Business. How to do well in the exam. Types of Business Activity primary, secondary and tertiary sectors
|
|
|
- Jeffery Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Business and People The Best Time to Pass is the First Time Business How to do well in the exam Know your facts almost 50% of the marks in this exam are for the recalling of facts. Get your notes in order use the MLE/R Drive to check you have got all the notes you need. Print off any you are missing. Be familiar with the type of question to be asked mock exams will help you. Give full answers the number of lines available on your answer sheet is a good guide. If there are 10 lines and you ve filled in just 2, that s not good! Read the question carefully and refer to the case study in the exam. Always explain your answers - PEE: point, explain, example. If you feel you need more info in the case study to answer the question, state what info you need! Types of Business Activity primary, secondary and tertiary sectors Type of Business Activity Definition Examples primary sector produces or extracts raw materials for other businesses to use fishing, mining, farming secondary sector manufactures (makes) products with raw materials car manufacturer tertiary sector provides a service for its customers retail, banking, travel, entertainment, customer service, education, health Interdependence = all businesses depend on other sectors - e.g. a farmer grows potatoes, Walkers make crisps, Tesco sell them! This is an example of a chain of production where each businesses specialises in one kind of work (specialisation) and the secondary sector add value to the original raw material (e.g. Walkers add value to the potato this is called added value!) Changes in the three sectors of business activity in the UK what has changed and why? Type of Business Activity Less or more important Reason for change primary sector Less raw materials used up (e.g. coal), machines have replaced jobs (e.g. farming) foreign competition can produce cheaper raw materials (e.g. coal) secondary sector Less (the decline of foreign competition means many goods made overseas (cheaper to produce e.g. clothes in Primark!) manufacturing is called machinery has replaced jobs (e.g. car plants) de-industrialisation) tertiary sector much more Increase in wealth so more money spent in shops, on travel, entertainment etc Increase in leisure time Customer service is more important so businesses can keep their customers
2 Business Objectives (aims) and private, public and voluntary (not for profit sectors) Objectives (often found Explanation Conflict in mission statements) Profit Maximisation of profit main aim of most businesses in the private sector *Profit v. growth the desire to grow quickly Growth Usually the best way to raise profit and the aim of most businesses in the private sector: could soak up profit (some shareholders will Sales growth not like this!) Increased market share (e.g. Ford having a greater percentage share of the UK car sales) *Profit v. survival profit may have to be put Eliminate competition on hold if a business is struggling to survive Survival Very important for a new business or an established business facing problems *Profit or growth v. service some might Providing a service All businesses will want to provide a service but it is the most important aim for the public sector want to get rich quick at expense of service Sector Definition Examples Objectives Private sector Public sector Voluntary (not for profit) sector businesses owned by private individuals organisations controlled by central and local government Charities and social clubs. Tesco NHS, education, police, fire and local councils + public corporations like the BBC and the Post Office Oxfam Scout/guide groups Usually profit and growth but with new or struggling businesses, main aim is survival Most important aim is service! Raise money, further a cause, provide a service for its members Stakeholders = individuals or groups with an interest in a business You should be able to think why some or all of the following could be stakeholders in a business and why they often have conflicting interests: Workers Managers Owners Customers Suppliers Government Local community Competitor Interest and pressure groups
3 Type of Business Organisation in the Private Sector Definition Definition Common features Main difference Advantages Unincorporated Sole proprietors and partnerships are easier to set up but have no separate legal identity Sole proprietor Partnership (or trader) One person owns the A min of 2 and a max of 20 business. partners own the business. A deed of partnership states how profit will be shared. Unlimited liability owners are personally liable for all business debts so personal possessions may be lost in insolvency The owner(s) pays income tax is paid on profit Financial information is private stays with the owner(s) A sole proprietor company is owned by one person but a partnership is owned by 2-20 partners *Easy to set up *More capital available *Not much start-up capital *More specialist skills available needed *Illness not such a problem *Owner has 100% control *The company s financial info *Owner can keep profit stays private with partners *The company s financial info *Easy to set up stays private *Sleeping partners can contribute capital Incorporated Incorporation is a legal process which Ltd and PLC businesses must go through. The Registrar of Companies issues a Certificate of Incorporation once companies have registered. Private Limited Company Public Limited Company (PLC) (Ltd) Shares are sold to private These companies sell their shares on the London Stock Exchange to the investors (managers, public they must have an issued share capital of > and are friends, family, wealthy usually the largest companies. Minority shareholders own a small backers). percentage of the shares and major shareholders, known as institutional shareholders, like investment companies, own a large number of shares Limited liability the liability of the owners (shareholders) is limited to the amount of money they have invested in the business (i.e. the shares they bought) Companies are owned by shareholders The business has a separate legal entity from its owners Corporation tax (tax paid by businesses) is paid on any profit Finance can be raised through sale of shares Financial info is available to public A Board of Directors runs the company, made up of directors elected by shareholders at the Annual General Meeting (AGM). The Chair of the Board of Directors is responsible for the way the board operates and the Managing Director runs the overall company. Shares in a PLC are sold to the public on the stock exchange and so PLCs can raise more money than a Private Limited Company *Limited liability *Capital from investors who buy shares in the company * Company has a separate legal identity from owners * Continuity company continues to trade in the event of a death of one of the owners (shareholders) *Limited liability *PLCs can easily raise large sums of finance through sales of shares much more than most Private Limited Companies *Company has a separate legal identity from owners * Continuity company continues to trade in the event of a death of one of the owners (shareholders) Disadvantages *Unlimited liability *Possible shortage of capital can t always borrow money *Illness! *Hard work needed *Owner might not be able to sell/pass business on *Shortage of skills *Profit has to be shared among partners *Unlimited liability *Disagreements! *Can still be short of capital * Financial info has to be made available to public which means competitors can see it! *Incorporation costs money and takes time *Shares cannot be sold to general public so capital might be short *Shareholders will expect a share of the profits in the form of dividends * Financial info has to be made available to public in the form of an annual report so competitors can see it! *Incorporation costs money and takes time *Takeover it is possible for other companies to buy up large numbers of shares and takeover the ownership of the company *Shareholders will expect a share of the profits in the form of dividends
4 There are also some other types of business organisation: Co-operatives some independent producers (e.g. dairy farmers) work together and trade as though they are a single larger business (and get a better price) Social Enterprise a business that is run for the benefit of the community. Not all the profits are kept by the owners some are put back into community projects Multinational companies these are usually large PLCs that have a head office in one country with offices/factories in other countries e.g. Sony. With increasing globalisation, there has been a growth in the number of MNCs. Advantages: production can be located in countries where labour costs are low. Disadvantages: communication problems caused by location in different countries. Franchise is not a type of business arrangement but is a marketing arrangement. An existing business (franchisor) sells to another business (the franchisee) the right to use its products, services and logos. A franchise can be organised into any one of the four main forms of business organisation in the private sector. Reasons for Business Failure Poor management No demand for product or service Wrong location Poor cash flow money is not coming in for large parts of the year (e.g. a Xmas decoration shop!) Running costs are too high Too much competition Poor quality of goods or services Not enough profit made Unfavourable exchange rate can affect companies if they are trading outside of the UK Types of Business Growth Merging one business decides to merge (join together) with another Takeover one business buys control of another by buying enough shares in the business to be able to outvote other shareholders Internal expansion a business grows by increasing its production e.g. by building a new factory Integration = when a company merges with or takes over another business. There are different types of integration try to think of advantages & disadvantages for each. Type of integration Explanation: one business merges with or takes over another business: Example: a brewery buys Horizontal in the same industry at the same stage of production another brewery Backwards vertical that is a supplier of goods/services for this company a hops farm (hops is used to make beer!) Forwards vertical that provides an outlet for its products or services a pub chain Diversification (or conglomerate) in an unrelated business activity a coffee shop chain
