Performance Planning Guide. Version: 2.1 Last Updated: April 2015
|
|
|
- Cathleen Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Performance Planning Guide Version: 2.1 Last Updated: April 2015
2 Table of contents Performance planning: Staff development and feedback at Ryerson University... 2 Introduction... 2 Our Time to Lead: Ryerson s Academic Plan Ryerson s Mission... 2 Ryerson s Vision... 2 Ryerson s Priorities... 2 Ryerson s Values... 3 Commitment to Excellence... 3 Commitment to the Whole Person... 3 Commitment to Community and Inclusion... 3 Performance Planning: Staff Development and Feedback Objectives... 3 Increased Communication... 3 Improved Performance... 3 Employee Development... 3 Human Resources Management... 3 OPSEU performance planning year-at-a-glance... 2 MAC performance planning year-at-a-glance... 3 Six phases of the performance planning process Planning Goal Setting Monitoring Coaching and feedback End of year discussion Recognition and rewards
3 Performance planning: Staff development and feedback at Ryerson University Introduction This guide is designed to assist leaders and staff in communicating about performance. Continuous application of these guidelines will ensure that employees know what is expected of them, how they are performing and what can be done to strengthen performance. In addition, development plans focus upon coaching and developing employees, helping them reach their full potential. Our Time to Lead: Ryerson s Academic Plan The Development and Feedback process allows staff members to understand how their work directly links and contributes to the mission, vision and priorities of Ryerson University. Through their approach to their work, staff members can demonstrate the values of the institution as outlined in Ryerson Academic Plan. Ryerson s Mission To serve societal need by providing career-related and professional education, and scholarly, creative and research activities. Ryerson s Vision Ryerson will be Canada s leading comprehensive innovation university, recognized for its highquality, career-related and professional bachelor, master s and doctoral programs and relevant scholarly, research and creative activities. It will be a global leader in interdisciplinary, entrepreneurial zone learning. Ryerson s students, graduates and faculty will contribute significantly to Ontario s and Canada s social, cultural and economic well-being. Ryerson s Priorities Enable greater student engagement and success through exceptional experiences Increase SRC excellence, intensity and impact Foster an innovation ecosystem Expand community engagement and city building 2
4 Ryerson s Values Commitment to Excellence Excellence Academic Freedom Integrity Enterprising Sustainability Commitment to the Whole Person People First Collegiality Lifelong Learning Commitment to Community and Inclusion Community Inclusion Respect for Aboriginal Perspectives Equity Diversity Access Performance planning: Staff development and feedback Objectives The four primary objectives include: Increased Communication, Improved Performance, Employee Development and Human Resource Management. Increased communication Improving communication between leaders and staff Clarifying job responsibilities and standards Giving staff feedback on their performance Improved performance Establishing challenging performance goals in support of organizational objectives Encouraging individuals and work teams to strive for continuous improvement and quality Identifying and eliminating obstacles to performance Employee development Focusing upon and addressing staff growth and career development Recognizing individual performance Optimizing staff skills, abilities and knowledge for mutual benefit Human resources management Planning for development, resources and other issues 3
5 OPSEU performance planning year-at-a-glance Ryerson University s annual performance planning cycle for OPSEU employees runs in any 12- month period. Month 1 Months 2 11 Month 12 Step 1. Planning Review the principal responsibilities of the job Discuss standards of performance Identify university priorities and department objectives Decide upon projects within the scope of the position and assign specific goals and objectives Step 2. Goal Setting Review university and team objectives for the coming year Define performance expectations that align with team and university objectives Create SMART goals that will help to achieve team objectives and address professional development Deliverable: Completed plan Step 3. Monitoring Meet regularly to review progress on performance goals to-date and discuss successes and roadblocks Redefine expectations and update the goals if performance expectations change throughout the year Step 4. Coaching and Feedback Provide ongoing feedback on the staff member s performance Establish open, ongoing communication channels Staff member Proactively solicit feedback to ensure that performance is in line with expectations Provide objective information and examples of performance to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement throughout the year Deliverables: Regular meetings between leader and staff member Updated (if necessary) Step 5. End of Year Discussion Staff member Provide comments related to the documented performance expectations and goals Provide feedback related to the staff member s performance expectations and objectives Support each assessment with specific results and objective examples of performance throughout the year Meet to discuss the staff member s performance, identifying key areas of strength and accomplishment and areas for improvement Step 6. Recognition and Rewards Recognize and reward performance frequently throughout the year. This can include simple verbal recognition and other forms of nonmonetary acknowledgement of good work Deliverable: Completed Staff Development and Feedback form 2
6 MAC performance planning year-at-a-glance Ryerson University s annual performance planning cycle for MAC employees runs from July June annually. July August April May June Step 1. Planning Review the principal responsibilities of the job Discuss standards of performance Identify university priorities and department objectives Decide upon projects within the scope of the position and assign specific goals and objectives Step 2. Goal Setting Review university and team objectives for the coming year Define performance expectations that align with team and university objectives Create SMART goals that will help to achieve team objectives and address professional development Deliverable: Completed plan Step 3. Monitoring Meet regularly to review progress on performance goals to-date and discuss successes and roadblocks Redefine expectations and update the goals if performance expectations change throughout the year Step 4. Coaching and Feedback Provide ongoing feedback on the staff member s performance Establish open, ongoing communication channels Staff member Proactively solicit feedback to ensure that performance is in line with expectations Provide objective information and examples of performance to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement throughout the year Deliverables: Regular meetings between leader and staff member Updated (if necessary) Step 5. End of Year Discussion Staff member Provide comments related to the documented performance expectations and goals Provide feedback related to the staff member s performance expectations and objectives Support each assessment with specific results and objective examples of performance throughout the year Meet to discuss the staff member s performance, identifying key areas of strength and accomplishment and areas for improvement Step 6. Recognition and Rewards Recognize and reward performance frequently throughout the year. This can include simple verbal recognition and other forms of nonmonetary acknowledgement of good work Deliverable: Completed performance review 3
7 Six phases of the performance planning process 1. Planning Planning is the first step in the cycle which the leader and staff member spend time planning for the coming year. Planning includes a review of university and department/ team objectives to ensure that the staff member s individual performance aligns with the university s objectives and needs. In addition, the staff member and leader review principal responsibilities, determine projects and milestones to be achieved in the coming year and discuss standards of performance. If the staff member is new, planning should take place during their first month of employment. 4
8 Principle responsibilities Review the principal responsibilities of the job (e.g., job description) Discuss standards of performance (e.g., Standards & Expectations) Identify university priorities and department objectives Decide upon projects within the scope of the position and assign specific goals and objectives Identify the knowledge, skills and abilities that need to be developed to achieve the goals and objectives Link to Ryerson s Academic Plan A major goal of planning is for the leader and staff member to explicitly identify the link between the staff member s job responsibilities and performance and the objectives and mission of the department/ team and university. This alignment helps the leader and staff member prioritize work and establish measurements and performance standards that will be monitored throughout the year. 2. Goal setting After the leader and staff member review the job responsibilities, establish performance standards and align the staff member s performance objectives to the mission and objectives of the university and department/ team, the next step is to establish specific, measurable performance and development goals. Principle responsibilities Define performance expectations that align with team and university objectives Define developmental objectives Create SMART goals that will help to achieve team objectives and address professional development Performance goals The performance goals define what is expected of the staff member during the year. They support the basic areas of responsibility and specific university, department or team goals. These goals may be addressed throughout the year or they could be associated with specific projects that involve a shorter timeframe. The purpose is to align the staff member goals with the goals and strategies of the university. Developmental goals Development plans offer your staff the opportunity to identify the strengths and development areas that merit their attention and yours. Not all development plans are created equal, however. A good development plan focuses on the development of a few skills, balances the need to develop both strengths and development areas that are tied to your performance objectives, has concrete action steps, and sets gradual, realistic, and achievable success measures. As you and your employees think about their development plans, remember the following: 5
