Using GIS, MODFLOW and MODPATH for groundwater management of an alluvial aquifer of the River Sieg, Germany
|
|
|
- Susanna Lyons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, Using GIS, MODFLOW and MODPATH for groundwater management of an alluvial aquifer of the River Sieg, Germany CHRISTIAN MICHL Geographisches Institut, Friedrich-Schiller-Universitàt Jena, Lôbdergraben 32, D Jena, Germany Abstract During the past years Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have been increasingly applied for geohydrological research studies and water resources assessments. However, the coupling of GIS with geohydrological models is still a subject for future research. To evaluate the benefits of linking a GIS with the groundwater model MODFLOW, the alluvial sediments of the lower Sieg River catchments were selected for a case study. The aquifer is located east of Bonn. It is bounded by the Rheinische Schiefergebirge in the south and the rivers Sieg and Rhine in the north and west. The study area covers about 45 km 2 and groundwater extraction is supporting the water supply of about half a million people. Two-thirds of the groundwater recharge is attributed by stream leakage of the Sieg River and the rest is recharge from infiltrating precipitation. Using MODFLOW, the infiltration parameters of the River Sieg and the hydraulic conductivity were calibrated in a stationary approach. Subsequently, parameters were verified and optimized for a transient model, based on 120 time steps of 1 month. The particle pathlines were calculated using the groundwater particle tracking code MODPATH. MODFLOW simulated the groundwater dynamics in the aquifer with good fit to the observed data for steady-state and transient conditions and grid-based leakage terms could be defined. Future research will focus on the linkage of MODBRANCH and MODFLOW for a better simulation of the river dynamics and the integration of the GIS ARC/INFO. INTRODUCTION In Germany about 90% of the total groundwater production is provided by alluvial aquifers, which receive recharge by infiltration of rainwater and river bank storage. Considering the increasing demand of this water resource in the future as well as the qualitative affects caused by human activities, groundwater protection against pollution from various types of land uses became a paramount issue in water resources management. The use of Geographic Information Systems, combined with application of mathematical models has significantly expanded our ability to understand and manage the water resources (Friedman et al., 1984), both in terms of quantity and quality. Geographic Information Systems such like the PC-based GIS IDRISI (Eastman, 1992) provide a flexible tool for water resources management (Fltigel, 1995; Kovar &
2 552 Christian Michl Nachtnebel, 1993), as data pre- and postprocessing can be automatized to a high degree. Additionally, the raster database of the GIS permits an efficient data transformation between the spatial distribution represented in the GIS and the areal discretization obtained by the groundwater model using finite elements or finite differences. Commonly used finite difference models in groundwater hydrology are based on the mathematical techniques developed by Trescott et al. (1976) or those of Prickett & Lonnquist (1971). Both models have been widely used in the United States, are well documented and are available for IBM-compatible personal computers at nominal cost. Regional applications in Germany, however, are very limited and often not documented. MODFLOW (McDonald & Harbaugh, 1988) is a three-dimensional, modularly structured open system groundwater flow model and is a further development of the Trescott model (Trescott et al., 1976). In this case study the raster GIS IDRISI, the finite element model MODFLOW and the particle tracking code MODPATH (Pollock, 1989) were applied to simulate management strategies for the alluvial aquifer of the lower River Sieg supplying water for half a million people in the area near Bonn, Germany. OBJECTIVES The purpose of the study was a very practical one. The aim was to establish a regional management system which consists of a GIS database and a mathematical model to understand the aquifer system and to develop guidelines for further water withdrawal. Applying a 10-year data set, the GIS IDRISI was linked to the groundwater flow model MODFLOW. This main goal is threefold, containing the following steps: (a) the groundwaterflowmodel MODFLOW was calibrated using the particle tracking program MODPATH for steady-state and transient conditions, (b) the performance of the MODFLOW modules RIV and STR1 (Prudic, 1989) describing the interaction of the aquifer and the River Sieg to delineate areas of different seepage dynamics was analysed on a grid cell basis; and (c) the groundwater model was linked with the raster GIS IDRISI and a database for aquifer management. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The alluvial aquifer of the River Sieg, a tributary of the River Rhine, is located on the northern bound of the Rheinische Schiefergebirge, Germany. It is part of the tectonic subsidence of the Niederrheinische Bucht which started to decline in the Eocene (early period of Tertiary). The Tertiary clay as impervious layer builds the lower non-flow boundary condition underlying the alluvial gravel sediments which were accumulated in the Pleistocene. The clay layer throughout the whole area was interpolated within the GIS, based on over 200 boreholes. The Pleistocene terrace system distinguishes three different terrace levels. They are composed of gravel formations originating from the River Sieg and the River Rhine. Its pétrographie spectrum is a homogeneous composition of white quartzites, sandstones and grey-white clayey shales. The average depth of the Pleistocene deposits is increasing from the lower to the middle terrace from 13 to about 20 m. All of them consist of predominantly coarse gravel, which is well-rounded.
3 Using GIS, MODFLOW and MODPATH for groundwater management of an alluvial aquifer553 Inclusions of sandy layers are found in the two older terraces. Depending on the heterogeneity of the gravel deposits, hydraulic conductivity varies from 2.0 X 10" 2 to 2.0 X 10" 3 m s" 1. The hydraulic conductivity was determined using flownet analysis, pumping tests and granumetric analysis on various points. CONCEPTUAL MODEL FOR MODFLOW The conceptual model for MODFLOW is depicted in Fig. 1. The conceptualization has to be carried out before the numerical simulation. It determines the dimensions of the numerical model and the design of the grid. As shown in Fig. 1, the conceptual model integrates the data and includes (a) the hydrogeological framework, (b) the physical framework, (c) a detailed description of the water budget, (d) the physical and hydraulic boundary conditions, (e) estimates of groundwater sources and sinks, and (f) information about regional flow paths (Anderson & Woessner, 1992). By using GIS techniques, the process of conceptualization and the selection of data can be aided easily to help the modeller to make the best choice. For the lower Sieg basin, the following methodology was applied: (a) the geohydrological data of a 10-year period ( ) including observations of groundwater heads in 200 wells, discharge measurements of the River Sieg and the River Rhine and climatological data, all stored in a project database, (b) a digital elevation model (DEM) having a 50 X 50 m grid size System Input - hydrogeological framework (1) water withdraw (5)» hydrometeorological data (2). vegetation (6)» potentiometric surface (3) - to pogra phy (7)» surface hydrology (4) Conceptual Model >* (1,3) basin boundaries (A) * BAS (A.B) - (3) starting heads (B) -»BCF2 (C) * (1) hydraulic parameters (C) -»GHB (A) * (2,4,6,7) évapotranspiration rates (D) -»STR1 (C,G) "» (2,4,6) recharge rates (E) -»EVT (D) "» (4,5) discrete flux (F) -»RCH (E) * (4,7) channel routing (G) * WEL (F) The numbers and letters indicate the direction of flow. Fig. 1 Conceptual model for development of arrays for MODFLOW.
