Leadership communication: the three levels
|
|
|
- Darrell Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From the SelectedWorks of Peter Miller 2012 Leadership communication: the three levels Peter Miller, Southern Cross University Available at:
2 PUBLICATION: SIM Today s Manager Miller, P. 2012, Leadership Communication the three levels, Today s Manager, Singapore Institute of Management, Issue February March 2012, pp Leadership communication: The three levels Winston Churchill, one of the acknowledged great British Prime Ministers once said, the difference between mere management and leadership is communication. While management and leadership have been shown to be much more than communication, there is little doubt that communication skills are at the heart of effective leadership. Good communication skills alone, however, will not make an effective leader. Research on leaders over many years has demonstrated that leaders spend from around 75% to 90% of their time on communication activities. The aim of this article is therefore to map out the critical communication skills leaders need at the various levels in the organisational hierarchy. Space limits how comprehensively I can describe each skill. However, for each skill that will be identified, you can find additional resources on the Internet and in books to assist you to learn and develop it. There are three levels of communication skills for leaders: core communication skills, team communication skills, and strategic and external communication skills. As a leader gains more responsibility in an organisation and undertakes more complex and demanding roles, the leader will need to improve core skills and become more effective in the higher level team and strategic skills. To be effective, the skills should be acquired and developed in a sequence, that is from core to strategic skills. Core communication skills Sometimes communication skills are categorised under a broader term known as interpersonal skills or people skills.. Interpersonal skills are the skills needed to develop relationships with other people. Whatever term is used, research over decades has shown that these skills are most important for leaders at all levels. Within the interpersonal skills framework, the following key skills are known to be essential: Oral and written communication There are many good books available in these areas. However, what needs to be said is that leaders are expected to have reached at least an acceptable standard in these areas and the standard will be dependent upon the organisational context in which the leader works and within its usual communication practices. Every communication, oral or written, builds a picture and creates an impression about you and your
3 leadership. A leader s skills will be most visible when speaking informally, one-onone, with groups, and when giving formal presentations. Effective leaders use these occasions to connect with people, so techniques like posture and eye contact are important to learn. Practice is often the best way to be good at formal presentations and public speaking. Leaders should take every opportunity to develop and practice these skills. Non-verbal communication Facial expressions, body language, the way a person dresses, the way a person moves their hands when talking, the distance between them and the other person when talking, and their general demeanor all send messages to others. Understanding your own body language and ensuring that oral and non-verbal communication is coherent is important to leaders who wish to improve their communications with others. Some research indicates that up to 90 per cent of the meaning of a communication is captured in the non-verbal clues. What is important is that leaders understand the significance of non-verbal communication as a communication technique and as part of their interpersonal skills that are in need of constant attention and development. Active listening Genuinely listening to others requires intellectual and physical effort. It is a skill that many leaders find demanding. Some leaders hear when others talk, but far too often they do not listen to what is being transmitted, either verbally or non-verbally. Active listening is listening for the full meaning of what is being transmitted and observing. It includes listening to the non-verbal clues contained with the message without making premature judgments or interpretations. There are eight specific behaviours that leaders should endeavour to practice to build active listening skills (Robbins, Bergman, Stagg & Coulter 2003). These are: Make eye contact with the speaker so that they know you have focused your attention on them, that you are not distracted and that you can see their facial expressions and other non-verbal clues. Make affirmative nods and other appropriate facial expressions to show interest in what is being said. Appropriate movements and non-verbal listening responses on your part let the speaker know you are listening. Avoid distracting gestures that might make the speaker think you are bored or tired of what is being said. It is important that the speaker thinks they have your full and undivided attention. Ask questions to seek clarification and to ensure your own understanding but leave it until the end so as not to be interruptive. Use the paraphrasing technique by restating and rephrasing the communication in your own words by commencing with, Do you mean or As I understand it, what you are saying is. This technique checks for accuracy and verifies you have listened correctly.
4 Avoid interrupting the speaker until the end of the communication. Avoid talking over the top of the speaker. You cannot listen and speak at the same time! Make smooth transitions between the roles of speaker and listener try not to think what you might say as you listen to the other person. These behaviours can be learned, even though they may seem awkward and insincere at first try. The behaviours will become more natural if practiced and will bring about attitudes of tolerance and empathy if persevered with. Giving and receiving feedback Giving feedback on performance (both praise and criticism) is an integral part of effective leadership. It is also an activity which makes many leaders uncomfortable. It should, however, be daily activity in a team that is working effectively. Feedback from leaders can be very diverse in nature. It can range from feedback on team member work performance to feedback on a team member s interpersonal behaviour. It can be both positive and negative. Research demonstrates that leaders like to give positive feedback and usually do so promptly and enthusiastically. Negative feedback, however, is often avoided by leaders, is inappropriately delayed, and often distorted by the leader to make it more acceptable to the receiver. Feedback skills are related both to other communication skills listed in this article and to active listening, but often leaders who are good communicators are not good with feedback skills. The most significant point when giving feedback is to separate the behaviour from your interpretation of the behaviour. Focusing on behaviour when giving feedback is the key to giving good feedback, but many leaders find this much easier in theory than in practice. Take, for example, a leader responsible for assisting team members to improve their customer service who observes a team member speaking inappropriately to a customer. Interpretative feedback from this leader might be: You were rude and unhelpful, or You do not seem to care. The problem with interpretative feedback is that it often triggers a defensive reaction from the team member. The team member takes the feedback as a personal issue rather than a work issue. When people are defensive they put all their energy into counter-attacks and excuses, rather than listening with an open mind to ways in which they could improve. Therefore, when giving feedback, leaders need to focus on behaviour. Focusing on behaviour makes the feedback easier to accept by the team member. Focusing on behaviour, the leader might have said: Do you remember when you were talking to that customer? I noticed that: 1. You didn t look at the customer when you spoke to them. 2. You interrupted the customer in mid-sentence.
