TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
|
|
|
- Winfred Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis and Design (and partly Operation) of Processes and Utility Systems, with focus on Efficient Use of Energy while considering Economy, Operation and (to some extent) Environment Requirements to be able to join the Course None (meaning previous courses), but it is an advantage to have some basic knowledge about the following: heat exchangers, distillation columns, evaporators turbines, heat pumps and simple thermodynamics Fall 98: 100 students from 8 departments in 4 faculties!! From Spring 2009: Compulsory for the PuP Program Truls Gundersen
2 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy and Process The Course Content is primarily System based Strategy for Design of integrated Process Plants with corresponding Utility Systems Systematic Methods for Analysis and Design of Reactor Systems (very limited and not in depth) Thermally driven Separation Systems, such as (primarily) Distillation and (to a much less extent) Evaporation Heat Exchanger Networks and Correct Heat Integration Utility Systems (heating, cooling and power) The Thermodynamically based Pinch Analysis Brief Introduction to the use of Optimization Environmental Issues related to Energy Usage New Design and Retrofit of Existing Plants Truls Gundersen
3 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy and Process The Curriculum for the Course is: R. Smith: Chemical Process Design and Integration, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, January Alternative Text Book: I.C. Kemp: Pinch Analysis and, Elsevier, Butterworth Heinemann, December : Basic Concepts for Heat Recovery in Retrofit Design of Continuous Processes, Ch. 6 in A Primer, IEA, 2000 (18 pages). Lectures and Assignments. Assignments are Examination oriented (most are previous Ex Q s) Examination will test Understanding through Calculation Examples. This requires Training established by working with Assignments. Home Page: Truls Gundersen
4 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Plan for Assignments with Guidance Ass. Topic Supervised Deadline 1 Sequence of Distillation Columns Minimum Energy Requirements and Pinch Design of Heat Exchanger Networks (1) Optimization of Heat Exchanger Networks Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks Indirect Integration of Plants using Steam Integration of Distillation Columns Optimal Use of Heat Pump Area in Heat Exchanger Networks Heat Integration and Forbidden Matches Design of Heat Exchanger Networks (2) none Guidance: ½ Scientific Assistant, 6 Student Assistants and the Lecturer Truls Gundersen
5 Reactor System (R) No questions so far à Any Questions now? Relevance for the Exam? à Lecturer to provide some wise words.. à Or: See the next Slide!! Q - 01
6 Reactor System (R) Q from 2010 What is expected by the Students on this topic à Q: Chapter is part of the list describing what is curriculum from the text book by Robin Smith. Are we expected to be able to reproduce (or derive) the formulas here, or should we be able to use them? à A: These Sections are listed with importance 1, meaning that this is Background material. No formulas need to be derived or used, these Sections are included (as 1 ) to provide background for the discussion about effects of T and p in the lectures Q - 02
7 Reactor Separator Interface (R/S) No questions so far à Any Questions now? Relevance for the Exam? à Lecturer to provide some wise words.. F F R R R F R R X P X S P B P y R = X S y P = X S (1+ω) Q - 03
8 Separation System (S) No questions so far à Any Questions now? Relevance for the Exam? à Lecturer to provide some wise words.. à Or: See next Slide!! Q - 04
9 Separation System (S) Q from 2009 Curriculum for Distillation Sequences à Q: I would like to know what is relevant for the Exam in the topic Sequence of Distillation Columns. There is no (?) Exam Tasks where the entire process should be developed (such as in Assignment 1). Does this mean it is not very relevant? à A: True, not given during è about time? à A: The topic is relevant, and one should know the Heuristic Rules, have a good Strategy for developing the sequence, and be able to handle Heat Integration. Q - 05
10 Separation System (S) Q from 2009 Hot and Cold Streams in Distillation Columns à Q: Why is the Reboiler identified as a Cold Stream, while the Condenser is identified as a Hot Stream, when the Reboiler has higher Temperature? à A: A mixture is boiling in the Reboiler (liquid to vapor) and condensing in the condenser (vapor to liquid), thus heat must be supplied to the Reboiler and removed from the Condenser à A: Hot/Cold refers to change in Thermodynamic State, not the absolute Temperature level of streams Q - 06
11 Separation System (S) Q from 2009 mcp Values in Distillation Columns & Utilities à Q: Why are mcp values of condensers and reboilers as well as utilities said to be infinity? à A: Consider the following (use Blackboard) à The slope of condensing/vaporizing streams in TQ diagrams à Enthalpy change for sensible vs. latent heat à A: Some Software Packages use ΔT=1 C for condensing and vaporizing streams (results in very large mcp values, but not infinity ) Q - 07
12 Interface Separation System (S) and Heat Recovery System (H) No questions so far à Any Questions now? Relevance for the Exam? à Lecturer to provide some wise words Q - 08
13 Questions related to Targeting for Energy: à Q: I understand that heat transfer across the Pinch temperature is unfavorable, but does such a process require more energy? à A: Yes, the point is that the Pinch decomposes the process into two parts; one with heat deficit (above Pinch) and one with heat surplus (below Pinch). As a result, any heat transfer across the Pinch will make BOTH the deficit and surplus larger, and thus increase both external heating and cooling (i.e. energy) Q - 09
14 Questions related to Targeting for Energy: à Q: In the solution to Exam 2012, the simplified heat cascade is used. Stream C2 has a target temperature of 215C, while in the simplified cascade, the interval temperature is 245C. Of course, in kw, this is accounted for. However, I get the same result using all temperatures, and it is then more clear à A: Yes, there are advantages (fewer intervals) and disadvantages (have to be careful with heat supply and rejection) with using the simplified heat cascade!! Q - 10
15 Questions related to Targeting for Units: à Q: In Assignment 7, how do we get U min,mer = 9? à A: See Grid Diagram below with Column A integrated above Pinch (i.e. Condenser H3) 200 C 140 C 120 C H1 à Q: Why U total = C H2 à A: C3, C4 & H4 140 C 140 C H3 also need heat 170 C exchangers!! 120 C (with Utilities) 120 C 100 C 60 C 80 C 60 C C1 30 C C2 Q - 11
16 Questions related to Targeting for Units: à Q: Euler s Rule says U = N + L S, where S stands for Subnetwork. What is a Subnetwork? à A: A Subnetwork means that some streams and units are in heat balance, and that there are no connections with other streams/units. Notice that S = 1 means that the entire network is connected, while S = 2 means there are 2 independent Subnetworks. Q - 12
