LABOUR ECONOMICS 2 February th. lecture Overview over lecture
|
|
|
- Georgina Cameron
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LABOUR ECONOMICS 2 February th. lecture Overview over lecture Introduction to course Topic: Labour supply Motivation Optimisation: One worker/consumer 1. Optimisation problem 2. 1st. order conditions 3. Illustration 4. Comparative statics (slutsky-equations) 5. Reservation wage 6. Tax-effects READING LIST: F & V, Ch. 1 and Ch. 2. NEXT TIME: Labour supply continued
2 LABOUR ECONOMICS 6 February th. lecture Overview over lecture Topic: Labour supply *Motivation Optimisation: One worker/consumer 1. *Optimisation problem 2. *1st. order conditions 3. Illustration 4. Comparative statics (slutsky-equations) 5. Reservation wage 6. Tax-effects READING LIST: F & V, Ch. 1 and Ch. 2. NEXT TIME: Labour supply continued
3 LABOUR ECONOMICS 9 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture Topic: Labour supply 1. *Motivation 2. Optimisation: One worker/consumer a) *Optimisation problem b) *1st. order conditions c) *Illustration d) *Comparative statics (slutsky-equations) e) *Reservation wage f) Tax-effects 3. The family as supplier of working hours 4. Home production 5. Leisure as a production factor (Becker). 6. Intertemporal allocation of working time Reading list: F & V, Ch. 1 and Ch. 2. Next time: Labour supply continued
4 LABOUR ECONOMICS 13 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture Topic: Labour supply 1. * Motivation 2. * Optimisation: One worker/consumer 3. * The family as supplier of working hours 4. * Home production 5. * Leisure as a production factor (Becker). 6. Intertemporal allocation of working time 7. Estimation techniques Main problem: Sample selection Explained "Solved" 8. Empirical assessment: Nina s article - estimation procedure (modification of variables) - results Reading list: F & V, Ch. 1 and Ch. 2. Next time: Labour supply continued
5 LABOUR ECONOMICS 16 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture Topic: Labour supply 1. * Motivation 2. * Optimisation: One worker/consumer 3. * The family as supplier of working hours 4. * Home production 5. * Leisure as a production factor (Becker). 6. * Intertemporal allocation of working time 7. Estimation techniques Main problem: Sample selection * Explained "Solved" 8. Empirical assessment: Nina s article - estimation procedure (modification of variables) - results Reading list: F & V, Nina s article Next time: Labour demand
6 LABOUR ECONOMICS 20 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. Topic: Labour supply Empirical assessment: Nina s article - * estimation procedure (modification of variables) - results B. TOPIC: Labour demand 1. Motivation 2. Concepts - Elasticity of substitution - Marshall-Hicks equations 3. Production functions - Cobb-Douglas -CES - Multifactor production functions 4. The elasticity of complementarity 5. Some results Reading list: Nina s article, Hamermesh Next time: Labour demand, Johnson
7 LABOUR ECONOMICS 23 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Labour demand 1. * Motivation 2. * Concepts - Elasticity of substitution - Marshall-Hicks equations 3. Production functions - * Cobb-Douglas -CES - Multifactor production functions 4. The elasticity of complementarity 5. Some results B. TOPIC: Labour demand, skill bias - the concept - demand and supply factors (formula) - empirical evidence - explanations Reading list: Hamermesh, Johnson Next time: Human Capital
8 LABOUR ECONOMICS 27 February th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Labour demand, skill bias - the concept - demand and supply factors (formula) - empirical evidence - explanations B.TOPIC: WAGES AND INCOME Main theme: Reward to education 1. Human capital theory (investment calculation) - Formal education - Experience and on the job training 2. Human capital - empirical investigations - Mincer s schooling equation - Ability and school attendance 3. Other topics - Signaling - Discrimination Reading list: Johnson, F. & V. Next time: Human Capital
9 LABOUR ECONOMICS 1 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: WAGES AND INCOME A. Theory, Main theme: Reward to education 1. *Human capital theory (investment calculation) - Formal education - Experience and on the job training 2. Human capital - empirical investigations - Mincer s schooling equation - Ability and school attendance 3. Other topics - Signaling - Discrimination B. Empirical evidence: Nordic countries - return to education - return to experience Reading list: F. & V., Becker, Nordic paper Next time: Human Capital
10 LABOUR ECONOMICS 5 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture I. TOPIC: WAGES AND INCOME A. Theory, Main theme: Reward to education 1. *Human capital theory (investment calculation) 2. * Human capital - empirical investigations 3. Other topics - * Signaling - Discrimination B. Empirical evidence: Nordic countries - return to education - return to experience II. TOPIC: trade unions 1. The monopoly trade union. Characteristics: - The trade union determines the wage rate - The firm determines employment a. determination of optimum b. comparative statics 2. Efficient contracts, Negotiation on: Wage rate and employment Reading: F & V, Ch. 5, Becker, Niels Westergaard Nielsen et. al., Oswald. NEXT TIME: Trade Unions, Oswald + Moene
11 LABOUR ECONOMICS 8 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: trade unions 1. The monopoly trade union. Characteristics: - The trade union determines the wage rate - The firm determines employment a. determination of optimum b. comparative statics 2. Efficient contracts Negotiation on: Wage rate and employment 3. Right to manage model Reading: Oswald. NEXT TIME: Trade Unions, Oswald + Moene
12 LABOUR ECONOMICS 12 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. Unions, GENERAL 1. * The monopoly trade union. Characteristics: - The trade union determines the wage rate - The firm determines employment a. determination of optimum b. comparative statics 2. Efficient contracts Negotiation on: Wage rate and employment 3. Right to manage model B. NORDIC: Solidaristic bargaining? 1. The Rehn-Meidner model 2. A putty clay growth model interpretation Reading: Oswald + Moene & Wallerstein NEXT TIME: Temporary Layoffs (Feldstein)
13 LABOUR ECONOMICS 15 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Temporary layoffs (contract theory) - definition - states: one good and one bad - model -FOC - interpretation (policy) READING: Feldstein NEXT TIME: Search theory (Mortensen)
14 LABOUR ECONOMICS 19 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Search 1. Basic model: Transition from unemployment to employment - assumptions - the Bellman equation (optimality expression) - the reservation wage - expected spell length - comparative statics 2. Extensions of basic model - non-stationarity - search on the job - learning process about the job READING: Mortensen NEXT TIME: Search theory (Mortensen)
15 LABOUR ECONOMICS 22 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Search 1. Basic model: Transition from unemployment to employment - * assumptions - * the Bellman equation (optimality expression) - * the reservation wage - expected spell length - comparative statics 2. Extensions of basic model - non-stationarity - search on the job - learning process about the job READING: Mortensen NEXT TIME: Search theory (Mortensen)
16 LABOUR ECONOMICS 26 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Search 1. Basic model: Transition from unemployment to employment - * assumptions - * the Bellman equation (optimality expression) - * the reservation wage - *expected spell length - *comparative statics 2. Extensions of basic model - non-stationarity - search on the job - learning process about the job READING: Mortensen Next time: Lancaster
17 LABOUR ECONOMICS 29 March th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Search - Theory 1. Basic model: Transition from unemployment to employment 2. Extensions of basic model - * non-stationarity - * search on the job - learning process about the job B. TOPIC: Search - empirical analysis of spell lengths 1. The hazard function 2. Sampling scheme and likelihood 3. The Weibull distribution 4. Unobserved heterogeneity Reading: Mortensen, Lancaster Next time: Lancaster, Pissarides
18 LABOUR ECONOMICS 2 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Search - empirical analysis of spell lengths 1. * The hazard function 2. Sampling scheme and likelihood 3. The Weibull distribution 4. Unobserved heterogeneity B.TOPIC: Search theory - macro model Analysis of flows on the labour market Sectors: Trade sector (new) Production sector 1. Deduction of basic model - Job creation - Wage curve - uv-curve 2. Interpretation of basic model Reading: Lancaster, Pissarides Next time: Pissarides
19 LABOUR ECONOMICS 5 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Search theory - macro model Analysis of flows on the labour market Sectors: Trade sector (new) Production sector 1. Deduction of basic model - Job creation - Wage curve - uv-curve 2. Interpretation of basic model Reading: Pissarides Next time: Pissarides
20 LABOUR ECONOMICS 16 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Search theory - macro model Analysis of flows on the labour market Sectors: Trade sector (new) Production sector 1. Deduction of basic model - * uv-curve - Job creation - Wage curve 2. Interpretation of basic model Reading: Pissarides Next time: Layard et al.
