Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant
|
|
|
- Aileen Elinor Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): doi: /j.ajee ISSN: (Print); ISSN: X (Online) Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant Nursen Akgun, Zehra Ozcelik * Chemical Engineering Department, Ege University, İzmir, Turkey address: nursen.akgun.1986@gmail.com (N. Akgun), zehra.ozcelik@ege.edu.tr (Z. Ozcelik) * Corresponding author To cite this article: Nursen Akgun, Zehra Ozcelik. Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant. American Journal of Energy Engineering. Vol. 5, No. 5, 2017, pp doi: /j.ajee Received: October 2, 2017; Accepted: October 27, 2017; Published: December 11, 2017 Abstract: Energy saving, global warming and greenhouse gas emissions have become major technological, social and political issues. Being closely related to energy supply, they are of a strategic significance. Today, especially energy-sensitive industries such as refining and petrochemical are targeting to recover maximum amount of energy by applying Process Integration (PI) that deals with the energy efficiency, waste minimization and effective use of raw materials. Pinch Analysis is a structured approach and a systematic tool of PI. The prime objective of Pinch Analysis is to achieve financial savings by better process heat integration and reduce the externally provided energy requirements by recovering the maximum amount of energy within the system. It is also employed to improve effluent quality, reduce emissions, increase product yield and improve the flexibility and safety of the process. Properly calculated pinch targets have economic implications such as reduction of operating cost and capital investment. This study deals with energy saving strategies in a real VCM (Vinyl-Chloride-Monomer) plant by applying pinch method. The prime objective of this work is to achieve financial savings by better process heat integration (maximizing process-to-process heat recovery and reducing the external utility loads). It examines the existing process and introduces two alternative retrofit cases. Targets for heat recovery and utilities have been calculated (taking T min =10 C). Existing process and alternative cases have been compared. According to Retrofit 1, energy recovery reaches up to 12.51% whereas utility reduction is 57.24%. Retrofit 2 states that the recovered energy is 10.45% while the utility reduction is 47.83%. The results obtained indicate that there is a remarkable improvement in energy recovery and utility saving. Keywords: Process Integration, Pinch Analysis, Heat Recovery, Energy Saving 1. Introduction The past decade has seen significant industrial and academic efforts devoted to the development of process design methodologies that target energy conservation for a large variety of chemical process industries [1]. Especially energy saving is the most important issue in the petrochemical industry associated with cost. The petrochemical industry is a capital intensive industry consuming much energy and the energy cost contributes significantly to the total cost [2]. The majority of energy consumed in industry is typically used mainly for heating and cooling purposes. Efficient design of heating and cooling systems in industry is therefore vital and can be accomplished through design optimal heat recovery network using tools such as Pinch Analysis (PA). PA is a systematic technique for the design of thermally efficient systems. It allows the designer to identify the minimum heating and cooling requirements and maximum energy recovery potential by identifying a thermodynamic bottleneck or the pinch point for heat recovery [3]. The development of PA started in the late 1970s and still continues. Besides the applications in energy conservation, new developments are being made in the areas of water use minimization, waste minimization, hydrogen management and so on. The application of Pinch Technology has resulted in significant improvements in the energy and capital efficiency of industrial facilities worldwide. It has been
2 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): successfully applied in many different industries from petroleum and base chemicals to food and paper. This study is an example on the application of Pinch Analysis to save energy in VCM Plant of Petkim Petrochemical Industy. Although it won t provide something new to the field, this work will contribute to the current literature by improving the existing knowledge about Pinch Technology on a real large scale process. 2. Methodology Methods of energy saving in petrochemical processes are various. Renowned methods are optimization of operating conditions and retrofit of Heat Exchange Network (HEN) [2]. One of the most extensively studied and single most important industrial application area for Process Integration (PI) is Heat Exchange Network Synthesis (HENS). The principal aspects of HENS can be found in the fact that most industrial processes involve the transfer of heat from one process stream to another process stream (interchanging) or from a utility stream to a process stream. Consequently, the target in any industrial process design is to maximize the process-to-process heat recovery and to minimize the utility requirements. To meet this goal, industrial cost effective HEN (consisting of one or more heat exchangers that collectively satisfy the energy conservation tasks) is of particular importance [1]. Pinch Technology provides a systematic methodology for energy saving in processes and total sites. The methodology is based on thermodynamic principles. Pinch Analysis starts with the heat and material balance for the process. Thus, in order to start the PA, the necessary thermal data must be extracted from the process [4]. This involves inlet and outlet temperatures, heat capacities and heat duties of process streams requiring energy transfer [2]. The starting point for an energy integration analysis is the calculation of the minimum heating and cooling requirements for a HEN. Cascade Diagram is a visual representation that shows the net heating and cooling requirements in each temperature interval [5]. Also Composite Curves (CCs) and Grand Composite Curve (GCC) have been among the most popular graphical tools for describing optimal Heat Exchanger Networks [3]. To handle multiple streams, the heat loads or heat capacity flow rates of all streams existing over any given temperature range can be added. Thus, a single composite for all hot streams and a single composite curve for all cold streams can be produced by plotting temperature versus enthalpy diagram. The overlap between the composite curves represents the maximum amount of heat recovery possible within the process. The overshoot at the bottom of the hot composite represents the minimum amount of external cooling required and the overshoot at the top of the cold composite represents the minimum amount of external heating [6]. A further development for heat integration targeting has been the Grand Composite Curve (GCC). The GCC shows a clearer view of the areas of internal process heat