17 Questions related to Targeting for Units: à Q: Euler s Rule says U = N + L S; is N the number of heaters, coolers and streams? à A: No!! N is the number of process streams and utility types!! (A very common misunderstanding) à Q: My notes say that L = U actual U min, and it is emphasized that U actual U min,mer. In the solution to Assignment 7, it is said that U = U min,mer?? à A: Distinguish Targets (before) from Design (after). Assign. 7 simply counts units. Remember Assign. 3 Q - 13
18 Questions related to Targeting for Units: à Q: In the Exam for 2008 there is one heater and two coolers. One of the coolers operates across Pinch. The task is to find U min,mer. How to count for the cooler operating across Pinch? à A: Yet another misunderstanding about the targeting formula for minimum number of units. The N-1 rule is applied at the targeting stage ahead of design, and should not be applied to a network. The background for the Exam question is to highlight that the network has 5 units while the minimum for MER is 7 units. Q - 14
19 Questions related to Targeting for Units: 270 H Pinch kw H2 2 Cb H 2500 kw kw Ca kw 160 C kw C1 mcp (kw/ C) Q - 15
20 Questions related to Design of HENs: à Q: In order to find the log mean temperature difference (LMTD) for heat exchangers one uses the inlet and outlet temperatures for the hot and cold side of the exchanger. What about utility exchangers (heaters and coolers) where we only have 2 temperatures? à A: Utility exchangers have a hot and cold side in the same way as process/process exchangers. LMTD is calculated based on the supply and target temperatures of the streams and the utilities. See previous Slide!! Q - 16
21 Questions related to Design of HENs: à Q: In the Solution for Exam 2011(?), a match below Pinch is made between a hot stream with mcp=20 and a cold stream with mcp=40, while another cold stream with mcp=30 and a more favorable inlet temperature could have been used? à A: The Pinch Design Method has 2 important elements; decompose the problem at the Pinch (i.e. design separate networks above and below Pinch) and start the design at the Pinch. Considering cold inlet temperatures means starting in the cold end! See next Slide!! Q - 17
22 Questions related to Design of HENs: 300 C H1 250 C 220 C H 3000 kw I 160 C H2 Pinch 160 C α β 150 C 150 C II 3000 kw 72.5 C III IV C 65 C 150 C C 2000 kw 50 C 80 C 50 C C1 60 C C2 mcp kw 3400 kw 200 kw Q - 18
23 Questions related to Design of HENs: à Q: In the Solution for Exam 2010 (Task 1.c), cold stream C1 is split above Pinch. Why can we not do without this split? à A: This is a crucial question and goes directly into the heart of the Pinch Design Method and the issues of Pinch Exchangers and mcp Rules. The next slide shows the split design and the split-free design. Unfortunately, this is a very common mistake in previous Exams!! Q - 19
24 Network from the Solution to the Exam 2010 Process, Energy and System 150 C H1 180 C H2 140 C 180 C I III C II C C 110 C 2000 H C 100 C 100 C α 90 C C1 β 90 C 90 C IV C C a 1200 C b C 50 C 50 C C2 mcp An MER Design meeting Targets for Energy and Units Q - 20
25 Network from one of the Students Process, Energy and System 150 C H1 180 C H2 140 C 180 C H C III C 100 C II 100 C II C 90 C C C 90 C IV C C a 2000 C b C 50 C 50 C C2 mcp Violating mcp Rules for Pinch Exchangers Q - 21
26 Questions related to Design of HENs: à Q: Could you say something about Utility Pinch, how it arise, and what kind of Effects does it have? à A: Utility Pinch points arise only when we have more than one hot or more than one cold utility while at the same time maximizing the load (duty) of the cheaper utility to reduce total energy cost. à A: Utility Pinch will directly and strongly affect the design of the network (one more Region for each such Pinch), and will result in a more complex network (more units and stream splits) with increased total area. Q - 22
27 Advanced Design Tools for HENs: à Q: How do we construct the Driving Force Plot (DFP) and what is it used for? à A: Starting with the Composite Curves, the DFP is constructed by plotting corresponding values of cold composite temperatures and the temperature difference between the hot and the cold Composite Curves. à A: The DFP is used as a qualitative tool for good distribution of driving forces and thus minimizing total heat transfer area. More specifically it is used to find stream split ratios and to tame the tick-off rule. Q - 23
28 Advanced Design Tools for HENs: H1 ΔT H2 2 3 Nice, but not relevant for the Exam!! T α α T β β C1 3 C2 Q T C Pinch Pinch Q - 24
29 Advanced Design Tools for HENs: à Q: What is the Remaining Problem Analysis (RPA), and how/when do we use it? à A: The RPA is used as a quantitative tool to provide feedback to the designer who makes one decision at a time. The effect of accepting a specific heater, cooler or process/process heat exchangers is measured by estimating the final values for Energy, Area and Units by combining data for the accepted unit and the target values for the Remaining Problem. See next Slide!! Q - 25
30 Advanced Design Tools for HENs: H1 Nice, 220 but not relevant for the Exam!! H C C kw 160 Q - 26
31 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: In Assignment 7, can I disregard process and utility Pinch points during Optimization? à A: Notice there is no Utility Pinch here, integrating the Condenser creates a new process Pinch!! à A: The observation is correct though. After the MER design, we forget about the Pinch point(s), but still focus on having feasible driving forces (ΔT ΔT min ). Energy consumption will increase when reducing units, and heat will flow across the Pinch point(s)!! Q - 27
32 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: What is the definition of Loops and Paths? à A: A Heat Load Loop is a connection between units and streams in such a way that the heat exchangers can change their duties (+/- x) without affecting the total enthalpy change of the streams involved. à A: A Heat Load Path is similar to a Loop in the sense that the enthalpy change of the streams remains the same. A Path is used to repair ΔT problems after breaking a Loop. Thus it involves Utility exchangers. Q - 28
33 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: Can a stream that is split into two branches be part of a Heat Load Loop or Path? à A: Yes, as long as the stream enthalpy change remains the same, it does not matter whether the + x kw unit is in serial or parallel arrangement with the - x kw unit. Q - 29
34 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: Is the objective of Optimization to break Loops by removing Units or is it to remove Units, and breaking Loops is a consequence of this? à A: The objective of Optimization (or Evolution) is both to reduce Total Annual Cost and to simplify network complexity (number of units and stream splits). This can be done by removing small Units, since these have a considerable cost while not recovering much energy. Network complexity is also a consequence of the PDM with Pinch decomposition. Q - 30
35 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: Can you explain the procedure for removing units from the MER-(i) design in the solution for Exam 2007, in particular the arguments why cooler Ca of 100 kw can not be removed? à A: The strategy is to try to remove the smallest units, and these can be both proc./proc. heat exchangers, heaters and coolers, but they have to be part of a loop. Quite often, however, some of these units can not be removed, since it turns out to be impossible to restore driving forces (ΔT min ). See next Slides!! Q - 31