5 3. You walked away to talk to a colleague before the customer was finished. 1, 2 and 3 are examples of specific behaviours. A specific description of behaviour is more neutral. Team members are generally more receptive to feedback which is presented in this way. Check whether the team member was aware of the required standards before he or she did the work and choose an opportunity to talk to the person in private, without interruption. Aim to give the feedback as soon after the event as possible so that the details of the task are still fresh in the team member s mind. Finally, ensure that your feedback is clearly and fully understood. Ask the team member to rephrase the content of your feedback to ensure they fully capture the meaning that was intended. Feedback is also more effective when it is designed specifically for the personality type of person receiving it. Emotional intelligence Goleman (2004) introduced the concept of emotional intelligence (EI). EI refers to the capacity of a leader to deal effectively with their own and others emotions. EI is a core communication skill for leaders. When applied to the workplace, emotional intelligence is about thinking intelligently with emotions perceiving, expressing, understanding and managing emotions in a professional and effective manner at work. A number of recent research studies have demonstrated a positive relationship between the ability to manage emotions and the quality of social interactions and therefore leadership potential. EI is a combination of self-management and social skills that can transform and optimise individual or team performance. EI for any leader can be measured and the good news is that it can be increased over time. Conflict resolution and negotiating skills Leaders devote around 20% of their time to negotiating outcomes or resolving conflict. This is may be a low estimate, however, and in many organisational cultures the percentage is much higher. The 80/20 rule often also applies i.e. that 80% of one s time as a leader will be spent on conflict involving around 20% of the team members. Negotiating and resolving conflict is a difficult but necessary role for leaders. Many leaders are not only poorly skilled at negotiation and conflict resolution but also avoid conflict, allowing it to fester and to build into situations that are much more difficult to handle than if they were dealt with quickly at the first surface of the conflict or potential conflict. No leader likes having to intervene in conflict situations. As a rule of thumb, however, leaders must be the initiators of conflict resolution. They should handle any conflict situation when it arises. This frees the leader from having to think about the conflict and makes the leader, and those involved, much more productive. Having the ability to handle conflict situations constructively also has a direct influence on how the leader is perceived by others. According to Lussier and Achua (2004), there are five
6 conflict management styles that leaders may choose from. Every leader has a preferred style based on their personality and other leadership traits. No single conflict management style works best in all situations, so leaders should be skilled in each of the styles, selecting the one best-suited to the conflict situation. The five styles include - avoidance, accommodation, force, negotiation, and collaboration. Team communication skills Leading teams of people is somewhat different to leading individuals and leaders of teams must have a number of team communication skills. The most critical skills include: MBWA Managing by walking around (MBWA) is a skill that leaders can learn in order to be more available for communication with team members. It enables the leader to find out what s happening in the work team and gives team members the opportunity to make informal contributions. Leaders who get out of touch with the individuals in their work team are also out of touch with their customers. Two important channels of communication are therefore opened using the MBWA technique. To open up these channels of communication in an informal way a good habit to develop is to walk around your area of responsibility on a regular basis. On these regular wanderings a leader is able to: use informal conversations to teach and reinforce organisational values to individuals in the team; listen and pay close attention to team members in their own work space where they feel most comfortable and confident; discover and acknowledge innovation and systems improvements not formally reported and spread them across other areas; and coach and mentor individuals in their own surroundings. Often MBWA, may seem awkward and insincere at first try or can even be perceived as spying on the team. However, perseverance will be rewarded by better team performance in the long run. Facilitating meetings Research shows that about 15% of the salary cost of large organisations is spent on employee meeting time. An improvement in meeting skills by the leader can have a significant effect on leadership effectiveness and productivity of work teams. Dalglish and Miller (2010) suggest that leaders need to acquire the communication skills to manage productive meetings and to use the four Ps of effective meetings namely: purpose, participants,
7 planning, and process. There are many good books that expand of the four Ps and that can help you run more effective meetings and have better team outcomes. Strategic and external communication skills Strategic and external communication skills are needed by leaders at every level. However, as leaders rise towards the top of the organisation, these skills become critical. Communication becomes more complex as leaders need to address both internal and external stakeholders. Statements of vision, mission and values Leaders of organisations have long recognised the importance of clear vision and mission statements to articulate the future aspirations of the organisation s leaders to its stakeholders. Most large organisations have formal vision and mission statements in place. Values statements are a recent addition to the corporate statements issued by organisations to inform people outside the organisation (such as investors and potential employees) about the organisation and where it might be heading. They are designed to complement vision and mission statements and are the fundamental beliefs of the leaders and members of the organisation. That is, they represent underlying reasons for the actions and behaviours of organisational members. Leaders must ensure that all forms of internal communication align with and reinforce the organisation s mission, vision and values, and that internal communications connect to them and are integrated into operational processes. Research has demonstrated that many organisations and their leaders do not communicate their vision as well as they might, leaving employees and external stakeholders confused about the direction of the organisation and where they fit in to it. Regularity of communication is also important. Senior leaders must ensure that the people in the organisations they lead are regularly informed about progress towards the vision, long-term goals, principles and strategies of the organisation. They must reinforce the values of the organisation. Regularity can be achieved with techniques like regular (monthly) newsletters to staff or in broadcast s. Communication systems Organisations that have effective communication systems are known to be more effective than organisations with poor communication systems. Communication systems include such things as manual and paper-based reporting systems, information technology systems (intranets and ) and statements of policy and procedures. Leaders need to ensure that these internal communication systems are working to align with and reinforce the organisation s mission, vision and values statements.
8 Polices are particularly important as part of the communication system. They provide the guidance and direction that the employees need in order to communicate effectively with each other and express expected standards and norms. Leaders as communication role models While policies are important, what leaders actually do and say have a greater impact on employee behaviour in the organisation. Leaders, therefore, need set the standards for communication. They need to be role models for the types and tone of the communication they expect in the organisation. When leaders interact with others on a one-to-one basis, in groups, by , by internal correspondence or any other form of communication, employees observe and then generally adopt what the leaders do. Leaders set the climate for communications in the organisation by the way they communicate with team members and other leaders, the transparency of their decision making, how often they are seen around the organisation and how often they address staff in person. Knowledge management Knowledge in all its forms is the new basis of competition in the global economy. As such, it is an organisational asset that should be closely managed as part of the communication system. Knowledge is not only data or information it is a mix of organisational experience that provides a framework for evaluating and incorporating new experience and information. It originates in the minds of employees and is captured in documents or filing systems, organisational routines, processes, practices, and norms. If we accept this broad definition of what constitutes knowledge, then the generation, documentation, transfer and creation of knowledge (known as knowledge management) is an important communication function for senior leaders. Senior leaders need the skills to design and monitor the management of knowledge and the management information systems that transmit it. Communication systems should be a regular item at senior planning meetings when discussion on the way employees in the organisation can be educated in the organisation s vision, mission and values sets the agenda. External relations Developing and maintaining a positive public image is a high priority task for all leaders in an organisation. An organisation s reputation is a significant resource to be protected. Any communication from an organisation that goes outside the organisation s internal boundaries (such as sales promotions, advertising and public relations initiatives) is a component of the organisation s external relations. Such matters must be managed very carefully. Leaders need skills in media and public relations if they are to be successful and effective at the top levels. Communication across cultures
9 All communication is undertaken in a cultural context. There are many barriers preventing a leader from being an effective communicator and the different cultural backgrounds of people can be one of them. Cultural differences can affect the way a leader chooses to implement any of the skills listed in this article. If cultural barriers are not recognised and acted upon they can stand in the way of achieving shared experience and mutual understanding. There are many good books giving guidance on communication across cultures they cover topics such as gift-giving, greetings, gestures to avoid, exchanging business cards, and business dinners. Summary Everything a leader does to influence others involves communicating. Good communication skills are the foundation of effective leadership. Our new book titled The Leader in You: Developing your leadership potential, has been designed to assist both individual leaders and organisations to achieve greater effectiveness in communication. The book provides the practical tools and techniques necessary to assist leaders to become more effective communicators at all three levels. The book may be ordered by contacting UBDS Distribution SDN BHD, or enquiry@ubsd-dist.com. References Dalglish, C. and Miller, P. 2010, Leadership: Understanding its Global Impact, Tilde University Press (Palgrave Macmillan), Melbourne. Goleman, D. 2004, What makes a leader?, Harvard Business Review, The best of HBR edition, January, Article first published Lussier, R. & Achua, C. 2004, Leadership: Theory, application, skills development, 2 nd edn., Thomson, USA. Miller, P. and Dalglish, C. 2011, The Leader in You: Developing your leadership potential, Tilde University Press (Palgrave Macmillan), Melbourne. Robbins, S., Bergman, R., Stagg, I. & Coulter, M. 2003, Management, 3rd edn., Prentice Hall, Frenchs Forest.
