Global Climatic Change. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
|
|
|
- Leon Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
2 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks
3 Climatic change! Climate! Long-term description of weather patterns! Expectations! Mean, variability, extremes, frequency! Climatic change! A change in these statistical values! Climate change, such as warming, may vary differentially across the globe
4 Climate and weather! Weather changes happen all the time! These are regular features of a complex system! Local climate changes can occur as a result of changes to local conditions! Albedo, landforms, water bodies! Global climate changes require changes in the global energy balance
5 Climate change history Ahrens: Fig. 16.5
6 Recent global warming Zero line is Ahrens: Fig. 16.7
7 Thermodynamics! First Law of Thermodynamics! Energy cannot be created or destroyed! E in = E out + ΔE stored! At equilibrium, ΔE stored = 0 and E in = E out! Note that T is a function of E stored
8 Thermodynamics! Stefan-Boltzmann Law! All matter emits radiation proportional to the fourth power of its temperature! E out is proportional tot 4! For the Earth:! E in is radiation coming from the sun! E out is radiation emitted by Earth
9 Thermodynamics! So:! At equilibrium, Earth s temperature must be E out = E in! If E out is less than E in there will be an increase in E stored! This will cause T to increase until the fluxes are equal again! If the amount of radiation emitted by the Earth is less than what it receives from the Sun, there will be a global warming
10 Earth s Energy Balance! We calculated the effective radiative temperature of Earth: 255 K (-18 C)
11 The Greenhouse Effect 255 K 288 K Ahrens, Fig. 2.12
12 What can change the global energy balance?! Incoming energy! Solar strength! Aerosols (e.g. volcanoes)! Outgoing energy! Greenhouse gases! Change in land use
13 Greenhouse effect Natural! H 2 O! CO 2! CH 4! N 2 O! O 3 Enhanced! CO 2! CH 4! N 2 O! O 3! Halocarbons (CFCs)! SF 6! Perfluorocarbons (PFCs)
14 Carbon Dioxide Preindustrial concentration was 280 ppmv Current concentration is about 400 ppmv Emissions: Fossil fuels, 9 GtC/year Deforestation, 2 GtC/year Ahrens: Fig. 1.5 CO 2 doubling will occur around 2050 (560 ppmv)
15 Historical Carbon Dioxide years from the present
16 Methane: CH 4 Preindustrial Current Atmospheric Lifetime Anthropogenic Emissions 0.7 ppmv 1.78 ppmv 8-12 years Strength vs. CO 2 26 times Livestock (cattle) Natural Gas Leaks Oil and Coal Extraction Landfills Biomass Burning Sewage Treatment Rice Paddies years before present
17 Nitrous Oxide: N 2 O Preindustrial Current Atmospheric Lifetime Anthropogenic Emissions Strength vs. CO ppmv 0.32 ppmv 120 years Fertilizers Fossil Fuels Deforestation 206 times Ahrens: Fig
18 Halocarbons: CFCs, HCFCs, HFCs! Used in refrigeration and air conditioning! Per molecule, often several thousand times as strong as CO 2! Rapid increase in concentration since 1960s! CFCs deplete stratospheric ozone; replaced by HCFCs and HFCs
19 Other anthropogenic gases! Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF 6 )! Electrical insulator for power distribution! Lifetime: years! Strength: times as strong as CO 2! Perfluorocarbons (PFCs)! Solvents, refrigerants! Lifetime: thousands of years! Strength: thousands of times as strong as CO 2
20 Tropospheric ozone: O 3! Doubled in the NH; in many cities it is up by 5-10 times preindustrial levels.! Very short lifespan (hours)! Ozone precursors:! NO and NO 2! Hydrocarbons! CO! Main sources:! Burning biomass and fossil fuels
21 Stratospheric ozone: also O 3! Decreasing trend due to CFCs, HCFCs, and others! Loss contributes to global cooling in the stratosphere
22 Other contributors to global climatic change! Aerosols! Tiny particles suspended in the air! Reflect sunlight and increase cloud reflectivity! Tropospheric air pollution (SO x, NO x )! Volcanoes
23 Other contributors to global climatic change! Land cover change! Urban heat islands! Deforestation increases surface albedo! Solar variation! Observed changes have been small! Long-term cycles not well-understood
24 Feedbacks! A response to an change that acts to amplify or diminish the initial change! E.g. sound system amplifier, thermostat! A climate feedback responds to a change in climate by causing less or further change! Positive feedback: more change! Negative feedback: less change