9 Performance and learning are linked to each other: Your staff can build the skills they need by focusing on the work experiences and assignments that are most closely tied to their performance objectives. While the skills may change, the strengths staff draw upon do not: The strengths that have made a staff member successful in the past do not go away. Although they may need to address development weaknesses, do not forget to continue to build their strengths. Staff success depends on the people asked to help them: By sharing their development goals with you, their peers, and/or a mentor, your staff can check in at various points to make sure that they are making a strong plan. Writing SMART objectives For objectives to be effective, they need to be clear, specific, realistic and measurable. SMART Objectives Specific Describes what the end result will look like Measureable Achievable Relevant Time-bound Expressed in quantifiable terms The objective is realistic Job-related and linked to the university s and department s goals (within job duties) Provide target dates Sample SMART objective "To recommend,......at the June......department meeting, the three......vendors that best meet the defined criteria, at a cost that is at least 10% less than our present annual contract." Achievable Time bound Specific Realistic and Measurable How do you write a SMART objective? Ask these questions. 1. Do what? Identify what visible action is to be taken use action verbs: conduct, analyze Describe what or whom the action will affect or whom it will involve 2. To what extent? Indicate qualities, timeframes, frequencies and other measurable results to be achieved How much is needed, by when and/or how often 3. For what results? 6
10 Describe the desired end result, as well as the impact of that end result 4. How will the staff member know whether they ve achieved the objectives? Develop key measures for each objective to help the staff member determine if they achieved what they set out to do Measures are the specific outcome expected, allowing the staff member and leader to monitor/evaluate success Non-SMART objectives versus SMART objectives Maintain department website Ensure accuracy of the department website by conducting a comprehensive audit of the department s website every two weeks. Work with leaders, staff and faculty in the department to edit information provided on the website. Make requested edits within two workdays. Respond to all and phone inquiries Write department handbook Database project Improve customer service by responding to all and phone inquiries within 24 hours. Create a quarterly report detailing the number and types of inquiries received by the department. Create a departmental orientation for new employees, introducing them to the technology, resources and policies and procedures of the department. Develop a departmental employee handbook and checklist for on-boarding new employees to our department. Present new materials to the department at the February staff meeting. Implement department orientation beginning March 1. Improve the efficiency of logging and reporting inquiries to the department by creating a tracking system using Excel spreadsheets. Complete the tracking system by August 1. Train all front desk staff in how to use the system by September 1. Monitor and maintain the system and begin using it to generate quarterly reports by December 31. Note: For OPSEU employees, leaders should refer the Development and Feedback form. For all other employees, refer to the Performance Planning & Review form. 3. Monitoring Monitoring is an ongoing effort throughout the year and a responsibility of both the leader and staff member. Principle responsibilities Meet regularly throughout the year to review progress on performance goals to-date and discuss successes and roadblocks 7
11 Redefine expectations and update the goals if expectations change throughout the year Information management Communication between the leader and staff member must be open, honest and ongoing. Staff can and should initiate the communication, particularly when any significant changes or obstacles occur that management should be aware of. Oftentimes responsibilities, projects, objectives and performance plans need to be modified as a result of changing circumstances and shifting priorities. s and staff members are expected to keep each other apprised and current. Self-monitoring Since staff are aware of their own responsibilities, projects, objectives and skills, they are expected to monitor their own performance. Each staff member is best able to measure their own performance against expectations and is encouraged to periodically keep their leader informed of progress and/or problems. Staff should keep track of their performance by documenting major activities and results whenever possible. When staff have trouble making progress toward the achievement of objectives or responsibilities, they are responsible for taking suitable action to remedy the situation and close performance gaps. They may take action on their own or they may need assistance from their leader. It is incumbent upon each staff member to keep focused on their effectiveness. Monitoring by leader Throughout the review period, the leader monitors performance by reviewing and documenting work activities, milestones, costs, obstacles and results. They are aware if adjustments are necessary. Consistent and accurate documentation during the review period facilitates regular feedback and end of year discussions. Monitoring performance can be accomplished through formal and informal approaches. Some formal methods might include: -Staff Member meetings Group or team meetings When deciding your approach, you will want to consider factors that impact effectiveness, such as frequency of meetings; quality, quantity and format of information to be shared; and the desired outcomes. Formal conversations are not the only option to monitoring performance. Some situations might make informal conversations such as hallway chats appropriate for addressing very current work tasks and performance. Performance log The use of a Performance Log can help the leader in tracking performance and feedback given to the staff member throughout the year. A sample Performance Log and Template can be found in the Tools and Templates Section at the end of this manual. Management assistance While self-development tends to be the most beneficial and effective, at times even superior performers need some assistance. Staff members are encouraged to seek out opportunities for 8
12 discussion of their performance and development, including regular feedback and coaching from their leaders. Development is a shared responsibility best initiated by the staff member and supported by the leader. s can use their experience, knowledge and skills to help track staff performance and provide the necessary support and opportunities for development. 4. Coaching and feedback Throughout the year, both the leader and staff member monitor the staff member s progress. Each has information regarding the performance to date. The coaching process provides a forum for the mutual exchange of this information. A leader s role is similar to that of a coach in sports. An effective coach motivates, provides feedback, offers encouragement toward the achievement of goals and helps players to focus on the game plan. Coaching involves two key leader activities: Providing constructive feedback to change or improve performance Recognizing and encouraging excellence For a staff member to improve, develop or take on more responsibility, they need regular feedback on how they are doing. In addition, when they are performing well, their efforts should be acknowledged and supported. Coaching may be either formal or informal. Formal coaching involves setting aside time to meet privately, free from interruptions. Informal coaching is usually provided on a day-to-day basis as situations arise. Principle responsibilities Throughout the year, provide ongoing feedback on the staff member s performance Establish open, ongoing communication channels Staff member Proactively solicit feedback to ensure that performance is in line with expectations Provide objective information and examples of performance to identify areas of strength and areas for improvement throughout the year Effective coaching Effective coaching takes place when the leader and employee: Are prepared and informed Cite specific examples Focus on behavior, not personality Listen to each other Ask clarifying questions Reach agreement Develop an action plan Follow up 9