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES. Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop HOW WE DO THINGS: OUR CORE COMPETENCIES
 NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
CORE COMPETENCIES. For all faculty and staff
 SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
SELF-AWARENESS & PROFESSIONALISM Being mindful of one s impact on others and managing thoughts, feelings and actions in an effective manner. INTEGRITY Conducting oneself and activities according to the
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES. Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop HOW WE DO THINGS: OUR CORE COMPETENCIES
 NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
NZ POLICE CORE COMPETENCIES Communicate, Partner, Solve, Deliver, Lead, Innovate, Develop 1 INTRO These are behaviours that are important to achieving our goals. They describe how we work as opposed to
Behavioural Attributes Framework
 Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
John Doe 12/18/2012. Your Business Inc Page 1 of 34
 John Doe 12/18/2012 Your Business Inc. - 1 407 242 8724 - http://mabelkatz.com - Page 1 of 34 This Customer Service Skills Feedback Report consists of four components, which are described below. 1. Overall
John Doe 12/18/2012 Your Business Inc. - 1 407 242 8724 - http://mabelkatz.com - Page 1 of 34 This Customer Service Skills Feedback Report consists of four components, which are described below. 1. Overall
Our purpose, values and competencies
 Our purpose, values and competencies Last updated October 2013 The work we do and how we behave and carry out our work at The Pensions Regulator are driven by our purpose, values and competency framework.
Our purpose, values and competencies Last updated October 2013 The work we do and how we behave and carry out our work at The Pensions Regulator are driven by our purpose, values and competency framework.
Putting our behaviours into practice
 Putting our behaviours into practice Introduction Our behaviours are an important part of One Housing. They are designed to shape how we work - they are the ideas and approaches that form the foundation
Putting our behaviours into practice Introduction Our behaviours are an important part of One Housing. They are designed to shape how we work - they are the ideas and approaches that form the foundation
Mentoring Programmes
 Mentoring Programmes 1. What is Mentoring? Mentoring is a development activity, which is firmly rooted in self management enabling the mentee to: Foster self reliance, self confidence and a belief in their
Mentoring Programmes 1. What is Mentoring? Mentoring is a development activity, which is firmly rooted in self management enabling the mentee to: Foster self reliance, self confidence and a belief in their
UBT143X Working with colleagues in the beauty industry
 UBT143X Working with in the beauty industry Unit reference number: R/507/5501 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring working within a team in the beauty industry.
UBT143X Working with in the beauty industry Unit reference number: R/507/5501 Level: 3 Guided Learning (GL) hours: 25 Overview This unit is about exploring working within a team in the beauty industry.
UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018. Title Page 1
 UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018 Title Page 1 Performance Management at UAB 3 What is Performance Management? 3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement 4 UAB Success Model 5 Performance Management
UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018 Title Page 1 Performance Management at UAB 3 What is Performance Management? 3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement 4 UAB Success Model 5 Performance Management
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council
 City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
City of Cardiff Council Behavioural Competency Framework Supporting the Values of the Council 1.CM.250 Issue 3 Nov-2014 Process Owner: Organisational Development Team Authorisation: Deborah Morley Page
Training and Assessment Guide. Deliver and monitor a service to customers
 Training and Assessment Guide Deliver and monitor a service to customers Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance outcomes, skills and knowledge required to identify customer needs and monitor
Training and Assessment Guide Deliver and monitor a service to customers Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance outcomes, skills and knowledge required to identify customer needs and monitor
IQ Level 2 NVQ Certificate in Customer Service (QCF) Specification
 IQ Level 2 NVQ Certificate in Customer Service (QCF) Specification Regulation No: 600/2832/4 Page 1 of 154 IQB/0.2/019 Version 1.0 29/09/2011 Author: D Mallinson Contents Page Industry Qualifications...
IQ Level 2 NVQ Certificate in Customer Service (QCF) Specification Regulation No: 600/2832/4 Page 1 of 154 IQB/0.2/019 Version 1.0 29/09/2011 Author: D Mallinson Contents Page Industry Qualifications...
Soft Skills for Enterprise Architects: The Key to Unlocking Value from EA
 Soft Skills for Enterprise Architects: The Key to Unlocking Value from EA Sally Bean (with some help from Keith Flanagan) 1 Sally Bean 2015 Questions for discussion today Why are soft skills important
Soft Skills for Enterprise Architects: The Key to Unlocking Value from EA Sally Bean (with some help from Keith Flanagan) 1 Sally Bean 2015 Questions for discussion today Why are soft skills important
NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework. Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results. Communication. Team Working
 NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results Leading Others Acting as a positive role model for NS&I s values and behaving with integrity by reinforcing positive
NS&I Consolidated Competency Framework Setting Direction Engaging People Delivering Results Leading Others Acting as a positive role model for NS&I s values and behaving with integrity by reinforcing positive
CBI SKILLS FRAMEWORK. Interpersonal The ability to interact with others positively and constructively to support completion of work
 CBI SKILLS FRAMEWORK Managing & leading others The ability to manage and lead others collaboratively, inclusively and inspirationally to create a high-performance culture within the CBI Planning & organisation
CBI SKILLS FRAMEWORK Managing & leading others The ability to manage and lead others collaboratively, inclusively and inspirationally to create a high-performance culture within the CBI Planning & organisation
DO YOU WANT A MENTOR?
