Laboratory Soil Classification
|
|
|
- Alyson Hoover
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Laboratory Soil Classification Lin Li, Ph.D. Center for Environmentally Sustainable Transportation in Cold Climates University of Alaska Fairbanks June 6 th, Summer Transportation Institute, Fairbanks, AK
2 Outline Introduction Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) Sieve analysis and Hydrometer test Atterberg limits Examples 2
3 Introduction Coarse < mm < Fine 3
4 Engineering Characterization of Soils Soil Properties that Control its Engineering Behavior Coarse-grained Particle/Grain Size Distribution Particle Shape Fine-grained Soil Plasticity 4
5 Coarse Aggregate Application 5
6 Fine-Grained Soil Application 6
7 Problems Frost heave Non-uniform settlement Sand liquefaction 7
8 Purpose Classifying soils into groups with similar behavior Communicate between engineers Simple indices GSD, LL, PI Classification system (Language) Estimate engineering properties Achieve engineering purposes Use the accumulated experience 8
9 Classification Systems Two commonly used systems: Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) System 9
10 Unified Soil Classification System Origin of USCS: Developed by Professor A. Casagrande (1948) Modified by Professor Casagrande, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Four major divisions: Coarse-grained Fine-grained Organic soils Peat 10
11 Organic Soils Highly organic soils- Peat (Group symbol PT) Composed primarily of vegetable tissue in various stages of decomposition, Has a fibrous to amorphous texture, a dark-brown to black color, and an organic odor. Organic clay or silt ( group symbol OL or OH): Liquid limit (LL) after oven drying is less than 75 % of its liquid limit before oven drying. 11
12 General Guidance 50 % Coarse-grained soils: Fine-grained soils: Gravel Sand Silt Clay 50% NO mm NO mm Grain size distribution Required tests: Sieve analysis Atterberg limits PL, LL Plasticity chart LL>50 LL <50 12
13 Symbols Soil symbols: G: Gravel S: Sand M: Silt C: Clay O: Organic Pt: Peat Liquid limit symbols: H: High LL (LL>50) L: Low LL (LL<50) Gradation symbols: W: Well-graded P: Poorly-graded Examples: SW, Well-graded sand SC, Clayey sand SM, Silty sand 13
14 Particle Size Analysis Sieve analysis used for particle sizes larger than mm in diameter (larger than the No. 200 sieve), ASTM C136 Hydrometer analysis used for particle sizes smaller than mm in diameter (passing the No. 200 sieve), ASTM D422 14
15 Sieve Analysis Step 1: a) Clean each sieve to remove any left over soil. (use fine brush for the sieve with smaller mesh, don t destroy the mesh) b) Determine the masses of each sieve and the pan. 15
16 Sieve Analysis Assemble the sieves in order with the sieve with the largest size opening on top and the pan underneath. Place the soil sample into the top sieve
17 Sieve Analysis Place the stack of sieves on the shaker and secure them with the screws. Set the shaker s intensity level on 4 or 5 and the timer on 5 minutes. 17
18 Sieve Analysis Remove the sieves from the shaker. Tap each sieve over a sheet of paper to make sure all of the appropriate particles have passed through. Put any material that falls through into the next sieve. 18
19 Sieve Analysis Sieve # Diameter (mm) Mass of soil retained on each sieve (g) % of soil retained on each sieve % passing (% finer) Pan Total weight of soil =
20 Example Calculations For sieve #4: 93g % R i = 100 = 4.84% g % P = = 95.16% i 20
21 Gradation Chart 21
22 Connecting two Methods 22
23 Hydrometer Analysis Based on the principle of spherical particle sedimentation in water. In order to perform this test, a small amount of soil is mixed into a suspension and the change in specific gravity due to the settling of the suspension is observed over time. 23
24 Hydrometer Analysis Using an g of soil, determine the water content. (Microwave Oven Method) Obtain the equivalent of 50 g of dry soil from the material passing the #200 sieve. 24
25 Hydrometer Analysis Mix the soil into a thick slurry using 125 ml of the distilled water-dispersing agent solution. (The deep blue one) Mix the slurry in the stirring apparatus for 60 seconds. 25
26 Hydrometer Analysis Transfer to the sedimentation cylinder and fill with distilled water up to the 1000 ml mark. Cover the cylinder using a rubber glove and mix it by turning the cylinder upside down and back for 1 minute. 26
27 Hydrometer Analysis Place the cylinder down Insert the hydrometer, Take readings at 4, 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120 seconds. 27
28 Connecting two Methods 28
29 Atterberg Limits The physical and mechanical behavior of soils can be correlated to the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit. These form the boundaries between four states: Solid Semisolid Plastic Liquid 29
30 Liquid Limit The moisture content (%) at which a length of 13 mm along the bottom of the groove of the liquid limit device cup closes when receiving 25 blows. 30
31 Liquid Limit Use portion of sample passing #40 (425mm) sieve. Mix soil sample with water thoroughly with a spatula. Using the spatula, spread the soil sample evenly over the bottom 2/3 of the cup. Make a groove through the soil sample. Crank the cam (2 blow/sec) until you see the groove in the sample close a distance along the groove of 13mm. 31
32 Liquid Limit 34 blows, 39% 23 blows, 47% 19 blows, 52% Liquid Limit 32
33 Plastic Limit Plastic Limit - Moisture content at which the soil crumbles when rolled into threads of 1/8 in diameter (3.175 mm). Select about 1.5 to 2.0 g. Roll over the plate to slowly and evenly dry the soil. Roll until the soil crumbles at 1/8 in. Collect at least 6 grams of soil, obtain a water content. This water content is the plastic limit, PL. 33
34 Plasticity Index Plasticity Index (PI) - The difference between the Plastic Limit and the Liquid Limit is called the Plasticity Index. PI = LL - PL PI (%) Description 0 Non plastic 1-5 Slightly plastic 5-10 Low plasticity Medium plasticity High plasticity >40 Very high plasticity 34
35 Plasticity Chart 35
36 Example 36
Classification of Soils
 Classification of Soils Soils - What are they? Particulate materials - Sedimentary origins (usually) - Residual Wide range of particle sizes - larger particles: quartz, feldspar - very small particles:
Classification of Soils Soils - What are they? Particulate materials - Sedimentary origins (usually) - Residual Wide range of particle sizes - larger particles: quartz, feldspar - very small particles:
SOIL CLASSIFICATION BASICS Commonly based on grain size and soil consistency. Several classification systems exist:
 SOIL CLASSIFICATION BASICS Commonly based on grain size and soil consistency. Several classification systems exist: 1. Unified System (USCS) (ASTM D2487-11). 2. American Association of State Highway and
SOIL CLASSIFICATION BASICS Commonly based on grain size and soil consistency. Several classification systems exist: 1. Unified System (USCS) (ASTM D2487-11). 2. American Association of State Highway and
SOIL MECHANICS Assignment #2: Soil Classification Solution.