self sufficiency as well as the demand for external heating and cooling, all in the context of the corresponding temperature levels [7]. In Pinch Technology, choosing a suitable minimum allowable temperature ( T min ) has significance. Since higher values of T min give higher hot and cold utility requirements, it therefore seems that T min should be as low as possible to give maximum energy efficiency. However, there is a drawback; lower T min values give larger and more costly heat exchangers [7]. Thus an optimal allowable temperature should be chosen. The temperature level at which T min is observed in the process is referred to as Pinch Point. The pinch defines the minimum driving force ( T min ) allowed in the exchanger unit. To design a heat exchange network, the most helpful representation is the Grid Diagram. It is much easier to draw than a flowsheet, especially as heat exchangers can be placed in any order without redrawing the stream system. Also, the grid represents the counter current nature of the heat exchange, making it easier to check exchanger temperature feasibility. The pinch is easily represented in the grid [6]. During the construction of grid diagram, stream splitting or cycling matching can be done. Stream splitting is dividing a stream to satisfy the CP criteria. Cyclic matching is adding a series of smaller heat exchangers on a stream. After construction of grid diagram, relaxation paths and loops are found. The heat exchangers on the paths and loops are removed and their loads are added to hot and cold utilities. 3. Results and Discussion In this study, an existing VCM plant was taken into consideration and retrofit was made by using pinch analysis. In the process 28 hot and 17 cold steams exist. By making heat and material balances according to the stream data taken from the process, the heat capacities and heat loads of each stream were calculated by using ASPEN Plus and ASPEN HYSYS (Table 1 and Table 2). Then the adjusted supply and target temperatures are obtained by considering the minimum approach temperature to be 10 C. These temperatures are shown from the highest value to the smallest in cascade design. The heat capacity flow rates and heat loads for each interval are calculated. Then the pinch temperature and minimum requirement of hot and cold utilities are obtained. The pinch temperature is found to be C; hence the pinch temperatures for hot and cold streams are calculated as C and 97.5 C, respectively. Also the minimum hot and cold utilities required are found to be kw and kw, respectively (Table 3). Table 1. Data of cold process streams. Stream Number T in ( C) T out ( C) CP (kw/ C) (kw) C C C C
3 41 Nursen Akgun and Zehra Ozcelik: Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant Stream Number T in ( C) T out ( C) CP (kw/ C) (kw) C C C C C C C C C C C C C After plotting the hot and cold composite curves by using actual temperatures, the pinch temperature is also found to be C. The composite curve is a graphical approach to the process while the cascade design is a mathematical approach. It can be seen from Table 3 and Figure 1, both cascade algorithm and composite curve give the approximate results. Then by using shifted temperatures, the grand composite curve is plotted (Figure 2). It is seen that the minimum hot and cold utilities are the same with the ones calculated from cascade diagram and composite curves. Also it is seen that at C, no heat is transferred between streams. Hence the pinch point is found to be again C [11]. Table 2. Data of hot process streams. Stream Number T in ( C) T out ( C) CP (kw/ C) (kw) H H H H H H H H H H H H H Stream Number T in ( C) T out ( C) CP (kw/ C) (kw) H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H By using the pinch temperatures obtained in three different ways, the grid diagram is plotted. While composing the grid diagram, process is divided into two parts according to supply and target temperatures of the streams where one side is the cold utility which is used to cool the hot streams and the other side is the hot utility which is used to heat the cold streams. The streams are matched by making some assumptions, such as: i. Heat should not be transferred across the pinch. ii. Above pinch, heat capacity of the cold streams should be greater than hot streams and vice versa. iii. Minimum temperature approach should be satisfied between the hot and cold streams at each side of the heat exchanger. iv. In each match, outlet temperature of the hot stream could not be smaller than the inlet temperature of the cold stream and outlet temperature of the cold stream could not be greater than the inlet temperature of the hot stream. This thermodynamic property should be checked in each heat exchanger. Table 3. Calculations of the cascade T min =10 C. T shifted Interval T( C) CP cold(kw/c) CP hot(kw/c) HCFR(kW/C) H(kW) , ,986 Q H,min ! 0 3,58-3, , , ,7 2 86, , , ,7 115, , , , , ,85 22, ,4 3925,4-5583, , , ,45 202, , , ,4 6 3,6 28, ,83 103, , , ,4 28,83 9,62 19,21 26, , , ,7 9,62 22,08 110,4-6026, , ,4 9,62 22,78 45, , , ,4 157,6-125,2-876,4-5195, , ,1 157,6 3354,5 3354,5-8550, , ,4 157,6-125,2-2378,8-6171, ,445
4 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): T shifted Interval T( C) CP cold(kw/c) CP hot(kw/c) HCFR(kW/C) H(kW) ,8 157,6 4936,2 4936, , , ,9 14 3,1 32,4 157,6-125,2-388, , , ,9 32,4 192, , , ,43 192,4 1537, , , , ,43 192,4-161,97-161, , , ,13 192,4 364,73 364, , , ,5 19 1,5 30,43 192,4-161,97-242, , , , ,93 192,4 695,53 695, ,986 0,000 PINCH ,5 30,43 192,4-161,97-890, , , ,43 292,74-262,31-524, , , ,43 298,41-267, ,9-9532, ,355 87,5 24 2,5 30,43 303,72-273,29-683, , ,580 85,9 25 1,6 30, , , , , , ,9 537, ,19-569,76-512, , ,180 84,9 27 0,1 537, ,68-867,25-86, , ,905 83,8 28 1,1 30, , , , , , ,8 30, , , , , ,548 81,3 30 1,7 37, , , , , ,239 80,4 31 0,9 728, ,64-677,73-609, , ,196 80,3 32 0,1 728, ,12-678,21-67, , ,017 76,5 33 3,8 37, , , , , , ,5 37,41 603,65-566,24-283, , ,035 75,5 35 0,5 42,68 853,28-810,6-405,3 4984, , ,5 42,68 847,61-804,93-402, , ,800 70,4 37 4,6 45, ,45-703, , , , ,4 45, ,02-712, , , , , ,4-723, , , , , ,4-730, , , , ,17 769,4-758, , , , ,17 835,51-824, , , , ,17 515,24-504, , , , ,17 318,38-307, , , , ,7 262,98-251, , , , ,9 262,98-257,08-514, , , ,2 228,18-222, , , ,163 39,5 48 0,5 5,2 229,16-223,96-111, , , ,5 5,2 327,89-322,69-161, , , ,2 316,51-311,31-311, , , ,2 271,43-266,23-798, , , ,2 3067,4-3062,2-3062, , , ,2 129,7-124, , , ,2 33,83-28,63-57, , , ,2 17,82-12,62-176, , , ,87 17,82-14,95-164, , , ,87 1,46 1,41 7, , ,028-15, ,3 2,87 0,48 2,39 36, , , ,7 2,87 0 2,87 22, , , , , ,48-284, , , ,282 Q C,min
5 43 Nursen Akgun and Zehra Ozcelik: Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant Figure 1. Hot and cold composite curves. Figure 2. Grand Composite Curve.
6 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): Figure 3. Grid diagram of the existing process.
7 45 Nursen Akgun and Zehra Ozcelik: Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant Figure 4. Grid diagram of Retrofit 1.
8 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): Figure 5. Grid diagram of Retrofit 2.
