Chapter 21: 1/28/2014. Demand. Changes in Demand. Supply
|
|
|
- Silas Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Demand Chapter 21: Demand and Supply Desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service Law of Demand Buy more at lower prices Buy less at higher prices Diminishing Marginal Utility satisfaction decreases as more of a product is consumed Changes in Demand Changes in numbers of consumers Changes in consumers tastes Changes in consumers expectations Changes in substitutes Changes in complements Demand Elasticity Elasticity measure of how a quantity supplied or demanded changes in response to a price change Elastic demand: change in price causes a large change in demand Substitutes are available Purchase can wait Inelastic demand change in price has little effect on demand No substitute Examples: milk, pepper, gas Supply Changes in Supply Quantity producers are willing to sell at all possible prices Law of Supply Produce more at higher prices Produce less at lower prices Supply is based on profit Changes in cost of resources Productivity Technology Changes in government policies Changes in taxes Number of suppliers 1
2 Supply Elasticity Elasticity measure of how a quantity supplied or demanded changes in response to a price change Supply elastic: quantity changes in response to change in price Supply inelasticity: quantity changes very little to change in price Example: Oil (cannot quickly dig new oil wells, but oil is always needed) Markets and Prices Surplus Shortage Equilibrium Price Price Ceiling Price Floor Minimum wage Supply/Demand Graphs See Smart Notebook Chapter 22: Business and Labor Section 1: Types of Businesses Business Organizations Sole Proprietorships Most common form of business organization Business Organizations Sole Proprietorships Partnerships Corporations Full pride in ownership Receives all profits Complete responsibility for all debts and damages Small businesses owned by one person Ex: drug stores, gas stations, hair salons Businesses in which two or more people share the responsibilities, costs, profits, and losses Ex: law firms, contractors Big business organization run by many people and charted by the state; a permanent organization Ex: Walmart, Lowes, Food Lion 2
3 Partnerships Partnerships Two kinds General All partners are equally responsible for business Limited At least one partner is not involved in daily running of the business Sharing ownership Raise more money Special talents from each partner Larger more efficient operations Complex structure Each owner is responsible for debts Corporations Corporations Must receive a charter from the state Must have stocks Board of Directors Easily raise money to expand Easily raise capital Expensive and complex Owners have little say in running the business More government regulation Organization of Corporations Common Stockholders: people who buy stock * provide capital as stockholders * elects directors Board of Directors: * makes corporation policies * votes dividends (profits paid to stockholders) * appoints president and other officers Corporate Officers: * corporate president, chief executive officer, treasure, vice presidents of divisions Department Heads: * Leaders of departments: advertising, finance, personnel, sales Other Business Organizations Nonprofit Organizations Provide goods and services without seeking to earn a profit charities Cooperatives Voluntary business to perform economic activities that benefit members electricity Employees: * work in all areas to contribute to the corporation s success 3
4 LABOR AND MANAGEMENT Section 2: The American Labor Force Rise of Labor Unions American businesses expanded Groups formed to improve wages and working conditions Organization of workers became labor unions Collective bargaining representatives of labor union meet with representatives of employer to reach an agreement METHODS USED BY LABOR Strike members walk off job if employers refuse to bargain Picketing prevent hiring of replacement workers by walking back and forth in front of building carrying signs Job Action workers stay on the job but work more slowly than usual METHODS USED BY EMPLOYERS Hire strikebreakers to replace workers on strike Blacklists list sent to other companies asking them not to hire anyone on the list (workers active in labor union) Lockouts closed the factory and locked out workers, preventing them from earning wages CLOSED AND OPEN SHOPS AFL verses CIO Closed shop workers cannot be hired until they first become members of the union Open shop anyone can be hired Union shop employer can hire any qualified worker, but workers must join union within a short time period to keep their job Agency shop worker cannot be forced to join the union, but they must still pay the union dues Right-to-work laws passed by many states; no one may be forced to join a union American Federation of Labor (AFL) Created by Samuel Gompers Formed by craft unions (carpenters, plumbers, bakers, etc) Weakened by factories of mass production Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) Led by Walter Reuther Formed by industries (steel, automobile, electrical, etc) Included unions that had African Americans, immigrants, and women as members 4
5 AFL verses CIO LABOR LAWS Workers confused about which union to join Rivalry between AFL and CIO lasted for years 1955 AFL and CIO merged to form AFL- CIO Largest American labor group 13 million workers (not all unions belong) National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act) Provides ways of settling disputes between labor unions and employers using representatives Labor-Management Relations Act (Taft-Hartley Act) Allows the president to order any union to delay a strike for 80 days Landrum-Griffin Act Prevents abuses by union officials; prohibits convicted criminals from serving as union officials for 5 years after being released from prison COLLECTIVE BARGAINING TODAY Mediation Labor union and employers cannot reach an agreement; call in an expert to examine the issue and recommend a solution Recommendations are suggestions and do not have to be followed Arbitration Expert called in to make a decision Decision is final and binding on both sides 5
Economics Unit 2. The United States Economic System
 Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
Economics Unit 2 The United States Economic System Demand Objective 2.01: Illustrate how supply and demand affects prices. What is Demand? Demand: The desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or
EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN. Looking at the Chapter. Date Period. Chapter. Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words.
 EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. of labor of labor What Determines Wages? for labor Demand for the labor produces for labor Practices
EMPLOYMENT AND WAGES BEFORE YOU BEGIN Looking at the Fill in the blank spaces with the missing words. of labor of labor What Determines Wages? for labor Demand for the labor produces for labor Practices
Types of Unions. Craft or Trade Unions. Industrial Unions. Workers who perform the same kind of work. All workers in the same industry
 The Labor Movement In 2003 there were approximately 291 million people in the United States. Slightly less than half or about 146 million belong to the civilian labor force. Excludes armed forces and prisoners.
The Labor Movement In 2003 there were approximately 291 million people in the United States. Slightly less than half or about 146 million belong to the civilian labor force. Excludes armed forces and prisoners.
Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power
 29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
29 Unions and Labor Market Monopoly Power Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. outline the essential history of the labor union movement; 2. discuss the current
COMMON LABOR TERMS. Arbitration A way of settling disputes by calling in an impartial third party whose decision is final and binding on both parties.
 COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
COMMON LABOR TERMS Agency Shop A union security clause providing that an employee in the bargaining unit refusing to join the union must pay a service fee to the union equal to union dues. Arbitration
SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP. Business that is organized by one single owner.
 BUSINESS & LABOR Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Non-Profit Organization Types of Workers Labor Unions Labor Unions (Organization) Collective Bargaining SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP Business that is
BUSINESS & LABOR Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Non-Profit Organization Types of Workers Labor Unions Labor Unions (Organization) Collective Bargaining SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP Business that is
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Chapter 9: Labor Section 3 Objectives 1. Describe why American workers have formed labor unions. 2. Summarize the history of the labor movement in the United States. 3. Analyze reasons for the decline
Chapter Eleven. Learning Objectives
 Chapter Eleven Enhancing Union Management Relations Learning Objectives 1. Explain how and why labor unions came into being. 2. Discuss the sources of unions negotiating power and trends in union membership.
Chapter Eleven Enhancing Union Management Relations Learning Objectives 1. Explain how and why labor unions came into being. 2. Discuss the sources of unions negotiating power and trends in union membership.
Labor, Employment and Wages. Chapter 9
 Labor, Employment and Wages Chapter 9 The Unit 3 Test Thursday for periods 2 and 4; Friday for period 7 Chapters 7-9 and 16 (100 points possible) 60 multiple choice and 4 short answer questions Approximately
Labor, Employment and Wages Chapter 9 The Unit 3 Test Thursday for periods 2 and 4; Friday for period 7 Chapters 7-9 and 16 (100 points possible) 60 multiple choice and 4 short answer questions Approximately
Managing Labor Relations
 11 Managing Labor Relations Copyright 2016 Cengag e Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. LEARNING OUTCOMES
11 Managing Labor Relations Copyright 2016 Cengag e Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price
 1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price 2. The two things needed for demand to exist are: willingness
1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price 2. The two things needed for demand to exist are: willingness
Principles of Economics
 Principles of Economics 2nd edition by Fred M Gottheil PowerPoint lides prepared by Ken Long Chapter 16 Wages and Employment: Monopsony & Labor Unions 2/26/2013 1 2 What is a Labor Union? An association
Principles of Economics 2nd edition by Fred M Gottheil PowerPoint lides prepared by Ken Long Chapter 16 Wages and Employment: Monopsony & Labor Unions 2/26/2013 1 2 What is a Labor Union? An association
Economics Unit 8. Labor and Unions
 Economics Unit 8 Labor and Unions These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School District, its trustees,
Economics Unit 8 Labor and Unions These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School District, its trustees,
Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.
 Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.1 499-500 Section B Other Basic Definitions 2 Chapter 2 Fundamental
Table of Contents Unit 1 Introduction to Economics TB Section TB Pages Chapter 1 What is Economics? 2 Section A 2 Parts of Economics 2 18.1 499-500 Section B Other Basic Definitions 2 Chapter 2 Fundamental
Unit 4 Labor and Careers
 Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
Unit 4 Labor and Careers - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1. Describe our Labor force 2. Learning Effect 3. Equilibrium wage 4. Labor pool 5. White Collar 6. Blue Collar 7. Skilled
Unit 2 Supply and Demand
 Unit 2 Supply and Demand -Study Guide- Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) Demand 2) Consumer 3) Supply 4) Producer 5) Subsidy 6) Give examples of goods that would have inelastic demand 7) Give
Unit 2 Supply and Demand -Study Guide- Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) Demand 2) Consumer 3) Supply 4) Producer 5) Subsidy 6) Give examples of goods that would have inelastic demand 7) Give
Learning Objectives. The Labor Relations Framework. The Labor Relations Framework. Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage
 Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
Handout 6-1 Human Resource Management Gaining a Competitive Advantage Chapter 14 Collective Bargaining and Labor Relations Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Describe
1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price
 1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price 2. Quantity demanded vs demand: quantity demanded is
1. Demand: willingness to buy a good or service and the ability to pay for it; how much of an item an individual is willing to purchase at each price 2. Quantity demanded vs demand: quantity demanded is
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1
 Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
Chapter 9: Labor Section 1 Key Terms labor force: all nonmilitary people who are employed or unemployed outsourcing: the practice of contracting with another company to do a specific job that would otherwise
Review Questions. Unions and Collective Bargaining. Choose the letter that represents the BEST response.
 192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
192 Ehrenberg/Smith Modern Labor Economics: Theory and Public Policy, Tenth Edition Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. Unions and Collective Bargaining 1. Which of the
Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining
 15 Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 15-1 Learning Objectives 1. Give a brief history of the American labor movement. 2. Discuss the main features of at least three major pieces of labor legislation.
15 Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining 15-1 Learning Objectives 1. Give a brief history of the American labor movement. 2. Discuss the main features of at least three major pieces of labor legislation.
EOCT Test Semester 2 final
 EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
EOCT Test Semester 2 final 1. The best definition of Economics is a. The study of how individuals spend their money b. The study of resources and government c. The study of the allocation of scarce resources
Unit 2 Supply and Demand
 Unit 2 Supply and Demand Microeconomics - analyzes the Small Unit economic behavior of Individuals, Households and Firms to understand their decision-making process. -America s Free Enterprise- An economy
Unit 2 Supply and Demand Microeconomics - analyzes the Small Unit economic behavior of Individuals, Households and Firms to understand their decision-making process. -America s Free Enterprise- An economy
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4
 SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
SUMMARY OF THE MODELS OF UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market
Economics Review. Part 2
 Economics Review Part 2 . law of demand demand quantity demanded The willingness and ability of buyers to The number of units of a good purchased at a specific price. purchase a good or service. law of
Economics Review Part 2 . law of demand demand quantity demanded The willingness and ability of buyers to The number of units of a good purchased at a specific price. purchase a good or service. law of
NAME DATE CLASS. In the first column, answer the questions based on what you know before you study. After this lesson, complete the last column.
 NAME DATE CLASS Lesson 1: How Businesses Are Organized ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how do people make economic choices? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a sole proprietorship?
NAME DATE CLASS Lesson 1: How Businesses Are Organized ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how do people make economic choices? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a sole proprietorship?
Economics Final Exam
 Economics Final Exam Study Guide- - - - Chapters 1,2,11 Study Guide Congratulations! You have been creating your very own study guide for the past three months from your outside reading of the text, your
Economics Final Exam Study Guide- - - - Chapters 1,2,11 Study Guide Congratulations! You have been creating your very own study guide for the past three months from your outside reading of the text, your
Econ: CH 7 Test Review Demand & Supply
 Econ: CH 7 Test Review Demand & Supply The Big Idea: 1. Scarcity is the basic economic problem that requires people to make choices about how to use limited resources 2. Buyers and sellers voluntarily
Econ: CH 7 Test Review Demand & Supply The Big Idea: 1. Scarcity is the basic economic problem that requires people to make choices about how to use limited resources 2. Buyers and sellers voluntarily
ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON THREE. Supply and Demand. CHAPTER 7 Supply and Demand. Lesson Three Supply and Demand 93
 ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON THREE Supply and Demand CHAPTER 7 Supply and Demand Lesson Three Supply and Demand 93 EXERCISES Matching (28 points) From the list below, select the term that matches each of the
ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON THREE Supply and Demand CHAPTER 7 Supply and Demand Lesson Three Supply and Demand 93 EXERCISES Matching (28 points) From the list below, select the term that matches each of the
DEMAND. Economics Unit 2 Just the Facts Handout
 DEMAND Economics Unit 2 Just the Facts Handout What is Demand? A market is a place where people buy and sell things. A market has two sides. There is a buying side and a selling side. The buying side of
DEMAND Economics Unit 2 Just the Facts Handout What is Demand? A market is a place where people buy and sell things. A market has two sides. There is a buying side and a selling side. The buying side of
Homework 2 Answer Key
 Econ 226 Principles of Microeconomics Fall, 24 Dr. Kathryn Wilson Due Date: Tuesday, September 28 th Homework 2 Answer Key 1. When the of movie admissions increases from $7 to $8, the demanded falls from
Econ 226 Principles of Microeconomics Fall, 24 Dr. Kathryn Wilson Due Date: Tuesday, September 28 th Homework 2 Answer Key 1. When the of movie admissions increases from $7 to $8, the demanded falls from
What Is a Labor Union? Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
 LABOR What Is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members. Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
LABOR What Is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members. Less than 14% of U.S. workers belong to a labor union.