 Geotechnical Engineering Research Laboratory One University Avenue Lowell, Massachusetts 01854 Edward L. Hajduk, D.Eng, PE Lecturer PA105D Tel: (978) 934 2621 Fax: (978) 934 3052 e mail: Edward_Hajduk@uml.edu
Geotechnical Engineering Research Laboratory One University Avenue Lowell, Massachusetts 01854 Edward L. Hajduk, D.Eng, PE Lecturer PA105D Tel: (978) 934 2621 Fax: (978) 934 3052 e mail: Edward_Hajduk@uml.edu
Laboratory 2 Hydrometer Analysis Atterberg Limits Sand Equivalent Test
 Laboratory 2 Hydrometer Analysis Atterberg Limits Sand Equivalent Test INTRODUCTION Grain size analysis is widely used for the classification of soils and for specifications of soil for airfields, roads,
Laboratory 2 Hydrometer Analysis Atterberg Limits Sand Equivalent Test INTRODUCTION Grain size analysis is widely used for the classification of soils and for specifications of soil for airfields, roads,
CEEN Geotechnical Engineering
 CEEN 3160 - Geotechnical Engineering Lab Report 1 Soil Classification prepared by Student Name 1 Student Name 2 Student Name 3 Student Name 4 Tuesday Lab Time 9:30 10:45 Lab Team 1 Submission Date INTRODUCTION
CEEN 3160 - Geotechnical Engineering Lab Report 1 Soil Classification prepared by Student Name 1 Student Name 2 Student Name 3 Student Name 4 Tuesday Lab Time 9:30 10:45 Lab Team 1 Submission Date INTRODUCTION
Standard Test Procedures Manual
 STP 205-10 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the quantitative determination of the distribution of particle sizes in soils. The distribution
STP 205-10 Standard Test Procedures Manual Section: 1. SCOPE 1.1. Description of Test This method describes the quantitative determination of the distribution of particle sizes in soils. The distribution
Engineering Properties of Soils
 2 Engineering Properties of Soils 2 1 SOIL TYPES Soils may be classified into three very broad categories: cohesionless, cohesive, and organic soils. In the case of cohesionless soils, the soil particles
2 Engineering Properties of Soils 2 1 SOIL TYPES Soils may be classified into three very broad categories: cohesionless, cohesive, and organic soils. In the case of cohesionless soils, the soil particles
ENGINEERING CLASSIFICATION OF SOILS
 ENGINEERING CLASSIFICATION OF SOILS An engineer often considers a soil as any cemented or weakly cemented accumulation of mineral or rock particles formed by the weathering of rocks. The void space separating
ENGINEERING CLASSIFICATION OF SOILS An engineer often considers a soil as any cemented or weakly cemented accumulation of mineral or rock particles formed by the weathering of rocks. The void space separating
Typical Subsurface Profile. November 28, 2016
 November 28, 2016 RSCCD Facility Planning, District Construction and Support Services 2323 N. Broadway, Suite 112, Santa Ana, CA 92706 Attn: Re: Ms. Allison Coburn Facilities Project Manager P: (714) 480-7530
November 28, 2016 RSCCD Facility Planning, District Construction and Support Services 2323 N. Broadway, Suite 112, Santa Ana, CA 92706 Attn: Re: Ms. Allison Coburn Facilities Project Manager P: (714) 480-7530
HCMTCB SOILS CERTIFICATION KEY ELEMENTS LIST
 HCMTCB SOILS CERTIFICATION KEY ELEMENTS LIST Release Date: September 15, 2008 AASHTO T 87 Dry Preparation of Disturbed Soil and Soil Aggregate Samples for Test Apparatus KEY ELEMENTS 1. Any suitable drying
HCMTCB SOILS CERTIFICATION KEY ELEMENTS LIST Release Date: September 15, 2008 AASHTO T 87 Dry Preparation of Disturbed Soil and Soil Aggregate Samples for Test Apparatus KEY ELEMENTS 1. Any suitable drying
Geotechnical Engineering Report
 Geotechnical Engineering Report Pavement Subgrade Survey State Highway 125 over Hudson Creek Ottawa County, Oklahoma September 23, 21 Terracon Project No. 415121 Prepared for: Guy Engineering Services,
Geotechnical Engineering Report Pavement Subgrade Survey State Highway 125 over Hudson Creek Ottawa County, Oklahoma September 23, 21 Terracon Project No. 415121 Prepared for: Guy Engineering Services,
GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION I-15 SIGN BRIDGES LAS VEGAS EA JANUARY
 GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION I-15 SIGN BRIDGES LAS VEGAS EA 73171 JANUARY 06 MATERIALS DIVISION STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MATERIALS DIVISION GEOTECHNICAL SECTION GEOTECHNICAL REPORT I-15
GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION I-15 SIGN BRIDGES LAS VEGAS EA 73171 JANUARY 06 MATERIALS DIVISION STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MATERIALS DIVISION GEOTECHNICAL SECTION GEOTECHNICAL REPORT I-15
You also requested information regarding a sieve analysis at each boring locations. The test results are attached.
 FORENSICS CONSULTANTS ENVIRONMENTAL GEOTECHNICAL MATERIALS October 4, 2016 Washington County Public Works 11660 Myeron Road Stillwater, MN 55082 Attn: Mr. Marc Briese Re: Additional Borings CSAH 22 (70
FORENSICS CONSULTANTS ENVIRONMENTAL GEOTECHNICAL MATERIALS October 4, 2016 Washington County Public Works 11660 Myeron Road Stillwater, MN 55082 Attn: Mr. Marc Briese Re: Additional Borings CSAH 22 (70
METHOD A2 THE DETERMINATION OF THE LIQUID LIMIT OF SOILS BY MEANS OF THE FLOW CURVE METHOD
 METHOD A2 1 SCOPE THE DETERMINATION OF THE LIQUID LIMIT OF SOILS BY MEANS OF THE FLOW CURVE METHOD Definition The liquid limit of a soil as defined below is determined by using the device specified to
METHOD A2 1 SCOPE THE DETERMINATION OF THE LIQUID LIMIT OF SOILS BY MEANS OF THE FLOW CURVE METHOD Definition The liquid limit of a soil as defined below is determined by using the device specified to
 FIGURES Printed By: aday Print Date: 3/23/2011 12:48:08 PM File Name: \\geodesign.local\files\jobs\m-r\penskeauto\penskeauto-1\penskeauto-1-01\figures\cad\penskeauto-1-01-vm01.dwg Layout: FIGURE 1 VICINITY
FIGURES Printed By: aday Print Date: 3/23/2011 12:48:08 PM File Name: \\geodesign.local\files\jobs\m-r\penskeauto\penskeauto-1\penskeauto-1-01\figures\cad\penskeauto-1-01-vm01.dwg Layout: FIGURE 1 VICINITY
LABORATORY TESTING SECTION. Method of Test for CALIBRATION OF MECHANICAL SIEVE SHAKER
 Commonwealth of Pennsylvania PA Test Method No. 608 Department of Transportation 7 Pages 1. SCOPE LABORATORY TESTING SECTION Method of Test for CALIBRATION OF MECHANICAL SIEVE SHAKER 1.1 This method of
Commonwealth of Pennsylvania PA Test Method No. 608 Department of Transportation 7 Pages 1. SCOPE LABORATORY TESTING SECTION Method of Test for CALIBRATION OF MECHANICAL SIEVE SHAKER 1.1 This method of
Effect of hydrometer type on particle size distribution of fine grained soil