4 554 Christian Michl resolution was imported into the GIS, together with digitized geology, soil and land use maps, and (c) using overlay analysis maps of the hydraulic conductivity, the transmissivity and groundwater recharge areas were derived. As a result of the conceptualization, the MODFLOW model arrays were constructed within the GIS and PROCESSING MODFLOW (Chiang & Kinzelbach, 1993) and by using a data transfer module converted into MODFLOW for the numerical simulation. A data transfer vice versa was additionally implemented. MODEL RESULTS The finite element groundwater model MODFLOW was calibrated for the alluvial aquifer of the River Sieg by calculating hydraulic heads as well as drawdowns for steady-state and transient conditions. Additionally, the water budget of the aquifer and particle travelling times were calculated using MODPATH. The aquifer of the study area and its discretization is shown in Fig. 2. Its boundary conditions are given by the River Rhine in the west, and the River Sieg in the north (specified boundary flux), and by the barrier between the Tertiary sediments and the gravel deposits in the southeast (specified boundary groundwater head). geological border between tertiary clay and quartary deposits x^-/ rivers Rhine. Sieg and Pleisbach j finite difference grid (grid size 50, and 300 m) production weîls (S141 mentioned in text) UENOEN villages (adding up to 40 % of the landuse of the total study area) Q observation wells (mentioned in text) Fig. 2 Study area of the lower River Sieg, Germany, showing the model grid, the three reference groundwater wells and the boundary conditions.
5 Using GIS, MODFLOW and MODPATH for groundwater management of an alluvial aquifer 555 Steady-state and transient simulation Based on the adopted conceptualization, the steady-state calibration yielded the following results: (a) groundwater recharge consists of 30% recharge from precipitation and 70% of seepage from the River Sieg, (b) inflow along the southeastern boundary is negligible, and (c) flow paths computed by MODPATH indicate travelling periods between 5 month near the production wells and about 10 years at the southeastern boundary of the aquifer. The transient simulation was based on the insight obtained by the steady-state model. Twenty-seven groundwater observation wells and three production wells were selected for the calibration exercise. From the evaluation of measured and simulated variation in hydraulic head (over 120 time steps of 1 month), areas of different infiltration were delineated. Simulated and measured hydraulic heads are shown in Fig. 3. Curve I at the production well S141 reflects the variation of hydraulic head in the River Sieg. The groundwater recharge is strongly influenced by the flow dynamics in the river. At the observation well S161 (curve II), this influence has decreased considerably, and curve III for observation well S204 shows the dynamics of the aquifer recharged only by infiltrating rainfall, indicated by small amplitudes of the head-time curve. All three curves, however, show a very good fit between simulated and measured hydraulic heads described by correlation coefficients of r = 0.91 for curve I, r = 0.89 for curve II and r = 0.80 for curve III. The dynamics of infiltration between the river bed and adjacent aquifer obtained from the steady-state simulation was verified by means of several transient runs _49.E. " <D X 47 i46 i Years measured simulated Fig. 3 Hydraulic head-time curves for three reference wells showing the measured and simulated hydraulic heads: curve I for production well S141, curve II for observation well SI61, and curve III for observation well S204. Stream-aquifer interaction To account for the interaction between the aquifer and the two rivers Rhine and Sieg, the MODFLOW modules RIV and STR1 were used to simulate seepage from the aquifer
6 556 Christian Michl into the rivers and vice versa. The utilized concepts simulating the stream-aquifer interaction are based on a linear function of the hydraulic head and the stream stage. The flow values are calculated using Darcy's law. The input parameters needed for this modelling task were derived from field data from gauging stations in the rivers Sieg and Rhine and the adjacent aquifer. They were optimized by various model runs. For the steady-state simulation, the data were statistically analysed for every grid cell affected by the stream-aquifer interaction. According to the mean average and the variance eight different infiltration classes were distinguished. They are summed up in Table 1 showing the location of the grid cells, the infiltration area, the length of the infiltration channel, the leakage and the average infiltration. Considering the mean annual flow, the river seepage varies from about 901 s" 1 km" 1 near the production wells to 5 1 s" 1 km" 1 in the northern and western parts of the aquifer. Compared to other seepage evaluation in the area, the calculated values show a similar value range. Even at flood events the simulation results are of the same magnitude than former calculations. They range between 7 and s" 1 km 4 for the above mentioned infiltration areas. For the Rhine River, values of over s" 1 km" 1 can be expected during high floods. The advantage of the applied method to former calculations is its distribution over the total infiltration area on a grid basis for all time steps. Table 1 Classes of infiltration areas giving the location of the grid cells, the infiltration area, the length of the channel, the leakage and the average infiltration. The location of the grid cells refers to Fig. 2. The numbers are counted from right to left, beginning at the diversion of Pleisbach and Sieg. The bold columns indicate the average values for the rivers Sieg and Rhine. For the Sieg River, the table shows two averages (for models STRI and RIV). Location of grid cells Infiltration area (km 2 ) Length of infiltration channel (m) Leakage Infiltration (1 s" 1 km"') x 1.1 X 1.1 X 10' 6 io Sieg (RIV) X 2.1 x 1.8 x x 3 Sieg (STRI) Rhine (RIV) x 10' 6 5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH NEEDS The groundwater flow in the aquifer adjacent to the lower Sieg could be successfully simulated for steady-state and transient conditions using the finite difference model MODFLOW and MODPATH. The derivation of the conceptual model was obtained combining the raster-based GIS IDRISI with PROCESSING MODFLOW and
7 Using GIS, MODFLOW and MODPATH for groundwater management of an alluvial aquifer 551 MODFLOW. The GIS based data model permits fast presentation and improved interpretation of the models input and output. In a second step, the MODFLOW modules RIV and STR1 were applied to delineate areas of different river bank seepage and the results were compared to existing data. The applied methodology enabled a fast evaluation of areally distributed grid-based infiltration rates. Furthermore, an analysis over all time steps is feasible. Based on the presented results, the following research needs can be defined: (a) to improve the simulation of the stream-aquifer interaction with regard to backwater conditions, to be done by linking the MODFLOW modules RIV and STR1 with MODBRANCH (Swain, 1994), and (b) to enable the use the GIS techniques for the conceptual model design, to be done by developing more GIS linkages to ARC/INFO. Acknowledgement The authors are pleased to acknowledge the cooperation with Dr Keith Turner, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, USA, the US Geological Survey, Denver, USA (model code) and the Wahnbachtalsperrenverband, Germany for the supply of the model data. REFERENCES Anderson, M. P. &Woessner, W. W. (1992)AppliedGroundwaterModeling: Simulationoj'FlowandAdvective Transport. Academic Press, Inc., New York. Chiang, W. H. & Kinzelbach, W. (1993) ProcessingModflow. Hamburg, Heidelberg. Eastman, J. R. (1992) 1DRISI Version 4.0. User's Guide and Technical Reference. Worcester. Flùgel, W. A. (1995) Delineating hydrological response units by geographical information system analyses for regional hydrological modelling using PRMS/MMS in the drainage basin of the River Brôl. Hydrol. Processes 9, Friedman, R., Ansell, C, Diamond, S. & Haïmes, Y. Y. (1984) The use of models for water resources management, planning and policy. Wat. Resour. Res. 20(7), Kovar, K. & Nachtnebel, H. P. (eds) (1993) Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proc. Int. Conf. HydroGIS'93, Vienna, April 1993). IAHS Publ. no McDonald, M. G. & Harbaugh, A. W. (1988) A modular three-dimensional finite difference groundwater flow model. USGS Techniques of Water Resources Investigations Report, Book 6, chapter Al. Pollock, D. W. (1989) Documentation of computer programs to complete and display pathlines using results from the USGS modular three-dimensional finite difference groundwater model. USGS Open File Report Prickett.T. A. &Lonnquist,C. G. (1971) Selected digital computer techniquesfor groundwater resource evaluation. Illinois State Water Survey 55. Prudic, D. E. (1989) Documentation of a computer program to simulate stream-aquifer-interactionsusing a modular, finite difference groundwater flow model. USGS Open File Report Swain, E. D. (1994) Implementation and use of direct-flow connections in a coupled groundwater and surface-water model. Groundwater32(1), Trescott,P. C., Pinder,G. F. &Larson,S. P. (1976) Finite difference model for aquifer simulations in twodimensions with results of numerical experiments. USGS Techniques of Water Research Investigations no. 7.
