Calculate the Costs of Piping System Elements
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
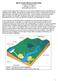
1 Calculate the Costs of Piping System Elements by Ray Hardee, Engineered Software, Inc. Last month s column described the process of creating an energy cost balance sheet for a piping system (see Figure 1). The manufacturer s curve was used to calculate the cost of operation for the centrifugal pump. This column explains how to perform the detailed cost calculation for other items in the system. Evaluating Parts Figure 1 shows the operating data from the installed plant instrumentation. This operating data and the manufacturer s equipment data sheets will be used to calculate the differential pressure and flow rate through each item. With that information, the cost of electrical power and the annual rate of operation, the annual operating cost and energy use can be calculated for each item in the system s energy cost balance sheet. To calculate the operating cost for an item in the system, its head loss and corresponding flow rate must be determined. Insufficient installed instrumentation means these values need to be calculated with data from the equipment manufacturers.
2 Figure 1. The operating data from installed plant instrumentation and elevations of selected tanks and equipment Determining Pump Flow Rate Last month s column calculated a pump head of 235 feet (ft) and a flow rate of 4,000 gallons per minute (gpm). From the pump curve, it was determined that the pump had an efficiency of 83 percent at its flow rate. The pump s operating costs were calculated after looking at the pump s motor efficiency, annual hours of operation and cost of electrical power. So how was the flow rate through the pump of 4,000 gpm established? The flow to the destination tank is 2,500 gpm, but because there is no flow element in the bypass circuit, the pump s total flow rate cannot be calculated. Without this value, the pump efficiency and power consumed also cannot be calculated. The pump curve is the key to this process because it provides manufacturer-supplied test data on how the pump operates for its flow range. Knowing the pump s total head, the pump curve can be entered on the head axis and move across until the known pump head value intersects the pump curve. Dropping straight down on the pump curve gives the flow rate, and the intersection point provides the pump efficiency. In Figure 1, the process pump s discharge pressure is pounds per square inch (psig). Centrifugal pump curves use head instead of pressure, so the discharge pressure must be converted to feet of fluid using Equation 1.
3 Where: H = Head in feet of fluid P = Pressure in lb/inch 2 ρ = Fluid density in lb/ft is a conversion factor for ft 2 to in 2 A pressure gauge is not installed on the pump suction, so a temporary gauge was mounted on a suction vent. The temporary suction pressure gauge reads 1.7 psig, resulting in 3.95 ft of fluid. Subtracting the discharge and suction heads (239 ft minus 3.95 ft), the pump s total head is 235 ft. Reading from the pump curve (see Figure 2), the resulting flow rate through the pump is 4,000 gpm, and the pump is 83 percent efficient. the flow rate and pump efficiency from calculated total head of 235 ft Figure 2. Determining
4 Next, the cost to operate the system s process elements will be evaluated using their flow rates and head loss. Advertisement Static Head Cost The static head accounts for the difference in fluid energy between the destination and supply tanks. Per the Bernoulli equation, fluid energy is composed of three types of head: elevation, pressure and velocity. Because the fluid is at rest in the supply and destination tanks, the velocity head has no value (see Equation 2). Where: Z B = Elevation of tank bottom in ft L FS = Level of fluid surface above tank bottom in ft P FS = Pressure on fluid surface in psi ρ = Fluid density in lb/ft 3 1 = Supply tank 2 = Destination tank The static head is the energy difference between the supply and destination tanks. It remains the same regardless of the flow rate between the tanks. The static head can be used to calculate the annual operating cost due to the head component within the process circuit. The 2,500 gpm flow rate through the process circuit is used in the annual operating cost formula (see Equation 3). The 83 percent pump efficiency comes from the pump curve with a 4,000 gpm flow rate. The pump efficiency applies to the 4,000 gpm flow rate because the pump supplies both the process and bypass circuits. Inserting the static head pump efficiency, flow rate, hours of operating and cost of power results in an annual energy cost of $22,800 for the static head.
5 Where: Q = Flow rate H = Head ρ = Fluid density η ρ = Pump efficiency η m = Motor efficiency Process Element Cost Process equipment characterized by a head loss that is a function of flow rate is the next item in the energy cost balance sheet. In the system shown in Figure 1, the process element has no installed pressure gauges. The manufacturer s equipment data sheet will be used to calculate head loss. The manufacturer s supplied data sheet could have a curve showing the pressure drop and head loss for a range of flow rates, a C v value or a single value of pressure drop versus a given flow rate. For this example, the manufacturer provided a 14.4 psi pressure drop with a flow rate of 3,000 gpm. To determine the pressure drop through the process element at 2,500 gpm, the C v must be calculated using the manufacturer s supplied data points of 3,000 gpm and 14.4 psi (see Equation 4). Where: C v = Flow coefficient Q = Volumetric flow rate in gpm dp = Differential pressure in psi SG = Specific gravity
6 The differential pressure across the process element is 10 psi, after calculating the C v of the process elements, the specific gravity of the process fluid and the flow rate using Equation 5. The 10 psi differential pressure converts to 23.3 ft head loss across the process equipment. The head loss results in a $5,592 annual energy cost for the process element as calculated in Equation 6. Piping Cost The head loss in a pipeline can be calculated using the Darcy equation (see Equation 7). However, Equation 8 makes calculating the head loss with the flow rate in gallons per minute and pipe inside diameter in inches easier. Where: h L = pipeline head loss in ft f = Darcy friction factor (unitless) L = pipe length in ft D = pipe inside diameter in ft v = fluid velocity in ft/s g = gravitational constant in 32.2 ft/s 2
7 Q = volumetric flow rate in gal/min d = inside pipe diameter in inches In this example, we ll calculate the head loss for a 50-foot suction pipeline made of 16-inch schedule 40 steel. Two gate valves and a sharp edge transition lie along the pipeline from the tank. The pipeline is passing 4,000 gpm of a fluid with a fluid density of 62 lb/ft 3 and viscosity of 0.68 centipoise. The steps required to arrive at the pipeline s head loss are listed below along with the intermediate results. Reynolds number = 1.23 x 10 6 unitless Relative roughness = in Darcy friction factor = unitless Pipe head loss = 0.44 ft Valve and fitting loss = 0.57 ft Pipeline head loss = 1.01 ft (The detailed head loss calculation for this example can be found at The head losses for the circuit s remaining pipelines are added to obtain the total pipeline head loss in Table 1.
8 Table 1. Pipeline summary, calculated head loss and annual operating costs for the pipelines in the process circuit The operating cost for the pipelines is $5,376, after plugging in the sum of the pipeline s head loss and the flow element, as shown in Equation 9. Control Valve Cost Control valves regulate flow rate to achieve the desired set point in this case, the level in the destination tank. The tank s outflow (not shown on the drawing) feeds the plant s demands. When the flow rates into and out of the tank are equal, the level in the destination tank is constant. To determine the operating cost, the flow rate through and the differential pressure across the level control valve are needed. Most systems do not measure the valve s differential pressure, which can be calculated knowing the valve position, flow rate and C v values as a function of valve position. But that requires involved calculations. Instead, the interaction between the pump, process and control elements can be used to calculate the head loss across the control valve. As shown in past articles, all the energy provided by the pump is used by the process and control elements (see Equation 10).