 Effect of hydrometer type on particle size distribution of fine grained soil A. Kaur* & G.C. Fanourakis University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa ABSTRACT: The particle size distribution of
Effect of hydrometer type on particle size distribution of fine grained soil A. Kaur* & G.C. Fanourakis University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa ABSTRACT: The particle size distribution of
PD - 6 THRUST RESTRAINT DESIGN EQUATIONS AND SOIL PARAMETERS FOR DUCTILE IRON AND PVC PIPE
 PD - 6 THRUST RESTRAINT DESIGN EQUATIONS AND SOIL PARAMETERS FOR DUCTILE IRON AND PVC PIPE 4 3 2 1 D D C C B B A A 4 3 2 1 Thrust Restraint Design Equations and Soil Parameters These equations and soil
PD - 6 THRUST RESTRAINT DESIGN EQUATIONS AND SOIL PARAMETERS FOR DUCTILE IRON AND PVC PIPE 4 3 2 1 D D C C B B A A 4 3 2 1 Thrust Restraint Design Equations and Soil Parameters These equations and soil
Site Location. Figure 1: Site Location Map US-24 and I-275 Interchange Ash Township, Monroe County, Michigan
 Site Location 0606 1771 North Dixie Highway Monroe, Michigan 48162 Tel: 734-289-2200 Fax: 734-289-2345 www.manniksmithgroup.com Figure 1: Site Location Map US-24 and I-275 Interchange Ash Township, Monroe
Site Location 0606 1771 North Dixie Highway Monroe, Michigan 48162 Tel: 734-289-2200 Fax: 734-289-2345 www.manniksmithgroup.com Figure 1: Site Location Map US-24 and I-275 Interchange Ash Township, Monroe
GEOTECHNICAL REPORT B-1942
 GEOTECHNICAL REPORT TUSCARORA BRIDGE REPLACEMENT B-1942 E.A. 73561 March 2011 MATERIALS DIVISION STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MATERIALS DIVISION GEOTECHNICAL SECTION GEOTECHNICAL REPORT
GEOTECHNICAL REPORT TUSCARORA BRIDGE REPLACEMENT B-1942 E.A. 73561 March 2011 MATERIALS DIVISION STATE OF NEVADA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION MATERIALS DIVISION GEOTECHNICAL SECTION GEOTECHNICAL REPORT
Soil Mechanics Laboratory Manual
 2014 Soil Mechanics Laboratory Manual Prepared by: Dr. Arabinda Sharma Civil Engineering Department BRCM College of Engg. & Tech. Bahal-127 028, Bhiwani Haryana LIST OF EXPERIMENTS Sr. No. Name of the
2014 Soil Mechanics Laboratory Manual Prepared by: Dr. Arabinda Sharma Civil Engineering Department BRCM College of Engg. & Tech. Bahal-127 028, Bhiwani Haryana LIST OF EXPERIMENTS Sr. No. Name of the
Soil Investigation Report November, 2014
 Soil Investigation Report November, 2014 Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh. Email: jidpusinfo@jidpus.buet.ac.bd, Phone: +8802-9662975, Fax: +8802-9662975
Soil Investigation Report November, 2014 Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh. Email: jidpusinfo@jidpus.buet.ac.bd, Phone: +8802-9662975, Fax: +8802-9662975
USCS Site Soil Classification For OWDP Project
 B&B ENGINEERING INC. Northern Arizona University USCS Site Soil Classification For OWDP Project September 23, 2013 Prepared By: Patrick Belsheim TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Purpose...1 2 Methodology...1 2.1 Method
B&B ENGINEERING INC. Northern Arizona University USCS Site Soil Classification For OWDP Project September 23, 2013 Prepared By: Patrick Belsheim TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Purpose...1 2 Methodology...1 2.1 Method
SOIL PHASE RELATIONSHIPS, INDEX PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION
 CHAPTER 3 SOIL PHASE RELATIONSHIPS, INDEX PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION 3.1 SOIL PHASE RELATIONSHIPS Soil mass is generally a three phase system. It consists of solid particles, liquid and gas. For all
CHAPTER 3 SOIL PHASE RELATIONSHIPS, INDEX PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION 3.1 SOIL PHASE RELATIONSHIPS Soil mass is generally a three phase system. It consists of solid particles, liquid and gas. For all
APPENDIX D ANSWERS TO STUDY QUESTIONS/PROBLEMS
 APPENDIX D ANSWERS TO STUDY QUESTIONS/PROBLEMS Chapter 2 Quality Assurance Program Questions 1. What determines the lot size for a specified material accepted under the Statistical QA Program? B. The discretion
APPENDIX D ANSWERS TO STUDY QUESTIONS/PROBLEMS Chapter 2 Quality Assurance Program Questions 1. What determines the lot size for a specified material accepted under the Statistical QA Program? B. The discretion
SECTION AGGREGATES
 SECTION 32 05 00 AGGREGATES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Aggregate base 2. Engineered fill 3. Backfill 4. Fine filter aggregate (non-frost susceptible fill) 5. Riprap 6. Recreational
SECTION 32 05 00 AGGREGATES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Aggregate base 2. Engineered fill 3. Backfill 4. Fine filter aggregate (non-frost susceptible fill) 5. Riprap 6. Recreational
THE INFLUENCE OF FINES CONTENT AND PLASTICITY ON THE STRENGTH AND PERMEABILITY OF AGGREGATE FOR BASE COURSE MATERIAL
 THE INFLUENCE OF FINES CONTENT AND PLASTICITY ON THE STRENGTH AND PERMEABILITY OF AGGREGATE FOR BASE COURSE MATERIAL Bambang Ismanto SISWOSOEBROTHO Department of Civil Engineering Bandung Institute of
THE INFLUENCE OF FINES CONTENT AND PLASTICITY ON THE STRENGTH AND PERMEABILITY OF AGGREGATE FOR BASE COURSE MATERIAL Bambang Ismanto SISWOSOEBROTHO Department of Civil Engineering Bandung Institute of
SWELL AND SWELLING POTENTAL PRESSURE TESTS
 SWELL AND SWELLING POTENTAL PRESSURE TESTS When geotechnical engineers refer to expansive soils, we usually are thinking about clays, and the volume changes that occur as a result of changes in moisture
SWELL AND SWELLING POTENTAL PRESSURE TESTS When geotechnical engineers refer to expansive soils, we usually are thinking about clays, and the volume changes that occur as a result of changes in moisture
This page intentionally left blank
 This page intentionally left blank NOTATION Letters A = cross-sectional area c = effective cohesion C c = compression index C r = recompression index c v = coefficient of vertical consolidation D = particle
This page intentionally left blank NOTATION Letters A = cross-sectional area c = effective cohesion C c = compression index C r = recompression index c v = coefficient of vertical consolidation D = particle
7. The diagram below represents cross sections of equal-size beakers A, B, and C filled with beads.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The diagram represents four tubes, labeled A, B, C, and D, each containing 150 ml of sediments. Tubes
EFFECT OF CEMENT CONTENT ON UNCONFINED COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF JAMSHORO SOIL
 International Symposium on Sustainable Geosynthetics and Green Technology for Climate Change (SGCC) 2 to 21 June 212 Bangkok, Thailand EFFECT OF CEMENT CONTENT ON UNCONFINED COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF JAMSHORO