5 Factors Affecting Location of a Business For some companies, location is less important. They are footloose e.g. call centres or internet companies do not need to be in town centres (expensive!) Factor Type of product or service Availability of and access to raw materials The cost of the location Access to and nearness to markets Climate and physical geography Availability of transport links Tradition Cost of labour Central government Local government Explanation/example A shipbuilder will be near the sea so that the finished boat can be launched! A paper mill might be near a forest! The cost of land and buildings varies e.g. costs in central London will be more than in rural Suffolk A Tesco superstore will be near a large centre of population! East Anglia is flat so is suited to growing cereal crops e.g. wheat Many warehouses are located in Rugby as it is near the M1 and the M6 Many Cornish pasties are made in Cornwall! With increasing globalisation, companies often move production overseas where wages are lower and they can reduce costs Central government often encourage businesses to locate in a certain area by providing grants. It has announced that the Regional Development Agencies (RDAs) will close at the end of March Economic development and regeneration will in future be led by Local Enterprise Partnerships in 22 new Enterprise Zones (e.g. Alconbury Airfield) Councils encourage businesses to locate in their area with grants e.g. provision of industrial estates or technology parks on greenfield (sites with no previous business) or brownfield (sites with previous business activity) sites. People Recruitment and Selection (carried out by the Personnel or Human Resources Dept in most companies) Recruitment = process by a company to seek out interested and qualified applicants for a job vacancy Selection = the process of choosing one person from all the applicants to fill the vacancy The main stages: Needs analysis a company decides how many workers it needs to employ, what type and when. A job description (lists the duties a worker must perform) and a person specification (lists the knowledge, experience, qualifications and qualities needed for the job) are drawn up at this stage. Advertising the post: a job advert should get the right people applying! Think what it should contain (duties, requirements, salary etc) and where the advert should appear. Think why some jobs adverts appear in local newspapers but some appear in national newspapers, specialist magazines, job centres or the internet. At this stage, a company decides if it is to use internal recruitment (only staff already in the company apply) or external recruitment (people from outside the business can apply). You should be able to think of advantages and disadvantages of internal and external recruitment!
6 Selecting from the applicants firstly, the organisation draws up a shortlist of applicants to invite to interview from all the people who applied for the jobs. Letters of application, application forms and CVs are used to decide the shortlist. Secondly, there is the final stage of selection: interviews are usually used to decide who will get the job, but references, psychometric tests (testing personality), presentations and tests (e.g. maths, IT) can also be used. There are advantages and disadvantages for all these methods use to decide who should get the job e.g. an interview shows how well applicants present themselves but of course, they can put on a show and deceive! You need to be able to explain why finding the right people to work for a company and then retaining them (retention) are so important. Recruitment agencies and employment agencies are also involved in recruitment and selection. A recruitment agency will, for a fee, do much of the recruitment and selection work for a company. An employment agency, for a fee, provides workers (e.g. office staff)to a company for short periods of time. Motivation the encouragement given to staff to work hard and work well so that they feel good about the company and have high productivity. What motivates workers? Maslow s theory, pay and non-pay methods of motivation. Maslow s hierarchy of needs workers have a variety of needs that need to be satisfied in the workplace if they are to be motivated. Starting at the bottom of the pyramid are physiological needs (enough wages to provide food, shelter and the basics) safety needs social needs (e.g. teamwork) self-esteem (e.g. worker gets an award) self-fulfilment (self-fulfilment) (e.g. worker feels that he has achieved his potential) Non-Pay Methods of Motivation Method Description Comment Fear Fear of being told off or getting the sack makes workers work harder Won t work in the long term as workers may leave or lack motivation Job rotation Different jobs are performed by staff. Often used on production lines to stop boredom Job enlargement Workers given different tasks in addition to the work they already do Provides variety for the workers Job enrichment Workers given more responsibility and so have self-esteem Training is often given so workers can cope with new responsibilities Team working Workers placed in teams to perform tasks or take part in social events or team-building courses as most workers like the social contact and perform better Workers in groups may be given responsibility for what they do they are empowered (empowerment can also be used for individuals) Award schemes E.g. employer of the month award scheme Meets self-esteem needs of a worker Promotion Recognises achievement of worker (self-actualisation) Possibility of gaining promotion also encourages workers Leadership A good leader/manager motivates: most workers are more likely to be motivated by laissez-faire or democratic leadership than by autocratic leadership Working environment Good working conditions (e.g. good canteen) will make staff happy to work for a company Autocratic leadership the leader decides and workers obey! Laissez-faire leadership the leader decides objectives but workers are given responsibility for deciding how to achieve them Democratic leadership workers discuss plans with management and contribute to decision making
7 Pay Methods of Motivation Method of Pay Description Comment Time rate Set sum paid for each hour worked No reward for quality of work done Overtime pay A higher rate of pay to persuade workers to work extra hours Costs company more money but may be cheaper than hiring new staff Salary Worker is paid set sum for the year e.g. teacher Worker may not want to work hard as is not paid more for working longer hours Piece rate Sum of money paid for each item produced Workers may rush their work and produce poor quality Bonus Extra lump sum paid to worker for reaching a target Will not motivate if the target set is too high Profit-sharing A share of company profit is paid to workers Not all workers will deserve this! Fringe benefits (perks) Non-money rewards (e.g. gym membership) given to staff 100 of vouchers costs a company less than giving 100 take-home pay (no tax!) Training You need to know why training is important for the individual and for a business. Remember, the UK needs a highly trained workforce if it is to compete in a global economy. Training needs: workers need training for different reasons. Some might need to acquire technical, personal (e.g. how to communicate better), management or team work skills. New workers need induction training to introduce them to the organisation so that they can settle in (tour of the workplace, meeting new colleagues etc) Some need product knowledge training (e.g. to help them sell products to customers) Some workers starting a new career will need retraining A business will allow personal development of workers that might not be linked directly to work to boost their self-esteem (e.g. contribute to evening classes) On-the-job training Off-the-job training Definitions/methods Advantages Disadvantages Training carried out in the worker s place of work. Either someone with *Trainee gets individual training experience helps the trainee when he/she is doing the job or the trainee *Cheaper for company shadows another worker and so learns by watching. Coaching can be part of *Trainee is trained in the way of the on-the-job training: one worker (the coach) works with another (coachee) in firm the workplace and then makes suggestions as to how the coachee might *Worker might still be working whilst improve. training workers The trainee completes training away from where he/she normally works, either in a college or training centre, or in another part of the company s site (e.g. in a lecture room). Lectures, demonstrations, role-play and team building exercises can all be part of off-the-job training. *Experts may provide training *Workers often enjoy change of environment *Trainer cannot fully do own job if training *Trainee may not produce good quality work *Not suitable for groups of *Usually more expensive (e.g. fee for outside trainer) Staff appraisals: at least once a year, an employee (appraisee) will meet with his/her boss (appraiser). Last year s performance and targets will be reviewed and next year s targets (together with any training needed) are decided. This is particularly important where a worker is on performance-related pay. Investors in People (IIP) award is a quality assurance scheme for organisations who provide structured opportunities for staff development. Lifelong Learning: a government programme to encourage learning throughout a worker s life so that workers have the necessary skills and qualifications.