9 h Pump = h Process + h Control Equation 10a Substituting the calculated value for pump head and the sum of the head loss of the circuit s process elements, we can determine the head loss across the control valve. 235 = ( ) + h Control Equation 10b The annual operating cost of the level control valve is $22,633, after solving for the known flow rate with 94.3 ft of control valve head loss in Equation 11. Bypass Circuit Cost The annual operation costs of the bypass and process circuits follow the same approach. The bypass circuit provides minimum flow through the pump back to prevent pump damage, and its process elements consist of the static head and the pipelines. The static head in the bypass circuit is the difference in elevations between the end of the pipeline discharging into the supply tank (30 ft) and the liquid level in the supply tank (5 ft). The head losses associated with the pipelines consist of the common pump suction and discharge header, along with the recirculation pipelines returning to the supply tank (3 ft). The control element in the bypass circuit consists of a back pressure valve (BPV) designed to maintain a 100-psi pressure on the pump discharge regardless of the system flow rate. The set point was selected so the flow rate through the pump is always greater than the manufacturer s minimum flow rate regardless of the flow to the destination tank.
10 Like the control valve example, the energy in the bypass circuit must balance (see Equation 12). This results in a head loss of 207 ft for the back pressure valve in the bypass circuit. 235 = (25 + 3) + h Control Equation 12 Next month s column will explain how to cross-validate the calculated results of the energy cost balance sheet and determine if the system is operating properly. ABOUT THE AUTHOR Ray Hardee is a principal founder of Engineered Software, creators of PIPE-FLO and PUMP- FLO software. At Engineered Software, he helped develop two training courses and teaches these courses in the U.S. and internationally. He is a member of the ASME ES-2 Energy Assessment for Pumping Systems standards committee and the ISO Technical Committee 115/Working Group 07 Pumping System Energy Assessment. Hardee was a contributing member of the HI/Europump Pump Life Cycle Cost and HI/PSM Optimizing Piping System publications. He may be reached at ray.hardee@eng-software.com.
AR No. # Efficient Irrigation
 AR No. # Efficient Irrigation Recommendation Optimize the facilities irrigation pumping system by ensuring pumps are operating at their Best Efficiency Point (BEP). We estimate the system pumping efficiency
AR No. # Efficient Irrigation Recommendation Optimize the facilities irrigation pumping system by ensuring pumps are operating at their Best Efficiency Point (BEP). We estimate the system pumping efficiency
AALSO Summary of Formulas needed for Levels I, II and III.
 AALSO Summary of Formulas needed for Levels I, II and III. The information provided below is used in the math portion of the proficiency exams. Please take time to review and learn how to use these formulas
AALSO Summary of Formulas needed for Levels I, II and III. The information provided below is used in the math portion of the proficiency exams. Please take time to review and learn how to use these formulas
AALSO Proficiency Program Level I, II & III
 AALSO Proficiency Program Level I, II & III Hello, and welcome to AALSO s 2010 Proficiency Program! AALSO offers a multi-level operator competency acknowledgment program based on test scores received from
AALSO Proficiency Program Level I, II & III Hello, and welcome to AALSO s 2010 Proficiency Program! AALSO offers a multi-level operator competency acknowledgment program based on test scores received from
Successfully dosing pipe networks. Kevin Sherman, Ph.D., P.E., D.WRE Vice President of Engineering Clearstream Wastewater Systems, Inc.
 Successfully dosing pipe networks Kevin Sherman, Ph.D., P.E., D.WRE Vice President of Engineering Clearstream Wastewater Systems, Inc. What is a successful dose? Spreads effluent throughout soil disp.
Successfully dosing pipe networks Kevin Sherman, Ph.D., P.E., D.WRE Vice President of Engineering Clearstream Wastewater Systems, Inc. What is a successful dose? Spreads effluent throughout soil disp.
Pump ED 101. Pump Selection for VFD Operation Part 3 Q / H Pump Down vs Level Control. Introduction. Pump Down vs Level Control
 Pump Selection for VFD Operation Part 3 Q / H Pump Down vs Level Control Joe Evans, Ph.D joeeevans@gmail.com Pump ED 101 http://www.pumped101.com Introduction In Part 2 we took a look at the pump selection
Pump Selection for VFD Operation Part 3 Q / H Pump Down vs Level Control Joe Evans, Ph.D joeeevans@gmail.com Pump ED 101 http://www.pumped101.com Introduction In Part 2 we took a look at the pump selection
Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050. Name: Date:
 Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050 Name: Date: Note: Please show all of your calculations for each problem no matter how simple the problem may seem. Please use the accompanying pieces
Water Utility Science Water Math and Hydraulics 050 Name: Date: Note: Please show all of your calculations for each problem no matter how simple the problem may seem. Please use the accompanying pieces
VENTURI FLOWMETERS. Your First Choice in Intelligent Flow Management...
 VENTURI FLOWMETERS Your First Choice in Intelligent Flow Management... VENTURI FLOWMETERS Preso s complete line of Venturis offer reduced operating costs, proven accuracy, and great rangeability. Low permanent
VENTURI FLOWMETERS Your First Choice in Intelligent Flow Management... VENTURI FLOWMETERS Preso s complete line of Venturis offer reduced operating costs, proven accuracy, and great rangeability. Low permanent
Session 2 Pump Selection. Mark Markham, P.E. Gresham, Smith and Partners September 14, 2017
 Session 2 Pump Selection Mark Markham, P.E. Gresham, Smith and Partners September 14, 2017 Quick Refresh System Curves graphically show the relationship between flow rates and associated total dynamic
Session 2 Pump Selection Mark Markham, P.E. Gresham, Smith and Partners September 14, 2017 Quick Refresh System Curves graphically show the relationship between flow rates and associated total dynamic
Chilled Water Distribution Systems. APPA Institute for Facilities Management New Orleans, LA January 19, 2016
 Chilled Water Distribution Systems APPA Institute for Facilities Management New Orleans, LA January 19, 2016 1 Purpose of Today s Presentation To provide a broad understanding of chilled water distribution
Chilled Water Distribution Systems APPA Institute for Facilities Management New Orleans, LA January 19, 2016 1 Purpose of Today s Presentation To provide a broad understanding of chilled water distribution
FLUID FLOW - PUMPS. Discharge Section. Section. Two main types of pumps: Positive Displacement pumps Centrifugal pumps.
