OSMOSIS. After osmosis has taken place, both solutions have the same concentration of solute.
|
|
|
- Blake Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOLOGY: OSMOSIS
2 OSMOSIS Osmosis is the physical process by which, in a solution, the concentration of solute is regulated by the movement of the solvent, water, through a semipermeable membrane (permeable to the solvent but not to the solute). This process takes place because matter always tends to find its equilibrium, and it happens with no appliance of energy. After osmosis has taken place, both solutions have the same concentration of solute.
3 Osmosis also takes place in cells. In this case, the concentration of solutes such as sugars or salts is regulated by water as solvent, which moves through the cell membrane. Three different things can happen: If the concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell, the movement of water is balanced (isotonic). If the concentration of solutes is higher inside the cell than outside, water enters the cell and it swells (hypotonic). If the concentration of solutes is lower inside the cell than outside, waters gets out of the cell and it shrinks (hypertonic). OSMOSIS IN CELLS
4 OSMOSIS EXPERIMENT Material needed: 3 beakers 1 small container A scale A potato, a raisin and a carrot Salt Water A knife
5 OSMOSIS EXPERIMENT Procedure: 1. Measure the weight of salt that you are going to pour on each beaker (30, 20 and 5 grams respectively). 2. Pour the same volume of water in the beakers (90 ml), then add the corresponding quantity of salt (make sure you distinguish the different solutions by labeling them!). Measure the volume of the solutions. 3. Measure the molarity of the solutions (moles of NaCl/volume of solution). 4. Peal the potato and the carrot. Then, measure the weight of the raisin, the carrot and the potato, and write it down. 5. Submerge the three of them in the corresponding solutions (the potato, in the most saturated one, and the raisin in the most diluted one). 5. After 48 hours, take them out of the water, dry them, and weight them again. 6. Calculate the differences in weight and the percentage of variation.
6 OSMOSIS EXPERIMENT: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Identify the problem: we have to prove the process of osmosis with a biological semipermeable membrane. We have 48 hours to do it. Hypothesis: if we place a carrot, a potato or a raisin in salty water, after 48hours, they will have dried up because water will have got out of them due to osmosis. Conclusion: So, from this experiment we can conclude that due to the process of osmosis, water moves through semipermeable membranes in order to balance the concentration of solutes.
7 POTATO TEST WEIGHT OF SOLVENT/SOLUTE (gr) WEIGHT (gr) OF 1 MOLE QUANTITY OF MATTER (moles) VOLUME OF SOLUTION (ml) WATER (H 2 O) SALT (NaCl) (90+14) MOLARITY = QUANTITY OF SOLUTE (moles) = 0.5 = 4.8M VOLUME OF DISSOLUTION (liters) Salt Density: 2160 gr/l INITIAL WEIGHT FINAL WEIGHT PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT THAT REMAINS PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT LOST 103 gr 85.1 gr 82.62% 17.37%
8 CARROT TEST WEIGHT OF SOLVENT/SOLUTE (gr) WEIGHT (gr) OF 1 MOLE QUANTITY OF MATTER (moles) VOLUME OF SOLUTION (ml) WATER (H 2 O) SALT (NaCl) (90+9) MOLARITY = QUANTITY OF SOLUTE (moles) VOLUME OF DISSOLUTION (liters) = = 3.53M Salt Density: 2160 gr/l INITIAL WEIGHT FINAL WEIGHT PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT THAT REMAINS PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT LOST 66 gr 50 gr 75.75% 24.25%
9 RAISIN TEST WEIGHT OF SOLVENT/SOLUTE (gr) WEIGHT (gr) OF 1 MOLE QUANTITY OF MATTER (moles) VOLUME OF SOLUTION (ml) WATER (H 2 O) SALT (NaCl) (90+2) MOLARITY = QUANTITY OF SOLUTE (moles) VOLUME OF DISSOLUTION (liters) = = 0.92M Salt Density: 2160 gr/l INITIAL WEIGHT FINAL WEIGHT PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT THAT INCREASES PERCENTAGE OF WEIGHT GAINED 0.7 gr 1.1 gr % 57.14%
10 DURING AND AFTER THE EXPERIMENT PROBLEMS WE HAD DURING THE EXPERIEMNT: When we wanted to put the carrot and the potato into the beakers, we realized they were too big, so we had to cut them into pieces before. AFTER THE EXPERIMENT: Re-hypothesis: After 48 hours, we saw that both the potato and the carrot had decreased in mass, but the raisin had won weight. This means that our first hypothesis was partly wrong. As expected, water from potato and the carrot had gone out of them because the concentration of salts was higher outside than inside them. However, contrary to what we had thought, the raisin had increased in weight. This may be because the concentration of the solution (0.92M) wasn t enough to make water of the raisin get out of it; so it happened right the opposite, water entered the raisin because the concentration there was higher. Further researches: We could make another experiment to find out the needed concentration of solution to make water get out of the raisin.
11 DONE BY: KATERINA KOZITSKI GARCÍA PAULA SÁEZ SOTO ANDREA SÁNCHEZ SÁNCHEZ INÉS UTRERO BORLAZ RUBÉN VICENTE LÓPEZ 4ºA h OSMOSIS Subject: Biology and Geology Teacher: Maribel Cuenca Asenjo High School: I.E.S.B. Ciudad de los Poetas Tuesday, 21 st of January 2014
Water Potential - AP SBI4UP
 Water Potential - AP SBI4UP Remember... Osmosis Osmosis: net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves with its concentration gradient. Remember... Osmosis in an Animal Cell
Water Potential - AP SBI4UP Remember... Osmosis Osmosis: net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves with its concentration gradient. Remember... Osmosis in an Animal Cell
Science Starts. *Upcoming Dates: Wednesday Test. 1. How was your weekend? 2. What surrounds a cell? 3. What is it made of?