9 47 Nursen Akgun and Zehra Ozcelik: Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant Table 4. Temperature and heat load calculations of exchangers for Retrofit 1. ABOVE PINCH BELOW PINCH Heat Ex HOT COLD T in ( C) T out ( C) T in ( C) T out ( C) () 1 [H28-C6] [H11-C6] [H16-C9] [H11-C8] [H16-C10] [H11-C12] [H11-C15] [H24-C11] [H24-C10] [H24-C4] [H24-C3] [H24-C2] [H24-C1] [H3-C5] [H10-C7] [H6-C14] [H6-C17] [H16-C3] [H27-C3] [H18-C3] [H28-C1] [H28-C9] [H11-C2] [H23-C2] [H5-C2] [H13-C2] [H11-C3] Q-recovered = kw Table 5. Temperature and heat load calculations of exchangers for Retrofit 2. ABOVE PINCH BELOW PINCH Heat Ex HOT COLD T in ( C) T out ( C) T in ( C) T out ( C) () 1 [H11-C6] [H11-C12] [H11-C15] [H28-C8] [H16-C9] [H16-C10] [H24-C16] [H3-C5] [H10-C7] [H6-C17] [H6-C14] [H11-C1] [H11-C3] [H11-C9] [H16-C4] [H28-C2] Q-recovered = kW Table 6. Heat loads of utilities (heaters and coolers). Heat Load (kw) Utility Retrofit 1 Retrofit 2 Existing Process Before Network After Network Before Network After Network Relaxation Relaxation Relaxation Relaxation Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler
10 American Journal of Energy Engineering 2017; 5(5): Heat Load (kw) Utility Retrofit 1 Retrofit 2 Existing Process Before Network After Network Before Network After Network Relaxation Relaxation Relaxation Relaxation Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler Cooler , = Heater ,8 Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater Heater , = First of all, the grid diagram of the existing process was drawn (Figure 3). In the existing process only two matching is done between the hot and cold process streams. So, only 270 kw heat is recovered. Then two alternative cases were presented. While composing the grid diagram, some rules were taken into consideration such as During the construction of grid diagram, it is avoided using stream splitting. Because stream splitting requires extra pipework and valve, and the flow down each section of the split need to be controlled. Hence cyclic matching is preferred and a series of smaller heat exchangers are placed on a stream. In each match, temperatures around the exchangers are checked to see if they are thermodynamically feasible or not. Also violation of T min is avoided. In the case of Retrofit 1, it is avoided using heaters and coolers with small heat loads. Instead, using more exchangers with smaller heat loads is preferred. The temperatures around exchangers and heat loads of heaters, coolers and exchanger are calculated. The minimum hot and cold utilities and loads of heat exchangers (hence the heat recovery) are found to be the same with the results obtained from cascade. Then Network Relaxation is done on VCM plant. One relaxation path is found on the grid diagram of Retrofit 1. One heat exchanger on the path is eliminated and its heat load is added to the heater and cooler at each side of the path. It is seen that the heat recovery is kw which is less than the value calculated from cascade algorithm (12288 kw). In the case of Retrofit 2, it is tried to use heat exchangers with higher heat loads. Thus in Retrofit 2, the number of utilities (heaters and coolers) is increased while the number of exchangers is decreased. In this grid diagram, no loop exists but seven relaxation paths are found. This time seven heat exchangers on the paths are removed and their heat loads are added to the utilities. At the end, it is seen that the recovery of heat between process streams are kw which is smaller than the heat recovery calculated for the case of Retrofit 1. The temperatures around exchangers and their heat loads are calculated both for Retrofit 1 and Retrofit 2 and the results are given in Table 4 and Table 5. The exchangers eliminated after network relaxation are shown in red color. So their heat loads are not taken into consideration in the calculation of heat recovery. Also the heat loads of utilities (coolers and heaters) for each cases are calculated and given in Table 6. The heat loads before and after network relaxation are given since after network relaxation the heat loads of some of the utilities are increased with the addition of heat loads of eliminated exchangers.
11 49 Nursen Akgun and Zehra Ozcelik: Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch Analysis in a Chemical Plant The comparison of existing process, Retrofit 1 and Retrofit 2 is given in Table 7. It seems that Retrofit 1 is better for higher energy recovery but there are more equipments. Since heat exchangers may cost so much, an optimization should be made between the cost of utilities (operating cost) and the cost of equipments (capital cost) in order to decide which case is better. 4. Conclusion This study deals with the energy saving strategies in a real VCM plant by applying pinch method. It examines the existing process and introduces 2 alternative retrofit cases. Results obtained indicate that there is a remarkable improvement in energy usage: According to the pinch analysis made before, the yield reduction is 0.5% for cold and 1.06% for hot utilities. Also the energy recovery is only 0.34%. But according to Retrofit 1, the reductions in cold and hot utilities are 18.26% and 38.98%, respectively. Also the energy recovery increases up to 12.51%. On the other hand, Retrofit 2 states that there is 15.25% saving of cold and 32.58% saving of hot utilities. Also, in Retrofit 2, the recovered energy is 10.45%. If we compare the requirement for hot and cold utilities and recovered energy between the process streams, it seems that Retrofit 1 gives the best results. But as it seen from Table 7, the number of equipment in Retrofit 1 is 50 whereas it is 44 in Retrofit 2. The best process can be chosen after making cost calculations since heat exchangers may cost so much. An optimization should be done between the cost of utilities (operating cost) and the cost of equipments (capital cost). Hence, as a further investigation the heat exchanger network can be optimized by comparing energy cost and the capital cost of the network so that the total annual cost is minimized. Table 7. Comparison of existing process and alternative cases. Existing Process Retrofit 1 Retrofit 2 Heat Loads, () , () () Number of Equipments # Heat Exch # Heaters # Coolers U min Existing Process Retrofit 1 Retrofit 2 Heat Loads Saving of Utilities (%) Cold Hot Total Heat Recovery (%) Acknowledgements The technical support of PETKİM is sincerely acknowledged. References [1] Raskovic, P., Stoiljkovic, S., Pinch design method in the case of a limited number of process streams, Enery 34, 2009, pp [2] Yoon, S. G., Lee, J., Park, S., Heat integration analysis for an industrial etylbenzene plant using pinch analysis, Applied Thermal Engineering, 27, 2007, pp [3] Wan Alwi, S. R., Manan, Z. A., STEP-a graphical tool for simultaneous targeting and design of heat exchanger network, Chemical Engineering Journal 162, 2010, pp [4] March, L., Introduction to Pinch Technology, Targeting House, England, [5] Douglas, J. M., Conceptual Design of Chemical Processes, McGraw-Hill, New York, [6] Kemp, J. C., Pinch Analysis and Process Integration: A User Guide on Process Integration of Efficient Use of Energy, 2 nd Ed., Elsevier, Oxford, [7] Friedler, F., Process integration, modelling and optimization for energy saving and pollution, reduction, Applied Thermal Engineering 30, 2010, pp [8] Tovazhryanski, L., Kapustenko, P., Ulyev, L., Boldyryev, S., Arsenyeva, O., Process integration of sodium hypophosphite production, Applied Thermal Engineering 30, 2010, pp [9] El-Halwagi, M. M., Process Integration, Vol 7, Elsevier, Oxford, UK, [10] AspenTech Software User Guide, Aspen Plus 11.1, Aspen HYSYS [11] Akgün N., Debottlenecking and Retrofitting by Pinch and Exergetic Analysis in a Chemical Plant, MSc Thesis, Ege University, Chemical Engineering Department, 2013.
pinch 70 C 70 C 4 We want to cool both the hot streams to the pinch temperature. The next step is to find the duty for the two heat exchangers:
 Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Ene-47.5130 Process Integration (3 ECTS credits) P Espoo 2016 EXERCISE 2 SOLUTIONS 1 MER heat exchanger network First we draw the stream-grid and calculate the enthalpy rate change, Q, above and below
Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas
 Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas Leonid Tovazhnyansky, Petro Kapustenko, Leonid Ulyev, Stanislav Boldyryev * National Technical University "Kharkiv Polytechnic
Heat Integration Improvement for Benzene Hydrocarbons Extraction from Coke-Oven Gas Leonid Tovazhnyansky, Petro Kapustenko, Leonid Ulyev, Stanislav Boldyryev * National Technical University "Kharkiv Polytechnic
Quiz Questions. For Process Integration. Fill in the blanks type Questions
 Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
Quiz Questions For Process Integration Fill in the blanks type Questions 1. is the key parameter used in the Pinch Technology. ( T min ) 2. In onion diagram pinch technology in applied at. (the boundary
A Modified Energy Transfer Diagram for Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Bridge Analysis
 907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
907 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
3.17. PROCESS INTEGRATION AND PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENERGY BALANCES 111 pressure is expanded over the throttle value and fed to the condenser, to provide cooling to condense the vapour from the column. The vapour from the condenser is compressed
The Grid Diagram The Heat-Content Diagram Pinch Subnetworks Minimum Number of Heat-Exchange Units...
