WHAT ARE THE CORE VALUES GENERATED BY COMMUNICATION?
|
|
|
- Lucas Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
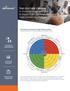
1 WHAT ARE THE CORE VALUES GENERATED BY COMMUNICATION? THE COMMUNICATION VALUE CIRCLE: A NEW FRAMEWORK VISUALIZES THE VALUE OF COMMUNICATION Communication professionals use numerous and multifaceted rationales to explain the value of their work. These range from building reputation and brands to boosting sales and fostering employee motivation. However, communicators seldom share a consistent understanding of the multiple dimensions of communication value. At the same time, a variety of different theoretical concepts exist, which explain the contribution of communication toward organizational goals yet they have never been analyzed and combined in order to draw a big picture of communication value. In order to advance the debate, we have developed a new interdisciplinary framework that has successfully been tested and applied in practice. The notion of value creation describes the transformation of resources into goods or services with a higher financial value. This is the foremost goal of each business. As a consequence, all corporate decisions should focus on increasing the overall value of the company and not only on short-term objectives. This holds true for corporate communications as well (Argenti, 2016; Zerfass, 2008). In our understanding, contributing to the value creation by communicative means is the primary task of any communication department. But how exactly can communication add value to the business? Searching for the big picture Our literature survey across different disciplines revealed that the question of how communication contributes to value creation for organizations has not been answered until now. There are many approaches, indicators, measurement methods and concepts for evaluation. However, they lead to different results, and a coherent and integrative approach is missing. There is a tendency among professional communicators and in the research community to focus on soft factors such as creating reputation, brands or relationships. Other contributions such as issues management, internal communication consulting, mastering crisis situations or providing innovation support are not often seen as a priority. In order to explain the process of value creation through communication more effectively, we have summarized the most relevant value dimensions of communication and developed a new interdisciplinary framework the Communication Value Circle. It combines and expands on insights from an extensive literature review and expert interviews with the CCOs of global corporations. The Communication Value Circle The Communication Value Circle (CVC) describes value creation on two levels: corporate management and corporate communications. At the core of the framework is the corporate strategy, which should be the starting point for all organizational decisions. Adapting and expanding on classical distinctions in management theory (e.g. Gälweiler, 2005), four generic corporate goals were combined to create a matrix in the inner circle. Tangible and intangible assets contribute to creating corporate value, whereas room for maneuver and opportunities for development contribute to enabling value creation. and room for maneuver represent the current value creation of the corporation, while intangible assets and opportunities for development foster future value creation. Every function within the corporation supports these four dimensions of corporate value. As such, the generic goals are applicable to human resources management, sales or, as in this case, corporate communications. Four overarching communication goals with twelve value dimensions The corners of the framework illustrate four overarching goals for communication that are clustered into twelve communication value dimensions (outer circle). They were all derived from the four corporate value dimensions (inner circle). 1 Enabling operations: communication supports business operations, e.g. through stimulating publicity, customer, and employee. By disseminating content and messages and raising attention and awareness for strategic issues, products or services, communication keeps an organization running and enables the creation of material assets. By managing dialogues with employees, suppliers, customers etc. on a daily basis, communication builds the basis for delivering value to key stakeholders. 2 Building intangibles: communication helps to create intangible assets, such as reputation, brands or corporate. Intangibles are part of the overall company value. A positive reputation and strong brands create a strong corporate identity. Integrating the specific and history of a corporation into its internal and external communication is a basic task of any communication department. 22 COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3
2 Communication Value Circle CURRENT VALUE CREATION 1 Enabling Ensuring 3 operations flexibility CREATING VALUE CORPORATE ENABLING VALUE CREATION 2 Buildings intangibles communication Adjusting strategy 4 FUTURE VALUE CREATION 3 Ensuring flexibility: being flexible as a corporation means having relationships that are based on trust or, at the very least, are based on a perception of legitimacy of the corporation s values and actions. Communication can build stakeholder networks, which ensure room for maneuver, especially in times of change and crisis. If the license to operate is questioned by relevant stakeholders, every other value dimension will be affected negatively. 4 Adjusting strategy: communication supports the strategic positioning by fostering thought, identifying and communicating innovation, and building up crisis. This value dimension is based first and foremost on the communication department s capacity to listen. Systematically monitoring public opinion in the mass media, social media, markets, politics and society helps to adapt strategies to upcoming socio-political and economic developments. Thus, corporate communications contribute to identifying competitive advantages. COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3 23
3 CORPORATE CORPORATE Measuring communication value in the 12 dimensions Business logic requires communication executives to prove how communications have contributed to annual business targets. Demonstrating the value contribution of communication is certainly somewhat more challenging for communications than for other departments. The value of communication is difficult to express in financial terms. It requires multi-indexed approaches and non-financial measures. Numerous established sets of key performance indicators (KPIs), measurement tools and evaluation methods exist and should be integrated (Stacks, 2017; Watson & Noble, 2014). Some of the established KPIs are proprietary and based on methods provided by media analytics or research companies. This requires the organization to adapt to the specific goals established through the Communication Value Circle or by other means. Overall, the best approach is always to build up a measurement approach from scratch by starting with identifying business goals, defining communication targets, establishing KPIs, identifying suitable research methods and evaluation techniques, and selecting the latter from the broad range of techniques and services available in the field. In this way, all communication goals in the Communication Value Circle can be measured to show the value-add of communication to value creation. In the following, we provide a brief explanation of all 12 communication dimensions and present a selection of possible KPIs. PUBLICITY EMPLOYEE COMMITMENT emphasizes the importance of visibility for any organization. Media publicity facilitates the process through which key stakeholders learn about the organization s products, services and unique characteristics e.g. as employers. Some organizations might also be interested in staying away from public debates, and so avoiding publicity can be a goal for communications as well. KPIs: e.g. media reach, media resonance, (un)aided awareness, page impressions, conversion rate, unique visitors, visits, likes, shares, followers, tonality, share of voice, message recall, recognition. Research tools and methods: e.g. public opinion polls, media content analyses, social media analyses, big data analyses. is the attitude of employees towards their