 Science Starts 1. How was your weekend? 2. What surrounds a cell? 3. What is it made of? *Upcoming Dates: Wednesday Test Cell Membrane & Cell Transport (Page 45) EQ: What is the structure of the cell membrane
Science Starts 1. How was your weekend? 2. What surrounds a cell? 3. What is it made of? *Upcoming Dates: Wednesday Test Cell Membrane & Cell Transport (Page 45) EQ: What is the structure of the cell membrane
7 Easy Steps to Understanding Water Potential
 Water Potential & Practice Problems Name: Date: Class: 7 Easy Steps to Understanding Water Potential 1) Log onto the PH School LabBench...copy and paste this link: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/
Water Potential & Practice Problems Name: Date: Class: 7 Easy Steps to Understanding Water Potential 1) Log onto the PH School LabBench...copy and paste this link: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/
Pre-lab preparation for the Osmosis/Diffusion lab
 Pre-lab preparation for the Osmosis/Diffusion lab Got to this link http://phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab1/intro.html Only do the first 5 concepts for now: Define diffusion Quick aside:
Pre-lab preparation for the Osmosis/Diffusion lab Got to this link http://phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab1/intro.html Only do the first 5 concepts for now: Define diffusion Quick aside:
01/08/2018. Microbiology Lab. General Information. My Web Page 3 BIO3126
 Microbiology Lab BIO3126 1 General Information 2 Instructor: John Basso Email: jbasso@uottawa.ca Tel. 613-562-5800 Poste 6358 Office: BSC102 My web page: http://mysite.science.uottawa.ca/jbasso/home.htm
Microbiology Lab BIO3126 1 General Information 2 Instructor: John Basso Email: jbasso@uottawa.ca Tel. 613-562-5800 Poste 6358 Office: BSC102 My web page: http://mysite.science.uottawa.ca/jbasso/home.htm
Water Potential (Ψ) Ψ = ΨS + ΨP
 Water Potential (Ψ) Ψ = ΨS + ΨP Water potential (Ψ) is a measure of water s potential to do work. In order to do work, an object must be able to apply enough force to another object to cause displacement.
Water Potential (Ψ) Ψ = ΨS + ΨP Water potential (Ψ) is a measure of water s potential to do work. In order to do work, an object must be able to apply enough force to another object to cause displacement.
BIO 2 GO! Osmosis 3121
 BIO 2 GO! Osmosis 3121 Osmosis is a process. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration through a membrane to an area of lower water concentration. Osmosis continues until
BIO 2 GO! Osmosis 3121 Osmosis is a process. Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration through a membrane to an area of lower water concentration. Osmosis continues until
Diffusion, osmosis. Physics-Biophysics 1. I. Diffusion Medical Biophysics book: chapter III/ October Tamás Huber
 Diffusion, osmosis Physics-Biophysics 1. 27. October 2015. Tamás Huber I. Diffusion Medical Biophysics book: chapter III/2. 1 Experiment 1: add a droplet of ink to a glass of water Observation 1: the stain
Diffusion, osmosis Physics-Biophysics 1. 27. October 2015. Tamás Huber I. Diffusion Medical Biophysics book: chapter III/2. 1 Experiment 1: add a droplet of ink to a glass of water Observation 1: the stain
Biology: Assignment #4 Cell Membrane
 Root Words: For the following root words, define the term and provide an example of a biological term that incorporates the root word. Term Definition Example 1. Iso - 2. -lys 3. Adip - 4. Amphi - 5. Ecto
Root Words: For the following root words, define the term and provide an example of a biological term that incorporates the root word. Term Definition Example 1. Iso - 2. -lys 3. Adip - 4. Amphi - 5. Ecto
Water Potential. Water potential ( ) = pressure potential ( ) + solute potential ( )
 Water Potential Water potential is a measurement that combines the effects of solute concentration and pressure Determines the direction of movement of water Water flows from regions of higher water potential
Water Potential Water potential is a measurement that combines the effects of solute concentration and pressure Determines the direction of movement of water Water flows from regions of higher water potential
Microbiology lab (BIO 3126) Teaching Staff. My Availability. Lab coordinator: John Basso. Lecturer: Benoît Pagé. By Office hours:
 Microbiology lab (BIO 3126) 1 Teaching Staff Lab coordinator: John Basso Email: jbasso@uottawa.ca Office: Bioscience 102 Tel.: 613-562-5800 Ext. 6358 Lecturer: Benoît Pagé Email: bpage051@uottawa.ca Office:
Microbiology lab (BIO 3126) 1 Teaching Staff Lab coordinator: John Basso Email: jbasso@uottawa.ca Office: Bioscience 102 Tel.: 613-562-5800 Ext. 6358 Lecturer: Benoît Pagé Email: bpage051@uottawa.ca Office:
Diffusion Osmosis And Cell Transport Answer Key. : Download / Read Online Here
 Diffusion Osmosis And Cell Transport Answer Key : Download / Read Online Here osmosis, diffusion and cell transport - passive transport there are 3 types of passive transport: 1. diffusion: involves small
Diffusion Osmosis And Cell Transport Answer Key : Download / Read Online Here osmosis, diffusion and cell transport - passive transport there are 3 types of passive transport: 1. diffusion: involves small
Laboratory 8B Dialysis
 Laboratory 8B Dialysis Concepts: Dialysis is used to effect buffer exchange. Dialysis is not a purification method. Dialysis takes advantage of the properties of a semipermeable membrane. Protein solubility
Laboratory 8B Dialysis Concepts: Dialysis is used to effect buffer exchange. Dialysis is not a purification method. Dialysis takes advantage of the properties of a semipermeable membrane. Protein solubility
Experiment: Measurements
 Experiment: Measurements I. INTRODUCTION Measurements are essential to experimental sciences such as chemistry, physics, biology, and geology. The measurements are usually made using the metric system
Experiment: Measurements I. INTRODUCTION Measurements are essential to experimental sciences such as chemistry, physics, biology, and geology. The measurements are usually made using the metric system