25 Water vapour! Saturation vapour pressure depends on temperature! Higher temperatures lead directly to increased water vapour! Water vapour is a greenhouse gas! Positive feedback
26 Ice and snow! Ice and snow are very reflective! Sensitive to changes in temperature! Also a positive feedback Ahrens: Fig. 2.13
27 Clouds! Reflect shortwave (solar) radiation! Cover 50% of surface, albedo of 50%! Absorb longwave (terrestrial) radiation! Emit radiation to space and back down to the surface! Changes in the extent of clouds affects all three
28 Forcing from Doubling CO 2! Pre-industrial CO 2 : 280 ppmv! Actual doubling of CO 2 : 560 ppmv! Likely around 2050! However, other greenhouse gases are increasing as well! Equivalent 2 CO 2 when the combined radiative forcing is equal to that of 560 ppmv of CO 2
29 Climate sensitivity! The globally averaged equilibrium change in temperature in response to a given radiative forcing! Decades after a change in forcing, climate will approach a new equilibrium! The predicted climate sensitivity to 2 CO 2 is between 1.5 and 4.5 C! To date,
30 Continentality! With warmer temperatures, rate of evaporation will increase! Evaporation causes latent cooling! Increase in evaporation will be larger over open water! Continents will warm more than the average! And oceans will warm less! Mid-continents with dry soil will warm the most
31 Latitude 1. Greater warming is occurring at higher latitudes due to the ice albedo feedback 2. In the winter, sea ice insulates cold air from warmer water! Thinner ice means less insulation! Even greater polar amplification in winter
32
33 Hydrological cycle! More intense overall! Increased evapotranspiration, precipitation! Likely (but less certain):! Drier soils at mid-continents in summer! Midlatitude precipitation belts will shift poleward! Increased variability of precipitation More droughts and floods! Stronger monsoons in Asia and West Africa
34
35 Storms! Summer thunderstorms! High confidence in becoming more intense and frequent! Midlatitude cyclones! May get weaker! Tropical cyclones (hurricanes)! Opposing factors at work! Could become less frequent but more intense
36 Rise in sea level! Melting ice sheets! Greenland! Antarctica! Mountains! Thermal expansion
37 Rise in sea level! IPCC expects cm by 2100! Probably a low estimate! Much more on the way; sea level rise is slow! Inundation! Infiltration! Storm damage
38 ENSO! Average climatic conditions could become more El Niño-like! El Niño events could become stronger or more frequent, increasing climatic variability.
39 Impacts on natural systems! Loss of habitat! Species extinctions! Ecosystem reorganization! Forest diebacks! Increased fire frequency
40 Impacts on built systems! Agricultural losses, especially in tropics! Heat-sensitive crops! Valuable coastal land lost to sea level! Droughts and floods! Population centres affected by sea level rise! Melting permafrost at high latitudes! Buildings, road, railways, pipelines
41 Impacts on humans! Water supply! Moisture deficits more common! Timing of rainfall can cause stress! Saline intrusion along coastlines! Infectious diseases! Disease vectors will shift poleward! E.g. Malaria mosquito! Heat stress
42 Conference of the Parties (COP) Paris, France COP 21
43 Final exam! Saturday, December 12! 1 pm 4 pm! Gymnasium W and Y! Cumulative for all lecture material! Same format as the midterm! 80 multiple choice! 8 short answer
44 Atmospheric circulations! Thermal winds! Land/lake breeze! Mountain/valley breeze! Monsoon! Global circulation! Three cell model! Jet Streams! Planetary Waves! ENSO
45 Moving air! Air masses! Source regions and classification! Modifying air masses! Fronts! Warm, cold, stationary, occluded, dryline! Changes in temperature, humidity, wind direction, pressure and cloud cover
46 Midlatitude cyclones! Polar front theory! Life cycle and dissipation! Upper air divergence! Baroclinic instability! Jet streaks! Vorticity
47 Thunderstorms! Ordinary storms! Multicell storms! Supercell storms! Lightning and thunder! Hail! Tornadoes
48 Hurricanes (Tropical Cyclones)! Climatology! Dynamics! Lifespan! Hazards! High winds! Storm surge! Heavy rains! Forecasting! Polar lows
49 Climate Classification! The Köppen system! Based on vegetation! 5 types, plus Highland
50 Global climatic change! Causes! Review of the radiation balance! Anthropogenic greenhouse gases! Radiative forcing! Feedbacks! Results! Climate sensitivity! Distribution of changes in temperature and precipitation! Sea level rise