employer. Typically, employees with high identify themselves strongly with the goals, values, and norms of an organization. Strong relates to increased satisfaction, engagement and motivation, as well as more efficient internal processes and lower employee turnover rates. KPIs: e.g. readiness for change, employee, employee motivation, employee satisfaction, engagement with the company, employee turnover rate, employee loyalty, employee trust, knowledge of the company s values, advocacy of the organization, emotion towards the company, identification with the organization. Research tools and methods: e.g. employee surveys (e.g. TNS Engagement survey, Communication Satisfaction Questionnaire), focus groups. CUSTOMER PREFERENCES include attitudes or opinions towards a product, service, brand or company held by (prospective) customers. Preference is often based on previous experiences. High customer satisfaction typically leads to customer loyalty and product repurchase. Satisfied customers are also more likely to recommend products to their peers and influence their. KPIs: e.g. customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, customer expectations, word of mouth, cross-buying intention, net promoter score, intention to buy, virality of social media messages. Research tools and methods: e.g. customer surveys (e.g. Satisfaction Index, Lifetime Value), recall and recognition tests, experiments. REPUTATION is a generalized collective perception of an organization of multiple stakeholders, including consumers, employees, investors, and other groups that are critical for corporate success. As such, reputation is formed externally and is based on subjective impressions and expectations about the organization s future behavior. The corporate image in contrast is more based on a temporary, often intuitive assessment, while reputation is more enduring. can have a positive impact on overall financial performance or purchase intentions of customers and serve as a buffering shield in crises. Media reputation, on the other hand, is the reputation of a company reported in the mass media or on social media. This is only an indicator of the reputation among key stakeholders as there are many other ways of shaping impressions and expectations about an organization, e.g. word of mouth, personal experiences, etc. 24 COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3
4 CORPORATE KPIs: e.g. reputational capital, admiration of the organization, emotional appeal of the organization, perceived quality of the company s products and services, perception of the company s financial soundness, perceived quality of the company s management, perception of the company s social responsibility. Research tools and methods: e.g. reputation analyses (e.g. Global Pulse Score, Monitor), reputation rankings (e.g. AMAC Index), media reputation analyses (e.g Media Index), stakeholder surveys, focus groups. BRANDS are mental pictures of an organization or their products/ services held by its stakeholders. They serve different purposes such as identification and differentiation. are valuable immaterial assets and help companies to distinguish themselves from their competitors. engender trust in the consumer, which typically results in brand loyalty and brand preference. Strong brands can command a higher price, boost sales and market share. KPIs: e.g. brand equity, brand image, brand recall, brand preference, brand advocacy, brand mentions, brand identification. Research tools and methods: e.g. advertising impact analysis, brand analyses (e.g. Brand Potential Index, Brand Scorecard, Brand Asset Valuator, Brand Championship, Brand Potential Analysis, Brand Performancer, Interbrand Brand Valuation), focus groups, experiments. CORPORATE CULTURE is a collection of key values, symbols, meanings, beliefs, assumptions and expectations that organizational members share. Culture is how things get done and how employees feel about the company. It is created, sustained and changed by all members of the organization and may be split into subs. A strong corporate is typically related to higher productivity, lower employee turnover rates, and higher attractiveness for employees. KPIs: e.g. communication, change, of constructive criticism, teamwork and collaboration, feedback, employee awareness of corporate strategy, employee support for the corporate mission, vision and values, employee agility, employee feeling of empowerment, company attractiveness among needed talent groups. Research tools and methods: e.g. employee surveys, focus groups. RELATIONSHIPS s are the state or ties that exist between an organization and its key stakeholders and are intricately interwoven with dimensions such as trust or satisfaction. Beneficial relationships with investors, journalists, employees and critical stakeholders may serve as a buffering shield in crisis situations and safeguard the organization s room for action. High quality relationships with customers are a key success factor, often managed via Management systems. KPIs: e.g. stakeholder attitudes toward the values of the company, stakeholder satisfaction with information provision, stakeholder perception of control mutuality, stakeholder, stakeholder trust, network quality, customer relationship quality, relationship capital, social capital. Research tools and methods: e.g. focus groups, relationship analysis, (social) network analysis, stakeholder touch points analysis, journalist survey (e.g. Organization-Public Quality measure). COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3 25
5 CORPORATE HOW BEST TO APPLY THE COMMUNICATION VALUE CIRCLE INSIGHTS FROM PRACTICE Our case studies across German organizations have confirmed that the Communication Value Circle (CVC) can be used as an analytical tool in practice. It helps to identify and structure communication goals and align communication targets with the overarching corporate strategy. The CVC also provides a useful tool for testing existing communication strategies. By analyzing gaps between corporate and communication goals, communicators can detect misalignments and refocus their activities. The CVC can also be used to match all communication goals with performance indicators. This helps to reflect on existing measurement activities. They can be integrated into a consistent performance management system focused on communication and business objectives alike. Key findings of our qualitative interviews with Chief Communication Officers are: Not every single goal is as relevant for each communication department or situation. For example, communication goals such as employee or corporate become more relevant during restructuring, while trust and legitimacy are critical goals during a corporate crisis. is often considered the most important goal for communications but linking the success of communication to the company s reputation only is risky due to the fact that reputation is not only driven by communication. Communication leaders often underestimate relationship building and crisis prevention as goals. Measurement methods and key performance indicators exist for those fields as well. They should be integrated in order to document how communication reduces costs and contributes to corporate success indirectly. s are a central aspect in most business strategies. Yet promoting innovations and establishing thought are seldom mentioned as communication goals. Concepts to define targets and measure results in these fields are missing. The same is true for the field of corporate listening, e.g. for monitoring megatrends. This helps to adapt corporate strategies to external challenges. TRUST is the level of confidence in the organization s ability to do what it says it will do and that it will act consistently and dependably. is closely related to credibility and integrity. Future employees have to trust that an organization will treat them fairly. s who buy products or services with key importance for their own businesses (e.g. machinery or software in business-to-business markets) have to trust that the seller will offer continuing service and updates according to unknown future standards. replaces control in an unstable world and is important for future-oriented decisions. KPIs: e.g. credibility, transparency, trustworthiness, authenticity, integrity, competence, dependability, belief in the organization s promises, perception as a fair organization, confidence in the organization s concern for people and