13 The GROW Coaching Model The GROW coaching model provides a structure to follow, so that the conversation can progress to a successful outcome. It is designed to be collaborative, powerful and intentional. Step Description Sample leader questions 1. Establish a GOAL 2. Examine the Current REALITY 3. Explore the OPTIONS 4. Establish the WILL Key Question: What do you want to achieve? You and your staff member look at the behaviour you want to change, and structure the change as a goal. Positive Agreed to Understood Key Question: What is happening now? Together, ensure the current situation is known and understood. Be objective (not opinions, judgments, expectations, prejudices, concerns, hope, fears) Be descriptive, not evaluative Key Question: What could you do? Be as creative as possible to generate the maximum number of options (options the staff member may not have thought of before). Quantity, not quality or feasibility Challenge negative assumptions Look at the benefits and costs of each Key Question: What will you do? Convert a discussion into a decision by constructing an action plan. What do you hope to achieve (in the short, medium, long term)? How will you know when you get there? Is it achievable? When by? When would you like to meet again to review this? What is happening now (what, who, when, and how often)? What is the effect or result of this? Have you already taken any steps towards your goal? What is getting in the way? What are the options? What else? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each option? What factors or considerations will you use to weigh the options? How many ways are there to achieve your goal? Which appeal to you the most? What are you going to do? What is your first step in this? What support do you need? On a scale from 1-10, how committed are you to doing this? What prevents your commitment from being a 10? When do you need to review progress? Daily, weekly, monthly? 10
14 5. End of year discussion Among the final stages of the process are the written feedback and the discussion. Human Resources recommends that all new staff receive feedback prior to the conclusion of their first six months, and that all other staff receive a feedback discussion annually. Principle responsibilities Staff member Provide comments related to the documented performance expectations and goals Self-Review: The staff member is encouraged to track their own performance and to keep a list of accomplishments and/or results relating to their documented performance goals, job responsibilities, objectives and professional development goals. Provide feedback related to the staff member s performance expectations and objectives s Review: After the leader has received the staff member s self-review and consolidated their own observations, notes, reports and other documentation, they provide feedback to the staff member. Support each assessment with specific results and objective examples of performance throughout the year Meet to discuss the staff member s performance, identifying key areas of strength and accomplishment and areas for improvement Preparation Toward the end of the year, the leader and staff member should carefully review their notes, reports, observations and other documentation to prepare an accurate assessment. Performance throughout the entire year must be considered rather than just recent activities. No surprises If the leader and staff member have communicated consistently and continuously throughout the year, there will not be any surprises during the end of year discussion. It should simply be a culmination of previous communications. Surprises occur when there has been little or no specific communication regarding performance during the review period, a practice that is unproductive and contrary to organizational objectives. Prior to the actual discussion, the leader is expected to give a copy of the completed form to the staff member. This gives the staff member an opportunity to plan for the meeting and facilitates two-way communication. For the discussion to be productive, the leader and staff member need to: Set aside at least an hour of uninterrupted time to meet Prepare a list of questions Anticipate possible questions Bring a copy of the completed form to the meeting Focus on actual behaviors and skills Actively listen to each other 11
15 TIP: Schedule meetings at least two weeks in advance. This gives the leader and staff member time to make final preparations for the discussion. Additionally, if a leader has multiple direct reports, setting appointments in advance helps to manage the demand on everyone s schedule. The Performance Review Preparation Checklist found in the Tools and Templates Section can help you prepare. Meeting The meeting should be a two-way conversation in which leader and staff member: Review and discuss responsibilities, results, progress toward objectives and core behaviors Identify strengths, citing specific examples Identify development needs, citing specific examples Make any necessary adjustments to final ratings o This applies to non-opseu staff only, as OPSEU staff do not receive ratings TIP: Discussing weaknesses or developmental areas can be challenging, especially for new leaders. The Tools and Templates Section includes Ten Tips on Delivering Performance Feedback on Weaknesses. Signatures and record keeping At the conclusion of the meeting, the leader and staff member sign the last page of the form, signifying discussion of the review, and each receives a copy for their records. The original review is then forwarded to the second-level reviewer (the reviewer s leader) for approval. A second-level reviewer signature is required to: Ensure that the discussions are conducted in a timely manner Check for possible rater bias on the part of leaders (harshness and/or leniency) Red flag any continued performance problems for further review Remain informed of progress and successes 6. Recognition and rewards Recognizing and rewarding performance should occur frequently throughout the year. This can include simple verbal recognition and other forms of nonmonetary acknowledgement of good work. Principle responsibilities Recognize and reward performance frequently throughout the year. This can include simple verbal recognition and other forms of nonmonetary acknowledgement of good work Recognition Positive feedback for effective performance can be highly motivational. Suggested steps for giving positive feedback are: Describe the specific performance for which the staff member is being recognized Explain how the performance benefits the department and the university 12
16 Express confidence in the staff member s ability to maintain performance Thank the staff member There are many opportunities for giving recognition. Some examples are to provide recognition when a staff member: Consistently meets or exceeds performance expectations Does a good job on routine tasks Is learning a new job or task Has improved their performance Accomplishes an especially difficult assignment or task Demonstrates a significant level of a particular skill Volunteers for a difficult or unwanted assignment Displays creativity in problem solving Discovers a way to save (or make) the organization money Rewards Some examples of rewards include: More autonomy Development opportunities Team projects, etc. These and other examples will vary by individual, department and situation. 13
University of the District of Columbia Performance Appraisal System For Non-Faculty Employees. Supervisor Guide
 University of the District of Columbia Performance Appraisal System For Non-Faculty Employees 1. Purpose 2. Overview 3. Performance Planning Supervisor Guide 4. Monitoring Employee Performance: Ongoing
University of the District of Columbia Performance Appraisal System For Non-Faculty Employees 1. Purpose 2. Overview 3. Performance Planning Supervisor Guide 4. Monitoring Employee Performance: Ongoing
Oregon Institute of Technology. COMPLETING A PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Instructions for Supervisors
 Oregon Institute of Technology COMPLETING A PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Instructions for Supervisors For Employees in Classified Information Technology Positions Represented by the SEIU/OPEU Introduction The
Oregon Institute of Technology COMPLETING A PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Instructions for Supervisors For Employees in Classified Information Technology Positions Represented by the SEIU/OPEU Introduction The
2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation
 2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation h t t p s : / / p e d i. n n g o v. c o m Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Objectives of the Performance Evaluation 3 Core Values 3 Core Competencies
2018 Supervisor s Guide to Performance Evaluation h t t p s : / / p e d i. n n g o v. c o m Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Objectives of the Performance Evaluation 3 Core Values 3 Core Competencies
Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations
 1. Introduction Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations Performance evaluations are just one element of effective performance management. The overall goal of performance management is to
1. Introduction Guide to Conducting Effective Performance Evaluations Performance evaluations are just one element of effective performance management. The overall goal of performance management is to
Employee Performance Management Process
 Employee Performance Management Process Summer 2009 EPMP GUIDE: CONTENT Introduction... 4 Overview... 5 DPS Commitment to Performance Management... 6 Employee Performance Management Process (EPMP) Defined...
Employee Performance Management Process Summer 2009 EPMP GUIDE: CONTENT Introduction... 4 Overview... 5 DPS Commitment to Performance Management... 6 Employee Performance Management Process (EPMP) Defined...
UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018. Title Page 1
 UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018 Title Page 1 Performance Management at UAB 3 What is Performance Management? 3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement 4 UAB Success Model 5 Performance Management
UAB Performance Management 07/03/2018 Title Page 1 Performance Management at UAB 3 What is Performance Management? 3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement 4 UAB Success Model 5 Performance Management
THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture
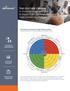 denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
denison TM THE CULTURE CANVAS A Working Guide and Checklist to Support the Development of a High-Performing Culture The Denison Model of High Performance A Systems Approach to Understanding and Managing
Performance Excellence Program (PEP)
 Performance Excellence Program (PEP) Goal Setting Guidelines ACC Faculty & Staff Evaluation www.austincc.edu/hr/eval Highland Business Center 5930 Middle Fiskville Road Austin, Texas 78752 For more information
Performance Excellence Program (PEP) Goal Setting Guidelines ACC Faculty & Staff Evaluation www.austincc.edu/hr/eval Highland Business Center 5930 Middle Fiskville Road Austin, Texas 78752 For more information
Performance and Professional Growth Systems
 Performance and Professional Growth Systems Non-Instructional Staff For use by Supervisors, Managers, Directors, Principals, and Superintendents Who Supervise Non-Instructional Employees (both salaried
Performance and Professional Growth Systems Non-Instructional Staff For use by Supervisors, Managers, Directors, Principals, and Superintendents Who Supervise Non-Instructional Employees (both salaried
BC Assessment - Competencies
 BC Assessment - Competencies This document provides a list and description of all of BC Assessment s core competencies, as well as the level of competency required for a given position, as defined in each
BC Assessment - Competencies This document provides a list and description of all of BC Assessment s core competencies, as well as the level of competency required for a given position, as defined in each
Staff Performance Evaluation Process
 Staff Performance Evaluation Process 2019 Introductions & Housekeeping Name? Position? How long at NKU? How long as manager at NKU? Have you been a manager at a previous employer and done performance evaluations
Staff Performance Evaluation Process 2019 Introductions & Housekeeping Name? Position? How long at NKU? How long as manager at NKU? Have you been a manager at a previous employer and done performance evaluations
EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE REVIEW GUIDELINES
 EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE REVIEW GUIDELINES DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN RESOURCES SPRING 2009 Employee Performance Review Guidelines The performance review process helps individual employees and organizations throughout
EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE REVIEW GUIDELINES DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN RESOURCES SPRING 2009 Employee Performance Review Guidelines The performance review process helps individual employees and organizations throughout
Development Planning Instructions and Tip Sheet
 Development Planning Instructions and Tip Sheet 1 Development Planning Myths Myth 1 Development planning is not related to my job. It is something that I have to do that is separate from my job. Development
Development Planning Instructions and Tip Sheet 1 Development Planning Myths Myth 1 Development planning is not related to my job. It is something that I have to do that is separate from my job. Development
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND APPRAISAL PROGRAM TOOLKIT
 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND APPRAISAL PROGRAM TOOLKIT THIS TOOLKIT SUPPLEMENTS DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE INSTRUCTION 1400.25 VOLUME 431, DOD CIVILIAN PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: PERFORMANCE
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT AND APPRAISAL PROGRAM TOOLKIT THIS TOOLKIT SUPPLEMENTS DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE INSTRUCTION 1400.25 VOLUME 431, DOD CIVILIAN PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: PERFORMANCE
Signet s FY 2016/2017 Performance Appraisal Guide. Dallas Field
 Signet s FY 2016/2017 Performance Appraisal Guide Dallas Field 2/22/2017 Table of Contents Getting Started Overview 1 Important Dates & Information 1 Completing the Performance Appraisal 2 Tips for Comments
Signet s FY 2016/2017 Performance Appraisal Guide Dallas Field 2/22/2017 Table of Contents Getting Started Overview 1 Important Dates & Information 1 Completing the Performance Appraisal 2 Tips for Comments
California State University San Marcos. MPP Performance Planning and Review Program Handbook
 California State University San Marcos MPP Performance Planning and Review Program Handbook Updated May, 2008 Table of Contents Section I Introduction...................................... Page 2 Section
California State University San Marcos MPP Performance Planning and Review Program Handbook Updated May, 2008 Table of Contents Section I Introduction...................................... Page 2 Section
COACHING I 5. BUSINESS MANAGEMENT COACHING TIPS & STRATEGIES The Influence of the Human Resource Department
 COACHING I 5. BUSINESS MANAGEMENT COACHING TIPS & STRATEGIES 5.1. The Influence of the Human Resource Department "There is a great man who makes every man feel small. But the real great man is the man
COACHING I 5. BUSINESS MANAGEMENT COACHING TIPS & STRATEGIES 5.1. The Influence of the Human Resource Department "There is a great man who makes every man feel small. But the real great man is the man
University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit for Staff March 2018
 University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit for Staff March 2018 What is Performance Development? Performance development is the name generally given to the process a manager undertakes
University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit for Staff March 2018 What is Performance Development? Performance development is the name generally given to the process a manager undertakes
Behavioural Attributes Framework
 Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Behavioural Attributes Framework There are eight attributes in the University of Cambridge Behavioural Attributes Framework: Communication; Relationship Building; Valuing Diversity; Achieving Results;
Employee Performance Management Process. Management Training Participant Workbook
 Employee Performance Management Process Management Training Participant Workbook Welcome to Training on EPMP Today s course is focused on preparing managers for the immediate implementation of the DPS
Employee Performance Management Process Management Training Participant Workbook Welcome to Training on EPMP Today s course is focused on preparing managers for the immediate implementation of the DPS
Be a Leader Not a Boss. Management Excellence. Clearly Define Duties. Be a Leader Not a Boss. Your Staff. Determine job titles 10/17/2014
 Be a Leader Not a Boss Management Excellence Skills for the First Time Manager Bosses: Create fear Drive people Say do Relies on authority Fix blame Knows all Makes work drudgery Say I www.eyesystems.info
Be a Leader Not a Boss Management Excellence Skills for the First Time Manager Bosses: Create fear Drive people Say do Relies on authority Fix blame Knows all Makes work drudgery Say I www.eyesystems.info
University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit October 2016
 University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit October 2016 What is Performance Development? Performance development is the process of planning for, discussing and evaluating employee performance.
University Human Resources Performance Development Toolkit October 2016 What is Performance Development? Performance development is the process of planning for, discussing and evaluating employee performance.
MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES
 MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES Mission, Vision, Core Values and People Philosophy Our Mission MGM Resorts International is the leader in entertainment and hospitality - a diverse collection
MGM RESORTS INTERNATIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES Mission, Vision, Core Values and People Philosophy Our Mission MGM Resorts International is the leader in entertainment and hospitality - a diverse collection
Dynamic Leadership How to Develop, Inspire and Retain an Effective Team
 How to Develop, Inspire and Retain an Effective Team Presenter: Tom Schulte Leadership Summit Engaging the New Faces of APICS MANAGING VS. LEADING Manager A person responsible for controlling or administering
How to Develop, Inspire and Retain an Effective Team Presenter: Tom Schulte Leadership Summit Engaging the New Faces of APICS MANAGING VS. LEADING Manager A person responsible for controlling or administering
Games Recognizing your home s achievements in Show-Me Quality: QAPI in Action
