Marine Microbial Processes
|
|
|
- Marjory Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving concepts 1
2 Definitions Autotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from non-organic sources. For example, phytoplankton are autotrophs because they use CO 2 for their carbon source and use sunlight for their energy source Heterotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from pre-formed organic material. For example, herbivorous zooplankton are heterotrophs because they consume phytoplankton for their carbon and energy needs. Oligotrophic: Refers to low nutrient and low productivity environments. For example the subtropical gyres are oligotrophic regions Eutrophic: Refers to high nutrient and high productivity environments. For example the coastal upwelling areas are eutrophic regions 2
3 Optimal Prey Size of Pelagic Animals Marine Food Webs are Size-Structured Our conceptualization of marine food webs is built on the general rule that preferred prey size is approximately 1/10 consumer size 3
4 Traditional Food Chain Concept (early1970 s) 4
5 Traditional Bacterial Concentrations Estimated from Transmission Light Microscopy and Culture-Plate Colony Counts Use of Epifluorescent Microscopy and Fluorescent DNA Stains Became Widespread Between 1975 and 1985 dramatically increased estimates of bacterial concentrations in the ocean Allowed easy distinction between autotrophic and heterotrophic cells (i.e., chlorophyll containing or chlorophyll lacking) 5
6 Bacterial Concentrations Before (Red Fill) and After (Blue Fill) the Introduction of Epifluorescent Microscopy New view of marine food webs that recognizes the importance of high bacterial biomass and a large fraction of nanoflagellates (2-20-micron diameter cells) that are heterotrophic What is the carbon and energy source for all this newly discovered heterotrophic bacteria? 6
7 Heterotrophic Bacteria are growing on dissolved organic matter released from phytoplankton by steady leakage,sudden cell senescence or sloppy feeding by zooplankton The term Microbial Loop is coined by Azam et al. (1983) to describe the role that microbes play in the marine ecosystem carbon cycle 7
8 Most carbon entering the heterotrophic bacteria is eventually respired back to carbon dioxide Summary: Early 1970 s versus Early 1980 s 8
9 Discovery of an Important New Bacteria-Sized Autotroph In 1988 Sally Chisholm and Others Published a Paper Describing the Presence of a New Type of Very Small Autotroph that is Present in High Abundance - Especially in Oligotrophic Regions The Discovery was Made using a New Technique called Analytical Flow Cytometry This Important New Autotroph Came to be Known as Prochlorococcus Simple Diagram of Flow Cytometeric Method 9
10 Prochlorococcus abundance is similar in magnitude to that of heterotrophic bacteria New View (1990 s) of Marine Food Webs that Recognizes the Importance of Prochlorococcus 10
11 Relative Importance of Prochlorococcus and Heterotrophic Bacteria in Oligotrophic Systems The Role of Microbes in Material Flow Through Marine Ecosystems 11
12 The Changing Role of Marine Microbes Along a Nutrient Gradient Microbes are Recyclers > Microbes are Direct Trophic Link The role of marine microbes as recyclers in eutrophic waters versus a direct trophic link in oligotrophic waters derives solely from the concept that the dominant cell size in the phytoplankton community shifts to smaller forms as nutrient concentration is reduced. 12
13 Role of Microbes in Carbon Cycling in the Ocean Carbon Cycling When the dominant phytoplankton cells are large, the dominant grazers are large and the large fecal material easily sinks to the deep ocean taking organic carbon with it - this forms an efficient biological carbon pump. The opposite is true when the dominant phytoplankton is small and the biological pump is more inefficient. 13
14 Seasonal Variation in the Global Biosphere 14
15 Magnitude of CO 2 flux between Land and Ocean Reservoirs Conclusions Heterotrophic and autotrophic bacteria make up a significant percentage of the total community biomass in the ocean In eutrophic systems the microbial community acts as a sink for organic carbon - i.e. most microbial carbon is respired back to CO 2 In oligotrophic systems, Prochlorococcus is an extremely important component of the phytoplankton the microbial community forms a direct trophic link between primary production and higher trophic levels 15
16 Conclusions As nutrient concentration is reduced the competitive growth advantage shifts to small phytoplankton cells Small phytoplankton cells enhance the importance of microbial grazers and increases the level of nitrogen recycling in the upper ocean Small phytoplankton cells also enhance the percentage of organic carbon that is respired back to carbon dioxide and consequently is NOT pumped to the deep ocean Evolving Concepts of Microbial Food Webs 16
17 High Nutrient Low Chlorophyll Regions (HNLC) Iron Cycling in HNLC Regions 17
18 Station Aloha - Subtropical North Pacific Station Aloha Time Series of N:P Ratio for Total Dissolved, Suspended Particulates in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (from Karl 1999) 18
19 Conclusion Iron limits primary production in high nutrient low chlorophyll (HNLC) regions of the Subarctic Pacific, Equatorial Pacific and Southern Ocean. North Pacific subtropical gyre seems to be moving toward phosphorus limitation due to added inputs of nitrogen to the system via nitrogen fixation. This is probably a climate change response 19
20 Good Luck to Those Students Who Are Going out on Seneca Lake Today! will be like this? or this? 20
SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION
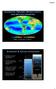 PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans
 Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Patterns of Productivity
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Name Hour. Section 3-1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63-65) Interactions and Interdependence (page 63) 1. What is ecology?
