11/16/10. Why do climates change? Take away ideas and understandings. Our first climate model. Climate changes over the last millennium
|
|
|
- Meghan O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why do climates change? Climate changes over the last millennium Take away ideas and understandings What factors influence climate change over decadal to century timescales? Solar variability, volcanic eruptions, and greenhouse gases. How we can quantify their effects? Climate history of the last millennium Our first climate model Recall how to calculate Earth s effective temperature, or the temperature the Earth would be without an atmosphere. The Stefan-Bolzmann equation: Blackbody radiation: I (w/m 2 ) = σ T 4 Earth s incoming radiation (α = Earth albedo, or reflectivity) I incoming = (1-α) σ T sun 4 1
2 Our first climate model Earth incoming radiation (α = Earth albedo, or reflectivity) I incoming = ((1-α) I solar ) / 4, or ((1-α) σ T 4 sun )/ 4 Earth outgoing radiation I outgoing = σ T 4 earth α is ~0.3, or 30% ε (emissivity) = 1 σ = 5.67 x 10-8 W m -2 K -4 Archer Fig. 3.3 (p. 23) Earth s temperature with no greenhouse effect T effective = 254.8K (-18 C) At equilibrium, I incoming = I outgoing ((1-α) σ T sun 4 ) / 4 = σ T 4 earth Solve for T earth Eqn. 3.1 in Archer Chapter 3 Surface temperature readings Galileo s Thermoscope (1500s) Daniel Fahrenheit (1714) closed thermometer First weather stations established ~250 years ago Widespread measurements for last 150 years only. 2
3 Stockholm Observatory 31 December, 1768: No one can recall such a mild Autumn: the ground is as green as in the Spring, and today I have picked sufficient young nettles, dandelions, and other herbs to cook green cabbage tomorrow, which is New Year's day. Many 1000s of stations 3
4 There are only 3 ways to change Earth s temperature Change input a) Solar variability b) Earth reflectivity (volcanoes) Change output c) Greenhouse gases 1. Volcanoes cool climate, briefly Mt. Tambora Mt. Pinatubo
5 α = ~30% on average T effective = 254.8K Volcanic eruption can change albedo by 1% Recalling I in = (1-α) σ T 4 ((1-α) σ T sun 4 )/ 4 = σ T 4 earth Increase α to 31% New T effective = 253.9K or -1 C cooler due a volcanic eruption Climate Impacts of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanoes inject aerosols and particles into the stratosphere which can scatter and/or absorb incoming solar radiation. Cools the troposphere by up to C for only 2-4 years. Warms the Stratosphere by 2-3 C (!) Short-term but significant impact 1815 eruption Mt. Tambora Year Without a Summer Poverty Year 1800-and-froze-to-death 5
6 11/16/10 Mt. Merapi (Indonesia) tropical volcanoes cool climate most 2. Solar Variability 6
7 Sunspots, Facular brightening, and Irradiance 30 years of satellite observations: ±1 W/m2 What if the solar radiation changes by +2 W/m 2? Recalling I solar = 1365 W/m 2 Set I solar = 1367 W/m 2 α = 0.3 Solve for T earth ((1-α) I solar )/ 4 = σ T 4 earth T = 0.1 C (Small!) 7
8 Sunspot Cycles ~0.1% - Sunspots Very weak forcing, but significant climate responses to it. Little Ice Age ( AD) LIA Cooling was the result of lower solar radiation and some big volcanic eruptions 8
9 11/16/10 Little Ice Age ( ) London Frost Fair (1814) Rhône Glacier Solar Variability Forcing is very weak (in visible spectrum), only ± %, so climate response should be weak. Climate response is actually quite high - still not sure why. One possibility is UV part of spectrum - much greater changes (±10%) suggests that global climate is very sensitive 9
10 11/16/10 How do we estimate past climate change, before there were thermometers Proxies - getting temperatures from trees a) Measure ring widths b) Calibrate ring widths Growth Temp. ( C) Ring Width (mm) C) Validate and Apply warm T ( C) cool Year AD 10
11 Temperatures over the last 2,000 years * 2005 Date (AD) Measured CO 2 trends since 1958 Atmospheric CO 2 : Last 250 years 11
12 Results from the IPCC AR4 report Natural forcing only Natural + Human most of modern warming is due to humans Natural only Natural + GHG Modeling the climate of the last 1000 years 12