Students will predict the net movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
 Edvo-Kit #S-74 What is Osmosis? S-74 Experiment Objective: Students will predict the net movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Students will defi ne what molecules move during diffusion
Edvo-Kit #S-74 What is Osmosis? S-74 Experiment Objective: Students will predict the net movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane. Students will defi ne what molecules move during diffusion
Monday, April 18. AZ Merit Reading and Math part 2
 Monday, April 18 AZ Merit Reading and Math part 2 Tuesday, April 19 Please start a new warm-up Write the date and the question 4/19: What are 3 things that You think all living things must Have in order
Monday, April 18 AZ Merit Reading and Math part 2 Tuesday, April 19 Please start a new warm-up Write the date and the question 4/19: What are 3 things that You think all living things must Have in order
A FACT, A CONCEPT. The cell is THE fundamental unit of living organisms
 A FACT, A CONCEPT The cell is THE fundamental unit of living organisms CELL THEORY HISTORY Robert Hooke observed cork and saw this: 2 IMAGINE Some world made up of free moving materials Under some conditions,
A FACT, A CONCEPT The cell is THE fundamental unit of living organisms CELL THEORY HISTORY Robert Hooke observed cork and saw this: 2 IMAGINE Some world made up of free moving materials Under some conditions,
Chapter 9. Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria
 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Water potential measurement Tissue tension
 Water potential measurement Tissue tension (L, M) Authors: Niels Sievertsen, nielssi@student.ethz.ch Stefan Zeyen, zeyens@student.ethz.ch Connie Müller, conmuell@student.ethz.ch Melanie Weis, mweis@student.ethz.ch
Water potential measurement Tissue tension (L, M) Authors: Niels Sievertsen, nielssi@student.ethz.ch Stefan Zeyen, zeyens@student.ethz.ch Connie Müller, conmuell@student.ethz.ch Melanie Weis, mweis@student.ethz.ch
Biology 4A Laboratory: Membrane Transport
 Biology 4A Laboratory: Membrane Transport Objectives To observe Brownian motion and understand its importance in diffusion To study the movement of diffusion of different materials in various media To
Biology 4A Laboratory: Membrane Transport Objectives To observe Brownian motion and understand its importance in diffusion To study the movement of diffusion of different materials in various media To
Osmosis and Diffusion, Egg Lab Setup. December 3, 2014
 Osmosis and Diffusion, Egg Lab Setup December 3, 2014 Welcome! 12/3/14 OBJECTIVE: Students will: 1. Define and compare osmosis, diffusion and types of solutions using a POGIL; and 2. Set up osmosis lab
Osmosis and Diffusion, Egg Lab Setup December 3, 2014 Welcome! 12/3/14 OBJECTIVE: Students will: 1. Define and compare osmosis, diffusion and types of solutions using a POGIL; and 2. Set up osmosis lab
M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc,
 Experiment 2 Density Part I: Density of a solid Density is defined as mass per unit volume, D = V M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc, g/ml, lb/ft 3, etc. Determination of mass is done by weighing
Experiment 2 Density Part I: Density of a solid Density is defined as mass per unit volume, D = V M. It is expressed in units such a g/cc, g/ml, lb/ft 3, etc. Determination of mass is done by weighing
Curriculum Guide. National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science
 National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
Chapter 1 Section 3: Tools and Techniques. Key Vocabulary Terms
 Chapter 1 Section 3: Tools and Techniques Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 SI The International System of Units is used by all scientists because scientists need to share a common measurement
Chapter 1 Section 3: Tools and Techniques Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 SI The International System of Units is used by all scientists because scientists need to share a common measurement
SNC 2L Unit 1: Science in the Media Topic: Experiment #1: Product Testing SJHS Testing Absorbency of Different Brands of Paper Towel
 EXPERIMENT #1: Testing Absorbency of Different Brands of Paper Towel PURPOSE: (this is what the point or goal of an experiment is) to see which brand of paper towel is the most absorbent. HYPOTHESIS: (an
EXPERIMENT #1: Testing Absorbency of Different Brands of Paper Towel PURPOSE: (this is what the point or goal of an experiment is) to see which brand of paper towel is the most absorbent. HYPOTHESIS: (an
EXPERIMENT 6. Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R. Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction,
 EXPERIMENT 6 Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction, Mg + 2 HCl MgCl 2 + H 2 (g) In this experiment you will use
EXPERIMENT 6 Determination of the Ideal Gas Law Constant - R Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the following reaction, Mg + 2 HCl MgCl 2 + H 2 (g) In this experiment you will use
Evaluate long- range plans concerning resource use and by- product disposal for environmental, economic, and political impact
 Title: Author: Course: A Fluid State Of Mind Amanda Brewer Brookland High School Brookland Physical Science, Chemistry Duration: Three 45 minute class periods Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: The process of
Title: Author: Course: A Fluid State Of Mind Amanda Brewer Brookland High School Brookland Physical Science, Chemistry Duration: Three 45 minute class periods Grade Level: 9-12 Objective: The process of
2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1
 2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4
2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Equilibrium problems involve 3 parts: The End of Equilibrium! K sp. (well, for us!) What is the solubility of FeCO 3?