51 That s all, and DO WELL!
GLOBAL WARMING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12
 GLOBAL WARMING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12 Previous lecture Radiation budget review Driving factors Albedo Solar forcing Greenhouse gases Feedbacks The climate machine
GLOBAL WARMING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 21 Ahrens: Chapter 16; Turco: Chapter 12 Previous lecture Radiation budget review Driving factors Albedo Solar forcing Greenhouse gases Feedbacks The climate machine
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge
 ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
Climate Change. (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88
 Climate Change An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88 The following is an Information Statement intended to
Climate Change An Information Statement of the American Meteorological Society (Adopted by AMS Council on 1 February 2007) Bull. Amer. Met. Soc., 88 The following is an Information Statement intended to
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change
 Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE
 1 GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE From About Transportation and Climate Change (Source; Volpe center for Climate Change and Environmental forecasting, http://climate.volpe.dot.gov/trans.html Greenhouse effect has
1 GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE From About Transportation and Climate Change (Source; Volpe center for Climate Change and Environmental forecasting, http://climate.volpe.dot.gov/trans.html Greenhouse effect has
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ
 Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Scrambled Information Source: EPA Climate Change FAQ Instructions: The questions and answers below have been scrambled. Cut the answers and questions apart. Separate
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Contents. Permafrost Global Warming: An Introduction...4. Earth Is Getting Hotter...6. Green Homes The Greenhouse Effect...
 Contents Global Warming: An Introduction...4 Earth Is Getting Hotter...6 The Greenhouse Effect...8 Greenhouse Gases...10 Ozone Layer Depletion...12 The Carbon Cycle...14 The Kyoto Protocol...16 Climate
Contents Global Warming: An Introduction...4 Earth Is Getting Hotter...6 The Greenhouse Effect...8 Greenhouse Gases...10 Ozone Layer Depletion...12 The Carbon Cycle...14 The Kyoto Protocol...16 Climate
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING
 Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study
 Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
II. CLIMATE CHANGE AND ADAPTATION
 II. CLIMATE CHANGE AND ADAPTATION Human beings have been adapting to the variable climate around them for centuries. Worldwide local climate variability can influence peoples decisions with consequences
II. CLIMATE CHANGE AND ADAPTATION Human beings have been adapting to the variable climate around them for centuries. Worldwide local climate variability can influence peoples decisions with consequences
Global Climate Change. The sky is falling! The sky is falling!
 Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 PRESENTATION HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING?
 SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 PRESENTATION HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? CLIMATE CHANGE IS HAPPENING RIGHT NOW! CLICK TO PLAY Video opens in YouTube 1 WHAT IS CLIMATE CHANGE? What
SHAPING OUR FUTURE: THE CLIMATE CHALLENGE KS3 LESSON 1 PRESENTATION HOW IS OUR CLIMATE CHANGING? CLIMATE CHANGE IS HAPPENING RIGHT NOW! CLICK TO PLAY Video opens in YouTube 1 WHAT IS CLIMATE CHANGE? What
Concentrations of several of these greenhouse gases (CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O and CFCs) have increased dramatically in the last hundred years due to human
 Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1
 OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
Chemistry 471/671. Global Climate Change
 Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
Climate Change Questions, Condensed
 Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change MODULE 11: GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT 1: BIODIVERSITY Objectives Define terms. Understand global climate change. Describe the basic predictions of the global climate models. Understand
Global Climate Change MODULE 11: GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT 1: BIODIVERSITY Objectives Define terms. Understand global climate change. Describe the basic predictions of the global climate models. Understand
Climate Change Vocabulary Global Challenges for the 21 st Century Tony Del Vecchio, M.Ed. Atmosphere
 Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals. October 2011
 1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
Greenhouse Effect. How we stay warm
 Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I
 Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System
 1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
Feedback loops modify atmospheric processes
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Climate Change. Some solar radiation is reflected by Earth and the atmosphere. Earth s Surface
 Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
Global warming is already happening
 Climate change Global warming is already happening and it is not just temperature Is the change significant? why, yes We are no longer involved in just a scientific debate over how observations fit theories
Climate change Global warming is already happening and it is not just temperature Is the change significant? why, yes We are no longer involved in just a scientific debate over how observations fit theories
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Climate
 1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
20 Global Climate Change
 20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
E Eco Generatio n. School Kit CLIMATE CHANGE
 School Kit CLIMATE CHANGE This Power Point presentation is a part of the Samsung Engineering's Eco-generation School Kit The Power Point presentation is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial-ShareAlike
School Kit CLIMATE CHANGE This Power Point presentation is a part of the Samsung Engineering's Eco-generation School Kit The Power Point presentation is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial-ShareAlike
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
There has been an increase in the average global temperature in the last 150 years. Explain the human factors causing global warming.