International Symposium on Sustainable Geosynthetics and Green Technology for Climate Change (SGCC) 2 to 21 June 212 Bangkok, Thailand EFFECT OF CEMENT CONTENT ON UNCONFINED COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF JAMSHORO
Geotechnical Engineering Report
 Geotechnical Engineering Report Turner Turnpike Widening Milepost 210 to 218 Drainage Structure Pipe Jacking Creek County, Oklahoma July 1, 2016 Terracon Project No. 04165017 Prepared for: Benham Tulsa,
Geotechnical Engineering Report Turner Turnpike Widening Milepost 210 to 218 Drainage Structure Pipe Jacking Creek County, Oklahoma July 1, 2016 Terracon Project No. 04165017 Prepared for: Benham Tulsa,
Geotechnical Engineering Report
 Geotechnical Engineering Report Shaw AFB East Gate Entrance Control Facility Amendment Sumter, South Carolina September 13, 2010 Terracon Project No. 73105020A Prepared for: TranSystems North Charleston,
Geotechnical Engineering Report Shaw AFB East Gate Entrance Control Facility Amendment Sumter, South Carolina September 13, 2010 Terracon Project No. 73105020A Prepared for: TranSystems North Charleston,
Tex-121-E, Soil-Lime Testing
 Overview Effective dates: August 1999 - July 2002. This method consists of two parts. 'Part I, Compressive Strength Test Methods (Laboratory Mixed)' determines the unconfined compressive strength as an
Overview Effective dates: August 1999 - July 2002. This method consists of two parts. 'Part I, Compressive Strength Test Methods (Laboratory Mixed)' determines the unconfined compressive strength as an
NLA Test & Measurement 2011 Workshops Roodevallei conference & meeting Hotel 19 th 20 th September 2011
 NLA Test & Measurement 2011 Workshops Roodevallei conference & meeting Hotel 19 th 20 th September 2011 Currents test methods on SABS website Summary of changes for granular methods Grading revisions General
NLA Test & Measurement 2011 Workshops Roodevallei conference & meeting Hotel 19 th 20 th September 2011 Currents test methods on SABS website Summary of changes for granular methods Grading revisions General
Section 25 Aggregate Subbase
 Black text from standard FAA spec Strikeout text deletions from FAA standard spec Blue text additions to FAA standard spec Red text notes to the Engineer/won t appear in spec I. DESCRIPTION A. GRANULAR
Black text from standard FAA spec Strikeout text deletions from FAA standard spec Blue text additions to FAA standard spec Red text notes to the Engineer/won t appear in spec I. DESCRIPTION A. GRANULAR
Subsurface Environmental Investigation
 Subsurface Environmental Investigation Lake Development East Lake and 21 st Avenue South February 23, 201 Terracon Project No. MP14738A Prepared for: Minneapolis Public Schools Prepared by: Terracon Consultants,
Subsurface Environmental Investigation Lake Development East Lake and 21 st Avenue South February 23, 201 Terracon Project No. MP14738A Prepared for: Minneapolis Public Schools Prepared by: Terracon Consultants,
cttp Soils Course Overview Testing Technician Atterberg Limits LL, PL, PI
 cttp Center for Training Transportation Professionals Soils Testing Technician Course Overview Terminology Soil Classification Sampling Soil Preparation Moisture Content Oven Speedy Moisture Tester Atterberg
cttp Center for Training Transportation Professionals Soils Testing Technician Course Overview Terminology Soil Classification Sampling Soil Preparation Moisture Content Oven Speedy Moisture Tester Atterberg
Apparent Coefficient of Friction, f* to be Used in the Design of Reinforced Earth Structures. Technical Bulletin: MSE - 6
 The Reinforced Earth Company 8614 Westwood Center Drive Suite 1100 Vienna, Virginia 22182-2233 Telephone: (703) 821-1175 Telefax: (703) 821-1815 www.reinforcedearth.com Apparent Coefficient of Friction,
The Reinforced Earth Company 8614 Westwood Center Drive Suite 1100 Vienna, Virginia 22182-2233 Telephone: (703) 821-1175 Telefax: (703) 821-1815 www.reinforcedearth.com Apparent Coefficient of Friction,
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Geotechnical Engineering Lab LAB MANUAL- 10CVL67
 APPROVED BY AICTE NEW DELHI, AFFILIATED TO VTU BELGAUM DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Geotechnical Engineering Lab LAB MANUAL- 10CVL67 2016-2017 Prepared by: Reviewed by: Approved by: Kalyani Dongarkar
APPROVED BY AICTE NEW DELHI, AFFILIATED TO VTU BELGAUM DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Geotechnical Engineering Lab LAB MANUAL- 10CVL67 2016-2017 Prepared by: Reviewed by: Approved by: Kalyani Dongarkar
April 7, Webster Street Sub-Surface Stormwater Storage System Bid No Bid Date: 4/13/17 ADDENDUM NO 1
 PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT David A. Jones, P.E., Director April 7, 2017 Webster Street Sub-Surface Stormwater Storage System Bid No. 2017-022 Bid Date: 4/13/17 ADDENDUM NO 1 Please make the following changes
PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT David A. Jones, P.E., Director April 7, 2017 Webster Street Sub-Surface Stormwater Storage System Bid No. 2017-022 Bid Date: 4/13/17 ADDENDUM NO 1 Please make the following changes
Hydraulic Conductivity of Cement-Treated Soils and Aggregates after Freezing
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2010-12-14 Hydraulic Conductivity of Cement-Treated Soils and Aggregates after Freezing Michael Scott Shea Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2010-12-14 Hydraulic Conductivity of Cement-Treated Soils and Aggregates after Freezing Michael Scott Shea Brigham Young University
Math Matters: Dissecting Hydrometer Calculations
 Math Matters: Dissecting Hydrometer Calculations By Jonathan Sirianni, Senior Laboratory Assessor 2 Posted: April 2013 In the 16th century Galileo and the Tower of Pisa made famous the fact that two objects,
Math Matters: Dissecting Hydrometer Calculations By Jonathan Sirianni, Senior Laboratory Assessor 2 Posted: April 2013 In the 16th century Galileo and the Tower of Pisa made famous the fact that two objects,
1 Testing Equipment. Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert
 1 Testing Equipment Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert Test Equipment Verification Laboratory Set-Up 1 CHAPTER ONE: TESTING EQUIPMENT LABORATORY
1 Testing Equipment Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert Test Equipment Verification Laboratory Set-Up 1 CHAPTER ONE: TESTING EQUIPMENT LABORATORY
2.3. KT-3; Material Passing No. 200 (75µm) Sieve by the Wash Method
 5.9.02 SIEVE ANALYSIS OF AGGREGATES (Kansas Test Method KT-2) 1. SCOPE This method of test covers procedures for the determination of the particle size distribution of aggregates using standard sieves.