employees, level of forgiveness in a crisis, stakeholder emotions towards the company. Research tools and methods: e.g. credibility analyses, public opinion polls, stakeholder analyses, media trust analyses (e.g. Index). LEGITIMACY relates to the long-term ability of organizations to act in a manner that is consistent with socially accepted norms, values, commonly held beliefs and stakeholder expectations. Organizations that are perceived as legitimate safeguard their license to operate. Their ability to survive critical situations is increased. While reputation emphasizes the differences to other organizations, legitimacy emphasizes the attempt of organizations to resemble societal norms and similarities with other organizations. KPIs: e.g. perceived appropriateness of corporate actions, support from key stakeholders such as owners and governing bodies, confidence in the organization s responsibility for society or the environment, acceptance quotient. Research tools and methods: e.g. public opinion polls, stakeholder analyses, social media analyses. THOUGHT LEADERSHIP is the practice of positioning the organization as an opinion leader of new, compelling and innovative ideas in a community of interest. leaders provide new information, analysis and insights that help 26 COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3
6 others to make sense of today s complex world and better understand the future. helps organizations to raise awareness, increase the status of their brand or reputation, and recognition by other influential opinion leaders such as political or regulatory institutions. KPIs: e.g. share of voice, citations or downloads of white papers/studies, backlinks or quotations of voiced thoughts, participation in thought leader think tanks or groups; visibility on relevant platforms such as conferences or blogs, endorsement by multipliers. Research tools and methods: e.g. trends analyses, opinion leader analyses, network analyses, media and social media monitoring. INNOVATION POTENTIAL is the ability to identify opportunities for new products and services and understand trends and ideas. These insights can be used in a strategic manner to initiate or support innovative business models and functional strategies. can be fostered by a communication that promotes creativity and openness among employees and is capable of coping with constant change. Communications can also support innovation by identifying and attracting external partners, e.g. in open innovation processes. KPIs: e.g. staff engagement in innovation processes, an innovation-friendly corporate, strategic readiness of employees, employee familiarity with innovation goals, willingness to innovate, employee willingness to participate in team rotations, use of innovation communication platforms, employee willingness to think outside of the box, positioning of innovative ideas in specialist media and platforms, response to open innovation activities. Research tools and methods: e.g. employee surveys, social media and media analyses. CRISIS RESILIENCE is the ability to identify and monitor emergent critical issues, which may threaten an organization s people, assets or reputation, and utilize these insights systematically for crisis anticipation and prevention. Issues management and integrated monitoring or listening systems help to identify issues at an early stage, whereas crisis management plans enable to respond quickly and effectively to any incident. KPIs: e.g. emergent issues identified, employee awareness of crisis plans, responsibilities and guidelines, employee willingness to take risks, crisis readiness and responsiveness of leaders, number of crisis trainings performed by employees, costs of successful mitigated crises. Research tools and methods: e.g. issues analyses, sentiment analyses, social media analyses, media content analyses. Sources: Bentele et al., 2009; DPRG/ICV, 2011; Einwiller, 2014; Frandsen & Johansen, 2011; Gandomi & Haider, 2015; Heide & Simonsson, 2014; Homburg, 2012; Hon & Grunig, 1999; Liehr et al., 2010; Macnamara, 2014; Mazzei et al., 2012; Meng & Pan, 2012; Menninger, 2010; Möller et al., 2009; Pfannenberg & Zerfaß, 2010; Rolke & Sass, 2016; Schwaiger, 2004; Schwalbach, 2015; Stieglitz et al., At a glance Explaining and reporting the impact of communication in the language of top managers remains a key challenge. A consistent and integrative understanding of how communication adds value to the organization is still missing both in corporate practice and in communication and management research. The Communication Value Circle provides a new framework to help communication professionals explain the value of communication more effectively. It illustrates four generic corporate goals (inner circle) and twelve major communication goals (outer circle). In order to prove the value-add of communication to value creation, each communication goal in the Communication Value Circle can be measured using established key performance indicators (KPIs) and research methods. FURTHER READINGS Zerfass, A., & Viertmann, C. (2017). Creating Business Value through Communication: A Theory-Based Framework and its Practical Application. Journal of Communication Management, 21(1), COMMUNICATION INSIGHTS ISSUE 3 27
Quality management principles
 quality Quality management principles This document introduces seven quality management principles (QMPs). ISO 9000, ISO 9001 and related ISO quality management standards are based on these seven QMPs.
quality Quality management principles This document introduces seven quality management principles (QMPs). ISO 9000, ISO 9001 and related ISO quality management standards are based on these seven QMPs.
Behavioural Attributes Framework
 Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in highperforming organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
DON T JUST MEASURE, EVALUATE!
 DON T JUST MEASURE, EVALUATE! 31.08.2017, HAMAR ASST PROF. DR. ALEXANDER BUHMANN CO DIRECTOR @BI CENTRE FOR CORPORATE COMMUNICATION Question Can measurement of our communication activities make us better?
DON T JUST MEASURE, EVALUATE! 31.08.2017, HAMAR ASST PROF. DR. ALEXANDER BUHMANN CO DIRECTOR @BI CENTRE FOR CORPORATE COMMUNICATION Question Can measurement of our communication activities make us better?
Visionary Leadership. Systems Perspective. Student-Centered Excellence
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
CORE COMPETENCIES. For all faculty and staff
 SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
The power of provenance
 The power of provenance Shaping brands in a changing world Revenue Goodwill Member Trust Loyalty Value VIP The Provenance Chain " A brand's provenance... is not about preserving the past, it is about preserving
The power of provenance Shaping brands in a changing world Revenue Goodwill Member Trust Loyalty Value VIP The Provenance Chain " A brand's provenance... is not about preserving the past, it is about preserving
DNA 25. Dina Sample. Talent. ABC Corp NEW 25. Copyright Target Training International, Ltd.
 DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
DNA 25 Talent ABC Corp 12-23-2015 NEW 25 Introduction Your success in any job depends on the value of your contribution to the organization. Managers, mentors and professional coaches can encourage, advise
WHICH ROLES ARE PERFORMED BY CHIEF COMMUNICATION OFFICERS? THE COMMUNICATION MANAGER ROLES GRID REFLECTS THE MULTIPLE ROLES OF TODAY S COMMUNICATORS
 WHICH ROLES ARE PERFORMED BY CHIEF COMMUNICATION OFFICERS? THE COMMUNICATION MANAGER ROLES GRID REFLECTS THE MULTIPLE ROLES OF TODAY S COMMUNICATORS Communication leaders have manifold responsibilities,
WHICH ROLES ARE PERFORMED BY CHIEF COMMUNICATION OFFICERS? THE COMMUNICATION MANAGER ROLES GRID REFLECTS THE MULTIPLE ROLES OF TODAY S COMMUNICATORS Communication leaders have manifold responsibilities,
Loyalty. Engaging Employees through Corporate Responsibility. Employee Relationship Management
 Loyalty Engaging Employees through Corporate Responsibility Employee Relationship Management 3 Contents 4 Introduction 6 Corporate Responsibility (CR) - The Employee Perception 7 Attracting and Retaining
Loyalty Engaging Employees through Corporate Responsibility Employee Relationship Management 3 Contents 4 Introduction 6 Corporate Responsibility (CR) - The Employee Perception 7 Attracting and Retaining
EXECUTIVEVIEW360 ExecutiveView360 Profile for: Sally Sample Envisia Learning Feb Envisia Learning, Inc.