21 LABOUR ECONOMICS 19 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Search theory - macro model A couple of graphs illustrating the relevance of the analysis B, TOPIC: Efficiency wages 1. Deduction of the Solow condition 2. The 5 reasons for efficiency wage effects 4. The Macro level 5. Evidence: i. Inter-industry wage differentials? ii. Absenteeism? Reading: Layard et al., Edin & Zetterberg Next time: Blanchard
22 LABOUR ECONOMICS 23 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Efficiency wages 1. * Deduction of the Solow condition 2. * The 5 reasons for efficiency wage effects 4. The Macro level 5. Evidence: i. Inter-industry wage differentials? ii. Absenteeism? B. TOPIC: Persistence, Unemployment Channels for persistence: 1. Capital accumulation 2. Wage negotiations a. Hysteresis models b. Unemployment and wage negotiations (u up, w down) c. Duration effects (long term unemployed not efficient job seekers) Reading: Layard et al., Edin & Zetterberg, Blanchard Next time: Employment protection (Bertola)
23 LABOUR ECONOMICS 26 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Persistence, Unemployment Channels for persistence: 1. Capital accumulation 2. Wage negotiations a. Hysteresis models b. Unemployment and wage negotiations (u up, w down) c. Duration effects (long term unemployed not efficient job seekers) B. TOPIC: Employment protection - Theory 1. Motivation 2. Model: two-state model incl. firing costs 3. Consequences - employment fluctuation - employment level 4. Wage formation 5. Ideosyncratic shocks and wage compression 6. Concluding remarks Reading: Blanchard, Bertola Next time: Employment protection (Bertola)
24 LABOUR ECONOMICS 30 April th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Employment protection - Theory 1. *Motivation 2. Model: two-state model incl. firing costs 3. Consequences - employment fluctuation ideosyncratic shocks business cycle - employment level 4. Wage formation 5. Ideosyncratic shocks and wage compression 6. Concluding remarks Reading: Bertola Next time: Employment protection (Bertola + Albæk et al.)
25 LABOUR ECONOMICS 3 May th. Lecture, Overview over lecture TOPIC: Employment protection - Theory 1. *Motivation 2. * Model: two-state model incl. firing costs 3. * Consequences - employment fluctuation ideosyncratic shocks business cycle - employment level 4. Wage formation 5. Ideosyncratic shocks and wage compression 6. Concluding remarks Reading: Bertola+ Albæk et al. Next time: Nickell
26 LABOUR ECONOMICS 10 May th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Employment protection - Theory - some graphs and conclusion B. TOPIC: Employment protection - Empirical evidence Displaced workers in Belgium and Denmark: - Subsequent unemployment and employment - Subsequent wages and income C. TOPIC: Unemployment and Labor Market Regidities Impact on unemployment level (and LF participation) - short-run - long-run Differences in institutions - direct rigidities - treatment of unemployed - wage determination and unions - labour taxes Reading: Bertola+ Albæk et al. + Nickell Next time: Borjas
27 LABOUR ECONOMICS 17 May th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: Unemployment and Labor Market Regidities Impact on unemployment level (and LF participation) - short-run - long-run Differences in institutions - direct rigidities - treatment of unemployed - wage determination and unions - labour taxes B. TOPIC: Immigration The Roy model Reading: Nickell + Maddala Next time: Borjas
28 LABOUR ECONOMICS 21 May th. Lecture, Overview over lecture A. TOPIC: The Roy model (continued) B. TOPIC: Immigration - skills of immigrants: theory - impact on host country economy (income and wages) - skills of immigrants: empirics Reading: Maddala + Borjas Next time: Borjas + OECD
Technical Appendix. Resolution of the canonical RBC Model. Master EPP, 2010
 Technical Appendix Resolution of the canonical RBC Model Master EPP, 2010 Questions What are the causes of macroeconomic fluctuations? To what extent optimal intertemporal behavior of households in a walrasssian
Technical Appendix Resolution of the canonical RBC Model Master EPP, 2010 Questions What are the causes of macroeconomic fluctuations? To what extent optimal intertemporal behavior of households in a walrasssian
Review Questions. The Own-Wage Elasticity of Labor Demand. Choose the letter that represents the BEST response.
 Chapter 4 Labor Demand Elasticities 49 Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. The Own-Wage Elasticity of Labor Demand 1. If the wage paid to automobile workers goes up by
Chapter 4 Labor Demand Elasticities 49 Review Questions Choose the letter that represents the BEST response. The Own-Wage Elasticity of Labor Demand 1. If the wage paid to automobile workers goes up by
Lecture 1 : The Diamond- Mortensen- Pissarides framework
 Lecture 1 : The Diamond- Mortensen- Pissarides framework ARNAUD CHÉRON (GAINS-TEPP, UNIVERSITY OF LE MANS) Attribution Non commercial - No Derivative Work : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/2.0/fr/
Lecture 1 : The Diamond- Mortensen- Pissarides framework ARNAUD CHÉRON (GAINS-TEPP, UNIVERSITY OF LE MANS) Attribution Non commercial - No Derivative Work : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/2.0/fr/
5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market
 Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Summary - Chapter 5 Labour Markets and Unemployment 5.2 Demand and Supply in the Labour Market 5.2.1 Labour Supply and the Consumption Leisure Trade-off - The consumption leisure trade-off is the fundamental
Econ 440: Economics of Labor Markets
 Evangelia Chalioti, Econ 440: Economics of Labor Markets 1 Econ 440: Economics of Labor Markets University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Economics Fall 2012 Tuesday & Thursday, 9:30-10:50
Evangelia Chalioti, Econ 440: Economics of Labor Markets 1 Econ 440: Economics of Labor Markets University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Economics Fall 2012 Tuesday & Thursday, 9:30-10:50
Restrictions in labor supply estimation: Is the MaCurdy critique correct?