8 Employment Laws laws in place to protect workers against unfair treatment. Law Description THE EQUALITY ACT 2010 is now in place instead of all the laws with stars below!!!!!! *Equal Pay Act 1970 Women are paid same as men when they do the same work *Race Relations Act 1976 People cannot be treated differently (discrimination) on grounds of race, colour, nationality or ethnic origin *Sex Discrimination Act 1975 Stops discrimination on gender. Job adverts can only ask for a specific gender in exceptional circumstances (e.g. female PE teacher) *Employment Rights Act 1996 A written contract of work (or a statement of particulars) with job title, hours etc must be given to worker within 2 months of start *Disability Discrimination Act 1995 Employers cannot discriminate against the disabled when recruiting or in the workplace. Premises must provide access, unless it is physically impossible to do so (e.g. install a lift) Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 Employer is responsible for protecting worker from dangers in the workplace. The law covers training, safety equipment, breaks etc. All companies with more than 5 employees must have a written health and safety policy. Minimum Wage Act 1997 Minimum wage set for 16-17, and 22+ to avoid exploitation of workers. A few exceptions e.g. au pair Employment tribunals courts of law that deal with disputes between workers and the employer. Redundancy workers employment is ended because they are no longer needed by the firm (e.g. if bankrupt, using more machines, restructuring or cutting costs). The employer must pay redundancy money if the employee has worked for > 2 years. A firm may ask its workers if any want voluntary redundancy. Dismissal for gross misconduct (e.g. assaulting a customer!) or for incompetence (not doing the job properly) Trade Unions organisations that protect the interests of workers (e.g. National Union of Teachers) They have strength in numbers (they may represent a lot of workers in a business) and do two main jobs: Act as a pressure group i.e. they seek to influence the UK government (or sometimes the EU) to make laws in the interests of its members, the workers. Protect the interests of its members e.g. working conditions, hours, redundancy, unfair dismissal, safety, discrimination, pay etc. and give expert advice and support (e.g.in legal cases at tribunals). They also seek to secure good pay for their members by negotiating pay deals with a company. There are 3 main types of industrial action: Industrial action Strike Overtime ban Work to rule Description Workers withdraw their labour (refuse to work!). A strike can damage the employer, customers and the workers think why?! Workers only work the hours stated in their contracts and do not work overtime hours. Workers only do tasks that are included in their job descriptions and refuse to do anything else. Industrial relations is the term for dealings between unions and management Single union agreements all workers in a firm are in the same union which may make it easier for management to negotiate and may give workers more strength. ACAS Advisory Conciliation and Arbitration Service is an organisation which helps to settle disputes between workers and employers
9 Communication (within companies) Types of communication One-way: message is sent but the sender is not expecting a reply (e.g. a report) Two-way: person receiving the message can reply to the sender (e.g. phone call, conversation, ) Internal: between people who work in the same organisation (can be vertical between people on different layers of the hierarchy or horizontal between people at the same level in the organisation). External: between one person in an organisation and one person outside that organisation. Formal: official means of communication e.g. letter, report, appraisal documents Informal: not formal! E.g. conversation at break Methods of communication you need to think of advantages and disadvantages for each method Verbal (e.g. face-to-face conversation, lectures, telephone) Written (e.g. letters, reports, s) With images (e.g. poster, video clip) There can be barriers to communication factors that stop the receiver understanding fully the message from the sender: Timing message sent at wrong time (e.g. receiver not there!) Clarity if a message isn t clear, it might not be understood fully Attitudes the sender or receiver may not be in the right frame of mind for clear communication to work! Wrong method an urgent doesn t work if s aren t checked all the time! Technical hitch e.g. server is down so s cannot be sent or received ICT (Information and Communications Technology) includes applications on PCs (Word etc), internet, , mobile phone technology etc Advantages of ICT for companies Productivity is higher Quality of presentation is improved Info can be processed and then shared more easily Better communications within a firm and with customers and other businesses Workers can work at home. Meetings can be held by video-conferencing ( less travel is good for the environment!). Disadvantages of ICT for companies Training needed ICT equipment can be expensive Technical problems can occur Health and safety issues (repetitive strain injury if using keyboard too much!) Security problems if the firm s system is hacked into Working from home can be good for the worker (e.g. no commuting) but also has some disadvantages (no social contact in workplace). Can you think of other points?
10 Organisation Charts you should be able to understand why organisations have organisation charts?! Most are organised by function (department -e.g. Finance, Marketing, IT) They show a hierarchy with several layers. Higher layers have more authority and responsibilities (but they also are accountable will be blamed if something goes wrong in their area) There is a chain of command running down the layers. The number of subordinates for whom a manager has responsibility is called a span of control. Staff are delegated responsibility by their Line Managers. Organisation charts only show formal groups, not informal groups. Tall structures have lots of layers so lines of communication & responsibilities are clear and there are plenty of opportunities for promotion. Managers have narrow spans of control so do not have too many workers to look after. Flat structures have fewer layers so communication is quicker, more ideas pass from bottom to top and managers have wider spans of control and so have to trust their workers who feel empowered. De-layering (getting rid of layers) leads to flatter structures and can save money (fewer manager salaries have to be paid!)