36 180 C H1 150 C H2 135 C 160 C H II α III β I ºC x 153.0ºC x 147.5ºC C 140 C 140 C γ Pinch 140 C 120 C C1 δ 120 C IV ºC Ca x Cb x 90 C 120 C 60 C C2 mcp The smallest Unit Ca (100 kw) is part of a Loop: H1 (II) C1 (I) H2 (Cb) CW (Ca) H1 Q - 32
37 180 C H1 150 C H2 135 C 160 C H y α β Tγ Tδ II y 147.5ºC III 1100 I y 138 C 138 C C γ δ 120 C Pinch 138 C 120 C C1 IV y Cb y 90 C 120 C 60 C When removing Cooler Ca (100 kw) by the Loop, Exchangers II, III and IV have ΔT min Violations Use Path H IV II I Cb (short form) C2 mcp Q - 33
38 180 C H1 150 C H2 135 C 160 C H 900 α β Tγ Tδ II ºC III 1100 I C 130 C C γ δ 110 C Pinch 130 C 120 C C1 IV 2000 Cb C 120 C 60 C With y = 400 kw, driving forces are restored for heat exchangers III and IV, but the problems have increased for heat exchanger II. Thus, Ca can not be removed!! C2 mcp Q - 34
39 180 C H1 β 150 C H2 135 C 160 C H II α III I ºC 600 x - y 153.0ºC y 140 C 140 C 140 C γ Pinch 140 C 120 C C1 δ x + y 120 C 147.5ºC y IV ºC Ca x Cb x + y 90 C 120 C 60 C C2 mcp The 2 nd smallest Unit H (500 kw) is not part of a Loop The 3 rd smallest Unit I is part of a Loop but has to be removed by a Path and thus y = x = 600 kw Q - 35
40 Questions related to Optimization of HENs: à Q: When manipulating a Heat Load Path by adding or subtracting a certain duty, how do we know which temperatures to focus on to assure sufficient driving forces? à A: Not easy to provide a simple answer here. Focus has to be on the heat exchanger(s) with driving force problems, and then to identify a heat load path that will improve these driving forces. Two situations: An easy one where one temperature is fixed and a more difficult one where both temperatures change. Q - 36
41 300 C H1 250 C Remember our 3 Stream Problem (WS-1) H y C I 200 è ºC 200 C H2 180 è 175 C II 55 C III 150 è y è 0 C y 100 C 100 C 50 C C1 mcp (kw/ C) The easy case when one temperature (175 C) is constant More complicated: Several Units with ΔT problems and cases where both temperatures for a unit change Q - 37
42 Questions related to Forbidden Matches in HENs: à Q: In Exam June 2010, Task 1.d a forbidden match is introduced for H2 and C1. Why is not Pinch and mcp rules relevant here, and (general) when to use Pinch? à A: A forbidden match results in increased energy use and thus heat transfer across Pinch. Thus, Pinch decomposition and mcp rules cannot be used, and the match information comes from the extended heat cascade. à A: The Pinch Concept is only used for MER design (Grassroots), XP Analysis (Retrofit) and Correct Integr. of dist. columns, evaporators, heat pumps/engines. Q - 38
43 H2 900 kw 1500 kw H kw 300 kw 2500 kw 2000 kw ST 190 C 180 C C 170 C C 140 C C 90 C C 50 C C 40 C CW Q H R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 Q C 200 kw 600 kw 1000 kw 4500 kw 800 kw C1 C2 H2-C1 is Forbidden Match Exam 2010, Task 1.d See Calculations on the Blackboard Q H,min = = 1400 kw, Q C,min = = 2700 kw Q - 39
44 Questions related to Forbidden Matches in HENs: à Q: In Exam June 2010, Task 1.d the forbidden match (H2-C1) results in extra steam and cooling water use of 800 kw each. How should this be referred to when the question asks about additional energy consumption? à A: Please do not say 1600 kw, since the two utility types are very different and with very different cost!! à Q: In the same task, it is stated (in the solution) that one advantage is larger driving forces in heat exchangers. How is this explained, and is it visible? à A: See next Slide!! Q - 40
45 Questions related to Forbidden Matches in HENs: 150 C H1 180 C H2 140 C 180 C H a 2000 H b C 170 C II 2400 I C 100 C 90 C C1 C b 1500 C a C 50 C 50 C C2 mcp Q - 41
46 Questions related to Forbidden Matches in HENs: à Q: In the cases of heat recovery problems with Forbidden Matches, when can the simplified Heat Cascade based only on Supply Temperatures be used? à A: Since we use the Heat Cascade to argue about how we can reach maximum heat recovery when there are forbidden matches, I strongly recommend the use of the complete heat cascade. This will make the reasoning easier and we do not have to worry about streams ending in the middle if temperature intervals!! Q - 42
47 Procedure for Retrofit Design: à Q: A more clear recipe for how to propose changes to an existing network. What is important? Removal of small units? Reduce area? Reduce heating/cooling? Etc. à A: The Objective of retrofit is to save energy, thus one should look for changes (new units, additional area, repiping, resequencing, etc., that will reduce external heating and cooling. à A: Unfortunately, retrofit requires creativity, and it is impossible to provide a water proof procedure. Q - 43
48 Procedure for Retrofit Design (1): à Identify causes for excess energy consumption è find all occurrences of Cross Pinch heat transfer (3 comps.) à Look for Shifting opportunities (changes in operating temperatures for heat exchangers) that will eliminate or reduce cross pinch heat transfer. Address the largest cross pinch violations first. à Sometimes Repiping is a good option; look for cases where the driving forces are not properly utilized. à Add New Units that will reduce Energy consumption Q - 44
49 Procedure for Retrofit Design (2): à The above mentioned new units are introduced after shifting that has opened up for unused heating/cooling. à Calculate new Duties and Temperatures in the network. à Perform a UA-analysis to evaluate the re-use of existing units and the need for additional area in existing units. à Use heat load Loops and Paths in a way that maximizes the utilization of existing units, minimizes investments (area of new units and/or additional area to existing units) and (if possible) maximizes energy savings. Q - 45
50 Procedure for Retrofit Design: à Q: I find it difficult to know where to start and also when to stop. In the solution to previous exams, several different projects are presented. The exam in 2009 is one example, and I noticed that Design B2 violates ΔT min. à A: For the start, see previous slides. For the end, please focus on demonstrating understanding and ability to use the tools and procedures. Repeating for several alternative cases does not give much more score, but these alternatives could be briefly mentioned!! After XP analysis, we forget about ΔT min!! Q - 46
51 Procedure for Retrofit Design: à Q: How to identify the placement of heat exchangers above, across and below Pinch in Retrofit cases, such as Assignment 5? à A: The Grid Diagram is used, and the key guideline for this placement of heat exchangers is the actual values of hot inlet and outlet temperatures and cold inlet and outlet temperatures relative to the hot and cold Pinch temperatures. For details, see the next Slide (from the solution to Assignment 5). Q - 47
52 Procedure for Retrofit Design: 175 H H C C2 3 mcp (kw/ C) [10] [40] [20] [15] 105 Q - 48
53 Procedure for Retrofit Design: 175 H H C C2 3 mcp (kw/ C) [10] [40] [20] [15] 105 Q - 49
54 Procedure for Retrofit Design: 175 H T H2 A 4 T 4 T Y X +Y 0 + X A B 0 + X - Y T X C1 40 mcp (kw/ C) [10] [40] [20] Q - 50