5.9.02 SIEVE ANALYSIS OF AGGREGATES (Kansas Test Method KT-2) 1. SCOPE This method of test covers procedures for the determination of the particle size distribution of aggregates using standard sieves.
METHOD OF TEST FOR QUANTITATIVE EXTRACTION OF ASPHALT CEMENT AND ANALYSIS OF EXTRACTED AGGREGATE FROM BITUMINOUS PAVING MIXTURES
 4. APPARATUS 4.1 BALANCES: Of sufficient capacity and sensitivity for miscellaneous weighing, with associated accessories such as balance pans... 4.2 DRYING PANS: Seamless enamel, stainless steel, or aluminum
4. APPARATUS 4.1 BALANCES: Of sufficient capacity and sensitivity for miscellaneous weighing, with associated accessories such as balance pans... 4.2 DRYING PANS: Seamless enamel, stainless steel, or aluminum
Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils 1
 Designation: D 4318 05 Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4318; the number immediately following
Designation: D 4318 05 Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4318; the number immediately following
8 Testing Equipment. Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert
 8 Testing Equipment Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert Test Equipment Verification Laboratory Set-Up CHAPTER EIGHT: TESTING EQUIPMENT Before entering
8 Testing Equipment Laboratory General Sampling Sample Reduction Sieve Analysis Decantation Deleterious and Chert Test Equipment Verification Laboratory Set-Up CHAPTER EIGHT: TESTING EQUIPMENT Before entering
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 3.3. Soil Compaction (Das, Ch. 5)
 CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 3.3 Soil Compaction (Das, Ch. 5) Class Outlines Soil compaction introduction Standard Proctor Compaction Test Effect of Compaction Energy Modified Proctor Compaction
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 3.3 Soil Compaction (Das, Ch. 5) Class Outlines Soil compaction introduction Standard Proctor Compaction Test Effect of Compaction Energy Modified Proctor Compaction
Characterizing Engineering Properties of Foundry Sands
 Characterizing Engineering Properties of Foundry Sands Craig H. Benson, PhD, PE Recycled Materials Resource Center University of Washington chbenson@u.washington.edu www.recycledmaterials.org Recycled
Characterizing Engineering Properties of Foundry Sands Craig H. Benson, PhD, PE Recycled Materials Resource Center University of Washington chbenson@u.washington.edu www.recycledmaterials.org Recycled
Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils 1
 This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically
Liquid limit of soils from equilibrium water content in one-dimensional normal compression
 & Liquid limit of soils from equilibrium water content in one-dimensional normal compression A. Sridharan, PhD, DSc, H. B. Nagaraj, MTech and P. S. Prasad, ME Consistency limits are extensively used in
& Liquid limit of soils from equilibrium water content in one-dimensional normal compression A. Sridharan, PhD, DSc, H. B. Nagaraj, MTech and P. S. Prasad, ME Consistency limits are extensively used in
t ghi yr Cop
 In many situations, soil itself is used as a construction material Highway embankments Railway embankments Earth dams Highway / Airfield pavements Backfilled trenches Landfills When soil is used as foundation
In many situations, soil itself is used as a construction material Highway embankments Railway embankments Earth dams Highway / Airfield pavements Backfilled trenches Landfills When soil is used as foundation
2 ADAPTER MOUNTING & APPLICATION
 2 ADAPTER MOUNTING & APPLICATION TABLE OF CONTENT 2 ADAPTER MOUNTING & APPLICATION 1. 7 MEASURING A 100 ML SOIL SAMPLE WITH KSAT AND ADDITIONAL HYPROP 1.1 9 SATURATING THE SOIL SAMPLE FOR KSAT MEASUREMENTS
2 ADAPTER MOUNTING & APPLICATION TABLE OF CONTENT 2 ADAPTER MOUNTING & APPLICATION 1. 7 MEASURING A 100 ML SOIL SAMPLE WITH KSAT AND ADDITIONAL HYPROP 1.1 9 SATURATING THE SOIL SAMPLE FOR KSAT MEASUREMENTS
PRESENTATION OF "GSA"
 PRESENTATION OF "GSA" We are glad to submit to your attention our NEW PATENTED instrument G S A (Grain Size Analyser) which allows particle size characterisation of soil by sedimentation according to ASTM
PRESENTATION OF "GSA" We are glad to submit to your attention our NEW PATENTED instrument G S A (Grain Size Analyser) which allows particle size characterisation of soil by sedimentation according to ASTM
TRENCH EXCAVATION AND BACKFILL
 SUDAS Standard Specifications Division 3 - Trench and Trenchless Construction Section 300 - Trench Excavation and Backfill TRENCH EXCAVATION AND BACKFILL PART - GENERAL.0 SECTION INCLUDES A. Trench Excavation
SUDAS Standard Specifications Division 3 - Trench and Trenchless Construction Section 300 - Trench Excavation and Backfill TRENCH EXCAVATION AND BACKFILL PART - GENERAL.0 SECTION INCLUDES A. Trench Excavation
Prepared for: HDR Engineering, Inc. 200 West Forsyth Street, Suite 800 Jacksonville, Florida Prepared by:
 REPORT OF GEOTECHNICAL EXPLORATION REHABILITATE WHARF STRUCTURE AT BERTHS 6 AND ½ OF BERTH 5 TALLEYRAND MARINE TERMINAL, JACKSONVILLE, FLORIDA E&A PROJECT NO. 0756-0081 Prepared for: HDR Engineering, Inc.
REPORT OF GEOTECHNICAL EXPLORATION REHABILITATE WHARF STRUCTURE AT BERTHS 6 AND ½ OF BERTH 5 TALLEYRAND MARINE TERMINAL, JACKSONVILLE, FLORIDA E&A PROJECT NO. 0756-0081 Prepared for: HDR Engineering, Inc.