 Show-Me Quality Games Recognizing your home s achievements in Show-Me Quality: QAPI in Action Copper Bronze Silver Gold 1 Show-Me Quality Games Program Primaris is pleased to offer an exciting new program
Show-Me Quality Games Recognizing your home s achievements in Show-Me Quality: QAPI in Action Copper Bronze Silver Gold 1 Show-Me Quality Games Program Primaris is pleased to offer an exciting new program
Description. Award Categories. Customer Service. Engagement
 Description The Rowan Recognition program recognizes and rewards faculty and staff for work and behaviors that support the mission, goals, values and initiatives of Rowan University. The work and behavior
Description The Rowan Recognition program recognizes and rewards faculty and staff for work and behaviors that support the mission, goals, values and initiatives of Rowan University. The work and behavior
Performance Management Behaviors that Matter
 2011 Performance Management Behaviors that Matter Why do most performance management systems fail to actually improve performance? PDRI s research has shown that effective performance management is not
2011 Performance Management Behaviors that Matter Why do most performance management systems fail to actually improve performance? PDRI s research has shown that effective performance management is not
Marathon County Employee Performance Appraisal Form
 Employee Name: Last First Job Title: Employee #: Department: Supervisor: Division: Evaluation Period: 6/01/20 5/31/20 Evaluation Type Mid Year Comment & Signatures Only No Ratings Annual New Employee Initial
Employee Name: Last First Job Title: Employee #: Department: Supervisor: Division: Evaluation Period: 6/01/20 5/31/20 Evaluation Type Mid Year Comment & Signatures Only No Ratings Annual New Employee Initial
About This Document... 2 Overview Why We Conduct Performance Reviews... 3 Who Participates... 3 Supporting Documents... 4
 Contents About This Document... 2 Overview... 2 Why We Conduct... 3 Who Participates... 3 Supporting Documents... 4 Performance Review Process... 5 Step 1. Prepare... 5 Step 2. Complete First Draft Performance
Contents About This Document... 2 Overview... 2 Why We Conduct... 3 Who Participates... 3 Supporting Documents... 4 Performance Review Process... 5 Step 1. Prepare... 5 Step 2. Complete First Draft Performance
Leadership Agility Profile: 360 Assessment. Prepared for J. SAMPLE DATE
 Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
Prepared for J. SAMPLE About this Report Introduction LEADERSHIP that special quality that enables leaders to achieve extraordinary success. In today's uncertain world the need for leadership is at an
GPS GROWTH, PLANNING, & SUPPORT
 GPS GROWTH, PLANNING, & SUPPORT PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS An employee evaluation is the assessment and review of an employees job performance for the past year. THE EVALUATION Self Evaluation Basic Job Requirement
GPS GROWTH, PLANNING, & SUPPORT PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS An employee evaluation is the assessment and review of an employees job performance for the past year. THE EVALUATION Self Evaluation Basic Job Requirement
Performance Skills Leader. Individual Feedback Report
 Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Performance Skills Leader Individual Feedback Report Jon Sample Date Printed: /6/ Introduction REPORT OVERVIEW Recently, you completed the PS Leader assessment. You may recall that you were asked to provide
Copyright 2016 The William Averette Anderson Fund 501(c)(3)
 Mentee Guide Table of Contents BAF Background... 2 BAF Mentoring Program... 2 Defining Mentoring... 3 Being an Effective Mentee... 4 Key Considerations for Prospective Mentees... 5 Next Steps... 8 The
Mentee Guide Table of Contents BAF Background... 2 BAF Mentoring Program... 2 Defining Mentoring... 3 Being an Effective Mentee... 4 Key Considerations for Prospective Mentees... 5 Next Steps... 8 The
HR SERIES: 006 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL AND GOAL SETTING. Presenter: Rhoda Serem
 HR SERIES: 006 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL AND GOAL SETTING Presenter: Rhoda Serem Email: info@achrp.org Sessions Learning Objectives Adopt a holistic and positive mindset towards performance management. Align
HR SERIES: 006 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL AND GOAL SETTING Presenter: Rhoda Serem Email: info@achrp.org Sessions Learning Objectives Adopt a holistic and positive mindset towards performance management. Align
Managing and Evaluating Employee Performance. January 2018
 Managing and Evaluating Employee Performance January 2018 Timelines Non-Instructional Academic Staff and Limited Fiscal year Processes begin in July for prior year (July 1 June 30) Due by end of August
Managing and Evaluating Employee Performance January 2018 Timelines Non-Instructional Academic Staff and Limited Fiscal year Processes begin in July for prior year (July 1 June 30) Due by end of August
Conducting Performance Reviews Kurtis Neal, SPHR Director of Human Resources
 The Office of Human Resources Conducting Performance Reviews Kurtis Neal, SPHR Director of Human Resources Outline Presentation/Discussion Why performance reviews are important ASU performance review process
The Office of Human Resources Conducting Performance Reviews Kurtis Neal, SPHR Director of Human Resources Outline Presentation/Discussion Why performance reviews are important ASU performance review process
LSP. Leadership Skills Profile. Development Guide. Douglas N. Jackson, Ph.D. Leadership Skills Profile
 LSP Leadership Skills Profile Douglas N. Jackson, Ph.D. Development Guide Leadership Skills Profile Advancing the Science of Human Assessment since 967. LSP DEVELOPMENT GUIDE Congratulations on completing
LSP Leadership Skills Profile Douglas N. Jackson, Ph.D. Development Guide Leadership Skills Profile Advancing the Science of Human Assessment since 967. LSP DEVELOPMENT GUIDE Congratulations on completing
Your Guide to Individual Development Planning
 Your Guide to Individual Development Planning Introduction A commitment to continuously learning and developing knowledge and skills that are valued by the University opens the door to career options and
Your Guide to Individual Development Planning Introduction A commitment to continuously learning and developing knowledge and skills that are valued by the University opens the door to career options and
S & T Management Core Competency Profile
 (Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
(Publié aussi en français sous le titre Profil des compétences essentielles des gestionnaires en S-T) Table of Contents Overview...1 1.0 Technical...1 1.1 Possesses knowledge of, and demonstrated ability
A Guide to Employee Development and Review Scheme Professional/General Managers
 A Guide to Employee Development and Review Scheme Professional/General Managers Edition 1.0 Human Resources ManagerToolkit Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 3 Manager Responsibilities...
A Guide to Employee Development and Review Scheme Professional/General Managers Edition 1.0 Human Resources ManagerToolkit Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Introduction... 3 Manager Responsibilities...
Performance Management Training for Managers
 Performance Management Training for Managers Office of Human Resources May 21, 2018 Agenda Performance Management Overview & Cycle Performance Appraisal Framework Incorporating Current and Future Goals
Performance Management Training for Managers Office of Human Resources May 21, 2018 Agenda Performance Management Overview & Cycle Performance Appraisal Framework Incorporating Current and Future Goals
Introduction to the DoD Performance Management and Appraisal Program (DPMAP)
 Introduction to the DoD Performance Management and Appraisal Program (DPMAP) DPMAP Rev. 2 Welcome Why we are here: -To learn about the new Defense Performance Management Appraisal Program (DPMAP). -Gain
Introduction to the DoD Performance Management and Appraisal Program (DPMAP) DPMAP Rev. 2 Welcome Why we are here: -To learn about the new Defense Performance Management Appraisal Program (DPMAP). -Gain
Development Suggestions for Political Savvy
 Development Suggestions for Political Savvy Suggested Readings Title Political Savvy: Systematic Approaches for Leadership Behind-the-Scenes Don't Sabotage Your Success! Making Office Politics Work Author/Publisher
Development Suggestions for Political Savvy Suggested Readings Title Political Savvy: Systematic Approaches for Leadership Behind-the-Scenes Don't Sabotage Your Success! Making Office Politics Work Author/Publisher
Performance Appraisal 16/17
 Performance Appraisal 16/17 Employee Training Today s Session In today s session, you will: Receive an overview and timeline of the 2016-2017 performance process Understand the process to develop a SMART
Performance Appraisal 16/17 Employee Training Today s Session In today s session, you will: Receive an overview and timeline of the 2016-2017 performance process Understand the process to develop a SMART
!"##$%&'#("')*+#'*,#'*-'.*,/'+#0--'1' 2*+$#$*%'3"+4/$2#$*%+'0%3'"506,0#$*%' 76,8'9:4"66"%4"'7*%-"/"%4"'
 !"##$%&'#("')*+#'*,#'*-'.*,/'+#0--'1' 2*+$#$*%'3"+4/$2#$*%+'0%3'"506,0#$*%' 76,8'9:4"66"%4"'7*%-"/"%4"' ;,"+30.?
!"##$%&'#("')*+#'*,#'*-'.*,/'+#0--'1' 2*+$#$*%'3"+4/$2#$*%+'0%3'"506,0#$*%' 76,8'9:4"66"%4"'7*%-"/"%4"' ;,"+30.?