55 UA Analysis in Retrofit Design: à Q: In the Solution to Exam 2009, a path is used to make UA new = UA exist for a heater that is moved from C1 to C2. We have noticed that ΔT < ΔT min in the cold end of exchanger 1. Is this an error in the solution, or? à A: In retrofit design, the specification of ΔT min or HRAT is only used to identify cross-pinch heat transfer. In the design phase, focus is on minimizing energy consumption and maximizing utilization of existing units. Loops and Paths are used for this. See next Slide!! Q - 51
56 UA Analysis in Retrofit Design: 300 H1 140 III III H2 94 I 70 II II C 400kW - y C1 mcp (kw/ C) [20] [90] [50] 180 H kw I 2700 kw 50 C2 [30] 1600 kw - y 2300 kw + y Q - 52
57 180 H1 200 H Cross Pinch Heat Transfer and Heat Pumping : H II II 3600 I Ca 4300 III I 1300 C III 77.5 Cb C1 60 C3 mcp (kw/ C) [60] [40] [20] 100 [80] [50] Exam 2008, Task 1.c See Calculations on the Blackboard 100 Q - 53
58 300 H I I kw C 1100kW C2 mcp (kw/ C) [20] [30] 90 Q XP = 20 ( ) - 30 (180-90) = = 1100 kw Q XP = 30 (90-50) - 20 ( ) = = 1100 kw More details on the Blackboard!! Q - 54
59 Retrofit Design General Question: à Q: In a retrofit project, do we normally add a new unit, or can it be sufficient to shift a heat exchanger away from its cross Pinch situation? à A: It is extremely seldom that only repiping will improve heat recovery, but it happens. When shifting a heat exchanger, the purpose is to reduce Cross Pinch heat transfer, and this will result in the release of heating resources above or release of cooling resources below Pinch. To take advantage of this, new units (one or more) are needed. Q - 55
60 General Question for Grassroot and Retrofit: à Q: When do we use HRAT? à A: In the early age of Pinch Analysis, people working closely with industry (Oil Refineries) noticed that there was a large difference between the ΔT min corresponding to the level of heat recovery and the smallest ΔT in the individual heat exchangers. As a result, they introduced HRAT (Heat Recovery Approach Temperature) and EMAT (Exchanger Minimum Approach Temperature). Today, HRAT is most often used in Retrofit as a target value indicating level of ambitions in energy savings. Q - 56
61 Correct Integration: à Q: Assignment 8, at the end of the proposed solution, it is stated that without integration of the distillation column and use of heat pump, Q H = 1200 kw and Q C = 1300 kw. Can you explain this in more detail? à Q: This is simply because the distillation column has to be accounted for, not only the background process. The external heating and cooling requirements of the process is (see next slide) 800 and 900 kw, and then the distillation column (if not integrated) requires 400 kw. Q - 57
62 Correct Integration: T' ( C) Q P = 400 kw Q R = 400 kw Distillation Column Q C = 900 kw Q (kw) Q - 58
63 Interface between Utility System and Heat Recovery System (H/U) Correct Integration of Turbines: à Q: Could you repeat the topic about turbines (back pressure and condensing), both about the types and how these should be integrated? à Q: The general class of equipment is referred to as Heat Engines (opposite of Heat Pump). For the sake of simplicity, the discussion here focuses (as in the question) on Steam Turbines, where there are 3 types; Condensing, Back Pressure and Extracting (the last one is simply a combination of the two first). See next Slides!! Q - 59
64 Interface between Utility System and Heat Recovery System (H/U) Correct Integration of Turbines: HP LP CW HP LP HP CW Back Pressure Condensing Extracting Q - 60
65 Utility System (U) No questions so far à Any Questions now? Relevance for the Exam? à Lecturer to provide some wise words.. Q - 61
66 Other Topics Mathematical Programming à Q: What should we know about this topic? As an example, should we be able to answer Task 3.d from 2008 (What kind of Math Programming models do we have for minimum energy cost w/wo forbidden matches and for minimum number of units)? à A: This topic has been considerably reduced in the course (lectures & assignments) over the years, and is now a demonstration topic only. Forbidden matches is dealt with using logic in the Heat Cascade Q - 62
67 Other Topics Weights for the different Exam Tasks à Q: Are all sub-tasks given the same weight when grading the Exam? à A: No, these weights can actually change during the grading process, either to avoid negative effects (for the students) or after discussions between the internal and external examiners. Basically, these weights reflect a combination of work load and difficulty. Also notice that work load is not counting pages in the proposed exam solution!! Q - 63
TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Saturday 20 May C 180 C C 130 C C 60 C kw 50 C 30 C C 20 C
 Page 1 of 10 NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (NTNU) - TRONDHEIM DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND PROCESS ENGINEERING PROPOSED SOLUTION EXAMINATION IN COURSE TEP 4215 PROCESS INTEGRATION Saturday
Page 1 of 10 NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (NTNU) - TRONDHEIM DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND PROCESS ENGINEERING PROPOSED SOLUTION EXAMINATION IN COURSE TEP 4215 PROCESS INTEGRATION Saturday
Quiz Questions. For Process Integration. Fill in the blanks type Questions
 Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
pinch 70 C 70 C 4 We want to cool both the hot streams to the pinch temperature. The next step is to find the duty for the two heat exchangers:
 Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Grand Composite Curve Module 04 Lecture 12
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Introduction to Pinch Technology
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 07, 2018 Introduction to Pinch Technology Rokni, Masoud Publication date: 2016 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Rokni,
HDA Process. compressor. Reactor. Flash. heat. cool. Stabilizer. Recycle. Product
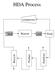 HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
3.17. PROCESS INTEGRATION AND PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
Module 04 : Targeting. Lecture 11: PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM 1 st Part
 Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
Module 04 : Targeting Lecture : PROBLEM TABLE ALGORITHM st Part Key words: Problem Table Algorithm, shifted temperature, composite curve, PTA, For a given ΔT min, Composite curves can be used to obtain
Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant
 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): 39-49 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajee doi: 10.11648/j.ajee.20170505.13 ISSN: 2329-1648 (Print); ISSN: 2329-163X (Online) Debottlenecking
The Grid Diagram The Heat-Content Diagram Pinch Subnetworks Minimum Number of Heat-Exchange Units...
 3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology. Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch
 Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch Key words: Pinch, T H diagram, Hot utility, Cold Utility, Composite Curve, T min Pinch analysis
Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology Lecture 07 : Hot and Cold Composite Curves and The Pinch Key words: Pinch, T H diagram, Hot utility, Cold Utility, Composite Curve, T min Pinch analysis
Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis Practical Considerations By Richard Beaman, PE, and Cliff Reese, PE, SSOE Group Pinch analysis is a systematic method to maximize energy recovery from process streams
Energy Optimization Using Pinch Analysis Practical Considerations By Richard Beaman, PE, and Cliff Reese, PE, SSOE Group Pinch analysis is a systematic method to maximize energy recovery from process streams
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency
 Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD
 Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ 49 (6) (2011) 117-126 DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD Nguyen Huu Tung Hanoi University of Science and Technology Email: tungnguyenhu@gmail.com Received:
Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ 49 (6) (2011) 117-126 DESIGN OF A HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK BY GRAPH METHOD Nguyen Huu Tung Hanoi University of Science and Technology Email: tungnguyenhu@gmail.com Received:
Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method
 Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method Thermoptim optimization method is dedicated to complex systems where a large number of fluids exchange heat, the overall behaviour of the system being governed
Utilization of THERMOPTIM Optimization Method Thermoptim optimization method is dedicated to complex systems where a large number of fluids exchange heat, the overall behaviour of the system being governed
Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system
 Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
Refrigeration System Module 05 Lecture 35 : Low temperature process design Key words: Refrigeration system A refrigerator is simply a heat pump where heat is rejected to atmosphere( the sink). Fig.41.3(lecture
First Semester Course Handout (Part-II)
 First Semester 2017-2018 Course Handout (Part-II) Date: 02/08/2017 In addition to Part I (General Handout for all courses appended to the Time Table), this portion gives further specific details regarding
First Semester 2017-2018 Course Handout (Part-II) Date: 02/08/2017 In addition to Part I (General Handout for all courses appended to the Time Table), this portion gives further specific details regarding
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison. Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner
 Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Comparison Trevor Hallberg and Sarah Scribner Table of Contents Executive Summary... 4 Introduction... 5 Paper Overview... 6 Example 1... 7 Example 2... 9 1. Mixed Integer
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration
 CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration Sachin V JANGAM Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering National University of Singapore Singapore Email: chejsv@nus.edu.sg Office location: E4-05-46
CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration Sachin V JANGAM Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering National University of Singapore Singapore Email: chejsv@nus.edu.sg Office location: E4-05-46
Retrofit of Crude Units Preheating Trains: Mathematical Programming versus Pinch Technology
 pubs.acs.org/iecr Retrofit of Crude Units Preheating Trains: Mathematical Programming versus Pinch Technology Miguel Bagajewicz,*,, Gary Valtinson, and DuyQuang Nguyen Thanh University of Oklahoma, 100
pubs.acs.org/iecr Retrofit of Crude Units Preheating Trains: Mathematical Programming versus Pinch Technology Miguel Bagajewicz,*,, Gary Valtinson, and DuyQuang Nguyen Thanh University of Oklahoma, 100
Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas
 Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas Leonid Tovazhnyansky, Petro Kapustenko, Leonid Ulyev, Stanislav Boldyryev * National Technical University "Kharkiv Polytechnic
Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas Leonid Tovazhnyansky, Petro Kapustenko, Leonid Ulyev, Stanislav Boldyryev * National Technical University "Kharkiv Polytechnic
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 27: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) 2 nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN
 Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks
 Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Investigation of Heat Exchanger Network Flexibility of Distillation Unit for Processing Different Types of Crude Oil
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration
 Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
Energy efficiency and carbon footprint reduction for Croatian regions by Total Site integration Stanislav Boldyryev, Goran Krajačić Department of Energy, Power Engineering and Environment, Faculty of Mechanical
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology
 Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis
 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 3967 3971 3967 Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis Bao-Hong Li Department of Chemical Engineering, Dalian Nationalities UniVersity, Dalian
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 3967 3971 3967 Retrofitting Heat Exchanger Networks Based on Simple Pinch Analysis Bao-Hong Li Department of Chemical Engineering, Dalian Nationalities UniVersity, Dalian
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery
 Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
Analysis of Heat Exchanger Network of Distillation Unit of Shiraz Oil Refinery J. Khorshidi, E. Zare, A.R. Khademi Abstract The reduction of energy consumption through improvements in energy efficiency
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production. Thorsten Spillmann
 IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology
 Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology Salomeh Chegini, Reza Dargahi, Afshin Mahdavi Abstract In this work, the Hint software
Modification of Preheating Heat Exchanger Network in Crude Distillation Unit of Arak Refinery Based on Pinch Technology Salomeh Chegini, Reza Dargahi, Afshin Mahdavi Abstract In this work, the Hint software
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation
 Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Researcher, 1(2), 2009, Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle. Introduction
 Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle Dmitriy A. Sladkovskiy, St.Petersburg State Institute of Technology (technical university), Saint-
Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle Dmitriy A. Sladkovskiy, St.Petersburg State Institute of Technology (technical university), Saint-
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery
 Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
Energy Saving in Atmospheric Distillation Unit by Retrofit Design of Heat Exchanger Networks of Al Basra Refinery Adnan A. Ateeq Engineering Technical College Southern Technical University Basra, Iraq
Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems
 Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems 1.0 Introduction As we have discussed in class, one of the largest irreversibilities associated with simple gas turbine cycles is the high temperature exhaust.