Topic: What are some factors that affect the PRICE of goods and services? 1. If you believe an item is too expensive (not worth the money they are
 Topic: What are some factors that affect the PRICE of goods and services? 1. If you believe an item is too expensive (not worth the money they are asking for it) you don t have to buy it. All transactions
Topic: What are some factors that affect the PRICE of goods and services? 1. If you believe an item is too expensive (not worth the money they are asking for it) you don t have to buy it. All transactions
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 6: Elasticity Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
Chapter 5: Price Controls: Multiple Choice Questions 1. ANSWER: d. ceiling. 2. ANSWER: a. a shortage, which cannot be eliminated through market adjustment. 3. ANSWER: b. the equilibrium price is below
Chapter 4. Demand, Supply and Markets. These slides supplement the textbook, but should not replace reading the textbook
 Chapter 4 Demand, Supply and Markets These slides supplement the textbook, but should not replace reading the textbook 1 What is a market? A group of buyers and sellers with the potential to trade 2 What
Chapter 4 Demand, Supply and Markets These slides supplement the textbook, but should not replace reading the textbook 1 What is a market? A group of buyers and sellers with the potential to trade 2 What
GRAPHS WHAAAA???!!!???
 Mumford and Sons Supply and Demand GRAPHS WHAAAA???!!!??? Demand Combination of desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product Question: Demand Schedule Price Quantity How many movie DVDs Demanded would
Mumford and Sons Supply and Demand GRAPHS WHAAAA???!!!??? Demand Combination of desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product Question: Demand Schedule Price Quantity How many movie DVDs Demanded would
This is what we call a demand schedule. It is a table that shows how much consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
 Demand Market: an institution or mechanism, which brings together buyers ("demanders") and sellers ("suppliers") of particular goods and services. The remainder of this unit assumes a perfectly competitive
Demand Market: an institution or mechanism, which brings together buyers ("demanders") and sellers ("suppliers") of particular goods and services. The remainder of this unit assumes a perfectly competitive
Government Regulation
 Government Regulation What do you think is the market price for renting an apartment in Plainfield? What happens to the quantity of demand and supply after the price change? List four outcomes that would
Government Regulation What do you think is the market price for renting an apartment in Plainfield? What happens to the quantity of demand and supply after the price change? List four outcomes that would
Labor supply is the willingness and ability to work specific amounts of time at alternative wage rates in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
 Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Labor Unions Part I The role of a labor union is to ensure that the balance is not tipped in favor of the employer when employees do not receive wages and benefits commensurate with their contribution.
Supply and Demand. Objective 8.04
 Supply and Demand Objective 8.04 Supply and Demand Pages 258-259 259 copy bold terms and give a definition or description of each. Page 261 Copy the questions Worksheet A-2A 1. Surplus When the amount
Supply and Demand Objective 8.04 Supply and Demand Pages 258-259 259 copy bold terms and give a definition or description of each. Page 261 Copy the questions Worksheet A-2A 1. Surplus When the amount
7-1 L ECTURE LAUNCHER PAGES PAGES
 7-1 L ECTURE LAUNCHER Proctor & Gamble s introduced disposable diapers to the marketplace in 1961. At first parents only used Pampers for special occasions. Today, 95% of American parents use disposable
7-1 L ECTURE LAUNCHER Proctor & Gamble s introduced disposable diapers to the marketplace in 1961. At first parents only used Pampers for special occasions. Today, 95% of American parents use disposable
Labor Market Trends. Chapter 9 Section Main Menu
 Labor Market Trends How do economists define the labor force? What occupational trends exist in the U.S. economy? What is temporary employment? What are the current trends in wages and benefits? The United
Labor Market Trends How do economists define the labor force? What occupational trends exist in the U.S. economy? What is temporary employment? What are the current trends in wages and benefits? The United
WHAT IS DEMAND? CHAPTER 4.1
 Economics Unit 2 TEACHER WHAT IS DEMAND? CHAPTER 4.1 What is demand? THE DESIRE, ABILITY, AND WILLINGNESS TO BUY A PRODUCT. What is microeconomics? THE AREA OF ECONOMICS THAT DEALS WITH BEHAVIOR AND DECISION
Economics Unit 2 TEACHER WHAT IS DEMAND? CHAPTER 4.1 What is demand? THE DESIRE, ABILITY, AND WILLINGNESS TO BUY A PRODUCT. What is microeconomics? THE AREA OF ECONOMICS THAT DEALS WITH BEHAVIOR AND DECISION
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final day 2 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What determines how a change in prices will affect total revenue for a company?