13 Climate = Solar Irrad. + Volcanoes + GHG Sum of all forcings ( ) Net = +1.6 W 4 lights per square meter * * * Another way to imagine global warming 13
14 11/16/10 What global warming really looks like Data source: NASA / GISS Timescales of Natural Climate Variability A. Short time scales (1-2 years): Random weather-related variations of turbulent, chaotic atmosphere. C. Interannual (2-8 years): Primarily ENSO and Volcanic eruptions. E. Decadal-to-century scale: - Solar Variability (decades to centuries) Anthropogenic greenhous gas emissions (decades to centuries) What s in store for the future? Most probable estimate is +2 to +4 C in next 100 years All scenarios warmer. past future Today 14
15 Global Temperature in 2050 Recent warming is unusual, Future warming is another world 2010 * +3 C warming 15
ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due TONIGHT by 11:59 pm
 Thursday Nov 20th Topic #13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) SIT ANYWHERE TODAY! But pick up an INDEX CARD when you come it! ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due
Thursday Nov 20th Topic #13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) SIT ANYWHERE TODAY! But pick up an INDEX CARD when you come it! ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING
 TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Part B The Key To It All: SORTING OUT THE RADIATIVE FORCINGS OF CLIMATE Class Notes p 83 Greenhouse Gas emissions from Forestry (Deforestation, biomass
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Part B The Key To It All: SORTING OUT THE RADIATIVE FORCINGS OF CLIMATE Class Notes p 83 Greenhouse Gas emissions from Forestry (Deforestation, biomass
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.)
 TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 89 THE KEY TO IT ALL: p 89 RADIATIVE FORCING (linked to the Energy Balance!) expressed in Watts per square
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 89 THE KEY TO IT ALL: p 89 RADIATIVE FORCING (linked to the Energy Balance!) expressed in Watts per square
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING
 WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW. Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics...
 FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics.... The wavelength range of infrared 1. < 0.4 micrometers radiation. 2. > 0.7 micrometers
FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics.... The wavelength range of infrared 1. < 0.4 micrometers radiation. 2. > 0.7 micrometers
A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS FIRST -- The answers to the G-5 GROUP ACTIVITY on VOLCANISM & CLIMATE G-5 VOLCANISM & CLIMATE ACTIVITY #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted
A MINI FINAL EXAM REVIEW: SOME PRACTICE QUESTIONS FIRST -- The answers to the G-5 GROUP ACTIVITY on VOLCANISM & CLIMATE G-5 VOLCANISM & CLIMATE ACTIVITY #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming.
 Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
TOPIC # 13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.)
 TOPIC # 13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 86 Recap: CARBON DIOXIDE: Two big sources Fossil Fuel combustion Land use p 80 Photosynthesis & Respiration
TOPIC # 13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 86 Recap: CARBON DIOXIDE: Two big sources Fossil Fuel combustion Land use p 80 Photosynthesis & Respiration
Wrap Up of: RADIATIVE FORCING OF CLIMATE
 Wrap Up of: RADIATIVE FORCING OF CLIMATE The Key To It All: RADIATIVE FORCING OF CLIMATE CLICKERS Ch 32 Class notes pp 83 The figure shows that the forcing mechanism that is BEST understood by scientists
Wrap Up of: RADIATIVE FORCING OF CLIMATE The Key To It All: RADIATIVE FORCING OF CLIMATE CLICKERS Ch 32 Class notes pp 83 The figure shows that the forcing mechanism that is BEST understood by scientists
Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20
 Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained?