Using MODFLOW/MODPATH combined with GIS analysis for groundwater modelling in the alluvial aquifer of the River Sieg, Germany
 Models for Assessing and Monitoring Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium July 1995). IAHSPubl.no. 227, 1995. 117 Using MODFLOW/MODPATH combined with GIS analysis for groundwater modelling
Models for Assessing and Monitoring Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium July 1995). IAHSPubl.no. 227, 1995. 117 Using MODFLOW/MODPATH combined with GIS analysis for groundwater modelling
Purpose. Utilize groundwater modeling software to forecast the pumping drawdown in a regional aquifer for public drinking water supply
 MODFLOW Lab 19: Application of a Groundwater Flow Model to a Water Supply Problem An Introduction to MODFLOW and SURFER The problem posed in this lab was reported in Chapter 19 of "A Manual of Instructional
MODFLOW Lab 19: Application of a Groundwater Flow Model to a Water Supply Problem An Introduction to MODFLOW and SURFER The problem posed in this lab was reported in Chapter 19 of "A Manual of Instructional
Monitoring and modelling catchment water quantity and quality
 INTERNATIONAL HYDROLOGICAL PROGRAMME Monitoring and modelling catchment water quantity and quality 8 th Conference of the European Network of Experimental and Representative Basins (ERB) Ghent (Belgium),
INTERNATIONAL HYDROLOGICAL PROGRAMME Monitoring and modelling catchment water quantity and quality 8 th Conference of the European Network of Experimental and Representative Basins (ERB) Ghent (Belgium),
4.4 MODEL CODE DESCRIPTION 4.5 WATER SOURCES AND SINKS 4.6 MODEL DOMAIN AND BOUNDARIES. SLR South Africa
 Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
Page 4-18 The developed model should therefore be seen as an initial site model which should be refined and recalibrated once more groundwater monitoring and other data become available. 4.4 MODEL CODE
Is it time for us to go to fully integrated models for stream-aquifer management?
 Is it time for us to go to fully integrated models for stream-aquifer management? Tissa H. Illangasekare, PhD, PE, P.Hyd, BCEE,DWRE AMAX Distinguished Chair and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Is it time for us to go to fully integrated models for stream-aquifer management? Tissa H. Illangasekare, PhD, PE, P.Hyd, BCEE,DWRE AMAX Distinguished Chair and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Groundwater Modeling
 Groundwater Modeling 8:00-8:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction (Course Goals) 8:30-9:45 a.m. 1.1 Lecture Occurrence and Movement of Groundwater 9:45-10:00 a.m. Break A. Hydrologic Cycle B. Subsurface Distribution
Groundwater Modeling 8:00-8:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction (Course Goals) 8:30-9:45 a.m. 1.1 Lecture Occurrence and Movement of Groundwater 9:45-10:00 a.m. Break A. Hydrologic Cycle B. Subsurface Distribution
Simulation of horizontal well performance using Visual MODFLOW
 Environ Earth Sci (2013) 68:1119 1126 DOI 10.1007/s12665-012-1813-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Simulation of horizontal well performance using Visual MODFLOW Wan Mohd Zamri W. Ismail Ismail Yusoff Bahaa-eldin E.
Environ Earth Sci (2013) 68:1119 1126 DOI 10.1007/s12665-012-1813-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Simulation of horizontal well performance using Visual MODFLOW Wan Mohd Zamri W. Ismail Ismail Yusoff Bahaa-eldin E.
MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION IN THE AQUIFER OF N. MOUDANIA, GREECE
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Assessment of the Groundwater Quantity Resulting from Artificial Recharge by Ponds at Ban Nong Na, Phitsanulok Province, Thailand
 Research article erd Assessment of the Groundwater Quantity Resulting from Artificial Recharge by Ponds at Ban Nong Na, Phitsanulok Province, Thailand SIRIRAT UPPASIT* Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen
Research article erd Assessment of the Groundwater Quantity Resulting from Artificial Recharge by Ponds at Ban Nong Na, Phitsanulok Province, Thailand SIRIRAT UPPASIT* Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen
CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING
 148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan ABSTRACT
 1 Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan Ali M. Elhassan (1), A. Goto (2), M. Mizutani (2) (1) New Mexico Interstate Stream Commission, P.
1 Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan Ali M. Elhassan (1), A. Goto (2), M. Mizutani (2) (1) New Mexico Interstate Stream Commission, P.
SOLUTE POLLUTANTS TRANSPORT MODELING IN LANDFILL VALEA MANASTIRII, GORJ COUNTY ROMANIA
 SOLUTE POLLUTANTS TRANSPORT MODELING IN LANDFILL VALEA MANASTIRII, GORJ COUNTY ROMANIA 3 Robert BEILICCI, Erika BEILICCI Politehnica University of Timisoara, Department of Hydrotechnical Engineering George
SOLUTE POLLUTANTS TRANSPORT MODELING IN LANDFILL VALEA MANASTIRII, GORJ COUNTY ROMANIA 3 Robert BEILICCI, Erika BEILICCI Politehnica University of Timisoara, Department of Hydrotechnical Engineering George
GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE Judith Schenk'
 July 1-3 GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE 2002 326x6 pjf= INTEGRATION OF DATA USING GIS AND STATEPP TO ESTIMATE GROUNDWATER MODEL INPUT PARAMETERS Judith Schenk'
July 1-3 GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE 2002 326x6 pjf= INTEGRATION OF DATA USING GIS AND STATEPP TO ESTIMATE GROUNDWATER MODEL INPUT PARAMETERS Judith Schenk'
Dynamic groundwater-river interaction model for planning water allocation in a narrow valley aquifer system of the Upper Motueka catchment
 Dynamic groundwater-river interaction model for planning water allocation in a narrow valley aquifer system of the Upper Motueka catchment Timothy Hong t.hong@gns.cri.nz Gilles Minni g.minni@gns.cri.nz
Dynamic groundwater-river interaction model for planning water allocation in a narrow valley aquifer system of the Upper Motueka catchment Timothy Hong t.hong@gns.cri.nz Gilles Minni g.minni@gns.cri.nz
Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in Karst Aquifer, Makeng Mining Area
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences 6 (1): 78-82, 2010 ISSN 1553-345X 2010 Science Publications Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in Karst Aquifer, Makeng Mining Area 1,2 F.M. Rani and 1 Z.H.
American Journal of Environmental Sciences 6 (1): 78-82, 2010 ISSN 1553-345X 2010 Science Publications Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in Karst Aquifer, Makeng Mining Area 1,2 F.M. Rani and 1 Z.H.