2018 Performance Evaluation Process LOUISVILLE.EDU
 2018 Performance Evaluation Process Salary Increases At this time, no decision has been made regarding: Fiscal vs. calendar cycle Potential pay increases Purpose of the Performance Evaluation Candid performance
2018 Performance Evaluation Process Salary Increases At this time, no decision has been made regarding: Fiscal vs. calendar cycle Potential pay increases Purpose of the Performance Evaluation Candid performance
Department of Defense INSTRUCTION
 Department of Defense INSTRUCTION NUMBER 1400.25, Volume 2011 May 7, 2016 USD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Civilian Personnel Management System: Defense Civilian Intelligence Personnel System (DCIPS) Performance
Department of Defense INSTRUCTION NUMBER 1400.25, Volume 2011 May 7, 2016 USD(P&R) SUBJECT: DoD Civilian Personnel Management System: Defense Civilian Intelligence Personnel System (DCIPS) Performance
Performance Management Resource Guide
 Performance Management Resource Guide Managing Performance for Success Note: To prepare for a transition to the new Workday system later in 2018, some changes have been made to the performance templates
Performance Management Resource Guide Managing Performance for Success Note: To prepare for a transition to the new Workday system later in 2018, some changes have been made to the performance templates
Laying the Groundwork for Successful Coaching Efforts
 B e t h e t e a m o f c h o i c e f o r e d u c a t i o n, d i s c o v e r y a n d h e a l t h c a r e. Laying the Groundwork for Successful Coaching Efforts Your Guide for Developing Effective Coaching
B e t h e t e a m o f c h o i c e f o r e d u c a t i o n, d i s c o v e r y a n d h e a l t h c a r e. Laying the Groundwork for Successful Coaching Efforts Your Guide for Developing Effective Coaching
Lesson 4: Continuous Feedback
 PURPOSE The purpose of Lesson 4 is to describe how effective performance management is critical to the DoD culture of high performance; identify trust behaviors between supervisors and employees that build
PURPOSE The purpose of Lesson 4 is to describe how effective performance management is critical to the DoD culture of high performance; identify trust behaviors between supervisors and employees that build
Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance
 Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance P R E S E N T E R : D R. P E T E R M E T O F E D A T E : A U G U S T 2 5 2 7, 2 0 1 4 L O C A T I O N : L O N G B E A C H, C A 9 0 8 3 1 Building
Developing Management Competence for Higher Performance P R E S E N T E R : D R. P E T E R M E T O F E D A T E : A U G U S T 2 5 2 7, 2 0 1 4 L O C A T I O N : L O N G B E A C H, C A 9 0 8 3 1 Building
Development Suggestions for Strategic Thinking
 Development Suggestions for Strategic Thinking Suggested Readings Title Author/Publisher Enlightened Leadership Oakley, Ed and Doug Krug/ 1991/ Simon & Schuster Managing Transitions: Making the Most William
Development Suggestions for Strategic Thinking Suggested Readings Title Author/Publisher Enlightened Leadership Oakley, Ed and Doug Krug/ 1991/ Simon & Schuster Managing Transitions: Making the Most William
Performance Management
 Performance Management Setting Goals & Expectations Presented by: HRM Agenda Key Points Performance Cycle Setting Goals Alignment SMART Practice Draft & Align Metrics 2 The Performance Management Cycle
Performance Management Setting Goals & Expectations Presented by: HRM Agenda Key Points Performance Cycle Setting Goals Alignment SMART Practice Draft & Align Metrics 2 The Performance Management Cycle
How to Engage Employees. A Guide for Employees, Supervisors, Managers, & Executives
 How to Engage Employees A Guide for Employees, Supervisors, Managers, & Executives 1 Introduction Employee Engagement is a good in and of itself. What is Employee Engagement? Employee engagement is the
How to Engage Employees A Guide for Employees, Supervisors, Managers, & Executives 1 Introduction Employee Engagement is a good in and of itself. What is Employee Engagement? Employee engagement is the
SUCCESSION PLANNING and LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT
 SUCCESSION PLANNING and LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT TOOLKIT April 2015 CONTENTS 1 Succession planning 3 What is succession planning? Succession planning process Leadership development 4 What is leadership development?
SUCCESSION PLANNING and LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT TOOLKIT April 2015 CONTENTS 1 Succession planning 3 What is succession planning? Succession planning process Leadership development 4 What is leadership development?
The expectations of my role are clear to me
 The expectations of my role are clear to me MY JOB Copyright Evolve Performance Group. All rights reserved. Weekly SETTING CLEAR EXPECTATIONS Complete the following steps: 1. Gather team together for a
The expectations of my role are clear to me MY JOB Copyright Evolve Performance Group. All rights reserved. Weekly SETTING CLEAR EXPECTATIONS Complete the following steps: 1. Gather team together for a
SMART Goals: A How to Guide
 SMART Goals: A How to Guide 1 Table of Contents What are SMART Goals?... 3 What is the SMART criteria?... 3 How do I decide the right scope for my SMART Goals? (How big? How many?)... 3 Where to start?...
SMART Goals: A How to Guide 1 Table of Contents What are SMART Goals?... 3 What is the SMART criteria?... 3 How do I decide the right scope for my SMART Goals? (How big? How many?)... 3 Where to start?...
Managing Essentials. Introduction MANAGING ESSENTIALS - 1
 Introduction A manager is someone who has the ability to lead others and a desire to engage in continuous learning and development of themselves and their employees. It is a manager s responsibility to
Introduction A manager is someone who has the ability to lead others and a desire to engage in continuous learning and development of themselves and their employees. It is a manager s responsibility to
NO , Chapter 1 TALLAHASSEE, February 13, Human Resources
 CFOP 60-35, Chapter 1 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF CF OPERATING PROCEDURE CHILDREN AND FAMILIES NO. 60-35, Chapter 1 TALLAHASSEE, February 13, 2018 Human Resources PERFORMANCE EVALUATION PROGRAM FOR
CFOP 60-35, Chapter 1 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF CF OPERATING PROCEDURE CHILDREN AND FAMILIES NO. 60-35, Chapter 1 TALLAHASSEE, February 13, 2018 Human Resources PERFORMANCE EVALUATION PROGRAM FOR
Conducting Performance Evaluations
 LUCY R. COHEN Manager Personnel and Payroll Services University of Michigan Library Ann Arbor, Michigan Conducting Performance Evaluations ABSTRACT In order for any performance evaluation system to be
LUCY R. COHEN Manager Personnel and Payroll Services University of Michigan Library Ann Arbor, Michigan Conducting Performance Evaluations ABSTRACT In order for any performance evaluation system to be
ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR ABOUT THE ORGANIZATION: Rocky Mountain Performance Excellence (RMPEx) is a Colorado nonprofit corporation
ROCKY MOUNTAIN PERFORMANCE EXCELLENCE POSITION DESCRIPTION FOR THE EXECUTIVE/MANAGING DIRECTOR ABOUT THE ORGANIZATION: Rocky Mountain Performance Excellence (RMPEx) is a Colorado nonprofit corporation
OPPORTUNITY PROFILE. Senior Advisor & Council Relations
 OPPORTUNITY PROFILE Senior Advisor & Council Relations ABOUT THE ASSOCIATION OF PROFESSIONAL ENGINEERS AND GEOSCIENTISTS OF ALBERTA (APEGA) The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of
OPPORTUNITY PROFILE Senior Advisor & Council Relations ABOUT THE ASSOCIATION OF PROFESSIONAL ENGINEERS AND GEOSCIENTISTS OF ALBERTA (APEGA) The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of
CAREER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM APPRAISAL GUIDE EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION
 2018-2019 CAREER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM APPRAISAL GUIDE 1 In 2016, Dallas Independent School District s Board of Trustees adopted new District goals that prioritize measurable improvement of student outcomes.