 Question 1 There has been an increase in the average global temperature in the last 150 years. Explain the human factors causing global warming. (5) Question 2 Study Diagram Q2. Describe the possible consequences
Question 1 There has been an increase in the average global temperature in the last 150 years. Explain the human factors causing global warming. (5) Question 2 Study Diagram Q2. Describe the possible consequences
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
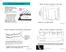 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
20 Global Climate Change
 20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
20 Global Climate Change Overview of Chapter 20 Introduction to Climate Change Causes of Global Climate Change Effects of Climate Change Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level Changes in Precipitation Patterns
ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE -- 2013 1. Y (visible) 2. Z (infrared) 3. X (ultraviolet) 4. d (the absorption is occurring almost entirely in the infrared (LW) part
ANSWER KEY TO THE PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON THE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE -- 2013 1. Y (visible) 2. Z (infrared) 3. X (ultraviolet) 4. d (the absorption is occurring almost entirely in the infrared (LW) part
Earth s Dynamic Climate
 UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
CONTENTS. Introduction x
 CONTENTS Introduction x Chapter 1: Climate 1 Solar Radiation and Temperature 2 The Distribution of Radiant Energy from the Sun 2 The Effects of the Atmosphere 3 Average Radiation Budgets 6 Surface-Energy
CONTENTS Introduction x Chapter 1: Climate 1 Solar Radiation and Temperature 2 The Distribution of Radiant Energy from the Sun 2 The Effects of the Atmosphere 3 Average Radiation Budgets 6 Surface-Energy
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
GREENHOUSE GASES 3/14/2016. Water Vapor, CO 2, CFCs, Methane and NO x all absorb radiation Water vapor and CO 2 are the primary greenhouse gases
 GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission
 Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reshmi Banerjee Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, W.B., India ABSTRACT: Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called
Effects of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reshmi Banerjee Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, W.B., India ABSTRACT: Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called
Def: Climate is the average weather. Averages all the local, regional and global extremes in weather. - Occurs on long time scales
 Climate Change Def: Climate is the average weather. Averages all the local, regional and global extremes in weather. - Occurs on long time scales Most important factor in climate is how the Earth responds
Climate Change Def: Climate is the average weather. Averages all the local, regional and global extremes in weather. - Occurs on long time scales Most important factor in climate is how the Earth responds
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report
 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report Andrea J. Ray, Ph.D. NOAA Earth Systems Research Lab & NOAA-CIRES Western Water Assessment Boulder, CO Andrea.Ray@noaa.gov http:/www.cdc.noaa.gov
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report Andrea J. Ray, Ph.D. NOAA Earth Systems Research Lab & NOAA-CIRES Western Water Assessment Boulder, CO Andrea.Ray@noaa.gov http:/www.cdc.noaa.gov
The Climate System. Goal of this session: Session contents. Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change
 Training package Providing Regional Climates for Impacts Studies - PRECIS Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change Joseph D. Intsiful CGE Hands-on training Workshop on V & A, Asuncion, Paraguay,
Training package Providing Regional Climates for Impacts Studies - PRECIS Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change Joseph D. Intsiful CGE Hands-on training Workshop on V & A, Asuncion, Paraguay,
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN. Climate Disruption. Cengage Learning 2015
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 19 Climate Disruption 19-1 How Is the Earth s Climate Changing? Considerable scientific evidence indicates that the earth s atmosphere is
National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change
 National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change Our planet is encased in a blanket of gases, held in place by the force of gravity. This mixture gives us our life and makes our planet unique and distinctive.
National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change Our planet is encased in a blanket of gases, held in place by the force of gravity. This mixture gives us our life and makes our planet unique and distinctive.
Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since Estimated global mean temperature
 1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING. gogreen. Shop visit An Ekotribe Initiative
 FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING Shop Online @ www.thegreenecostore.com Definition The earth is a natural greenhouse and is kept warm by water vapors, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other gases in the atmosphere,
FACTS ABOUT GL BAL WARMING Shop Online @ www.thegreenecostore.com Definition The earth is a natural greenhouse and is kept warm by water vapors, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other gases in the atmosphere,
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols
 Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Global warming and climate change
 Chapter 2 Global warming and climate change Introduction This chapter provides resource material to create energy awareness the link to environmental pollution global warming and its impact on climate
Chapter 2 Global warming and climate change Introduction This chapter provides resource material to create energy awareness the link to environmental pollution global warming and its impact on climate
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Climate Climate is characterized by the statistical properties of the weather over a period of time, including averages of local variables such as temperature, winds, humidity, pressure,
Global Climate Change Climate Climate is characterized by the statistical properties of the weather over a period of time, including averages of local variables such as temperature, winds, humidity, pressure,
Chapter Overview. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Change
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Outline Last IPCC report : 2001 Last IPCC report :
 Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
Working Group II: Climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability
 Fact sheet: Climate change science The status of climate change science today United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Enough is known about the earth s climate system and the greenhouse effect
Fact sheet: Climate change science The status of climate change science today United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Enough is known about the earth s climate system and the greenhouse effect
6. If the relative humidity is 100% the air is said to be: A) condensed B) saturated C) at dew point D) a cloud E) a condensation nuclei
 UNIT ONE HOMEWORK 1. The daily conditions in our surroundings, including temperature and rainfall is called: A) climate B) weather C) biome D) climate zone E) zonation 2. The climate zone on either side
UNIT ONE HOMEWORK 1. The daily conditions in our surroundings, including temperature and rainfall is called: A) climate B) weather C) biome D) climate zone E) zonation 2. The climate zone on either side
Global Ocean and Atmosphere Temperature Trends Compared
 Warmer Oceans result in coral bleaching and the death of coral reefs support more powerful hurricanes 32 Global Ocean and Atmosphere Temperature Trends Compared 33 Warmer Oceans and Coral Bleaching 1997-1998
Warmer Oceans result in coral bleaching and the death of coral reefs support more powerful hurricanes 32 Global Ocean and Atmosphere Temperature Trends Compared 33 Warmer Oceans and Coral Bleaching 1997-1998
Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give.
 Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
1.1 The Greenhouse Effect
 1.1 The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere s Role on the Greenhouse Effect Energy flows, expressed in W/m 2 with or without greenhouse gases (GHG) 342 17 342 17 235 235 235-19 C 67 168 +14 C Source: after
1.1 The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere s Role on the Greenhouse Effect Energy flows, expressed in W/m 2 with or without greenhouse gases (GHG) 342 17 342 17 235 235 235-19 C 67 168 +14 C Source: after
Normal equatorial flow. Climate Variability. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources
 Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste
 Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
Figure 1 - Global Temperatures - A plot from the EarthScience Centre at
 GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
Introduction to Climate Change. Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines
 RD Lasco 1 Introduction to Climate Change Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines Outline The climate system What is climate change? Evidence for climate change Predicted change in climate
RD Lasco 1 Introduction to Climate Change Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines Outline The climate system What is climate change? Evidence for climate change Predicted change in climate
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank
 How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give.
 Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
Environmental Impacts of. Energy Production
 CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
Chapter 19: Global Change
 1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
Climate Change not New
 Chapter 19: Climate Change and Ozone Depletion APES 2013 1 Climate Change not New Altered by volcanic emissions, changes in solar input, meteor impacts Relatively stable over the last thousand years, but
Chapter 19: Climate Change and Ozone Depletion APES 2013 1 Climate Change not New Altered by volcanic emissions, changes in solar input, meteor impacts Relatively stable over the last thousand years, but
Title: Global Warming Issued by: Environment Department
 Guideline No.: EN/034 Issue Date: July 2010 1.0 General Title: Global Warming Issued by: Environment Department Measurements of temperature taken by instruments all over the world, on land and at sea have
Guideline No.: EN/034 Issue Date: July 2010 1.0 General Title: Global Warming Issued by: Environment Department Measurements of temperature taken by instruments all over the world, on land and at sea have
The instrumental record goes back to about A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern
 The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1. Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE
 Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
4.4 CLIMATE CHANGE. Concentrations of gases in the atmosphere affect climates experiences at the Earth s surface
 4.4 CLIMATE CHANGE Concentrations of gases in the atmosphere affect climates experiences at the Earth s surface Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Carbon dioxide and water vapour are the most significant greenhouse
4.4 CLIMATE CHANGE Concentrations of gases in the atmosphere affect climates experiences at the Earth s surface Greenhouse Gases (GHG) Carbon dioxide and water vapour are the most significant greenhouse
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Chapter 20: Climate change and ozone depletion. March 18, 2014
 Chapter 20: Climate change and ozone depletion March 18, 2014 March 18, 2014 Predicting Climate Change Volcanic eruption 1991 Philippines Cool earth 0.5ºC over 15months, return to normal by 1995 Model
Chapter 20: Climate change and ozone depletion March 18, 2014 March 18, 2014 Predicting Climate Change Volcanic eruption 1991 Philippines Cool earth 0.5ºC over 15months, return to normal by 1995 Model
Today s s lab. Discussion: Climate vs. weather Components of the climate system Forcing and response Response time Feedback Equilibrium
 Today s s lab Discussion: Climate vs. weather Components of the climate system Forcing and response Response time Feedback Equilibrium Earth s s Climate &Weather Climate Long-term (years and longer) average
Today s s lab Discussion: Climate vs. weather Components of the climate system Forcing and response Response time Feedback Equilibrium Earth s s Climate &Weather Climate Long-term (years and longer) average
The science of the Kyoto protocol
 The science of the Kyoto protocol Vicky Pope Hadley Centre with lots of help from Climate Chemistry and Ecosystem group ECMWF seminar September 2005 Page 1 Outline Kyoto protocol Observations relevant
The science of the Kyoto protocol Vicky Pope Hadley Centre with lots of help from Climate Chemistry and Ecosystem group ECMWF seminar September 2005 Page 1 Outline Kyoto protocol Observations relevant
3/5/2012. Study Questions. Global Warming. Weather: daily temperature and moisture conditions Climate: long-term weather patterns
 Study Questions Global Warming 1. Explain what is meant by the term Greenhouse effect. 2. List 3 indications that global climate is currently increasing. 3. Describe 3 possible consequences of global warming.
Study Questions Global Warming 1. Explain what is meant by the term Greenhouse effect. 2. List 3 indications that global climate is currently increasing. 3. Describe 3 possible consequences of global warming.
The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future?
 Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
 Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Biogeography + Climate Change Student 2014 Biogeography and Climate Change Biogeography is the study of species distribution and their environments currently and
Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Biogeography + Climate Change Student 2014 Biogeography and Climate Change Biogeography is the study of species distribution and their environments currently and
Animal Agriculture Newsletter
 & CLIMATE CHANGE Animal Agriculture Newsletter WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION LIVESTOCK NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT In This Issue Why Does Climate Change? Climate changes.................... 1 Earth s Atmosphere..................
& CLIMATE CHANGE Animal Agriculture Newsletter WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION LIVESTOCK NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT In This Issue Why Does Climate Change? Climate changes.................... 1 Earth s Atmosphere..................
Frumkin, 2e Part Two: Environmental Health on a Global Scale. Chapter 10: Climate Change
 Frumkin, 2e Part Two: Environmental Health on a Global Scale Chapter 10: Climate Change Climate Change Climate change results from natural variability and human activity, and depends on the overall energy
Frumkin, 2e Part Two: Environmental Health on a Global Scale Chapter 10: Climate Change Climate Change Climate change results from natural variability and human activity, and depends on the overall energy
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE. Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTANTS Acid Rain Acid Rain is the precipitation that carries
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTANTS Acid Rain Acid Rain is the precipitation that carries
Global Warming & Climate Change Review Learning Target 1
 Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
Acid deposition accumulation of potential acid-forming particles on a surface acids can result from natural causes
 1 Air Quality Issues: Part 2 - Acid Deposition, Greenhouse Gases EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Air Quality Issues Air Pollution Indoor Air Pollution Acid Deposition Greenhouse Gases & Global Warming 3
1 Air Quality Issues: Part 2 - Acid Deposition, Greenhouse Gases EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Air Quality Issues Air Pollution Indoor Air Pollution Acid Deposition Greenhouse Gases & Global Warming 3
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings. Climate changes (1900 to 2000) due to human activity. Climate Variability and Climate Change
 Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva
 Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