 5. MODEL DESCRIPTION Several models were used in combination to estimate the impacts of the proposed 100,000 acre-ft dryyear yield program. MODFLOW and MODPATH were used to estimate the groundwater and
5. MODEL DESCRIPTION Several models were used in combination to estimate the impacts of the proposed 100,000 acre-ft dryyear yield program. MODFLOW and MODPATH were used to estimate the groundwater and
Groundwater Recharge from Wala Dam Reservoir in Jordan
 Groundwater Recharge from Wala Dam Reservoir in Jordan Abbas Z. Ijam Hamed Raja Alnaimat Civil and Environmental Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering, Mutah University, Mutah, Jordan e-mail: abbasa@mutah.edu.jo
Groundwater Recharge from Wala Dam Reservoir in Jordan Abbas Z. Ijam Hamed Raja Alnaimat Civil and Environmental Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering, Mutah University, Mutah, Jordan e-mail: abbasa@mutah.edu.jo
1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER
 1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER 1.1 Introduction The Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes River Basin (HMCRB) under the USGS Modular Modeling System (MMS) uses a
1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER 1.1 Introduction The Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes River Basin (HMCRB) under the USGS Modular Modeling System (MMS) uses a
Saul Montoya Heredia M.Sc. Senior Hidrogeologist Numerical Modeler Gidahatari
 Profile: Mr. Montoya is a Civil Engineer graduated from the Peruvian Catholic University in Lima with postgraduate studies in Management and Engineering of Water Resources (WAREM Program) from Stuttgart
Profile: Mr. Montoya is a Civil Engineer graduated from the Peruvian Catholic University in Lima with postgraduate studies in Management and Engineering of Water Resources (WAREM Program) from Stuttgart
Numerical Estimation of the future sustainable Groundwater Yield in the Kok River Basin, Northern Thailand
 Numerical Estimation of the future sustainable Groundwater Yield in the Kok River Basin, Northern Thailand PHATCHARASAK ARLAI 1, MANFRED KOCH 2 and ARUN LUKJAN 1 1 Research Center of Water Resources and
Numerical Estimation of the future sustainable Groundwater Yield in the Kok River Basin, Northern Thailand PHATCHARASAK ARLAI 1, MANFRED KOCH 2 and ARUN LUKJAN 1 1 Research Center of Water Resources and
The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18. NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York
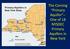 The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18 NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York NYSDEC Primary and Principal Aquifers PRIMARY AQUIFERS (18) Highly productive aquifers presently being utilized by major municipal
The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18 NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York NYSDEC Primary and Principal Aquifers PRIMARY AQUIFERS (18) Highly productive aquifers presently being utilized by major municipal
Manfred KOCH 1 and Phatsaratsak ARLAI 1, Department of Geotechnology and Engineering Hydrology, University of Kassel, Germany
 Deterministic and stochastic modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in the heavily-stressed Bangkok coastal aquifer, Thailand, and investigation of optimal management strategies for possible
Deterministic and stochastic modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in the heavily-stressed Bangkok coastal aquifer, Thailand, and investigation of optimal management strategies for possible
Impact Study of a check dam on Ground Water Recharge
 Impact Study of a check dam on Ground Water Recharge 1 P.Arun Raja, C. Dinesh, B.Jagadeesan 1,, UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Mamallan Institute of Technology, Kanchipuram, INDIA Abstract:
Impact Study of a check dam on Ground Water Recharge 1 P.Arun Raja, C. Dinesh, B.Jagadeesan 1,, UG Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Mamallan Institute of Technology, Kanchipuram, INDIA Abstract:
CHRISTCHURCH CITY GROUNDWATER MODEL
 CHRISTCHURCH CITY GROUNDWATER MODEL Mike Thorley 1, Peter Callander 1, Howard Williams 1, Hilary Lough 1, Mike Kininmonth 2, Bruce Henderson 2 1 Pattle Delamore Partners Ltd Level 2, Radio New Zealand
CHRISTCHURCH CITY GROUNDWATER MODEL Mike Thorley 1, Peter Callander 1, Howard Williams 1, Hilary Lough 1, Mike Kininmonth 2, Bruce Henderson 2 1 Pattle Delamore Partners Ltd Level 2, Radio New Zealand
Questions: What is calibration? Why do we have to calibrate a groundwater model? How would you calibrate your groundwater model?
 Questions: What is calibration? Why do we have to calibrate a groundwater model? How would you calibrate your groundwater model? 13-11-2009 1 Uncertainties in groundwater models Conceptual model uncertainty
Questions: What is calibration? Why do we have to calibrate a groundwater model? How would you calibrate your groundwater model? 13-11-2009 1 Uncertainties in groundwater models Conceptual model uncertainty
GIS-based components for rainfall-runoff models
 HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 477 GIS-based components
HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 477 GIS-based components
GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS 1-3 AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE 2002
 JULY,. I GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS 1-3 AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE 2002 MODELING FLOW AT THE STREAM-AQUIFER INTERFACE A REVIEW OF THIS FEATURE IN TOOLS OF THE TRADE Varda S. Blum', Deborah
JULY,. I GROUND WATER/SURFACE WATER INTERACTIONS 1-3 AWRA SUMMER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE 2002 MODELING FLOW AT THE STREAM-AQUIFER INTERFACE A REVIEW OF THIS FEATURE IN TOOLS OF THE TRADE Varda S. Blum', Deborah
LAKE LABELLE DEWATERING MODEL. AUTHOR Gail Murray Doyle, P.G. September Murray Consultants, Inc 769 Skyview Dr Hayesville, NC
 LAKE LABELLE DEWATERING MODEL AUTHOR Gail Murray Doyle, P.G. September 2013 Murray Consultants, Inc 769 Skyview Dr Hayesville, NC 28904 828-389-2476 LAKE LABELLE DEWATERING MODEL INTRODUCTION Purpose The
LAKE LABELLE DEWATERING MODEL AUTHOR Gail Murray Doyle, P.G. September 2013 Murray Consultants, Inc 769 Skyview Dr Hayesville, NC 28904 828-389-2476 LAKE LABELLE DEWATERING MODEL INTRODUCTION Purpose The
Investigation of sustainable development potential for Ulubey Aquifer System, Turkey
 doi:10.5194/piahs-364-513-2014 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
doi:10.5194/piahs-364-513-2014 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
Module 2 Measurement and Processing of Hydrologic Data
 Module 2 Measurement and Processing of Hydrologic Data 2.1 Introduction 2.1.1 Methods of Collection of Hydrologic Data 2.2 Classification of Hydrologic Data 2.2.1 Time-Oriented Data 2.2.2 Space-Oriented
Module 2 Measurement and Processing of Hydrologic Data 2.1 Introduction 2.1.1 Methods of Collection of Hydrologic Data 2.2 Classification of Hydrologic Data 2.2.1 Time-Oriented Data 2.2.2 Space-Oriented
Memorandum. Introduction. Carl Einberger Joe Morrice. Figures 1 through 7
 Memorandum TO: Michelle Halley, NWF DATE: October 9, 2007 FROM: Carl Einberger Joe Morrice PROJ. NO.: 9885.000 CC: Project File PROJ. NAME: National Wildlife Federation ATTACHMENTS: Tables 1 through 6
Memorandum TO: Michelle Halley, NWF DATE: October 9, 2007 FROM: Carl Einberger Joe Morrice PROJ. NO.: 9885.000 CC: Project File PROJ. NAME: National Wildlife Federation ATTACHMENTS: Tables 1 through 6
Hydrological design of flood reservoirs by utilization of GIS and remote sensing
 Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems for Design and Operation of Water Resources Systems (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S3, April 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 242, 1997 173 Hydrological design of
Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems for Design and Operation of Water Resources Systems (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S3, April 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 242, 1997 173 Hydrological design of
6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic. Jiri Sima
 6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic Jiri Sima General content Regional hydrogeological units Groundwater resources assessment Water balancing background