 EXECUTIVEVIEW360 ExecutiveView360 Profile for: Sally Sample Envisia Learning Feb 13 2015 2015 Envisia Learning, Inc. Summary Feedback Report Introduction This Feedback Report provides you information about
EXECUTIVEVIEW360 ExecutiveView360 Profile for: Sally Sample Envisia Learning Feb 13 2015 2015 Envisia Learning, Inc. Summary Feedback Report Introduction This Feedback Report provides you information about
Leading Change to Improve Student Learning RAPPS Webinar Series
 Leading Change to Improve Student Learning RAPPS Webinar Series Webinar #2: Empowering School Staffs to Improve Student Learning Through Collective Efficacy Cherie Lyons, Ph.D. Principal Consultant McREL
Leading Change to Improve Student Learning RAPPS Webinar Series Webinar #2: Empowering School Staffs to Improve Student Learning Through Collective Efficacy Cherie Lyons, Ph.D. Principal Consultant McREL
SKILLS FRAMEWORK FOR HOTEL AND ACCOMMODATION SERVICES SKILLS STANDARDS FOR ASSISTANT EXECUTIVE HOUSEKEEPER
 Occupation: Assistant Executive Housekeeper Occupation Description: Reporting to the Executive Housekeeper or Director of Housekeeping, the Assistant Executive Housekeeper ensures consistently high operating
Occupation: Assistant Executive Housekeeper Occupation Description: Reporting to the Executive Housekeeper or Director of Housekeeping, the Assistant Executive Housekeeper ensures consistently high operating
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Sales Management version
 TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Sales Management version John Demonstration File Opportunity for Talent 4-19-2006 Copyright 2004-2006. Target Training International, Ltd. and Dr. D. Mefford. INTRODUCTION
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Sales Management version John Demonstration File Opportunity for Talent 4-19-2006 Copyright 2004-2006. Target Training International, Ltd. and Dr. D. Mefford. INTRODUCTION
How to Succeed in Social Selling with Employee Advocacy
 How to Succeed in Social Selling with Employee Advocacy What is social selling? Social selling is about leveraging social networks to interact with potential buyers to build revenuedriving relationships.
How to Succeed in Social Selling with Employee Advocacy What is social selling? Social selling is about leveraging social networks to interact with potential buyers to build revenuedriving relationships.
BRAND MANAGER. Reporting Relationship and Location. Purpose and Major Challenges of the Role. Role Accountabilities.
 Job Description BRAND MANAGER This job description provides an indicative outline of the purpose and accountabilities of the role. Specific performance requirements and expectations will be included in
Job Description BRAND MANAGER This job description provides an indicative outline of the purpose and accountabilities of the role. Specific performance requirements and expectations will be included in
GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation
 GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation 1 Introduction Governments are facing challenges in meeting societal expectations and have an interest in Governmental Social Responsibility
GSR Management System - A Guide for effective implementation 1 Introduction Governments are facing challenges in meeting societal expectations and have an interest in Governmental Social Responsibility
Achieving customer intimacy with IBM SPSS products
 Achieving customer intimacy with IBM SPSS products Transformative technologies for the new era of customer interactions Highlights: Customer intimacy is an innovative strategy for helping organizations
Achieving customer intimacy with IBM SPSS products Transformative technologies for the new era of customer interactions Highlights: Customer intimacy is an innovative strategy for helping organizations
Corporate Digital Communications is a 20-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 7 modules.
 Module Specification: Corporate Digital Communications Corporate Digital Communications is a 20-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 7 modules. To gain the CIM Level 7 Postgraduate
Module Specification: Corporate Digital Communications Corporate Digital Communications is a 20-credit mandatory module which sits within the suite of Level 7 modules. To gain the CIM Level 7 Postgraduate
Competencies. Working in Partnership. Creativity and Innovation Organisational and People Development
 Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
Competencies Leadership Competency Framework - Summary Technical Expertise Demonstrates an avid interest in continuously enhancing current skills and learning new ones; applies advanced functional or technical
Fife Cultural Trust PEOPLE STRATEGY Foreword by the Chief Executive. Our Fife Cultural Trust (FCT)
 Fife Cultural Trust PEOPLE STRATEGY 2014-2017 People are FCT s greatest and most important asset. Our job is to ensure that Fife is a culturally vibrant and rewarding place to live, work study and visit.
Fife Cultural Trust PEOPLE STRATEGY 2014-2017 People are FCT s greatest and most important asset. Our job is to ensure that Fife is a culturally vibrant and rewarding place to live, work study and visit.
Employee engagement: An illusive force of motivation and emotional commitment of employees to the organization and its goals.
 ISSN-2379-1047 Volume 4, Issue 1, 10 Pages Research Article Employee engagement: An illusive force of motivation and emotional commitment of employees to the Dr. Almas Sabir 1, Dr. Arisha Fatima Rizvi
ISSN-2379-1047 Volume 4, Issue 1, 10 Pages Research Article Employee engagement: An illusive force of motivation and emotional commitment of employees to the Dr. Almas Sabir 1, Dr. Arisha Fatima Rizvi
RepTrak. Measuring and managing the reputation of some of the largest and best performing companies around the world
 RepTrak Measuring and managing the reputation of some of the largest and best performing companies around the world RepTrak Model Your firm s reputation is held in the hearts and minds of every person
RepTrak Measuring and managing the reputation of some of the largest and best performing companies around the world RepTrak Model Your firm s reputation is held in the hearts and minds of every person
NCEA Level 2 Business Studies (90843) 2014 page 1 of 6
 Assessment Schedule 2014 NCEA Level 2 Business Studies (90843) 2014 page 1 of 6 Business Studies: Demonstrate understanding of the internal operations of a large business (90843) Evidence Statement Notes:
Assessment Schedule 2014 NCEA Level 2 Business Studies (90843) 2014 page 1 of 6 Business Studies: Demonstrate understanding of the internal operations of a large business (90843) Evidence Statement Notes:
Communication Plan Workbook
 TALK POINTS COMMUNICATION Communication Plan Workbook Templates for Six Steps to Improving Corporate Performance with a Communication Plan A Higher Level Learning Company www.talkpointscommunication.com
TALK POINTS COMMUNICATION Communication Plan Workbook Templates for Six Steps to Improving Corporate Performance with a Communication Plan A Higher Level Learning Company www.talkpointscommunication.com
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS
 CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
CORE VALUES AND CONCEPTS The Criteria are built on the following set of interrelated core values and concepts: visionary leadership customer-driven excellence organizational and personal learning valuing
THREE-YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN UPDATE v1
 THREE-YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN UPDATE v1 FY2017-FY2019 OUR STRATEGY To develop future professionals through relevant and accessible credentialing programs 100% Member Market Penetration To deliver member value
THREE-YEAR STRATEGIC PLAN UPDATE v1 FY2017-FY2019 OUR STRATEGY To develop future professionals through relevant and accessible credentialing programs 100% Member Market Penetration To deliver member value
VITAL SIGNS. MEASURING the Drivers of Organizational Effectiveness
 VITAL SIGNS MEASURING the Drivers of Organizational Effectiveness BLUEGG 2015 70% of organizational change efforts fail - primarily due the people side. How do you develop the insight to stay in the 30%?
VITAL SIGNS MEASURING the Drivers of Organizational Effectiveness BLUEGG 2015 70% of organizational change efforts fail - primarily due the people side. How do you develop the insight to stay in the 30%?