Types of Business Ownership
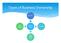 Types of Business Ownership Sole Trader Public Limited Company PLC Business types Partnerships Limited Liability Company LTD Sole traders A sole trader describes any business that is owned and controlled
Types of Business Ownership Sole Trader Public Limited Company PLC Business types Partnerships Limited Liability Company LTD Sole traders A sole trader describes any business that is owned and controlled
Why businesses exist?
 Why businesses exist? A business is an organisation that produces goods and services to satisfy people s wants and needs Why Exist? to make a profit, to provide income for owners, other reasons ethical,
Why businesses exist? A business is an organisation that produces goods and services to satisfy people s wants and needs Why Exist? to make a profit, to provide income for owners, other reasons ethical,
2. Recruitment and Selection
 1. Human Resources Human resource management (HRM) is the area of administrative focus dealing with an organization's employees. There are Four Main Job Roles in a business: Directors: Appointed to run
1. Human Resources Human resource management (HRM) is the area of administrative focus dealing with an organization's employees. There are Four Main Job Roles in a business: Directors: Appointed to run
Managing People and Finance. Outcome One. Pupil Notes. National 5
 Managing People and Finance Outcome One Pupil Notes National 5 The Human Resources Department is the department that deals with all aspects of employee relations on behalf of the owners. The HR department
Managing People and Finance Outcome One Pupil Notes National 5 The Human Resources Department is the department that deals with all aspects of employee relations on behalf of the owners. The HR department
GCSE Revision Questions- Unit 2 The Business Organisation. 1. Explain four reasons why businesses may want to expand/grow.
 GCSE Revision Questions- Unit 2 The Business Organisation 1. Explain four reasons why businesses may want to expand/grow. (4 To increase market share- the larger the market share the business has the more
GCSE Revision Questions- Unit 2 The Business Organisation 1. Explain four reasons why businesses may want to expand/grow. (4 To increase market share- the larger the market share the business has the more
Chapter 13: Motivation at work Motivation. Motivation theories
 Chapter 13: Motivation at work Motivation People work for a number of reasons. Most people work because they need to earn money to survive, while others work voluntarily for other reasons. Motivation is
Chapter 13: Motivation at work Motivation People work for a number of reasons. Most people work because they need to earn money to survive, while others work voluntarily for other reasons. Motivation is
GCSE BUSINESS (8132) Specification For teaching from September 2017 onwards For exams in 2019 onwards. Version August 2016
 GCSE BUSINESS (8132) Specification For teaching from September 2017 onwards For exams in 2019 onwards Version 1.0 19 August 2016 2 Specification at a glance This qualification is linear. Linear means that
GCSE BUSINESS (8132) Specification For teaching from September 2017 onwards For exams in 2019 onwards Version 1.0 19 August 2016 2 Specification at a glance This qualification is linear. Linear means that
Chapter 6. Motivating Workers
 Chapter 6 Motivating Workers Motivation is the reason why employees want to work hard and work effectively for the business. It is a feeling or drive that stimulates employees to work hard for achieving
Chapter 6 Motivating Workers Motivation is the reason why employees want to work hard and work effectively for the business. It is a feeling or drive that stimulates employees to work hard for achieving
This document consists of 17 printed pages.
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 Short Answered Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 Short Answered Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80
This document consists of 17 printed pages.
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/12 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/12 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an
1. What is a business and why do they exist? 2. Aims and Objectives
 1. What is a business and why do they exist? Why set up in business? Some reasons: Fed up with working for someone else, Quality of life, Buzz of success, Feel in control, financial reward, I could do
1. What is a business and why do they exist? Why set up in business? Some reasons: Fed up with working for someone else, Quality of life, Buzz of success, Feel in control, financial reward, I could do
IB Business Management Human Resource Management 2.4 Motivation Summary Notes
 www.businessmanagementib.com PAYMENT OR FINANCIAL REWARD SYSTEMS HOURLY WAGE RATE An hourly wage rate or time rate is set for the job perhaps by comparing with other firms or similar jobs. The wage level
www.businessmanagementib.com PAYMENT OR FINANCIAL REWARD SYSTEMS HOURLY WAGE RATE An hourly wage rate or time rate is set for the job perhaps by comparing with other firms or similar jobs. The wage level
Entrepreneurs and leaders. Chapter (December, 2018)
 Entrepreneurs and leaders Chapter 21 25 (December, 2018) BUSINESS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Distinction between aims and objectives aims: general ideas what business wants to achieve in long-term (i.e., be a
Entrepreneurs and leaders Chapter 21 25 (December, 2018) BUSINESS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Distinction between aims and objectives aims: general ideas what business wants to achieve in long-term (i.e., be a
UNIT 1 - STARTING A BUSINESS. AQA GCSE Business Studies
 UNIT 1 - STARTING A BUSINESS AQA GCSE Business Studies ENTREPRENEUR DEFINITION QUALITIES A person who has an idea for a Hard working new business and is prepared Willing to take advice QUALITIES Enthusiastic
UNIT 1 - STARTING A BUSINESS AQA GCSE Business Studies ENTREPRENEUR DEFINITION QUALITIES A person who has an idea for a Hard working new business and is prepared Willing to take advice QUALITIES Enthusiastic
Commerce and Trade. Difference between commerce and trade. TRADE is divided into:
 Commerce and Trade Difference between commerce and trade Commerce General term used to describe the sale and distribution of goods and services. Trade It is the commercial activity of buying and selling
Commerce and Trade Difference between commerce and trade Commerce General term used to describe the sale and distribution of goods and services. Trade It is the commercial activity of buying and selling
BUSINESS AND ENVIRONMENT
 Business Activity:- BUSINESS AND ENVIRONMENT Transformation of resources into goods and services to satisfy the needs of customers with profit as an aim. Resources / Factors of Production - Land - Labour
Business Activity:- BUSINESS AND ENVIRONMENT Transformation of resources into goods and services to satisfy the needs of customers with profit as an aim. Resources / Factors of Production - Land - Labour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/1 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/1 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
Business IGCSE Section 1 Study this set online at:
 Definition of need A need is a good or service essential for living. Definition of want A want is a good or service which people would like to have, but wh ich is not essential for living. Definition of
Definition of need A need is a good or service essential for living. Definition of want A want is a good or service which people would like to have, but wh ich is not essential for living. Definition of
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Business Management. Business Enterprise. Student Notes [INTERMEDIATE 1]
![NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Business Management. Business Enterprise. Student Notes [INTERMEDIATE 1] NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT. Business Management. Business Enterprise. Student Notes [INTERMEDIATE 1]](/thumbs/90/103064872.jpg) NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Business Management Business Enterprise Student Notes [INTERMEDIATE 1] The Scottish Qualifications Authority regularly reviews the arrangements for National Qualifications.