 FLUID FLOW - PUMPS 4 3 Control valve Suction Section Discharge Section Two main types of pumps: Positive Displacement pumps Centrifugal pumps ChE 453 - Design I FLUID FLOW - PUMP PERFORMANCE Mechanical
FLUID FLOW - PUMPS 4 3 Control valve Suction Section Discharge Section Two main types of pumps: Positive Displacement pumps Centrifugal pumps ChE 453 - Design I FLUID FLOW - PUMP PERFORMANCE Mechanical
Fluid Mechanics. The Energy Equation [7] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri
![Fluid Mechanics. The Energy Equation [7] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Fluid Mechanics. The Energy Equation [7] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri](/thumbs/77/76088370.jpg) 1 Fluid Mechanics The Energy Equation [7] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri http://sites.google.com/site/mohammadnablus/home 2 Introduction There are various types of devices and components that are utilized in
1 Fluid Mechanics The Energy Equation [7] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri http://sites.google.com/site/mohammadnablus/home 2 Introduction There are various types of devices and components that are utilized in
Flow Test Data Book and Flow Handbook for 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate
 Test Book and Handbook for 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Title Page 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Test Book NOTICE Read this manual before
Test Book and Handbook for 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Title Page 405 Compact Orifice Series and 1595 Conditioning Orifice Plate Test Book NOTICE Read this manual before
Application of Variable Frequency Drives for Energy Savings
 Application of Variable Frequency Drives for Energy Savings Scott McGlamery,.E. Department of Electrical Engineering, Hixson, Cincinnati, OH Abstract- While almost any facility could potentially benefit
Application of Variable Frequency Drives for Energy Savings Scott McGlamery,.E. Department of Electrical Engineering, Hixson, Cincinnati, OH Abstract- While almost any facility could potentially benefit
Hydraulics Laboratory Experiment Report
 Hydraulics Laboratory Experiment Report Name: Ahmed Essam Mansour Section: Title: "1", Monday 2-5 pm Centrifugal Pumps Date: 27 November, 2006 Objectives: To study the performance of a centrifugal pumps
Hydraulics Laboratory Experiment Report Name: Ahmed Essam Mansour Section: Title: "1", Monday 2-5 pm Centrifugal Pumps Date: 27 November, 2006 Objectives: To study the performance of a centrifugal pumps
SAWEA Workshop 2010 Innovative Water and Wastewater Networks Presented by Greg Welch, AECOM
 SAWEA Workshop 2010 Innovative Water and Wastewater Networks Presented by Greg Welch, AECOM Basic Hydraulic Principles Open channel flow Closed conduit / pressurized flow systems Orifices, weirs and flumes
SAWEA Workshop 2010 Innovative Water and Wastewater Networks Presented by Greg Welch, AECOM Basic Hydraulic Principles Open channel flow Closed conduit / pressurized flow systems Orifices, weirs and flumes
Basic Irrigation Design
 Basic Irrigation Design Basic Irrigation Design Table of Contents Introduction............................ii Terminology...........................iii System Diagram.........................1 Hydraulics..............................2
Basic Irrigation Design Basic Irrigation Design Table of Contents Introduction............................ii Terminology...........................iii System Diagram.........................1 Hydraulics..............................2
Honeywell Thermal Solutions. Engineering Guide
 Engineering Guide Honeywell Thermal Solutions Engineering Guide Copyright 2017 by Honeywell Thermal Solutions All Rights Reserved CONTENTS 1. Orifices & Flows Coefficients of Discharge for Various Types
Engineering Guide Honeywell Thermal Solutions Engineering Guide Copyright 2017 by Honeywell Thermal Solutions All Rights Reserved CONTENTS 1. Orifices & Flows Coefficients of Discharge for Various Types
SPILL ESTIMATION. Not Just A Guess Anymore
 SPILL ESTIMATION Not Just A Guess Anymore SPILL ESTIMATION Under current regulations accurate spill estimation has become critical to the operation and maintenance of a sanitary collection system Reporting
SPILL ESTIMATION Not Just A Guess Anymore SPILL ESTIMATION Under current regulations accurate spill estimation has become critical to the operation and maintenance of a sanitary collection system Reporting
CHAPTER 12 TRICKLING FILTER PLANTS
 CHAPTER 12 TRICKLING FILTER PLANTS TM 5-814-3/AFM 88-11, Volume III 12-1. General considerations. Trickling filter plants have been justified by their low initial cost, low operating and maintenance costs,
CHAPTER 12 TRICKLING FILTER PLANTS TM 5-814-3/AFM 88-11, Volume III 12-1. General considerations. Trickling filter plants have been justified by their low initial cost, low operating and maintenance costs,
VENTURI FLOW METER CALIBRATIONS SERIAL NUMBERS: , , , Prepared for. Imperial Flange and Fitting.
 VENTURI FLOW METER CALIBRATIONS SERIAL NUMBERS: 23034-1, 23034-2, 23034-3, 23034-4 Prepared for Imperial Flange and Fitting January 2007 UTAH WATER RESEARCH LABORATORY Utah State University Report No.
VENTURI FLOW METER CALIBRATIONS SERIAL NUMBERS: 23034-1, 23034-2, 23034-3, 23034-4 Prepared for Imperial Flange and Fitting January 2007 UTAH WATER RESEARCH LABORATORY Utah State University Report No.
Rolairtrol Air Separator For Hot and Chilled Water Systems
 REMOVES ENTRAINED AIR To protect the system against damage To eliminate system noise TANGENTIAL FLOW PATTERN Increases air separation efficiency Allows use of smaller sizes than required with straight
REMOVES ENTRAINED AIR To protect the system against damage To eliminate system noise TANGENTIAL FLOW PATTERN Increases air separation efficiency Allows use of smaller sizes than required with straight
TECHNICAL INFORMATION Bulletin NUMBER Thirty-Four
 Peerless Pump Company Indianapolis IN, 46207-7026 TECHNICAL INFORMATION Bulletin NUMBER Thirty-Four Peerless Pump Hydroconstant fluid drive applications in breweries New brewery techniques, based upon
Peerless Pump Company Indianapolis IN, 46207-7026 TECHNICAL INFORMATION Bulletin NUMBER Thirty-Four Peerless Pump Hydroconstant fluid drive applications in breweries New brewery techniques, based upon
LIQUID-SPECIFIC PRODUCT LINE: ABRASIVE LIQUID PUMPS SERIES DESCRIPTION OPERATING RANGE: IMPROVEMENTS NOMINAL FLOW RATES:
 SERIES 4624B (Cast Iron - Replaces Series 4625 Models) Page 410.1 Issue K SERIES DESCRIPTION The Abrasive Liquid Series heavy duty internal gear pumps utilize hard parts in key wear areas, combined with
SERIES 4624B (Cast Iron - Replaces Series 4625 Models) Page 410.1 Issue K SERIES DESCRIPTION The Abrasive Liquid Series heavy duty internal gear pumps utilize hard parts in key wear areas, combined with
Performance Testing of The Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant and Sir Adam Beck Generating Station