Design Features of Combined Cycle Systems 1.0 Introduction As we have discussed in class, one of the largest irreversibilities associated with simple gas turbine cycles is the high temperature exhaust.
Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process
 October 2014, Volume 5, No.5 International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process Sangsun Lee a ; Dongju Moon b ; Sungwon
October 2014, Volume 5, No.5 International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering Optimized Heat Exchanger Network design of GTL (Gas-To-Liquid) process Sangsun Lee a ; Dongju Moon b ; Sungwon
Energy savings in commercial refrigeration. Low pressure control
 Energy savings in commercial refrigeration equipment : Low pressure control August 2011/White paper by Christophe Borlein AFF and l IIF-IIR member Make the most of your energy Summary Executive summary
Energy savings in commercial refrigeration equipment : Low pressure control August 2011/White paper by Christophe Borlein AFF and l IIF-IIR member Make the most of your energy Summary Executive summary
Cleaning Schedule Operations in Heat Exchanger Networks
 Cleaning Schedule Operations in Heat Exchanger Networks Hairul Huda 1, Renanto Handogo 1,*, and Totok Ruki Biyanto 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, Indonesia
Cleaning Schedule Operations in Heat Exchanger Networks Hairul Huda 1, Renanto Handogo 1,*, and Totok Ruki Biyanto 2 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, Indonesia
Energy Balances and Numerical Methods Design Project. Production of Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether
 Energy Balances and Numerical Methods Design Project Production of Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether () is a gasoline additive used to increase octane number that is produced from
Energy Balances and Numerical Methods Design Project Production of Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether () is a gasoline additive used to increase octane number that is produced from
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI
 Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
Dr. Nasr Professor in Chem. Eng. Member of Board of Director RIPI nasrmrj@ripi.ir 21 MAY 2015 HVAC AND HEATING & COOLING SYSTEM CONFERENCE TEHRAN, IRAN 1 Energy and economy savings in the process of
Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10. David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University
 Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10 David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University 1 Module 5: Outline The environmental performance of a process
Module 5: Process Integration of Heat and Mass Chapter 10 David R. Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering Michigan Technological University 1 Module 5: Outline The environmental performance of a process
Heat Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit
 Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention. by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen
 Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen The environmental performance of a process flowsheet depends on both the performance of the individual
Chapter 10. Flowsheet Analysis for Pollution Prevention by Kirsten Sinclair Rosselot and David T. Allen The environmental performance of a process flowsheet depends on both the performance of the individual
CHAPTER 19 HEAT ENGINES AND REFRIGERATORS
 CHAPTER 19 HEAT ENGINES AND REFRIGERATORS In this chapter, we will examine devices that turn heat into work. I swear, I haven t confused you people for Mechanical Engineering majors! Biological processes
CHAPTER 19 HEAT ENGINES AND REFRIGERATORS In this chapter, we will examine devices that turn heat into work. I swear, I haven t confused you people for Mechanical Engineering majors! Biological processes
University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015
 University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015 PROCESS HEAT INTEGRATION: A REVIEW U. A. Isah, A.L. Yaumi, M.M. Ahmed Department of Chemical Engineering, University
University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015 PROCESS HEAT INTEGRATION: A REVIEW U. A. Isah, A.L. Yaumi, M.M. Ahmed Department of Chemical Engineering, University
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen NITROGEN-BASED FERTILIZER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at an Ammonia Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process
 Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process Master s Thesis within the Sustainable Energy Systems programme LISA LECEROF Department of Energy and Environment Division of
Opportunities for Energy Efficiency Improvement in a Renewable Fuels Process Master s Thesis within the Sustainable Energy Systems programme LISA LECEROF Department of Energy and Environment Division of
Course of Energy Conversion A 2014/2015
 Course of Energy Conversion A 2014/2015 Prof. G. Valenti 3 rd project Diverse Heat recovery steam cycles Index: 1. Introduction; 2. 1-level combined cycle analysis 3. 2-levels combined cycle analysis 4.
Course of Energy Conversion A 2014/2015 Prof. G. Valenti 3 rd project Diverse Heat recovery steam cycles Index: 1. Introduction; 2. 1-level combined cycle analysis 3. 2-levels combined cycle analysis 4.
APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 6, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 73-84 APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS * A. H. Javid, A. Emamzadeh, 3 A.
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 6, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 73-84 APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS * A. H. Javid, A. Emamzadeh, 3 A.