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS CURRICULUM SUPPORT Business Management Business Enterprise Student Notes [INTERMEDIATE 1] The Scottish Qualifications Authority regularly reviews the arrangements for National Qualifications.
Personalised Learning Checklist for GCSE Business Studies
 Personalised Learning Checklist for Business Studies The outline below shows the overview for the Business Studies course You can use this PLC in a number of ways: 1) Tick off the topics as they are covered
Personalised Learning Checklist for Business Studies The outline below shows the overview for the Business Studies course You can use this PLC in a number of ways: 1) Tick off the topics as they are covered
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1)
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1) BUSINESS STUDIES 0986/01 Paper 1 For examination from 2019 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Specimen
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1) BUSINESS STUDIES 0986/01 Paper 1 For examination from 2019 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Specimen
Centralisation and decentralisation
 Centralisation and decentralisation One of the issues that a business needs to address is where decision-making power is in the organisational structure. The key question is whether it is kept with senior
Centralisation and decentralisation One of the issues that a business needs to address is where decision-making power is in the organisational structure. The key question is whether it is kept with senior
Syllabus Snapshot. by Amazing Brains. Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Business
 Syllabus Snapshot by Amazing Brains Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Business 2 Specification at a Glance The table below summarises the structure of this GCSE course. Assessment Weightings Availability
Syllabus Snapshot by Amazing Brains Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Business 2 Specification at a Glance The table below summarises the structure of this GCSE course. Assessment Weightings Availability
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
BUSINESS STUDIES OPTION
 BUSINESS STUDIES OPTION BUSINESS STUDIES ALL WEEKS Research is vital for your success in this exam your exam context is an electrical retailer who also manufactures mobile phones, MP3 players, ipods etc.
BUSINESS STUDIES OPTION BUSINESS STUDIES ALL WEEKS Research is vital for your success in this exam your exam context is an electrical retailer who also manufactures mobile phones, MP3 players, ipods etc.
7115 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 100 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 100 This mark scheme is published as
Unit 1: Business Fundamentals Review
 Unit 1: Business Fundamentals Review For-Profit vs. Non-Profit/Not-for-Profit Organisations For-Profit Business: A for-profit business produces goods and/or services to satisfy the needs, wants, and demands
Unit 1: Business Fundamentals Review For-Profit vs. Non-Profit/Not-for-Profit Organisations For-Profit Business: A for-profit business produces goods and/or services to satisfy the needs, wants, and demands
 Why do people work? Affiliation It is the responsibility of management to make sure that their employees are motivated they do that via three main ways: 1. Financial Rewards 2. Non-Financial Rewards 3.
Why do people work? Affiliation It is the responsibility of management to make sure that their employees are motivated they do that via three main ways: 1. Financial Rewards 2. Non-Financial Rewards 3.
7115 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 100 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 100 This mark scheme is published
Year 11 Business Studies Unit A292 Revision guidance
 The examination is called Unit A292: Business and People. What will the exam be like? The examination will last for 1 hour. There will be a total of 60 marks. The marks will count for 25% of your overall
The examination is called Unit A292: Business and People. What will the exam be like? The examination will last for 1 hour. There will be a total of 60 marks. The marks will count for 25% of your overall
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 (Short Answer/Structured
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 (Short Answer/Structured
Recruitment & Selection
 Recruitment & Selection Revision Presentations 2004 The Recruitment Process Reasons to Recruit Staff Business is expanding due to: Increasing sales of existing products Developing new products Entering
Recruitment & Selection Revision Presentations 2004 The Recruitment Process Reasons to Recruit Staff Business is expanding due to: Increasing sales of existing products Developing new products Entering
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/1 Paper 1 Short Answer and Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BUSINESS 9609/1 Paper 1 Short Answer and Essay MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark
Edexcel GCSE Business Studies: Key Terms for Unit 1
 Unit 1: Introduction to Small Business Topic 1.1: Spotting a Business Opportunity 1.1.1 Businesses Edexcel GCSE Business Studies: Key Terms for Unit 1 Supplier Customer Consumer Markets A business which
Unit 1: Introduction to Small Business Topic 1.1: Spotting a Business Opportunity 1.1.1 Businesses Edexcel GCSE Business Studies: Key Terms for Unit 1 Supplier Customer Consumer Markets A business which
Golspie High School. Business Management National 4/5. Understanding Business 1 Role of business in society Pupil Notes
 Golspie High School Business Management National 4/5 Understanding Business 1 Role of business in society Pupil Notes Understanding Business Role of business in society National 5 how businesses satisfy
Golspie High School Business Management National 4/5 Understanding Business 1 Role of business in society Pupil Notes Understanding Business Role of business in society National 5 how businesses satisfy
7115 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/22
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/22
E: Human resource management in the UK health and fitness industry
 E: Human resource management in the UK health and fitness industry Lesson Objectives To be able to discuss human resource management in the UK Health and Fitness industry Starter What kinds of jobs do
E: Human resource management in the UK health and fitness industry Lesson Objectives To be able to discuss human resource management in the UK Health and Fitness industry Starter What kinds of jobs do
GCSE Business & Communication Systems
 GCSE Business & Communication Systems Unit 8 ICT Systems in Business Mark scheme 434 June 205 Version.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant
GCSE Business & Communication Systems Unit 8 ICT Systems in Business Mark scheme 434 June 205 Version.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant
Industrial Relations Conflicts Business Leaving Cert Quick Notes
 Industrial Relations Conflicts Business Leaving Cert Quick Notes Industrial Relations Conflicts Importance of good Employer-Employee Relationships 1. Employee morale is increased-willing to do better for
Industrial Relations Conflicts Business Leaving Cert Quick Notes Industrial Relations Conflicts Importance of good Employer-Employee Relationships 1. Employee morale is increased-willing to do better for
Introduction Role of a union The structure of an organisation
 Introduction UNISON is the UK s biggest public service trade union. It represents 1.3 million members who deliver essential services to the public. These are services that protect, enrich and change lives.
Introduction UNISON is the UK s biggest public service trade union. It represents 1.3 million members who deliver essential services to the public. These are services that protect, enrich and change lives.
[GBS21] FRIDAY 24 MAY, MORNING
![[GBS21] FRIDAY 24 MAY, MORNING [GBS21] FRIDAY 24 MAY, MORNING](/thumbs/88/114844148.jpg) General Certificate of Secondary Education 2013 Business Studies Unit 2 Business Development [GBS21] FRIDAY 24 MAY, MORNING MARK SCHEME 8154.01 F General Marking Instructions Introduction Mark schemes
General Certificate of Secondary Education 2013 Business Studies Unit 2 Business Development [GBS21] FRIDAY 24 MAY, MORNING MARK SCHEME 8154.01 F General Marking Instructions Introduction Mark schemes
This document consists of 16 printed pages.