 Name Hour Section 3-1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63-65) Interactions and Interdependence (page 63) 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain? _ Levels of Organization (page 64) 3. Why do ecologists
Name Hour Section 3-1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63-65) Interactions and Interdependence (page 63) 1. What is ecology? 2. What does the biosphere contain? _ Levels of Organization (page 64) 3. Why do ecologists
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism
 Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
The Open Ocean. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
Primary Production in the Ocean
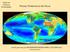 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean
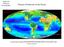 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter
 Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
Marine Processes and Ecology
 T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
Multiple Choice. Name Class Date
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
We share the Earth. Ecology & Environmental Issues
 We share the Earth Ecology & Environmental Issues 1 with a whole lot of other creatures We don t share very well. 2 Ecology Putting it all together study of interactions between creatures & their environment,
We share the Earth Ecology & Environmental Issues 1 with a whole lot of other creatures We don t share very well. 2 Ecology Putting it all together study of interactions between creatures & their environment,
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
3.4 Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary
 3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
MARINE BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: EFFECTS ON CLIMATE AND RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE
 MARINE BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: EFFECTS ON CLIMATE AND RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE Gattuso, Laboratoire d'océanographie de Villefranche, CNRS-UPMC, B. P. 28, F-06234 Villefranche-sur-mer Cedex, France. Keywords:
MARINE BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: EFFECTS ON CLIMATE AND RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE Gattuso, Laboratoire d'océanographie de Villefranche, CNRS-UPMC, B. P. 28, F-06234 Villefranche-sur-mer Cedex, France. Keywords:
Ecosystems. Studying Organisms In Their Environment. Division Ave. High School AP Biology. organism. population. community. ecosystem.
 Ecosystems Studying Organisms In Their Environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere 1 Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
Ecosystems Studying Organisms In Their Environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere 1 Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Classification of systems. Aquatic Ecosystems. Lakes 9/9/2013. Chapter 25
 Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Deep sea gradients in [DOC]
![Deep sea gradients in [DOC] Deep sea gradients in [DOC]](/thumbs/72/66709616.jpg) Deep sea gradients in [DOC] NMR and carbohydrate analyses of deep sea HMWDOC monosaccharide distribution surface relative % 5200m relative % NMR and carbohydrate analyses of deep sea HMWDOC 13 C- and 1
Deep sea gradients in [DOC] NMR and carbohydrate analyses of deep sea HMWDOC monosaccharide distribution surface relative % 5200m relative % NMR and carbohydrate analyses of deep sea HMWDOC 13 C- and 1
Cycles of Matter. Slide 1 of 33. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Denitrification 2/11/2011. Energy to be gained in oxidation. Oxidized N. Reduced N
 Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Ecology, the Environment, and Us
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives Life Depends on the Sun From Producers to Consumers An Exception: Deep-Ocean Ecosystems What Eats What Cellular Respiration: Burning
Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives Life Depends on the Sun From Producers to Consumers An Exception: Deep-Ocean Ecosystems What Eats What Cellular Respiration: Burning
Ecosystems Part 2. Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy
 Ecosystems Part 2 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Autotrophs Organisms that use the energy in sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into Glucose (food) Also called Producers because they produce
Ecosystems Part 2 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Autotrophs Organisms that use the energy in sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into Glucose (food) Also called Producers because they produce
Ecology: Part 2. Biology Mrs. Bradbury
 Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Food Webs K.Selph, OCN 621 Spring 2010
 Food Webs Relatively few species (discounting the controversy over the number of microbes) Yet: 1) High diversity in terms of trophic mode, e.g., herbivory, carnivory, mixotrophy, omnivory 2) Trophic level
Food Webs Relatively few species (discounting the controversy over the number of microbes) Yet: 1) High diversity in terms of trophic mode, e.g., herbivory, carnivory, mixotrophy, omnivory 2) Trophic level
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Cultural accelerated by anthropogenic activities
 EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world
 Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world Louis Legendre Villefranche Oceanography Laboratory, France Richard B. Rivkin Memorial University of Newfoundland,
Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world Louis Legendre Villefranche Oceanography Laboratory, France Richard B. Rivkin Memorial University of Newfoundland,
an ecosystem is a community of different species interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment of matter and energy
 1 Ecocsystems: Energy Flow and Materials Cycling 2 EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen Spring 2004 Energy Flow and Matter Cycling Energy flow s through ecosystems ecosystems global energy budget physical laws
1 Ecocsystems: Energy Flow and Materials Cycling 2 EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen Spring 2004 Energy Flow and Matter Cycling Energy flow s through ecosystems ecosystems global energy budget physical laws
What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive?
 Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles
 How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles Bubble in your ID and the answer to the 25 questions. You can look up the answers to these question on line. 1. The flow of solar energy through an
How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles Bubble in your ID and the answer to the 25 questions. You can look up the answers to these question on line. 1. The flow of solar energy through an
Does Ocean acidification change the C-flux to depth, or the strength or the efficiency of the biological pump?
 Ocean Carbon Ballasting Respiration, decomposition and export Uta Passow (AWI, Bremerhaven and MSI, UC Santa Barbara) Does Ocean acidification change the C-flux to depth, or the strength or the efficiency
Ocean Carbon Ballasting Respiration, decomposition and export Uta Passow (AWI, Bremerhaven and MSI, UC Santa Barbara) Does Ocean acidification change the C-flux to depth, or the strength or the efficiency
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles
 Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE. nutrients: aka.
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5
 Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5 Energy Exchange in Ecosystems Cells Cells - minute compartments in a living organism which carry out processes of life Surrounded by lipid membrane controlling flow of materials
Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5 Energy Exchange in Ecosystems Cells Cells - minute compartments in a living organism which carry out processes of life Surrounded by lipid membrane controlling flow of materials
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability. Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612
 Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612 Sunlight CO 2 + 2H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 + H 2 O + heat Gross Primary Production (GPP): The rate of organic
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612 Sunlight CO 2 + 2H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 + H 2 O + heat Gross Primary Production (GPP): The rate of organic
Dynamics of Ecosystems. Chapter 57
 Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Part IV Living World
 Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG
 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in
 Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
Chapter 4. Ecosystems
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles
 The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Reading Questions
 APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea. Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton
 10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
Seasonal Stable Isotope Trends In Finger Lake Food Webs. Peter Smyntek, Mark Teece, Kim Schulz, and Adam Storch
 Seasonal Stable Isotope Trends In Finger Lake Food Webs Peter Smyntek, Mark Teece, Kim Schulz, and Adam Storch Overview Stable Isotope (SI) Basics & Food Web Diagrams Why Consider Seasonality? Project
Seasonal Stable Isotope Trends In Finger Lake Food Webs Peter Smyntek, Mark Teece, Kim Schulz, and Adam Storch Overview Stable Isotope (SI) Basics & Food Web Diagrams Why Consider Seasonality? Project
SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS
 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Earth's Life Support System Earth's major components Ecosystem System of interaction among all living (biotic) organisms of an area and their interactions with the (abiotic) environment.
SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Earth's Life Support System Earth's major components Ecosystem System of interaction among all living (biotic) organisms of an area and their interactions with the (abiotic) environment.
Energy Transfer p
 Energy Transfer 22-1 p. 415-419 Essential Questions 1. Identify and describe the main types of producers and consumers in an ecosystem. 2. Calculate the amount of energy stored in biomass transferred from
Energy Transfer 22-1 p. 415-419 Essential Questions 1. Identify and describe the main types of producers and consumers in an ecosystem. 2. Calculate the amount of energy stored in biomass transferred from
What does each part of the equation mean? q=cm T
 Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
CHAPTER 49 ECOSYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 49 ECOSYSTEMS I. INTRODUCTION A. An ecosystem 1. Whereas a community consists of all the organisms in a certain boundary that are close enough for some sort of interaction, an ecosystem: -is defined
CHAPTER 49 ECOSYSTEMS I. INTRODUCTION A. An ecosystem 1. Whereas a community consists of all the organisms in a certain boundary that are close enough for some sort of interaction, an ecosystem: -is defined
4/13/2015. The Biosphere
 The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background
 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
The Carbon Cycle. Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 DATE: NAME: CLASS:
 CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
1. What are the 8 levels of organization in ecology? 1. Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population
 1. What are the 8 levels of organization in ecology? 1. Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population (from large to small) Species Tissues Cells - Molecules 2. What is the smallest unit of life? 2. The cell
1. What are the 8 levels of organization in ecology? 1. Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population (from large to small) Species Tissues Cells - Molecules 2. What is the smallest unit of life? 2. The cell
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Trophic Interactions
 Trophic Cascading Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Control of Primary Production Only about one-half of the variation in primary production among lakes worldwide can be explained
Trophic Cascading Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Control of Primary Production Only about one-half of the variation in primary production among lakes worldwide can be explained
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling
 Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
3 2 Energy Flow. Slide 1 of 41. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
1 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the
 Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY. Interspecific Interactions. Ecosystems unit
 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
3-1 What is Ecology?! The study of the. interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
 Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
Ecosystems: What are they and how do they work? C H A P T E R 3
 Ecosystems: What are they and how do they work? C H A P T E R 3 Ecology and Life Ecology- study of relationships between organisms and their environment Ecology examines how organisms interact with their
Ecosystems: What are they and how do they work? C H A P T E R 3 Ecology and Life Ecology- study of relationships between organisms and their environment Ecology examines how organisms interact with their
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Communities What organizes biology above the level of the population?