6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic Jiri Sima General content Regional hydrogeological units Groundwater resources assessment Water balancing background
Groundwater Modeling Guidance
 Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
Coupling of MODFLOW and WATFLOOD in hydrological modelling of a small watershed
 294 Weather Radar Information and Distributed Hydrological Modelling (Proceedings of symposium HS03 held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 282. 2003. Coupling of MODFLOW and WATFLOOD
294 Weather Radar Information and Distributed Hydrological Modelling (Proceedings of symposium HS03 held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 282. 2003. Coupling of MODFLOW and WATFLOOD
B-7. Predictive Assessment Model of Quaternary Alluvium Hydrogeology. J:\scopes\04w018\10000\FVD reports\final EIA\r-EIA app.doc
 B-7 Model of Quaternary Alluvium Hydrogeology J:\scopes\04w018\10000\FVD reports\final EIA\r-EIA app.doc PREDICTIVE ASSESSMENT MODELING OF THE QUATERNARY ALLUVIUM HYDROGEOLOGY EAGLE PROJECT MARQUETTE COUNTY,
B-7 Model of Quaternary Alluvium Hydrogeology J:\scopes\04w018\10000\FVD reports\final EIA\r-EIA app.doc PREDICTIVE ASSESSMENT MODELING OF THE QUATERNARY ALLUVIUM HYDROGEOLOGY EAGLE PROJECT MARQUETTE COUNTY,
Rainwater Harvesting for Enhanced Groundwater Recharge Through Capture of Increased Runoff from Site Development
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2006 Conference Proceedings 7-18-2006 Rainwater Harvesting for Enhanced Groundwater Recharge Through Capture of Increased Runoff from Site Development Mark
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC 2006 Conference Proceedings 7-18-2006 Rainwater Harvesting for Enhanced Groundwater Recharge Through Capture of Increased Runoff from Site Development Mark
ENG. MUSLEM B. KASHOB MINISTRY OF REGIONAL MUNICIPALITY AND WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL MODELING MUSCAT, OMAN
 Put your Organizati on logo here ENG. MUSLEM B. KASHOB MINISTRY OF REGIONAL MUNICIPALITY AND WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL MODELING MUSCAT, OMAN Overview Introduction Objectives Study area
Put your Organizati on logo here ENG. MUSLEM B. KASHOB MINISTRY OF REGIONAL MUNICIPALITY AND WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL MODELING MUSCAT, OMAN Overview Introduction Objectives Study area
3.2.3 Groundwater Simulation. (1) Purpose
 The Study on Water Supply Systems in Mandalay City and in the Central Dry Zone Part II Study for Mandalay City 3.2.3 Groundwater Simulation (1) Purpose Because the Central Dry Zone, Myanmar, including
The Study on Water Supply Systems in Mandalay City and in the Central Dry Zone Part II Study for Mandalay City 3.2.3 Groundwater Simulation (1) Purpose Because the Central Dry Zone, Myanmar, including
Available online at Procedia Engineering 00 (2011) I-SEEC2011
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 00 (2011) 000 000 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia I-SEEC2011 Modeling Investigation of the future permissible Yield
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 00 (2011) 000 000 Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia I-SEEC2011 Modeling Investigation of the future permissible Yield
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area
 Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China
 Conference on Environmental Pollution and Public Health Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China Sun Jinyu Zhang Qiang Xu Mo College of Environment and Civil Engineering, Chengdu
Conference on Environmental Pollution and Public Health Regional Groundwater Flow Modeling of Yarkant Basin in West China Sun Jinyu Zhang Qiang Xu Mo College of Environment and Civil Engineering, Chengdu
GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
 GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE K.C. Scott, P.G., and D. J. Folkes, P.E. EnviroGroup Limited, 7208 South Tucson Way, Suite 125, Englewood, CO 80112; Phone:
GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE K.C. Scott, P.G., and D. J. Folkes, P.E. EnviroGroup Limited, 7208 South Tucson Way, Suite 125, Englewood, CO 80112; Phone:
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGES ON THE HYDROGEOLOGICAL AQUIFERS- CASE STUDY DIBDIBA AQUIFER AT KARBALA NAJAF AREA, IRAQ
 IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGES ON THE HYDROGEOLOGICAL AQUIFERS- CASE STUDY DIBDIBA AQUIFER AT KARBALA NAJAF AREA, IRAQ *Moutaz Al-Dabbas, **Raad Al- Khafaji, ***Mohanad H. A. Al-Jaberi *College of Science,
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGES ON THE HYDROGEOLOGICAL AQUIFERS- CASE STUDY DIBDIBA AQUIFER AT KARBALA NAJAF AREA, IRAQ *Moutaz Al-Dabbas, **Raad Al- Khafaji, ***Mohanad H. A. Al-Jaberi *College of Science,
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in the Navajo Sandstone Aquifer at the Tuba City, Arizona, Disposal Site 15167
 Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in the Navajo Sandstone Aquifer at the Tuba City, Arizona, Disposal Site 15167 ABSTRACT Richard Bush*, Timothy Bartlett** *US DOE, Office of Legacy Management **Stoller
Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow in the Navajo Sandstone Aquifer at the Tuba City, Arizona, Disposal Site 15167 ABSTRACT Richard Bush*, Timothy Bartlett** *US DOE, Office of Legacy Management **Stoller
Hydraulic Head in 1999 Saline plume migration in 1999
 Numerical Modeling of possible Saltwater Intrusion Mechanisms in the Multiple Layer Coastal Aquifer System of the Gulf of Thailand by Mr.Phatcharasak Arlai Contents of Presentation 1. Introduction 2. Literature
Numerical Modeling of possible Saltwater Intrusion Mechanisms in the Multiple Layer Coastal Aquifer System of the Gulf of Thailand by Mr.Phatcharasak Arlai Contents of Presentation 1. Introduction 2. Literature
FAX
 21335 Signal Hill Plaza Suite 100 Sterling, Virginia 20164 www.geotransinc.com 703-444-7000 FAX 703-444-1685 Mr. William Kutash Florida Department of Environmental Protection Waste Management Division
21335 Signal Hill Plaza Suite 100 Sterling, Virginia 20164 www.geotransinc.com 703-444-7000 FAX 703-444-1685 Mr. William Kutash Florida Department of Environmental Protection Waste Management Division
Modelling contamination of a drinking water supply well in the Sabarmati river bed aquifer, Ahmedabad, India
 Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 73 Modelling contamination of a drinking water
Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 73 Modelling contamination of a drinking water
High-Resolution Groundwater Models for the Assessment of Riparian Restoration Options and River Conveyance Efficiency
 High-Resolution Groundwater Models for the Assessment of Riparian Restoration Options and River Conveyance Efficiency Karen L. MacClune 1, Gilbert Barth 1, Nabil Shafike 2, Deborah Hathaway 1 1 S. S. Papadopulos
High-Resolution Groundwater Models for the Assessment of Riparian Restoration Options and River Conveyance Efficiency Karen L. MacClune 1, Gilbert Barth 1, Nabil Shafike 2, Deborah Hathaway 1 1 S. S. Papadopulos
WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002
 WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002 Prepared by: Gosling Czubak Engineering Sciences, Inc. 1280 Business Park Drive Traverse City, Michigan 48686 Telephone:
WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002 Prepared by: Gosling Czubak Engineering Sciences, Inc. 1280 Business Park Drive Traverse City, Michigan 48686 Telephone:
DYNFLOW accepts various types of boundary conditions on the groundwater flow system including:
 Section 6 Groundwater Flow Model A groundwater flow model was developed to evaluate groundwater flow patterns in the site area and to provide a basis for contaminant transport modeling. 6.1 Model Code
Section 6 Groundwater Flow Model A groundwater flow model was developed to evaluate groundwater flow patterns in the site area and to provide a basis for contaminant transport modeling. 6.1 Model Code
MODELING INVESTIGATION ON THE SUSTAINABLE GROUNDWATER YIELD FOR WIANG PA PAO AQUIFERS SYSTEM
 MODELING INVESTIGATION ON THE SUSTAINABLE GROUNDWATER YIELD FOR WIANG PA PAO AQUIFERS SYSTEM Phatcharasak Arlai 1*, Manfred Koch 2, Sitisak Munyu 3, Kriangsak Pirarai 3 and Arun Lukjan 1 1 Research Unit
MODELING INVESTIGATION ON THE SUSTAINABLE GROUNDWATER YIELD FOR WIANG PA PAO AQUIFERS SYSTEM Phatcharasak Arlai 1*, Manfred Koch 2, Sitisak Munyu 3, Kriangsak Pirarai 3 and Arun Lukjan 1 1 Research Unit
Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available?
 Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available? Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Company Assessing Sustainability is All About: Predicting (or describing) how potentiometric
Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available? Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Company Assessing Sustainability is All About: Predicting (or describing) how potentiometric
OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION
 GROUNDWATER?? OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION What is groundwater? Geologic investigation Definitions: aquifer and aquitard, unconfined and semi-confined Water level and interpretation of water level data Well
GROUNDWATER?? OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION What is groundwater? Geologic investigation Definitions: aquifer and aquitard, unconfined and semi-confined Water level and interpretation of water level data Well
Figure 5.7 Histogram of calibrated residuals of the difference in calculated versus observed heads in the White Limestone aquifer of the Rio Cobre
 Figure 5.7 Histogram of calibrated residuals of the difference in calculated versus observed heads in the White Limestone aquifer of the Rio Cobre and Rio Minho-Milk river basins. 141 142 EXPLANATION RIO
Figure 5.7 Histogram of calibrated residuals of the difference in calculated versus observed heads in the White Limestone aquifer of the Rio Cobre and Rio Minho-Milk river basins. 141 142 EXPLANATION RIO
Effects of irrigation on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition To cite this article: DONG Qiguang et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of on groundwater recharge under deep buried depth condition To cite this article: DONG Qiguang et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.:
CHAPTER 4: Risk Assessment Risk in Groundwater Contamination
 CHAPTER 4: Risk Assessment Risk in Groundwater Contamination Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir -١ Introduction: Water pollution is nowadays one of the most crucial environmental problems world-wide. Pollution
CHAPTER 4: Risk Assessment Risk in Groundwater Contamination Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir -١ Introduction: Water pollution is nowadays one of the most crucial environmental problems world-wide. Pollution
Estimating Streambed and Aquifer Parameters from a Stream/Aquifer Analysis Test
 Hydrology Days 2003, 68-79 Estimating Streambed and Aquifer Parameters from a Stream/Aquifer Analysis Test Garey Fox 1 Ph.D. Candidate, Water Resources, Hydrologic, and Environmental Sciences Division,
Hydrology Days 2003, 68-79 Estimating Streambed and Aquifer Parameters from a Stream/Aquifer Analysis Test Garey Fox 1 Ph.D. Candidate, Water Resources, Hydrologic, and Environmental Sciences Division,
Topography and the Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Recharge and Evapotranspiration:
 Topography and the Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Recharge and Evapotranspiration: A Need to Revisit Distributed Water Budget Analysis when Assessing Impacts to Ecological Systems. By M.A. Marchildon,
Topography and the Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Recharge and Evapotranspiration: A Need to Revisit Distributed Water Budget Analysis when Assessing Impacts to Ecological Systems. By M.A. Marchildon,
Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in alluvial aquifer Based on MODFLOW Program, Case Study: Evan plain (Iran)
 International Journal of Agriculture and Crop Sciences. Available online at www.ijagcs.com IJACS/2013/5-11/1164-1170 ISSN 2227-670X 2013 IJACS Journal Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in alluvial aquifer
International Journal of Agriculture and Crop Sciences. Available online at www.ijagcs.com IJACS/2013/5-11/1164-1170 ISSN 2227-670X 2013 IJACS Journal Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in alluvial aquifer
Surface Water Accounting Model, SWAc linking surface flow and recharge processes to groundwater models
 Surface Water Accounting Model, SWAc linking surface flow and recharge processes to groundwater models Alastair Black 1, Marco Lagi 2 1 Groundwater Science Ltd (a.black@gwscience.co.uk) 2 New England Complex
Surface Water Accounting Model, SWAc linking surface flow and recharge processes to groundwater models Alastair Black 1, Marco Lagi 2 1 Groundwater Science Ltd (a.black@gwscience.co.uk) 2 New England Complex
Characterizing Groundwater and Surface- Water Interactions in Selected Northeast Twin Cities Lakes
 Characterizing Groundwater and Surface- Water Interactions in Selected Northeast Twin Cities Lakes Chapter A: Statistical Analysis and Field Study Chapter B: Groundwater-Flow Simulation Perry M. Jones,
Characterizing Groundwater and Surface- Water Interactions in Selected Northeast Twin Cities Lakes Chapter A: Statistical Analysis and Field Study Chapter B: Groundwater-Flow Simulation Perry M. Jones,
J. Wetstein and V. Hasfurther Conference Proceedings WWRC
 RESPONSE OF A SURFACE AQUIFER TO FLOOD IRRIGATION J. Wetstein and V. Hasfurther 1989 Conference Proceedings WWRC- 8 9-32 In Proceedings of the Specialty Conference Sponsored by the Irrigation and Drainage
RESPONSE OF A SURFACE AQUIFER TO FLOOD IRRIGATION J. Wetstein and V. Hasfurther 1989 Conference Proceedings WWRC- 8 9-32 In Proceedings of the Specialty Conference Sponsored by the Irrigation and Drainage
Aquifer Science Staff, January 2007
 Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Supplemental Guide II-Delineations
 Supplemental Guide II-Delineations Contents Source Water Protection Area Delineation... 1 Delineation Criteria for Systems Using Groundwater Sources... 2 Time of Travel... 4 Flow Boundaries... 4 Delineation
Supplemental Guide II-Delineations Contents Source Water Protection Area Delineation... 1 Delineation Criteria for Systems Using Groundwater Sources... 2 Time of Travel... 4 Flow Boundaries... 4 Delineation
7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING
 7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING 7.1 Introduction The concept of passive site remediation is the slow injection of stabilizing materials at the up gradient edge of a site and delivery
7.0 GROUNDWATER AND STABILIZER TRANSPORT MODELING 7.1 Introduction The concept of passive site remediation is the slow injection of stabilizing materials at the up gradient edge of a site and delivery
Ground Water Issues of the South Platte River Basin. Presented by: James L. Jehn, C.P.G. Jehn Water Consultants, Inc.