 I ELSEVIER Economics Letters 47 (1995) 229-235 economics letters Restrictions in labor supply estimation: Is the MaCurdy critique correct? Soren Blomquist Department of Economics, Uppsa/a University, Box
I ELSEVIER Economics Letters 47 (1995) 229-235 economics letters Restrictions in labor supply estimation: Is the MaCurdy critique correct? Soren Blomquist Department of Economics, Uppsa/a University, Box
On-the-Job Search and Wage Dispersion: New Evidence from Time Use Data
 On-the-Job Search and Wage Dispersion: New Evidence from Time Use Data Andreas Mueller 1 Stockholm University First Draft: May 15, 2009 This Draft: August 11, 2010 Abstract This paper provides new evidence
On-the-Job Search and Wage Dispersion: New Evidence from Time Use Data Andreas Mueller 1 Stockholm University First Draft: May 15, 2009 This Draft: August 11, 2010 Abstract This paper provides new evidence
Contents. Introduction
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction to Economics... 1 Meaning of Economics... 1 Definitions of Economics... 2 Introduction to Economic Theory... 3 The Structure of Theories... 5 Importance of
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction to Economics... 1 Meaning of Economics... 1 Definitions of Economics... 2 Introduction to Economic Theory... 3 The Structure of Theories... 5 Importance of
Productivity, Output, and Employment. Chapter 3. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada
 Productivity, Output, and Employment Chapter 3 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada This Chapter We will now shift from economic measurement to economic analysis In this lecture we will discuss: Production
Productivity, Output, and Employment Chapter 3 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Canada This Chapter We will now shift from economic measurement to economic analysis In this lecture we will discuss: Production
Growth, Labor and Inequality
 Growth, Labor and Inequality in the Global Economy Titel Lecturer CP W/P Term min/max Schwerpunktmodul Foundations in Growth, Labor and Inequality in the Global Economy A: Growth, Inequality and Structural
Growth, Labor and Inequality in the Global Economy Titel Lecturer CP W/P Term min/max Schwerpunktmodul Foundations in Growth, Labor and Inequality in the Global Economy A: Growth, Inequality and Structural
IV Monopsony and Oligopsony
 IV Monopsony and Oligopsony Bruno Van der Linden May 11, 2005 Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique and Department of Economics, Université Catholique de Louvain 1 Introduction Monopsony in the traditional
IV Monopsony and Oligopsony Bruno Van der Linden May 11, 2005 Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique and Department of Economics, Université Catholique de Louvain 1 Introduction Monopsony in the traditional
Estimation of a DSGE Model Lawrence J. Christiano
 Estimation of a DSGE Model Lawrence J. Christiano Based on: Christiano, Eichenbaum, Evans, `Nominal Rigidities and the Dynamic Effects of a Shocks to Monetary Policy, JPE, 2005 Altig, Christiano, Eichenbaum
Estimation of a DSGE Model Lawrence J. Christiano Based on: Christiano, Eichenbaum, Evans, `Nominal Rigidities and the Dynamic Effects of a Shocks to Monetary Policy, JPE, 2005 Altig, Christiano, Eichenbaum
Understanding unemployment
 Chapter 3 Understanding unemployment 0 Why you should be interested in unemployment Unemployment is closely related to the emergence of capitalism But mass unemployment as a permanent phenomenon only appeared
Chapter 3 Understanding unemployment 0 Why you should be interested in unemployment Unemployment is closely related to the emergence of capitalism But mass unemployment as a permanent phenomenon only appeared
Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Economics 3070 Summer Introduction and Review: Chapters 1, 2 (plus corresponding study guide)
 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Economics 3070 Summer 1994 Professor M.J. Greenwood Office: Econ 208 Office Hours: 3:40-4:20 daily and by appointment A Term COURSE OUTLINE Part I. Text: Robert H. Frank,
Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Economics 3070 Summer 1994 Professor M.J. Greenwood Office: Econ 208 Office Hours: 3:40-4:20 daily and by appointment A Term COURSE OUTLINE Part I. Text: Robert H. Frank,
Mc Graw Hill Education
 Labor Economics Seventh Edition George J. Borjas Harvard University Mc Graw Hill Education Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Labor Economics 1 1-1 An Economic Story of the Labor Market 2 1-2 The Actors
Labor Economics Seventh Edition George J. Borjas Harvard University Mc Graw Hill Education Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Labor Economics 1 1-1 An Economic Story of the Labor Market 2 1-2 The Actors
Proposal 1: Require that each medical student complete one rotation at a qualified geriatric care facility.
 Instructions The questions below are arranged into two groups according to the estimated time and difficulty. Group A are relatively short, should require 5 10 minute each, and are worth 25 points each.
Instructions The questions below are arranged into two groups according to the estimated time and difficulty. Group A are relatively short, should require 5 10 minute each, and are worth 25 points each.
Mathematical Economics dr Wioletta Nowak. Lecture 3-4
 Mathematical Economics dr Wioletta Nowak Lecture 3-4 Properties of the Demand Function: the Marginal Demand, the Price, Income and Cross Price Elasticity of Demand, Classification of Goods: Normal Goods,
Mathematical Economics dr Wioletta Nowak Lecture 3-4 Properties of the Demand Function: the Marginal Demand, the Price, Income and Cross Price Elasticity of Demand, Classification of Goods: Normal Goods,
CONTENTS PART ONE -BASIC CONCEPTSCONCEPTS
 CONTENTS PART ONE -BASIC CONCEPTSCONCEPTS Chapter-1 The Scope and Nature of Economics Introduction; The subject matter of Economics; Robbins Definition of Economics; Superiority of Robbins Definition;
CONTENTS PART ONE -BASIC CONCEPTSCONCEPTS Chapter-1 The Scope and Nature of Economics Introduction; The subject matter of Economics; Robbins Definition of Economics; Superiority of Robbins Definition;
BACHELOR OF BUSINESS. Sample FINAL EXAMINATION
 BACHELOR OF BUSINESS Sample FINAL EXAMINATION Subject Code : ECO201 Subject Name : LABOUR ECONOMICS This examination carries 50% of the total assessment for this subject. Examiner(s) Moderator(s) Joyce
BACHELOR OF BUSINESS Sample FINAL EXAMINATION Subject Code : ECO201 Subject Name : LABOUR ECONOMICS This examination carries 50% of the total assessment for this subject. Examiner(s) Moderator(s) Joyce
This guide compares the new GCSE Economics qualification to the previous economics qualifications.
 Summary of changes This guide compares the new GCSE Economics qualification to the previous economics qualifications. Overview of changes Structure There is now only one GCSE Economics qualification available.
Summary of changes This guide compares the new GCSE Economics qualification to the previous economics qualifications. Overview of changes Structure There is now only one GCSE Economics qualification available.