 Performance Testing of The Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant and Sir Adam Beck Generating Station By Albert F. Mikhail, P.Eng., Ontario Power Generation and Robert J. Knowlton, P.E., New York Power Authority
Performance Testing of The Robert Moses Niagara Power Plant and Sir Adam Beck Generating Station By Albert F. Mikhail, P.Eng., Ontario Power Generation and Robert J. Knowlton, P.E., New York Power Authority
HYDRAULIC DEMONSTRATION CHANNEL
 HYDRAULIC DEMONSTRATION CHANNEL PACKING LIST Pitot-Static Tube and Manometer Tube Flow Meters 1. 48 Long Differential Manometer 2. Clear Tubing 3. Pitot-static Tube Clamp 4. Pitot-static Tube 1. Venturi
HYDRAULIC DEMONSTRATION CHANNEL PACKING LIST Pitot-Static Tube and Manometer Tube Flow Meters 1. 48 Long Differential Manometer 2. Clear Tubing 3. Pitot-static Tube Clamp 4. Pitot-static Tube 1. Venturi
Distribution System Basics Course Syllabus
 Distribution System Basics Course Syllabus Purpose This course qualifies as specialized training for the CA and NV distribution operator exams. Topics Basic Water Math Unit Conversions Working with Formulas
Distribution System Basics Course Syllabus Purpose This course qualifies as specialized training for the CA and NV distribution operator exams. Topics Basic Water Math Unit Conversions Working with Formulas
Water Quality Specification for Power Supplies
 Technical Note #6 Water Quality Specification for Power Supplies Introduction The cooling water for Alpha Scientific Power Supplies must meet certain minimum specifications in regard to quality and flow
Technical Note #6 Water Quality Specification for Power Supplies Introduction The cooling water for Alpha Scientific Power Supplies must meet certain minimum specifications in regard to quality and flow
Read Only Copy Not For Distribution. Chapter 17. Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.2 QUANTITY OF WATER REQUIRED
 Chapter 17 Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.1.1 Applicability The regulations in this chapter apply to any private potable water supply system where plumbing fixtures are
Chapter 17 Private Potable Water Supply Systems 17.1 GENERAL REGULATIONS 17.1.1 Applicability The regulations in this chapter apply to any private potable water supply system where plumbing fixtures are
System & Equipment Checkout Procedure Client Name Plant Location
 System & Equipment Checkout Procedure Client Name Plant Location Procedure Title: Boiler Feed Water System Prepared By: Applied Performance Strategies 1 of 7 Approved By: Date: 01/11/08 Date: Purpose:
System & Equipment Checkout Procedure Client Name Plant Location Procedure Title: Boiler Feed Water System Prepared By: Applied Performance Strategies 1 of 7 Approved By: Date: 01/11/08 Date: Purpose:
MEMORANDUM. The general findings of the assessment are as follows:
 November 28, 2006 MEMORANDUM Project No.: 030009-002-01 To: From: Re: WRIA 31 Planning Unit Steve Germiat, LHG, CGWP, and Timothy J. Flynn, LHG, CWGP Evaluation of Winterizing Existing River Pump/Conveyance
November 28, 2006 MEMORANDUM Project No.: 030009-002-01 To: From: Re: WRIA 31 Planning Unit Steve Germiat, LHG, CGWP, and Timothy J. Flynn, LHG, CWGP Evaluation of Winterizing Existing River Pump/Conveyance
FlowSet. Balancing Procedure
 FlowSet Balancing Procedure Select the flow tolerance required As per the attached chart (ASHRAE Systems Guide, 1984), ± 10% is generally accepted as a reasonably cost effective flow tolerance, but special
FlowSet Balancing Procedure Select the flow tolerance required As per the attached chart (ASHRAE Systems Guide, 1984), ± 10% is generally accepted as a reasonably cost effective flow tolerance, but special
Ivins City Standard Specifications for Design and Construction Part 2 Engineering and Design Standards
 2.9. WATER SYSTEM DESIGN Ivins City Standard Specifications for Design and Construction All culinary water mains and appurtenances shall be designed to provide for adequate future service for all contiguous
2.9. WATER SYSTEM DESIGN Ivins City Standard Specifications for Design and Construction All culinary water mains and appurtenances shall be designed to provide for adequate future service for all contiguous
NAU Hydraulic Testing System
 2015 NAU Hydraulic Testing System HYDRAULIC TESTING CORPORATION (HTC) BRANDON SCHMALZEL, MARIAH PAZ, BENOIT COUSINEAU COTE, YOUSEF AL AQUEEL, AND ALI ABDULLAH HYDRAULIC TESTING CORPORTATION (HTC) 1 1.0
2015 NAU Hydraulic Testing System HYDRAULIC TESTING CORPORATION (HTC) BRANDON SCHMALZEL, MARIAH PAZ, BENOIT COUSINEAU COTE, YOUSEF AL AQUEEL, AND ALI ABDULLAH HYDRAULIC TESTING CORPORTATION (HTC) 1 1.0
Energetic Efficiency Analysis of Water Pumping Installations
 Energetic Efficiency Analysis of Water Pumping Installations ANCA CONSTANTIN, CLAUDIU STEFAN NITESCU, MADALINA STANESCU Hydraulic Engineering Department, Faculty of Civil Engineering Ovidius University
Energetic Efficiency Analysis of Water Pumping Installations ANCA CONSTANTIN, CLAUDIU STEFAN NITESCU, MADALINA STANESCU Hydraulic Engineering Department, Faculty of Civil Engineering Ovidius University
GETTING A GRIP ON PRESSURE. Background
 GETTING A GRIP ON PRESSURE James W. Dettmer, P.E., Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., Tucson, Arizona Karen K. Dotson, AICP, Tucson Water, Tucson, Arizona Todd J. Schram, P.E., Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., Tucson, Arizona
GETTING A GRIP ON PRESSURE James W. Dettmer, P.E., Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., Tucson, Arizona Karen K. Dotson, AICP, Tucson Water, Tucson, Arizona Todd J. Schram, P.E., Malcolm Pirnie, Inc., Tucson, Arizona
GREEN THREAD Piping Systems
 Bulletin No. A1300 February 15, 2006 SMITH FIBERCAST GREEN THREAD Piping Systems PRODUCT GREEN THREAD pipe is filament wound using an amine cured epoxy resin and fiberglass and has a resin-rich liner reinforced
Bulletin No. A1300 February 15, 2006 SMITH FIBERCAST GREEN THREAD Piping Systems PRODUCT GREEN THREAD pipe is filament wound using an amine cured epoxy resin and fiberglass and has a resin-rich liner reinforced
Target Inline Flowmeter
 Principle of Operation Flow is measured in terms of dynamic force acting on a target (solid disk) in the flow stream. Hermetically sealed, bonded strain gages in a bridge circuit configuration mounted
Principle of Operation Flow is measured in terms of dynamic force acting on a target (solid disk) in the flow stream. Hermetically sealed, bonded strain gages in a bridge circuit configuration mounted
EC It Pays to Test Your Irrigation Pumping Plant
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1980 EC80-713 It Pays to Test Your Irrigation
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Historical Materials from University of Nebraska- Lincoln Extension Extension 1980 EC80-713 It Pays to Test Your Irrigation
Overview. We will not study pipe systems in detail as these are always solved with software. Wednesday, September 01, :21 PM.
