Answers. Earth s Resources. Year 7 Science Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Joshua Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answers Earth s Resources Year 7 Science Chapter 6 p132 1 Five of Earth s resources that are vital for human survival: Water, air, plants, animals, salt, soil. 2 Ten of Earth s resources that, while not vital for human survival, improve our quality of life: Oil, coal, gas, iron, copper, timber, cotton, wool, sand, limestone. 3 Five of Earth s resources that are used to increase wealth: Gold, diamonds, platinum, sapphire, ruby. 4 Three of Earth s resources that are inexhaustible (cannot be used up): Air, soil, salt water. 5 Three of Earth s resources that are extremely rare: Gold, diamonds, scandium, terbium. 6 Less waste and more resources suggests that the less we waste, the more resources that will be available for us to use. p133 1 Renewable resources can be replaced relatively quickly. 2 Non-renewable resources are not able to be replaced or take a very long time to be replaced. 3 Label each of the following Earth s resources as either renewable or non-renewable Oil - non-renewable Sugar - renewable Rice - renewable Timber - renewable Gas - non-renewable Iron - non-renewable Fish - renewable Diamonds - non-renewable Beef - renewable Sand - non-renewable Water - renewable Coal - non-renewable 4 Is the tragedy of the commons an example of how a renewable resource can become a non-renewable resource? Grass is a renewable resource if given time to regrow after grazing. The tragedy of the commons suggests that severe continued over grazing will kill the grass and grass will then become a non-renewable resource. 5 Can you think of another resource, other than grass in a common paddock, that can be destroyed by the Tragedy of the Commons? The tragedy of the commons could apply to many renewable resources such as timber. Severe use of timber could use up all timber stocks and it may then need 15 to 20 years to grow new stock making it a long time to be replaced - non-renewable. Fisheries would be another example. p135 1 Australia s three major energy sources: Oil, coal, gas. 2 If 95% of Australia s energy comes from non-renewable sources, then 5% of Australia s energy comes from renewable sources. 3 Australia s major renewable energy source is biomass (wood and bagasse). 4 a) Coal is the energy source expected to reduce the most by b) Gas is the energy source is expected to increase the most by c) Given that a petajoule is the equivalent of tonnes of coal, roughly how many tonnes of coal was used in 2010? The graph suggests that 2200 petajoules of energy was supplied by coal in petajoules equivalent to = tonnes of coal used in 2010
2 p136 1 Coal is called a fossil fuel because it was formed from the remains of plants and animals. 2 Coal is described as non-renewable because will take a very long time to be replaced. 3 The major advantage of using coal as an energy source is that it is cheap. 4 The major disadvantage of using coal as an energy source is that it produces carbon dioxide and adds to the greenhouse effect. 5 The two main Earth resources needed for a coal power plant is coal and water 6 Open cut mining would be cheaper than underground mining. 7 High quality coal will burn easily. A coal fire in a large open cut mine is difficult to extinguish and a major strategy is to restrict oxygen from the fire by using water and foam for example. Coal fires are often left to burn themselves out. p137 1 Oil is called a fossil fuel because it was formed from the remains of plants and animals. 2 Oil is described as non-renewable because will take a very long time to be replaced. 3 The major advantage of using oil as an energy source is that it is a cheap fuel that is easy to extract and transport. 4 The major disadvantage is that burning oil produces carbon dioxide and adds to the greenhouse effect. 5 I would expect the price of oil to rise steeply in the next 20 years as oil becomes scarce. 6 I would expect the current rate of use of oil to decrease over the next 20 years as oil becomes scarce. 7 Another 10 transport machines that use petrol or diesel for power: Cars, motorbikes, trains, ships, helicopters, buses, jet ski, tanks, tractors, air cushion amphibious vehicle. p138 1 Natural gas is called a fossil fuel because it was formed from the remains of plants and animals. 2 Gas is described as non-renewable because will take a very long time to be replaced. 3 Gas is easy to extract and to transport through pipelines. This makes gas a cheap fuel. 4 The major disadvantage of using coal as an energy source is that it produces carbon dioxide and adds to the greenhouse effect. 5 The Huntly power station uses water from the nearby river. A condition of use is that water returned to the river must be less than 25 C. a) 25 C is set as the maximum temperature of returned water to avoid damage to the environment. b) In hot weather, the 25 C condition would be difficult to achieve and would add cost to the production of electricity. 6 The Huntly power station contributes more than 50% of New Zealand s greenhouse carbon dioxide emissions. The Huntly power station may be able to reduce its carbon dioxide emissions by trapping the carbon dioxide and converting it to a solid form such as carbon. Other reductions may be obtained by reducing the use of electricity throughout the country.