Chapter 11 Market-Clearing Models of the Business Cycle 108
 Problems 1. The response to a temporary change in government spending in the real business cycle model is the same as the response to such a disturbance in the monetary intertemporal model, as the two
Problems 1. The response to a temporary change in government spending in the real business cycle model is the same as the response to such a disturbance in the monetary intertemporal model, as the two
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9708 ECONOMICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9708 ECONOMICS 9708/42 Paper 4 (Data Response and Essays Supplement),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9708 ECONOMICS 9708/42 Paper 4 (Data Response and Essays Supplement),
Research on Theoretical Analysis of Unemployment Rates Interim Report. Summary
 Research on Theoretical Analysis of Rates Interim Report Summary Authors Hirokazu Fujii Research Director, The Japan Institute for Labour Policy and Training (JILPT) (Chapters 1 and 2) Hiroshi Amari Assistant
Research on Theoretical Analysis of Rates Interim Report Summary Authors Hirokazu Fujii Research Director, The Japan Institute for Labour Policy and Training (JILPT) (Chapters 1 and 2) Hiroshi Amari Assistant
Econ 792. Labor Economics. Lecture 6
 Econ 792 Labor Economics Lecture 6 1 "Although it is obvious that people acquire useful skills and knowledge, it is not obvious that these skills and knowledge are a form of capital, that this capital
Econ 792 Labor Economics Lecture 6 1 "Although it is obvious that people acquire useful skills and knowledge, it is not obvious that these skills and knowledge are a form of capital, that this capital
Wage Dispersion, Markets and Institutions: The Effects of the Boom in Education on the Wage Structure
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2181 Wage Dispersion, Markets and Institutions: The Effects of the Boom in Education on the Wage Structure Erling Barth Claudio Lucifora June 2006 Forschungsinstitut
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2181 Wage Dispersion, Markets and Institutions: The Effects of the Boom in Education on the Wage Structure Erling Barth Claudio Lucifora June 2006 Forschungsinstitut
Interpreting Europe and US labor markets differences : the specificity of human capital investments
 Interpreting Europe and US labor markets differences : the specificity of human capital investments Etienne WASMER First version: February 27, 2002 REVISED: April 2004 Abstract: We show a fundamental property
Interpreting Europe and US labor markets differences : the specificity of human capital investments Etienne WASMER First version: February 27, 2002 REVISED: April 2004 Abstract: We show a fundamental property
OPTIMAL LABOR CONTRACTS, IMPERFECT COMPETITION AND UNDREMPLOYMENT EQUILIBRIA: A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYSIS. Working Paper No. 2060
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL LABOR CONTRACTS, IMPERFECT COMPETITION AND UNDREMPLOYMENT EQUILIBRIA: A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYSIS Russell Cooper Working Paper No. 2060 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL LABOR CONTRACTS, IMPERFECT COMPETITION AND UNDREMPLOYMENT EQUILIBRIA: A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYSIS Russell Cooper Working Paper No. 2060 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH
Preface. Chapter 1 Basic Tools Used in Understanding Microeconomics. 1.1 Economic Models
 Preface Chapter 1 Basic Tools Used in Understanding Microeconomics 1.1 Economic Models 1.1.1 Positive and Normative Analysis 1.1.2 The Market Economy Model 1.1.3 Types of Economic Problems 1.2 Mathematics
Preface Chapter 1 Basic Tools Used in Understanding Microeconomics 1.1 Economic Models 1.1.1 Positive and Normative Analysis 1.1.2 The Market Economy Model 1.1.3 Types of Economic Problems 1.2 Mathematics
«ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ», Τόμος 53, Τεύχος 3ο, (2003) / «SPOUDAI», Vol. 53, No 3, (2003), University of Piraeus, pp ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ / SPOUDAI
 «ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ», Τόμος 53, Τεύχος 3ο, (2003) / «SPOUDAI», Vol. 53, No 3, (2003), University of Piraeus, pp. 3-13 ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ / SPOUDAI ΕΤΟΣ 2003 ΙΟΥΛΙΟΣ-ΣΕΠΤΕΜΒΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΜΟΣ 53 ΤΕΥΧ. 3 YEAR 2003 JULY-SEPTEMBER VOL.
«ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ», Τόμος 53, Τεύχος 3ο, (2003) / «SPOUDAI», Vol. 53, No 3, (2003), University of Piraeus, pp. 3-13 ΣΠΟΥΔΑΙ / SPOUDAI ΕΤΟΣ 2003 ΙΟΥΛΙΟΣ-ΣΕΠΤΕΜΒΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΜΟΣ 53 ΤΕΥΧ. 3 YEAR 2003 JULY-SEPTEMBER VOL.
Mobility Costs and Localization of Labor Markets
 Mobility Costs and Localization of Labor Markets Andreas Kopp a,1 a Hamburg Institute of International Economics Neuer Jungfernstieg 21 20347 Hamburg Germany Abstract The paper seeks an explanation for
Mobility Costs and Localization of Labor Markets Andreas Kopp a,1 a Hamburg Institute of International Economics Neuer Jungfernstieg 21 20347 Hamburg Germany Abstract The paper seeks an explanation for
SRI LANKA INSTITUTE OF ADVANCED TECHNOLOGICAL EDUCATION. (Established in the Ministry of Higher Education, vide in Act No.
 Q1. Select the correct answer and Under line it (Total 16 Marks) 01. Economics is a science. Because, (a) Evidences are observable (b) Findings are measurable (c) Findings can be analyzed i a and b correct
Q1. Select the correct answer and Under line it (Total 16 Marks) 01. Economics is a science. Because, (a) Evidences are observable (b) Findings are measurable (c) Findings can be analyzed i a and b correct
Wage Floors and Unemployment: A Two-Sector Analysis
 Cornell University ILR School DigitalCommons@ILR Articles and Chapters ILR Collection 1997 Wage Floors and Unemployment: A Two-Sector Analysis Gary S. Fields Cornell University, gsf2@cornell.edu Follow
Cornell University ILR School DigitalCommons@ILR Articles and Chapters ILR Collection 1997 Wage Floors and Unemployment: A Two-Sector Analysis Gary S. Fields Cornell University, gsf2@cornell.edu Follow
UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE
 15 UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: the data used to measure the amount of unemployment. how unemployment can result from minimum-wage
15 UNEMPLOYMENT AND ITS NATURAL RATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: the data used to measure the amount of unemployment. how unemployment can result from minimum-wage
FINALTERM EXAMINATION FALL 2006
 FINALTERM EXAMINATION FALL 2006 QUESTION NO: 1 (MARKS: 1) - PLEASE CHOOSE ONE Compared to the equilibrium price and quantity sold in a competitive market, a monopolist Will charge a price and sell a quantity.
FINALTERM EXAMINATION FALL 2006 QUESTION NO: 1 (MARKS: 1) - PLEASE CHOOSE ONE Compared to the equilibrium price and quantity sold in a competitive market, a monopolist Will charge a price and sell a quantity.
Macroeconomic policy and South African unemployment: developing a three segment macroeconomic model
 REDI3x3 Working paper 6 May 2015 Macroeconomic policy and South African unemployment: developing a three segment macroeconomic model Philippe Burger and Frederick Fourie Abstract A recent survey of South
REDI3x3 Working paper 6 May 2015 Macroeconomic policy and South African unemployment: developing a three segment macroeconomic model Philippe Burger and Frederick Fourie Abstract A recent survey of South
3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets
 3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets Labour market equilibrium: The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour is determined by those who want to be employed
3.5.3 Wage determination in competitive and non-competitive markets Labour market equilibrium: The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour is determined by those who want to be employed
Why and how wage curves differ: Evidence by union status for the United States, Great Britain and Norway
 Why and how wage curves differ: Evidence by union status for the United States, Great Britain and Norway Erling Barth, 1 Bernt Bratsberg, 2 Robin A. Naylor 3 and Oddbjørn Raaum 4 February 2002 Abstract
Why and how wage curves differ: Evidence by union status for the United States, Great Britain and Norway Erling Barth, 1 Bernt Bratsberg, 2 Robin A. Naylor 3 and Oddbjørn Raaum 4 February 2002 Abstract
Chapter 12. Incentive Pay. Introduction
 Chapter 12 12-1 Incentive Pay 12-2 Introduction The chapter analyses how and why different methods of compensation arise in the labour market and how they affect worker productivity and firm profitablility.