 Ground Water Issues of the South Platte River Basin Presented by: James L. Jehn, C.P.G. Jehn Water Consultants, Inc. Ground Water Wells South Platte Alluvial Wells Approx. 10,000 Alluvial Wells in the
Ground Water Issues of the South Platte River Basin Presented by: James L. Jehn, C.P.G. Jehn Water Consultants, Inc. Ground Water Wells South Platte Alluvial Wells Approx. 10,000 Alluvial Wells in the
Introduction to Groundwater Environmental Level Setting
 Introduction to Groundwater Environmental Level Setting 1.0 Introduction As part of work towards a Rangitāiki Water Management Area (WMA) plan change process for water quality and quantity, we will consider
Introduction to Groundwater Environmental Level Setting 1.0 Introduction As part of work towards a Rangitāiki Water Management Area (WMA) plan change process for water quality and quantity, we will consider
A simulation of groundwater discharge and nitrate delivery to Chesapeake Bay from the lowermost Delmarva Peninsula, USA
 326 A New Focus on Groundwater Seawater Interactions (Proceedings of Symposium HS11 at IUGG27, Perugia, July 27). IAHS Publ. 312, 27. A simulation of groundwater discharge and nitrate delivery to Chesapeake
326 A New Focus on Groundwater Seawater Interactions (Proceedings of Symposium HS11 at IUGG27, Perugia, July 27). IAHS Publ. 312, 27. A simulation of groundwater discharge and nitrate delivery to Chesapeake
Development and Application of Surface-Water Groundwater Flow Model of the Tuul River Basin near Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
 Development and Application of Surface-Water Groundwater Flow Model of the Tuul River Basin near Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia November 2016 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. REPORT DOCUMENTATION
Development and Application of Surface-Water Groundwater Flow Model of the Tuul River Basin near Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia November 2016 Approved for Public Release. Distribution Unlimited. REPORT DOCUMENTATION
Simulation of Sub-Drains Performance Using Visual MODFLOW for Slope Water Seepage Problem
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Sub-Drains Performance Using Visual MODFLOW for Slope Water Seepage Problem To cite this article: M F T Baharuddin
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Simulation of Sub-Drains Performance Using Visual MODFLOW for Slope Water Seepage Problem To cite this article: M F T Baharuddin
GreenPlan Modeling Tool User Guidance
 GreenPlan Modeling Tool User Guidance Prepared by SAN FRANCISCO ESTUARY INSTITUTE 4911 Central Avenue, Richmond, CA 94804 Phone: 510-746-7334 (SFEI) Fax: 510-746-7300 www.sfei.org Table of Contents 1.
GreenPlan Modeling Tool User Guidance Prepared by SAN FRANCISCO ESTUARY INSTITUTE 4911 Central Avenue, Richmond, CA 94804 Phone: 510-746-7334 (SFEI) Fax: 510-746-7300 www.sfei.org Table of Contents 1.
K.Sangeetha, B.Narasimhan Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Analytic Element Method (AEM) and its Relevance with Subbasin/HRU concept of SWAT for potential integration of AEM based simple ground water model K.Sangeetha, B.Narasimhan Department of Civil Engineering,
Analytic Element Method (AEM) and its Relevance with Subbasin/HRU concept of SWAT for potential integration of AEM based simple ground water model K.Sangeetha, B.Narasimhan Department of Civil Engineering,
Scale Effects in Large Scale Watershed Modeling
 Scale Effects in Large Scale Watershed Modeling Mustafa M. Aral and Orhan Gunduz Multimedia Environmental Simulations Laboratory School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
Scale Effects in Large Scale Watershed Modeling Mustafa M. Aral and Orhan Gunduz Multimedia Environmental Simulations Laboratory School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology
Development of a GIS Tool for Rainfall-Runoff Estimation
 Development of a GIS Tool for Rainfall-Runoff Estimation Ashraf M. Elmoustafa * M. E. Shalaby Ahmed A. Hassan A.H. El-Nahry Irrigation and Hydraulics Department, Ain Shams University, Egypt NARSS, Egypt
Development of a GIS Tool for Rainfall-Runoff Estimation Ashraf M. Elmoustafa * M. E. Shalaby Ahmed A. Hassan A.H. El-Nahry Irrigation and Hydraulics Department, Ain Shams University, Egypt NARSS, Egypt
OPTIMIZED REMEDIAL GROUNDWATER EXTRACTION USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING
 John J. Q U ~ M EAD 9 Argonne, IL 6439 Tel.: 78-252-5357, Fax: 78-252-3611 OPTIMIZED REMEDIAL GROUNDWATER EXTRACTION USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING ABSTRACT Groundwater extraction systems are typically installed
John J. Q U ~ M EAD 9 Argonne, IL 6439 Tel.: 78-252-5357, Fax: 78-252-3611 OPTIMIZED REMEDIAL GROUNDWATER EXTRACTION USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING ABSTRACT Groundwater extraction systems are typically installed
Documentation of Groundwater Agent-based Model
 Documentation of Groundwater Agent-based Model Comments or suggestions to 1. Introduction In environmental resources management there is the recognition of need for combined socio-environmental
Documentation of Groundwater Agent-based Model Comments or suggestions to 1. Introduction In environmental resources management there is the recognition of need for combined socio-environmental
Documentation of Groundwater Model
 Documentation of Groundwater Model Groundwater Model The primary tool used to evaluate potential impacts on groundwater was a groundwater flow and solute transport model developed by San Benito County
Documentation of Groundwater Model Groundwater Model The primary tool used to evaluate potential impacts on groundwater was a groundwater flow and solute transport model developed by San Benito County
Evaluation of groundwater modelling
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 1, No. 6, p. 174-178, 2011 http://www.innspub.net SHORT COMMUNICATION OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 1, No. 6, p. 174-178, 2011 http://www.innspub.net SHORT COMMUNICATION OPEN ACCESS Evaluation of
6.0 USGS MODEL. 6.1 Background
 6.0 USGS MODEL 6.1 Background A groundwater flow model is a simplification of a real groundwater flow system. Real groundwater flow systems are complex, and they are often simplified with a model for the
6.0 USGS MODEL 6.1 Background A groundwater flow model is a simplification of a real groundwater flow system. Real groundwater flow systems are complex, and they are often simplified with a model for the
ESTIMATION OF GROUNDWATER RECHARGE IN NATIONAL CAPITAL TERRITORY, DELHI USING GROUNDWATER MODELING
 Journal of Indian Water Resources Society, Vol 34, No.1, January, 2014 ESTIMATION OF GROUNDWATER RECHARGE IN NATIONAL CAPITAL TERRITORY, DELHI USING GROUNDWATER MODELING Vikrant Vishal 1, Sudhir Kumar
Journal of Indian Water Resources Society, Vol 34, No.1, January, 2014 ESTIMATION OF GROUNDWATER RECHARGE IN NATIONAL CAPITAL TERRITORY, DELHI USING GROUNDWATER MODELING Vikrant Vishal 1, Sudhir Kumar
organized by INDUCED RIVERBANK FILTRATION FOR MANAGED ARTIFICIAL GROUNDWATER RECHARGE AT APAČE FIELD Matevž Vremec, Irena Kopač
 organized by INDUCED RIVERBANK FILTRATION FOR MANAGED ARTIFICIAL GROUNDWATER RECHARGE AT APAČE FIELD Matevž Vremec, Irena Kopač Objectives Shallow aquifer of Apače field Efficiency analysis of a MAR system
organized by INDUCED RIVERBANK FILTRATION FOR MANAGED ARTIFICIAL GROUNDWATER RECHARGE AT APAČE FIELD Matevž Vremec, Irena Kopač Objectives Shallow aquifer of Apače field Efficiency analysis of a MAR system
