater in large pools for 20 years, then placed in storage casks in purpose-built underground store where air can circulate to remove the heat produced. High level waste decays into intermediate level waste over many thousands of years. Watch You may wish to view this BBC News item from 2006 about the arguments for and against nuclear power. Nuclear fission - higher only Nuclear power stations use the heat released by nuclear reactions to boil water to make steam The type of nuclear reaction used is called nuclear fission. In nuclear fission: Watch 1. A neutron collides with a uranium nucleus. A uranium nucleus is large and unstable. 2. The uranium nucleus splits into two similar-sized smaller nuclei. 3. More neutrons are released. 4. These neutrons can then collide with more uranium nuclei. These processes are repeated continuously, forming a chain
9 9 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM reactionchain reaction: A nuclear chain reaction occurs when a neutron splits a nucleus, releasing more neutrons, which in turn go on to split even more nuclei.. Rate of energy released In a nuclear reactor, the reaction is controlled so that energy is released at a steady rate. The energy released in nuclear fission is far greater than the energy released in a chemical reaction, such as burning fuel. This means that the power output of a nuclear power station is large. The lifetime of a nuclear power station is about 20 years. Advantages and disadvantages In considering the subject of nuclear power, it is important to weigh up the advantages and the disadvantages. These are some of the advantages: no carbon dioxide is produced when the station is operating, as stated earlier there is a high power output a small amount of fuel is needed, when compared with coal or gas These are some of the disadvantages: hazardous radioactive waste is produced, as stated earlier building the power stations is quite expensive decommissioning, ie taking apart, the power stations at the end of their lifetime is very costly
10 10 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM Outline of a nuclear reactor The nuclear fuel, usually uranium oxide, is held in metal containers called fuel rods. These are lowered into the reactor core. A coolant, usually water or carbon dioxide, is circulated through the reactor core to remove the heat. Control rods are also lowered into the core. These absorb neutrons and control the rate of the chain reaction. They are raised to speed it up, or lowered to slow it down. Ideas about science - making decisions Scientific applications give people things that they value, but may have undesirable impacts on the environment. Our society uses more and more energy every year, but the carbon dioxide produced by most power stations is believed to be causing serious damage to the climate. Natural resources should be used in a sustainable way. The use of renewable energy sources would guarantee energy for the future. At the moment, renewable energy
11 11 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM sources cannot provide enough energy. There are official regulations and laws which control scientific research and applications. The nuclear industry is regularly inspected to ensure that standards of safety are maintained. Some applications of science have ethical implications. One point of view is that the right decision is the one which gives the best outcome for most people. Another point of view is that certain actions are never justified because they are wrong. Disposal of nuclear waste raises ethical problems: Some people say that we must have nuclear power, or we will not be able to combat global warming and still produce enough energy. Others say that it is unethical to produce waste that will still be dangerous in many thousands of years time. Weighing up the arguments - higher only Before deciding on a course of action, it is important to ask if it is feasible. Can it be done? Then it is possible to consider if it ought to done. If nuclear waste could be sent down into the Earth s mantle, it would take millions of years to resurface. Unfortunately, there doesn t seem to be any way to do this. It is not feasible. Nuclear waste could be sent into space in rockets so that it falls harmlessly into the Sun. Unfortunately, this would be far too expensive, and any accident on take-off would spread dangerous waste over a large area. It ought not to be done. In different social and economic contexts, different decisions might be taken.
12 12 of 12 1/24/2013 9:01 AM Many developing countries insist that they need to burn fossil fuels in their power stations, even if it produces global warming. They need this to allow them to catch up with the standard of living that we enjoy. Now try a Test Bite - foundation. Now try a Test Bite - higher. Back to Revision Bite
IB Topic 8.1: Energy Production, Energy Sources
 IB Topic 8.1: Energy Production, Energy Sources World use of energy sources 91% Nonrenewable Only approximate values are needed Energy density of fuels Energy in MJ/kg Uranium 235 90,000,000 Crude Oil
IB Topic 8.1: Energy Production, Energy Sources World use of energy sources 91% Nonrenewable Only approximate values are needed Energy density of fuels Energy in MJ/kg Uranium 235 90,000,000 Crude Oil
What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence. Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects.