 How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate Change. Greenhouse Effect & Global Warming
 Climate Change What is climate change Greenhouse Effect & Global Warming Global Warming = World wide increase in average Temp. Cause = greenhouse effect 1 Some would argue the Global Warming trend is natural
Climate Change What is climate change Greenhouse Effect & Global Warming Global Warming = World wide increase in average Temp. Cause = greenhouse effect 1 Some would argue the Global Warming trend is natural
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
NASA Global Hawk Altitude Cruising Range: 45,000 65,000 ft Duration: 33 hrs DU Aerosol Payload First Science Mission: Winter 2010
 DU Aerosol Group Develops Instruments, Makes In situ Aerosol Measurements: Air Quality, O 3 Depletion, Aerosol-Cloud Interactions, Volcanic Clouds, New Particle Formation NASA Global Hawk Altitude Cruising
DU Aerosol Group Develops Instruments, Makes In situ Aerosol Measurements: Air Quality, O 3 Depletion, Aerosol-Cloud Interactions, Volcanic Clouds, New Particle Formation NASA Global Hawk Altitude Cruising
SOME QUICKIE CLICKER REVIEW QUESTIONS
 SOME QUICKIE CLICKER REVIEW QUESTIONS ATTENTION!! THESE ARE UNREGISTERED CLICKERS WITH POINTS BUT NO NAME ATTACHED CHECK YOUR CLICKER DEVICE ID ON THE BACK DOES IT MATCH ANY OF THESE NUMBERS WHICH HAVE
SOME QUICKIE CLICKER REVIEW QUESTIONS ATTENTION!! THESE ARE UNREGISTERED CLICKERS WITH POINTS BUT NO NAME ATTACHED CHECK YOUR CLICKER DEVICE ID ON THE BACK DOES IT MATCH ANY OF THESE NUMBERS WHICH HAVE
Anthropogenic atmospheric CO 2 increases. A warming Earth. The rise in atmospheric CO 2 (and other GHGs) is responsible for global warming
 IPCC AR4 Anthropogenic atmospheric CO 2 increases A warming Earth The rise in atmospheric CO 2 (and other GHGs) is responsible for global warming Required amount of CO 2 reduction to mitigate global warming
IPCC AR4 Anthropogenic atmospheric CO 2 increases A warming Earth The rise in atmospheric CO 2 (and other GHGs) is responsible for global warming Required amount of CO 2 reduction to mitigate global warming
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page:
 ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
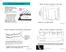 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
A topic of the times. Climate Change & Global Warming. Do we notice Global Warming? How do we find the facts? Proxies
 A topic of the times Climate Change & Global Warming Courtesy IPCC 1 2 Do we notice Global Warming? Aberdeen mean temps Jan 1996-15th Feb 2003 20.00 15.00 Degrees Celsius Daily events don t show up global
A topic of the times Climate Change & Global Warming Courtesy IPCC 1 2 Do we notice Global Warming? Aberdeen mean temps Jan 1996-15th Feb 2003 20.00 15.00 Degrees Celsius Daily events don t show up global
Climate Change & Global Warming. Courtesy IPCC
 Climate Change & Global Warming Courtesy IPCC 1 A topic of the times 2 3 Do we notice Global Warming? Daily events don t show up global warming Degrees Celsius Aberdeen mean temps Jan 1996-15th Feb 2003
Climate Change & Global Warming Courtesy IPCC 1 A topic of the times 2 3 Do we notice Global Warming? Daily events don t show up global warming Degrees Celsius Aberdeen mean temps Jan 1996-15th Feb 2003
ATS 421/521. Climate Modeling. Spring Lecture 3 HW1 due. Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity. Monday, April 8, 13
 ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2013 Lecture 3 HW1 due Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity Special lecture at the LaSells Stewart Center: Title: Air Bubbles in Ice, Salt in the Sea Speakers:
ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2013 Lecture 3 HW1 due Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity Special lecture at the LaSells Stewart Center: Title: Air Bubbles in Ice, Salt in the Sea Speakers:
Skeptics have no clothes
 Skeptics have no clothes Man-made global warming is the greatest hoax ever perpetrated on the American people. Senator James Inhofe (R-OK) You re entitled to your own opinion but not your own facts Patrick
Skeptics have no clothes Man-made global warming is the greatest hoax ever perpetrated on the American people. Senator James Inhofe (R-OK) You re entitled to your own opinion but not your own facts Patrick
High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals. October 2011
 1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2
 Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
WEDNESDAY Dec 9 th OUR LAST CLASS!