Final day 2 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What determines how a change in prices will affect total revenue for a company?
Demand & Supply of Resources
 Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Resource Markets 1 Demand & Supply of Resources Resource demand Firms demand resources As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost To maximize profit Resource supply People supply resources To the
Chapter 14. Labor Law. Statutory Basis. Coming Together on Issues 1/12/2009. Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed.
 Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed. Bennett-Alexander Chapter 14 Labor Law Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Statutory Basis Employees shall have the right to selforganization,
Employment Law for Business, 6 th ed. Bennett-Alexander Chapter 14 Labor Law Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Statutory Basis Employees shall have the right to selforganization,
Price = The Interaction of Supply and Demand WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 17 THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 18
 Price = The Interaction of Supply and Demand WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 17 THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 18 Chapter 4: Section 1 Understanding Demand What Is Demand? Markets are where people come together to buy and sell
Price = The Interaction of Supply and Demand WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 17 THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 18 Chapter 4: Section 1 Understanding Demand What Is Demand? Markets are where people come together to buy and sell
Labor notes. Chapter 9
 Labor notes Chapter 9 I. The Civilian Labor Force: the total number of people 16 years and older who are either employed or ac@vely seeking work. It is nearly 156 million people. A. Classifica@on 1 1.
Labor notes Chapter 9 I. The Civilian Labor Force: the total number of people 16 years and older who are either employed or ac@vely seeking work. It is nearly 156 million people. A. Classifica@on 1 1.
Glossary of Labour Terms
 Glossary of Labour Terms ACCOMODATION: the process and implementation of changes to a job which enable a person with a disability to perform the job productively and/or to the environment in which the
Glossary of Labour Terms ACCOMODATION: the process and implementation of changes to a job which enable a person with a disability to perform the job productively and/or to the environment in which the
Domain 3 MICROECONOMICS
 Domain 3 MICROECONOMICS Georgia Standards of Excellence MICRO CONCEPT CLUSTER SSEMI1 Describe how households and businesses are interdependent and interact through flows of goods, services, resources,
Domain 3 MICROECONOMICS Georgia Standards of Excellence MICRO CONCEPT CLUSTER SSEMI1 Describe how households and businesses are interdependent and interact through flows of goods, services, resources,
L: What happens in a market?
 L: What happens in a market? REMINDER: TYPES OF ECONOMIES 1. Traditional 2. Command 3. Market 4. Mixed *all about who answers basic economic questions/controls factors of production (land/labor/capital/
L: What happens in a market? REMINDER: TYPES OF ECONOMIES 1. Traditional 2. Command 3. Market 4. Mixed *all about who answers basic economic questions/controls factors of production (land/labor/capital/
LESSON FIVE. Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor. CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing. CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution
 ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON FIVE Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution CHAPTER 12 The American Labor Force Lesson Four Competition
ECON (ENT) COURSE LESSON FIVE Finance, Marketing Distribution, and Labor CHAPTER 10 Financing and Producing CHAPTER 11 Marketing and Distribution CHAPTER 12 The American Labor Force Lesson Four Competition
Microeconomics. Use the graph below to answer question number 3
 More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
Microeconomics. Use the graph below to answer question number 3
 More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
More Tutorial at Microeconomics 1. Opportunity costs are the values of the: a. minimal budgets of families on welfare b. hidden charges passed on to consumers c. monetary costs of goods and services *
Supply and Demand Issues
 Supply and Demand Issues Supply and demand are the starting point of all economic analysis The essence of choice is being able to balance the two Touro University International 1 S U P P L Y The different
Supply and Demand Issues Supply and demand are the starting point of all economic analysis The essence of choice is being able to balance the two Touro University International 1 S U P P L Y The different
Supply and Demand. Worksheet A-2A 2014
 Supply and Demand Worksheet A-2A 2014 Worksheet A-2A 1. Surplus When the amount supplied exceeds the demand 2. Shortage When the amount demanded exceeds the supply 3. Utility The power to satisfy your
Supply and Demand Worksheet A-2A 2014 Worksheet A-2A 1. Surplus When the amount supplied exceeds the demand 2. Shortage When the amount demanded exceeds the supply 3. Utility The power to satisfy your
Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product.
 Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product. The Law of Demand states that the quantity demanded of a good will be greater at lower prices than will be demanded at higher prices. Thus
Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product. The Law of Demand states that the quantity demanded of a good will be greater at lower prices than will be demanded at higher prices. Thus
causing MARGINAL PRODUCT OF LABOR to fall beyond some point. iv. PRODUCT PRICE : Because this is a competitive market, the PRODUCT PRICE = MARKET
 WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
WAGE DETERMINATION I. A FOCUS ON LABOR a. The basic principles for labor also apply to other factors of production b. About 70% of all income in the U.S. flows to households in the form of wages and salaries.
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET OR TURN IT OVER [until told to do so]
![DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET OR TURN IT OVER [until told to do so] DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET OR TURN IT OVER [until told to do so]](/thumbs/81/84156510.jpg) (last, first): ON YOUR QUESTION BOOKLET: ON YOUR SCANTRON: 5 points DURING THE EXAM: MUST DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET OR TURN IT OVER [until told to do so] p. 1 v. 09 Figure SSD. The graph below describes
(last, first): ON YOUR QUESTION BOOKLET: ON YOUR SCANTRON: 5 points DURING THE EXAM: MUST DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET OR TURN IT OVER [until told to do so] p. 1 v. 09 Figure SSD. The graph below describes
AP Microeconomics Chapter 3 Outline
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students should learn: II. Markets III. Demand A. What demand is and how it can change. B. What supply is and how it can change. C. How supply and demand interact
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students should learn: II. Markets III. Demand A. What demand is and how it can change. B. What supply is and how it can change. C. How supply and demand interact
Labor Management Relationship
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Right Reserved The Legal & Regulatory Environment of Business 16e Labor Management Relationship Chapter 22 Reed Pagnattaro Cahoy
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Right Reserved The Legal & Regulatory Environment of Business 16e Labor Management Relationship Chapter 22 Reed Pagnattaro Cahoy
Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product.
 Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product. 1. You must have the desire for the product 2. You must be able to make a purchase 3. You must be willing to make a purchase 4. Purchases
Demand - the desire, ability, and willingness to buy a product. 1. You must have the desire for the product 2. You must be able to make a purchase 3. You must be willing to make a purchase 4. Purchases
Unit 1 Notes Fundamental Econ Concepts PART 1.1 THE BASICS OF ECONOMICS
 Economics Unit 1 Notes Fundamental Econ Concepts Name Date Per. PART 1.1 THE BASICS OF ECONOMICS What is economics? The study of how people try to satisfy seemingly unlimited and competing needs and wants
Economics Unit 1 Notes Fundamental Econ Concepts Name Date Per. PART 1.1 THE BASICS OF ECONOMICS What is economics? The study of how people try to satisfy seemingly unlimited and competing needs and wants
12) What determines the distribution of goods and services in a market economy?
 The Principles of Economics: EOCT Review 1) What is scarcity? How is scarcity different from shortages? 2) What are the three factors of production: 3) Define "labor" and give an example: 4) Define "land"
The Principles of Economics: EOCT Review 1) What is scarcity? How is scarcity different from shortages? 2) What are the three factors of production: 3) Define "labor" and give an example: 4) Define "land"
Macro Unit 1b. This is what we call a demand schedule. It is a table that shows how much consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
 Macro Unit 1b Demand Market: an institution or mechanism, which brings together buyers ("demanders") and sellers ("suppliers") of particular goods and services. Notice that the remainder of this unit assumes
Macro Unit 1b Demand Market: an institution or mechanism, which brings together buyers ("demanders") and sellers ("suppliers") of particular goods and services. Notice that the remainder of this unit assumes
Chapter 5: Supply Section 1
 Chapter 5: Supply Section 1 Key Terms supply: the amount of goods available law of supply: producers offer more of a good as its price increases and less as its price falls quantity supplied: the amount
Chapter 5: Supply Section 1 Key Terms supply: the amount of goods available law of supply: producers offer more of a good as its price increases and less as its price falls quantity supplied: the amount
4. A mixed economy combines two different economic types. Which two economic types are combined?
 1. Identify the type of economy featured in the United States. A. Command Economy B. Market Economy C. Mixed Economy D. Traditional Economy 2. Which is the strongest motivating force within a market economy
1. Identify the type of economy featured in the United States. A. Command Economy B. Market Economy C. Mixed Economy D. Traditional Economy 2. Which is the strongest motivating force within a market economy
Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics Fall Semester
 Duration: 50 minutes Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics 2016-17 Fall Semester ECON101 - Introduction to Economics I Quiz 2 Answer Key 16 December
Duration: 50 minutes Eastern Mediterranean University Faculty of Business and Economics Department of Economics 2016-17 Fall Semester ECON101 - Introduction to Economics I Quiz 2 Answer Key 16 December
Supply. Understanding Economics, Chapter 5
 Supply Understanding Economics, Chapter 5 What is Supply? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 What is Supply?! Supply the amount of a product a producer or seller would be willing to offer for sale at all possible prices
Supply Understanding Economics, Chapter 5 What is Supply? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 What is Supply?! Supply the amount of a product a producer or seller would be willing to offer for sale at all possible prices
BLUE COLLAR WORKERS Production and maintenance workers as contrasted to office and professional personnel.