UC Core Competency Model
 UC Core Competency Model Developed and Endorsed by: UC Learning and Development Consortium Chief Human Resources Officers Date: May 2011 University of California Staff Employees Core Competencies Communication
UC Core Competency Model Developed and Endorsed by: UC Learning and Development Consortium Chief Human Resources Officers Date: May 2011 University of California Staff Employees Core Competencies Communication
Work Expectations Profile
 Work Expectations Profile Explores the psychological contract of needs and expectations between employees and employers Work Expectations Profile Explores the psychological contract of need and expectations
Work Expectations Profile Explores the psychological contract of needs and expectations between employees and employers Work Expectations Profile Explores the psychological contract of need and expectations
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Core Values and Concepts
 Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Core Values and Concepts These beliefs and behaviors are embedded in high-performing organizations. They are the foundation for integrating key performance and operational requirements within a results-oriented
Leadership Development Survey
 Leadership Development Survey LTP Name: V. Example Date: August 17, 2016 LTP BV 2016. All Rights Reserved. Your responses will be processed with utmost care to produce a fair and correct assessment of
Leadership Development Survey LTP Name: V. Example Date: August 17, 2016 LTP BV 2016. All Rights Reserved. Your responses will be processed with utmost care to produce a fair and correct assessment of
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing
 A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing 9.14.2015 HR Toolkit http://www.unitedwayofcolliercounty.org/maphr 2015 Competence is the ability of an individual to do a job properly. Job competencies
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing 9.14.2015 HR Toolkit http://www.unitedwayofcolliercounty.org/maphr 2015 Competence is the ability of an individual to do a job properly. Job competencies
FMEP: Facilities Management Evaluation Program
 The Self-Evaluation Criteria FMEP: Facilities Management Evaluation Program 1.0 Leadership Senior leaders in an effective facilities organization set direction and establish customer focus, clear and visible
The Self-Evaluation Criteria FMEP: Facilities Management Evaluation Program 1.0 Leadership Senior leaders in an effective facilities organization set direction and establish customer focus, clear and visible
SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits)
 SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits) The strength and magnitude of an organisation s reputation represents the way in which a complex range of stakeholders perceive an organisation, entity
SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits) The strength and magnitude of an organisation s reputation represents the way in which a complex range of stakeholders perceive an organisation, entity
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing. HR Toolkit
 A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing HR Toolkit 2015 Competency models help make transparent the skills an agency needs to be successful. Start by identifying competencies that predict
A Guide to Competencies and Behavior Based Interviewing HR Toolkit 2015 Competency models help make transparent the skills an agency needs to be successful. Start by identifying competencies that predict
SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits)
 SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits) Total Qualification Time: 110 Hours The strength and magnitude of an organisation s reputation represents the way in which a complex range of stakeholders
SYLLABUS - MANAGING CORPORATE REPUTATION (10 Credits) Total Qualification Time: 110 Hours The strength and magnitude of an organisation s reputation represents the way in which a complex range of stakeholders
Performance Skills Leader. Individual Feedback Report
 Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
An individual's talents and personal skills are a fundamental and integral part of who they are.
 INTRODUCTION Research suggests that the most effective people are those who understand themselves, both their strengths and weaknesses, so they can develop strategies to meet the demands of their environment.
INTRODUCTION Research suggests that the most effective people are those who understand themselves, both their strengths and weaknesses, so they can develop strategies to meet the demands of their environment.
How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0
 Social Sector Practice How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0 OCAT 2.0 is an updated and improved version of our original OCAT survey. It asks nonprofit staff to rate their organization s operational
Social Sector Practice How it works: Questions from the OCAT 2.0 OCAT 2.0 is an updated and improved version of our original OCAT survey. It asks nonprofit staff to rate their organization s operational
Enabling, Engaging, & Rewarding Employees A Study of Most Admired Companies
 Enabling, Engaging, & Rewarding Employees A Study of Most Admired Companies Tom McMullen Mexico City (April 6, 2011) Fortune survey of World s Most Admired Companies What is it? Fortune has combined the
Enabling, Engaging, & Rewarding Employees A Study of Most Admired Companies Tom McMullen Mexico City (April 6, 2011) Fortune survey of World s Most Admired Companies What is it? Fortune has combined the
2012 ceo, social media & leadership survey
 2012 ceo, social media & leadership survey Foreword by Ann Charles, CEO BRANDfog In today s digital world, social media has become an increasingly important communications channel for building a connection
2012 ceo, social media & leadership survey Foreword by Ann Charles, CEO BRANDfog In today s digital world, social media has become an increasingly important communications channel for building a connection
Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership
 Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership ICMA delivers the latest research in the 14 core areas critical for effective local government leadership and management. ICMA University is the premier
Practices for Effective Local Government Leadership ICMA delivers the latest research in the 14 core areas critical for effective local government leadership and management. ICMA University is the premier
Public Health Competency Based Employee Performance Management Self Assessment Tool - Front Line Provider
 Public Health Competency Based Employee Performance Management Self Assessment Tool - Front Line Provider Public Health Competency Based Employee Performance Management Toolkit OPHA & Partners, Version
Public Health Competency Based Employee Performance Management Self Assessment Tool - Front Line Provider Public Health Competency Based Employee Performance Management Toolkit OPHA & Partners, Version
Dr. Ralph Pim
 Dr. Ralph Pim ralphpim@gmail.com https://twitter.com/keepdrivinon Today s Game Plan The principles of greatness. Leadership tips for creating greatness. Leading change. Building a culture of greatness.
Dr. Ralph Pim ralphpim@gmail.com https://twitter.com/keepdrivinon Today s Game Plan The principles of greatness. Leadership tips for creating greatness. Leading change. Building a culture of greatness.