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/11 Paper 1 Short Answer / Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/11 Paper 1 Short Answer / Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80
GCSE Business Studies
 GCSE Business Studies Carolyn Lawder Series Editor: Jayne de Courcy Contents Get the most out of your Instant Revision ebook v Ownership and control 1 Forms of business 5 Objectives and growth 9 Recruitment
GCSE Business Studies Carolyn Lawder Series Editor: Jayne de Courcy Contents Get the most out of your Instant Revision ebook v Ownership and control 1 Forms of business 5 Objectives and growth 9 Recruitment
7115 BUSINESS STUDIES
 www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark
www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 7115 BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark
Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing)
 Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing) Forms of Business Organization Sole Trader Partnership Limited Company Sole Trader What is your understanding
Ibrahim Sameer (MBA - Specialized in Finance, B.Com Specialized in Accounting & Marketing) Forms of Business Organization Sole Trader Partnership Limited Company Sole Trader What is your understanding
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 Short Answer / Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/12 Paper 1 Short Answer / Structured Response MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark:
Worksheet WBA1: Types of business
 Worksheet WBA1: Types of business Worksheet WBA1.2: Setting up a partnership Business Activity: WBA1 Types of business Scenario Liza Cream has proved to be a success in Elizabeth s town and she would like
Worksheet WBA1: Types of business Worksheet WBA1.2: Setting up a partnership Business Activity: WBA1 Types of business Scenario Liza Cream has proved to be a success in Elizabeth s town and she would like
IB Business Management Pre-Released Case Study May 2018 Key Terms: Activity II
 IB Business and Management: www.businessmanagementib.com IB BUSINESS MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY MAY 2018: KEY TERMS AND DEFINITIONS Below are the definitions for all key terms as they appear in the IB Business
IB Business and Management: www.businessmanagementib.com IB BUSINESS MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY MAY 2018: KEY TERMS AND DEFINITIONS Below are the definitions for all key terms as they appear in the IB Business
Golspie High School. Business Management Higher Understanding Business. 7 Stakeholders
 Golspie High School Business Management Higher Understanding Business 7 Stakeholders Learners should be aware of the differing objectives of groups of stakeholders in terms of: stakeholder conflict and
Golspie High School Business Management Higher Understanding Business 7 Stakeholders Learners should be aware of the differing objectives of groups of stakeholders in terms of: stakeholder conflict and
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/22 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum
2016 Business Management. National 5. Finalised Marking Instructions
 National Qualifications 2016 2016 Business Management National 5 Finalised ing Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 2016 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications
National Qualifications 2016 2016 Business Management National 5 Finalised ing Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 2016 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications
GCSE. Applied Business. Mark Scheme for June General Certificate of Secondary Education A241 Business in Action
 GCSE Applied Business General Certificate of Secondary Education A241 Business in Action Mark Scheme for June 2010 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
GCSE Applied Business General Certificate of Secondary Education A241 Business in Action Mark Scheme for June 2010 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding
Nat 5 Business Management Study Notes
 Nat 5 Business Management Study Notes 1.1 Role of Business Organisations Sectors of Economy Private - profit making, owned and controlled by private individuals Public - created by the government eg school,
Nat 5 Business Management Study Notes 1.1 Role of Business Organisations Sectors of Economy Private - profit making, owned and controlled by private individuals Public - created by the government eg school,
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Business 05834/05835/05836/05837/05878 Unit 1: The business environment
 Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Business 05834/05835/05836/05837/05878 Unit 1: The business environment Thursday 18 May 2017 Afternoon Time allowed: 2 hours You must have: a clean copy of the pre-release
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Business 05834/05835/05836/05837/05878 Unit 1: The business environment Thursday 18 May 2017 Afternoon Time allowed: 2 hours You must have: a clean copy of the pre-release
How to recruit trainees, graduates & apprentices
 How to recruit trainees, graduates & apprentices Advice featured in: how to recruit trainees, graduates & apprentices Business owners are currently facing recruitment challenges that have never been seen
How to recruit trainees, graduates & apprentices Advice featured in: how to recruit trainees, graduates & apprentices Business owners are currently facing recruitment challenges that have never been seen
Introduction to Business and Marketing Semester 1 Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: Introduction to Business and Marketing Semester 1 Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. wants are wants that are widely shared by many people. 2. Most companies that sell
Name: Class: Date: Introduction to Business and Marketing Semester 1 Exam Review Completion Complete each statement. 1. wants are wants that are widely shared by many people. 2. Most companies that sell
Manage staff redundancies
 Manage staff redundancies A redundancy plan will help you manage each stage of the redundancy process. It should show how you ll: avoid compulsory redundancies consult staff select staff for redundancy
Manage staff redundancies A redundancy plan will help you manage each stage of the redundancy process. It should show how you ll: avoid compulsory redundancies consult staff select staff for redundancy
Job description. Shortlisting
 Recruitment Vacancies in a business can arise for a number of reasons. These include: expansion, retirement of existing workers, workers leaving for a new job elsewhere, workers having promotion or temporary
Recruitment Vacancies in a business can arise for a number of reasons. These include: expansion, retirement of existing workers, workers leaving for a new job elsewhere, workers having promotion or temporary
CIMA E2 Course Notes. Chapter 1. Introduction to Organisations
 CIMA E2 Course Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Organisations by CIMA under the CIMA code of ethics. 6 1. Organisations Introduction An organisation is a social group of people that is organised and managed
CIMA E2 Course Notes Chapter 1 Introduction to Organisations by CIMA under the CIMA code of ethics. 6 1. Organisations Introduction An organisation is a social group of people that is organised and managed
BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS
 BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS MARKETING 1.1 Part 1 BUSINESS A business is an organisation whose purpose is to produce goods and services to meet the needs of customers. QUALITATIVE DATA
BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 1 KNOWLEDGE ORGANISERS MARKETING 1.1 Part 1 BUSINESS A business is an organisation whose purpose is to produce goods and services to meet the needs of customers. QUALITATIVE DATA
Introduction to Small Business