2018-2019 CAREER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM APPRAISAL GUIDE 1 In 2016, Dallas Independent School District s Board of Trustees adopted new District goals that prioritize measurable improvement of student outcomes.
Chapter One PROJECT MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
 Chapter One PROJECT MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW Project management itself is not a new concept. It has been practiced for hundreds, even thousands of years. Any large undertaking requires a set of objectives,
Chapter One PROJECT MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW Project management itself is not a new concept. It has been practiced for hundreds, even thousands of years. Any large undertaking requires a set of objectives,
Vacation Work Guidelines for Employers
 Vacation Work Guidelines for Employers Attracting and retaining skilled professionals is critical to the success of the minerals industry, particularly during a period of sustained growth. Vacation work
Vacation Work Guidelines for Employers Attracting and retaining skilled professionals is critical to the success of the minerals industry, particularly during a period of sustained growth. Vacation work
Subject Matter Professional Performance Appraisal FY17. Demographics. General Instructions. Rating Scale. Department:
 Subject Matter Professional Performance Appraisal FY17 Demographics Name: Employee ID: Job Title: Supervisor: Department: General Instructions The annual Performance Appraisal is intended to summarize
Subject Matter Professional Performance Appraisal FY17 Demographics Name: Employee ID: Job Title: Supervisor: Department: General Instructions The annual Performance Appraisal is intended to summarize
Continuous Improvement Manager Position Description
 Job Title: Continuous Improvement Manager Department: Administration Reports To: President FLSA Status: Exempt Prepared By: Jenny Redes Prepared Date: May 29, 2009 Approved By: Sam Nicholas Approved Date:
Job Title: Continuous Improvement Manager Department: Administration Reports To: President FLSA Status: Exempt Prepared By: Jenny Redes Prepared Date: May 29, 2009 Approved By: Sam Nicholas Approved Date:
Introductions. Chris Berger. Debby LaRocco
 Icebreaker! Agenda Introductions Performance Management Timelines Process Alignment Employee Responsibilities Supervisor Responsibilities PeopleAdmin The System Supervisor Slides Introductions Chris Berger
Icebreaker! Agenda Introductions Performance Management Timelines Process Alignment Employee Responsibilities Supervisor Responsibilities PeopleAdmin The System Supervisor Slides Introductions Chris Berger
Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff
 Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff Starting Points The following points made by Jim Collins (author of the bestseller Good to Great; Why Some Companies Make the Leap And others Don t) are
Chapter 7E: Nurturing Human Capital/Focus on Staff Starting Points The following points made by Jim Collins (author of the bestseller Good to Great; Why Some Companies Make the Leap And others Don t) are
Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations
 Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations Table of Contents Introduction... - 2 - Benefits of Productive Performance Meetings... - 3 - Performance Goals Help Employees... - 3 - Performance Goals Help
Supervisor s Guide: Performance Evaluations Table of Contents Introduction... - 2 - Benefits of Productive Performance Meetings... - 3 - Performance Goals Help Employees... - 3 - Performance Goals Help
Designing and Implementing Mentoring Programs for Early Career Faculty
 Designing and Implementing Mentoring Programs for Early Career Faculty November 19, 2010 Mentoring is vital to both individual and institutional success. Good mentorship is a hallmark of successful academic
Designing and Implementing Mentoring Programs for Early Career Faculty November 19, 2010 Mentoring is vital to both individual and institutional success. Good mentorship is a hallmark of successful academic
Coaching Fundamentals
 Coaching Fundamentals Introduction and Background 1. Coaching as a business model began appearing: a. In the early 1990 s b. In the late 2000 s c. In the early 2000 s d. In the late 1980 s Answer is In
Coaching Fundamentals Introduction and Background 1. Coaching as a business model began appearing: a. In the early 1990 s b. In the late 2000 s c. In the early 2000 s d. In the late 1980 s Answer is In
Performance Appraisal System
 Performance Appraisal System 2017 University of New England Performance Appraisal System Purpose and Philosophy The purpose of the Performance Appraisal System at UNE is to ensure that managers and employees
Performance Appraisal System 2017 University of New England Performance Appraisal System Purpose and Philosophy The purpose of the Performance Appraisal System at UNE is to ensure that managers and employees
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
 PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Employee Job Title Appraisal Given By PREVIOUS KEY OBJECTIVES, GOALS, PERFORMANCE 1. Goal / Objectives Result / Performance 2. Goal / Objective s Result / Performance 3. Goal / Objective
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL Employee Job Title Appraisal Given By PREVIOUS KEY OBJECTIVES, GOALS, PERFORMANCE 1. Goal / Objectives Result / Performance 2. Goal / Objective s Result / Performance 3. Goal / Objective
Performance Management: Best Practices in Paula H. Harvey, MBA, SPHR, GPHR
 Performance Management: Best Practices in 2014 Paula H. Harvey, MBA, SPHR, GPHR Be Nice to Penny! Is this how you handle Performance Management? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7cem BZyGF8 2 Learning Objectives
Performance Management: Best Practices in 2014 Paula H. Harvey, MBA, SPHR, GPHR Be Nice to Penny! Is this how you handle Performance Management? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7cem BZyGF8 2 Learning Objectives
Transformatio. competency model. Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0. updated, career-spanning. for health sector leaders
 Transformatio National Center Healthcare Leadership Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0 updated, career-spanning competency model for health sector leaders Executive Summary The National Center for
Transformatio National Center Healthcare Leadership Health Leadership Competency Model 3.0 updated, career-spanning competency model for health sector leaders Executive Summary The National Center for
ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors. May 27, 2015
 Background ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors May 27, 2015 - Values work launched at the February Directors Retreat. - A Values work group (Directors) determined and recommended a draft of 5 ANA
Background ANA Adopted Values and Associated Behaviors May 27, 2015 - Values work launched at the February Directors Retreat. - A Values work group (Directors) determined and recommended a draft of 5 ANA
CAMPUS ADVANTAGE INC. Job Description. JOB TITLE: Corporate Intern
 CAMPUS ADVANTAGE INC. Job Description JOB TITLE: Corporate Intern Reports To: Director of Employee Engagement & Training Prepared by: ADP TotalSource January 30, 2016 SUMMARY This position is primarily
CAMPUS ADVANTAGE INC. Job Description JOB TITLE: Corporate Intern Reports To: Director of Employee Engagement & Training Prepared by: ADP TotalSource January 30, 2016 SUMMARY This position is primarily
Team Conversation Starters
 Team Conversation Starters This guide is intended to help you get started during your action planning session and/or to dig deeper into understanding the feedback you receive from your employees during
Team Conversation Starters This guide is intended to help you get started during your action planning session and/or to dig deeper into understanding the feedback you receive from your employees during
Why Create an Individual Development Plan? How Will an IDP Guide My Progress? How Can I Use This Template? EXPECTATIONS
 YEAR - 1 Why Create an Individual Development Plan? An individual development plan (IDP) helps you to align your personal and professional goals with your academic expectations and responsibilities. Developing
YEAR - 1 Why Create an Individual Development Plan? An individual development plan (IDP) helps you to align your personal and professional goals with your academic expectations and responsibilities. Developing
Thank You! SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
 **Please print this packet for your advisor. Your advisor will be able to use the information within this packet to assist them in effectively working with your organization throughout the coming year.
**Please print this packet for your advisor. Your advisor will be able to use the information within this packet to assist them in effectively working with your organization throughout the coming year.
Innovation Skills Profile.