 Page 1 What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects. What type of surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of infrared
Page 1 What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects. What type of surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of infrared
Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Name Date Class. How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources?
 Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Y7 Energy Summary Booklet
 Y7 Energy Summary Booklet Energy Units Energy changes are measured in joules (J) or kilojoules (kj). Energy Stores and Transfers Energy stores Key word Description Examples Magnetic The energy stored in
Y7 Energy Summary Booklet Energy Units Energy changes are measured in joules (J) or kilojoules (kj). Energy Stores and Transfers Energy stores Key word Description Examples Magnetic The energy stored in
Questions that science may help to answer. This module offers opportunities to develop mathematics skills. For example:
 3.3.3 Module P3: Sustainable energy Overview Energy supply is one of the major issues that society must address in the immediate future. Citizens are faced with complex choices and a variety of messages
3.3.3 Module P3: Sustainable energy Overview Energy supply is one of the major issues that society must address in the immediate future. Citizens are faced with complex choices and a variety of messages
Activity 3 Information sheet
 Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Energy. Solar Energy. Energy Resource A natural resource that. humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable.
 Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
Energy & Power Unit 5, Lesson 1 Explanation
 Energy & Power 5.1.1 Unit 5, Lesson 1 Explanation The Unit Big Idea The designed world is the product of a design process, which provides ways to turn resources - materials, tools and machines, people,
Energy & Power 5.1.1 Unit 5, Lesson 1 Explanation The Unit Big Idea The designed world is the product of a design process, which provides ways to turn resources - materials, tools and machines, people,
WORK Potential Kinetic
 Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES. Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon
 ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY
 CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & SOCIETY L & (P.242-249) Incandescent light bulbs were invented over 150 years ago. Today, billions of light bulbs (lamps) illuminate vast areas of Earth at night. January
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & SOCIETY L & (P.242-249) Incandescent light bulbs were invented over 150 years ago. Today, billions of light bulbs (lamps) illuminate vast areas of Earth at night. January
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
 Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
World Energy Sources, Fossil Fuel Power Production, and Nuclear Power. By Henry Aoki, Nathan Carroll, Cameron Fudeh and Casey Lee-Foss
 World Energy Sources, Fossil Fuel Power Production, and Nuclear Power By Henry Aoki, Nathan Carroll, Cameron Fudeh and Casey Lee-Foss Part 1: World Energy Sources and Fossil Fuel Power Production Different
World Energy Sources, Fossil Fuel Power Production, and Nuclear Power By Henry Aoki, Nathan Carroll, Cameron Fudeh and Casey Lee-Foss Part 1: World Energy Sources and Fossil Fuel Power Production Different
Alternative Energy. 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear. 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power)
 Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
atom biofuel biomass the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
 atom the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons biofuel any fuel that comes directly from organic matter found in present-day living things biomass organic matter
atom the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons biofuel any fuel that comes directly from organic matter found in present-day living things biomass organic matter
Power Technologies. Question. Answer. Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. Answer. Question. What are the various sources of energy?
 What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
Crossword Puzzle Energy and Power. Name: Class: Date:
 Crossword Puzzle - 5.1.1 Energy and Power Name: Class: Date: Fill in the crossword puzzle by using the clues. 1 2 3 2 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 10 6 7 11 8 12 9 13 10 11 12 Across 1. These nonrenewable resources
Crossword Puzzle - 5.1.1 Energy and Power Name: Class: Date: Fill in the crossword puzzle by using the clues. 1 2 3 2 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 10 6 7 11 8 12 9 13 10 11 12 Across 1. These nonrenewable resources
Comparing Renewable Energy Sources
 Section 1 - Supply and Demand Fossil Fuels At present our main sources of energy are the fossil fuels. These are coal, oil and gas. Fossil fuels are the remains of plants and animals that died millions
Section 1 - Supply and Demand Fossil Fuels At present our main sources of energy are the fossil fuels. These are coal, oil and gas. Fossil fuels are the remains of plants and animals that died millions
HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED?
 SOURCES OF ENERGY HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED? Most of the living things on Earth obtain their energy directly or indirectly from the Sun. Humans consume solar energy by eating plants and animals.
SOURCES OF ENERGY HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED? Most of the living things on Earth obtain their energy directly or indirectly from the Sun. Humans consume solar energy by eating plants and animals.
