Productivity and fisheries. Energy flow. Biological pyramids. Why study production processes?
|
|
|
- Allyson Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret population dynamics Energy flow Production begins with plants Fix carbon and transfer to higher trophic levels Energy flows through trophic interactions Food chains of various lengths (affects transfer efficiency) Biological pyramids Summer C 3 - Top carnivores C 2 - medium size fish C 1 - large zooplankton,small fish H- herbivorous fish, small zooplankton P- phytoplankton, algae = ~1000 kcal/m 2 /year Winter 1
2 Sources of marine production About 90% of net primary production from phytoplankton (oceanic and coastal) Macroalgae accounts for about 5% Remaining from several sources (mangroves, reef algae, seagrasses, marsh plants) Variation in marine production Fine scale processes sinking swimming turbulence Generate nutrient diffusion Large scale processes wind and mixing ocean circulation upwelling 2
3 What are the limiting factors for primary productivity? 1) Light 2) Nutrients a. Phosphorous-phosphates b. Nitrogen- ammonia, nitrate, nitrite c. Potassium 3) Temperature 4) Dissolved gases - carbon dioxide and oxygen What are the limiting factors for primary productivity? Light limitation: The sea covers 71% of earth s surface, but most of it is at depths >1km Most production occurs over continental shelf waters < 200m deep (only 7-8% of ocean) 3
4 Depth What are the limiting factors for primary productivity? Light limitation: Available light levels fall rapidly with depth Longer wavelengths absorbed at surface Photosynthesis restricted to upper water column in turbid coastal areas Compensation depth Depth at which respiration rate equals photosynthetic rate shallow waters contain ample light, thus photosynthesis exceeds respiration deeper waters have less light penetration, thus respiration exceeds photosynthesis Rate Respiration Photosynthesis Compensation depth Similar to Fig 2.3 4
5 Depth Aphotic Depth Photic What are the limiting factors for primary productivity? Temperature limitation: In addition to light levels, temperature also decreases with depth Formation of thermocline Thermocline shifts seasonally depending on wind stress Physical structure Percent light (red) o 5 o 10 o 15 o C (Blue) 5 Epilimnon 10 Metalimnon Thermocline 15 Hypolimnon 20 Seasonal variation Differences in mixing among seasons changes the position of the thermocline Mixing Temperature mixed layer depth Winter Summer 5
6 Depth Depth What are the limiting factors for primary productivity? Nutrient limitation: Stratification prevents plankton from sinking below compensation depth, but also prevents nutrient transfer up from deep waters mixed layer depth Leads to seasonal and spatial variation in production Summer What causes the spring bloom? Mixing followed by stratification Shallower mixed layer Plankton held in euphotic zone Population growth? Rate Respiration Photosynthesis Compensation depth Critical depth What causes the spring bloom? Rate Total Production integrated over all depths 6
7 Depth Depth What causes the spring bloom? Rate Total Respiration integrated over all depths What causes the spring bloom? Total production must be > total respiration for population growth to occur Respiration increases with depth, relative to production Critical depth (of mixed layer) exists where total production = total respiration Known as Gran effect or Sverdrup mechanism Depth of mixed layer Critical depth March April May 7
8 Spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Climate variation (temp, winds) leads to latitudinal variation in production Different seasonal patterns at temperate, polar, and tropical latitudes 8
9 phytoplankton zooplankton Change in structure offshore Depth of euphotic zone Phytoplankton productivity Nutrient concentration Estuary Inshore Offshore Global scale variation in primary productivity Upwelling affects production by surfacing nutrients Generates global patterns of productivity 9
10 offshore winds longshore currents diverging currents 10
11 Transfer of energy (Food webs) All organisms ultimately rely upon energy captured by primary producers Each step = 1 trophic level Carbon lost at each step, based on gross growth efficiency (GGE) Transfer Efficiency = GGE Χ % of prey eaten Water Lake food web Human; fishing Predator; Bass Insect Adults Insect Larvae Omnivore; Sunfish Predatory Insects Terrestrial Insects Insect Adults Phytoplankton Zooplankton Sunlight Production and fisheries Fish production thus depends on: 1) levels of primary production 2) length of the food chain 3) transfer efficiency Highest catches (fish production) come from coastal and shelf areas 11
12 production biomass NW Atlantic Baltic Sea Open ocean 12
13 Production and fisheries Five major coastal currents associated with upwelling areas California current (US west coast) Peru current (west coast of South America) Canary current (NW Africa) Benguela current (SW Africa) Somali current (Indian ocean) Highly productive clupeid fisheries of major social and economic importance 13
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Biological Oceanography
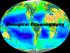 Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13
 OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Lesson Overview 4.5 Aquatic Ecosystems
 Lesson Overview 4.5 Conditions Underwater What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems? Aquatic organisms are affected primarily by the water s depth, temperature, flow, and amount of dissolved nutrients.