 Centre for Business Innovation Innovation Skills Profile. The Skills, Attitudes, and Behaviours You Need to Contribute to Innovation in the Workplace The Innovation Skills Profile (ISP 2018) isolates the
Centre for Business Innovation Innovation Skills Profile. The Skills, Attitudes, and Behaviours You Need to Contribute to Innovation in the Workplace The Innovation Skills Profile (ISP 2018) isolates the
Performance Management: Giving and Receiving Feedback
 Performance Management: Giving and Receiving Feedback Seminar for Supervisors Presenter: Stephanie Flanagan slm114@psu.edu; 814-863-4614 Fall 2017 2017 The Pennsylvania State University. All rights reserved.
Performance Management: Giving and Receiving Feedback Seminar for Supervisors Presenter: Stephanie Flanagan slm114@psu.edu; 814-863-4614 Fall 2017 2017 The Pennsylvania State University. All rights reserved.
Performance Management. Leadership Roundtable May 14, 2008
 Performance Management Leadership Roundtable May 14, 2008 Today s Presentation: The Performance Management Approach Guidelines and Resources for Performance Evaluations Performance Management Defined:
Performance Management Leadership Roundtable May 14, 2008 Today s Presentation: The Performance Management Approach Guidelines and Resources for Performance Evaluations Performance Management Defined:
JOB DESCRIPTION VP of Branch Member Experience September 2017
 JOB TITLE: Branch Member Experience Manager DEPARTMENT: Operations REPORTS TO: FLSA STATUS: Exempt SALARY GRADE: 11 JOB DESCRIPTION SUMMARY: The Branch Manager of Member Experience is responsible for directing
JOB TITLE: Branch Member Experience Manager DEPARTMENT: Operations REPORTS TO: FLSA STATUS: Exempt SALARY GRADE: 11 JOB DESCRIPTION SUMMARY: The Branch Manager of Member Experience is responsible for directing
Performance Evaluations Demystified
 Performance Evaluations Demystified Presented by: Joyel Crawford, MBA, CPCC, PHR Today s session will help you to: Discuss the importance of effective performance management Learn your role and responsibilities
Performance Evaluations Demystified Presented by: Joyel Crawford, MBA, CPCC, PHR Today s session will help you to: Discuss the importance of effective performance management Learn your role and responsibilities
Performance Evaluation Workshop. Human Resources December 2018
 Performance Evaluation Workshop Human Resources December 2018 Agenda Overview New Performance Ratings New Performance Factors The New Form Preparing for the Evaluation Meeting Tools and Resources Overview
Performance Evaluation Workshop Human Resources December 2018 Agenda Overview New Performance Ratings New Performance Factors The New Form Preparing for the Evaluation Meeting Tools and Resources Overview
JOB DESCRIPTION Branch Operations Supervisor September 2017
 JOB TITLE: DEPARTMENT: Operations REPORTS TO: Manager of Member Experience FLSA STATUS: Non-exempt SALARY GRADE: 9 SUMMARY: The is responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of the assigned branch
JOB TITLE: DEPARTMENT: Operations REPORTS TO: Manager of Member Experience FLSA STATUS: Non-exempt SALARY GRADE: 9 SUMMARY: The is responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of the assigned branch
A Guide for Writing S.M.A.R.T. Goals
 A Guide for Writing S.M.A.R.T. Goals What are S.M.A.R.T. Goals? Statements of the important results you are working to accomplish Designed in a way to foster clear and mutual understanding of what constitutes
A Guide for Writing S.M.A.R.T. Goals What are S.M.A.R.T. Goals? Statements of the important results you are working to accomplish Designed in a way to foster clear and mutual understanding of what constitutes
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities
 Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
Policing Professional Framework Personal qualities Executive (ACPO / Force Command Team) Promotes a real belief in public service, focusing on what matters to the public and will best serve their interests.
6 Managing performance
 SECTION 6 Managing performance It can be a rewarding experience to lead a team when each individual is contributing to the success of the whole team. However, difficult challenges facing a line manager
SECTION 6 Managing performance It can be a rewarding experience to lead a team when each individual is contributing to the success of the whole team. However, difficult challenges facing a line manager
INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN. Why Create an Individual Development Plan? How Will an IDP Guide My Progress? How Can I Use This Template?
 EXPECTATIONS Why Create an Individual Development Plan? An individual development plan (IDP) helps you to align your personal and professional goals with your academic expectations and responsibilities.
EXPECTATIONS Why Create an Individual Development Plan? An individual development plan (IDP) helps you to align your personal and professional goals with your academic expectations and responsibilities.
TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS
 OFFICE OF HUMAN RESOURCES TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS SUMMARY The Talent Review process is a means to gain a better understanding of what is expected of the employee and how the employee can improve his/her
OFFICE OF HUMAN RESOURCES TALENT REVIEW INSTRUCTIONS SUMMARY The Talent Review process is a means to gain a better understanding of what is expected of the employee and how the employee can improve his/her
Building a Professional Development Program with Lynda.com Administrative Manual St. Olaf Human Resources Department
 Building a Professional Development Program with Lynda.com Administrative Manual St. Olaf Human Resources Department Professional Development at St. Olaf College Employees facilitate the growth of our
Building a Professional Development Program with Lynda.com Administrative Manual St. Olaf Human Resources Department Professional Development at St. Olaf College Employees facilitate the growth of our
NinerTalent STAKES. Succeeding through Teamwork, Active feedback, Knowledge transfer, Engagement, and Support
 NinerTalent STAKES Succeeding through Teamwork, Active feedback, Knowledge transfer, Engagement, and Support Institutional Goals Success Tip! Use the given verbiage to help you communicate your expectations
NinerTalent STAKES Succeeding through Teamwork, Active feedback, Knowledge transfer, Engagement, and Support Institutional Goals Success Tip! Use the given verbiage to help you communicate your expectations
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators
 UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
UC San Diego Core Competency Model Behavioral Indicators Rev. 08/21/2014 COM M UNI C AT I O N Shares and receives information using clear oral, written, and interpersonal communication skills. Behavioral
Understanding the Research Academy for Faculty and Postdoctoral Fellows Research Mentoring Program
 Understanding the Research Academy for Faculty and Postdoctoral Fellows Research Mentoring Program How do I become an RAFPF Research mentor or mentee? I'm looking for a mentor! I m ready to mentor! Mentoring
Understanding the Research Academy for Faculty and Postdoctoral Fellows Research Mentoring Program How do I become an RAFPF Research mentor or mentee? I'm looking for a mentor! I m ready to mentor! Mentoring
INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN (IDP)
 INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN (IDP) An Individual Development Plan (IDP) is an essential planning document that identifies your goals and objectives. It is expected that all graduate students will utilize
INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN (IDP) An Individual Development Plan (IDP) is an essential planning document that identifies your goals and objectives. It is expected that all graduate students will utilize
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CONVERSATION GUIDE
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CONVERSATION GUIDE TOOL FOR /COLLEAGUE PERFORMANCE CONVERSATIONS PURPOSE This document describes the various types of conversations managers may have with colleagues with regard
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT CONVERSATION GUIDE TOOL FOR /COLLEAGUE PERFORMANCE CONVERSATIONS PURPOSE This document describes the various types of conversations managers may have with colleagues with regard
Coaching and Mentoring
 Coaching and Mentoring TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 2 Setting Goals 4 Checking Reality 5 Exploring Options 6 Wrapping it Up 7 The Art of Mentoring 8 2000-2016 Coaching and Mentoring Printable Guide 2
Coaching and Mentoring TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 2 Setting Goals 4 Checking Reality 5 Exploring Options 6 Wrapping it Up 7 The Art of Mentoring 8 2000-2016 Coaching and Mentoring Printable Guide 2