Sources of Electricity
 Sources of Electricity S C I E N C E L I N K S 9 U N I T 4 T O P I C 4. 1 B R A I N P O P S : E N E R G Y S O U R C E S N U C L E A R E N E R G Y W I N D E N E R G Y S O L A R E N E R G Y F O S S I L F
Sources of Electricity S C I E N C E L I N K S 9 U N I T 4 T O P I C 4. 1 B R A I N P O P S : E N E R G Y S O U R C E S N U C L E A R E N E R G Y W I N D E N E R G Y S O L A R E N E R G Y F O S S I L F
Name Class Date. What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable energy resources? What are renewable energy resources?
 CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
2010 Culver Media, LLC 1
 Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Boardworks Ltd Energy Resources
 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Energy Resources Energy Resources 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are energy resources? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 An energy resource is anything that can be used to generate
1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Energy Resources Energy Resources 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are energy resources? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 An energy resource is anything that can be used to generate
UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO
 UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO 1. WHAT IS ENERGY? Definition: Energy is a physical quantity which produces a change or an effect Unit: International System Joule (J) Other Calorie (cal) 1cal =4,19J
UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO 1. WHAT IS ENERGY? Definition: Energy is a physical quantity which produces a change or an effect Unit: International System Joule (J) Other Calorie (cal) 1cal =4,19J
ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION
 1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
Energy and Energy Resources
 Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
ENERGY. 1. Non-renewable or finite energy resources are. 2. Renewable or infinite energy resources are source of
 Energy is the ability to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed: it can only be transformed, from one type into another. Energy can be either potential or kinetic. Kinetic energy is found in anything
Energy is the ability to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed: it can only be transformed, from one type into another. Energy can be either potential or kinetic. Kinetic energy is found in anything
Energy Energy is the ability to do work or move something.
 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or move something. www.mrcjcs.com 1 There are 2 main groups of Energy, 1. Stored energy Forms of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or move something. Potential
Energy Energy is the ability to do work or move something. www.mrcjcs.com 1 There are 2 main groups of Energy, 1. Stored energy Forms of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or move something. Potential
Voltage: electrical energy that is used to push electricity through a wire
 Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS / IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS / IB PHYSICS LSN 7-1: ENERGY DEGRADATION AND POWER GENERATION Questions From Reading Activity? IB Assessment Statements 8.1. Energy Degradation and
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS / IB PHYSICS LSN 7-1: ENERGY DEGRADATION AND POWER GENERATION Questions From Reading Activity? IB Assessment Statements 8.1. Energy Degradation and
Card #1/24. Describe how thermal energy is passed on in terms of ions Using these ideas explain how a convection current occurs
 Card #1/24 Card #2/24 Topic: Conduction Topic: Convection In what state of matter does conduction occur? In what states of matter does convection occur? Explain why it needs to be in this state? Define
Card #1/24 Card #2/24 Topic: Conduction Topic: Convection In what state of matter does conduction occur? In what states of matter does convection occur? Explain why it needs to be in this state? Define
GENERATING ELECTRICITY AT A POWER PLANT ???? Law of Conservation of Energy. Three Major Components THE SCIENCE BEHIND ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS
 THE SCIENCE BEHIND ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Q1 GENERATING ELECTRICITY AT A POWER PLANT Unit Essential Question: How are Earth s energy resources used to generate electricity What are the advantages and disadvantages
THE SCIENCE BEHIND ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Q1 GENERATING ELECTRICITY AT A POWER PLANT Unit Essential Question: How are Earth s energy resources used to generate electricity What are the advantages and disadvantages
GraspIT AQA Energy Questions
 A. Energy changes and energy stores part 1 Energy systems and energy changes 1. Describe the energy store changes when a rocket firework is lit, goes up in the air and then falls back to the ground. (4)
A. Energy changes and energy stores part 1 Energy systems and energy changes 1. Describe the energy store changes when a rocket firework is lit, goes up in the air and then falls back to the ground. (4)
Work done = force distance. The distance moved in the formula must be the distance moved in the direction of the force.
 Work If a builder is lifting up a stone, we say that he is doing work. Similarly, you would be doing work when you carry your school bag up a flight of steps to your classroom. Work is done when a force
Work If a builder is lifting up a stone, we say that he is doing work. Similarly, you would be doing work when you carry your school bag up a flight of steps to your classroom. Work is done when a force
Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy.
 Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Generating Electricity
 Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
GraspIT AQA Energy Questions
 A. Energy changes and energy stores part 1 Energy systems and energy changes 1. Describe the energy store changes when a rocket firework is lit, goes up in the air and then falls back to the ground. (4)
A. Energy changes and energy stores part 1 Energy systems and energy changes 1. Describe the energy store changes when a rocket firework is lit, goes up in the air and then falls back to the ground. (4)
M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]
![M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]](/thumbs/85/92444350.jpg) M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
FOSSIL FUELS THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE WORLD'S ELECTRICAL POWER, AND 95% OF THE WORLD'S TOTAL ENERGY DEMANDS.
 ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS COAL, OIL AND NATURAL GAS ARE CALLED "FOSSIL FUELS" BECAUSE THEY HAVE BEEN FORMED FROM THE FOSSILIZED REMAINS OF PREHISTORIC PLANTS AND ANIMALS. THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE
ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS COAL, OIL AND NATURAL GAS ARE CALLED "FOSSIL FUELS" BECAUSE THEY HAVE BEEN FORMED FROM THE FOSSILIZED REMAINS OF PREHISTORIC PLANTS AND ANIMALS. THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE
Energy Vocabulary. Word Definition Memory Aid the ability to cause an object to 1. energy move, change, or work
 the ability to cause an object to 1. move, change, or work 2. trade-off something that you do not want, but have to accept in order to have something that you want (disadvantage) 3. variable a changing
the ability to cause an object to 1. move, change, or work 2. trade-off something that you do not want, but have to accept in order to have something that you want (disadvantage) 3. variable a changing
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what. conduction is. Does conduction happen best in solids, liquids or gases?
 What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
Topic P3 Sustainable Energy Homework booklet
 Name Key terms and spellings on back page Topic P3 Sustainable Energy Homework booklet Due Date Teacher Comment Homework 1 Homework 2 Homework 3 Homework 4 Homework One: Energy and Power Stations Add these
Name Key terms and spellings on back page Topic P3 Sustainable Energy Homework booklet Due Date Teacher Comment Homework 1 Homework 2 Homework 3 Homework 4 Homework One: Energy and Power Stations Add these
Characteristics of source of energy
 Energy Sources Characteristics of source of energy Provide adequate amount of useful energy at a steady rate over a long period of time. It should be safe & convenient to use economical & easy to store
Energy Sources Characteristics of source of energy Provide adequate amount of useful energy at a steady rate over a long period of time. It should be safe & convenient to use economical & easy to store
4/30/12. Chapter: Energy Sources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal
![T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal](/thumbs/78/78599564.jpg) T8-1 [166 marks] 1. Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal 2. For a black-body at absolute temperature T the power emitted per unit area is P. What is the power
T8-1 [166 marks] 1. Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal 2. For a black-body at absolute temperature T the power emitted per unit area is P. What is the power
Energy Resources. A resource that can be used continuously without being used up. Often referred to as sustainable energy resource
 Energy Energy Resources Non-Renewable Resources that are not replaced or regenerated naturally within a reasonable period of time. For example, fossil fuels and minerals. Renewable A resource that can
Energy Energy Resources Non-Renewable Resources that are not replaced or regenerated naturally within a reasonable period of time. For example, fossil fuels and minerals. Renewable A resource that can
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives.