Chapter 12 12-1 Incentive Pay 12-2 Introduction The chapter analyses how and why different methods of compensation arise in the labour market and how they affect worker productivity and firm profitablility.
What policy to reduce labour market segmentation?
 What policy to reduce labour market segmentation? Clémence Berson Banque de France Nicolas Ferrari* French Treasury Department The ideas presented in this document reflect the personal opinion of their
What policy to reduce labour market segmentation? Clémence Berson Banque de France Nicolas Ferrari* French Treasury Department The ideas presented in this document reflect the personal opinion of their
Labour Demand. 1 The Simple Model of Labour Demand. 2 De nitions (refreshing your memory) 3 Labour Demand in the Short Run.
 Labour Demand Lecture notes Dan Anderberg Royal Holloway College January 2003 1 The Simple Model of Labour Demand Question: Where does labour demand come from? ² Labour demand is a DERIVED DEMAND: rms
Labour Demand Lecture notes Dan Anderberg Royal Holloway College January 2003 1 The Simple Model of Labour Demand Question: Where does labour demand come from? ² Labour demand is a DERIVED DEMAND: rms
THE DYNAMICS OF SKILL MISMATCHES IN THE DUTCH LABOR MARKET
 THE DYNAMICS OF SKILL MISMATCHES IN THE DUTCH LABOR MARKET Wim Groot* Department of Health Sciences, Maastricht University and "Scholar" Research Centre for Education and Labor Market Department of Economics,
THE DYNAMICS OF SKILL MISMATCHES IN THE DUTCH LABOR MARKET Wim Groot* Department of Health Sciences, Maastricht University and "Scholar" Research Centre for Education and Labor Market Department of Economics,
Human Resources Development, Skills and Labour Mobility Union approaches fostering the acquisition and use of skills
 Human Resources Development, Skills and Labour Mobility Union approaches fostering the acquisition and use of skills OECD-ILO-G20-OECD Knowledge Sharing Workshop, Paris 7-8 October 2015 Presentation by
Human Resources Development, Skills and Labour Mobility Union approaches fostering the acquisition and use of skills OECD-ILO-G20-OECD Knowledge Sharing Workshop, Paris 7-8 October 2015 Presentation by
Cobb-Douglas Production Function: The Case of a Converging Economy
 UDC: 519.866;330.11;330.35 JEL Classification: O47, E23 Keywords: potential output, production function, labor share, total factor productivity Cobb-Douglas Production Function: The Case of a Converging
UDC: 519.866;330.11;330.35 JEL Classification: O47, E23 Keywords: potential output, production function, labor share, total factor productivity Cobb-Douglas Production Function: The Case of a Converging
Labor Economics. Evidence on Efficiency Wages. Sébastien Roux. ENSAE-Labor Economics. April 4th 2014
 Labor Economics Evidence on Efficiency Wages Sébastien Roux ENSAE-Labor Economics April 4th 2014 Sébastien Roux (ENSAE) Labor Economics April 4th 2014 1 / 36 Introduction Efficiency wages Explain why wages
Labor Economics Evidence on Efficiency Wages Sébastien Roux ENSAE-Labor Economics April 4th 2014 Sébastien Roux (ENSAE) Labor Economics April 4th 2014 1 / 36 Introduction Efficiency wages Explain why wages
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
OCR Economics A-level Microeconomics Topic 4: Labour Market 4.1 Wage determination Notes The main influences on demand and supply in labour markets The labour market is a factor market. The supply of labour
Macro CH 23 sample test question
 Class: Date: Macro CH 23 sample test question Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Potential GDP is defined as a. the level of GDP created by
Class: Date: Macro CH 23 sample test question Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Potential GDP is defined as a. the level of GDP created by
Employer Size or Skill-Group Size Effect on Wages?
 Employer Size or Skill-Group Size Effect on Wages? by Erling Barth and Harald Dale-Olsen Institute for Social Research 2002-02 Paper to be presented at DILEED 2002 in Wellington, New Zealand. Thanks to
Employer Size or Skill-Group Size Effect on Wages? by Erling Barth and Harald Dale-Olsen Institute for Social Research 2002-02 Paper to be presented at DILEED 2002 in Wellington, New Zealand. Thanks to
6. The law of diminishing marginal returns begins to take effect at labor input level: a. 0 b. X c. Y d. Z
 Chapter 5 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The short run is defined as a period in which: a. the firm cannot change its output level b. all inputs are variable but technology is fixed c. input prices are fixed
Chapter 5 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The short run is defined as a period in which: a. the firm cannot change its output level b. all inputs are variable but technology is fixed c. input prices are fixed
Curriculum Standard One: The students will understand common economic terms and concepts and economic reasoning.