Lesson Overview 4.5 Conditions Underwater What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems? Aquatic organisms are affected primarily by the water s depth, temperature, flow, and amount of dissolved nutrients.
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Production and Life OCEA 101
 Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity
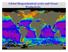 Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems?
 Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
biology Slide 1 of 39 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and
biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and
4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems
 biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
The Open Ocean. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
Chapter Concepts LIFE IN WATER. The Hydrologic Cycle. The Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Taxonomy. Classification of Marine Organisms 11/7/2012. CH 12 Marine Life and the Marine Environment
 CH 12 Marine Life and the Marine Environment There are more than 250,000 identified marine species Most live in sunlit surface seawater A species success depends on the ability to o find food o avoid predation
CH 12 Marine Life and the Marine Environment There are more than 250,000 identified marine species Most live in sunlit surface seawater A species success depends on the ability to o find food o avoid predation
Marine lifestyles and relationships
 Marine lifestyles and relationships Marine Lifestyles and Enviros. Benthic organisms (benthos) live on or buried in the ocean floor (sediment) Can be sessile (attached) or mobile (moving) Pelagic organisms
Marine lifestyles and relationships Marine Lifestyles and Enviros. Benthic organisms (benthos) live on or buried in the ocean floor (sediment) Can be sessile (attached) or mobile (moving) Pelagic organisms
(Brief) History of Life
 Oldest fossils are 3.5 Ga Cyanobacteria (?) from the Australian Warraroona Group (ancient marine sediments) Bacteria represent the only life on Earth from 3.5 to ~1.5 Ga - and possibly longer Hard to kill
Oldest fossils are 3.5 Ga Cyanobacteria (?) from the Australian Warraroona Group (ancient marine sediments) Bacteria represent the only life on Earth from 3.5 to ~1.5 Ga - and possibly longer Hard to kill
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
MAR 650-Lecture 1: Influences of Light on Biological Production. Importance: In the ocean: 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production
 MAR 650-Lecture 1: nfluences of Light on Biological Production 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production photosynthesis CO 2 H 2 O Carbohydrate O 2 respiration mportance: Photosynthesis requires lights,
MAR 650-Lecture 1: nfluences of Light on Biological Production 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production photosynthesis CO 2 H 2 O Carbohydrate O 2 respiration mportance: Photosynthesis requires lights,
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology
 Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
Today: Dinner Time! Yum Yum
 Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
The Global Ocean. Ocean Features and Abiotic Conditions
 The Global Ocean Ocean Features and Abiotic Conditions The Global Ocean Earth is made up of 71% water, most of that water is marine (salt). Only 3% of the Earth s water is freshwater. The Global Ocean
The Global Ocean Ocean Features and Abiotic Conditions The Global Ocean Earth is made up of 71% water, most of that water is marine (salt). Only 3% of the Earth s water is freshwater. The Global Ocean
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
Producers. living systems need energy to function. autotrophs. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
 Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
6/27/11. Aquatic Community Ecology (BIOL 312) Summer I. Ecological Principles. What is an ecological community? Ecological Principles
 Aquatic Community Ecology (BIOL 312) Summer 2011 Day 1 Outline Introduction, Class Overview I. Ecological Principles II. Life in Water III. Zonation/Vertical Structure For Tuesday: Read Ch 5 Conesus Lake
Aquatic Community Ecology (BIOL 312) Summer 2011 Day 1 Outline Introduction, Class Overview I. Ecological Principles II. Life in Water III. Zonation/Vertical Structure For Tuesday: Read Ch 5 Conesus Lake
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Instructions: Answer the questions 1-8 to set up basic rules for how lateral current direction controls vertical motion of seawater.
 Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION
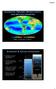 PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
Today: Dinner Time! Yum Yum. Primary Producers = base of food web
 Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Ecology. Climate. Global Climate. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Ecosystems. Trophic relationships determine the routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems.
 AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline
 Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
1. Global Climate. Latitude and Sunlight Intensity 12/4/2014. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere. 1.
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
BIOLOGY NOTES. Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment
 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 1: ECOLOGY SUBTOPIC : 12.1 Introduction to ecology. LEARNING OUTCOMES: Define basic terminologies in ecology. - niche, habitat, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere..
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 1: ECOLOGY SUBTOPIC : 12.1 Introduction to ecology. LEARNING OUTCOMES: Define basic terminologies in ecology. - niche, habitat, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere..
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
Ecology: Chapters Worksheet
 Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
3 2 Energy Flow Slide 1 of 41
 1 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. 2 of 41 Producers In a few ecosystems, some organisms
1 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. 2 of 41 Producers In a few ecosystems, some organisms
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters. Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU
 Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Lesson Overview. What is Ecology? Lesson Overview. 3.1 What Is Ecology?
 Lesson Overview 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet The biosphere consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. The
Lesson Overview 3.1 What Is Ecology? Studying Our Living Planet The biosphere consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere. The
10/17/ Energy Flow. Producers. Where does the energy for life processes come from?
 2 of 41 Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. 4 of 41 1 Only
2 of 41 Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. 4 of 41 1 Only
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS
 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Ecology. Limiting factors. Introduction to Marine Ecology. Ecological communities and ecosystems
 Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Biology. Slide 1 of 41. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016
 Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abundant light and constant nutrient input make
Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abundant light and constant nutrient input make
MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture Dan Cogalniceanu Course content Overview of marine systems
 Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Biology Slide 1 of 41
 Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Objectives: You will Create food webs that follow the flow of energy through an ecosystem 3 of 41 Vocabulary autotroph producer photosynthesis chemosynthesis heterotroph consumer
Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Objectives: You will Create food webs that follow the flow of energy through an ecosystem 3 of 41 Vocabulary autotroph producer photosynthesis chemosynthesis heterotroph consumer
ECOLOGY Energy Flow Packet 2 of 4
 ECOLOGY Energy Flow Packet 2 of 4 3 2 Energy Flow Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight
ECOLOGY Energy Flow Packet 2 of 4 3 2 Energy Flow Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight
What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive?
 Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
Energy and Life What Keeps Us and Other Organisms Alive? Four major components of the earth s life-support system: atmosphere (air) hydrosphere (water) geosphere (rock, soil, sediment) biosphere (living
4/13/2015. The Biosphere
 The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
Food Webs. March 16, Photosynthesis and Respiration on ecosystem scales
 Lecture 18 Productivity and Food Webs March 16, 2005 Photosynthesis and Respiration on ecosystem scales Analysis of global productivity Energy flow through trophic levels and ecosystems Three weeks in
Lecture 18 Productivity and Food Webs March 16, 2005 Photosynthesis and Respiration on ecosystem scales Analysis of global productivity Energy flow through trophic levels and ecosystems Three weeks in
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Multiple Choice. Name Class Date
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Biogeographic realms By 1800s, many naturalists began to identify broad patterns of distribution biogeographic realms
 Biogeographic realms By 100s, many naturalists began to identify broad patterns of distribution biogeographic realms Nearctic Tropic of Cancer (23.5 N) Equator (23.5 S) Tropic of Capricorn Neotropical
Biogeographic realms By 100s, many naturalists began to identify broad patterns of distribution biogeographic realms Nearctic Tropic of Cancer (23.5 N) Equator (23.5 S) Tropic of Capricorn Neotropical
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem
 Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
THS Sci-O Water Quality Tryout Test. Partner 1: Partner 2: Total Score: /104
 THS Sci-O 2018-19 Water Quality Tryout Test Partner 1: Partner 2: Total Score: /104 1 Part One: 1-6. Label the times each part of the thermal stratification cycle occurs (ex: summer, spring turnover, etc.)