Using Fractran Fracture Flow Modeling in Tandem with Modflow to Assist in the Development of Wellfield Protection Zones for Municipal Wells in Bedrock
 Using Fractran Fracture Flow Modeling in Tandem with Modflow to Assist in the Development of Wellfield Protection Zones for Municipal Wells in Bedrock T.K. Wiezel 1, G.G. Violette 1 and S.T. Hamilton 2
Using Fractran Fracture Flow Modeling in Tandem with Modflow to Assist in the Development of Wellfield Protection Zones for Municipal Wells in Bedrock T.K. Wiezel 1, G.G. Violette 1 and S.T. Hamilton 2
NUMERICAL MODELING TO INVESTIGATE SAFE YIELD IN MAE SAI MULTILAYERED AQUIFERS
 NUMERICAL MODELING TO INVESTIGATE SAFE YIELD IN MAE SAI MULTILAYERED AQUIFERS Phatcharasak Arlai 1*, Sitisak Munyu 2, Kriangsak Pirarai 2 and Arun Lukjan 1 1 International Program of M.Eng in Water Resources
NUMERICAL MODELING TO INVESTIGATE SAFE YIELD IN MAE SAI MULTILAYERED AQUIFERS Phatcharasak Arlai 1*, Sitisak Munyu 2, Kriangsak Pirarai 2 and Arun Lukjan 1 1 International Program of M.Eng in Water Resources
Groundwater modelling study for sustainable water management in Town of High River. Han Sang-Yoon WaterTech, April 12, 2013
 Groundwater modelling study for sustainable water management in Town of High River Han Sang-Yoon WaterTech, April 12, 2013 Acknowledgements Town of High River: Reiley McKerracher Jasen Craigie Project
Groundwater modelling study for sustainable water management in Town of High River Han Sang-Yoon WaterTech, April 12, 2013 Acknowledgements Town of High River: Reiley McKerracher Jasen Craigie Project
Developing Decision Support System (DSS) for Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM)
 Department of Water Resources Studies Success Stories: Developing Decision Support System (DSS) for Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) The situation of the water supply in the Arab region is
Department of Water Resources Studies Success Stories: Developing Decision Support System (DSS) for Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) The situation of the water supply in the Arab region is
Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin
 Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin A. Karimov, 1 I. Gracheva, 2 F. Miryusupov 2 1 International Water Management Institute (IWMI) Central
Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin A. Karimov, 1 I. Gracheva, 2 F. Miryusupov 2 1 International Water Management Institute (IWMI) Central
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda
 University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Final exam - 12 May 1997 Open books and notes The test contains 8 problems on 7 pages. Read the
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Final exam - 12 May 1997 Open books and notes The test contains 8 problems on 7 pages. Read the
4. Groundwater Resources
 4. Groundwater Resources 4-1 Majority (97 %) of unfrozen fresh water on earth exists as groundwater. In comparison to surface water, - groundwater is available all year around - groundwater is mostly invisible
4. Groundwater Resources 4-1 Majority (97 %) of unfrozen fresh water on earth exists as groundwater. In comparison to surface water, - groundwater is available all year around - groundwater is mostly invisible
BANAT PLAIN THE ROMANIAN CASE STUDY FREEWAT PLATFORM APPLICATION
 Open Workshop 1st FREEWAT User and Developers International Workshop September 21 st 2017 IDAEA. CID - CSIC 16 Jordi Girona. 08034 Barcelona BANAT PLAIN THE ROMANIAN CASE STUDY FREEWAT PLATFORM APPLICATION
Open Workshop 1st FREEWAT User and Developers International Workshop September 21 st 2017 IDAEA. CID - CSIC 16 Jordi Girona. 08034 Barcelona BANAT PLAIN THE ROMANIAN CASE STUDY FREEWAT PLATFORM APPLICATION
Groundwater Flow Evaluation and Spatial Geochemical Analysis of the Queen City Aquifer, Texas
 Groundwater Flow Evaluation and Spatial Geochemical Analysis of the Queen City Aquifer, Texas Abstract The Queen City Aquifer is a saturated sandstone unit in the coastal plain of East Texas. The goals
Groundwater Flow Evaluation and Spatial Geochemical Analysis of the Queen City Aquifer, Texas Abstract The Queen City Aquifer is a saturated sandstone unit in the coastal plain of East Texas. The goals
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF SALTWATER PLUME MOVEMENT IN A FRACTURED AQUIFER ON SUB-REGIONAL SCALE
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF SALTWATER PLUME MOVEMENT IN A FRACTURED AQUIFER ON SUB-REGIONAL SCALE Sascha E. Oswald (Groundwater Protection and Restoration Group, University of Sheffield, United Kingdom) INTRODUCTION
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF SALTWATER PLUME MOVEMENT IN A FRACTURED AQUIFER ON SUB-REGIONAL SCALE Sascha E. Oswald (Groundwater Protection and Restoration Group, University of Sheffield, United Kingdom) INTRODUCTION
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda. HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Problem set #1 9 September 1998
 University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Problem set #1 9 September 1998 Problem 1. Read: Chapter 1 in Freeze & Cherry, 1979. McGuiness
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Problem set #1 9 September 1998 Problem 1. Read: Chapter 1 in Freeze & Cherry, 1979. McGuiness
Closure Water Balance Model to Support Closure Designs for a Mine in Laos
 Page 1 Closure Water Balance Model to Support Closure Designs for a Mine in Laos BR Luinstra SRK Consulting (Australasia) JT Chapman SRK Consulting (Australasia) A Hendry SRK Consulting (Australasia) A
Page 1 Closure Water Balance Model to Support Closure Designs for a Mine in Laos BR Luinstra SRK Consulting (Australasia) JT Chapman SRK Consulting (Australasia) A Hendry SRK Consulting (Australasia) A
Minimizing Energy Use in Large Groundwater Supply Systems
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Environmental & Water Resources Engineering Masters Projects Civil and Environmental Engineering 9-2009 Minimizing Energy Use in Large Groundwater
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Environmental & Water Resources Engineering Masters Projects Civil and Environmental Engineering 9-2009 Minimizing Energy Use in Large Groundwater
A three dimensional modeling approach to groundwater management in Paharpur Canal Command Area, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan
 European Water 57: 417-422, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications A three dimensional modeling approach to groundwater management in Paharpur Canal Command Area, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan A. Khan 1*, A. Qadir
European Water 57: 417-422, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications A three dimensional modeling approach to groundwater management in Paharpur Canal Command Area, Dera Ismail Khan, Pakistan A. Khan 1*, A. Qadir
The Study of Reservoir Immersion of a Hydropower Station
 2017 2 nd International Conference on Architectural Engineering and New Materials (ICAENM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-436-3 The Study of Reservoir Immersion of a Hydropower Station Shi You Zhang, Ai Guo Li
2017 2 nd International Conference on Architectural Engineering and New Materials (ICAENM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-436-3 The Study of Reservoir Immersion of a Hydropower Station Shi You Zhang, Ai Guo Li
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