3 p140 1 Examples of biomass are wood, bagasse, and animal fats. 2 5 examples of biomass that may be found at the garbage dump are timber, paper, cardboard, waste foods, waste oil, waste grease. 3 Biomass energy is described as renewable because can be replaced in a short time (Waste products are continually being produced). 4 Three safety problems that need to be considered when using a methane generator: Methane gase is explosive and dangerous, the biomass used is a health hazard, the production of methane involves many types of bacteria including dangerous bacteria. 5 Which is the more damaging greenhouse gas, methane or carbon dioxide? Methane is more effective in trapping heat than carbon dioxide while there is considerably more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 6 Reorder the following renewable energy sources from most used to least used: Biomass, Hydro energy, Wind energy, Solar energy, Geothermal energy,. 7 Biomass sources such as forests can take as long as 30/40 years to grow to maturity. Forests ar genrally considered to be renewable because there is a continual source of timber reaching maturity through controlled production. However, if very strong demand reduced the stocks and it would take 30/40 years for timber to become available then timber could be considered to be non-renewable. p141 1 Hydro is the Greek word for water. 2 Hydro energy described as renewable because the water used at the power station is being replaced by rain within a comparatively short time. 3 Hydroelectric generation doesn t pollute the atmosphere. The water storage can also be used for irrigation and tourist attractions. The amount of hydroelectricity can also be increased and decreased as needed. 4 A hydroelectric power station is very expensive to build. It usually takes decades for a hydroelectric power station to become profitable. 5 Energy can also be taken from waves and tides as the waves and tides rise and fall. 6 The Basslink project cost around $800 million to complete in a) The Basslink Interconnector enhances security of supply on both sides of Bass Strait; protecting Tasmania against the risk of drought-constrained energy shortages while providing Victoria and southern states with secure renewable energy during times of peak demand. b) Connecting all electricity power stations in Australia be would allow even distribution of electricity over different peak times from the eastern states to the western states. It would also allow sharing of renewable energy from advantaged areas to all areas. It would also allow more stable energy supply and less disruption. However the cost of connection would be enormous. 7 Two reasons why Australia has relatively little hydroelectric power resources: Australia has plenty of cheap coal as a power source, Australia has a relatively small number of locations suitable for hydroelectric power stations.
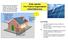
4 p142 1 Wind energy is described as renewable because is replaced in a short time. 2 Wind turbines take up small areas of land and produce few pollutants. The wind is free. Wind energy is most useful in remote areas that aren t connected to a power grid. 3 The initial cost of setting up a wind turbine is high. Wind turbines are noisy and their electricity production is dependent on wind which can vary from dead calm to storm force watt-hours = 17 kilowatt-hours. 5 Calculate the daily electrical output of a 1000 watt wind turbine (assume 20 hours of useful wind). Energy = 1000 watts 20 hours = watt-hours = 20 kilowatt-hours 6 Calculate the daily electrical output of five 5000 watt wind turbines (assume 15 hours of useful wind). Energy = watts 15 hours = watt-hours = 375 kilowatt-hours 7 Assuming that the average family uses 15 kilowatt-hours of power daily, how many hours of useful wind would be needed to supply their daily electricity needs (assume a 1000 watt wind turbine). Energy = 1000 watts x hours 15 kilowatt-hours = 1000 watts x hours watt-hours = 1000 watts x hours 15 hours = x hours Thus need 15 hours per day of useful wind. p143 1 Solar energy is described as renewable because is being continually produced by the Sun. 2 Solar energy has many advantages. It is quiet, doesn t use water, and doesn t produce pollutants. 3 The major disadvantage is the relatively high initial cost. 4 Calculate the daily electrical output of ten 200 watt panels (assume 5 hours of sunlight). Energy = watts 5 hours = watt-hours = 10 kilowatt-hours 5 Calculate the daily electrical output of fifteen 230 watt panels (assume 8 hours of sunlight). Energy = watts 8 hours = watt-hours = 27.6 kilowatt-hours 6 The above shed appears to have one hundred and twenty 200 watt panels. Calculate the daily electrical output assuming 8 hours of sunlight. Energy = watts 8 hours = watt-hours = 192 kilowatt-hours 7 Assuming that the average family uses 15 kilowatt-hours of power daily, how many 200 watt panels would be needed to supply their daily electricity needs (assume 5 hours of sunlight). Energy = 1000 watts x hours 15 kilowatt-hours = x 200 watts 8 hours watt-hours = x 1600 watts-hours = x Thus need ten 200 watt panels.