 Curriculum Standard One: The students will understand common economic terms and concepts and economic reasoning. *1. The students will examine the causal relationship between scarcity and the need for
Curriculum Standard One: The students will understand common economic terms and concepts and economic reasoning. *1. The students will examine the causal relationship between scarcity and the need for
A TEXTBOOK OF MICROECONOMIC THEORY. Pankaj Tandon. Boston University
 A TEXTBOOK OF MICROECONOMIC THEORY Pankaj Tandon Boston University DSAGE j TEXTS www.sagepu bl ications.com London Orth) SlntEpore WMhlnQton DC * Borton CONTENTS Preface About the Author xiii xv Chapter
A TEXTBOOK OF MICROECONOMIC THEORY Pankaj Tandon Boston University DSAGE j TEXTS www.sagepu bl ications.com London Orth) SlntEpore WMhlnQton DC * Borton CONTENTS Preface About the Author xiii xv Chapter
The Reallocation of Agricultural Labour across Sectors:
 No. 45, May 2013 Barbara Tocco, Alastair Bailey and Sophia Davidova The Reallocation of Agricultural Labour across Sectors: An Empirical Strategy for Micro Data ABSTRACT This paper presents an empirical
No. 45, May 2013 Barbara Tocco, Alastair Bailey and Sophia Davidova The Reallocation of Agricultural Labour across Sectors: An Empirical Strategy for Micro Data ABSTRACT This paper presents an empirical
LONG RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY
 The Digital Economist Lecture 8 -- Aggregate Supply and Price Level Determination LONG RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY Aggregate Supply represents the ability of an economy to produce goods and services. In the Long
The Digital Economist Lecture 8 -- Aggregate Supply and Price Level Determination LONG RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY Aggregate Supply represents the ability of an economy to produce goods and services. In the Long
PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS IN CONTEXT CONTENTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS IN CONTEXT By Neva Goodwin, Jonathan M. Harris, Julie A. Nelson, Brian Roach, and Mariano Torras CONTENTS PART ONE The Context for Economic Analysis Chapter 0: Economics and Well-Being
PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS IN CONTEXT By Neva Goodwin, Jonathan M. Harris, Julie A. Nelson, Brian Roach, and Mariano Torras CONTENTS PART ONE The Context for Economic Analysis Chapter 0: Economics and Well-Being
PROBLEM SET 1. Defining Economics, Methodology, and Models
 ADVANCED MICROECONOMIC ANALYSIS (ECON 5502) Spring 2014 Professor F. S. Lee PROBLEM SET 1 Defining Economics, Methodology, and Models 1. How is Lionel Robbin s definition of neoclassical economics reflected
ADVANCED MICROECONOMIC ANALYSIS (ECON 5502) Spring 2014 Professor F. S. Lee PROBLEM SET 1 Defining Economics, Methodology, and Models 1. How is Lionel Robbin s definition of neoclassical economics reflected
Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8
 Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.What determines the shape of the aggregate demand (AD) curve and what factors shift the entire curve. 2.What determines the shape
Lecture 10: THE AD-AS MODEL Reference: Chapter 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1.What determines the shape of the aggregate demand (AD) curve and what factors shift the entire curve. 2.What determines the shape
EMPLOYMENT FLEXIBILITY INDEX 2018 EU and OECD countries
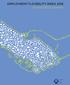 EMPLOYMENT FLEXIBILITY INDEX 2018 EU and OECD countries Lithuanian Free Market Institute, 2017 The index was prepared by the Lithuanian Free Market Institute in cooperation with the Institute of Market
EMPLOYMENT FLEXIBILITY INDEX 2018 EU and OECD countries Lithuanian Free Market Institute, 2017 The index was prepared by the Lithuanian Free Market Institute in cooperation with the Institute of Market
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY
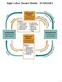 Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Eight Labor Market Models - SUMMARY 1 Eight Labor Market Models 1. Competitive labor market in a competitive product market 2. Competitive labor market in an imperfectly competitive product market 3. Monopsony
Productivity Growth, On-the-Job Search, and Unemployment
 Productivity Growth, On-the-Job Search, and Unemployment Hiroaki Miyamoto International University of Japan Yuya Takahashi University of Mannheim First Version: May 2008 This Version: November 2010 Abstract
Productivity Growth, On-the-Job Search, and Unemployment Hiroaki Miyamoto International University of Japan Yuya Takahashi University of Mannheim First Version: May 2008 This Version: November 2010 Abstract
Index. Cambridge University Press A Short Course in Intermediate Microeconomics with Calculus Roberto Serrano and Allan M.
 adverse selection, 361, 363 Akerloff, G., 360 allocation competitive equilibrium allocation, 275 feasible allocation, 266, 267, 275 nonfeasible allocation, 268 Arrow, K., 272 asymmetric information, 359,
adverse selection, 361, 363 Akerloff, G., 360 allocation competitive equilibrium allocation, 275 feasible allocation, 266, 267, 275 nonfeasible allocation, 268 Arrow, K., 272 asymmetric information, 359,
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION. A Mathematical Approach
 MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS A Mathematical Approach M. J. ALHABEEB L. JOE MOFFITT Isenberg School of Management University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA, USA WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION PREFACE
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS A Mathematical Approach M. J. ALHABEEB L. JOE MOFFITT Isenberg School of Management University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA, USA WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION PREFACE
The cost of employment protection in the presence of match-specific learning 1
 The cost of employment protection in the presence of match-specific learning 1 Éva Nagypál 2 April, 2002 Abstract This paper studies the effects of the introduction of employment protection policies that
The cost of employment protection in the presence of match-specific learning 1 Éva Nagypál 2 April, 2002 Abstract This paper studies the effects of the introduction of employment protection policies that
Comments on Bayoumi, Laxton and Pesenti by Patrick Minford*
 Comments on Bayoumi, Laxton and Pesenti by Patrick Minford* *Cardiff University. I am grateful to the authors and the conference participants for helpful reactions to my oral comments. This paper sets
Comments on Bayoumi, Laxton and Pesenti by Patrick Minford* *Cardiff University. I am grateful to the authors and the conference participants for helpful reactions to my oral comments. This paper sets
Gross Job Flows in Europe
 Gross Job Flows in Europe Ramón Gómez-Salvador (1) DG-Economics European Central Bank Julián Messina (2) DG-Research European Central Bank Giovanna Vallanti (3) * Centre for Economic Performance London
Gross Job Flows in Europe Ramón Gómez-Salvador (1) DG-Economics European Central Bank Julián Messina (2) DG-Research European Central Bank Giovanna Vallanti (3) * Centre for Economic Performance London
Cambridge Econometrics E3ME Macro-econometric Model
 New Developments for French Occupational Outlooks Cambridge Econometrics E3ME Macro-econometric Model Quantitative and qualitative methods used for employment projections Rachel Beaven, Director International
New Developments for French Occupational Outlooks Cambridge Econometrics E3ME Macro-econometric Model Quantitative and qualitative methods used for employment projections Rachel Beaven, Director International
A new model for the wage formation in Iceland
 A new model for the wage formation in Iceland Steinar Holden Department of Economics, UiO http://folk.uio.no/sholden/ 23 May Outline Background the need for coordinated wage restraint Experience from other
A new model for the wage formation in Iceland Steinar Holden Department of Economics, UiO http://folk.uio.no/sholden/ 23 May Outline Background the need for coordinated wage restraint Experience from other
AP Microeconomics Review With Answers
 AP Microeconomics Review With Answers 1. Firm in Perfect Competition (Long-Run Equilibrium) 2. Monopoly Industry with comparison of price & output of a Perfectly Competitive Industry (which means show
AP Microeconomics Review With Answers 1. Firm in Perfect Competition (Long-Run Equilibrium) 2. Monopoly Industry with comparison of price & output of a Perfectly Competitive Industry (which means show
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 11. Classical and Keynesian Macro Analyses
 Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 11 Classical and Keynesian Macro Analyses Introduction During the latter half of the 2000s, annual rates of U.S. real GDP growth varied
Copyright 2012 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 11 Classical and Keynesian Macro Analyses Introduction During the latter half of the 2000s, annual rates of U.S. real GDP growth varied
Mc Graw Hill Education
 Contemporary Labor Economics Eleventh Edition Campbell R. McConnell University of Nebraska Stanley L. Brue Pacific Lutheran University David A. Macpherson Trinity University Mc Graw Hill Education Contents
Contemporary Labor Economics Eleventh Edition Campbell R. McConnell University of Nebraska Stanley L. Brue Pacific Lutheran University David A. Macpherson Trinity University Mc Graw Hill Education Contents
BROWN UNIVERSITY. Teaching and Research Fields: Research fields: Economic Growth, Environmental Macroeconomics
 GREGORY CASEY www.gregorypcasey.com gregory_casey@brown.edu BROWN UNIVERSITY Placement Director: Emily Oster EMILY_OSTER@BROWN.EDU 401-863-2170 Graduate Administrator: Angelica Spertini ANGELICA_SPERTINI@BROWN.EDU
GREGORY CASEY www.gregorypcasey.com gregory_casey@brown.edu BROWN UNIVERSITY Placement Director: Emily Oster EMILY_OSTER@BROWN.EDU 401-863-2170 Graduate Administrator: Angelica Spertini ANGELICA_SPERTINI@BROWN.EDU
MICROECONOMICS. London School of Economics. University of Western Ontario. Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES
 .&*,- *>"> MICROECONOMICS Saul Estrin London School of Economics David Laidler University of Western Ontario Michael Dietrich University of Sheffield Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES An imprint of Pearson
.&*,- *>"> MICROECONOMICS Saul Estrin London School of Economics David Laidler University of Western Ontario Michael Dietrich University of Sheffield Prentice Hall FINANCIAL TIMES An imprint of Pearson
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing
 Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
Chapter 28 The Labor Market: Demand, Supply, and Outsourcing Learning Objectives After you have studied this chapter, you should be able to 1. define marginal factor cost, marginal physical product of
unemployed back to work?