 I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
Contents. 3(a) Useful Energy and Efficiency. 3(b) Electricity and Circuits. Dynamics. 3(c) 2 P h y s i c s
 1 P h y s i c s Contents 3(a) 3(b) 3(c) Useful Energy and Efficiency Electricity and Circuits Dynamics 3 9 19 2 P h y s i c s 3(a) Useful Energy and Efficiency It is useful for energy consultants to be
1 P h y s i c s Contents 3(a) 3(b) 3(c) Useful Energy and Efficiency Electricity and Circuits Dynamics 3 9 19 2 P h y s i c s 3(a) Useful Energy and Efficiency It is useful for energy consultants to be
Section 2: Energy and Resources
 Section 2: Energy and Resources Preview Key Ideas Bellringer The Search for Resources Making Oil Worldwide Energy Use by Fuel Type Alternative Sources of Energy The Efficiency of Energy Conversion Key
Section 2: Energy and Resources Preview Key Ideas Bellringer The Search for Resources Making Oil Worldwide Energy Use by Fuel Type Alternative Sources of Energy The Efficiency of Energy Conversion Key
Energy: Conservation and Transfer
 Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
Introduction to Energy
 Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Ch Energy. Energy = the ability to do work; energy is transferred by a force moving an object over a distance
 Ch. 15 - Energy Energy = the ability to do work; energy is transferred by a force moving an object over a distance Work --> a transfer of energy (when work is done on an object, energy is transferred to
Ch. 15 - Energy Energy = the ability to do work; energy is transferred by a force moving an object over a distance Work --> a transfer of energy (when work is done on an object, energy is transferred to
NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
 ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
Graham School. Name: P3 Questions. Class: Date: 58 minutes. Time: 58 marks. Marks: Comments: Page 1
 P3 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 58 minutes Marks: 58 marks Comments: Page Q. Wind and tides are renewable energy sources that are used to generate electricity. (a) Complete each sentence by putting
P3 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 58 minutes Marks: 58 marks Comments: Page Q. Wind and tides are renewable energy sources that are used to generate electricity. (a) Complete each sentence by putting
Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels.
 Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
1 Monday, May 16, 16
 1 Chapter 12 Nonrenewable Energy Resources Nonrenewable Energy Nonrenewable energy resources- fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear fuels. U.S. Energy Use 13% 1% 19% 42% 25% Coal Natural Gas
1 Chapter 12 Nonrenewable Energy Resources Nonrenewable Energy Nonrenewable energy resources- fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear fuels. U.S. Energy Use 13% 1% 19% 42% 25% Coal Natural Gas
- renewable - cheap - no pollution. - expensive equipment - no energy on cloudy or rainy days
 Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
Grade VIII Physics Work Sheet Name
 S Grade VIII Physics Work Sheet Name SOURCES OF ENERGY Energy: - Whenever a body is capable of doing work, the body is said to possess energy. Thus energy is defined as the ability of a body to do work
S Grade VIII Physics Work Sheet Name SOURCES OF ENERGY Energy: - Whenever a body is capable of doing work, the body is said to possess energy. Thus energy is defined as the ability of a body to do work
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives. Eric D. Graham
 Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
Day 5: Energy (Greener)
 Introduction Day 5: Energy (Greener) Before stating three alternative sources of energy and give their advantages and disadvantages, I believe I should say what is an alternative source of energy for me
Introduction Day 5: Energy (Greener) Before stating three alternative sources of energy and give their advantages and disadvantages, I believe I should say what is an alternative source of energy for me
Alternative Energy Resources. Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011
 Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
gas oil Sun tides waves wind
 Methods we use to generate electricity 1. (a) Different energy sources are used to generate electricity. Which two of the energy sources in the box are likely to be used up first? Draw a ring around each
Methods we use to generate electricity 1. (a) Different energy sources are used to generate electricity. Which two of the energy sources in the box are likely to be used up first? Draw a ring around each
Power_Climate_P2 [259 marks]
![Power_Climate_P2 [259 marks] Power_Climate_P2 [259 marks]](/thumbs/96/128465582.jpg) Power_Climate_P2 [259 marks] The radioactive nuclide beryllium-10 (Be-10) undergoes beta minus ( β ) decay to form a stable boron (B) nuclide. 1a. Identify the missing information for this decay. [1 mark]
Power_Climate_P2 [259 marks] The radioactive nuclide beryllium-10 (Be-10) undergoes beta minus ( β ) decay to form a stable boron (B) nuclide. 1a. Identify the missing information for this decay. [1 mark]
Nonrenewable Energy Sources
 Nonrenewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels and Nuclear Energy This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA Nonrenewable Energy Fossil Fuels coal, oil, natural gas Nuclear Fuels Uranium-235, Plutonium-239
Nonrenewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels and Nuclear Energy This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA Nonrenewable Energy Fossil Fuels coal, oil, natural gas Nuclear Fuels Uranium-235, Plutonium-239
8.3 FOSSIL FUEL PRODUCTION 8.4 NON-FOSSIL FUEL POWER PRODUCTION HW/Study Packet
 8.3 FOSSIL FUEL PRODUCTION 8.4 NON-FOSSIL FUEL POWER PRODUCTION HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 418-429 Hamper pp 273-293 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson pp 994-995 REMEMBER TO. Work
8.3 FOSSIL FUEL PRODUCTION 8.4 NON-FOSSIL FUEL POWER PRODUCTION HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 418-429 Hamper pp 273-293 SL/HL Supplemental: Cutnell and Johnson pp 994-995 REMEMBER TO. Work
Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources. Energy
 Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources Energy SOURCES OF ENERGY RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Infinite supply NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Limited supply Part 1 Fossil Fuels NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS Coal,
Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources Energy SOURCES OF ENERGY RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Infinite supply NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Limited supply Part 1 Fossil Fuels NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS Coal,
Lecture (3) on. Nuclear Reactors. By Dr. Emad M. Saad. Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering. Fayoum University
 1 Lecture (3) on Nuclear Reactors By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. 2015-2016 2 Nuclear Fission
1 Lecture (3) on Nuclear Reactors By Dr. Emad M. Saad Mechanical Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. 2015-2016 2 Nuclear Fission
Work, Energy and Power.
 Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Period 18: Consequences of Nuclear Energy Use
 Name Section Period 18: Consequences of Nuclear Energy Use As you watch the videos in class today, look for a pro-nuclear or anti-nuclear bias on the part of the video producers, narrators, and interviewers.
Name Section Period 18: Consequences of Nuclear Energy Use As you watch the videos in class today, look for a pro-nuclear or anti-nuclear bias on the part of the video producers, narrators, and interviewers.
Energy Resources and Fossil Fuels
 Nonrenewable Energy Energy Resources and Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels remains of ancient organisms that changed into coal, oil, or natural gas 2 main problems Supplies are limited environmental consequences
Nonrenewable Energy Energy Resources and Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels remains of ancient organisms that changed into coal, oil, or natural gas 2 main problems Supplies are limited environmental consequences
P2 Revision Questions
 P2 Revision Questions Part 1 Question 1 What is an alternating current? Answer 1 Where electrons move backwards and forwards across a point (not in one direction) Question 2 What is a direct current? Answer
P2 Revision Questions Part 1 Question 1 What is an alternating current? Answer 1 Where electrons move backwards and forwards across a point (not in one direction) Question 2 What is a direct current? Answer
Coal, oil, natural gas Nuclear (radioactivity from uranium) biomass fuel (such as wood
 16.1 Natural Resources and Energy For tens of thousands of years, people have depended on Earth s resources for food, clothing, shelter, energy, medicine, and even entertainment, arts, and riches. What
16.1 Natural Resources and Energy For tens of thousands of years, people have depended on Earth s resources for food, clothing, shelter, energy, medicine, and even entertainment, arts, and riches. What
Sources of Energy acid rain Conventional non-conventional sources of energy Renewable non-renewable sources of energy Renewable sources
 GOOD SOURCE OF ENERGY 1. a good source of energy would be one large amount of work per unit volume or mass, easily accessible, (iii) easy to store and transport, and (iv) economical. 2. We can classify
GOOD SOURCE OF ENERGY 1. a good source of energy would be one large amount of work per unit volume or mass, easily accessible, (iii) easy to store and transport, and (iv) economical. 2. We can classify
Section 1. Electricity and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Solar panels The Fizzics Organisation
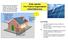 Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Effects of Energy Transfer. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009
 Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009 Science A Unit Physics P1a (Energy and Electricity)
Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009 Science A Unit Physics P1a (Energy and Electricity)
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision sheets
 Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
Q1. A student investigated the efficiency of a motor using the equipment in Figure 1.