 Slide 1 The End of Equilibrium! (well, for us!) 1 Slide 2 K sp What is the solubility of FeCO 3? Solubility = MAXIMUM amount of a compound that can dissolve in water. This is actually an equilibrium. 2
Slide 1 The End of Equilibrium! (well, for us!) 1 Slide 2 K sp What is the solubility of FeCO 3? Solubility = MAXIMUM amount of a compound that can dissolve in water. This is actually an equilibrium. 2
Differences in Free Energy of Solvation in a Two-Layer System
 Differences in Free Energy of Solvation in a Two-Layer System (Original exercise designed by William Steel and modified by James Foresman) Purpose: By observing the changes in the concentration of a solute
Differences in Free Energy of Solvation in a Two-Layer System (Original exercise designed by William Steel and modified by James Foresman) Purpose: By observing the changes in the concentration of a solute
Most working laboratory solutions are expressed in terms of molar concentrations. Question 1) What is a mole?
 Biology 324 Dilutions and Solutions For lab work, you have to be able to make up solutions. Somehow, this process is often perceived as ranging from difficult to impossible. This first lab will introduce
Biology 324 Dilutions and Solutions For lab work, you have to be able to make up solutions. Somehow, this process is often perceived as ranging from difficult to impossible. This first lab will introduce
Technical Presentation RO Basics. MWQA October Bill Loyd Technical Services & Development Dow Water & Process Solutions
 Technical Presentation RO Basics MWQA October 2017 Bill Loyd Technical Services & Development Dow Water & Process Solutions Factors that Impact RO Performance Temperature Pressure Salt Concentration Feed
Technical Presentation RO Basics MWQA October 2017 Bill Loyd Technical Services & Development Dow Water & Process Solutions Factors that Impact RO Performance Temperature Pressure Salt Concentration Feed
Week 3 Lesson 2. Desalination. 3.2: Desalination. Starter activities
 Week 3 Lesson 2 Desalination These activities should take about 1 ½ lessons. Aim: To show how fresh water can be obtained from salt water and how this process happens in the natural world. Keywords: aquifer,
Week 3 Lesson 2 Desalination These activities should take about 1 ½ lessons. Aim: To show how fresh water can be obtained from salt water and how this process happens in the natural world. Keywords: aquifer,
Solubility Equilibrium
 Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
1. An experiment was set up to test the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis, as shown in the diagram below.
 Name: Date: Period: 1. An experiment was set up to test the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis, as shown in the diagram below. Data were collected by counting gas bubbles released
Name: Date: Period: 1. An experiment was set up to test the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis, as shown in the diagram below. Data were collected by counting gas bubbles released
4-1 Cell biology Trilogy
 4- Cell biology Trilogy.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Cell C Oxygen molecules Cell D. Into which cell,
4- Cell biology Trilogy.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Cell C Oxygen molecules Cell D. Into which cell,
4-1 Cell biology Trilogy
 4- Cell biology Trilogy.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Cell C Oxygen molecules Cell D. Into which cell,
4- Cell biology Trilogy.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Cell C Oxygen molecules Cell D. Into which cell,
Sari Bornstein November 18, 2010 Thursday PM E.Y. Lab #6: Water Activity- Food Preservation by Means of Moisture Control
 Sari Bornstein November 18, 2010 Thursday PM E.Y. Lab #6: Water Activity- Food Preservation by Means of Moisture Control PURPOSE/OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab was to measure the water activity of
Sari Bornstein November 18, 2010 Thursday PM E.Y. Lab #6: Water Activity- Food Preservation by Means of Moisture Control PURPOSE/OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab was to measure the water activity of
Solutions and Crystallisation exam question
 Solutions and Crystallisation exam question 2012 - Higher An experiment was performed to investigate the effect of temperature on the solubility of carbon dioxide in water. The data obtained from this
Solutions and Crystallisation exam question 2012 - Higher An experiment was performed to investigate the effect of temperature on the solubility of carbon dioxide in water. The data obtained from this
National 5 Biology. Unit 1 Homework. Cell Biology
 National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
OSMOSIS. BIOPHYSICS I October 25. Beáta Bugyi University of Pécs, Medical School, Department of Biophysics,
 BIOPHYSICS I 2011. October 25. Beáta Bugyi University of Pécs, Medical School, Department of Biophysics, Overview 1. Diffusion brief overview 2. Osmosis: molecular basis and quatification 3. Medical &
BIOPHYSICS I 2011. October 25. Beáta Bugyi University of Pécs, Medical School, Department of Biophysics, Overview 1. Diffusion brief overview 2. Osmosis: molecular basis and quatification 3. Medical &
Solubility Equi librium Ksp. Chapter 17 Sections
 Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 1 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 1 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
EXPERIMENT 15 FREEZING POINT: A COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY OF SOLUTIONS
 EXPERIMENT 15 FREEZING POINT: A COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY OF SOLUTIONS INTRODUCTION Scientists seldom work alone today. Instead they work in teams on projects, sharing the labor of carrying out the experiments
EXPERIMENT 15 FREEZING POINT: A COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY OF SOLUTIONS INTRODUCTION Scientists seldom work alone today. Instead they work in teams on projects, sharing the labor of carrying out the experiments
Part III. Nanotubes Theory, Methodology
 Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Membrane Channels Part III. Nanotubes Theory, Methodology Summer School on Theoretical and Computational Biophysics June 2003, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Membrane Channels Part III. Nanotubes Theory, Methodology Summer School on Theoretical and Computational Biophysics June 2003, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Solution Concentrations
 Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting
Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting
Engage the student to formulate a Researchable Question (RQ) by making observations. principle or concept. Write it down.