May 1, 2000 LAB MANUAL SPECIFIC GRAVITY & ABSORPTION of COARSE AGGREGATE AASHTO Designation T 85 (Mn/DOT Modified)
 May 1, 2000 LAB MANUAL 1204.0 1204 SPECIFIC GRAVITY & ABSORPTION of COARSE AGGREGATE AASHTO Designation T 85 (Mn/DOT Modified) 1204.1 GENERAL This test method is intended for use in determining the bulk
May 1, 2000 LAB MANUAL 1204.0 1204 SPECIFIC GRAVITY & ABSORPTION of COARSE AGGREGATE AASHTO Designation T 85 (Mn/DOT Modified) 1204.1 GENERAL This test method is intended for use in determining the bulk
TOTAL EVAPORABLE MOISTURE CONTENT OF AGGREGATE BY DRYING FOP FOR AASHTO T 255 (11) Containers, clean, dry and capable of being sealed
 TOTAL EVAPORABLE MOISTURE CONTENT OF AGGREGATE BY DRYING FOP FOR AASHTO T 255 (11) Scope This procedure covers the determination of moisture content of aggregate in accordance with AASHTO T 255. It may
TOTAL EVAPORABLE MOISTURE CONTENT OF AGGREGATE BY DRYING FOP FOR AASHTO T 255 (11) Scope This procedure covers the determination of moisture content of aggregate in accordance with AASHTO T 255. It may
STABILIZATION OF PLASTIC SOIL USING MARBLE DUST, RICE HUSK AND FLY ASH : Review
 STABILIZATION OF PLASTIC SOIL USING MARBLE DUST, RICE HUSK AND FLY ASH : Review Krichphon Singh 1, V.K.Arora 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, NIT Kurukshetra, (India) 2 Department of Civil Engineering,
STABILIZATION OF PLASTIC SOIL USING MARBLE DUST, RICE HUSK AND FLY ASH : Review Krichphon Singh 1, V.K.Arora 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, NIT Kurukshetra, (India) 2 Department of Civil Engineering,
General Stabilization Methods
 Soil Stabilization General Stabilization Methods Mechanical Stabilization Compaction Geosynthetics Embankment Stabilization Chemical Treatment Soil Modification (low doses) Soil Stabilization (high doses)
Soil Stabilization General Stabilization Methods Mechanical Stabilization Compaction Geosynthetics Embankment Stabilization Chemical Treatment Soil Modification (low doses) Soil Stabilization (high doses)
PREDICTION OF COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS FROM ATTERBERG LIMITS FOR FINE-GRAINED SOILS
 ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY ADDIS ABABA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING PREDICTION OF COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS FROM ATTERBERG LIMITS FOR FINE-GRAINED SOILS A thesis submitted to School
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY ADDIS ABABA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING PREDICTION OF COMPACTION CHARACTERISTICS FROM ATTERBERG LIMITS FOR FINE-GRAINED SOILS A thesis submitted to School
FREEZING AND THAWING TESTS OF COMPACTED SOIL-CEMENT MIXTURE
 Test Procedure for FREEZING AND THAWING TESTS OF COMPACTED SOIL-CEMENT TxDOT Designation: Tex-135-E Effective Date: August 1999 1. SCOPE 1.1 This method determines the soil-cement losses, moisture changes,
Test Procedure for FREEZING AND THAWING TESTS OF COMPACTED SOIL-CEMENT TxDOT Designation: Tex-135-E Effective Date: August 1999 1. SCOPE 1.1 This method determines the soil-cement losses, moisture changes,
In preparation for constructing buildings on a property, the builder. Site Preparation CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 3 Site Preparation In preparation for constructing buildings on a property, the builder must consider a number of factors related to code requirements. The buildings must be located according to
CHAPTER 3 Site Preparation In preparation for constructing buildings on a property, the builder must consider a number of factors related to code requirements. The buildings must be located according to
PARKING LOTS 4, 7, AND 8 RECONSTRUCTION REPORT
 PARKING LOTS 4, 7, AND 8 RECONSTRUCTION REPORT Converse Project No. 15-81-177-01 Prepared For: David Evans and Associates, Inc. 17782 17th Street, Suite 200 Tustin, California 92780 Prepared By: 10391
PARKING LOTS 4, 7, AND 8 RECONSTRUCTION REPORT Converse Project No. 15-81-177-01 Prepared For: David Evans and Associates, Inc. 17782 17th Street, Suite 200 Tustin, California 92780 Prepared By: 10391
Chapter 7. Sand Castle Tests 3
 Chapter 7. Sand Castle Tests 3 7.1. Background To prevent continuous erosion through cracks, filter materials must satisfy two conditions. The first is that the gradation of the filter material falls within
Chapter 7. Sand Castle Tests 3 7.1. Background To prevent continuous erosion through cracks, filter materials must satisfy two conditions. The first is that the gradation of the filter material falls within
Proctor Compaction Testing
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Nebraska Department of Transportation Research Reports Nebraska LTAP 5-2008 Proctor Compaction Testing Joshua Connelly Wayne
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Nebraska Department of Transportation Research Reports Nebraska LTAP 5-2008 Proctor Compaction Testing Joshua Connelly Wayne
SECTION 1 STALOK FIBER FOR TURF PARKING / EVENT STAGING AND FIRE LANES
 SECTION 1 Stabilizer Solutions, Inc. 205 S. 28 th St. Phoenix, AZ 85034 800-336-2468 (Fax) 602-225-5902 Website: stabilizersolutions.com E-Mail: info@stabilizersolutions.com STALOK FIBER FOR TURF PARKING
SECTION 1 Stabilizer Solutions, Inc. 205 S. 28 th St. Phoenix, AZ 85034 800-336-2468 (Fax) 602-225-5902 Website: stabilizersolutions.com E-Mail: info@stabilizersolutions.com STALOK FIBER FOR TURF PARKING
Classification procedures for expansive soils
 Classification procedures for expansive soils A. Sridharan, PhD, DSc and K. Prakash, PhD Proc. Instn Civ. Engrs Geotech. Engng, 2000, 143, Oct., 235±240 Paper 12075 & Most of the national codes of practice
Classification procedures for expansive soils A. Sridharan, PhD, DSc and K. Prakash, PhD Proc. Instn Civ. Engrs Geotech. Engng, 2000, 143, Oct., 235±240 Paper 12075 & Most of the national codes of practice
Evaluation of cover soil properties of solid waste dumpsites in Colombo District, Sri Lanka
 J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2015 43 (2):189-194 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v43i2.7946 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of cover soil properties of solid waste dumpsites in Colombo District, Sri
J.Natn.Sci.Foundation Sri Lanka 2015 43 (2):189-194 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v43i2.7946 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of cover soil properties of solid waste dumpsites in Colombo District, Sri
Name Lab Section Date. Sediment Lab
 Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Name Lab Section Date. Investigating Stokes Law Sediment Lab ds = density of solid, g/cm dw = density of water, g/cm g = gravity, 980 cm/second 2 D = particle diameter in centimeters μ = molecular viscosity,
Excavation for Natural Gas Mains and Services
 Excavation for Natural Gas Mains and Services Trench Padding & Backfilling Requirements for Mains General Install mains with a minimum of 36 of cover. Exceptions may be made within state and federal codes