 AGREEMENT, COLLECTIVE A contract (agreement and contract are used interchangeably) between one or more unions acting as a bargaining agent, and one or more employers, covering wages, hours,working conditions,
AGREEMENT, COLLECTIVE A contract (agreement and contract are used interchangeably) between one or more unions acting as a bargaining agent, and one or more employers, covering wages, hours,working conditions,
CLEP Microeconomics Practice Test
 Practice Test Time 90 Minutes 80 Questions For each of the questions below, choose the best answer from the choices given. 1. In economics, the opportunity cost of an item or entity is (A) the out-of-pocket
Practice Test Time 90 Minutes 80 Questions For each of the questions below, choose the best answer from the choices given. 1. In economics, the opportunity cost of an item or entity is (A) the out-of-pocket
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY
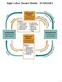 Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Unit 1: Introduction to Economics
 Microeconomics Syllabus AP Economics Textbooks & Resources: McConnell, Campbell & Stanley Brue. Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies. 16 th ed., New York, NY: McGraw Hill, 2005. Morton, John.
Microeconomics Syllabus AP Economics Textbooks & Resources: McConnell, Campbell & Stanley Brue. Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies. 16 th ed., New York, NY: McGraw Hill, 2005. Morton, John.
Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management
 Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management Unions generally believe that management exploits labor and is more interested in making a profit than in furthering the welfare of its employees Management
Differing Philosophies of Unions and Management Unions generally believe that management exploits labor and is more interested in making a profit than in furthering the welfare of its employees Management
Microeconomics Exam Notes
 Microeconomics Exam Notes Opportunity Cost What you give up to get it Production Possibility Frontier Maximum attainable combination of two products (Concept of Opportunity Cost). Main Decision Makers:
Microeconomics Exam Notes Opportunity Cost What you give up to get it Production Possibility Frontier Maximum attainable combination of two products (Concept of Opportunity Cost). Main Decision Makers:
Economics Challenge Online State Qualification Practice Test. 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from
 1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
1. An increase in aggregate demand would tend to result from A. an increase in tax rates. B. a decrease in consumer spending. C. a decrease in net export spending. D. an increase in business investment.
Demand/Supply Unit Essential Questions
 Demand/Supply Unit Essential Questions -What is the role of demand in free market capitalism? -How do changes in price influence quantity demanded? -What factors affect changes in demand that influence
Demand/Supply Unit Essential Questions -What is the role of demand in free market capitalism? -How do changes in price influence quantity demanded? -What factors affect changes in demand that influence
A Correlation of. To the Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies Table of Contents E.1... 3 E.2... 6 E.3... 7 E.4... 11 E.5... 15 E.6... 19 E.7... 24 E.8... 26 E.9... 28
A Correlation of To the 2018 Mississippi College- and Career- Readiness Standards Social Studies Table of Contents E.1... 3 E.2... 6 E.3... 7 E.4... 11 E.5... 15 E.6... 19 E.7... 24 E.8... 26 E.9... 28
Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions
 Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions Section One True/False Questions 1. Trade unions were developed in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. 2. The National Labor Union can be credited with the implementation
Chapter 11 Work with Labor Unions Section One True/False Questions 1. Trade unions were developed in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. 2. The National Labor Union can be credited with the implementation
Economics Final Review Economics 12
 Economics Final Review 2017 Economics 12 Chapter 1 What is Economics? Economics Study of how people try to satisfy their needs and wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources.(scarcity)
Economics Final Review 2017 Economics 12 Chapter 1 What is Economics? Economics Study of how people try to satisfy their needs and wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources.(scarcity)
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By
 Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
Eco402 - Microeconomics Glossary By Break-even point : the point at which price equals the minimum of average total cost. Externalities : the spillover effects of production or consumption for which no
CHAPTER 8. Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations
 CHAPTER 8 Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations Chapter Summary: Key Concepts Human Resource: The People Behind the People Human resource management The function of attracting,
CHAPTER 8 Human Resource Management: From Recruitment to Labor Relations Chapter Summary: Key Concepts Human Resource: The People Behind the People Human resource management The function of attracting,
Demand and Supply. Economics
 Demand and Supply Economics How Do Demand and Price Interact? Demand = What we are willing and able to buy at various prices. Demand is expressed in terms of a time frame: eg. per day or per week. Quantity
Demand and Supply Economics How Do Demand and Price Interact? Demand = What we are willing and able to buy at various prices. Demand is expressed in terms of a time frame: eg. per day or per week. Quantity
Economics Final Review Economics 12
 Economics Final Review 2018 Economics 12 Chapter 1 What is Economics? Economics Study of how people try to satisfy their needs and wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources.(scarcity)
Economics Final Review 2018 Economics 12 Chapter 1 What is Economics? Economics Study of how people try to satisfy their needs and wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources.(scarcity)