 Does subsidised temporary employment get the unemployed back to work? An econometric analysis of two different schemes Michael Gerfin Department of Economics, University of Bern Michael Lechner, Heidi
Does subsidised temporary employment get the unemployed back to work? An econometric analysis of two different schemes Michael Gerfin Department of Economics, University of Bern Michael Lechner, Heidi
EMPLOYMENT VOLATILITY, EMPLOYMENT PROTECTION AND UNEMPLOYMENT
 EMPLOYMENT VOLATILITY, EMPLOYMENT PROTECTION AND UNEMPLOYMENT * Pedro Portugal ** 1. INTRODUCTION This essay explores the richness of the Portuguese microdata provide for the characterisation of the job
EMPLOYMENT VOLATILITY, EMPLOYMENT PROTECTION AND UNEMPLOYMENT * Pedro Portugal ** 1. INTRODUCTION This essay explores the richness of the Portuguese microdata provide for the characterisation of the job
Fundamentals of Microeconomics Johns Hopkins University Center for Talented Youth
 Fundamentals of Johns Hopkins University Center for Talented Youth Day Time Topic/Concepts Activity AM Introduction to Introductions, Honor Code, Class Rules and Expectations. Principles of Pre-assessment
Fundamentals of Johns Hopkins University Center for Talented Youth Day Time Topic/Concepts Activity AM Introduction to Introductions, Honor Code, Class Rules and Expectations. Principles of Pre-assessment
Flexibility of new hires earnings Evidence from Ireland during the Great Recession
 Reamonn Lydon & Matija Lozej Flexibility of new hires earnings Evidence from Ireland during the Great Recession Banco de España 16 November 2017 Disclaimer The views presented here are those of the authors
Reamonn Lydon & Matija Lozej Flexibility of new hires earnings Evidence from Ireland during the Great Recession Banco de España 16 November 2017 Disclaimer The views presented here are those of the authors
Labor Demand. Rongsheng Tang. July, Washington U. in St. Louis. Rongsheng Tang (Washington U. in St. Louis) Labor Demand July, / 53
 Labor Demand Rongsheng Tang Washington U. in St. Louis July, 2016 Rongsheng Tang (Washington U. in St. Louis) Labor Demand July, 2016 1 / 53 Overview The production function The employment decision in
Labor Demand Rongsheng Tang Washington U. in St. Louis July, 2016 Rongsheng Tang (Washington U. in St. Louis) Labor Demand July, 2016 1 / 53 Overview The production function The employment decision in
Market Power, Dismissal Threat and Rent Sharing: The Role of Insider and Outsider Forces in Wage Bargaining
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2102 Market Power, Dismissal Threat and Rent Sharing: The Role of Insider and Outsider Forces in Wage Bargaining Anabela Carneiro Pedro Portugal April 2006 Forschungsinstitut
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 2102 Market Power, Dismissal Threat and Rent Sharing: The Role of Insider and Outsider Forces in Wage Bargaining Anabela Carneiro Pedro Portugal April 2006 Forschungsinstitut
Agricultural Labour Market Flexibility in the EU and Candidate Countries
 1 Agricultural Labour Market Flexibility in the EU and Candidate Countries Jason Loughrey, Trevor Donnellan, Kevin Hanrahan and Thia Hennessy Rural Economy Research Centre, Teagasc, Athenry, Ireland 2013
1 Agricultural Labour Market Flexibility in the EU and Candidate Countries Jason Loughrey, Trevor Donnellan, Kevin Hanrahan and Thia Hennessy Rural Economy Research Centre, Teagasc, Athenry, Ireland 2013
Labor Turnover Costs and the Behavior of Vacancies and Unemployment
 Labor Turnover Costs and the Behavior of Vacancies and Unemployment José I. Silva Manuel Toledo Draft: March 23, 2005 Preliminary Abstract It has recently been argued that the standard Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides
Labor Turnover Costs and the Behavior of Vacancies and Unemployment José I. Silva Manuel Toledo Draft: March 23, 2005 Preliminary Abstract It has recently been argued that the standard Diamond-Mortensen-Pissarides
The dynamics of second job holding in Britain
 The dynamics of second job holding in Britain René Böheim Department of Economics Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria email: Rene.Boeheim@jku.at Mark P. Taylor Institute for Social and Economic Research
The dynamics of second job holding in Britain René Böheim Department of Economics Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria email: Rene.Boeheim@jku.at Mark P. Taylor Institute for Social and Economic Research
Economics of labour. S.G. Berlinski, M. Manacorda. Undergraduate study in Economics, Management, Finance and the Social Sciences EC3015,
 Economics of labour S.G. Berlinski, M. Manacorda EC3015, 2790015 2011 Undergraduate study in Economics, Management, Finance and the Social Sciences This is an extract from a subject guide for an undergraduate
Economics of labour S.G. Berlinski, M. Manacorda EC3015, 2790015 2011 Undergraduate study in Economics, Management, Finance and the Social Sciences This is an extract from a subject guide for an undergraduate
A LABOUR MODEL FOR SOUTH AFRICA
 A LABOUR MODEL FOR SOUTH AFRICA CHARLOTTE DU TOIT AND RENEE KOEKEMOER SOUTH AFRICA'S PERFORMANCE has been dismal in dealing with the rising unemployment that the economy has been faced with since the 1970s.
A LABOUR MODEL FOR SOUTH AFRICA CHARLOTTE DU TOIT AND RENEE KOEKEMOER SOUTH AFRICA'S PERFORMANCE has been dismal in dealing with the rising unemployment that the economy has been faced with since the 1970s.