Excavation for Natural Gas Mains and Services Trench Padding & Backfilling Requirements for Mains General Install mains with a minimum of 36 of cover. Exceptions may be made within state and federal codes
Mr. Jody Wall Carolina Stalite P.O. Box 186 Phone: (704)
 March 19, 2015 Mr. Jody Wall Carolina Stalite P.O. Box 186 Phone: (704) 279-8614 Gold Hill, North Carolina 28071 Email: jwall@stalite.com Subject: Interim Report of ASTM C330 Dear Mr. Wall: Testing, Engineering
March 19, 2015 Mr. Jody Wall Carolina Stalite P.O. Box 186 Phone: (704) 279-8614 Gold Hill, North Carolina 28071 Email: jwall@stalite.com Subject: Interim Report of ASTM C330 Dear Mr. Wall: Testing, Engineering
Iowa Thickness Design Guide for Low Volume Roads Using Reclaimed Hydrated Class C Fly Ash Bases
 Bergeson and Barnes 1998 TRANSPORTATION CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS 253 Iowa Thickness Design Guide for Low Volume Roads Using Reclaimed Hydrated Class C Fly Ash Bases KENNETH L. BERGESON AND ANDREW G. BARNES
Bergeson and Barnes 1998 TRANSPORTATION CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS 253 Iowa Thickness Design Guide for Low Volume Roads Using Reclaimed Hydrated Class C Fly Ash Bases KENNETH L. BERGESON AND ANDREW G. BARNES
An Introduction to Soil Stabilization for Pavements
 PDHonline Course C450 (2 PDH) An Introduction to Soil Stabilization for Pavements Instructor: J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A., Fellow ASCE, Fellow AEI 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax,
PDHonline Course C450 (2 PDH) An Introduction to Soil Stabilization for Pavements Instructor: J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.A., Fellow ASCE, Fellow AEI 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax,
UNDERSTANDING UNPAVED ROAD MATERIAL PERFORMANCE INTERPRETATION David Jones, PhD University of California Pavement Research Center
 UNDERSTANDING UNPAVED ROAD MATERIAL PERFORMANCE INTERPRETATION David Jones, PhD University of California Pavement Research Center Unpaved road performance is linked to material properties, road shape and
UNDERSTANDING UNPAVED ROAD MATERIAL PERFORMANCE INTERPRETATION David Jones, PhD University of California Pavement Research Center Unpaved road performance is linked to material properties, road shape and
November 13, IP3406. Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112
 November 13, 2015 103IP3406 Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112 Subject: Infiltration Testing Hopeland Road Valve Site Sunoco Pennsylvania Pipeline
November 13, 2015 103IP3406 Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112 Subject: Infiltration Testing Hopeland Road Valve Site Sunoco Pennsylvania Pipeline
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS ENGINEER EQUIPMENT INSTRUCTION COMPANY MARINE CORPS DETACHMENT 1706E EAST 8 TH STREET FORT LEONARD WOOD, MISSOURI 65473-8963 LESSON PLAN SOILS EEO/EEC-B04 WARRANT OFFICER/CHIEF
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS ENGINEER EQUIPMENT INSTRUCTION COMPANY MARINE CORPS DETACHMENT 1706E EAST 8 TH STREET FORT LEONARD WOOD, MISSOURI 65473-8963 LESSON PLAN SOILS EEO/EEC-B04 WARRANT OFFICER/CHIEF
Laboratory Certification For. National Engineering Services for Rehabilitation of Afghanistan (NESRA)
 Laboratory Certification For National Engineering Services for Rehabilitation of Afghanistan (NESRA) Lab ID: LCP-004 Issue date: Feb 15 th, 2018 Expiry date: Aug 14 th, 2018 This extension letter confirms
Laboratory Certification For National Engineering Services for Rehabilitation of Afghanistan (NESRA) Lab ID: LCP-004 Issue date: Feb 15 th, 2018 Expiry date: Aug 14 th, 2018 This extension letter confirms
CIV E Geotechnical Engineering I Consolidation
 Purpose Determine the magnitude and time rate of settlement for a compressible cohesive soil. Required reading Das 2006 Sections 10.4 to 10.16 (pages 312 to 358). Theory Bringing soil samples into the
Purpose Determine the magnitude and time rate of settlement for a compressible cohesive soil. Required reading Das 2006 Sections 10.4 to 10.16 (pages 312 to 358). Theory Bringing soil samples into the
November 13, IP3406. Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112
 November 13, 2015 103IP3406 Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112 Subject: Infiltration Testing Gates Road Valve Site Sunoco Pennsylvania Pipeline
November 13, 2015 103IP3406 Mr. Uriah Sowell Rooney Engineering 115 Inverness Drive East, Suite 300, Englewood, CO 80112 Subject: Infiltration Testing Gates Road Valve Site Sunoco Pennsylvania Pipeline
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS ENGINEER EQUIPMENT INSTRUCTION COMPANY MARINE CORPS DETACHMENT EAST 8TH ST FORT LEONARD WOOD, MISSOURI 65473
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS ENGINEER EQUIPMENT INSTRUCTION COMPANY MARINE CORPS DETACHMENT 14813 EAST 8TH ST FORT LEONARD WOOD, MISSOURI 65473 LESSON PLAN SOILS LESSON ID EAC-A02 ENGINEER ASSISTANT CHIEFS
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS ENGINEER EQUIPMENT INSTRUCTION COMPANY MARINE CORPS DETACHMENT 14813 EAST 8TH ST FORT LEONARD WOOD, MISSOURI 65473 LESSON PLAN SOILS LESSON ID EAC-A02 ENGINEER ASSISTANT CHIEFS
Copper Odyssey. Chemical Reactions of Copper
 Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
Name Lab Partner(s) Copper Odyssey Chemical Reactions of Copper Date Period Elemental copper metal will be converted into copper (II) ion and then brought through a series of compound conversions until
Metal Finishing Products and Service META-MATE ZINCATE 40 "A CONCENTRATED LIQUID ZINCATE FORMULATION FOR THE PRETREATMENT OF ALUMINUM AND ITS ALLOYS"
 Metal Chem,inc. Metal Finishing Products and Service 29 Freedom Court Greer, SC 29650 864.877.6175 Fax 864.877.6176 DATA SHEET META-MATE ZINCATE 40 "A CONCENTRATED LIQUID ZINCATE FORMULATION FOR THE PRETREATMENT
Metal Chem,inc. Metal Finishing Products and Service 29 Freedom Court Greer, SC 29650 864.877.6175 Fax 864.877.6176 DATA SHEET META-MATE ZINCATE 40 "A CONCENTRATED LIQUID ZINCATE FORMULATION FOR THE PRETREATMENT
Standards for Soil Erosion and Sediment Control in New Jersey May 2012 STANDARD FOR RIPRAP. Conditions Where Practice Applies
 STANDARD FOR RIPRAP Definition A layer of loose rock, aggregate, bagged concrete, gabions, or concrete revetment blocks placed over an erodible soil surface. Purpose The purpose of riprap is to protect
STANDARD FOR RIPRAP Definition A layer of loose rock, aggregate, bagged concrete, gabions, or concrete revetment blocks placed over an erodible soil surface. Purpose The purpose of riprap is to protect
CBR of Soaked Clay Drained by Sandy Layer
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering (CSEE 16) Prague, Czech Republic March 3 31, 216 Paper No. ICGRE 116 DOI: 1.11159/icgre16.116 CBR of Soaked Clay Drained
Proceedings of the World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering (CSEE 16) Prague, Czech Republic March 3 31, 216 Paper No. ICGRE 116 DOI: 1.11159/icgre16.116 CBR of Soaked Clay Drained
Standard Test Methods for Wetting and Drying Compacted Soil-Cement Mixtures 1