Identity Is Destiny. Discussion and action guide. I am alive I The Law of Being
 I am alive I The Law of Being Is your company led and managed as a living being with a mind of its own, as described in Identity Is Destiny, or as an inert, mechanical entity? What are the signs? What
I am alive I The Law of Being Is your company led and managed as a living being with a mind of its own, as described in Identity Is Destiny, or as an inert, mechanical entity? What are the signs? What
» Kienbaum 360 Degree Feedback
 » Kienbaum 360 Degree Feedback Develop leaders. Improve leadership quality. What we offer 2» The Challenge 3 Self-reflected, authentic, confident Why leadership quality is so important good leaders make
» Kienbaum 360 Degree Feedback Develop leaders. Improve leadership quality. What we offer 2» The Challenge 3 Self-reflected, authentic, confident Why leadership quality is so important good leaders make
Social Media Manager Job Description: a Complete Guide
 - Social Media Manager Job Description: a Complete Guide Duties, responsibilities and qualifications required to succeed in today's digital marketing environment - Social Media Manager Job Description:
- Social Media Manager Job Description: a Complete Guide Duties, responsibilities and qualifications required to succeed in today's digital marketing environment - Social Media Manager Job Description:
affordability budgeting Method in which companies budget for marketing based on what they believe
 Glossary -1 Glossary for Wood, The Marketing Plan 2e affordability budgeting Method in which companies budget for marketing based on what they believe they can afford. (Chapter 10) annual plan control
Glossary -1 Glossary for Wood, The Marketing Plan 2e affordability budgeting Method in which companies budget for marketing based on what they believe they can afford. (Chapter 10) annual plan control
Engagement Marketing. Take care of your company's brand by engaging potential clients
 Engagement Marketing Take care of your company's brand by engaging potential clients TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 BUSINESS GOALS WOW EXPERIENCE - THE FIRST IMPRESSION NEWSLETTER EFFECTIVENESS
Engagement Marketing Take care of your company's brand by engaging potential clients TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 BUSINESS GOALS WOW EXPERIENCE - THE FIRST IMPRESSION NEWSLETTER EFFECTIVENESS
MKT624 Brand Management Solved MCQs By
 MKT624 Brand Management Solved MCQs By http://vustudents.ning.com 1. At the center of a brand s characteristics is the following: a. Identity b. Image c. Value d. None of the given options 2. Brand management
MKT624 Brand Management Solved MCQs By http://vustudents.ning.com 1. At the center of a brand s characteristics is the following: a. Identity b. Image c. Value d. None of the given options 2. Brand management
myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith
 myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith Management and Leadership Questionnaire 2 INTRODUCTION The Management and Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ30) assesses management and leadership
myskillsprofile MLQ30 Management and Leadership Report John Smith Management and Leadership Questionnaire 2 INTRODUCTION The Management and Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ30) assesses management and leadership
EMPLOYER BRANDING AS A RETENTION STRATEGY
 EMPLOYER BRANDING AS A RETENTION STRATEGY Mrs. Kruthika.s. Kumar [a] Abstract The term "employer branding" was first publicly introduced to a management audience in 1990, and defined by Simon Barrow, chairman
EMPLOYER BRANDING AS A RETENTION STRATEGY Mrs. Kruthika.s. Kumar [a] Abstract The term "employer branding" was first publicly introduced to a management audience in 1990, and defined by Simon Barrow, chairman
Consulting Highlights & Studies
 Consulting Highlights & Studies Master the change change management during project execution By Shula Hadi Introduction Today s business environment is characterized by one factor above all others: the
Consulting Highlights & Studies Master the change change management during project execution By Shula Hadi Introduction Today s business environment is characterized by one factor above all others: the
Charter of Good Practice in using Public Private Dialogue for Private Sector Development
 Fix www.publicprivatedialogue.org Charter of Good Practice in using Public Private Dialogue for Private Sector Development Recognising that economic progress depends on a business climate conducive to
Fix www.publicprivatedialogue.org Charter of Good Practice in using Public Private Dialogue for Private Sector Development Recognising that economic progress depends on a business climate conducive to
Feedback Report. Emotional Competency Inventory. James Corne 10/25/10
 Feedback Report Emotional Competency Inventory James Corne 10/25/10 Quick Note Before Reading As you will notice, some pages are missing in this document. For transparency reasons, I (James Corne) wanted
Feedback Report Emotional Competency Inventory James Corne 10/25/10 Quick Note Before Reading As you will notice, some pages are missing in this document. For transparency reasons, I (James Corne) wanted
IBM Cognos Consumer Insight
 IBM Cognos Consumer Insight Create Relationships. Build Advocacy. Improve Loyalty. Marco Loprete Enhancing Customer Loyalty is the Top Digital Priority Enhance customer loyalty/advocacy 67% Deploy tablet/mobile
IBM Cognos Consumer Insight Create Relationships. Build Advocacy. Improve Loyalty. Marco Loprete Enhancing Customer Loyalty is the Top Digital Priority Enhance customer loyalty/advocacy 67% Deploy tablet/mobile
BUILDING CREDIBILITY. For internal use only
 BUILDING CREDIBILITY Overview Topic Overview Being a credible business partner is critical to our ability to lead and develop trusted relationships, as well as to influence and deliver results. A key element
BUILDING CREDIBILITY Overview Topic Overview Being a credible business partner is critical to our ability to lead and develop trusted relationships, as well as to influence and deliver results. A key element
Chapter One: Introduction to Marketing... 2 Chapter Two: The Marketing Environment and Marketing Analysis Triple Bottom Line...
 CONTENTS Chapter One: Introduction to Marketing... 2 Chapter Two: The Marketing Environment and Marketing Analysis... 7 Triple Bottom Line... 9 Chapter Three: Market Research... 11 Chapter Four: Consumer
CONTENTS Chapter One: Introduction to Marketing... 2 Chapter Two: The Marketing Environment and Marketing Analysis... 7 Triple Bottom Line... 9 Chapter Three: Market Research... 11 Chapter Four: Consumer
Expert Report Chris Park
 Expert Report Chris Park Performance 0 Report for Chris Park Comparison Group: Professionals & Managers (20) Generated on: -Jan-20 Page 2 20 Willis Towers Watson. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction
Expert Report Chris Park Performance 0 Report for Chris Park Comparison Group: Professionals & Managers (20) Generated on: -Jan-20 Page 2 20 Willis Towers Watson. All rights reserved. Contents Introduction
Managing reputation risk. Laura Toni, Deloitte Romania November 28, 2014
 Managing reputation risk Laura Toni, Deloitte Romania November 28, 2014 Executive summary What is your company s reputation worth? According to a study by the World Economic Forum performed in 2012, on
Managing reputation risk Laura Toni, Deloitte Romania November 28, 2014 Executive summary What is your company s reputation worth? According to a study by the World Economic Forum performed in 2012, on
TCC Group s. Foundation Core Capacity Assessment Tool (FCCAT) Report for. 123 Foundation
 TCC Group s Foundation Core Capacity Report for FCCAT@tccgrp.com www.tccgrp.com 212.949.99 www.tccgrp.com info@tccgrp.com 219 TCC Group Table of Contents Overview of the Foundation Core Capacity...4 Summary
TCC Group s Foundation Core Capacity Report for FCCAT@tccgrp.com www.tccgrp.com 212.949.99 www.tccgrp.com info@tccgrp.com 219 TCC Group Table of Contents Overview of the Foundation Core Capacity...4 Summary
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Leadership/Management Version
 TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Leadership/Management Version Professional 6-4-2010 Maximizing Individual and Corporate Potential INTRODUCTION Research suggests that the most effective people are
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Leadership/Management Version Professional 6-4-2010 Maximizing Individual and Corporate Potential INTRODUCTION Research suggests that the most effective people are
2. Ofqual level 6 descriptors
 Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
Sample 360 Group Report KF Migration Testing-5.1
 Sample 360 Group Report KF Migration Testing-5.1 The PROFILOR for Mid-Level Leaders May 2015 The PROFILOR is an instrument developed to provide feedback and development focus and recommendations to individuals
Sample 360 Group Report KF Migration Testing-5.1 The PROFILOR for Mid-Level Leaders May 2015 The PROFILOR is an instrument developed to provide feedback and development focus and recommendations to individuals
WOMEN S FINANCIAL INCLUSION COMMUNITY OF PRACTICE (COP) CHARTER. February, 2017
 WOMEN S FINANCIAL INCLUSION COMMUNITY OF PRACTICE (COP) CHARTER February, 2017 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 MEMBERSHIP...3 JUSTIFICATION...3 SCOPE...3 1.1 Mission...3 1.2 Goals...4 COMMUNITY PARTICIPATION...4
WOMEN S FINANCIAL INCLUSION COMMUNITY OF PRACTICE (COP) CHARTER February, 2017 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 MEMBERSHIP...3 JUSTIFICATION...3 SCOPE...3 1.1 Mission...3 1.2 Goals...4 COMMUNITY PARTICIPATION...4
Violina Rindova and Luis Martins University of Texas at Austin
 SHOW ME THE MONEY: WHAT MAKES REPUTATION AN INTANGIBLE ASSET Violina Rindova and Luis Martins University of Texas at Austin Intangible Assets and Competitive Advantage Current strategy research emphasizes
SHOW ME THE MONEY: WHAT MAKES REPUTATION AN INTANGIBLE ASSET Violina Rindova and Luis Martins University of Texas at Austin Intangible Assets and Competitive Advantage Current strategy research emphasizes
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators
 UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
The Building of a Brand: An architecture to develop and integrate the 4 components to help an organization meet its brand objective.