5 p144 2 Geothermal energy is described as non-renewable because the amount of geothermal energy appears to be unlimited. 2 Geothermal energy is free and can be unlimited. 3 Geothermal power stations can release some greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Geothermal water can also contain toxic chemicals such as mercury and arsenic. 4 The Australian Cooper Basin has the hottest rocks in the world, away from volcanoes and at economic depth. 5 How many homes could be supplied by a 10 megawatt geothermal power station (assume the average household uses 16 kilowatt-hours of electricity daily)? Energy = x homes 16 kilowatt-hours kilowatts 24 hours = x 16 kilowatt-hours kilowatt-hours = x 16 kilowatt-hours = x = x A 10 megawatt geothermal power station would supply fifteen thousand homes. 6 How many homes could be supplied by a 20 megawatt geothermal power station (assume the average household uses 20 kilowatt-hours of electricity daily)? Energy = x homes 20 kilowatt-hours kilowatts 24 hours = x 20 kilowatt-hours kilowatt-hours = x 20 kilowatt-hours = x = x A 20 megawatt geothermal power station would supply twenty-four thousand homes. 7 Assuming that the average home uses 16 kilowatt-hours of power daily, what capacity geothermal power station would be needed to supply a village of 500 homes? Energy = 500 homes 16 kilowatt-hours x kilowatts 24 hours = 8000 kilowatt-hours x 24 kilowatt-hours = 8000 kilowatt-hours x = x = 333 A 350 kilowatt geothermal power station would supply five hundred homes. p kilowatt-hours = 5 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules = 18 kj (kilojoules) 2 10 kilowatt-hours = 10 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules = 36 kj (kilojoules) 3 12 kilowatt-hours = 12 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules = 43.2 kj (kilojoules) 4 16 kilowatt-hours = 16 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules = 57.6 kj (kilojoules) 5 Convert 20 kilowatt-hours to joules kilowatt-hours = 20 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules = 72 kj (kilojoules)
6 p145 6 How much energy, in joules, is produced by a 5 watt solar panel in direct sunlight for 2 hours? Energy = 5 watts 2 hours = 5 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules Energy = 36 kilojoules 7 How much energy, in joules, is produced by a 15 watt solar panel in sunlight for 5 hours? Energy = 15 watts 5 hours = 15 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules Energy = 270 kilojoules 8 How much energy, in joules, is produced by a 250 watt solar panel in sunlight for 5 hours? Energy = 250 watts 5 hours = 250 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules Energy = 4500 kilojoules 9 How much energy, in joules, is produced by a 20 watt wind turbine (assume 16 hours of useful wind)? Energy = 20 watts 16 hours = 20 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules Energy = 1152 kilojoules 10 How much energy, in joules, is produced by five 1000 watt wind turbines (assume 18 hours of useful wind)? Energy = watts 18 hours = 5000 watts seconds = watt-seconds = joules Energy = kilojoules p146 1 Renewable resources can be replaced relatively quickly. 2 Non-renewable resources are not able to be replaced or take a very long time to be replaced. 3 Label each of the following Earth s resources as either renewable or non-renewable Oil - non-renewable Sugar - renewable Rice - renewable Timber - renewable Gas - non-renewable Iron - non-renewable Fish - renewable Diamonds - non-renewable Beef - renewable Sand - non-renewable Water - renewable Coal - non-renewable 4 Three of Earth s resources that are inexhaustible (cannot be used up): Air, soil, saltwater, geothermal energy. 5 Less waste and more resources suggests that the less we waste, the more resources that will be available for us to use. 6 Is the tragedy of the commons an example of how a renewable resource can become a non-renewable resource? Grass is a renewable resource if given time to regrow after grazing. The tragedy of the commons suggests that severe continued over grazing will kill the grass and grass will then become a non-renewable resource.
7 p146 1 Coal, oil, and natural gas are called fossil fuels because they were formed from the remains of plants and animals. 2 Coal, oil, and natural gas are described as non-renewable because will take a very long time to be replaced. 3 Uranium described as non-renewable because will take a very long time to be replaced. 5 The major advantage of using coal, oil, and natural gas as an energy source is that they are cheap. 4 The major disadvantage of using coal, oil, and natural gas as an energy source is that they produce carbon dioxide and add to the greenhouse effect. 5 The two main Earth resources needed for a coal power plant is coal and water 6 The major disadvantage of using uranium as an energy source is the production of very dangerous waste products. 7 Two major advantages of using uranium as an energy source are that small quantities of uranium can produce massive amounts of cheap energy through nuclear fission. 8 I would expect the price of coal, oil, and natural gas to rise steeply in the next 20 years as these fossil fuels become scarce. p147 1 Mass = gram = grams = 1000 kilograms = 1 tonne 2 Increase of 10% = $ % of $100 = $ $100 = $100 + $10 = $110 Decrease of 10% = $110 10% of $110 = $ $110 = $110 $11 = $99 3 Calculate the volume of the cube of side 6 cm. Calculate the volume of the cube of side 8 cm. Volume = side side side = side 3 Volume = side side side = side 3 = (6 cm) 3 = (8 cm) 3 = cm 3 = cm 3 = 216 cm 3 = 512 cm 3 Calculate the volume of the cube of side 10 cm. Calculate the volume of the cube of side 12 cm. Volume = side side side = side 3 Volume = side side side = side 3 = (10 cm) 3 = (12 cm) 3 = cm 3 = cm 3 = 1000 cm 3 = 1728 cm 3 The balance will be balanced with the 12 cm cube on one side and the three other cubes on the other side.