 Introduction to Small Business Revision Notes Topic 1.4 Making the start-up effective Customer focus A business can only survive if it has customers. It must have enough customers willing to pay a high
Introduction to Small Business Revision Notes Topic 1.4 Making the start-up effective Customer focus A business can only survive if it has customers. It must have enough customers willing to pay a high
GCSE Business Studies. Mark Scheme for June Unit A292: Business and People. General Certificate of Secondary Education
 GCSE Business Studies Unit A292: Business and People General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
GCSE Business Studies Unit A292: Business and People General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
Understand Employer Organisations
 What s included? Organisational Structures Types of organisational structures The Organisational Environment Organisational Structures Employer organisations vary from those that supply goods and services
What s included? Organisational Structures Types of organisational structures The Organisational Environment Organisational Structures Employer organisations vary from those that supply goods and services
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM
 GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM
 GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM
 GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
GUIDELINES FOR MAKING A CLAIM AND COMPLETING THE CLAIM FORM WHAT DOES THE EMPLOYMENT AND DISCRIMINATION TRIBUNAL DO? The Employment and Discrimination Tribunal (Tribunal) hears cases and makes decisions
FACTFILE: GCE BUSINESS STUDIES
 FACTFILE: GCE BUSINESS STUDIES AS1 MOTIVATION Motivation Learning outcomes Students should be able to: demonstrate and apply knowledge and understanding of the theories of Taylor, Maslow and Herzberg;
FACTFILE: GCE BUSINESS STUDIES AS1 MOTIVATION Motivation Learning outcomes Students should be able to: demonstrate and apply knowledge and understanding of the theories of Taylor, Maslow and Herzberg;
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT PROFESSIONAL ISSUES IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS PRACTICE
 BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT PROFESSIONAL ISSUES IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS PRACTICE Wednesday 28th September 2016 - Afternoon Answer any
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT PROFESSIONAL ISSUES IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS PRACTICE Wednesday 28th September 2016 - Afternoon Answer any
Employment, tax and national insurance
 Every person working in the UK must pay National Insurance (NI). Your NI number is used as a reference in your dealings with certain government departments throughout your working life in the UK. Your
Every person working in the UK must pay National Insurance (NI). Your NI number is used as a reference in your dealings with certain government departments throughout your working life in the UK. Your
Engage Education Foundation
 E Free Exam for 2010-16 VCE study design Engage Education Foundation Units 3 and 4 Business Management Practice Exam Solutions Stop! Don t look at these solutions until you have attempted the exam. Any
E Free Exam for 2010-16 VCE study design Engage Education Foundation Units 3 and 4 Business Management Practice Exam Solutions Stop! Don t look at these solutions until you have attempted the exam. Any
Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS
 W J E C B U S I N E S S S T U D I E S A L E V E L R E S O U R C E S. 2009 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2012 Page 1 Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS Specification requirement Changing working practices
W J E C B U S I N E S S S T U D I E S A L E V E L R E S O U R C E S. 2009 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2012 Page 1 Employer/employee Relations Trade Unions and ACAS Specification requirement Changing working practices
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/13 Paper 1 (Short Answer/ Structured
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/13 Paper 1 (Short Answer/ Structured
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 Chapter 9 Human Resource Management 2014 Q5 (A) Outline the stages in a recruitment and selection process, using the following headings: (i) Internal and External Recruitment (ii) Job Description and Person
Chapter 9 Human Resource Management 2014 Q5 (A) Outline the stages in a recruitment and selection process, using the following headings: (i) Internal and External Recruitment (ii) Job Description and Person
BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/11. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/11 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BUSINESS STUDIES 7115/11 Paper 1 Short Answer/Structured Response May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is
Motivation: Theory & practice
 Motivation: Theory & practice 2017-18 IMPORTANCE OF MOTIVATION Employees may lack motivation even if they are satisfied with Salary Conditions at work Short run: lack of motivation may lead to Reduced
Motivation: Theory & practice 2017-18 IMPORTANCE OF MOTIVATION Employees may lack motivation even if they are satisfied with Salary Conditions at work Short run: lack of motivation may lead to Reduced
b. Informal letter c. Formal letter d. Dialogue a. Descriptive Writing b. Narrative Writing
 Grade 9 Syllabus for First term 2017-2018 Subject English Topics 1. Re Reading Descriptions (Explaining Writer s Choice of Language) 2. Summary Writing 3. Response Writing: a. Article 4. Creative Writing:
Grade 9 Syllabus for First term 2017-2018 Subject English Topics 1. Re Reading Descriptions (Explaining Writer s Choice of Language) 2. Summary Writing 3. Response Writing: a. Article 4. Creative Writing:
GCSE Business. Revision list, key terms and formulas. Paper 1 Friday 24 th May (AM) Paper 2 Tuesday 4 th June (PM) Building the Business
 GCSE Business Revision list, key terms and formulas Paper 1 Friday 24 th May (AM) Investigating Small Business Paper 2 Tuesday 4 th June (PM) Building the Business Name: Exam Paper 1: Investigating Small
GCSE Business Revision list, key terms and formulas Paper 1 Friday 24 th May (AM) Investigating Small Business Paper 2 Tuesday 4 th June (PM) Building the Business Name: Exam Paper 1: Investigating Small
Chapter One: Economic Basics
 Chapter One: Economic Basics Formula for Profit: Profit (or loss) = Revenue - (Costs + Expenses) Supply and Demand: The Law of Demand states that the relationship between prices and consumers quantity
Chapter One: Economic Basics Formula for Profit: Profit (or loss) = Revenue - (Costs + Expenses) Supply and Demand: The Law of Demand states that the relationship between prices and consumers quantity
MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 100
 JUNE 2003 INTERNATIONAL GCSE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 100 SYLLABUS/COMPONENT: 0450/01 BUSINESS STUDIES Page 1 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper IGCSE EXAMINATIONS JUNE 2003 0450 1 1 (a) (i) Ownership by one
JUNE 2003 INTERNATIONAL GCSE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 100 SYLLABUS/COMPONENT: 0450/01 BUSINESS STUDIES Page 1 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper IGCSE EXAMINATIONS JUNE 2003 0450 1 1 (a) (i) Ownership by one
Notes. Business Management. Higher Still. Higher. HSN82400 Unit 2 Outcome 4. Contents. Human Resource Management 1
 Higher Business Management Unit 2 Outcome 4 Contents Human Resource Management 1 What is HRM Responsible for? 1 The Working Environment 1 Implications of the Changing HRM Environment 2 What does HRM Involve?
Higher Business Management Unit 2 Outcome 4 Contents Human Resource Management 1 What is HRM Responsible for? 1 The Working Environment 1 Implications of the Changing HRM Environment 2 What does HRM Involve?