 3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
3.1 INTRODUCTION... 2 3.2 DESIGN TOOLS: REPRESENTING HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORKS... 4 3.2.1. The Grid Diagram...4 3.2.2. The Heat-Content Diagram...7 3.3 PRELIMINARY HEAT -EXCHANGER NETWORK DESIGN... 10 3.2.1
HDA Process. compressor. Reactor. Flash. heat. cool. Stabilizer. Recycle. Product
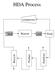 HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
HDA Process compressor heat Reactor cool Flash Recycle Product Stabilizer Why Energy Integration? (ICI Experience) 20 case studies In every case, there was a reduction in energy In almost every case, the
Researcher, 1(2), 2009, Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis
 Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Energy Integration Of Crude Distillation Unit Using Pinch Analysis K.R. AJAO (Ph.D) Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, Nigeria e-mail: ajaomech@unilorin.edu.ng H. F. Akande
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency
 Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
Pinch Analysis for Power Plant: A Novel Approach for Increase in Efficiency S. R. Sunasara 1, J. J. Makadia 2 * 1,2 Mechanical Engineering Department, RK University Kasturbadham, Rajkot-Bhavngar highway,
TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
OPTIMIZATION OF CRYOGENIC CARBON CAPTURE AND LNG PROCESSES BY SHAFTWORK TARGETING AND MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMING
 OPTIMIZATION OF CRYOGENIC CARBON CAPTURE AND LNG PROCESSES BY SHAFTWORK TARGETING AND MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMING Orakotch Padungwatanaroj a, Kitipat Siemanond a : a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College,
OPTIMIZATION OF CRYOGENIC CARBON CAPTURE AND LNG PROCESSES BY SHAFTWORK TARGETING AND MATHEMATICAL PROGRAMMING Orakotch Padungwatanaroj a, Kitipat Siemanond a : a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College,
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology
 Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
Energy Optimisation Of Upstream Separation And Stabilisation Plant Using Pinch Technology Ritesh Sojitra Srashti Dwivedi ITM University, Gwalior, India Abstract: Energy optimisation and process integration
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen. PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant
 PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRY Energy Recovery and Effluent Cooling at a TMP Plant PINCH ANALYSIS: For the Efficient Use of Energy, Water & Hydrogen
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 27: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) 2 nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN
 Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Module 05: Pinch Design Method for HEN synthesis Lecture 7: Rules of Pinch Design Method (PDM) nd Part Key words: PDM, HEN Some rules for pinch design methods such as Criteria for number of process streams
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology
 Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Retrofit for a Gas Separation Plant by Pinch Technology Napredakul, D. a, Siemanond, K.a, Sornchamni, T.b, Laorrattanasak, S.b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.9, No.06 pp 432-439, 2016 Pinch analysis of Acrylic Acid Process Plant K. Nagamalleswara Rao*
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 14: No. of units target Key Words: HEN, Subset, Loop, Separate component, MER design The fixed cost of a heat exchanger network (HEN) depends upon the number of heat exchanger
Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and GAMS Technology.
 EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
EngOpt 2012 3 rd International Conference on Engineering Optimization Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 01-05 July 2012. Heat Exchanger Network Optimization using integrated specialized software from ASPENTECH and
CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration
 CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration Sachin V JANGAM Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering National University of Singapore Singapore Email: chejsv@nus.edu.sg Office location: E4-05-46
CN4205R Pinch Analysis and Process Integration Sachin V JANGAM Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering National University of Singapore Singapore Email: chejsv@nus.edu.sg Office location: E4-05-46
Grand Composite Curve Module 04 Lecture 12
 Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Module 04: Targeting Lecture 12: Grand Composite Curve While composite curves provide overall energy targets, these do not indicate the amount of energy that should be supplied at different temperature
Cost Effective Heat Exchangers Network of Total Site Heat Integration
 541 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
541 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks
 Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Pressure Drop in Heat Exchanger Networks Topics: Heat Exchangers have (considerable) P Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop are related New Design: A new -way Trade-off Retrofit: Bottleneck Problems Basis:
Targeting Minimum Heat Transfer Area for Heat Recovery on Total Sites
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Energy Retrofit Studies in Diethyl Thiophosphoryl Chloride (DETC) Plant
 Energy Retrofit Studies in Diethyl Thiophosphoryl Chloride (DETC) Plant Y. P. Bhalerao, S. V. Patil, P. V. Vijay Babu, and S. J. Kulkarni Abstract The industrial application of detailed heat integration
Energy Retrofit Studies in Diethyl Thiophosphoryl Chloride (DETC) Plant Y. P. Bhalerao, S. V. Patil, P. V. Vijay Babu, and S. J. Kulkarni Abstract The industrial application of detailed heat integration
Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology VISHAL G. BOKAN 1, M.U.POPLE 2 1 Student of M.E. chemical, Department of Chemical Engineering,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Design of Heat Exchanger Network for VCM Distillation Unit Using Pinch Technology VISHAL G. BOKAN 1, M.U.POPLE 2 1 Student of M.E. chemical, Department of Chemical Engineering,
Heat Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit
 Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
Review Paper Abstract Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Integration of Crude Organic Distillation Unit Padole Manjusha 1, Sapkal Pradyumna 2, Dawande S.D. 3 and Nitin Kanse 4 1, 3
Participant Plants and Streams Selection for Interplant Heat Integration among Three Plants
 547 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
547 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES
 Congrès s Annuel ATIP Annecy 27-29 29 avril 2005 DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES David Brown Zoé Périn-Levasseur François Maréchal Jean Paris EP Montréal
Congrès s Annuel ATIP Annecy 27-29 29 avril 2005 DUAL REPRESENTATION OF MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIREMENTS APPLICATIONS TO P&P PROCESSES David Brown Zoé Périn-Levasseur François Maréchal Jean Paris EP Montréal
Process Integration Route For Water Conservation In Industrial Plants
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.3, pp 1124-1128, April-June 2013 IPACT-2013[14 th 15 th March 2013] National Conference on Industrial Pollution
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.5, No.3, pp 1124-1128, April-June 2013 IPACT-2013[14 th 15 th March 2013] National Conference on Industrial Pollution
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation
 Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
Process Integration: Unifying Concepts, Industrial Applications and Software Implementation by James Gainey Mann, Jr. Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State
PROCESS INTEGRATION FOR ENERGY CONSERVATION IN DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER THROUGH PINCH TECHNOLOGY
 PROCESS INTEGRATION FOR ENERGY CONSERVATION IN DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER THROUGH PINCH TECHNOLOGY Suneela Sardar, Syed Shamim Raza and S. R. Malik Department of Chemical Engineering, NFC IE&FR Faisalabad,
PROCESS INTEGRATION FOR ENERGY CONSERVATION IN DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER THROUGH PINCH TECHNOLOGY Suneela Sardar, Syed Shamim Raza and S. R. Malik Department of Chemical Engineering, NFC IE&FR Faisalabad,
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production. Thorsten Spillmann
 IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
IDRIST Temporal pinch-point analysis for energy demand reduction in batch production Thorsten Spillmann Content Introduction to IDRIST project Importance of pinch-methodology for energy demand reduction
TEP Energy Utilization and Process Integration in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process
 Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
Department of Energy and Process Engineering - Energy Utilization and in Industrial Plants, or for short: Energy and Process The Objective is to convey Systems Thinking and Systematic Methods for: Analysis
A New Optimisation Based Retrofit Approach for Revamping an Egyptian Crude Oil Distillation Unit
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 36 (2013 ) 454 464 TerraGreen 13 International Conference 2013 - Advancements in Renewable Energy and Clean Environment A New Optimisation
Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology: A Case Study of Orbit Chemicals Industry