 Ch4 Page 1 Overview Wednesday, September 01, 2010 4:21 PM We will not study pipe systems in detail as these are always solved with software EGL, HGL Wednesday, September 01, 2010 3:51 PM Energy drives
Ch4 Page 1 Overview Wednesday, September 01, 2010 4:21 PM We will not study pipe systems in detail as these are always solved with software EGL, HGL Wednesday, September 01, 2010 3:51 PM Energy drives
Page of ENGINEERING DATA - HOT WATER CAPACITIES, CALCULATIONS AND CORRECTION FACTORS Use the following two tables to determine
 ENGINEERING DATA - HOT WATER CAPACITIES, CALCULATIONS AND CORRECTION FACTORS Use the following two tables to determine The performances reflected in these tables are based on 1. Heating Capacity (MBH)
ENGINEERING DATA - HOT WATER CAPACITIES, CALCULATIONS AND CORRECTION FACTORS Use the following two tables to determine The performances reflected in these tables are based on 1. Heating Capacity (MBH)
Regulating valves REG 6-65, REG-SS 15-40
 MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Technical brochure Regulating valves REG 6-65, REG-SS 15-40 REG are angle-way and straight-way regulating valves, which act as normal stop valves in closed position. The valves
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE Technical brochure Regulating valves REG 6-65, REG-SS 15-40 REG are angle-way and straight-way regulating valves, which act as normal stop valves in closed position. The valves
Sanitary Sewer Extensions, Lift Stations, and Force Mains Engineering Report Form. I. General Information. 1. Name of Facility:
 Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality Water Quality Division Phone: 405-702-8100 Construction Permitting Section 707 N. Robinson, OKC, OK 73102-6010 P.O. Box 1677, OKC, OK 73101-1677 Sanitary Sewer
Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality Water Quality Division Phone: 405-702-8100 Construction Permitting Section 707 N. Robinson, OKC, OK 73102-6010 P.O. Box 1677, OKC, OK 73101-1677 Sanitary Sewer
Technical Information
 General Applications Process Applications Determining Heat Energy Lost The objective of any heating application is to raise or maintain the temperature of a solid, liquid or gas to or at a level suitable
General Applications Process Applications Determining Heat Energy Lost The objective of any heating application is to raise or maintain the temperature of a solid, liquid or gas to or at a level suitable
Large University Central Chiller Plant Design Considerations
 Carrier Engineering Newsletter Volume 5, Issue 3 Large University Central Chiller Plant Design Considerations Large campus chilled water plants have unique constraints and need careful evaluation for successful
Carrier Engineering Newsletter Volume 5, Issue 3 Large University Central Chiller Plant Design Considerations Large campus chilled water plants have unique constraints and need careful evaluation for successful
6. PUMPS AND PUMPING SYSTEM
 6. PUMPS AND PUMPING SYSTEM Syllabus Pumps and Pumping System: Types, Performance evaluation, Efficient system operation, Flow control strategies and energy conservation opportunities 6.1 Pump Types Pumps
6. PUMPS AND PUMPING SYSTEM Syllabus Pumps and Pumping System: Types, Performance evaluation, Efficient system operation, Flow control strategies and energy conservation opportunities 6.1 Pump Types Pumps
ORIFICE MTERE BASIC SELECTION & DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS. All rights reserved to thepetrostreet.com
 ORIFICE MTERE BASIC SELECTION & DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS All rights reserved to thepetrostreet.com METER SELECTION PHILOSOPHY Reliability/ Repeatability Rangeability Versatility Economicsi Installation Cost
ORIFICE MTERE BASIC SELECTION & DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS All rights reserved to thepetrostreet.com METER SELECTION PHILOSOPHY Reliability/ Repeatability Rangeability Versatility Economicsi Installation Cost
Section 5 - Planning Criteria. Section 5
 Section 5 - Planning Criteria Section 5 SECTION 5 PLANNING CRITERIA This section presents the design criteria and methodologies for analysis used to evaluate the existing distribution system and its facilities
Section 5 - Planning Criteria Section 5 SECTION 5 PLANNING CRITERIA This section presents the design criteria and methodologies for analysis used to evaluate the existing distribution system and its facilities
Section 7 Hydraulic Model Development and Evaluation Criteria
 Section 7 Hydraulic Model Development and Evaluation Criteria The hydraulic evaluation conducted to develop this master plan was performed using a computer model of the reclaimed water distribution system.
Section 7 Hydraulic Model Development and Evaluation Criteria The hydraulic evaluation conducted to develop this master plan was performed using a computer model of the reclaimed water distribution system.
Problems at the Cumene Production Facility, Unit 800
 Problems at the Cumene Production Facility, Unit 800 Background Cumene (isopropyl benzene) is produced by reacting propylene with benzene. During World War II, cumene was used as an octane enhancer for
Problems at the Cumene Production Facility, Unit 800 Background Cumene (isopropyl benzene) is produced by reacting propylene with benzene. During World War II, cumene was used as an octane enhancer for
VIKING BOLTED-LID BASKET-TYPE LINE STRAINERS
 Page 642.1 LOW PRESSURE DROP EASY TO CLEAN LIGHT IN WEIGHT SMALL IN OVERALL DIMENSION VIKING QUALITY DUCTILE CONSTRUCTION Series Description Viking Bolted-Lid Simplex Strainers provide protection for your
Page 642.1 LOW PRESSURE DROP EASY TO CLEAN LIGHT IN WEIGHT SMALL IN OVERALL DIMENSION VIKING QUALITY DUCTILE CONSTRUCTION Series Description Viking Bolted-Lid Simplex Strainers provide protection for your
MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008
 MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008 www.lightmypump.com A friend of mine asked me to help size a micro-hydro installation that he was thinking of installing at his cottage.
MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008 www.lightmypump.com A friend of mine asked me to help size a micro-hydro installation that he was thinking of installing at his cottage.
TENSION. Measuring Water Flow in Surface. (a) s h. (b) Irrigation Ditches and Gated Pipe. Units of Measuring Water. Edward C.
 E AZ1329 ARIZONA COOPERATIVE TENSION College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Revised 12/11 Measuring Water Flow in Surface Irrigation Ditches and Gated Pipe Edward C. Martin Arizona Water Series No.31
E AZ1329 ARIZONA COOPERATIVE TENSION College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Revised 12/11 Measuring Water Flow in Surface Irrigation Ditches and Gated Pipe Edward C. Martin Arizona Water Series No.31
Reclaimed Water Treatment, Distribution, Pumping and Storage Engineering Report Form
 Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality Water Quality Division Phone: 405-702-8100 Construction Permitting Section 707 N. Robinson, OKC, OK 73102-6010 P.O. Box 1677, OKC, OK 73101-1677 Reclaimed Water
Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality Water Quality Division Phone: 405-702-8100 Construction Permitting Section 707 N. Robinson, OKC, OK 73102-6010 P.O. Box 1677, OKC, OK 73101-1677 Reclaimed Water
SGM Engineering, Inc.
 SGM Engineering, Inc. 1. What is a typical Central Energy Plant consists of? BAS controls, chillers, pumps, cooling towers, electrical distribution, piping, chemicals, heating systems, and generators.
SGM Engineering, Inc. 1. What is a typical Central Energy Plant consists of? BAS controls, chillers, pumps, cooling towers, electrical distribution, piping, chemicals, heating systems, and generators.