 Science Lead Teacher Institute Summer 2010 Connecting Biology to Chemistry through Inquiry-based Learning General Approach Using the Scientific Method to develop better conceptual knowledge and reasoning
Science Lead Teacher Institute Summer 2010 Connecting Biology to Chemistry through Inquiry-based Learning General Approach Using the Scientific Method to develop better conceptual knowledge and reasoning
Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets
 Experiment 9 Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To perform a gravimetric exercise to determine weight percent of active ingredient in a
Experiment 9 Analysis of Calcium Carbonate Tablets Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To perform a gravimetric exercise to determine weight percent of active ingredient in a
to water. You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink. This observation tells you Na 2
 1A End of Lab Questions Notes 9/11/18 Lab 4 1 You add 100 g of to water You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink This observation tells you is a base 2 You add vinegar (09 M acetic
1A End of Lab Questions Notes 9/11/18 Lab 4 1 You add 100 g of to water You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink This observation tells you is a base 2 You add vinegar (09 M acetic
Louis Pasteur STEM Project
 Louis Pasteur 2015-2016 STEM Project Project Overview: The Effects of oil spills Oil is an organic fluid that has a lower density than water. When oil is spilled on water, it will float on the water surface
Louis Pasteur 2015-2016 STEM Project Project Overview: The Effects of oil spills Oil is an organic fluid that has a lower density than water. When oil is spilled on water, it will float on the water surface
Determination of the Molar Mass of a Compound by Freezing Point Depression
 Determination of the Molar Mass of a Compound by Freezing Point Depression Objective: The objective of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute by measuring the freezing point
Determination of the Molar Mass of a Compound by Freezing Point Depression Objective: The objective of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute by measuring the freezing point
COPPER CYCLE EXPERIMENT 3
 COPPER CYCLE EXPERIMENT 3 INTRODUCTION One simple way to state the aim of chemistry is: The study of matter and its transformations. In this experiment, a copper sample will appear in five different forms
COPPER CYCLE EXPERIMENT 3 INTRODUCTION One simple way to state the aim of chemistry is: The study of matter and its transformations. In this experiment, a copper sample will appear in five different forms
Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression
 E1 Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression PURPOSE The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: (a) In part 1, the FP of the pure solvent, cyclohexane, is determined
E1 Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression PURPOSE The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: (a) In part 1, the FP of the pure solvent, cyclohexane, is determined
Activity 2.1 Curious crystals
 Activity 2.1 Curious crystals Can you identify an unknown crystal by comparing its appearance to other known crystals? In this activity, students will carefully look at four known household crystals. After
Activity 2.1 Curious crystals Can you identify an unknown crystal by comparing its appearance to other known crystals? In this activity, students will carefully look at four known household crystals. After
Revised Molar Mass Measurement Lab Purpose: Background:
 Revised Molar Mass Measurement Lab (Based on prior Ch b experiment, incorporating revision suggestions from Tsze Tsang) Purpose: To use the colligative properties of cyclohexane solutions to determine
Revised Molar Mass Measurement Lab (Based on prior Ch b experiment, incorporating revision suggestions from Tsze Tsang) Purpose: To use the colligative properties of cyclohexane solutions to determine
Class 4J Spring Term Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D
 Class 4J Spring Term 2003 Science Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D ABOUT THE UNIT In this unit children learn about the differences between solids
Class 4J Spring Term 2003 Science Unit 4D Solids, liquids and how they can be separated Adapted from QCA Science Unit 4D ABOUT THE UNIT In this unit children learn about the differences between solids
Lab Report: Thermal Energy Transfer in Mixtures
 Lab Report: Thermal Energy Transfer in Mixtures Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to discover how exactly the final temperature of a mixture, involving a substance and hot water, is affected and
Lab Report: Thermal Energy Transfer in Mixtures Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to discover how exactly the final temperature of a mixture, involving a substance and hot water, is affected and
Experiment B-38 Monitoring Yeast Growth
 1 Experiment B-38 Monitoring Yeast Growth Objectives To learn about the life cycle of yeast. To monitor yeast growth by using a turbidity sensor. To plot a growth curve. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog
1 Experiment B-38 Monitoring Yeast Growth Objectives To learn about the life cycle of yeast. To monitor yeast growth by using a turbidity sensor. To plot a growth curve. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog
(a) Since there was no salt in the aquarium to start with, at any time t we have,
 24. pg 557 An aquarium pool has volume 2 0 6 liters. The pool initially contains pure fresh water. At t 0 minutes, water containing 0 grams/liter of salt is poured into the pool at a rate of 60 liters/minute.