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 3 Ver. I (May- Jun. 2014), PP 44-53 Energy Efficiency Analysis Using Pinch Technology:
Retrofit of Refinery Heat Exchanger Network under Different Kinds of Crude Oil by Pinch Design Method using Mathematical Programming
 A publication of 1411 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 1411 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Design by Eliminating Cross Pinch Heat Exchangers
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-05, pp-11-18 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Design by Eliminating
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-05, pp-11-18 www.ajer.us Research Paper Open Access Heat Exchanger Network Retrofit Design by Eliminating
Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries
 National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
National Seminar on Awareness and Implementation of Energy Management System Overview of pinch analysis and its application in hydrocarbon Industries 19t h January- 2015 SCOPE Conversion centre, Lodhi
Modelling of CO 2 capture using Aspen Plus for EDF power plant, Krakow, Poland
 Modelling of CO 2 capture using Aspen Plus for EDF power plant, Krakow, Poland Vipul Gupta vipul.gupta@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico,Lisboa, Portugal October 2016 Abstract This work describes
Modelling of CO 2 capture using Aspen Plus for EDF power plant, Krakow, Poland Vipul Gupta vipul.gupta@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico,Lisboa, Portugal October 2016 Abstract This work describes
Wastewater Minimization With Differentiated Regeneration of Contaminants using Water Source Diagrams (WSD)
 Wastewater Minimization With Differentiated Regeneration of Contaminants using Water Source Diagrams (WSD) B.E.P.C.Delgado 1, E.M.Queiroz 1, F. L. P. Pessoa 1 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Universidade
Wastewater Minimization With Differentiated Regeneration of Contaminants using Water Source Diagrams (WSD) B.E.P.C.Delgado 1, E.M.Queiroz 1, F. L. P. Pessoa 1 1 Chemical Engineering Department, Universidade
Minimizing Fresh and Wastewater Using Water Pinch Technique in Petrochemical Industries W. Mughees, M. Al-Ahmad, M. Naeem
 Minimizing Fresh and Wastewater Using Water Pinch Technique in Petrochemical Industries W. Mughees, M. Al-Ahmad, M. Naeem Abstract This research involves the design and analysis of pinch-based water/wastewater
Minimizing Fresh and Wastewater Using Water Pinch Technique in Petrochemical Industries W. Mughees, M. Al-Ahmad, M. Naeem Abstract This research involves the design and analysis of pinch-based water/wastewater
MULTI-PERIOD HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK RETROFIT UNDER FOULING EFFECTS.
 MULTI-PERIOD HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK RETROFIT UNDER FOULING EFFECTS. Supapol Rangfak a, Kitipat Siemanond a* a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Keywords:
MULTI-PERIOD HEAT EXCHANGER NETWORK RETROFIT UNDER FOULING EFFECTS. Supapol Rangfak a, Kitipat Siemanond a* a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Keywords:
Waste Management Pinch Analysis (WAMPA) with Economic Assessment
 145 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 45, 2015 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi
145 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 45, 2015 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi
Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 4(5): (ISSN: )
 Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 4(5): 731-736 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2013 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.org Journal of Emerging
Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 4(5): 731-736 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2013 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.org Journal of Emerging
Heat Integration Across Plants Considering Distance Factor
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
OPTIMISATION AND INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION AND MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
 OPTIMISATION AND INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION AND MANAGEMENT OPTIONS PhD Thesis Andreja NEMET Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Jiří J. Klemeš Co-supervisor: Dr. Zdravko Kravanja Doctoral School of Information
OPTIMISATION AND INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION AND MANAGEMENT OPTIONS PhD Thesis Andreja NEMET Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Jiří J. Klemeš Co-supervisor: Dr. Zdravko Kravanja Doctoral School of Information
Application of combined pinch and exergy analysis in retrofit of an olefin plant for energy conservation
 Scientific Research and Essays Vol. 6(12), pp. 2437-2446, 18 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/sre DOI: 10.5897/SRE10.726 ISSN 1992-2248 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
Scientific Research and Essays Vol. 6(12), pp. 2437-2446, 18 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/sre DOI: 10.5897/SRE10.726 ISSN 1992-2248 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
NEW RECYCLE PROCESS SCHEME FOR HIGH ETHANE RECOVERY NEW PROCESS SCHEME FOR HIGH NGL RECOVERY INTRODUCTION. Abstract PROCESS FUNDAMENTALS
 Author: Jorge Foglietta, ABB Randall Corporation Tel (713) 821-4313, Fax (713) 821-3544 Mailing Address: Randall Division ABB Lummus Global Inc. P.O. Box 420087 Houston, Texas 77242-0087 NEW PROCESS SCHEME
Author: Jorge Foglietta, ABB Randall Corporation Tel (713) 821-4313, Fax (713) 821-3544 Mailing Address: Randall Division ABB Lummus Global Inc. P.O. Box 420087 Houston, Texas 77242-0087 NEW PROCESS SCHEME
Model and Optimisation of a Multi-Effect Evaporator of Sugarcane Juice: Energy Consumption and Inversion Losses
 Model and Optimisation of a Multi-Effect Evaporator of Sugarcane Juice: Energy Consumption and Inversion Losses Daniela Galatro*, Elisa Verruschi, Roberto Guillen Universidad Nacional Experimental Politécnica
Model and Optimisation of a Multi-Effect Evaporator of Sugarcane Juice: Energy Consumption and Inversion Losses Daniela Galatro*, Elisa Verruschi, Roberto Guillen Universidad Nacional Experimental Politécnica
Canada. Iron and Steel Sector - PI Specifics
 How can process integration help me? Process integration (PI) is a very efficient approach to improving the energy efficiency of large and complex industrial facilities. PI refers to the application of
How can process integration help me? Process integration (PI) is a very efficient approach to improving the energy efficiency of large and complex industrial facilities. PI refers to the application of
Rigorous Optimisation of Refinery Hydrogen Networks
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET102100154 319
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET102100154 319
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS
 OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
OPTIMIZATION OF PARAMETERS FOR HEAT RECOVERY STEAM GENERATOR (HRSG) IN COMBINED CYCLE PLANTS Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic University of Belgrade-Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Laboratory of Thermal
Composite Table Algorithm - A Powerful Hybrid Pinch Targeting Method for Various Problems in Water Integration
 Composite Table Algorithm - A Powerful Hybrid Pinch Targeting Method for Various Problems in Water Integration R. Parand, H. M. Yao, M. O. Tadé, and V. Pareek Abstract Water management has become a very
Composite Table Algorithm - A Powerful Hybrid Pinch Targeting Method for Various Problems in Water Integration R. Parand, H. M. Yao, M. O. Tadé, and V. Pareek Abstract Water management has become a very
Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle. Introduction
 Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle Dmitriy A. Sladkovskiy, St.Petersburg State Institute of Technology (technical university), Saint-
Improvement of distillation column efficiency by integration with organic Rankine power generation cycle Dmitriy A. Sladkovskiy, St.Petersburg State Institute of Technology (technical university), Saint-
Efficiency improvement of steam power plants in Kuwait
 Energy and Sustainability V 173 Efficiency improvement of steam power plants in Kuwait H. Hussain, M. Sebzali & B. Ameer Energy and Building Research Center, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait
Energy and Sustainability V 173 Efficiency improvement of steam power plants in Kuwait H. Hussain, M. Sebzali & B. Ameer Energy and Building Research Center, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait
Exploitation of Low-Grade Heat in Site Utility Systems
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET102101762 367
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET102101762 367
Optimization of Steam Pressure Levels in a Total Site Using a Thermoeconomic Method
 Energies 2012, 5, 702-717; doi:10.3390/en5030702 Article OPEN ACCESS energies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/journal/energies Optimization of Steam Pressure Levels in a Total Site Using a Thermoeconomic Method
Energies 2012, 5, 702-717; doi:10.3390/en5030702 Article OPEN ACCESS energies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/journal/energies Optimization of Steam Pressure Levels in a Total Site Using a Thermoeconomic Method
APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 6, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 73-84 APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS * A. H. Javid, A. Emamzadeh, 3 A.