8 p148 1 Biomass is biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms. Examples of biomass are wood, bagasse, and animal fats. 2 Biomass energy, hydro energy, wind energy, solar energy, and geothermal energy is described as renewable because it can be replaced in a short time or is inexhaustible. 3 Which is the more damaging greenhouse gas, methane or carbon dioxide? Methane is more effective in trapping heat than carbon dioxide while there is considerably more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 4 Reorder the following renewable energy sources from most used to least used: Biomass, Hydro energy, Wind energy, Solar energy, Geothermal energy,. 5 Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using each of the following renewable energy sources: Solar energy, Geothermal energy, Hydro energy, Biomass, Wind energy. Advantages are that many of them are free and unlimited. Disadvantages are that it is expensive to establish the production of energy from these sources. 6 How many homes could be supplied by a 10 megawatt geothermal power station (assume the average household uses 16 kilowatt-hours of electricity daily)? Energy = x homes 16 kilowatt-hours kilowatts 24 hours = x 16 kilowatt-hours kilowatt-hours = x 16 kilowatt-hours = x = x A 10 megawatt geothermal power station would supply fifteen thousand homes. 7 How many homes could be supplied by a 20 megawatt geothermal power station (assume the average household uses 20 kilowatt-hours of electricity daily)? Energy = x homes 20 kilowatt-hours kilowatts 24 hours = x 20 kilowatt-hours kilowatt-hours = x 20 kilowatt-hours = x = x A 20 megawatt geothermal power station would supply twenty-four thousand homes. 8 Assuming that the average home uses 16 kilowatt-hours of power daily, what capacity geothermal power station would be needed to supply a village of 500 homes? Energy = 500 homes 16 kilowatt-hours x kilowatts 24 hours = 8000 kilowatt-hours x 24 kilowatt-hours = 8000 kilowatt-hours x = x = 333 A 350 kilowatt geothermal power station would supply five hundred homes. 9 Calculate the daily electrical output of a 1000 watt wind turbine (assume 20 hours of useful wind). Energy = 1000 watts 20 hours = watts (or 20 kilowatts) = watts seconds = watt-seconds Energy = kilojoules
9 p Calculate the daily electrical output of ten 200 watt panels (assume 5 hours of sunlight). Energy = watts 5 hours = watt-hours = 10 kilowatt-hours 11 Two reasons why Australia has relatively little hydroelectric power resources: Australia has plenty of cheap coal as a power source, Australia has a relatively small number of locations suitable for hydroelectric power stations. p149 1 b) 2 d) 3 c) 4 Assume a TV uses 650 joules of electrical energy. 400 joules goes to useful light energy, 150 joules goes to useful sound energy, and, a) 50 joules goes to wasted heat energy. b) 100 joules goes to wasted heat energy. c) 50 joules goes to useful chemical energy. d) 100 joules goes to useful chemical energy. Answer = b) p150 1 a) Solar energy shown on the graph because its use is too small to show on the graph. b) I would expect the amount of energy sourced from renewable sources such as solar to increase as governments support the use of renewable energy. I would also expect the amount of renewable energy to increase as the costs of energy from non-renewable sources such as oil, coal, and gas to increase as they become rarer. 2 a) The family is using 0.5 kilowatts early in the morning when everyone would be expected to be asleep as energy is used to power fridges, air conditioners, and other devices on standby. b) More energy used being used at 8 pm than at 8am as people use stoves and microwaves to cook dinner and take baths (More so than in the mornings). c) Roughly estimate how many kilowatt-hours this family uses in a day. A rough average is about 1.2 kilowatts over 24 hours = 28.8 kilowatt-hours d) If electricity is $0.30 per kilowatt-hour, what is the electricity cost for this family for a quarter (3 months)? Cost = 28.8 kilowatt-hours per day $0.30 per kilowatt-hour 90 days per quarter = $777.60
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Effects of Energy Transfer. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
Introduction to Energy
 Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Activity 3 Information sheet
 Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
Y7 Energy Summary Booklet
 Y7 Energy Summary Booklet Energy Units Energy changes are measured in joules (J) or kilojoules (kj). Energy Stores and Transfers Energy stores Key word Description Examples Magnetic The energy stored in
Y7 Energy Summary Booklet Energy Units Energy changes are measured in joules (J) or kilojoules (kj). Energy Stores and Transfers Energy stores Key word Description Examples Magnetic The energy stored in
Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy.
 Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Energy. Solar Energy. Energy Resource A natural resource that. humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable.
 Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
 ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources. Energy
 Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources Energy SOURCES OF ENERGY RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Infinite supply NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Limited supply Part 1 Fossil Fuels NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS Coal,
Chapter 4.2: Energy Sources Energy SOURCES OF ENERGY RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Infinite supply NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Limited supply Part 1 Fossil Fuels NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS Coal,
Generating Electricity
 Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives?
 Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives? Life requires energy it is stored, transferred, and converted Ultimate source of energy for life the Sun For humans, our source of energy
Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives? Life requires energy it is stored, transferred, and converted Ultimate source of energy for life the Sun For humans, our source of energy
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Energy is the ability to do work. Light Motion (kinetic) Heat Electrical Energy can be found in different forms. Chemical Sound
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Energy is the ability to do work. Light Motion (kinetic) Heat Electrical Energy can be found in different forms. Chemical Sound
Uma. V Embassy Public School
 Uma. V Embassy Public School Contents Introduction Need for renewable energy Sources of renewable energy Advantages of renewable energy Forms of renewable energy Sun, our saviour Introduction Energy is
Uma. V Embassy Public School Contents Introduction Need for renewable energy Sources of renewable energy Advantages of renewable energy Forms of renewable energy Sun, our saviour Introduction Energy is
Lesson 5 Energy. OAA Science Lesson 5 52
 Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
Coal, oil, natural gas Nuclear (radioactivity from uranium) biomass fuel (such as wood
 16.1 Natural Resources and Energy For tens of thousands of years, people have depended on Earth s resources for food, clothing, shelter, energy, medicine, and even entertainment, arts, and riches. What
16.1 Natural Resources and Energy For tens of thousands of years, people have depended on Earth s resources for food, clothing, shelter, energy, medicine, and even entertainment, arts, and riches. What
learning objectives subjects Environmental Education Science Social Studies materials Power to the People Background
 climate of causes change Power to the People learning objectives subjects Environmental Education Science Social Studies Students will: Identify sources of energy used in Wisconsin. Research different
climate of causes change Power to the People learning objectives subjects Environmental Education Science Social Studies Students will: Identify sources of energy used in Wisconsin. Research different
P2 Revision Questions
 P2 Revision Questions Part 1 Question 1 What is an alternating current? Answer 1 Where electrons move backwards and forwards across a point (not in one direction) Question 2 What is a direct current? Answer
P2 Revision Questions Part 1 Question 1 What is an alternating current? Answer 1 Where electrons move backwards and forwards across a point (not in one direction) Question 2 What is a direct current? Answer
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
4/30/12. Chapter: Energy Sources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
1. You can generate electricity for use in your own home using a wind turbine fixed above the roof.
 Generating electricity 1. You can generate electricity for use in your own home using a wind turbine fixed above the roof. (a) Wind is a renewable energy source. Which one of the following is not a renewable
Generating electricity 1. You can generate electricity for use in your own home using a wind turbine fixed above the roof. (a) Wind is a renewable energy source. Which one of the following is not a renewable
ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION
 1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
 Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Name Date Class. How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources?
 Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels.
 Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
Energy: Conservation and Transfer
 Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Chapter 14: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 14: Sources of Energy Question 1 What is a good source of energy? A good source of energy would be one, 1. Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or per unit mass 2. Which would
Chapter 14: Sources of Energy Question 1 What is a good source of energy? A good source of energy would be one, 1. Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or per unit mass 2. Which would
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009
 Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009 Science A Unit Physics P1a (Energy and Electricity)
Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier November 2009 Science A Unit Physics P1a (Energy and Electricity)
Power Technologies. Question. Answer. Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. Answer. Question. What are the various sources of energy?
 What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
S2 Science Physics. Energy Matters. Name:
 S2 Science Physics Energy Matters Name: Experiences and Outcomes SCN 3-04a - I can use use my knowledge of different ways in which heat is transferred to improve the energy efficiency of systems. SCN 3-04b/4-04a
S2 Science Physics Energy Matters Name: Experiences and Outcomes SCN 3-04a - I can use use my knowledge of different ways in which heat is transferred to improve the energy efficiency of systems. SCN 3-04b/4-04a
M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]
![M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M1. allow 1 mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3]](/thumbs/85/92444350.jpg) M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
M. allow mark for each correct line if more than one line goes from an energy source then all lines from that energy source are wrong [3] M2. (a) gas (burning) (b) (i) (transmission) cables and (step-up
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely
 Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Solar panels The Fizzics Organisation
 Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Environmental Resources: Renewable & Non-Renewable Resources & Energy
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Coal is obtained from mines. It's a black solid material that must be transported by ships, trains or big trucks to the power plants where it's burnt
 Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
Large gas reserves are found in: The Arctic Islands Beaufort Sea-Mackenzie Delta Eastern Canada offshore basin Western Canada
 1 12. Natural Gas It is formed from the remains of plankton that fell to the bottom of the sea, which were changed into gases over millions of years Since natural gas is lighter than both oil and water
1 12. Natural Gas It is formed from the remains of plankton that fell to the bottom of the sea, which were changed into gases over millions of years Since natural gas is lighter than both oil and water
A is any natural material that is used by humans.
 Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY
 CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision sheets
 Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
Academic Year 2016-2017 Second Term Science Revision sheets Name: Grade:8 Date: Section: (A) Science Practice : Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Coal is a natural
- renewable - cheap - no pollution. - expensive equipment - no energy on cloudy or rainy days
 Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
16.3 Electric generators and transformers
 ElEctromagnEts and InductIon Chapter 16 16.3 Electric generators and transformers Motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric generators do the opposite. They transform mechanical
ElEctromagnEts and InductIon Chapter 16 16.3 Electric generators and transformers Motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric generators do the opposite. They transform mechanical
Voltage: electrical energy that is used to push electricity through a wire
 Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY. Ajay Kumar Jakhar
 RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY Ajay Kumar Jakhar Renewable energy is energy that comes from resources which are continually replenished such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. In
RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY Ajay Kumar Jakhar Renewable energy is energy that comes from resources which are continually replenished such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. In
INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY SYSTEMS (ELE 210 ) Lecture 03 (Nonrenewable Energy)
 INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY SYSTEMS (ELE 210 ) Lecture 03 (Nonrenewable Energy) COAL, PETROLEUM, AND GAS Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are considered nonrenewable because they can not be replenished in a
INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY SYSTEMS (ELE 210 ) Lecture 03 (Nonrenewable Energy) COAL, PETROLEUM, AND GAS Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are considered nonrenewable because they can not be replenished in a
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S
 LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence. Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects.
 Page 1 What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects. What type of surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of infrared
Page 1 What type of radiation transmits heat energy? Complete this sentence Hotter objects emit infrared radiation than cooler objects. What type of surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of infrared
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment
 ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment British thermal unit (Btu) = amount of heat needed to raise one pound of water at maximum density through one degree Fahrenheit. 1Btu = 1.055 10 3 joules tonne of oil
ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment British thermal unit (Btu) = amount of heat needed to raise one pound of water at maximum density through one degree Fahrenheit. 1Btu = 1.055 10 3 joules tonne of oil
FOSSIL FUELS THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE WORLD'S ELECTRICAL POWER, AND 95% OF THE WORLD'S TOTAL ENERGY DEMANDS.
 ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS COAL, OIL AND NATURAL GAS ARE CALLED "FOSSIL FUELS" BECAUSE THEY HAVE BEEN FORMED FROM THE FOSSILIZED REMAINS OF PREHISTORIC PLANTS AND ANIMALS. THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE
ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUELS COAL, OIL AND NATURAL GAS ARE CALLED "FOSSIL FUELS" BECAUSE THEY HAVE BEEN FORMED FROM THE FOSSILIZED REMAINS OF PREHISTORIC PLANTS AND ANIMALS. THEY PROVIDE AROUND 66% OF THE
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what. conduction is. Does conduction happen best in solids, liquids or gases?
 What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
What are the 3 ways in which energy can travel? Explain what conduction is What type of materials are good conductors and what type of materials are bad conductors (good insulators)? Does conduction happen
Alternative Energy Resources. Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011
 Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
Renewable Energy Today
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information
 Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Natural Resources. Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School
 Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
sources, conserving energy & efficiency.notebook. December 15, Sources of Electrical Energy: How does a generator work?
 Sources of Electrical Energy Efficiency Cost of Electricity SNC 1P/D Sources of Electrical Energy: Energy comes in many different forms, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), chemical energy (energy
Sources of Electrical Energy Efficiency Cost of Electricity SNC 1P/D Sources of Electrical Energy: Energy comes in many different forms, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), chemical energy (energy
WORK Potential Kinetic
 Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Human Dependence on Natural Resources
 You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST
 RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Name Class Date. What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable energy resources? What are renewable energy resources?
 CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO
 UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO 1. WHAT IS ENERGY? Definition: Energy is a physical quantity which produces a change or an effect Unit: International System Joule (J) Other Calorie (cal) 1cal =4,19J
UNIT 10: ENERGY ISABEL CORONADO ROMERO 1. WHAT IS ENERGY? Definition: Energy is a physical quantity which produces a change or an effect Unit: International System Joule (J) Other Calorie (cal) 1cal =4,19J
Draw one line from each energy source in List A to the statement about the energy source in List B.
 1 Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in List
1 Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in List
Unit 5. Energy. 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 Unit 5. Energy 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández What is energy? Energy has no mass and occupies no space but it makes things happen. We know it exists because we see the effects
Unit 5. Energy 5 primary / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández What is energy? Energy has no mass and occupies no space but it makes things happen. We know it exists because we see the effects
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today
 Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
pages 98 and Renewable and non-renewable resources
 pages 98 and 99 8.1 Renewable and non-renewable resources Anything that people find useful is a resource. Human resources include labour, machinery and money. Stone, water, soil and timber are natural
pages 98 and 99 8.1 Renewable and non-renewable resources Anything that people find useful is a resource. Human resources include labour, machinery and money. Stone, water, soil and timber are natural
Use words from the box to answer the questions below. chemical electrical gravitational potential. kinetic light sound thermal
 Energy Transfer Exam Practice Q1. In a power station, coal can be used to generate electricity. Drayton Manor High School (a) Use words from the box to answer the questions below. chemical electrical gravitational
Energy Transfer Exam Practice Q1. In a power station, coal can be used to generate electricity. Drayton Manor High School (a) Use words from the box to answer the questions below. chemical electrical gravitational
Energy and Global Issues
 Energy and Global Issues Chemical reactions Reactions that release heat are exothermic Reactions that absorb heat from surroundings are endothermic The energy involved in chemical reactions is measured
Energy and Global Issues Chemical reactions Reactions that release heat are exothermic Reactions that absorb heat from surroundings are endothermic The energy involved in chemical reactions is measured
Boardworks Ltd Energy Resources
 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Energy Resources Energy Resources 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are energy resources? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 An energy resource is anything that can be used to generate
1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Energy Resources Energy Resources 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are energy resources? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 An energy resource is anything that can be used to generate
Unit 4 Energy Review. Student. 1. Which is a problem with using wind turbines to produce energy? A. Wind turbines are efficient only in certain areas.