Unit 5: The Resource Market. (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market)
 Unit 5: The Resource Market (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 Perfect Competition Resource Markets Monopsony Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: Many small firms are hiring workers
Unit 5: The Resource Market (aka: The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 Perfect Competition Resource Markets Monopsony Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: Many small firms are hiring workers
Section 1 Understanding Supply
 Chapter 5 - Supply Section 1 Understanding Supply Supply the amount of goods available Law of Supply Tendency for suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price. Law of Supply Price As price increases
Chapter 5 - Supply Section 1 Understanding Supply Supply the amount of goods available Law of Supply Tendency for suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price. Law of Supply Price As price increases
ECON 101 KONG Midterm 2 CMP Review Session. Presented by Benji Huang
 ECON 101 KONG Midterm 2 CMP Review Session Presented by Benji Huang Chapter 5 Efficiency and Equity Benefit, Cost, Surplus Consumers (1) A consumer benefits from the consumption of a product this benefit
ECON 101 KONG Midterm 2 CMP Review Session Presented by Benji Huang Chapter 5 Efficiency and Equity Benefit, Cost, Surplus Consumers (1) A consumer benefits from the consumption of a product this benefit
Unit 5: The Resource Market. (The Factor Market or Input Market)
 Unit 5: The Resource Market (The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 2 The Circular Flow Model The Product Market- The place where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households. The Resource
Unit 5: The Resource Market (The Factor Market or Input Market) 1 2 The Circular Flow Model The Product Market- The place where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households. The Resource
Chapter 5:1 Understanding Supply
 Chapter 5:1 Understanding Supply Necessity versus Luxury Objectives: We will explain the law of supply. We will interpret a supply schedule and a supply graph. We will examine the relationship between
Chapter 5:1 Understanding Supply Necessity versus Luxury Objectives: We will explain the law of supply. We will interpret a supply schedule and a supply graph. We will examine the relationship between
Name: Date: Period: Test: Supply and Demand
 Name: Date: Period: Test: Supply and Demand 1. What is the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at various possible prices during a given period? d. quantity supplied.
Name: Date: Period: Test: Supply and Demand 1. What is the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at various possible prices during a given period? d. quantity supplied.
Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA
 Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that customers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? If you
Economics Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit Two DA If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that customers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? If you
Goal 8 The United States Economic System
 Practice Test of Goal 8 The United States Economic System Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review state Goal 8 content, as well as practice for the Civics
Practice Test of Goal 8 The United States Economic System Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review state Goal 8 content, as well as practice for the Civics
Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century?
 Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century? It s 1911 and the worst industrial accident in American history has just occurred. 136 woman workers,
Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century? It s 1911 and the worst industrial accident in American history has just occurred. 136 woman workers,
5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market
 Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Chapter 13 Unions and the Labor Market
 Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Chapter 13 nions and the Labor Market ummary Chapter 12 introduced an objective framework for analyzing the earnings differences that accompany gender, race, and ethnicity. This framework was then used
Test Yourself: Labor
 Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Test Yourself: Labor If the workers took a notion they could stop all speeding trains; every ship upon the ocean they could tie with mighty chains. Every wheel in the creation every mine and every mill;
Unit II: Supply, Demand, and Consumer Choice Problem Set #2
 1. /20 4. /30 2. /20 5. /10 3. /10 6. /10 Total: /100 Name: Team: Unit II: Supply, Demand, and Consumer Choice Problem Set #2 1. EXPLAIN an experience or example that shows the real world application of
1. /20 4. /30 2. /20 5. /10 3. /10 6. /10 Total: /100 Name: Team: Unit II: Supply, Demand, and Consumer Choice Problem Set #2 1. EXPLAIN an experience or example that shows the real world application of
To produce more beach balls, you must give up ever increasing quantities of ice cream cones.
 Unit 01: Basic Concepts (Macro/Micro) Scarcity The Economic Problem: Unlimited wants, limited economic resources Factors of Production: -Land -Labor -Capital -Entrepreneurship Big 3 Questions: -What to
Unit 01: Basic Concepts (Macro/Micro) Scarcity The Economic Problem: Unlimited wants, limited economic resources Factors of Production: -Land -Labor -Capital -Entrepreneurship Big 3 Questions: -What to
What is Demand for Labor? Demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages.
 What is Demand for Labor? Demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages. What is the Law of Demand for Labor? There is an INVERSE relationship
What is Demand for Labor? Demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages. What is the Law of Demand for Labor? There is an INVERSE relationship