 Designation: D 559 96 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 00 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 9428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM Standard Test Methods for
Designation: D 559 96 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 00 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 9428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM Standard Test Methods for
DETERMINATION OF WORKABILITY OF FRESH CONCRETE BY SLUMP TEST
 DETERMINATION OF WORKABILITY OF FRESH CONCRETE BY SLUMP TEST Aim: To determine the workability of concrete by Slump test as per IS : 1199-1959 Mould - in the form of the frustum of a cone having the following
DETERMINATION OF WORKABILITY OF FRESH CONCRETE BY SLUMP TEST Aim: To determine the workability of concrete by Slump test as per IS : 1199-1959 Mould - in the form of the frustum of a cone having the following
The procedures that are currently being used for classification of fly ash are
 CHAPTER 2 PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF FLY ASH 2.1 Introduction The procedures that are currently being used for classification of fly ash are reviewed. Some of the significant properties so as to
CHAPTER 2 PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF FLY ASH 2.1 Introduction The procedures that are currently being used for classification of fly ash are reviewed. Some of the significant properties so as to
distribution from gravel to clay (can be check looking at the aspect
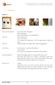 13 Soil analysis BAIDOA 1 Recommendations: From 1cm to fine component. 60 % of aggregate. Soil inert component are well graduated Very cohesive soil Clay is very active. Not enough fine component to fill
13 Soil analysis BAIDOA 1 Recommendations: From 1cm to fine component. 60 % of aggregate. Soil inert component are well graduated Very cohesive soil Clay is very active. Not enough fine component to fill
Under the Guidance of Prof. ASHIK BELLARY Department of Civil Engineering December
 VISVESVARAYA TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY BELGAUM KLS's VISHWANATHRAO DESHPANDE RURAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, HALIYAL. A Project Report On SOIL STABILIZATION USING GEOSYNTHETIC MATERIAL (BAMBOO FIBRES) (A
VISVESVARAYA TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY BELGAUM KLS's VISHWANATHRAO DESHPANDE RURAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, HALIYAL. A Project Report On SOIL STABILIZATION USING GEOSYNTHETIC MATERIAL (BAMBOO FIBRES) (A
Enhance the Performance of Permeability of Fine Sand Using Ceramic Tiles Waste and Plastic Waste as Admixture
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Enhance the Performance of Permeability of Fine Sand Using Ceramic Tiles Waste and Plastic Waste as Admixture Kapil Panwar 1, Ankit Laddha 1, Dr. D.G.M. Purohit 2 1 M.E. Scholar,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Enhance the Performance of Permeability of Fine Sand Using Ceramic Tiles Waste and Plastic Waste as Admixture Kapil Panwar 1, Ankit Laddha 1, Dr. D.G.M. Purohit 2 1 M.E. Scholar,
Porosity of Compost Water retention capacity of Compost Organic matter content of Compost Buffering capacity of Compost
 Porosity of Compost Water retention capacity of Compost Organic matter content of Compost Buffering capacity of Compost by Page 1/21 Contents What is the effect of compost on soil properties?... 3 Introduction:...
Porosity of Compost Water retention capacity of Compost Organic matter content of Compost Buffering capacity of Compost by Page 1/21 Contents What is the effect of compost on soil properties?... 3 Introduction:...
Design of Rigid Pavements
 Traffic and Highway Engineering (ІІ) CVL 4324 Chapter 20 Design of Rigid Pavements Dr. Sari Abusharar Assistant Professor Civil Engineering Department Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning
Traffic and Highway Engineering (ІІ) CVL 4324 Chapter 20 Design of Rigid Pavements Dr. Sari Abusharar Assistant Professor Civil Engineering Department Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning
Soils and Foundations for Architects and Engineers
 Soils and Foundations for Architects and Engineers Soils and Foundations for Architects and Engineers Chester I. Duncan, Jr., FASCE Professor of Architecture The University of Texas at Arlington I RUf?TURA~
Soils and Foundations for Architects and Engineers Soils and Foundations for Architects and Engineers Chester I. Duncan, Jr., FASCE Professor of Architecture The University of Texas at Arlington I RUf?TURA~
Tex-239-F, Asphalt Release Agent
 Contents: Section 1 Overview...2 Section 2 Part I, 7-day Asphalt Stripping Test...3 Section 3 Part II, Mixture Slide Test...5 Section 4 Part III, Asphalt Performance Test...7 Section 5 Part IV, Release
Contents: Section 1 Overview...2 Section 2 Part I, 7-day Asphalt Stripping Test...3 Section 3 Part II, Mixture Slide Test...5 Section 4 Part III, Asphalt Performance Test...7 Section 5 Part IV, Release
RESILIENT MODULUS TESTING OF OPEN GRADED DRAINAGE LAYER AGGREGATES FOR INTERLOCKING CONCRETE BLOCK PAVEMENTS
 RESILIENT MODULUS TESTING OF OPEN GRADED DRAINAGE LAYER AGGREGATES FOR INTERLOCKING CONCRETE BLOCK PAVEMENTS SUMMARY David Hein, P. Eng., Principal Engineer Applied Research Associates, Inc. 541 Eglinton
RESILIENT MODULUS TESTING OF OPEN GRADED DRAINAGE LAYER AGGREGATES FOR INTERLOCKING CONCRETE BLOCK PAVEMENTS SUMMARY David Hein, P. Eng., Principal Engineer Applied Research Associates, Inc. 541 Eglinton
TLT-413 (02) METHOD TO ESTIMATE STANDARD PROCTOR MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF FINE GRAINED SOILS
 METHOD TO ESTIMATE STANDARD PROCTOR MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF FINE GRAINED SOILS 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 This procedure is used for estimating the Standard Proctor maximum dry density and
METHOD TO ESTIMATE STANDARD PROCTOR MAXIMUM DRY DENSITY AND OPTIMUM MOISTURE CONTENT OF FINE GRAINED SOILS 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 This procedure is used for estimating the Standard Proctor maximum dry density and
PE Exam Review - Geotechnical
 PE Exam Review - Geotechnical Resources and Visual Aids Item Page I. Glossary... 11 II. Parameters... 9 III. Equations....11 IV. Tables, Charts & Diagrams... 14 1. Module 1 - Soil Classification... 14
PE Exam Review - Geotechnical Resources and Visual Aids Item Page I. Glossary... 11 II. Parameters... 9 III. Equations....11 IV. Tables, Charts & Diagrams... 14 1. Module 1 - Soil Classification... 14
Recommended Mix Design Guidelines For Cold Recycling Using Foamed (Expanded) Asphalt Recycling Agent CR202
 Recommended Mix Design Guidelines For Cold Recycling Using Foamed (Expanded) Asphalt Recycling Agent CR202 8/25/2017 NOTICE It is not intended or recommended that these guidelines be used verbatim within
Recommended Mix Design Guidelines For Cold Recycling Using Foamed (Expanded) Asphalt Recycling Agent CR202 8/25/2017 NOTICE It is not intended or recommended that these guidelines be used verbatim within