 Design With Results in Mind The Building of a Brand: An architecture to develop and integrate the 4 components to help an organization meet its brand objective. Valerie Lee Schutte The Design Depot June
Design With Results in Mind The Building of a Brand: An architecture to develop and integrate the 4 components to help an organization meet its brand objective. Valerie Lee Schutte The Design Depot June
Culture and behaviours Creating confidence in your biggest asset
 www.pwc.com/riskassurance Culture and behaviours Creating confidence in your biggest asset The executive summary series paper No.6 People are an organisation s greatest asset and also its greatest potential
www.pwc.com/riskassurance Culture and behaviours Creating confidence in your biggest asset The executive summary series paper No.6 People are an organisation s greatest asset and also its greatest potential
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development. An Empirical Study on Requirement of Customer Expectancy Management
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 5.71 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 5, Issue 02, February -2018 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 An
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 5.71 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 5, Issue 02, February -2018 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 An
BBC Finance Competencies. BBC Finance Competencies June 2012 Page 1 of 8
 BBC Finance Competencies BBC Finance Competencies June 2012 Page 1 of 8 Purpose The Finance Competency framework has been designed to provide a basis for assessing individuals during recruitment, development
BBC Finance Competencies BBC Finance Competencies June 2012 Page 1 of 8 Purpose The Finance Competency framework has been designed to provide a basis for assessing individuals during recruitment, development
CORPORATE VALUE CREATION, INTANGIBLES, AND VALUATION: A DYNAMIC MODEL OF CORPORATE VALUE CREATION AND DISCLOSURE
 CORPORATE VALUE CREATION, INTANGIBLES, AND VALUATION: A DYNAMIC MODEL OF CORPORATE VALUE CREATION AND DISCLOSURE by John Holland, Department of Accounting and Finance, University of Glasgow, 65-71 Southpark
CORPORATE VALUE CREATION, INTANGIBLES, AND VALUATION: A DYNAMIC MODEL OF CORPORATE VALUE CREATION AND DISCLOSURE by John Holland, Department of Accounting and Finance, University of Glasgow, 65-71 Southpark
EMPLOYMENT LIFE CYCLE
 Engaging and Retaining Employees through the EMPLOYMENT LIFE CYCLE Presented by: Shellie Haroski, SPHR, SHRM-SCP Assessing Engagement 1. List what works well to engage your employees 2. List areas of opportunity
Engaging and Retaining Employees through the EMPLOYMENT LIFE CYCLE Presented by: Shellie Haroski, SPHR, SHRM-SCP Assessing Engagement 1. List what works well to engage your employees 2. List areas of opportunity
The Value of Employee Engagement. A Guide to Discovering the Business Impact of High-Engagement Employees
 A Guide to Discovering the Business Impact of High-Engagement Employees Introduction Today s business leaders are faced with many challenges brought on by recent economic, technological, demographic, and
A Guide to Discovering the Business Impact of High-Engagement Employees Introduction Today s business leaders are faced with many challenges brought on by recent economic, technological, demographic, and
Strategic Planning Process
 Strategic Planning Process InterVISTAS Consulting employing the DestinationNext Model was contracted to facilitate the strategic process: Future Study on Key Trends (Survey, Focus Groups, Interview) Identified
Strategic Planning Process InterVISTAS Consulting employing the DestinationNext Model was contracted to facilitate the strategic process: Future Study on Key Trends (Survey, Focus Groups, Interview) Identified
The ClimateQUAL : OCDA survey measures the following organizational climates:
 The ClimateQUAL : OCDA survey measures the following organizational climates: ORGANIZATIONAL CLIMATE Organizational climate refers to the interpretative frameworks shared by employees regarding the priorities
The ClimateQUAL : OCDA survey measures the following organizational climates: ORGANIZATIONAL CLIMATE Organizational climate refers to the interpretative frameworks shared by employees regarding the priorities
ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION
 ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION Contact Center Management Competencies The ICMI Professional Certification Contact Center Management Competencies specify job role-specific knowledge, skills and abilities
ICMI PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATION Contact Center Management Competencies The ICMI Professional Certification Contact Center Management Competencies specify job role-specific knowledge, skills and abilities
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Risk management Principles and guidelines. Management du risque Principes et lignes directrices
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 31000 First edition 2009-11-15 Risk management Principles and guidelines Management du risque Principes et lignes directrices http://mahdi.hashemitabar.com Reference number ISO
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 31000 First edition 2009-11-15 Risk management Principles and guidelines Management du risque Principes et lignes directrices http://mahdi.hashemitabar.com Reference number ISO
Volunteer Coordinator
 Volunteer Coordinator Ronald McDonald House Charities believes that it s people are an essential part of the Charity and value them and their contribution. This Success Profile adds to the overall value
Volunteer Coordinator Ronald McDonald House Charities believes that it s people are an essential part of the Charity and value them and their contribution. This Success Profile adds to the overall value
COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS)
 COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS) 1 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Arena of Consultancy: Talent Management and Retention... 3 3. Competency Profile based on Interview
COURSE ASSESSMENT in Consulting and Influencing Skills (CIS) 1 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Arena of Consultancy: Talent Management and Retention... 3 3. Competency Profile based on Interview
Leadership Success Factors
 SEES THE BIGGER PICTURE Has a good head for business. Is commercially aware. Knows how to make money and save money. Is close to their customers and as a result of this spots opportunities. Is profit focussed
SEES THE BIGGER PICTURE Has a good head for business. Is commercially aware. Knows how to make money and save money. Is close to their customers and as a result of this spots opportunities. Is profit focussed
GUIDE TO EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
 the essential GUIDE TO EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT Better business performance through staff satisfaction Sarah Cook KOGAN PAGE London and Philadelphia Contents Preface ix 1. What is employee engagement? 1 What
the essential GUIDE TO EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT Better business performance through staff satisfaction Sarah Cook KOGAN PAGE London and Philadelphia Contents Preface ix 1. What is employee engagement? 1 What