 DO YOU WANT A MENTOR? TABLE OF CONTENTS I THINK I WANT A MENTOR--AM I READY?...2 HOW TO FIND A MENTOR THAT IS RIGHT FOR YOU...3 TIPS FOR A SUCCESSFUL RELATIONSHIP...4 THE GOALS ARE ACHIEVED--WHAT NEXT?...6
DO YOU WANT A MENTOR? TABLE OF CONTENTS I THINK I WANT A MENTOR--AM I READY?...2 HOW TO FIND A MENTOR THAT IS RIGHT FOR YOU...3 TIPS FOR A SUCCESSFUL RELATIONSHIP...4 THE GOALS ARE ACHIEVED--WHAT NEXT?...6
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK 1 Introduction to the Leadership Competency Framework The Leadership Competency Framework focuses on three levels of management: Team Leaders/Supervisors responsible for
KPA Level 3 NVQ Diploma In Customer Service (QCF) (QRN: 600/3535/3)
 KPA Level 3 NVQ Diploma In Customer Service (QCF) (QRN: 600/3535/3) Qualification for Optional ( units Copyright The content of this document is, unless otherwise indicated, Kaplan Professional Awards
KPA Level 3 NVQ Diploma In Customer Service (QCF) (QRN: 600/3535/3) Qualification for Optional ( units Copyright The content of this document is, unless otherwise indicated, Kaplan Professional Awards
Principles of customer service in hospitality, leisure, travel and tourism
 Unit 292 Principles of customer service in hospitality, leisure, travel and tourism QCF Level 2 Credit value 1 UAN T/600/1059 NOS N/A Unit aim and purpose To meet the requirements of the Hospitality, Leisure,
Unit 292 Principles of customer service in hospitality, leisure, travel and tourism QCF Level 2 Credit value 1 UAN T/600/1059 NOS N/A Unit aim and purpose To meet the requirements of the Hospitality, Leisure,
POSITION DESCRIPTION. Issue 1. Business Unit Department My Forever Family. Position number MFF03. Employee s Signature. Reports To CEO Reviewed By
 POSITION DESCRIPTION Position Title Engagement & Advocacy Manager Issue 1 Business Unit Department My Forever Family Position number MFF03 Employee s Signature Reports To CEO Reviewed By Location/s tbc
POSITION DESCRIPTION Position Title Engagement & Advocacy Manager Issue 1 Business Unit Department My Forever Family Position number MFF03 Employee s Signature Reports To CEO Reviewed By Location/s tbc
Learning Resource. Babcock International Group. Allocate and monitor the progress of work.
 Babcock International Group www.babcock.co.uk/theknowledge Learning Resource Allocate and monitor the progress of work Introduction This handout is about ensuring the work required in your area of responsibility
Babcock International Group www.babcock.co.uk/theknowledge Learning Resource Allocate and monitor the progress of work Introduction This handout is about ensuring the work required in your area of responsibility
CHRISTIAN AID GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL
 CHRISTIAN AID GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL Christian Aid s global competency model describes the main skills and abilities that everyone needs to demonstrate in order to perform effectively in their role at
CHRISTIAN AID GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL Christian Aid s global competency model describes the main skills and abilities that everyone needs to demonstrate in order to perform effectively in their role at
Emotional Intelligence and Mentoring
 Emotional Intelligence and Mentoring Ann Shannon consulting ann@.net.au www..net.au 0412 087 878 Emotional Intelligence was originally proposed to underlie Psychological well-being Life satisfaction The
Emotional Intelligence and Mentoring Ann Shannon consulting ann@.net.au www..net.au 0412 087 878 Emotional Intelligence was originally proposed to underlie Psychological well-being Life satisfaction The
Wales Millennium Centre Behavioral Competencies Framework 1
 Wales Millennium Centre Behavioural Competencies Framework Be Reflective Ensuring we understand who our customers are Taking time to listen to customers Proactively engaging with customers to find out
Wales Millennium Centre Behavioural Competencies Framework Be Reflective Ensuring we understand who our customers are Taking time to listen to customers Proactively engaging with customers to find out
Assistant Deputy Minister Profile
 Assistant Deputy Minister Profile September 2015 Role Summary: Reporting to the Deputy Minister, the primary areas of focus for the Assistant Deputy Minister are: Provide advice and support to the Deputy
Assistant Deputy Minister Profile September 2015 Role Summary: Reporting to the Deputy Minister, the primary areas of focus for the Assistant Deputy Minister are: Provide advice and support to the Deputy
british council behaviours
 british council behaviours Mat Wright Mat Wright Mat Wright CREATING SHARED PURPOSE I gain the active support of other people so they are fully engaged and motivated to contribute effectively. I do this
british council behaviours Mat Wright Mat Wright Mat Wright CREATING SHARED PURPOSE I gain the active support of other people so they are fully engaged and motivated to contribute effectively. I do this
To become a better active listener and thus reap the benefits of better relationships, less frustration and improved results, consider this PROPOSAL:
 To become a better active listener and thus reap the benefits of better relationships, less frustration and improved results, consider this PROPOSAL: P R O P O S A L Probe for understanding. As a listener,
To become a better active listener and thus reap the benefits of better relationships, less frustration and improved results, consider this PROPOSAL: P R O P O S A L Probe for understanding. As a listener,
How Improving Communication Skills Increases Bottom Line Results
 How Improving Communication Skills Increases Bottom Line Results Introduction Communication is the act of transferring information from one person to another. While it s simple enough to say, it s not
How Improving Communication Skills Increases Bottom Line Results Introduction Communication is the act of transferring information from one person to another. While it s simple enough to say, it s not
2. Ofqual level 6 descriptors
 Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria The learning outcomes and assessment criteria for the Chartered Manager Degree Apprenticeship have been based upon the following: 1. DfEdefinition - level 6 descriptor
E.M.S Leadership Development. Objectives. Leadership Development 11/4/2012. Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP. Help explain leadership techniques
 E.M.S Leadership Development Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP Objectives Help explain leadership techniques Define the role of officers as a manager How to use good communication skills Leadership Development
E.M.S Leadership Development Drew Fried, EMT-CC CHEP, CHSP Objectives Help explain leadership techniques Define the role of officers as a manager How to use good communication skills Leadership Development
Introduction. Communication: ion: Why Is Something So Simple, So Hard?
 How Improving Communication Skills Increases Bottom Line Results Introduction Communication is the act of transferring information from one person to another. While it s simple enough to say, it s not
How Improving Communication Skills Increases Bottom Line Results Introduction Communication is the act of transferring information from one person to another. While it s simple enough to say, it s not
Supporting the customer service environment
 Qualification Title Candidate: Assessor: Employer Job role (if applicable) Level 2 Certificate in Customer Service (QCF) QRN Candidate no: Centre Sector 600/3553/X Please explain why you chose this organisation
Qualification Title Candidate: Assessor: Employer Job role (if applicable) Level 2 Certificate in Customer Service (QCF) QRN Candidate no: Centre Sector 600/3553/X Please explain why you chose this organisation
SM&CR Culture Measurement Toolkit
 SM&CR Culture Measurement Toolkit November 2018 V 1.1 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Scope... 4 3 Cultural Drivers... 5 4 Culture Matrix... 7 5 Staff Survey... 10 6 Self Assessment... 10 7 Performance
SM&CR Culture Measurement Toolkit November 2018 V 1.1 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Scope... 4 3 Cultural Drivers... 5 4 Culture Matrix... 7 5 Staff Survey... 10 6 Self Assessment... 10 7 Performance
Performance Management for AUPE Leader Guide
 Performance Management for AUPE Leader Guide This guide will help managers support their AUPE employees through the management cycle. Manager and Employee Performance Management Accountabilities MANAGER
Performance Management for AUPE Leader Guide This guide will help managers support their AUPE employees through the management cycle. Manager and Employee Performance Management Accountabilities MANAGER
CGMA Competency Framework
 CGMA Competency Framework Leadership skills CGMA Competency Framework 1 Leadership skills : This requires a basic understanding of the business structures, operations and financial performance, and includes
CGMA Competency Framework Leadership skills CGMA Competency Framework 1 Leadership skills : This requires a basic understanding of the business structures, operations and financial performance, and includes
CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLANNING
 CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLANNING Preview 1 About this topic 1 Topic objectives 1 1. Strategic Planning Overview 2 1.1 Why is strategic planning important? 2 1.2 What is strategic planning?
CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE STRATEGIC BUSINESS PLANNING Preview 1 About this topic 1 Topic objectives 1 1. Strategic Planning Overview 2 1.1 Why is strategic planning important? 2 1.2 What is strategic planning?
Personal Qualities Framework for G3
 Personal Qualities Framework for G3 The following table below provides a summary of PQF behaviours by NCA grade. PQF - BEHAVIOURS DD G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 WORKING WITH OTHERS Communication A A B B C C D Teamwork
Personal Qualities Framework for G3 The following table below provides a summary of PQF behaviours by NCA grade. PQF - BEHAVIOURS DD G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 WORKING WITH OTHERS Communication A A B B C C D Teamwork
Giving and Receiving Feedback
 Penn State Performance Management: Giving and Receiving Feedback Adobe Connect Seminar: Individual Contributors Presenter: Stephanie Flanagan slm114@psu.edu; 814-863-4614 Fall 2017 2017 The Pennsylvania
Penn State Performance Management: Giving and Receiving Feedback Adobe Connect Seminar: Individual Contributors Presenter: Stephanie Flanagan slm114@psu.edu; 814-863-4614 Fall 2017 2017 The Pennsylvania
Roles, Responsibilities, and Communication
 Roles, Responsibilities, and Communication CHAPTER 5 We are very pleased to extend a warm welcome to LifeSPAN! Your willingness to be part of our work by acting as a Facilitator will, we re sure, offer
Roles, Responsibilities, and Communication CHAPTER 5 We are very pleased to extend a warm welcome to LifeSPAN! Your willingness to be part of our work by acting as a Facilitator will, we re sure, offer
Soft Skills. **Chart developed by the Seattle Jobs Initiative s Performance Skills Coalition, comprised of employer partners.
 1 Soft skills are habits, attitudes and personality traits that are increasingly important in the workplace. In fact, many of today s employers rank soft skills above technical skills. Part of the employment
1 Soft skills are habits, attitudes and personality traits that are increasingly important in the workplace. In fact, many of today s employers rank soft skills above technical skills. Part of the employment
The following guidelines will help you get the most out of your mentoring relationship.
 As a mentor, you will invest your time, energy and expertise to nurture the growth of another person. You are the special person who helps others reach their potential. Your style may range from that of
As a mentor, you will invest your time, energy and expertise to nurture the growth of another person. You are the special person who helps others reach their potential. Your style may range from that of
Chapter 8. Communicating with Employees
 Chapter 8 Communicating with Employees Word is not crystal, transparent and unchanged; it is the skin of a living thought and may vary greatly in color and content according to the circumstances and the
Chapter 8 Communicating with Employees Word is not crystal, transparent and unchanged; it is the skin of a living thought and may vary greatly in color and content according to the circumstances and the
6 Managing performance
 SECTION 6 Managing performance It can be a rewarding experience to lead a team when each individual is contributing to the success of the whole team. However, difficult challenges facing a line manager
SECTION 6 Managing performance It can be a rewarding experience to lead a team when each individual is contributing to the success of the whole team. However, difficult challenges facing a line manager
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE: A KEY SKILL FOR LEADERSHIP SUCCESS SPECIALISING IN OPTIMISING PLANNING, PEOPLE AND PERFORMANCE
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE: A KEY SKILL FOR LEADERSHIP SUCCESS SPECIALISING IN OPTIMISING PLANNING, PEOPLE AND PERFORMANCE In a study of skills that distinguish star performers in every field from entry-level
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE: A KEY SKILL FOR LEADERSHIP SUCCESS SPECIALISING IN OPTIMISING PLANNING, PEOPLE AND PERFORMANCE In a study of skills that distinguish star performers in every field from entry-level
Managing Up, Down, and Around
 Managing Up, Down, and Around Rich Orbé-Austin, PhD Dynamic Transitions Psychological Consulting January 2018 Session Objectives! To discuss the distinct challenges of management! To distinguish the varied
Managing Up, Down, and Around Rich Orbé-Austin, PhD Dynamic Transitions Psychological Consulting January 2018 Session Objectives! To discuss the distinct challenges of management! To distinguish the varied
Fairness Productive Strategic Business Focus Value-driven authentic behaviours. Openness Lean Customer Focus Cross-functional working
 livin Board Members Role Profile, Competency Framework and Person Specification Purpose of the Role Board Members are responsible for the overall governance and strategic direction of the business, committing
livin Board Members Role Profile, Competency Framework and Person Specification Purpose of the Role Board Members are responsible for the overall governance and strategic direction of the business, committing
The practice of constantly assessing personal knowledge and skills and following paths for improvement. have been done by
 Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Selection Process Rubric PERSONAL DOMAIN Personal competencies refer to the qualities, characteristics and attitudes necessary to achieve personal and system goals Continuous Growth The practice of constantly
Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources
 Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources University of Edinburgh Mentoring Connections Programme Table of Contents Mentoring Connections at the University of Edinburgh... 4 General information on the mentoring
Mentoring Toolkit Additional Resources University of Edinburgh Mentoring Connections Programme Table of Contents Mentoring Connections at the University of Edinburgh... 4 General information on the mentoring
I. Skills and Knowledge
 Facilitator Core Competencies 1 There are three components to this tool to help you identify strengths and opportunities for growth as a facilitator: (1) skills and knowledge; (2) emotional intelligence;
Facilitator Core Competencies 1 There are three components to this tool to help you identify strengths and opportunities for growth as a facilitator: (1) skills and knowledge; (2) emotional intelligence;
Being Smart. By Bob Wall
 Being Smart Only Takes you So Far The most successful leaders are masters of emotional intelligence but sometimes they need coaching. By Bob Wall In high-iq professions and companies, what distinguishes
Being Smart Only Takes you So Far The most successful leaders are masters of emotional intelligence but sometimes they need coaching. By Bob Wall In high-iq professions and companies, what distinguishes
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT
 A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT ENHANCING LEADERSHIP CAPABILITY Questions to consider What values should guide my actions? How do I best set an example for others? How do I articulate a vision of the future? How
A LEADERSHIP TOOLKIT ENHANCING LEADERSHIP CAPABILITY Questions to consider What values should guide my actions? How do I best set an example for others? How do I articulate a vision of the future? How
Delegated Authority Level 5. Human Resources Department. Job Purpose
 Post: Delegated Authority Level 5 Team: Responsible to: Responsible for: Human Resources Department Director of HR & OD Recruitment Administrators X Job Purpose To take a lead role in managing and developing
Post: Delegated Authority Level 5 Team: Responsible to: Responsible for: Human Resources Department Director of HR & OD Recruitment Administrators X Job Purpose To take a lead role in managing and developing
Team Conversation Starters
 Team Conversation Starters This guide is intended to help you get started during your action planning session and/or to dig deeper into understanding the feedback you receive from your employees during
Team Conversation Starters This guide is intended to help you get started during your action planning session and/or to dig deeper into understanding the feedback you receive from your employees during
Yale University. Pilot Mentoring Program. Mentee Guide. Rev 6/10
 Yale University Pilot Mentoring Program Mentee Guide Rev 6/10 Table of Contents Pilot Program Guidelines... 2 Program Purpose and Goals... 3 Benefits of Participation... 4 Role of Mentor... 5 Role of Mentee...