 WEDNESDAY Dec 9 th OUR LAST CLASS! 1) WHEN YOU ARRIVE: Submit these items in the separate BROWN FOLDER for your Group: (1) Your annotated LTL FILM COMMENTARY ROUGH DRAFT & (2) your PEER REVIEW CHECKLIST
WEDNESDAY Dec 9 th OUR LAST CLASS! 1) WHEN YOU ARRIVE: Submit these items in the separate BROWN FOLDER for your Group: (1) Your annotated LTL FILM COMMENTARY ROUGH DRAFT & (2) your PEER REVIEW CHECKLIST
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank
 How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate
 Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate Part 2 Learning outcomes list and describe the major natural and anthropogenic forcings of recent CC understand the effect of feedbacks on amplifying or dampening
Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate Part 2 Learning outcomes list and describe the major natural and anthropogenic forcings of recent CC understand the effect of feedbacks on amplifying or dampening
Chapter 19: Global Change
 1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
1 Summary Of the Case Study Polar Bear population in the Antarctic going down because temperatures are going up and melting the caps. Polar bears are losing their habitat, they also can t get their food
Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol?
 Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol? Barbara Wyslouzil, Sept. 10 2007 Outline Aerosols 101 The greenhouse effect Global temperature records The global warming problem How do aerosols play a role
Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol? Barbara Wyslouzil, Sept. 10 2007 Outline Aerosols 101 The greenhouse effect Global temperature records The global warming problem How do aerosols play a role
Climate Change and Energy
 1/31 Climate Change and Energy David S. Gutzler Earth & Planetary Sciences Dept gutzler@unm.edu * Global warming over the past century * Attribution of observed climate change à why we blame fossil fuels
1/31 Climate Change and Energy David S. Gutzler Earth & Planetary Sciences Dept gutzler@unm.edu * Global warming over the past century * Attribution of observed climate change à why we blame fossil fuels
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun
 Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun Announcements TONIGHT: HW #6 (paper outlines) due in lecture! bring up at Break HW #7 (presentation outlines) due in section next week Email
Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun Announcements TONIGHT: HW #6 (paper outlines) due in lecture! bring up at Break HW #7 (presentation outlines) due in section next week Email
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires,
 Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes
 Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Climate Change. Some solar radiation is reflected by Earth and the atmosphere. Earth s Surface
 Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
Understanding Global Warming
 Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
The Climate System. Goal of this session: Session contents. Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change
 Training package Providing Regional Climates for Impacts Studies - PRECIS Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change Joseph D. Intsiful CGE Hands-on training Workshop on V & A, Asuncion, Paraguay,
Training package Providing Regional Climates for Impacts Studies - PRECIS Modelling the Climate System and Climate Change Joseph D. Intsiful CGE Hands-on training Workshop on V & A, Asuncion, Paraguay,
1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse.