Golspie High School. Business Management National 5/Higher. Understanding Business. 1 Role of business in society
 Golspie High School Business Management National 5/Higher 1 Role of business in society Role of business in society National 5 how businesses satisfy human needs and wants how business activity create
Golspie High School Business Management National 5/Higher 1 Role of business in society Role of business in society National 5 how businesses satisfy human needs and wants how business activity create
The nature of business activity in each sector and the impact of sectoral change on business activity
 SL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT Syllabus Outline Unit 1: Business organization and environment 1.1 Introduction to business management The role of businesses in combining human, physical and financial resources
SL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT Syllabus Outline Unit 1: Business organization and environment 1.1 Introduction to business management The role of businesses in combining human, physical and financial resources
For personal use only
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 1 November 2016 Corporate Governance Statement 30 June 2016 The Board of Directors is committed to improving and achieving good standards of corporate governance and has established corporate
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 1 November 2016 Corporate Governance Statement 30 June 2016 The Board of Directors is committed to improving and achieving good standards of corporate governance and has established corporate
Unit 2 People in Business Categorised Past Papers
 1 Unit 2 People in Business Categorised Past Papers 10 2 5 Fig. 2 shows the organisational structure of ABC, a business that manufactures toys. As the business has grown, the management has found it difficult
1 Unit 2 People in Business Categorised Past Papers 10 2 5 Fig. 2 shows the organisational structure of ABC, a business that manufactures toys. As the business has grown, the management has found it difficult
SUGGESTED ASSESSMENT TASKS
 SUGGESTED ASSESSMENT TASKS The nature of business Extended response questions In the HSC examination you will be asked a number of short and extended response questions based on the HSC course. A report
SUGGESTED ASSESSMENT TASKS The nature of business Extended response questions In the HSC examination you will be asked a number of short and extended response questions based on the HSC course. A report
BUSINESS. Teachers guide to OCR GCSE (9 1) Business specification GCSE (9 1) Teachers guide. J204 For first teaching in
 Qualification Accredited GCSE (9 1) Teachers guide BUSINESS J204 For first teaching in 2017 Teachers guide to OCR GCSE (9 1) Business specification Version 1 www.ocr.org.uk/business Contents Business 1:
Qualification Accredited GCSE (9 1) Teachers guide BUSINESS J204 For first teaching in 2017 Teachers guide to OCR GCSE (9 1) Business specification Version 1 www.ocr.org.uk/business Contents Business 1:
EQUALITY AND DIVERSITY POLICY
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES PP6 EQUALITY AND DIVERSITY POLICY Approved by Version Issue Date Review Date Contact Person Trust Board Sept 2003 Three 01/03/2009 01/03/2011 Head of Personnel Equal Opportunities:
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES PP6 EQUALITY AND DIVERSITY POLICY Approved by Version Issue Date Review Date Contact Person Trust Board Sept 2003 Three 01/03/2009 01/03/2011 Head of Personnel Equal Opportunities:
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE STATEMENT
 CORPORATE GOVERNANCE STATEMENT In fulfilling its obligations and responsibilities to its various stakeholders, the Board is a strong advocate of corporate governance. This statement outlines the principal
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE STATEMENT In fulfilling its obligations and responsibilities to its various stakeholders, the Board is a strong advocate of corporate governance. This statement outlines the principal
Human Resource Management
 Unit 26: Human Resource Management Unit code: K/601/1264 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit provides an introduction to the concepts and practices of human resource management within the United
Unit 26: Human Resource Management Unit code: K/601/1264 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit provides an introduction to the concepts and practices of human resource management within the United
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Business Studies Assessment Unit AS 2. assessing. Managing Business Resources [AT121]
![ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Business Studies Assessment Unit AS 2. assessing. Managing Business Resources [AT121] ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Business Studies Assessment Unit AS 2. assessing. Managing Business Resources [AT121]](/thumbs/87/96622619.jpg) ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2011 Business Studies Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Managing Business Resources [AT121] MONDAY 20 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME 7455.01 1 (a) With
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2011 Business Studies Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Managing Business Resources [AT121] MONDAY 20 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME 7455.01 1 (a) With
0450 BUSINESS STUDIES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0450 BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/21 Paper 2 (Case Study), maximum raw mark
Syllabus Snapshot. by Amazing Brains. Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Applied Business Single Award
 Syllabus Snapshot by Amazing Brains Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Applied Business Single Award 2 Specification at a Glance The table below summarises the structure of this GCSE course. Please note
Syllabus Snapshot by Amazing Brains Exam Body: CCEA Level: GCSE Subject: Applied Business Single Award 2 Specification at a Glance The table below summarises the structure of this GCSE course. Please note
GCSE EXAMINERS' REPORTS
 GCSE EXAMINERS' REPORTS BUSINESS STUDIES SUMMER 2016 Grade boundary information for this subject is available on the WJEC public website at: https://www.wjecservices.co.uk/marktoums/default.aspx?l=en Online
GCSE EXAMINERS' REPORTS BUSINESS STUDIES SUMMER 2016 Grade boundary information for this subject is available on the WJEC public website at: https://www.wjecservices.co.uk/marktoums/default.aspx?l=en Online
FORM 3 BUSINESS STUDIES HALF YEARLY EXAM TIME: 1h 30 min. Sec E. Sec E. Case 1
 FORM 3 BUSINESS STUDIES HALF YEARLY EXAM 2017-2018 TIME: 1h 30 min Name: Class: Index No. FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY SEC A Sec B Sec C Sec D Sec E Sec E Sec F TOTAL Case 1 Case 2 MARK 20 20 0 ANSWER ALL SECTIONS
FORM 3 BUSINESS STUDIES HALF YEARLY EXAM 2017-2018 TIME: 1h 30 min Name: Class: Index No. FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY SEC A Sec B Sec C Sec D Sec E Sec E Sec F TOTAL Case 1 Case 2 MARK 20 20 0 ANSWER ALL SECTIONS
Discover the Journey to Work
 Discover the Journey to Work This Vocational Profile is intended to help you to consider your situation and identify any particular requirements you have. It helps you to look at six important areas. Why
Discover the Journey to Work This Vocational Profile is intended to help you to consider your situation and identify any particular requirements you have. It helps you to look at six important areas. Why
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BUSINESS 8132/1 PAPER 1. Mark scheme. Specimen Assessment Material V1.1
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BUSINESS 8132/1 PAPER 1 Mark scheme Specimen Assessment Material V1.1 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions,
SPECIMEN MATERIAL GCSE BUSINESS 8132/1 PAPER 1 Mark scheme Specimen Assessment Material V1.1 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions,
Business Studies 2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION. Total marks 100. Section I Pages 2 8
 2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Business Studies Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams
2006 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Business Studies Total marks 100 Section I Pages 2 8 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams
Level 3 Cambridge Technicals in Business 05878
 Level 3 Cambridge Technicals in Business 05878 Unit 9: Human resources Sample Assessment Material Date Morning/Afternoon Time Allowed: 2 hours You may use: Calculator First Name Last Name Centre Number
Level 3 Cambridge Technicals in Business 05878 Unit 9: Human resources Sample Assessment Material Date Morning/Afternoon Time Allowed: 2 hours You may use: Calculator First Name Last Name Centre Number
Decision-making Exercises and Tools
 Decision-making Exercises and Tools This Section presents four decision making exercises for use by advisors to help groups decide which organisational structure is most appropriate for their needs. The
Decision-making Exercises and Tools This Section presents four decision making exercises for use by advisors to help groups decide which organisational structure is most appropriate for their needs. The