Labour Market Flexibility and Regional Economic Performance in the UK,
 Labour Market Flexibility and Regional Economic Performance in the UK, 1979-1998 Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) by Vassilis Monastiriotis LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS AND POLITICAL
Labour Market Flexibility and Regional Economic Performance in the UK, 1979-1998 Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) by Vassilis Monastiriotis LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS AND POLITICAL
Working Less and Bargain Hunting More:
 Working Less and Bargain Hunting More: Macro Implications of Sales during Japan s Lost Decades N. Sudo, K. Ueda, K. Watanabe, T. Watanabe BOJ, Waseda U, CIGS, Tokyo U November 2016 SUWW Sales model November
Working Less and Bargain Hunting More: Macro Implications of Sales during Japan s Lost Decades N. Sudo, K. Ueda, K. Watanabe, T. Watanabe BOJ, Waseda U, CIGS, Tokyo U November 2016 SUWW Sales model November
The Rise in Danish Unemployment: Reallocation or Mismatch? Karsten Albæk Henrik Hansen
 CAM Centre for Applied Microeconometrics Institute of Economics University of Copenhagen http://www.econ.ku.dk/cam/ The Rise in Danish Unemployment: Reallocation or Mismatch? Karsten Albæk Henrik Hansen
CAM Centre for Applied Microeconometrics Institute of Economics University of Copenhagen http://www.econ.ku.dk/cam/ The Rise in Danish Unemployment: Reallocation or Mismatch? Karsten Albæk Henrik Hansen
Wage Bargaining in Germany. Dr. Hagen Lesch, Stockholm, Sept. 14th, 2011
 Wage Bargaining in Germany Dr. Hagen Lesch, Stockholm, Sept. 14th, 2011 Content Free collective bargaining and sector-level agreements Decentralisation and wage moderation Decline of collective bargaining
Wage Bargaining in Germany Dr. Hagen Lesch, Stockholm, Sept. 14th, 2011 Content Free collective bargaining and sector-level agreements Decentralisation and wage moderation Decline of collective bargaining
Course Outline. Business Undeclared School of Business & Economics ECON Applied Microeconomics for Sustainable Management
 Course Outline Calendar Description Business Undeclared School of Business & Economics ECON 6020-3.00 Applied Microeconomics for Sustainable Management Students examine more advanced microeconomic tools
Course Outline Calendar Description Business Undeclared School of Business & Economics ECON 6020-3.00 Applied Microeconomics for Sustainable Management Students examine more advanced microeconomic tools
Analyseinstitut for Forskning
 Analyseinstitut for Forskning Job Mobility LFS versus Registers Data Sources on Human Capital Mobility the Danish case Ebbe Krogh Graversen Notat 2002/7 fra Analyseinstitut for Forskning The Danish Institute
Analyseinstitut for Forskning Job Mobility LFS versus Registers Data Sources on Human Capital Mobility the Danish case Ebbe Krogh Graversen Notat 2002/7 fra Analyseinstitut for Forskning The Danish Institute
Practice Problems II EC Questions
 Practice Problems II EC 102.03 Questions 1. What do the following terms mean and how are they calculated? i. The unemployment rate ii. The labor force participation rate Answer: i.the unemployment rate
Practice Problems II EC 102.03 Questions 1. What do the following terms mean and how are they calculated? i. The unemployment rate ii. The labor force participation rate Answer: i.the unemployment rate
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS. MACROECONOMICS THEORY Preliminary Exam. August 10, :00 am - 2:00 pm
 UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MACROECONOMICS THEORY Preliminary Exam 9:00 am - 2:00 pm INSTRUCTIONS Please place a completed label (from the label sheet provided) on the top right corner
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MACROECONOMICS THEORY Preliminary Exam 9:00 am - 2:00 pm INSTRUCTIONS Please place a completed label (from the label sheet provided) on the top right corner
Understanding Inter-Industry Wage Structures in the Euro Area
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4114 Understanding Inter-Industry Wage Structures in the Euro Area Véronique Genre Karsten Kohn Daphne Momferatou April 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 4114 Understanding Inter-Industry Wage Structures in the Euro Area Véronique Genre Karsten Kohn Daphne Momferatou April 2009 Forschungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit
Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits)
 Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits) Semester 1/2014 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits) Semester 1/2014 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits)
 Lecture Time: Lecture Venue: Instructor: Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits) Semester 1/2015 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Time: Lecture Venue: Instructor: Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University EE 211 Principles of Microeconomics (3 credits) Semester 1/2015 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Microeconomics
 Microeconomics 978-1-63545-005-7 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Steve Greenlaw - University of Mary
Microeconomics 978-1-63545-005-7 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Steve Greenlaw - University of Mary
Division of Economic and Financial Studies ECON490: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS
 MACQUARIE UNIVERSITY Division of Economic and Financial Studies ECON490: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS UNIT OUTLINE Semester 2, 2007 ABOUT THIS UNIT ECON 490 ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS This unit provides the analytical
MACQUARIE UNIVERSITY Division of Economic and Financial Studies ECON490: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS UNIT OUTLINE Semester 2, 2007 ABOUT THIS UNIT ECON 490 ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS This unit provides the analytical
Specific Learning Goals/Benchmarks and Student Assessment. AP Macroeconomics
 Unit Bartram Trail HS Specific Learning Goals/Benchmarks and Student Assessment AP Macroeconomics # Benchmark Assessment 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 3 7 3 8 3 9 3 10 3 11 4 12 4 13 4 14 4 15 4 16 4 17 Define
Unit Bartram Trail HS Specific Learning Goals/Benchmarks and Student Assessment AP Macroeconomics # Benchmark Assessment 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 3 7 3 8 3 9 3 10 3 11 4 12 4 13 4 14 4 15 4 16 4 17 Define
Macroeconomics. 5. Causes of Unemployment. 5. Causes of Unemployment 5.1. Types of Unemployment. Types of Unemployment. 5. Causes of Unemployment
 Macroeconomics 5.1.2. Keynesian 5.1.3. Classical 5.1.3.3. Hysteresis- 5.1.3.5. Mismatch 5.2. The Concept of Productivity-oriented Wage Policy 5.3. abor Market aws in Germany 5.4. Questions for Review iterature:
Macroeconomics 5.1.2. Keynesian 5.1.3. Classical 5.1.3.3. Hysteresis- 5.1.3.5. Mismatch 5.2. The Concept of Productivity-oriented Wage Policy 5.3. abor Market aws in Germany 5.4. Questions for Review iterature:
PMT. GCE Economics. Unit F583: Economics of Work and Leisure. Advanced GCE. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Economics Unit F583: Economics of Work and Leisure Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Economics Unit F583: Economics of Work and Leisure Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
Macroeconomics. 5. Causes of Unemployment
 Macroeconomics - 1-5.1. Types of Unemployment 5.1.1. Frictional Unemployment 5.1.2. Keynesian Unemployment 5.1.3. Classical Unemployment 5.1.3.1. Insider/Outsider-Unemployment 5.1.3.2. Efficiency-Wage-Unemployment
Macroeconomics - 1-5.1. Types of Unemployment 5.1.1. Frictional Unemployment 5.1.2. Keynesian Unemployment 5.1.3. Classical Unemployment 5.1.3.1. Insider/Outsider-Unemployment 5.1.3.2. Efficiency-Wage-Unemployment
M12/3/ECONO/HP1/ENG/TZ1/XX/M MARKSCHEME. May 2012 ECONOMICS. Higher Level. Paper pages
 M12/3/ECONO/HP1/ENG/TZ1/XX/M MARKSCHEME May 2012 ECONOMICS Higher Level Paper 1 17 pages 2 M12/3/ECONO/HP1/ENG/TZ1/XX/M This markscheme is confidential and for the exclusive use of examiners in this examination
M12/3/ECONO/HP1/ENG/TZ1/XX/M MARKSCHEME May 2012 ECONOMICS Higher Level Paper 1 17 pages 2 M12/3/ECONO/HP1/ENG/TZ1/XX/M This markscheme is confidential and for the exclusive use of examiners in this examination