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 6, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 73-84 APPLYING THE HEAT INTEGRATION IN ORDER TO ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTANTS MINIMIZATION IN DISTILLATION COLUMNS * A. H. Javid, A. Emamzadeh, 3 A.
ENERGY SAVINGS OF INTERCOMPANY HEAT INTEGRATION - A METHODOLOGICAL FRAMEWORK PART I
 ENERGY SAVINGS OF INTERCOMPANY HEAT INTEGRATION - A METHODOLOGICAL FRAMEWORK PART I Ali Aydemir, Clemens Rohde, Simon Möhren Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, Breslauer Strasse
ENERGY SAVINGS OF INTERCOMPANY HEAT INTEGRATION - A METHODOLOGICAL FRAMEWORK PART I Ali Aydemir, Clemens Rohde, Simon Möhren Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, Breslauer Strasse
Conception of a Pulverized Coal Fired Power Plant with Carbon Capture around a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton Cycle
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 37 (2013 ) 1180 1186 GHGT-11 Conception of a Pulverized Coal Fired Power Plant with Carbon Capture around a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 37 (2013 ) 1180 1186 GHGT-11 Conception of a Pulverized Coal Fired Power Plant with Carbon Capture around a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton
Condensate Line Sizing for Gravity Returns from Steam Traps and Heat Recovery
 Condensate Line Sizing for Gravity Returns from Steam Traps and Heat Recovery With efficient energy use being important to all users of steam, maximizing the recovery of heat is of utmost importance. In
Condensate Line Sizing for Gravity Returns from Steam Traps and Heat Recovery With efficient energy use being important to all users of steam, maximizing the recovery of heat is of utmost importance. In
K.S. Rawat 1, H. Khulve 2, A.K. Pratihar 3 1,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, GBPUAT, Pantnagar , India
 Thermodynamic Analysis of Combined ORC-VCR System Using Low Grade Thermal Energy K.S. Rawat 1, H. Khulve 2, A.K. Pratihar 3 1,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, GBPUAT, Pantnagar-263145, India 2 Department
Thermodynamic Analysis of Combined ORC-VCR System Using Low Grade Thermal Energy K.S. Rawat 1, H. Khulve 2, A.K. Pratihar 3 1,3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, GBPUAT, Pantnagar-263145, India 2 Department
EXERGETIC AND ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF AN INDUSTRIAL DISTILLATION COLUMN
 Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 0104-6632 Printed in Brazil www.abeq.org.br/bjche Vol. 24, No. 03, pp. 461-469, July - September, 2007 EXERGETIC AND ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF AN INDUSTRIAL DISTILLATION
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 0104-6632 Printed in Brazil www.abeq.org.br/bjche Vol. 24, No. 03, pp. 461-469, July - September, 2007 EXERGETIC AND ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF AN INDUSTRIAL DISTILLATION
A Pattern-based Method for Scheduling of Energy-integrated Batch Process Networks
 Preprint, th IFAC Symposium on Dynamics and Control of Process Systems, including Biosystems June -, 0. NTNU, Trondheim, Norway A Pattern-based Method for Scheduling of Energy-integrated Batch Process
Preprint, th IFAC Symposium on Dynamics and Control of Process Systems, including Biosystems June -, 0. NTNU, Trondheim, Norway A Pattern-based Method for Scheduling of Energy-integrated Batch Process
Technology and Prospect of Process Heat Application of HTR(High temperature gas cooled reactor) Applications in Oil Refining Industry
 Technology and Prospect of Process Heat Application of HTR(High temperature gas cooled reactor) Applications in Oil Refining Industry Dr. Min Qi, Associate Professor Institute of Nuclear and New Energy
Technology and Prospect of Process Heat Application of HTR(High temperature gas cooled reactor) Applications in Oil Refining Industry Dr. Min Qi, Associate Professor Institute of Nuclear and New Energy
Solar Process Heat for Production and Advanced Applications. Methodologies and Software Tools for Integrating Solar Heat into Industrial Processes
 Solar IEA SHC Task 49 SolarPACES Annex IV Solar Process Heat for Production and Advanced Applications Methodologies and Software Tools for Integrating Solar Heat into Industrial Processes Version 2.0,
Solar IEA SHC Task 49 SolarPACES Annex IV Solar Process Heat for Production and Advanced Applications Methodologies and Software Tools for Integrating Solar Heat into Industrial Processes Version 2.0,
Simulation of Ethanol Production by Fermentation of Molasses
 Journal of Engineering (JOE) 69 Vol. 1, No. 4, 2013, ISSN: 2325-0224 Copyright World Science Publisher, United States www.worldsciencepublisher.org Simulation of Ethanol Production by Fermentation of Molasses
Journal of Engineering (JOE) 69 Vol. 1, No. 4, 2013, ISSN: 2325-0224 Copyright World Science Publisher, United States www.worldsciencepublisher.org Simulation of Ethanol Production by Fermentation of Molasses
WASTE TO ENERGY IN POWER PLANTS; INCREASING THERMAL EFFICIENCY AND DECREASING ENVIRONMENT DEFECTS
 WASTE TO ENERGY IN POWER PLANTS; INCREASING THERMAL EFFICIENCY AND DECREASING ENVIRONMENT DEFECTS Mohsen Sharifpur Department of Mechanical Engineering Eastern Mediterranean University G.Magosa, North
WASTE TO ENERGY IN POWER PLANTS; INCREASING THERMAL EFFICIENCY AND DECREASING ENVIRONMENT DEFECTS Mohsen Sharifpur Department of Mechanical Engineering Eastern Mediterranean University G.Magosa, North
HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A.
 HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A. Cardona 1 *, O.J. Sánchez 1,2, Gutiérrez L.F. 1 1 Department of Chemical
HEAT INTEGRATION OF FERMENTATION AND RECOVERY STEPS FOR FUEL ETHANOL PRODUCTION FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC BIOMASS R. Grisales 1, C.A. Cardona 1 *, O.J. Sánchez 1,2, Gutiérrez L.F. 1 1 Department of Chemical
Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants
 Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory of Thermal Turbomachinery
Optimization of parameters for heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) in combined cycle power plants Muammer Alus, Milan V. Petrovic - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory of Thermal Turbomachinery
Chapter Two. The Rankine cycle. Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah
 Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Chapter Two The Rankine cycle Prepared by Dr. Shatha Ammourah 1 The Ideal Rankine Cycle Schematic Diagram of ideal simple Rankine 2 Superheater Economizer line 3 Heat Addition Types In The Steam Generator
Eng Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1
 Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1 The final exam in Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I consists of four questions: (1) 1st Law analysis of a steam power cycle, or a vapour compression refrigeration
Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I: Sample Final Exam Questions 1 The final exam in Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I consists of four questions: (1) 1st Law analysis of a steam power cycle, or a vapour compression refrigeration
ENERGY CONSERVATION & ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR PRODUCTION OF MT/ANNUM ISOBUTYLENE PLANT USING PINCH ANALYSIS MOHD FAIRUZ BIN MOHD JAIS
 i ENERGY CONSERVATION & ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR PRODUCTION OF 50 000 MT/ANNUM ISOBUTYLENE PLANT USING PINCH ANALYSIS MOHD FAIRUZ BIN MOHD JAIS A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirement for the
i ENERGY CONSERVATION & ECONOMIC ANALYSIS FOR PRODUCTION OF 50 000 MT/ANNUM ISOBUTYLENE PLANT USING PINCH ANALYSIS MOHD FAIRUZ BIN MOHD JAIS A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirement for the
Reforming Natural Gas for CO 2 pre-combustion capture in Combined Cycle power plant
 Reforming Natural Gas for CO 2 pre-combustion capture in Combined Cycle power plant J.-M. Amann 1, M. Kanniche 2, C. Bouallou 1 1 Centre Énergétique et Procédés (CEP), Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines
Reforming Natural Gas for CO 2 pre-combustion capture in Combined Cycle power plant J.-M. Amann 1, M. Kanniche 2, C. Bouallou 1 1 Centre Énergétique et Procédés (CEP), Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines
Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation
 Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation Kanteyya A 1, Kiran Kumar Rokhade 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, HKESSLN College
Performance Analysis for Natural Draught Cooling Tower & Chimney through Numerical Simulation Kanteyya A 1, Kiran Kumar Rokhade 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, HKESSLN College
Thermodynamic analysis on post combustion CO 2 capture of natural gas fired power plant
 Thermodynamic analysis on post combustion CO 2 capture of natural gas fired power plant Abstract Zeinab Amrollahi, 1 Ivar S. Ertesvåg, Olav Bolland Department of Energy and Process Engineering, Norwegian
Thermodynamic analysis on post combustion CO 2 capture of natural gas fired power plant Abstract Zeinab Amrollahi, 1 Ivar S. Ertesvåg, Olav Bolland Department of Energy and Process Engineering, Norwegian
Organic Rankine Cycle Configurations
 Proceedings European Geothermal Congress 2007 Unterhaching, Germany, 30 May-1 June 2007 Organic Rankine Cycle Configurations Uri Kaplan Ormat Technologies, Inc., 6225 Neil Road, Suite 300 - Reno, NV 89511-1136,
Proceedings European Geothermal Congress 2007 Unterhaching, Germany, 30 May-1 June 2007 Organic Rankine Cycle Configurations Uri Kaplan Ormat Technologies, Inc., 6225 Neil Road, Suite 300 - Reno, NV 89511-1136,
Modeling, Simulation and Optimization of Energy Systems using Aspen Plus. Giovanni Manente University of Padova
 Modeling, Simulation and Optimization of Energy Systems using Aspen Plus Giovanni Manente University of Padova University of Ljubljana, April 2017 Outline of the presentation Flowsheet simulation 3 Sequential
Modeling, Simulation and Optimization of Energy Systems using Aspen Plus Giovanni Manente University of Padova University of Ljubljana, April 2017 Outline of the presentation Flowsheet simulation 3 Sequential
OPTIMIZATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF POST - COMBUSTION CARBON CAPTURE USING DEA SOLVENT IN A COAL FIRED POWER PLANT
 OPTIMIZATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF POST - COMBUSTION CARBON CAPTURE USING DEA SOLVENT IN A COAL FIRED POWER PLANT Isah Yakub Mohammed Department of Chemical Engineering, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University
OPTIMIZATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF POST - COMBUSTION CARBON CAPTURE USING DEA SOLVENT IN A COAL FIRED POWER PLANT Isah Yakub Mohammed Department of Chemical Engineering, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University
Simulation-Based Optimization Framework with Heat Integration
 Simulation-Based Optimization Framework with Heat Integration Yang Chen a,b, John Eslick a,b, Ignacio Grossmann a, David Miller b a. Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University b. National
Simulation-Based Optimization Framework with Heat Integration Yang Chen a,b, John Eslick a,b, Ignacio Grossmann a, David Miller b a. Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University b. National
A new re-liquefaction system of MRS-F (Methane Refrigeration System Full re-liquefaction) for LNG Carriers
 A new re-liquefaction system of MRS-F (Methane Refrigeration System Full re-liquefaction) for LNG Carriers DongKyu Choi *, Hyunjun Shin DAEWOO SHIPBUILDING AND MARINE ENGINEERING Co., Ltd. Dual fuel slow-speed
A new re-liquefaction system of MRS-F (Methane Refrigeration System Full re-liquefaction) for LNG Carriers DongKyu Choi *, Hyunjun Shin DAEWOO SHIPBUILDING AND MARINE ENGINEERING Co., Ltd. Dual fuel slow-speed
Comparison of micro gas turbine heat recovery systems using ORC and trans-critical CO 2 cycle focusing on off-design performance
 Comparison of micro gas turbine heat recovery systems using ORC and trans-critical CO 2 cycle focusing on - performance IV International Seminar on ORC Power Systems September 13-15, 2017 Suk Young Yoon,
Comparison of micro gas turbine heat recovery systems using ORC and trans-critical CO 2 cycle focusing on - performance IV International Seminar on ORC Power Systems September 13-15, 2017 Suk Young Yoon,
Energy-Saving Study of a System for Ammonium Sulfate Recovery from Wastewater with Mechanical Vapor Compression (MVC)
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 3(11): 1227-1232, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Submitted: July 20, 2011 Accepted: September 07, 2011 Published:
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 3(11): 1227-1232, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Submitted: July 20, 2011 Accepted: September 07, 2011 Published:
A crude oil refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into different petroleum products (i.e.