24. pg 557 An aquarium pool has volume 2 0 6 liters. The pool initially contains pure fresh water. At t 0 minutes, water containing 0 grams/liter of salt is poured into the pool at a rate of 60 liters/minute.
Chemistry 102 Freezing Point Depression Dr. Caddell. Depressing the Freezing Point of Cyclohexane
 Depressing the Freezing Point of Cyclohexane In this lab you will determine the molar mass of an unknown molecular compound by determining the freezing point depression of a sample of cyclohexane. Equipment
Depressing the Freezing Point of Cyclohexane In this lab you will determine the molar mass of an unknown molecular compound by determining the freezing point depression of a sample of cyclohexane. Equipment
Archer G11 Partner: Judy Aug Gravimetric Analysis of a Metal Carbonate
 Gravimetric Analysis of a Metal Carbonate Purpose The purpose of this lab is to identify the unknown carbonate. This can be done by finding the mass of the product carbonate and using stoichiometry on
Gravimetric Analysis of a Metal Carbonate Purpose The purpose of this lab is to identify the unknown carbonate. This can be done by finding the mass of the product carbonate and using stoichiometry on
Solutions Unit Exam Name Date Period
 Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Advanced Biology through Inquiry EVALUATION COPY
 Advanced Biology through Inquiry Student Guide PASCO scientific 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95747-7100 Toll Free 800-772-8700 916-786-3800 Fax 916-786-8905 CONTRIBUTORS PASCO Development Team
Advanced Biology through Inquiry Student Guide PASCO scientific 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95747-7100 Toll Free 800-772-8700 916-786-3800 Fax 916-786-8905 CONTRIBUTORS PASCO Development Team
The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts. 13+ Entrance Examination 2015
 The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts 13+ Entrance Examination 2015 CHEMISTRY Please follow these instructions The Science paper is divided into three sections (Biology, Chemistry and Physics).
The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts 13+ Entrance Examination 2015 CHEMISTRY Please follow these instructions The Science paper is divided into three sections (Biology, Chemistry and Physics).
Minnesota Comprehensive Assessments-Series III
 Name Minnesota Comprehensive Assessments-Series III Science Item Sampler Grade 8 ITEM SAMPLERS ARE NOT SECURE TEST MATERIALS. THIS ITEM SAMPLER TEST BOOK MAY BE COPIED OR 18 Point State of Minnesota Copyright
Name Minnesota Comprehensive Assessments-Series III Science Item Sampler Grade 8 ITEM SAMPLERS ARE NOT SECURE TEST MATERIALS. THIS ITEM SAMPLER TEST BOOK MAY BE COPIED OR 18 Point State of Minnesota Copyright
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Hardness. Concentration is. What s the concentration of red triangles? What s in your pipes? 500 ml
 Slide 1 Hardness What s in your pipes? Slide 2 What s the concentration of red triangles? 500 ml 1 g 1 g 1 g A. 10 B. 10 C. D. 1 g 1 g It s all of the above! Slide 3 Concentration is any statement of the
Slide 1 Hardness What s in your pipes? Slide 2 What s the concentration of red triangles? 500 ml 1 g 1 g 1 g A. 10 B. 10 C. D. 1 g 1 g It s all of the above! Slide 3 Concentration is any statement of the
LAB SAFETY & PROCEDURE GALLERY
 LAB SAFETY & PROCEDURE GALLERY EMPACTS PROJECT FALL, 2015 ERIKA ALAWDI, STEPHANIE AZENON, HAILEY MCCAIN, LISA MAE MALUYA, AND JONATHAN MUNOZ Biology is both a challenging and rewarding area of study. Throughout
LAB SAFETY & PROCEDURE GALLERY EMPACTS PROJECT FALL, 2015 ERIKA ALAWDI, STEPHANIE AZENON, HAILEY MCCAIN, LISA MAE MALUYA, AND JONATHAN MUNOZ Biology is both a challenging and rewarding area of study. Throughout
Heat of Fusion & Heat of Vaporization Lab
 Name: Period: Purpose Heat of Fusion & Heat of Vaporization Lab In this two-part activity, you will determine the change in heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization for water. Introduction In ancient times,
Name: Period: Purpose Heat of Fusion & Heat of Vaporization Lab In this two-part activity, you will determine the change in heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization for water. Introduction In ancient times,
The Hydrologic Cycle. Vocabulary condensation, evaporation, precipitation, transpiration
 The Hydrologic Cycle Strand Topic Geology Investigating the Hydrologic Cycle Primary SOL ES.8 The student will investigate and understand how freshwater resources are influenced by geologic processes and
The Hydrologic Cycle Strand Topic Geology Investigating the Hydrologic Cycle Primary SOL ES.8 The student will investigate and understand how freshwater resources are influenced by geologic processes and
Melting Range 3. Melting Range
 Melting Range 3 Melting Range Background Information The melting range of a pure solid organic is the temperature range at which the solid is in equilibrium with its liquid. As heat is added to a solid,
Melting Range 3 Melting Range Background Information The melting range of a pure solid organic is the temperature range at which the solid is in equilibrium with its liquid. As heat is added to a solid,
Extracting DNA in Your Kitchen Teacher Section
 Extracting DNA in Your Kitchen Teacher Section Overview DNA is the genetic material that has all the information about a cell. If the cell has a nucleus, the DNA is located in the nucleus. If not, it is
Extracting DNA in Your Kitchen Teacher Section Overview DNA is the genetic material that has all the information about a cell. If the cell has a nucleus, the DNA is located in the nucleus. If not, it is
Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression
 E1 Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression PURPOSE The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: (a) In part 1, the FP of the pure solvent, cyclohexane, is determined
E1 Colligative Properties of Solutions: Freezing Point Depression PURPOSE The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: (a) In part 1, the FP of the pure solvent, cyclohexane, is determined
Equilibria of Slightly Soluble Ionic Compounds: We lied to you in chem 115
 Precipitation Reactions Predicting Whether a Precipitate Will Form Note the ions present in the reactants Consider all possible cation-anion combinations Use the solubility rules to decide whether any
Precipitation Reactions Predicting Whether a Precipitate Will Form Note the ions present in the reactants Consider all possible cation-anion combinations Use the solubility rules to decide whether any
4-1 Cell biology Biology
 4- Cell biology Biology.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D. Into which cell,
4- Cell biology Biology.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D. Into which cell,
B2.5h Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (diffusion, osmosis hypertonic/hypotonic).