A Brand Equity Driving Model Based on Interaction Quality An Yan 1, a, Juanjuan Chen 2,b
 A Equity Driving Model Based on An Yan 1, a, Juanjuan Chen 2,b 1 School of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009, China 2 School of Management, Hefei University of Technology,
A Equity Driving Model Based on An Yan 1, a, Juanjuan Chen 2,b 1 School of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, Anhui, 230009, China 2 School of Management, Hefei University of Technology,
Interview Tools for Common Job Clusters for the Behavioural Competencies
 IV 72 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Supervision competency profile. It also includes the procedures
IV 72 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Supervision competency profile. It also includes the procedures
Smart Research for fresh Communication Designs
 Smart Research for fresh Communication Designs Communication design is the packaging and staging of preference-steering brand and product messages. Ideally, communications should be clear and simple but
Smart Research for fresh Communication Designs Communication design is the packaging and staging of preference-steering brand and product messages. Ideally, communications should be clear and simple but
UC Davis Career Compass Core Competencies Model
 UC Davis Career Compass Core Competencies Model Core Competencies (1 through 10 are listed in alphabetical order and 11 is an additional core competency specifically for managers and supervisors) 1. Communication
UC Davis Career Compass Core Competencies Model Core Competencies (1 through 10 are listed in alphabetical order and 11 is an additional core competency specifically for managers and supervisors) 1. Communication
LISA SMITH. Report Generated: 03/04/2008
 Administered By: Report Prepared for: ACheck America - HQ COMPLIMENTARY MERIT Applicant Name: LISA SMITH Report Generated: 03/04/2008 Report Version 2.0: Recruitment Report Intended Use Reminder The MERIT
Administered By: Report Prepared for: ACheck America - HQ COMPLIMENTARY MERIT Applicant Name: LISA SMITH Report Generated: 03/04/2008 Report Version 2.0: Recruitment Report Intended Use Reminder The MERIT
EMPIRICAL STUDY OF FACTORS AFFECTING VIRAL MARKETING
 EMPIRICAL STUDY OF FACTORS AFFECTING VIRAL MARKETING Dr. Arvinder Kour Humanities Department, YCCE, Wanadongri, Nagpur Abstract The present study has strived to trace the factors responsible for facilitating
EMPIRICAL STUDY OF FACTORS AFFECTING VIRAL MARKETING Dr. Arvinder Kour Humanities Department, YCCE, Wanadongri, Nagpur Abstract The present study has strived to trace the factors responsible for facilitating
The #1 Adsorption Technology Company FILTRATION PURIFICATION SEPARATION DEHYDRATION. Statement of Core Values and Beliefs
 The #1 Adsorption Technology Company FILTRATION PURIFICATION SEPARATION DEHYDRATION Statement of Core Values and Beliefs Issued by Kurt Sorschak, President October 2008 A message from the President Dear
The #1 Adsorption Technology Company FILTRATION PURIFICATION SEPARATION DEHYDRATION Statement of Core Values and Beliefs Issued by Kurt Sorschak, President October 2008 A message from the President Dear
Competency Catalog June 2010
 Competency Catalog June 2010 Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are those generic or cross-organizational competencies that are applicable to various functions and/or posts. They focus on
Competency Catalog June 2010 Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are those generic or cross-organizational competencies that are applicable to various functions and/or posts. They focus on
BALANCED SCORECARD STRATEGY MAPS FOR-PROFIT EXAMPLES
 BALANCED SCORECARD STRATEGY MAPS FOR-PROFIT EXAMPLES Strategy maps are used by many for-profit organizations and corporations to clearly communicate their strategic plan. A good strategy map should identify
BALANCED SCORECARD STRATEGY MAPS FOR-PROFIT EXAMPLES Strategy maps are used by many for-profit organizations and corporations to clearly communicate their strategic plan. A good strategy map should identify
ICMA PRACTICES FOR EFFECTIVE LOCAL GOVERNMENT LEADERSHIP Approved by the ICMA Executive Board June 2017; effective November 2017
 Reorganization The Credentialing Advisory Board proposed, and the Leadership Advisory and Executive Boards agreed, that the ICMA Practices should be organized as a narrative rather than a list. The following
Reorganization The Credentialing Advisory Board proposed, and the Leadership Advisory and Executive Boards agreed, that the ICMA Practices should be organized as a narrative rather than a list. The following
The concept of brand equity - A comparative approach
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The concept of brand equity - A comparative approach Ovidiu Ioan Moisescu 2005 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/32013/ MPRA Paper No. 32013, posted 4 July 2011
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The concept of brand equity - A comparative approach Ovidiu Ioan Moisescu 2005 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/32013/ MPRA Paper No. 32013, posted 4 July 2011
new Competency Model Detailed Description and Examples of Updated Capability Framework December 2016
 new Competency Model Detailed Description and Examples of Updated Capability Framework December 2016 New Competency Model Competencies - overview Competencies: The competencies are part of the Overall
new Competency Model Detailed Description and Examples of Updated Capability Framework December 2016 New Competency Model Competencies - overview Competencies: The competencies are part of the Overall
Leadership Agility Profile: 360 Assessment. Prepared for J. SAMPLE DATE
 Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
Interview Tools for Common Job Clusters for the Behavioural Competencies
 IV 54 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Senior Management competency profile. It also includes the procedures
IV 54 This tool provides a selection of sample behavioural questions for the Behavioural Competencies and proficiency levels relevant to the Senior Management competency profile. It also includes the procedures
Risk reduction? Value creation?
 The power of culture: Risk reduction? Value creation? Find out what applying a cultural lens to your organisation could reveal Measuring the effectiveness and value of culture and potential risks is one
The power of culture: Risk reduction? Value creation? Find out what applying a cultural lens to your organisation could reveal Measuring the effectiveness and value of culture and potential risks is one
The Social Marketer vs. the Social Enterprise Social media in financial institutions is in transition.
 DECEMBER 2014 THE STATE OF Social Media in Financial Services The Social Marketer vs. the Social Enterprise Social media in financial institutions is in transition. Although social media is largely perceived
DECEMBER 2014 THE STATE OF Social Media in Financial Services The Social Marketer vs. the Social Enterprise Social media in financial institutions is in transition. Although social media is largely perceived