 1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse. 5. A gradual increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide would warm Earth s because carbon dioxide is a A) poor reflector of ultraviolet radiation B) good reflector
1. The diagram below shows a greenhouse. 5. A gradual increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide would warm Earth s because carbon dioxide is a A) poor reflector of ultraviolet radiation B) good reflector
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE. Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTANTS Acid Rain Acid Rain is the precipitation that carries
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project ALTERING CLIMATE Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey ATMOSPHERIC POLLUTANTS Acid Rain Acid Rain is the precipitation that carries
Evidence for climate change
 Evidence for climate change Climate change over the quaternary period The quaternary period is the most recent geological time period spanning from around 2.6 million years ago to present day. This is
Evidence for climate change Climate change over the quaternary period The quaternary period is the most recent geological time period spanning from around 2.6 million years ago to present day. This is
Climate Change state of the science
 Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change
 FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
Chapter Overview. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. Earth s Climate System. CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Change
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 The Oceans and Climate Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity
 Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It
 Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
The greenhouse effect
 Sources of CO 2 It is an undisputable fact that the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing, see next page for the evidence. There are of course many sources of the CO 2 in the atmosphere,
Sources of CO 2 It is an undisputable fact that the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing, see next page for the evidence. There are of course many sources of the CO 2 in the atmosphere,
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist
 Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
CLIMATE CHANGE. controversies. a simple guide
 CLIMATE CHANGE controversies a simple guide The Royal Society has produced this overview of the current state of scientific understanding of climate change to help non-experts better understand some of
CLIMATE CHANGE controversies a simple guide The Royal Society has produced this overview of the current state of scientific understanding of climate change to help non-experts better understand some of
Radiation and Climate Change
 Radiation and Climate Change Earth s Energy Balance Forcing and Feedback Implications for climate change including the global water cycle Introduction / Motivations Past societies e.g. Jared Diamond: Collapse
Radiation and Climate Change Earth s Energy Balance Forcing and Feedback Implications for climate change including the global water cycle Introduction / Motivations Past societies e.g. Jared Diamond: Collapse
Climate Change 101. Dr. Dave DuBois. April 19, 2017
 Climate Change 101 Dr. Dave DuBois April 19, 2017 Is the climate changing? Past 1000 Years Northern Hemisphere temperature reconstructions Mann et al. 2008. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Climate Change 101 Dr. Dave DuBois April 19, 2017 Is the climate changing? Past 1000 Years Northern Hemisphere temperature reconstructions Mann et al. 2008. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer. Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June
 ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
You are almost done! TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9. 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam. After this week... here s what s left:
 Where are we now? You are almost done! After this week... here s what s left: TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam A few wrap-up questions to start.... CLICKER TIME!! FLIP BACK TO p 56 in
Where are we now? You are almost done! After this week... here s what s left: TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam A few wrap-up questions to start.... CLICKER TIME!! FLIP BACK TO p 56 in
CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System
 1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS!
 G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS! #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted in the largest GLOBAL cooling: #1 Low latitude eruption both hemispheres #2 Large amount of eruptive material
G-5 ACTIVITY ON VOLCANISM & CLIMATE THE ANSWERS! #1. List 4 reasons why Tambora in 1815 resulted in the largest GLOBAL cooling: #1 Low latitude eruption both hemispheres #2 Large amount of eruptive material
FOLLOW: Green House on Twitter
 Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
Feedback loops modify atmospheric processes
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Climate Change: Implications for Nebraska. Donald A. Wilhite School of Natural Resources University of Nebraska- Lincoln
 Climate Change: Implications for Nebraska Donald A. Wilhite School of Natural Resources University of Nebraska- Lincoln The Politics of Climate Change Sen. Jim Inhofe (R-Okla.) has, once and for all, disproven
Climate Change: Implications for Nebraska Donald A. Wilhite School of Natural Resources University of Nebraska- Lincoln The Politics of Climate Change Sen. Jim Inhofe (R-Okla.) has, once and for all, disproven
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter outline. introduction. Reference. Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science
 Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
GLOBAL WARMING. Earth should be in cool-down-period
 GLOBAL WARMING Global Warming is defined as the increase of the average temperature on Earth. As the Earth is getting hotter, disasters like hurricanes, droughts and floods are getting more frequent. Over
GLOBAL WARMING Global Warming is defined as the increase of the average temperature on Earth. As the Earth is getting hotter, disasters like hurricanes, droughts and floods are getting more frequent. Over
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century
 TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of
TERMS TO KNOW: Climate change:a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of
What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR
 What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR Weather: the outdoor conditions at a particular time and place Climate: an average of weather conditions in a given area over a period
What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR Weather: the outdoor conditions at a particular time and place Climate: an average of weather conditions in a given area over a period
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge
 ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test
 Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
Anthropogenic Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future. Dr. David Karowe Department of Biological Sciences. Earth s climate is always changing
 Anthropogenic Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future Dr. David Karowe Department of Biological Sciences Earth s climate is always changing 1 Antarctic ice cores provide a record of Earth s climate over
Anthropogenic Climate Change: Past, Present, and Future Dr. David Karowe Department of Biological Sciences Earth s climate is always changing 1 Antarctic ice cores provide a record of Earth s climate over
READING QUESTIONS: Global Climate Change GEOL /WI. 2. Fill in the blanks in the following sentences from the textbook (p.