 ECOLOGY part 2 Populations/Communities Similar species can co-exist more readily if they utilize different portions of shared niche axes have different niches (determined by traits) Coastal wetland So,
ECOLOGY part 2 Populations/Communities Similar species can co-exist more readily if they utilize different portions of shared niche axes have different niches (determined by traits) Coastal wetland So,
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
Interpreting Lake Data
 Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective
 Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective M. Rawson 1, Chen 2 C., Ji R.1, Zhu 3 M., Wang 4 D., C. Yarish 5, J. Sullivan 1 1 Georgia Sea Grant College Program, School of Marine Program,
Approaching Coastal Aquaculture from an Ecosystem Perspective M. Rawson 1, Chen 2 C., Ji R.1, Zhu 3 M., Wang 4 D., C. Yarish 5, J. Sullivan 1 1 Georgia Sea Grant College Program, School of Marine Program,
GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB
 Names: Lab Section: each group of 2 turns in one lab GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB This is a computer-based lab exercise in which we will use an incredible computer resource to visually explore a huge
Names: Lab Section: each group of 2 turns in one lab GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB This is a computer-based lab exercise in which we will use an incredible computer resource to visually explore a huge
buried in the sediment; the carbon they contain sometimes change into fossil fuels; this process takes millions of years
 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback
 Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback Resource M1 Source: NASA/GFSC Composite satellite image of phytoplankton abundance between 1978 and 1986. False colours code for low (blues and purples)
Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback Resource M1 Source: NASA/GFSC Composite satellite image of phytoplankton abundance between 1978 and 1986. False colours code for low (blues and purples)
1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods?
 Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017
 MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest
 Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
Energy Flow Through Living Systems
 1 The diagram below shows the overall flow of energy through living things. At each step, the transfer of energy involves a loss of energy in the form of heat and body activities. For example, when you
1 The diagram below shows the overall flow of energy through living things. At each step, the transfer of energy involves a loss of energy in the form of heat and body activities. For example, when you
Feeding Relationships and trophic levels
 Feeding Relationships and trophic levels All life needs a source of energy. Therefore, the life in an ecosystem need energy too! The sun provides that energy. The sun s energy is not DIRECTLY usable by
Feeding Relationships and trophic levels All life needs a source of energy. Therefore, the life in an ecosystem need energy too! The sun provides that energy. The sun s energy is not DIRECTLY usable by
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet
 ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
Chapter 3 The Biosphere. Section Objectives:
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section Objectives: Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Compare the different levels of biological organization and living relationships important
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section Objectives: Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Compare the different levels of biological organization and living relationships important
Ontogeny of Lakes. Successional Development of Lake Ecosystems
 Ontogeny of Lakes Successional Development of Lake Ecosystems Factors That Determine Rates of Ontogeny Filling rates Inorganic material Basin morphometry Drainage basin characteristics Climatic factors
Ontogeny of Lakes Successional Development of Lake Ecosystems Factors That Determine Rates of Ontogeny Filling rates Inorganic material Basin morphometry Drainage basin characteristics Climatic factors
The Carbon cycle. Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon
 The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
SC20F Ecology Unit Review Name:
 SC20F Ecology Unit Review Name: 1. Define the following terms. Give an example where appropriate: a. Ecosystem An area consisting of living organisms and their physical environment b. Habitat - the place
SC20F Ecology Unit Review Name: 1. Define the following terms. Give an example where appropriate: a. Ecosystem An area consisting of living organisms and their physical environment b. Habitat - the place
Lecture 2. Energy and Ecosystems. Lecture 2
 Lecture 2 Energy and Ecosystems Lecture 2 1. Ecology The Ecological Hierarchy 2. Energy Laws of Thermodynamics Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 3. Flow of Energy Through Ecosystems Producers, Consumers
Lecture 2 Energy and Ecosystems Lecture 2 1. Ecology The Ecological Hierarchy 2. Energy Laws of Thermodynamics Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 3. Flow of Energy Through Ecosystems Producers, Consumers
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