Wastewater Flow Monitoring Services
 Wastewater Flow Monitoring Services For San Gabriel, CA July 13, 2015 through July 21, 2015 Revised October 9, 2015 Leaders in Sewer Flow Monitoring Services 601 N. Parkcenter Dr., Suite 209 Santa Ana,
Wastewater Flow Monitoring Services For San Gabriel, CA July 13, 2015 through July 21, 2015 Revised October 9, 2015 Leaders in Sewer Flow Monitoring Services 601 N. Parkcenter Dr., Suite 209 Santa Ana,
Nodal Analysis Approach in Minimizing Pressure Losses to Improve Well Productivity
 Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 6(5): 353-359 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2015 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.com Journal of Emerging
Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 6(5): 353-359 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2015 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.com Journal of Emerging
GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC MUZAFFARPUR LAB MANUAL OF FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY LAB SUBJECT CODE
 GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC MUZAFFARPUR LAB MANUAL OF FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY LAB SUBJECT CODE - 1625407 Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur Name of the Lab: Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Lab Subject Code:
GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC MUZAFFARPUR LAB MANUAL OF FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY LAB SUBJECT CODE - 1625407 Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur Name of the Lab: Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Lab Subject Code:
2015 DW Module 1: General Overview VOLUME III Answer Key
 2015 DW Module 1: General Overview VOLUME III Answer Key Unit 1 Unit 1 Exercise 1) Coliform bacteria make good indicator organisms because: a) They are always present when pathogens are present. b) The
2015 DW Module 1: General Overview VOLUME III Answer Key Unit 1 Unit 1 Exercise 1) Coliform bacteria make good indicator organisms because: a) They are always present when pathogens are present. b) The
Clean energy saving: applied research into Etna s water supply systems in Catania, Italy
 Energy and Sustainability 35 Clean energy saving: applied research into Etna s water supply systems in Catania, Italy F. Patania, A. Gagliano, F. Nocera & I. Pellegrino Energy and Environment Division
Energy and Sustainability 35 Clean energy saving: applied research into Etna s water supply systems in Catania, Italy F. Patania, A. Gagliano, F. Nocera & I. Pellegrino Energy and Environment Division
North Domingo Baca Extension at Barstow
 Modeling Report April 5, 2001 North Domingo Baca Extension at Barstow Prepared for the Albuquerque Metropolitan Arroyo Flood Control Authority Julie Coonrod, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Civil Engineering
Modeling Report April 5, 2001 North Domingo Baca Extension at Barstow Prepared for the Albuquerque Metropolitan Arroyo Flood Control Authority Julie Coonrod, Ph.D., P.E. Department of Civil Engineering
SECTION PACKAGE BOOSTER PUMP STATIONS
 SECTION 331223 PACKAGE BOOSTER PUMP STATIONS Scope: The Contractor shall install a pump station at two locations to be determined by the Owner. These pump stations shall be designed to deliver flow to
SECTION 331223 PACKAGE BOOSTER PUMP STATIONS Scope: The Contractor shall install a pump station at two locations to be determined by the Owner. These pump stations shall be designed to deliver flow to
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2. Ch 11 Young
 Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2 Ch 11 Young Pump and Turbine Dimensional Analysis (11.5 Young) Say we want to replace turbines on the Hoover Dam Want to have a good design Essentially impossible
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2 Ch 11 Young Pump and Turbine Dimensional Analysis (11.5 Young) Say we want to replace turbines on the Hoover Dam Want to have a good design Essentially impossible
Wastewater Capital Projects Management Standard Construction Specification
 CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER ENGINEERING DIVISION Wastewater Capital Projects Management Standard Construction Specification 7.4 PERMEATION GROUTING 7.4.1 Definitions 7.4.1.1 Geotechnical Data Report (GDR)
CITY AND COUNTY OF DENVER ENGINEERING DIVISION Wastewater Capital Projects Management Standard Construction Specification 7.4 PERMEATION GROUTING 7.4.1 Definitions 7.4.1.1 Geotechnical Data Report (GDR)
Design and Development of Pico-hydro Generation System for Energy Storage Using Consuming Water Distributed to Houses
 Design and Development of Pico-hydro Generation System for Energy Storage Using Consuming Water Distributed to Houses H. Zainuddin, M. S. Yahaya, J. M. Lazi, M. F. M. Basar and Z. Ibrahim Abstract This
Design and Development of Pico-hydro Generation System for Energy Storage Using Consuming Water Distributed to Houses H. Zainuddin, M. S. Yahaya, J. M. Lazi, M. F. M. Basar and Z. Ibrahim Abstract This
TYPES OF SEWAGE PUMPS. Solids Handling Pumps: Grinder Pumps: Effluent Pumps:
 Effluent Pumps: Effluent pumps are the pumps most often used in small on-site systems. They are designed to pump effluent, the effluent flowing out of a septic tank. This effluent is relatively clear liquid
Effluent Pumps: Effluent pumps are the pumps most often used in small on-site systems. They are designed to pump effluent, the effluent flowing out of a septic tank. This effluent is relatively clear liquid
Section V WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES
 Section V WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES A. GENERAL 1. The following water system design guidelines are based on Federal, State and local health requirements and the Hilton Head No. 1 Public
Section V WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES A. GENERAL 1. The following water system design guidelines are based on Federal, State and local health requirements and the Hilton Head No. 1 Public
Volume method Volume being used Time required to fill. Weir Method Width of slot in weir Height of water above slot
 Micro Hydro Survey Basic Considerations Understanding how much power you need will make designing your micro hydro project much easier. Start by filling out the Energy Budget spreadsheet to determine your
Micro Hydro Survey Basic Considerations Understanding how much power you need will make designing your micro hydro project much easier. Start by filling out the Energy Budget spreadsheet to determine your
Steam balance optimisation strategies
 Steam balance optimisation strategies Publicado en Chemical Engineering, Noviembre 2002 Background Optimising a steam balance in a plant with several steam mains pressures is not always a simple intuitive
Steam balance optimisation strategies Publicado en Chemical Engineering, Noviembre 2002 Background Optimising a steam balance in a plant with several steam mains pressures is not always a simple intuitive
In-line Twin Pump. Type Series Booklet. Omega DSL
 In-line Twin Pump Type Series Booklet Legal information/copyright Type Series Booklet All rights reserved. The contents provided herein must neither be distributed, copied, reproduced, edited or processed