 READING QUESTIONS: Global Climate Change GEOL 131 18/WI NAME DUE: Tuesday, April 24 57pts Climate and Geology (p. 382) 1. List the five spheres included in the climate system. (5 pts) Detecting Climate
READING QUESTIONS: Global Climate Change GEOL 131 18/WI NAME DUE: Tuesday, April 24 57pts Climate and Geology (p. 382) 1. List the five spheres included in the climate system. (5 pts) Detecting Climate
ECC: WARM-UP Students review their homework and compare the effects of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide on energy and temperature.
 ECC: 4.2.1 WARM-UP Students review their homework and compare the effects of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide on energy and temperature. (5 min) For homework, you modeled what happens when incoming energy
ECC: 4.2.1 WARM-UP Students review their homework and compare the effects of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide on energy and temperature. (5 min) For homework, you modeled what happens when incoming energy
The Science of Climate Change
 The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic
 C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
Chapter 4: The Global Energy System
 Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 4: The Global Energy System The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Solar Energy Solar Energy as Radiation Electromagnetic energy transmitted
Discovering Physical Geography Third Edition by Alan Arbogast Chapter 4: The Global Energy System The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Solar Energy Solar Energy as Radiation Electromagnetic energy transmitted
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
The instrumental record goes back to about A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern
 The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
Energy and the Earth. Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation.
 S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
S c i e n c e Energy and the Earth Key words: Incoming Solar Radiation, Electromagnetic wave, Greenhouse effect, conduction, convection, radiation. Energy transfer Heat is energy in transit from warmer
GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere
 GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere Global Atmo Energy Balance In a stable climate, Solar Energy IN = IR Energy OUT IR Out Ahrens, Fig. 2.14 Solar in The Natural Greenhouse Effect: clear sky O 3 8% CH 4
GLOBAL Energy Flow Thru Atmosphere Global Atmo Energy Balance In a stable climate, Solar Energy IN = IR Energy OUT IR Out Ahrens, Fig. 2.14 Solar in The Natural Greenhouse Effect: clear sky O 3 8% CH 4
What factors can cause long-term climate change? 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 What factors can cause long-term climate change? Solar Brightening The Sun very gradually grows brighter with time, increasing the amount of sunlight warming the planets. Changes in Axis Tilt Greater tilt
What factors can cause long-term climate change? Solar Brightening The Sun very gradually grows brighter with time, increasing the amount of sunlight warming the planets. Changes in Axis Tilt Greater tilt
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? 12/13/2016. Yes!
 1 2 3 Yes! 4 Yes! But Earth's climate is always changing! 5 Yes! But Earth's climate is always changing! 6 Throughout its 4.5 billion year history, Earth's climate has alternated between periods of warmth
1 2 3 Yes! 4 Yes! But Earth's climate is always changing! 5 Yes! But Earth's climate is always changing! 6 Throughout its 4.5 billion year history, Earth's climate has alternated between periods of warmth
Global Climate Change 4
 Global Climate Change 4 Climate Change Consequences Climate Change Mitigation Climate Change Politics Tipping points GAT: we re heating up Hockey stick graph past 1000 years 2001 Data from thermometers
Global Climate Change 4 Climate Change Consequences Climate Change Mitigation Climate Change Politics Tipping points GAT: we re heating up Hockey stick graph past 1000 years 2001 Data from thermometers
The Earth s Global Energy Balance
 The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1
 OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
GREENHOUSE GASES 3/14/2016. Water Vapor, CO 2, CFCs, Methane and NO x all absorb radiation Water vapor and CO 2 are the primary greenhouse gases
 GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Outline Last IPCC report : 2001 Last IPCC report :
 Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future?
 Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
Answers to the Questions Posed by Judge Alsup
 Answers to the Questions Posed by Judge Alsup Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois SF March 21, 2018 Date Name of Meeting 1 Addressing Some Questions for the Tutorial
Answers to the Questions Posed by Judge Alsup Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois SF March 21, 2018 Date Name of Meeting 1 Addressing Some Questions for the Tutorial