 Alice Gryspeerd alice.gryspeerd@romeo.k12.mi.us Romeo High School Maritime Teacher Institute July 2013 Lesson #2: Why Is Salinity Value Important in Ballast Water Management? Target Subject/Grade: Biology
Alice Gryspeerd alice.gryspeerd@romeo.k12.mi.us Romeo High School Maritime Teacher Institute July 2013 Lesson #2: Why Is Salinity Value Important in Ballast Water Management? Target Subject/Grade: Biology
The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel.
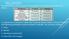 BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
BELL RINGER The table below shows some of the properties of the elements cobalt and nickel. A scientist has a sample of metal that could be either cobalt or nickel. Which of the following properties could
Solubility Equi librium Ksp. Chapter 17 Sections
 Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Date: Name and Period:
 Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Laboratory 1 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. investigate the processes of diffusion and osmosis in a model membrane system, and 2. investigate
Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Laboratory 1 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. investigate the processes of diffusion and osmosis in a model membrane system, and 2. investigate
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
4-1 Cell biology Biology
 4- Cell biology Biology.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D. Into which cell,
4- Cell biology Biology.0 Figure shows cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Figure Cell A Cell B Oxygen molecules Cell C Cell D. Into which cell,
Ocean Water. Evaluation copy
 Ocean Water Experiment 12 If you were to view the planet Earth from space, you would see that most of its surface is covered by water. Most of this is ocean water that cannot be consumed. Why can t ocean
Ocean Water Experiment 12 If you were to view the planet Earth from space, you would see that most of its surface is covered by water. Most of this is ocean water that cannot be consumed. Why can t ocean
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16)
 Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
Cu-AgNO 3 Lab Date: Hour: Question: What is the mole ratio of copper consumed to silver produced in the reaction?
 Chemistry Cu-ANO 3 Lab Name: Date: Hour: Partner: Question: What is the mole ratio of copper consumed to silver produced in the reaction? Hypothesis: (answer usin complete sentences) Research (answer questions
Chemistry Cu-ANO 3 Lab Name: Date: Hour: Partner: Question: What is the mole ratio of copper consumed to silver produced in the reaction? Hypothesis: (answer usin complete sentences) Research (answer questions
The Impact Of Fertilizer On Protozoa
 Knott, Young, Lavin 1 The Impact Of Fertilizer On Protozoa Elizabeth Knott, Jassmin Young, Megan Lavin April 30, 2009 Mr. Brock Knott, Young, Lavin 2 Protozoa or protozoans are any eukaryote that isn t
Knott, Young, Lavin 1 The Impact Of Fertilizer On Protozoa Elizabeth Knott, Jassmin Young, Megan Lavin April 30, 2009 Mr. Brock Knott, Young, Lavin 2 Protozoa or protozoans are any eukaryote that isn t
THE IMPORTANCE OF OSMOTIC POTENTIAL IN THE BRINE DISCHARGE
 THE IMPORTANCE OF OSMOTIC POTENTIAL IN THE BRINE DISCHARGE Authors: Dr. Manuel Latorre Presenter: Dr. Manuel Latorre Abstract To date, the environmental impact of brine discharge from RO plants has been
THE IMPORTANCE OF OSMOTIC POTENTIAL IN THE BRINE DISCHARGE Authors: Dr. Manuel Latorre Presenter: Dr. Manuel Latorre Abstract To date, the environmental impact of brine discharge from RO plants has been
National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1
 National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. The diagram below shows parts of a plant cell. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1 2. Which structural feature is found in a plant
National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. The diagram below shows parts of a plant cell. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1 2. Which structural feature is found in a plant
EXPLORING ZONES OF TOLERANCE WITH BRINE SHRIMP
 NAME: DATE: EXPLORING ZONES OF TOLERANCE WITH BRINE SHRIMP PRELAB DISCUSSION What are zones of tolerance? http://dtc.pima.edu/blc/105/503/tutor/tutor31.html Each species of animal, plant, or any living
NAME: DATE: EXPLORING ZONES OF TOLERANCE WITH BRINE SHRIMP PRELAB DISCUSSION What are zones of tolerance? http://dtc.pima.edu/blc/105/503/tutor/tutor31.html Each species of animal, plant, or any living
Mid Term Exam October th Year Biology. Name: Result:
 Mid Term Exam October 2016 5 th Year Biology Name: Result: Teacher Feedback: STAR STAR WISH Question 1- Food and Scientific Method 20m a) Name a reagent used to test for reducing sugar. b) Name the elements
Mid Term Exam October 2016 5 th Year Biology Name: Result: Teacher Feedback: STAR STAR WISH Question 1- Food and Scientific Method 20m a) Name a reagent used to test for reducing sugar. b) Name the elements
Do not write on the question paper, do not turn in the question paper. Put your answers on a new paper. Unless told otherwise.