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit
 PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
PINCH ANALYSIS : For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
Eng Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1
 Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1 The final exam in Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I consists of four questions: (1) 1st Law analysis of a steam power cycle, or a vapour compression refrigeration
Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1 The final exam in Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I consists of four questions: (1) 1st Law analysis of a steam power cycle, or a vapour compression refrigeration
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter
 Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Example SPC-2: Effect of Increasing Column P on a C3 splitter Consider the separation of a mixture of 50 mol/hr of propane C 3 H 8 (1) and 50 mol/hr propene, C 3 H 6 (2) at a pressure of 1.1 bar and a
Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study
 Chemical Engineering and Processing 44 (2005) 819 826 Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study Hilde K. Engelien, Sigurd Skogestad Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU),
Chemical Engineering and Processing 44 (2005) 819 826 Multi-effect distillation applied to an industrial case study Hilde K. Engelien, Sigurd Skogestad Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU),
WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS
 WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS Elvis Ahmetović a,b*, Nidret Ibrić a, Zdravko Kravanja b, Ignacio E. Grossmann c a University of
WATER AND ENERGY INTEGRATION: A COMPREHENSIVE LITERATURE REVIEW OF NON-ISOTHERMAL WATER NETWORK SYNTHESIS Elvis Ahmetović a,b*, Nidret Ibrić a, Zdravko Kravanja b, Ignacio E. Grossmann c a University of
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS
 OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur (Refer Slide Time: 00:54) Lecture - 4 Second law of Thermodynamics
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur (Refer Slide Time: 00:54) Lecture - 4 Second law of Thermodynamics
Furnace. 1. (10 points) mol/s 53.5% H2O CO2
 MEEBAL Exam 3 December 2012 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
MEEBAL Exam 3 December 2012 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen OIL REFINING INDUSTRY Energy Recovery at a Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) Unit PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water
A Modified Energy Transfer Diagram for Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Bridge Analysis
 907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR
 Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR 1) Objectives of the practical work The aim is to investigate the potential of Thermoptim in modeling and calculation of
Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR 1) Objectives of the practical work The aim is to investigate the potential of Thermoptim in modeling and calculation of
Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology VISHAL G. BOKAN 1, M.U.POPLE 2 1 Student of M.E. chemical, Department of Chemical Engineering,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology VISHAL G. BOKAN 1, M.U.POPLE 2 1 Student of M.E. chemical, Department of Chemical Engineering,
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall Design Project. Production of Dimethyl Ether
 Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall 2001 Design Project Production of Dimethyl Ether We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 tonne/y, (1 tonne
Fluid Mechanics, Heat Transfer, and Thermodynamics Fall 2001 Design Project Production of Dimethyl Ether We are investigating the feasibility of constructing a new, grass-roots, 50,000 tonne/y, (1 tonne
GTC TECHNOLOGY. GT-UWC SM How a Uniting Wall Column Maximizes LPG Recovery. Engineered to Innovate WHITE PAPER
 GTC TECHNOLOGY GT-UWC SM How a Uniting Wall Column Maximizes LPG Recovery WHITE PAPER Engineered to Innovate Maximizing LPG Recovery from Fuel Using a Uniting Wall Column Refiners have a challenge to recover
GTC TECHNOLOGY GT-UWC SM How a Uniting Wall Column Maximizes LPG Recovery WHITE PAPER Engineered to Innovate Maximizing LPG Recovery from Fuel Using a Uniting Wall Column Refiners have a challenge to recover
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics
 Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
Problems in chapter 9 CB Thermodynamics 9-82 Air is used as the working fluid in a simple ideal Brayton cycle that has a pressure ratio of 12, a compressor inlet temperature of 300 K, and a turbine inlet
A Novel Synergistic 4-column Methanol Distillation Process
 937 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
937 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants
 Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory of Thermal Turbomachinery
Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory of Thermal Turbomachinery
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process
 An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
An Energy Integration Approach on UHDE Ammonia Process Alnouss M. Ahmed, and Al-Nuaimi A. Ibrahim Abstract In this paper, the energy performance of a selected UHDE Ammonia plant is optimized by conducting
Utility-Heat Exchanger Grid Diagram: A Tool for Designing the Total Site Heat Exchanger Network
 7 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
7 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
A New Optimisation Based Retrofit Approach for Revamping an Egyptian Crude Oil Distillation Unit
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015
 University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015 PINCH ANALYSIS OF BENZENE PRODUCTION PROCESS VIA THE HYDRODEALKYLATION OF TOLUENE I. M. Idriss*, H. I. Mohammed and
University of Maiduguri Faculty of Engineering Seminar Series Volume 6, december 2015 PINCH ANALYSIS OF BENZENE PRODUCTION PROCESS VIA THE HYDRODEALKYLATION OF TOLUENE I. M. Idriss*, H. I. Mohammed and
Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy
 SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
SECTION 1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy Ed Haack Duke Energy 1-1 Modeling Techniques for Increased Accuracy By Ed Haack, Duke Power Company The PEPSE model for the Catawba Units have been
Chapter Two. The Rankine cycle. Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah
 Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology: A Case Study of Orbit Chemicals Industry
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES
 Congrès s Annuel ATIP Annecy 27-29 29 avril 2005 DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES David Brown Zoé Périn-Levasseur François Maréchal Jean Paris EP Montréal
Congrès s Annuel ATIP Annecy 27-29 29 avril 2005 DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES David Brown Zoé Périn-Levasseur François Maréchal Jean Paris EP Montréal
Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump
 National Centre for Nuclear Research in Poland Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump Anna Przybyszewska International Atomic Energy Agency 14-16
National Centre for Nuclear Research in Poland Low temperature cogeneration using waste heat from research reactor as a source for heat pump Anna Przybyszewska International Atomic Energy Agency 14-16
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method
 Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Guidance page for practical work: optimization of combined cycles by the pinch method 1) Objectives of the practical work The objective of the practical work is to study the implementation of the pinch
Innovative Air Separation Processes for Oxy-Combustion Power Plants