 Unit 4 Energy Review Student 1. Which is a problem with using wind turbines to produce energy? A. Wind turbines are efficient only in certain areas. B. Wind turbines occupy a small area of land. C. Wind
Unit 4 Energy Review Student 1. Which is a problem with using wind turbines to produce energy? A. Wind turbines are efficient only in certain areas. B. Wind turbines occupy a small area of land. C. Wind
Alternative Energy. 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear. 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power)
 Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
Work, Energy and Power.
 Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Name Date Class. Overview Resources
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Resources Directions: Use the following terms to complete the concept map below. oil sunlight wind water coal natural gas geothermal Renewable energy resources
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Resources Directions: Use the following terms to complete the concept map below. oil sunlight wind water coal natural gas geothermal Renewable energy resources
World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production. Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2
 World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2 Different World Energy Sources There are many different forms of energy used throughout
World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2 Different World Energy Sources There are many different forms of energy used throughout
Sources of Electricity
 Sources of Electricity S C I E N C E L I N K S 9 U N I T 4 T O P I C 4. 1 B R A I N P O P S : E N E R G Y S O U R C E S N U C L E A R E N E R G Y W I N D E N E R G Y S O L A R E N E R G Y F O S S I L F
Sources of Electricity S C I E N C E L I N K S 9 U N I T 4 T O P I C 4. 1 B R A I N P O P S : E N E R G Y S O U R C E S N U C L E A R E N E R G Y W I N D E N E R G Y S O L A R E N E R G Y F O S S I L F
Fossil Fuels. Coal. Natural Gas. Petroleum Oil. Propane
 Fossil Fuels Coal Natural Gas Petroleum Oil Propane Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you to conserve energy. Turn off the lights, they say. To scientists, energy conservation is not just about
Fossil Fuels Coal Natural Gas Petroleum Oil Propane Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you to conserve energy. Turn off the lights, they say. To scientists, energy conservation is not just about
Earth s Energy and Mineral Resources
 Earth s Energy and Mineral Resources Chapter 5, Section 1, Nonrenewable Energy Resources 1) is the ability to cause change. 2) Most current energy sources that are used to generate electricity are, which
Earth s Energy and Mineral Resources Chapter 5, Section 1, Nonrenewable Energy Resources 1) is the ability to cause change. 2) Most current energy sources that are used to generate electricity are, which
Introduction to Energy. Energy
 Introduction to Energy Dossin Energy- What is It? Alternative Vs. Renewable Energy Energy- Two Main Forms Conservation of Energy Energy Efficiency Measuring Energy Using Energy RESOURCES Information copied
Introduction to Energy Dossin Energy- What is It? Alternative Vs. Renewable Energy Energy- Two Main Forms Conservation of Energy Energy Efficiency Measuring Energy Using Energy RESOURCES Information copied
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability
 Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Renewable vs Nonrenewable. Energy Sources. Science, Social Science. Planning a Sustainable Future for New Zealand. Curriculum Levels 4-5
 Renewable vs Nonrenewable Energy Sources Planning a Sustainable Future for New Zealand Science, Social Science Curriculum Levels 4-5 Activity Description New Zealand has a government policy target to increase
Renewable vs Nonrenewable Energy Sources Planning a Sustainable Future for New Zealand Science, Social Science Curriculum Levels 4-5 Activity Description New Zealand has a government policy target to increase
Energy and Energy Resources
 Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
QUESTION 1 Which of the following groups contains only examples of renewable energy sources?
 QUESTION 1 Which of the following groups contains only examples of renewable energy sources? B D hydroelectric, coal, wind nuclear, natural gas, solar solar, wind, hydroelectric hydroelectric, natural
QUESTION 1 Which of the following groups contains only examples of renewable energy sources? B D hydroelectric, coal, wind nuclear, natural gas, solar solar, wind, hydroelectric hydroelectric, natural
Energy Unit Framework
 Energy Unit Framework Driving Question: How do we plan for future energy use? Enduring Understandings: Distinguish among forms of energy (e.g. nuclear, electrical, gravitational), sources of energy (e.g.,
Energy Unit Framework Driving Question: How do we plan for future energy use? Enduring Understandings: Distinguish among forms of energy (e.g. nuclear, electrical, gravitational), sources of energy (e.g.,
The Greenhouse Effect
 Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Exploring how humans affect the carbon cycle
 We are learning how to: Exploring how humans affect the carbon cycle Understand that human activities affect the carbon cycle. Appreciate the scale of this impact. Explain how the impact relates to carbon
We are learning how to: Exploring how humans affect the carbon cycle Understand that human activities affect the carbon cycle. Appreciate the scale of this impact. Explain how the impact relates to carbon
KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY Shell Global Solutions International B.V.
 KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY CONSERVATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY? ENERGY CONSERVATION involves reducing energy consumption, largely through behavioural change. ENERGY
KNOWLEDGE EXPANDER ENERGY WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ENERGY CONSERVATION AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY? ENERGY CONSERVATION involves reducing energy consumption, largely through behavioural change. ENERGY
HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED?
 SOURCES OF ENERGY HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED? Most of the living things on Earth obtain their energy directly or indirectly from the Sun. Humans consume solar energy by eating plants and animals.
SOURCES OF ENERGY HOW CAN THE SUN S ENERGY BE USED? Most of the living things on Earth obtain their energy directly or indirectly from the Sun. Humans consume solar energy by eating plants and animals.
RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES
 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Energy Efficiency Energy efficiency the amount of useful energy produced compared to the amount wasted as heat (2 nd Law of Thermodynamics); built into the device or system,
RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Energy Efficiency Energy efficiency the amount of useful energy produced compared to the amount wasted as heat (2 nd Law of Thermodynamics); built into the device or system,
Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability. Monday, February 26, 18
 Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 37 Conservation, Efficiency, and Renewable Energy After reading this module you should be able to describe strategies to conserve energy and increase energy
Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 37 Conservation, Efficiency, and Renewable Energy After reading this module you should be able to describe strategies to conserve energy and increase energy
Standard Grade Physics
 Standard Grade Physics Name: Vale of Leven Academy Physics Department UNIT 6 ENERGY MATTERS PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets Number : Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you have
Standard Grade Physics Name: Vale of Leven Academy Physics Department UNIT 6 ENERGY MATTERS PUPIL PACK Study Guides Summary Notes Homework Sheets Number : Working at Home TO THE PUPIL Each day you have
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives. Eric D. Graham
 Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88)
 ! I......... C H P'T ER Resources and Environmental Change Lee tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88) A. Soil 1. Throughout history, people have developed ways to conserve and enrich the soil.
! I......... C H P'T ER Resources and Environmental Change Lee tes I. SOIL AND FORESTS (pupil Edition pages 87-88) A. Soil 1. Throughout history, people have developed ways to conserve and enrich the soil.
atom biofuel biomass the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
 atom the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons biofuel any fuel that comes directly from organic matter found in present-day living things biomass organic matter
atom the smallest unit of a chemical element, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons biofuel any fuel that comes directly from organic matter found in present-day living things biomass organic matter
KS4 Physics. Renewable Energy. 1 of 44. Boardworks Ltd 2005
 1 of 44 KS4 Physics Renewable Energy 2 of 44 Contents Renewable Energy Solar power Wind power Water power Thermal power Summary activities 3 of 44 Solar cells Solar cells (or photocells) turn light energy
1 of 44 KS4 Physics Renewable Energy 2 of 44 Contents Renewable Energy Solar power Wind power Water power Thermal power Summary activities 3 of 44 Solar cells Solar cells (or photocells) turn light energy
Name Class Date. Conventional Energy Resources
 Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 1
 Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 1 4 Energy S1 Science Test Unit 4 Energy Name: ( ) Time and Marks Class: Date: Part A: 35 min / 100 marks Parts A & B: 45 min / 120 marks Note: 1 Attempt ALL questions.
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 1 4 Energy S1 Science Test Unit 4 Energy Name: ( ) Time and Marks Class: Date: Part A: 35 min / 100 marks Parts A & B: 45 min / 120 marks Note: 1 Attempt ALL questions.
14 Sources of Energy. Assignments in Science Class X (Term I) IMPORTANT NOTES
 Assignments in Science Class X (Term I) 14 Sources of Energy 1. Energy plays a vital role in all walks of life. For example, heat energy is essential for cooking our food and electrical energy is essential
Assignments in Science Class X (Term I) 14 Sources of Energy 1. Energy plays a vital role in all walks of life. For example, heat energy is essential for cooking our food and electrical energy is essential
Section 1. Electricity and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES
 Fusion: The Unlikely Union of Physics and English Comp NAME: ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES Use this handout as a guideline for the research you need to do for the final project. The first page is an
Fusion: The Unlikely Union of Physics and English Comp NAME: ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES Use this handout as a guideline for the research you need to do for the final project. The first page is an
Graham School. Name: P3 Questions. Class: Date: 58 minutes. Time: 58 marks. Marks: Comments: Page 1
 P3 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 58 minutes Marks: 58 marks Comments: Page Q. Wind and tides are renewable energy sources that are used to generate electricity. (a) Complete each sentence by putting
P3 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 58 minutes Marks: 58 marks Comments: Page Q. Wind and tides are renewable energy sources that are used to generate electricity. (a) Complete each sentence by putting