Yale University Pilot Mentoring Program Mentee Guide Rev 6/10 Table of Contents Pilot Program Guidelines... 2 Program Purpose and Goals... 3 Benefits of Participation... 4 Role of Mentor... 5 Role of Mentee...
INTRODUCTION TO TOASTMASTERS MENTORING
 INTRODUCTION TO TOASTMASTERS MENTORING LEVEL 2 PROJECT TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Introduction 3 Your Assignment 4 Assess Your Skills 5 Competencies 5 The Toastmasters Mentor 6 Traits of a Successful Mentor 8
INTRODUCTION TO TOASTMASTERS MENTORING LEVEL 2 PROJECT TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 Introduction 3 Your Assignment 4 Assess Your Skills 5 Competencies 5 The Toastmasters Mentor 6 Traits of a Successful Mentor 8
TEAM ALIGNMENT TRUST INSIDE. report. assessments. for Team Name January 30, 2010
 TRUST INSIDE assessments TEAM ALIGNMENT report for Team Name January 30, 2010 www.integroleadership.com support@integroleadership.com Copyright Integro Learning Company Pty Ltd, Australia Copyright Integro
TRUST INSIDE assessments TEAM ALIGNMENT report for Team Name January 30, 2010 www.integroleadership.com support@integroleadership.com Copyright Integro Learning Company Pty Ltd, Australia Copyright Integro
Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations
 1. Introduction Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations Performance evaluations are just one element of effective performance management. The overall goal of performance management is to
1. Introduction Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations Performance evaluations are just one element of effective performance management. The overall goal of performance management is to
The Management Development Series For Legal Managers
 The Management Development Series For Legal Managers To get great things done in today s legal firms, managers have to enable others to act. Managers foster collaboration and trust. They make it possible
The Management Development Series For Legal Managers To get great things done in today s legal firms, managers have to enable others to act. Managers foster collaboration and trust. They make it possible
Risk Culture. Reflections of Risk Managers March Sally Bennett Managing Director Enhance Solutions
 Risk Culture Reflections of Risk Managers March 2013 Sally Bennett Managing Director Enhance Solutions The Think Tank As Risk Managers we are tasked with the objective to embed a risk management culture
Risk Culture Reflections of Risk Managers March 2013 Sally Bennett Managing Director Enhance Solutions The Think Tank As Risk Managers we are tasked with the objective to embed a risk management culture
BUILDING YOUR CAREER. Reaching your potential. Building your career 1
 BUILDING YOUR CAREER Reaching your potential Building your career 1 At tesco we want you TO BUILD YOUR CAREER AND REACH YOUR POTENTIAL, IN A WAY THAT WORKS FOR YOU We want everyone to feel welcome and
BUILDING YOUR CAREER Reaching your potential Building your career 1 At tesco we want you TO BUILD YOUR CAREER AND REACH YOUR POTENTIAL, IN A WAY THAT WORKS FOR YOU We want everyone to feel welcome and
Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision. Situational Leadership
 Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision Situational Leadership Situational Leadership If you want to be a successful supervisor, you need to become expert at achieving through others by means of means directing,
Fundamentals Of Effective Supervision Situational Leadership Situational Leadership If you want to be a successful supervisor, you need to become expert at achieving through others by means of means directing,
Hafan Cymru Job Description
 Job title Grade / Salary Scale Location Contract hours Working Pattern Responsible to Responsible for (staff / finance / Service Users /Customers Job Purpose Competency and Level required Project Manager
Job title Grade / Salary Scale Location Contract hours Working Pattern Responsible to Responsible for (staff / finance / Service Users /Customers Job Purpose Competency and Level required Project Manager
Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques
 Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques Leadership and Motivation Megan Latzkowski A leader is like a shepherd. He stays behind the flock, letting them go out ahead, not realizing
Nelson Mandela s Influence Using Organizational Behaviour Techniques Leadership and Motivation Megan Latzkowski A leader is like a shepherd. He stays behind the flock, letting them go out ahead, not realizing
Customer Service. Dr. Bernie Sparks DA, MPA, CEIC. 21 st Century Leadership LLC
 Customer Service Dr. Bernie Sparks DA, MPA, CEIC 21 st Century Leadership LLC C H I L L Communications Honesty Integrity Listening Leadership Dr. Bernie Sparks DA, MPA, CEIC 21 st Century Leadership LLC
Customer Service Dr. Bernie Sparks DA, MPA, CEIC 21 st Century Leadership LLC C H I L L Communications Honesty Integrity Listening Leadership Dr. Bernie Sparks DA, MPA, CEIC 21 st Century Leadership LLC
Communication Rules for A Respectful Workplace
 Published on Sports Management Resources Communication Rules for A Respectful Workplace Note: The following material is excerpted from a pre-publication manuscript: Lopiano, D.A. and Zotos, C. (Publication
Published on Sports Management Resources Communication Rules for A Respectful Workplace Note: The following material is excerpted from a pre-publication manuscript: Lopiano, D.A. and Zotos, C. (Publication
building your career Reaching your potential
 building your career Reaching your potential At Tesco we want you to build your career and reach your potential, in a way that works for you We want everyone to feel welcome and valued. We are proud to
building your career Reaching your potential At Tesco we want you to build your career and reach your potential, in a way that works for you We want everyone to feel welcome and valued. We are proud to
MENTEE GUIDE ADVANCEM HIEVER LEARN FRIEND STUDENT START MENTEE GROW LISTEN
 HIEVER ENT FRIEND LEARN STUDENT MENTEE GUIDE ENT MENTEE GROW ADVANCEM START R IN ND LISTEN N AMB MENTEE GUIDE 1 MENTEE GUIDE Welcome to the HR Certification Institute s Certification Mentor Program, and
HIEVER ENT FRIEND LEARN STUDENT MENTEE GUIDE ENT MENTEE GROW ADVANCEM START R IN ND LISTEN N AMB MENTEE GUIDE 1 MENTEE GUIDE Welcome to the HR Certification Institute s Certification Mentor Program, and
Managerial Competency Guide
 Managerial Performance Evaluation and Reappointment Recommendation Managerial Competency Guide Division of Human Resources Competency List: I. Accountability II. III. IV. Communication Skills Customer
Managerial Performance Evaluation and Reappointment Recommendation Managerial Competency Guide Division of Human Resources Competency List: I. Accountability II. III. IV. Communication Skills Customer
Managerial Competency Guide
 Managerial Performance Evaluation and Reappointment Recommendation Managerial Competency Guide Division of Human Resources Competency List: I. Accountability II. III. IV. Communication Skills Customer