In-line Twin Pump Type Series Booklet Legal information/copyright Type Series Booklet All rights reserved. The contents provided herein must neither be distributed, copied, reproduced, edited or processed
ENGINEERING INFORMATION Hot water and steam service
 ENGINEERING INFORMTION Hot water and steam service What is steam? Like other substances, water can exist in the form of a solid, when we call it ice; as a liquid when we call it water or as a gas when
ENGINEERING INFORMTION Hot water and steam service What is steam? Like other substances, water can exist in the form of a solid, when we call it ice; as a liquid when we call it water or as a gas when
Chlorinated Organics Closed Loop Unloading of Solvent Tank Trailers
 Chlorinated Organics Closed Loop Unloading of Solvent Tank Trailers Closed loop unloading systems are designed to minimize solvent vapor emissions during transfer by exchanging the liquid solvent in the
Chlorinated Organics Closed Loop Unloading of Solvent Tank Trailers Closed loop unloading systems are designed to minimize solvent vapor emissions during transfer by exchanging the liquid solvent in the
PARTS & ACCESSORIES: EATON DUPLEX BASKET STRAINERS FEATURES OPTIONS MODEL 53BTX DUPLEX (3/4 TO 4 ) MODEL 50 DUPLEX (5, 6, 8 )
 PARTS & ACCESSORIES: MODEL BTX & 0 Section 64 Page 64. Issue E FEATURES MODEL BTX DUPLEX (/4 TO 4 ) Dynamic sealing design for long life Easy-to-operate lever handle no gear box required Unique seat and
PARTS & ACCESSORIES: MODEL BTX & 0 Section 64 Page 64. Issue E FEATURES MODEL BTX DUPLEX (/4 TO 4 ) Dynamic sealing design for long life Easy-to-operate lever handle no gear box required Unique seat and
SECTION 4 - DESIGN STANDARDS FOR WATER DISTRIBUTION FACILITIES
 SECTION 4 - DESIGN STANDARDS FOR WATER DISTRIBUTION FACILITIES 4.1 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS 4.1.1 Water and fire protection distribution facilities are to be provided solely for the purpose of supplying potable
SECTION 4 - DESIGN STANDARDS FOR WATER DISTRIBUTION FACILITIES 4.1 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS 4.1.1 Water and fire protection distribution facilities are to be provided solely for the purpose of supplying potable
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING THERMAL AND FLUID SYSTEMS STUDY PROBLEMS
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING THERMAL AND FLUID SYSTEMS STUDY PROBLEMS PRINCIPLES: THERMODYNAMICS & ENERGY BALANCES 1 Copyright 2018. All rights reserved. How to use this book The exam specifications in effect
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING THERMAL AND FLUID SYSTEMS STUDY PROBLEMS PRINCIPLES: THERMODYNAMICS & ENERGY BALANCES 1 Copyright 2018. All rights reserved. How to use this book The exam specifications in effect
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks. Ch 11 Young
 Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks Ch 11 Young Chapter Topics Types of pumps and turbines Moment of momentum review Pump and turbine theory Energy and power Pump selection Pump-pipe networks Use of pipe
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks Ch 11 Young Chapter Topics Types of pumps and turbines Moment of momentum review Pump and turbine theory Energy and power Pump selection Pump-pipe networks Use of pipe
3.0 DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SANITARY SEWER FACILITIES
 3.0 DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SANITARY SEWER FACILITIES All sanitary sewers shall be designed in accordance with these Design Standards, LBWD Rules and Regulations, and to accepted engineering principles. In
3.0 DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SANITARY SEWER FACILITIES All sanitary sewers shall be designed in accordance with these Design Standards, LBWD Rules and Regulations, and to accepted engineering principles. In
B. System Design and Performance Requirements
 15625 Water Chillers This document provides design standards only, and is not intended for use, in whole or in part, as a specification. Do not copy this information verbatim in specifications or in notes
15625 Water Chillers This document provides design standards only, and is not intended for use, in whole or in part, as a specification. Do not copy this information verbatim in specifications or in notes
SEWER SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES
 SEWER SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES A. The following sewer system design guidelines are based on Federal, State and Local health requirements, and the Berkeley County Water
SEWER SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDELINES PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES A. The following sewer system design guidelines are based on Federal, State and Local health requirements, and the Berkeley County Water
YARWAY HANCOCK CONTINUOUS BLOWDOWN GLOBE VALVE SERIES 5505
 Advanced construction features of this high pressure drop angle globe valve provide quality and long service life. FEATURES GENERAL APPLICATION In addition to continuous blowdown service, the Yarway high
Advanced construction features of this high pressure drop angle globe valve provide quality and long service life. FEATURES GENERAL APPLICATION In addition to continuous blowdown service, the Yarway high
Pump selection: a real example
 28 Feature WORLD PUMPS March 2010 Centrifugal pumps Pump selection: a real example Choosing the most appropriate and cost-effective centrifugal pump for a given duty requires strict adherence to a thorough
28 Feature WORLD PUMPS March 2010 Centrifugal pumps Pump selection: a real example Choosing the most appropriate and cost-effective centrifugal pump for a given duty requires strict adherence to a thorough
Lesson 2 Science Concepts. Chemical Characteristics of Water. The Operator as a Chemist
 Lesson 2 Science Concepts This one hour lesson will help you understand the chemical and biological characteristics of water as well as hydraulics related to water. Chemical Characteristics of Water Chemical
Lesson 2 Science Concepts This one hour lesson will help you understand the chemical and biological characteristics of water as well as hydraulics related to water. Chemical Characteristics of Water Chemical
2011 Standard for Performance Rating Of Water-Chilling and Heat Pump Water-Heating Packages Using the Vapor Compression Cycle
 ANSI/AHRI Standard 550/590 (I-P) with Addendum 3 2011 Standard for Performance Rating Of Water-Chilling and Heat Pump Water-Heating Packages Using the Vapor Compression Cycle Approved by ANSI on June 18,
ANSI/AHRI Standard 550/590 (I-P) with Addendum 3 2011 Standard for Performance Rating Of Water-Chilling and Heat Pump Water-Heating Packages Using the Vapor Compression Cycle Approved by ANSI on June 18,
Booster Pump Fundamentals. By: Bill Baglot
 Booster Pump Fundamentals By: Bill Baglot March 22, 2010 1 Booster Pumps Presentation Topics What are Booster Pumps and when do we need them Accurately sizing boosters and drawdown tanks Maximizing Energy
Booster Pump Fundamentals By: Bill Baglot March 22, 2010 1 Booster Pumps Presentation Topics What are Booster Pumps and when do we need them Accurately sizing boosters and drawdown tanks Maximizing Energy
The Impact Wear Behavior of Large Rocks on Slurry Pump Materials and Equipment.