 EFFICIENCY Q1. A student investigated the efficiency of a motor using the equipment in Figure 1. Figure 1 He used the motor to lift a weight of 2.5 N a height of 2.0 m. He measured the speed at which the
EFFICIENCY Q1. A student investigated the efficiency of a motor using the equipment in Figure 1. Figure 1 He used the motor to lift a weight of 2.5 N a height of 2.0 m. He measured the speed at which the
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information
 Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Graham School. Name: New Document 1. Class: Date: 90 minutes. Time: 89 marks. Marks: Comments: Page 1
 Graham School New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: 90 minutes Marks: 89 marks Comments: Page Graham School Q.All European Union countries are expected to generate 20% of their electricity using renewable
Graham School New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: 90 minutes Marks: 89 marks Comments: Page Graham School Q.All European Union countries are expected to generate 20% of their electricity using renewable
 UNIT- III NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS Basics of Nuclear Engineering, Layout and subsystems of Nuclear Power Plants, Working of Nuclear Reactors: Boiling Water Reactor (BWR), Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR), CANada
UNIT- III NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS Basics of Nuclear Engineering, Layout and subsystems of Nuclear Power Plants, Working of Nuclear Reactors: Boiling Water Reactor (BWR), Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR), CANada
7. Energy, Power and Climate Change. Chapter 7.1 Energy degradation and power generation
 7. Energy, Power and Climate Change Chapter 7.1 Energy degradation and power generation Degradation of energy Energy flows from hot bodies to cold bodies. The difference in temperature between two bodies
7. Energy, Power and Climate Change Chapter 7.1 Energy degradation and power generation Degradation of energy Energy flows from hot bodies to cold bodies. The difference in temperature between two bodies
08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers
 08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers Power generation 1. Copy and complete: Thermal energy may be completely converted into work in a single process such as the adiabatic expansion of a gas
08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers Power generation 1. Copy and complete: Thermal energy may be completely converted into work in a single process such as the adiabatic expansion of a gas
Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change
 Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change 8.1 Energy degradation and power generation 8.1.1 State that thermal energy may be completely converted to work in a single process, but that continuous conversion
Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change 8.1 Energy degradation and power generation 8.1.1 State that thermal energy may be completely converted to work in a single process, but that continuous conversion
Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water
 Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water 24.1 The Earth s Water Cycle 1) Components of the Earth s water cycle a) What can happen to some of the water in lakes, rivers, oceans, and in the soil as the Sun
Period 24 Solutions: Energy and Water 24.1 The Earth s Water Cycle 1) Components of the Earth s water cycle a) What can happen to some of the water in lakes, rivers, oceans, and in the soil as the Sun
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
4th Grade. Energy and Natural Resources.
 1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
3.3 Unit 1 Physics 1. Infrared radiation. d) Light, shiny surfaces are poor absorbers and poor emitters. of infrared radiation.
 3.3 Unit 1 Physics 1 P1.1 The transfer of energy by heating processes and the factors that affect the rate at which that energy is transferred Energy can be transferred from one place to another by work
3.3 Unit 1 Physics 1 P1.1 The transfer of energy by heating processes and the factors that affect the rate at which that energy is transferred Energy can be transferred from one place to another by work
Renewable Energy Alternatives
 Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY Shell Global Solutions International B.V.
 KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY CONSERVATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY? ENERGY CONSERVATION involves reducing energy consumption, largely through behavioural change. ENERGY
KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY CONSERVATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY? ENERGY CONSERVATION involves reducing energy consumption, largely through behavioural change. ENERGY
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet- 8th Ed. Guided Reading: Chapter 16: Alternative Energy and The Environment.
 Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet- 8th Ed. Guided Reading: Chapter 16: Alternative Energy and The Environment Name: Read: Using Wind Power in New Ways for an Old Application
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet- 8th Ed. Guided Reading: Chapter 16: Alternative Energy and The Environment Name: Read: Using Wind Power in New Ways for an Old Application
Draw one line from each energy source in List A to the statement about the energy source in List B.
 1 Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in List
1 Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in List
Chapter 14: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 14: Sources of Energy Question 1 What is a good source of energy? A good source of energy would be one, 1. Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or per unit mass 2. Which would
Chapter 14: Sources of Energy Question 1 What is a good source of energy? A good source of energy would be one, 1. Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or per unit mass 2. Which would
THE NUCLEAR FUEL CYCLE
 THE NUCLEAR FUEL CYCLE Uranium is a slightly radioactive metal that is found throughout the earth s crust It is about 500 times more abundant than gold and about as common as tin Natural uranium is a mixture
THE NUCLEAR FUEL CYCLE Uranium is a slightly radioactive metal that is found throughout the earth s crust It is about 500 times more abundant than gold and about as common as tin Natural uranium is a mixture
Lesson 5 Energy. OAA Science Lesson 5 52
 Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