Managerial Performance Evaluation and Reappointment Recommendation Managerial Competency Guide Division of Human Resources Competency List: I. Accountability II. III. IV. Communication Skills Customer
SUPERVISOR SKILLS MINI-WORKSHOP. Mike Fitch, PE, ODOT Central Office/LTAP Lloyd V. MacAdam, PE, PS, ODOT District 11 Ruth A. Klee, PE, OHM Advisors
 SUPERVISOR SKILLS MINI-WORKSHOP Mike Fitch, PE, ODOT Central Office/LTAP Lloyd V. MacAdam, PE, PS, ODOT District 11 Ruth A. Klee, PE, OHM Advisors SUPERVISOR SKILLS MINI-WORKSHOP Mike Fitch, PE, ODOT Central
SUPERVISOR SKILLS MINI-WORKSHOP Mike Fitch, PE, ODOT Central Office/LTAP Lloyd V. MacAdam, PE, PS, ODOT District 11 Ruth A. Klee, PE, OHM Advisors SUPERVISOR SKILLS MINI-WORKSHOP Mike Fitch, PE, ODOT Central
OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION
 OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION By always VALUING PEOPLE Leading myself and others Working together as a team ACHIEVING THE VISION... Delivering great service Taking a professional
OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION OUR UNIVERSITY CONTRIBUTION By always VALUING PEOPLE Leading myself and others Working together as a team ACHIEVING THE VISION... Delivering great service Taking a professional
BEING SMART ONLY TAKES YOU SO FAR. Based on article by Bob Wall, T+D, January 2007, p.64-68
 BEING SMART ONLY TAKES YOU SO FAR Based on article by Bob Wall, T+D, January 2007, p.64-68 THE MOST SUCCESSFUL LEADERS ARE MASTERS OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE (EQ) But sometimes they need coaching IQ AND
BEING SMART ONLY TAKES YOU SO FAR Based on article by Bob Wall, T+D, January 2007, p.64-68 THE MOST SUCCESSFUL LEADERS ARE MASTERS OF EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE (EQ) But sometimes they need coaching IQ AND
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
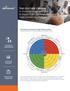 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Performance Management Competencies. for Schedule II Levels 1-6
 Performance Competencies for Schedule II Levels 1-6 Performance : What is it? Performance management is a systematic approach to setting performance standards, coaching employees to achieve standards,
Performance Competencies for Schedule II Levels 1-6 Performance : What is it? Performance management is a systematic approach to setting performance standards, coaching employees to achieve standards,
National Biodiversity Network Secretariat. Performance Management Guidelines
 National Biodiversity Network Secretariat Performance Management Guidelines Contents I. Performance Management Introduction... 3 a) Performance Management and Business Planning... 4 b) Performance Management
National Biodiversity Network Secretariat Performance Management Guidelines Contents I. Performance Management Introduction... 3 a) Performance Management and Business Planning... 4 b) Performance Management
Position Description Conciliator. Reports to Team Manager
 Position Description Conciliator Reports to Team Manager Background Utilities Disputes is a not-for-profit organisation, providing dispute resolution and other related services to the utilities sector.
Position Description Conciliator Reports to Team Manager Background Utilities Disputes is a not-for-profit organisation, providing dispute resolution and other related services to the utilities sector.
T E A L C O N S U L T I N G L T D I S O A G U I D E
 T E A L C O N S U L T I N G L T D I S O 4 4 0 0 1 A G U I D E W H A T I S I S O 4 4 0 0 1? There is much talk about collaboration but for many the concept seems ad hoc and without a clear perspective as
T E A L C O N S U L T I N G L T D I S O 4 4 0 0 1 A G U I D E W H A T I S I S O 4 4 0 0 1? There is much talk about collaboration but for many the concept seems ad hoc and without a clear perspective as
Introduction... CONTENT
 Introduction... Whether applying for a promotion or your very first job there are a number of steps you must take to be ready for that all important interview. When the email or SMS comes to invite you
Introduction... Whether applying for a promotion or your very first job there are a number of steps you must take to be ready for that all important interview. When the email or SMS comes to invite you
National Occupational Standards For Rail Operations - Supervisory. Unit 1 - Plan for Duty and Manage your Own Performance in the Rail Industry
 National Occupational Standards For Rail Operations - Supervisory Unit 1 - Plan for Duty and Manage your Own Performance in the Rail Industry What this unit is about This unit is about completing your
National Occupational Standards For Rail Operations - Supervisory Unit 1 - Plan for Duty and Manage your Own Performance in the Rail Industry What this unit is about This unit is about completing your
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK
 CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
CHARACTER ELSEVIER COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK CHARACTER: DISPLAYS INTEGRITY AND HONESTY DEFINITION: Leads by example; walks the talk ; models core values; follows through on promises; trusted by others; honest
Human Capital TRAINING COURSES. Leading people. Leading organizations
 Human Capital TRAINING COURSES CONTENTS Develop & Nurture Talent Assertiveness 2 days 4 Business Ethics Champion 1 day 5 Coaching & Counselling Skills for Managers 3 days 6 E-Colors & Personal Intervention
Human Capital TRAINING COURSES CONTENTS Develop & Nurture Talent Assertiveness 2 days 4 Business Ethics Champion 1 day 5 Coaching & Counselling Skills for Managers 3 days 6 E-Colors & Personal Intervention
Deputy Manager (Complex Needs) Islington Mental Health Services. Frontline Staff, Volunteers & Peer Mentors
 Post: Deputy Manager (Complex Needs) Delegated Authority Level 6 Team: Responsible to: Responsible for: Islington Mental Health Services Service Manager Frontline Staff, Volunteers & Peer Mentors Job Purpose
Post: Deputy Manager (Complex Needs) Delegated Authority Level 6 Team: Responsible to: Responsible for: Islington Mental Health Services Service Manager Frontline Staff, Volunteers & Peer Mentors Job Purpose
Understanding leadership. To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager.
 Module 1 Understanding leadership To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager. Learning outcomes (the learner will) Understand leadership
Module 1 Understanding leadership To develop knowledge and understanding of leadership as required by a practising or potential first line manager. Learning outcomes (the learner will) Understand leadership
Yorkshire Ambulance Service East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust. Mentoring Workshop. Background Information
 Yorkshire Ambulance Service East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust Mentoring Workshop Background Information June 2007 1 Yorkshire Ambulance Service East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust Mentoring
Yorkshire Ambulance Service East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust Mentoring Workshop Background Information June 2007 1 Yorkshire Ambulance Service East Midlands Ambulance Service NHS Trust Mentoring
Registration Details. How to Interpret the Report?