 The Impact Wear Behavior of Large Rocks on Slurry Pump Materials and Equipment. Robert J. Visintainer V.P. of Engineering and R&D GIW Industries Inc. Dan Wolfe Sr. Associate Mechanical Syncrude Canada
The Impact Wear Behavior of Large Rocks on Slurry Pump Materials and Equipment. Robert J. Visintainer V.P. of Engineering and R&D GIW Industries Inc. Dan Wolfe Sr. Associate Mechanical Syncrude Canada
Variable Speed Waste Water Pumping
 Variable Speed Waste Water Pumping Challenges & Opportunities Kristel Zaman Marketing & Business Development Manager Flygt Large Systems Xylem North America Background VFDs have become common during the
Variable Speed Waste Water Pumping Challenges & Opportunities Kristel Zaman Marketing & Business Development Manager Flygt Large Systems Xylem North America Background VFDs have become common during the
Hancor, Inc. Drainage Handbook Hydraulics 3-1
 Hancor, Inc. Drainage Handbook Hydraulics 3-1 3-0 HYDRAULICS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3-1 Overview of Hydraulic Considerations...3-2 3-2 Design Manning s Value...3-2 3-3 Discharge Curves...3-4 3-3 The Conveyance
Hancor, Inc. Drainage Handbook Hydraulics 3-1 3-0 HYDRAULICS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3-1 Overview of Hydraulic Considerations...3-2 3-2 Design Manning s Value...3-2 3-3 Discharge Curves...3-4 3-3 The Conveyance
Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models
 Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models Jerry L. Modisette, PhD, Consultant Jason P. Modisette, PhD, Energy Solutions International This paper is copyrighted to the Pipeline Simulation
Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models Jerry L. Modisette, PhD, Consultant Jason P. Modisette, PhD, Energy Solutions International This paper is copyrighted to the Pipeline Simulation
Lesson. Using Hydraulic Systems
 Lesson Using Hydraulic Systems Interest Approach n Have you ever used a floor jack or driven an automobile equipped with power brakes or power steering? Student Learning Objectives n Define hydraulics
Lesson Using Hydraulic Systems Interest Approach n Have you ever used a floor jack or driven an automobile equipped with power brakes or power steering? Student Learning Objectives n Define hydraulics
Field Evaluations of Irrigation Systems: Solid Set or Portable Sprinkler Systems 1
 Bulletin 266 Field Evaluations of Irrigation Systems: Solid Set or Portable Sprinkler Systems 1 A.G. Smajstrla, B.J. Boman, G.A. Clark, D.Z. Haman, D.J. Pitts and F.S. Zazueta 2 Introduction This bulletin
Bulletin 266 Field Evaluations of Irrigation Systems: Solid Set or Portable Sprinkler Systems 1 A.G. Smajstrla, B.J. Boman, G.A. Clark, D.Z. Haman, D.J. Pitts and F.S. Zazueta 2 Introduction This bulletin
Contact the Jurisdictional Engineer for materials allowed by each jurisdiction.
 Design Manual Chapter 3 - Sanitary Sewers 3C - Facility Design 3C-1 Facility Design A. Capacity of Pipe Pipe sizes 15 inches and smaller should carry the peak flow at a depth of no more than 0.67 of the
Design Manual Chapter 3 - Sanitary Sewers 3C - Facility Design 3C-1 Facility Design A. Capacity of Pipe Pipe sizes 15 inches and smaller should carry the peak flow at a depth of no more than 0.67 of the
SECTION GRAVEL PACKED WATER WELL
 SECTION 02520 GRAVEL PACKED WATER WELL PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. Gravel packed water well includes drilling, installing, cleaning, developing, testing, videoing, abandoning, and site clean
SECTION 02520 GRAVEL PACKED WATER WELL PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. Gravel packed water well includes drilling, installing, cleaning, developing, testing, videoing, abandoning, and site clean
Transportation of High Concentration Coal Ash Slurries through Pipelines
 International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology, Vol 1 [1] JUNE 1: 1-9 Society of Education, India ISSN 976-488 http:// www.soeagra.com ORGINAL ARTICLE Transportation of High Concentration Coal
International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology, Vol 1 [1] JUNE 1: 1-9 Society of Education, India ISSN 976-488 http:// www.soeagra.com ORGINAL ARTICLE Transportation of High Concentration Coal
Series A-C Single Stage Double Suction Large Split Case. TECHNICAL Brochure BAC9100
 Series A-C 9100 Single Stage Double Suction Large Split Case TECHNICAL Brochure BAC9100 TABLE OF CONTENTS Useful Pump Formulas 2 Pump Engineering Data 3 Materials of Construction 4 Exploded View 6 USEFUL
Series A-C 9100 Single Stage Double Suction Large Split Case TECHNICAL Brochure BAC9100 TABLE OF CONTENTS Useful Pump Formulas 2 Pump Engineering Data 3 Materials of Construction 4 Exploded View 6 USEFUL
Landon Carroll R. Weston Hudkins
 Advanced Pipeline Design Landon Carroll R. Weston Hudkins Table of Contents ABSTRACT...6 Introduction...7 Natural Gas Hydraulics...9 Mathematical Model General Hydraulic Equation...12 Economic Analysis...14
Advanced Pipeline Design Landon Carroll R. Weston Hudkins Table of Contents ABSTRACT...6 Introduction...7 Natural Gas Hydraulics...9 Mathematical Model General Hydraulic Equation...12 Economic Analysis...14
Enviro Voraxial Technology
 1.0 Introduction Enviro Voraxial Technology 821 NW 57 th Place, Fort Lauderdale, FL 33309 Phone 954.958.9968 Fax: 954.958.8057 sales@evtn.com www.evtn.com Case Study Voraxial 4000 Separator On Offshore
1.0 Introduction Enviro Voraxial Technology 821 NW 57 th Place, Fort Lauderdale, FL 33309 Phone 954.958.9968 Fax: 954.958.8057 sales@evtn.com www.evtn.com Case Study Voraxial 4000 Separator On Offshore
Flow Meters Demonstration Unit FMDU
 Engineering and Technical Teaching Equipment Flow Meters Demonstration Unit FMDU PROCESS DIAGRAM AND UNIT ELEMENTS ALLOCATION ISO 9001: Quality Management (for Design, Manufacturing, Commercialization
Engineering and Technical Teaching Equipment Flow Meters Demonstration Unit FMDU PROCESS DIAGRAM AND UNIT ELEMENTS ALLOCATION ISO 9001: Quality Management (for Design, Manufacturing, Commercialization
UNIFORM DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS FOR EXTENDING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS SECTION 2 DESIGN STANDARDS
 UNIFORM DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS FOR EXTENDING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS SECTION 2 DESIGN STANDARDS DESIGN STANDARDS SECTION 2 INDEX ITEM DESCRIPTION 2.00 GENERAL STATEMENT 2.01 WATER DISTRIBUTION
UNIFORM DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS FOR EXTENDING WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS SECTION 2 DESIGN STANDARDS DESIGN STANDARDS SECTION 2 INDEX ITEM DESCRIPTION 2.00 GENERAL STATEMENT 2.01 WATER DISTRIBUTION
A Multi-Faceted Approach to Odor Control for a 28.5-Mile Long Force Main
 A Multi-Faceted Approach to Odor Control for a 28.5-Mile Long Force Main Kristen L. Smeby*, David S. Ehrhardt, Brian F. Duane Hazen and Sawyer, P.C. *Email: ksmeby@hazenandsawyer.com ABSTRACT Upon startup
A Multi-Faceted Approach to Odor Control for a 28.5-Mile Long Force Main Kristen L. Smeby*, David S. Ehrhardt, Brian F. Duane Hazen and Sawyer, P.C. *Email: ksmeby@hazenandsawyer.com ABSTRACT Upon startup
Facilities Plan. Technical Memorandum No. TM-WW-7 Hydraulic Analysis and Effluent Pump Station
 City of St. Joseph, Missouri Hydraulic Analysis and Effluent Pump Station By Work Order No. 09-001 B&V Project 163509 May 20, 2010 Table of Contents 1.0 Executive Summary...1 2.0 Purpose of Study...2 3.0
City of St. Joseph, Missouri Hydraulic Analysis and Effluent Pump Station By Work Order No. 09-001 B&V Project 163509 May 20, 2010 Table of Contents 1.0 Executive Summary...1 2.0 Purpose of Study...2 3.0