THS Sci-O 2018-19 Water Quality Tryout Test Partner 1: Partner 2: Total Score: /104 1 Part One: 1-6. Label the times each part of the thermal stratification cycle occurs (ex: summer, spring turnover, etc.)
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY
 SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea. Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton
 10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
Glossary. hefreediction ary.com/algae. hefreediction ary.com/anth
 Algae noun Any of various chiefly aquatic, eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms, ranging in size from single-celled forms to the giant kelp. Algae were once considered to be plants but are now classified
Algae noun Any of various chiefly aquatic, eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms, ranging in size from single-celled forms to the giant kelp. Algae were once considered to be plants but are now classified
Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter
 Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
20 1 Properties of Ocean Water (1) for walkabout notes.notebook. April 24, 2018
 Although pure water is tasteless, odorless and colorless, ocean water is not pure. Ocean water is a complex mixture of: dissolved solids and gasses, small particles of matter, tiny organisms, chemicals
Although pure water is tasteless, odorless and colorless, ocean water is not pure. Ocean water is a complex mixture of: dissolved solids and gasses, small particles of matter, tiny organisms, chemicals
Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Classification of systems. Aquatic Ecosystems. Lakes 9/9/2013. Chapter 25
 Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES
 Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES 1 OUTLINE Marine Ecosystems Coasts - Sandy, Rocky, Salt Marsh, Mangrove Coral Reefs Open Ocean Hydrothermal Vents Freshwater Ecosystems - Lakes, Rivers, Wetlands Human Disturbance
Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES 1 OUTLINE Marine Ecosystems Coasts - Sandy, Rocky, Salt Marsh, Mangrove Coral Reefs Open Ocean Hydrothermal Vents Freshwater Ecosystems - Lakes, Rivers, Wetlands Human Disturbance
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work
 Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE, AND PLANKTON
 OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE, AND PLANKTON OVERVIEW Students will study videos, charts, ship scientist s logs, and data gathered over a week from the Research Vessel Sea Explorer (located at the Orange County
OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE, AND PLANKTON OVERVIEW Students will study videos, charts, ship scientist s logs, and data gathered over a week from the Research Vessel Sea Explorer (located at the Orange County
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones
 3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
Ch. 8 - Aquatic Ecology
 Ch. 8 - Aquatic Ecology Coral Reefs: the aquatic equivalent of the tropical rain forests The two major aquatic life zones are determined by salinity: saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs,
Ch. 8 - Aquatic Ecology Coral Reefs: the aquatic equivalent of the tropical rain forests The two major aquatic life zones are determined by salinity: saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs,
Think About It (not on notes)
 Aquatic Ecosystems Think About It (not on notes) We call our planet Earth, yet nearly three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered with water. Despite the vital roles aquatic ecosystems play in the biosphere,
Aquatic Ecosystems Think About It (not on notes) We call our planet Earth, yet nearly three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered with water. Despite the vital roles aquatic ecosystems play in the biosphere,
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
What is Ecology? Includes land, air, and water as well as life. Living organisms are NOT distributed uniformly throughout the biosphere.
 Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry
 Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry Prof. J. Keith Moore University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Weiwei Fu, Francois Primeau, Greg Britten, Keith Lindsay, Matthew Long,
Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry Prof. J. Keith Moore University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Weiwei Fu, Francois Primeau, Greg Britten, Keith Lindsay, Matthew Long,
Section 3 1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63 65)
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section 3 1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63 65) This section identifies the different levels of organization that ecologists study. It also describes methods used to study ecology. Interactions
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section 3 1 What Is Ecology? (pages 63 65) This section identifies the different levels of organization that ecologists study. It also describes methods used to study ecology. Interactions
MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD
 MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD Martha Sutula Southern California Coastal Water Research Project Workshop on The Science
MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD Martha Sutula Southern California Coastal Water Research Project Workshop on The Science
1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw?
 1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw? A. Organisms in the intertidal zone must be able to
1. Jill made the table below during her research on aquatic zones and living organisms. Based on Jill s observations, which conclusion could you draw? A. Organisms in the intertidal zone must be able to
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background
 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Energy. Raw materials to make building blocks of life. From sun or chemicals. From food
 Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. Ecosystem have two components: Biocenosis: is the set of living being in
Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. Ecosystem have two components: Biocenosis: is the set of living being in
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem:
 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem: The vast majority of life on Earth depends on sunlight as its source of energy. Of all the radiant energy that reaches the earth, some of it penetrates the earth's atmosphere
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem: The vast majority of life on Earth depends on sunlight as its source of energy. Of all the radiant energy that reaches the earth, some of it penetrates the earth's atmosphere
The Carbon cycle. Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon
 The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences.
 1 Ecosystems & Ecophysiology Lecture 7 Shallow seas Objectives 1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences. 2. Describe
1 Ecosystems & Ecophysiology Lecture 7 Shallow seas Objectives 1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences. 2. Describe
Qa iss. Q; How do Earth's living and nonliving parts interact and affect the survival of organisms?
 Name. mm Qa iss Date 3 The Biosphere Matter of Energy> Interdependence in Nature Q; How do Earth's living and nonliving parts interact and affect the survival of organisms? WHAT I KNOW WHAT i LEARNED 3.1
Name. mm Qa iss Date 3 The Biosphere Matter of Energy> Interdependence in Nature Q; How do Earth's living and nonliving parts interact and affect the survival of organisms? WHAT I KNOW WHAT i LEARNED 3.1
Biology Chapter Two. Principles of Ecology
 Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Studying organisms in their environment
 Ecosystems (Ch. 3) Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How does energy move through the
Ecosystems (Ch. 3) Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How does energy move through the
SAMPLE. AQA A Level Geography. Unit Assessment Water and Carbon Cycles (Edition 1)
 UNIT ASSESSMENT AQA A Level Geography Unit Assessment 3.1.1 Water and Carbon Cycles (Edition 1) h 45 minutes h The maximum mark for this unit assessment is 36 Name Centre Name AQA A Level Geography Unit
UNIT ASSESSMENT AQA A Level Geography Unit Assessment 3.1.1 Water and Carbon Cycles (Edition 1) h 45 minutes h The maximum mark for this unit assessment is 36 Name Centre Name AQA A Level Geography Unit
Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems
 Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems Key Ideas Living things are connected to each other in complex interrelationships. Biotic and abiotic factors are responsible for shaping a community of living things.
Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems Key Ideas Living things are connected to each other in complex interrelationships. Biotic and abiotic factors are responsible for shaping a community of living things.
We must protect aquatic life zones from the pollutants, water controls, and deterioration that we press upon them every day.
 Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Summary 1. The basic types of aquatic life zones are the surface, middle, and bottom layers. The life in aquatic life zones is influenced by temperature, access to sunlight
Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Summary 1. The basic types of aquatic life zones are the surface, middle, and bottom layers. The life in aquatic life zones is influenced by temperature, access to sunlight
Biology. Slide 1 of 41. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
Biology 1 of 41 2 of 41 Producers Where does the energy for life processes come from? 3 of 41 Producers Producers Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main