 APES Unit 2 Packet Due Sept 10 at the beginning of class Instructions for all homework and labs: Put your name and date on top right corner of all your papers. Put the name of the problem or lab at the
APES Unit 2 Packet Due Sept 10 at the beginning of class Instructions for all homework and labs: Put your name and date on top right corner of all your papers. Put the name of the problem or lab at the
Unit 3 - Solubility Practice Test # 2
 1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
CHEM J-8 June Answer: THE REMAINDER OF THIS PAGE IS FOR ROUGH WORKING ONLY.
 CHEM1101 2014-J-8 June 2014 A 1.0 kg sample of copper metal is heated to 100.0 C. The copper sample is immersed in a volume of water initially at 25.0 C. What volume of water is required so that the final
CHEM1101 2014-J-8 June 2014 A 1.0 kg sample of copper metal is heated to 100.0 C. The copper sample is immersed in a volume of water initially at 25.0 C. What volume of water is required so that the final
EXPERIMENT. The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen
 EXPERIMENT The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen PURPOSE In this experiment you will determine the volume of the hydrogen gas which is produced when a sample of
EXPERIMENT The Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid; The Molar Volume of Hydrogen PURPOSE In this experiment you will determine the volume of the hydrogen gas which is produced when a sample of
Soil Ecology Project. The Effect of Road Salt on Bacteria Density. Hope Duke, Irina Kolesnik and Clare O Brien Mr. Brock Biology 9 Honors
 Soil Ecology Project The Effect of Road Salt on Bacteria Density Hope Duke, Irina Kolesnik and Clare O Brien Mr. Brock Biology 9 Honors 5/31/2012 A. Background Report Soil is made out of four basic components:
Soil Ecology Project The Effect of Road Salt on Bacteria Density Hope Duke, Irina Kolesnik and Clare O Brien Mr. Brock Biology 9 Honors 5/31/2012 A. Background Report Soil is made out of four basic components:
The students will be able to: define porosity and relate it to the capacity of a common object's TEKS ADDRESSED:
 AUTHORS NAMES: TITLE OF THE LESSON: Porosity and Permeability TECHNOLOGY LESSON : No DATE OF LESSON: TIME LESSON: 2 (60 min class) NAME OF COURSE Biology SOURCE OF THE LESSON: Lynn Kirby TEKS ADDRESSED:
AUTHORS NAMES: TITLE OF THE LESSON: Porosity and Permeability TECHNOLOGY LESSON : No DATE OF LESSON: TIME LESSON: 2 (60 min class) NAME OF COURSE Biology SOURCE OF THE LESSON: Lynn Kirby TEKS ADDRESSED:
THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF A SOLUTE*
 Name Per THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF A SOLUTE* One of the most helpful things that can be known about an element or compound is its molecular weight (molecular mass, gram molecular mass, atomic mass, or gram
Name Per THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF A SOLUTE* One of the most helpful things that can be known about an element or compound is its molecular weight (molecular mass, gram molecular mass, atomic mass, or gram
Archer G11 Partner: Mi 6 Sept Analysis of Alum, AlK(SO 4 ) 2 *12H 2 O
 Analysis of Alum, AlK(SO 4 ) 2 *12H 2 O Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to determine the melting point of alum and the number of water molecules that can be attached to one alum molecule. The significance
Analysis of Alum, AlK(SO 4 ) 2 *12H 2 O Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to determine the melting point of alum and the number of water molecules that can be attached to one alum molecule. The significance
Quiz 2 practice Quiz
 Name: ate: 1. The following data were recorded while determining the solubility of a certain salt. Temp. ( C) 10 20 30 40 50 Grams Solute/ 100 g H 2 O 30 33 36 39 42 Which graph best represents the solubility
Name: ate: 1. The following data were recorded while determining the solubility of a certain salt. Temp. ( C) 10 20 30 40 50 Grams Solute/ 100 g H 2 O 30 33 36 39 42 Which graph best represents the solubility
Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor. Student. 90 minutes
 Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor 90 minutes Student Purpose of this lesson Investigate the variation of resistance with conductivity Construct a sensor to measure the conductivity of water Graph
Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor 90 minutes Student Purpose of this lesson Investigate the variation of resistance with conductivity Construct a sensor to measure the conductivity of water Graph
GEOL360 Homework 3 : Aqueous Geochemistry
 GEOL360 HOMEWORK 3: AQUEOUS GEOCHEMISTRY 1/8 GEOL360 Homework 3 : Aqueous Geochemistry Name: Fill in the final answers in the blank spaces provided after each question. Staple all other pieces of paper
GEOL360 HOMEWORK 3: AQUEOUS GEOCHEMISTRY 1/8 GEOL360 Homework 3 : Aqueous Geochemistry Name: Fill in the final answers in the blank spaces provided after each question. Staple all other pieces of paper
Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor. Teacher. 90 minutes
 Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor 90 minutes Teacher Purpose of this lesson Investigate the variation of resistance with conductivity Construct a sensor to measure the conductivity of water Graph
Module 2, Add on Lesson Conductivity Sensor 90 minutes Teacher Purpose of this lesson Investigate the variation of resistance with conductivity Construct a sensor to measure the conductivity of water Graph