 Mettl Leadership Assessment - Demo sample_report@mettl.com Test Taken on: June 14, 2017 07:02:4 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample_report@mettl.com First Name: Sample
Mettl Leadership Assessment - Demo sample_report@mettl.com Test Taken on: June 14, 2017 07:02:4 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample_report@mettl.com First Name: Sample
Planting the seed of customer service
 Planting the seed of customer service P - Professionalism - My customers are the students, faculty and staff, and my fellow employees who I will acknowledge with a positive greeting or by readily offering
Planting the seed of customer service P - Professionalism - My customers are the students, faculty and staff, and my fellow employees who I will acknowledge with a positive greeting or by readily offering
Interview. guide. Sam Sample. Emotional Intelligence Profile. Tuesday 16 May 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Sam Sample
 Interview guide Tuesday 16 May 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Emotional Intelligence Profile 1 Contents 04 About this report 06 Emotional Intelligence competencies 07 Competency potential
Interview guide Tuesday 16 May 2017 General Working Population (sample size 1634) Emotional Intelligence Profile 1 Contents 04 About this report 06 Emotional Intelligence competencies 07 Competency potential
PROFESSIONAL TRAINING SOLUTIONS CATALOG
 P R S S I N S P I N & R I N I N S U I N S SWINTON&ASSOCIATES, LLC The PROFESSIONAL TRAINING SOLUTIONS CATALOG GSA#: GS-02F-0199N 8(a) CERTIFIED PROGRAM 2013 EDITION Swinton & Associates, LLC Professional
P R S S I N S P I N & R I N I N S U I N S SWINTON&ASSOCIATES, LLC The PROFESSIONAL TRAINING SOLUTIONS CATALOG GSA#: GS-02F-0199N 8(a) CERTIFIED PROGRAM 2013 EDITION Swinton & Associates, LLC Professional
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities
 Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
BARRETT High Impact Selling & Leadership
 Discussion Paper BARRETT High Impact Selling & Leadership Workplace Emotional Intelligence in Sales & Leadership Article Resources: Dr Ben Palmer, Director of Research and Development for Genos Pty Ltd
Discussion Paper BARRETT High Impact Selling & Leadership Workplace Emotional Intelligence in Sales & Leadership Article Resources: Dr Ben Palmer, Director of Research and Development for Genos Pty Ltd
TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT
 TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT April 15, 2013 For further information about Team Emotional Intelligence: www.geipartners.com GEI Partners 2013 This report is the property of GEI Partners (Professor
TEAM EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE SURVEY REPORT April 15, 2013 For further information about Team Emotional Intelligence: www.geipartners.com GEI Partners 2013 This report is the property of GEI Partners (Professor
The New Leader. 3 Days. Introduction
 The New Leader 3 Days Introduction We have a wealth of experience at handling day to day management issues and are now ready for a bigger challenge. Are there extra skills they need to acquire to prepare
The New Leader 3 Days Introduction We have a wealth of experience at handling day to day management issues and are now ready for a bigger challenge. Are there extra skills they need to acquire to prepare
Creating an inclusive volunteering environment
 Creating an inclusive volunteering environment Why is creating an inclusive environment important? Understanding the needs of all of your volunteers and making sure they feel valued and respected increases
Creating an inclusive volunteering environment Why is creating an inclusive environment important? Understanding the needs of all of your volunteers and making sure they feel valued and respected increases
Maintaining a Harassment & Discrimination-Free Workplace. A Guide for Managers & Employees
 Maintaining a Harassment & Discrimination-Free Workplace A Guide for Managers & Employees 2 Maintaining a Harassment & Discrimination-Free Workplace A Guide for Managers and Employees 3 2 table of contents
Maintaining a Harassment & Discrimination-Free Workplace A Guide for Managers & Employees 2 Maintaining a Harassment & Discrimination-Free Workplace A Guide for Managers and Employees 3 2 table of contents
Registration Details. How to Interpret the Report?
 Mettl Leadership Development Report sample sample.report@mettl.com Test Taken on: September 13, 2017 0:4:09 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample.report@mettl.com First
Mettl Leadership Development Report sample sample.report@mettl.com Test Taken on: September 13, 2017 0:4:09 PM IST Finish State: Normal Registration Details Email Address: sample.report@mettl.com First
Introduction 1. Bad Apple Group Activity 2. Why do we Avoid Providing Coaching and Feedback to Employees?
 Introduction 1 Bad Apple Group Activity 2 Why do we Avoid Providing Coaching and Feedback to Employees? Balancing Positive & Negative Performance Communication 3 3 Coaching vs. Feedback 4 What Should Coaching
Introduction 1 Bad Apple Group Activity 2 Why do we Avoid Providing Coaching and Feedback to Employees? Balancing Positive & Negative Performance Communication 3 3 Coaching vs. Feedback 4 What Should Coaching
GUIDANCE NOTES ON THE ROLE OF THE MENTOR
 GUIDANCE NOTES ON THE ROLE OF THE MENTOR SDDU-Handout Contents Page 1. Why have a mentor? 3 2. What does a mentor do? 7 3. The role of the mentee 13 4. Are you ready to begin? 14 "Tell me and I forget.
GUIDANCE NOTES ON THE ROLE OF THE MENTOR SDDU-Handout Contents Page 1. Why have a mentor? 3 2. What does a mentor do? 7 3. The role of the mentee 13 4. Are you ready to begin? 14 "Tell me and I forget.
AccuVision WORKPLACE SUCCESS SKILLS
 For more information about This program, please contact: The Resource Connection 525 Sheridan Blvd. Orlando, Fl 32804 Phone: 407-426-0511 Fax: 407-426-0552 leilani@resourceconnection.com AccuVision WORKPLACE
For more information about This program, please contact: The Resource Connection 525 Sheridan Blvd. Orlando, Fl 32804 Phone: 407-426-0511 Fax: 407-426-0552 leilani@resourceconnection.com AccuVision WORKPLACE
MENTORING G UIDE MENTEES. for BY TRIPLE CREEK ASSOCIATES, INC Mentoring Guide for Mentees
 MENTORING G UIDE for MENTEES BY TRIPLE CREEK ASSOCIATES, INC. www.3creek.com 800-268-4422 Mentoring Guide for Mentees 2002 1 Table of Contents What Is Mentoring?... 3 Who Is Involved?... 3 Why Should People
MENTORING G UIDE for MENTEES BY TRIPLE CREEK ASSOCIATES, INC. www.3creek.com 800-268-4422 Mentoring Guide for Mentees 2002 1 Table of Contents What Is Mentoring?... 3 Who Is Involved?... 3 Why Should People