 2 nd International Oxyfuel Combustion Conference OCC2 12 th -16 th September 2011, Capricorn Resort, Yeppoon, Australia Innovative Air Separation Processes for Oxy-Combustion Power Plants by Chao Fu and
2 nd International Oxyfuel Combustion Conference OCC2 12 th -16 th September 2011, Capricorn Resort, Yeppoon, Australia Innovative Air Separation Processes for Oxy-Combustion Power Plants by Chao Fu and
On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration
 Computers and Chemical Engineering 27 (2003) 1707/1719 www.elsevier.com/locate/compchemeng On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration Miguel J. Bagajewicz *, Andrés F. Barbaro Department of
Computers and Chemical Engineering 27 (2003) 1707/1719 www.elsevier.com/locate/compchemeng On the use of heat pumps in total site heat integration Miguel J. Bagajewicz *, Andrés F. Barbaro Department of
An Exergy Analysis on a Crude Oil Atmospheric Distillation Column
 An Exergy Analysis on a Crude Oil Atmospheric Distillation Column Amir Hossein Tarighaleslami 1 *, Mohammad Reza Omidkhah 2, Soroush Younessi Sinaki 3 1 Chemical Engineering Faculty, Islamic Azad University,
An Exergy Analysis on a Crude Oil Atmospheric Distillation Column Amir Hossein Tarighaleslami 1 *, Mohammad Reza Omidkhah 2, Soroush Younessi Sinaki 3 1 Chemical Engineering Faculty, Islamic Azad University,
Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced Geothermal Systems
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Fundamental Investigation Of Whole-Life Power Plant Performance For Enhanced
Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration
 Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration Jiří Klemeš, Simon John Perry and Igor Bulatov Centre for Process Integration, School of Chemical Engineering and Analytical
Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration Jiří Klemeš, Simon John Perry and Igor Bulatov Centre for Process Integration, School of Chemical Engineering and Analytical
Flash Zone Optimization of Benzene-Toluene-Xylene Fractionation Unit
 2 nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization September 6-9, 2010, Lisbon, Portugal Flash Zone Optimization of Benzene-Toluene-Xylene Fractionation Unit M. Arjmand 1, K. Motahari 2 1 School
2 nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization September 6-9, 2010, Lisbon, Portugal Flash Zone Optimization of Benzene-Toluene-Xylene Fractionation Unit M. Arjmand 1, K. Motahari 2 1 School
Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through Pinch Technology:
 WASTEWATER MINIMIZATION IN PROCESS 101 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 22 (1)(2006) pp 101-110 Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through
WASTEWATER MINIMIZATION IN PROCESS 101 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 22 (1)(2006) pp 101-110 Enviromedia Printed in India. All rights reserved Wastewater Minimization in Process Industry Through
Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery. Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006
 Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006 Outline Plant Statistics and Energy History Tools Used to Identify Projects Sample of Projects
Challenges in Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Texas Technology 2006 Showcase Tony Dafft December 6 & 7, 2006 Outline Plant Statistics and Energy History Tools Used to Identify Projects Sample of Projects
Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration
 Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration Jiří Klemeš, Simon John Perry and Igor Bulatov Centre for Process Integration, School of Chemical Engineering and Analytical
Towards sustainable energy systems role and achievements of heat integration Jiří Klemeš, Simon John Perry and Igor Bulatov Centre for Process Integration, School of Chemical Engineering and Analytical
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF REGULATION AND ITS EFFICIENCY IN STEAM POWER CYCLES MASTER THESIS
 ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF REGULATION AND ITS EFFICIENCY IN STEAM POWER CYCLES MASTER THESIS Author: Ricardo Sánchez Pereiro Advisor: Piotr Krzyslak Poznan University of Technology 11/06/2012 INDEX
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF REGULATION AND ITS EFFICIENCY IN STEAM POWER CYCLES MASTER THESIS Author: Ricardo Sánchez Pereiro Advisor: Piotr Krzyslak Poznan University of Technology 11/06/2012 INDEX
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 12(1) (2012), pp. 39-48 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229 6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Using Simulation
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 12(1) (2012), pp. 39-48 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229 6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Using Simulation
Stationary Combustion Systems Chapter 6
 Stationary Combustion Systems Chapter 6 Stationary combustion systems presently supply most of the earth s electricity. Conversion will take time, so study of these systems in order to improve them is
Stationary Combustion Systems Chapter 6 Stationary combustion systems presently supply most of the earth s electricity. Conversion will take time, so study of these systems in order to improve them is
NEW RECYCLE PROCESS SCHEME FOR HIGH ETHANE RECOVERY NEW PROCESS SCHEME FOR HIGH NGL RECOVERY INTRODUCTION. Abstract PROCESS FUNDAMENTALS
 Author: Jorge Foglietta, ABB Randall Corporation Tel (713) 821-4313, Fax (713) 821-3544 Mailing Address: Randall Division ABB Lummus Global Inc. P.O. Box 420087 Houston, Texas 77242-0087 NEW PROCESS SCHEME
Author: Jorge Foglietta, ABB Randall Corporation Tel (713) 821-4313, Fax (713) 821-3544 Mailing Address: Randall Division ABB Lummus Global Inc. P.O. Box 420087 Houston, Texas 77242-0087 NEW PROCESS SCHEME
Towards the Use of Mathematical Optimization for Work and Heat Exchange Networks
 1351 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
1351 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries
 National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization
 Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization Eva Lovelady and Mahmoud El-Halwagi Department of Chemical Engineering Texas A & M University 1 1 Motivation
Effective Reduction of Industrial GHG Emissions via Energy Integration and Biomass Utilization Eva Lovelady and Mahmoud El-Halwagi Department of Chemical Engineering Texas A & M University 1 1 Motivation
1. To improve heat exchange between a gas & a liquid stream in a heat exchanger, it is decided to use fins. Correct the suitable option.
 1. To improve heat exchange between a gas & a liquid stream in a heat exchanger, it is decided to use fins. Correct the suitable option. a) Fins are generally attached on gas side. b) Fins are generally
1. To improve heat exchange between a gas & a liquid stream in a heat exchanger, it is decided to use fins. Correct the suitable option. a) Fins are generally attached on gas side. b) Fins are generally
Written Exam 02 March Problems - Time: 2 hours PLEASE NOTICE
 Politecnico di Milano Department of Energy - School of Industrial Engineering Course Energy Systems LM prof. S. Consonni, E. Martelli, M. Romano - Academic Year 2014/15 Written Exam 02 March 2015 - Problems
Politecnico di Milano Department of Energy - School of Industrial Engineering Course Energy Systems LM prof. S. Consonni, E. Martelli, M. Romano - Academic Year 2014/15 Written Exam 02 March 2015 - Problems
Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH Technology. Lecture 08 : Threshold Problems Q H
 hreshold Processes Module 03 Lecture 08 Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH echnology Key words: hreshold Lecture 08 : hreshold Problems here are some special category of problems, known as threshold
hreshold Processes Module 03 Lecture 08 Module 03 : Building blocks of PINCH echnology Key words: hreshold Lecture 08 : hreshold Problems here are some special category of problems, known as threshold