 A crude oil refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into different petroleum products (i.e. gasoline, diesel, kerosene, jet fuel) This figure shows a typical refinery
A crude oil refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into different petroleum products (i.e. gasoline, diesel, kerosene, jet fuel) This figure shows a typical refinery
Aspen Economic Evaluation Family
 Aspen Economic Evaluation Family A family of products that estimates project capital costs and lifecycle asset economics from conceptual definition through detailed engineering The Aspen Economic Evaluation
Aspen Economic Evaluation Family A family of products that estimates project capital costs and lifecycle asset economics from conceptual definition through detailed engineering The Aspen Economic Evaluation
Performance Evaluation of Deethanizer Column Using Real Time Optimization
 Performance Evaluation of Deethanizer Column Using Real Time Optimization Renanto Handogo, Indra Darmawan, Fadillah Akhbar Marsha, Juwari Department of Chemical Engineering Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember
Performance Evaluation of Deethanizer Column Using Real Time Optimization Renanto Handogo, Indra Darmawan, Fadillah Akhbar Marsha, Juwari Department of Chemical Engineering Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember
Co-production of Bioethanol and Power
 14 Co-production of Bioethanol and Power Atsushi Tsutsumi and Yasuki Kansha Collaborative Research Centre for Energy Engineering, Institute of Industrial Science The University of Tokyo, 4-6-1 Komaba,
14 Co-production of Bioethanol and Power Atsushi Tsutsumi and Yasuki Kansha Collaborative Research Centre for Energy Engineering, Institute of Industrial Science The University of Tokyo, 4-6-1 Komaba,
Performance Benefits for Organic Rankine Cycles with Flooded Expansion
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Publications of the Ray W. Herrick Laboratories School of Mechanical Engineering 6-2-2010 Performance Benefits for Organic Rankine Cycles with Flooded Expansion Brandon
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Publications of the Ray W. Herrick Laboratories School of Mechanical Engineering 6-2-2010 Performance Benefits for Organic Rankine Cycles with Flooded Expansion Brandon
Chapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Optimisation of WSA technology - Integration of energy and adaptation to the Chinese market
 Otimisation of WSA technology - Integration of energy and adatation to the Chinese market Annette Wendt Deartment of Chemical Engineering, Lund University Abstract The aim of this Master thesis was to
Otimisation of WSA technology - Integration of energy and adatation to the Chinese market Annette Wendt Deartment of Chemical Engineering, Lund University Abstract The aim of this Master thesis was to
Technical Analysis of the Natural Gas to Hydrocarbon Liquid Process
 American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 25-40 Published online May 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche) doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.s.2015030201.14 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print);
American Journal of Chemical Engineering 2015; 3(2-1): 25-40 Published online May 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajche) doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.s.2015030201.14 ISSN: 2330-8605 (Print);
Combined Mass and Energy Transients
 Lecture T3 Combined Mass and Energy Transients We now consider processes in which the amounts of both mass and energy are changing in the system. In these cases, the material and energy balances are both
Lecture T3 Combined Mass and Energy Transients We now consider processes in which the amounts of both mass and energy are changing in the system. In these cases, the material and energy balances are both
Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycles and Their Application as a Bottoming Cycle. Grant Kimzey UTSR Intern Project Summary Webcast September 7, 2012
 Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycles and Their Application as a Bottoming Cycle Grant Kimzey UTSR Intern Project Summary Webcast September 7, 2012 Contents Introduction Assumptions and Design Parameters Benchmarks
Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycles and Their Application as a Bottoming Cycle Grant Kimzey UTSR Intern Project Summary Webcast September 7, 2012 Contents Introduction Assumptions and Design Parameters Benchmarks
Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR
 Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR 1) Objectives of the practical work The aim is to investigate the potential of Thermoptim in modeling and calculation of
Guidance page for practical work 15: modeling of the secondary circuit of a PWR 1) Objectives of the practical work The aim is to investigate the potential of Thermoptim in modeling and calculation of
SIMULATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MIXED FLUID CASCADE LNG PLANT IN A TROPICAL CLIMATE USING A COMMERCIAL SIMULATOR
 SIMULATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MIXED FLUID CASCADE LNG PLANT IN A TROPICAL CLIMATE USING A COMMERCIAL SIMULATOR Gianfranco Rodríguez 1, Fabiana Arias 1, Maria G. Quintas 1, Alessandro Trigilio
SIMULATION AND SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF A MIXED FLUID CASCADE LNG PLANT IN A TROPICAL CLIMATE USING A COMMERCIAL SIMULATOR Gianfranco Rodríguez 1, Fabiana Arias 1, Maria G. Quintas 1, Alessandro Trigilio
Christian Ohler, ABB Switzerland Corporate Research Efficiency versus Cost - a Fundamental Design Conflict in Energy Science
 Christian Ohler, ABB Switzerland Corporate Research Efficiency versus Cost - a Fundamental Design Conflict in Energy Science ABB Group August 1, 2012 Slide 1 Purpose of this Presentation (1) Clarify the
Christian Ohler, ABB Switzerland Corporate Research Efficiency versus Cost - a Fundamental Design Conflict in Energy Science ABB Group August 1, 2012 Slide 1 Purpose of this Presentation (1) Clarify the
Performance Analysis of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Using Miscible System
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 5 (5): 548-552, 2008 ISSN 1546-9239 2008 Science Publications Performance Analysis of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Using Miscible System 1 M. Thirumarimurugan, 2 T.Kannadasan
American Journal of Applied Sciences 5 (5): 548-552, 2008 ISSN 1546-9239 2008 Science Publications Performance Analysis of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Using Miscible System 1 M. Thirumarimurugan, 2 T.Kannadasan
 Proceedings of 2nd Conference: People and Buildings, held at Graduate Centre, London Metropolitan University, London, UK, 18 th of September 212. Network for Comfort and Energy Use in Buildings: http://www.nceub.org.uk
Proceedings of 2nd Conference: People and Buildings, held at Graduate Centre, London Metropolitan University, London, UK, 18 th of September 212. Network for Comfort and Energy Use in Buildings: http://www.nceub.org.uk
Green FSRU for the future
 Green FSRU for the future Presentation at GREEN4SEA Athens April 6 th 2016 Dr. John Kokarakis Vice President Technology & Business Development, Africa, S. Europe Hellenic, Black Sea & Middle East Zone
Green FSRU for the future Presentation at GREEN4SEA Athens April 6 th 2016 Dr. John Kokarakis Vice President Technology & Business Development, Africa, S. Europe Hellenic, Black Sea & Middle East Zone
ABSTRACT. Christopher Somers, Masters of Science, Dr. Reinhard Radermacher, Mechanical Engineering
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: SIMULATION OF ABSORPTION CYCLES FOR INTEGRATION INTO REFINING PROCESSES Christopher Somers, Masters of Science, 2009 Directed By: Dr. Reinhard Radermacher, Mechanical Engineering
ABSTRACT Title of Document: SIMULATION OF ABSORPTION CYCLES FOR INTEGRATION INTO REFINING PROCESSES Christopher Somers, Masters of Science, 2009 Directed By: Dr. Reinhard Radermacher, Mechanical Engineering
