Change in Overhead Cost Change in Production Units
|
|
|
- Timothy Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
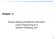
1 Test Series: October, 2018 MOCK TEST PAPER 2 FINAL (OLD) COURSE: GROUP II PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SUGGESTED ANSWERS/HINTS 1. (a) (*) P Q R I. Contribution per unit II. Units (Lower of Production / Market Demand) 2,000 2, III. Possible Contribution [I II] 8,000 6,000 4,500 IV. Opportunity Cost* 6,000 8,000 8,000 Opportunity cost is the maximum possible contribution forgone by not producing alternative product i.e. if Product P is produced then opportunity cost will be maximum of (Rs.6,000 from Q, Rs.4,500 from R). (b) Statement Showing Flexible Budget for 5,000 units Activity Level Particulars Overhead P (Rs per hour 2 hrs. per unit 5,000 units) Overhead Q* (Rs. 40,000 + Rs. 25 5,000 units) Overhead R (Rs per hour 2 hrs. per unit 4,000 units) Amount 1,20,000 1,65,000 1,00,000 Total 3,85,000 Working Note (*): Overhead Q Variable Cost (per unit) = Change in Overhead Cost Change in Production Units = = Rs. 1,90,000 - Rs. 1,40,000 6,000 units - 4,000 units Rs. 50,000 2,000units = Rs. 25 Fixed Cost = Rs.1,40,000 4,000 units Rs. 25 = Rs. 40,000 (c) Kaizen Costing emphasizes on small but continuous improvement. Targets once set at the beginning of the year or activities are updated continuously to reflect the improvement that has already been achieved and that are yet to be achieved.
2 The suggestive changes which are required to be adopted Kaizen Costing concepts in ZIL are as follows: Standard Cost Control System to Cost Reduction System: Traditionally Standard Costing system assumes stability in the current manufacturing process and standards are set keeping the normal manufacturing process into account thus the whole effort is on to meet performance cost standard. On the other hand Kaizen Costing believes in continuous improvements in manufacturing processes and hence, the goal is to achieve cost reduction target. The first change required is the standard setting methodology i.e. from earlier Cost Control System to Cost Reduction System. Reduction in the periodicity of setting Standards and Variance Analysis: Under the existing planning and control system followed by the ZIL, standards are set semi-annually and based on these standards monthly variance reports are generated for analysis. But under Kaizen Costing system cost reduction targets are set for small periods say for a week or a month. So the period covered under a standard should be reduced from semi-annually to monthly and the current practice of generating variance reports may be continued or may be reduced to a week. Participation of Executives or Workers in standard setting: Under the Kaizen Costing system participation of workers or executives who are actually involved i n the manufacturing process are highly appreciated while setting standards. So the current system of setting budgets and standards by the Finance department with the mere consent of Board of Directors required to be changed. (d) (i) Invalid Reason: As per the rules of network construction, parallel activities between two events, without intervening events, are prohibited. Dummy activities are needed when two or more activities have same initial and terminal events. Dummy activities do not consume time or resources. (ii) Valid Reason: As per the conventions adopted in drawing networks, the head event or terminal node always has a number higher than that of initial node or tail event. (iii) Invalid Reason: The difference between the latest event time and the earliest event time is termed as slack of an event. Free float is determined by subtracting head event slack from the total float of an activity. (iv) Invalid Reason: For every critical activity in a network, the earliest start time and the latest sta rt time is same and also the earliest finish time and the latest finish time is same. (v) Invalid Reason: The optimum duration is the time period in which the total cost of the project is minimum. 2. (a) Statement Showing Recommended Selling Price Department PTS: 100 Units (per Unit) 200 units (per Unit) Direct Labour 36 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs Overtime Premium # Total Labour Cost...(A) Variable Overheads 36 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs
3 Fixed Overheads 36 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs Total Overheads...(B) Department PTW: Direct Labour 18 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs Overtime Premium Total Labour Cost...(C) Variable Overheads 18 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs Fixed Overheads 18 hrs. Rs Hrs Rs Total Overheads...(D) Special Tool...(E) Rs.5,500 / Rs.5,500 / Direct Material..(F) Profit on Labour (10%) Rs. ( ) 10% Rs. ( ) 10% Profit on Overheads(15%) ( ) 15% ( ) 15% Total Profit...(G) Recommended Selling Price [(A)+ (B)+(C) + +(D)+(E)+(F)+(G)] 1, , ( # ) Statement Showing Overtime Premium Department PTS Department PTW Direct Labour Hours Available 12,000 8,000 Present workload 7,680 4,200 Balance Direct Labour Hours 4,320 3,800 Hours Required to produce 100 units: 3,600 1,800 Hours Required to produce 200 units: 5,760 (200 x 36 x 0.80) 2,520 (200 x 18 x 0.70) Overtime Required to produce 100 units Overtime Required to produce 200 units 1,440 Hrs --- Overtime Premium 10.8 $ per Unit --- (b) ($) 1,440 Hrs 3 50% / 200 Units Primal Minimize Z = 3x 1 4x 2 + 5x 3 Subject to the constraints 3
4 Dual 4x 1 + 3x 2 + 5x x 1 + 4x 2 + 3x 3 6 8x 1 + 3x 2 + 5x x 1 4x 2 + 5x 3 5 3x 1 + 6x 2 4x 3 4 3x 1 6x 2 + 4x 3 4 x 1, x 2, x 3 0 Maximize Z = 10y 1 + 6y 2 11y 3 + 5y 4 + 4y 5 4y 6 Subject to constraints 4y 1 + 3y 2 8y 3 + 7y 4 + 3y 5 3y 6 3 3y 1 + 4y 2 + 3y 3 4y 4 + 6y 5 6y 6 4 5y 1 + 3y 2 + 5y 3 + 5y 4 4y 5 + 4y 6 5 y 1, y 2, y 3, y 4, y 5, y 6 0 By substituting y 5 y 6= y 7 the dual can alternatively be expressed as: Maximize Z = 10y 1 + 6y 2 11y 3 + 5y 4 + 4y 7 Subject to constraints 3. (a) Workings 4y 1 + 3y 2 8y 3 + 7y 4 + 3y 7 3 3y 1 4y 2 3y 3 + 4y 4 6y 7 4 5y 1 + 3y 2 + 5y 3 + 5y 4 4y 7 5 y 1, y 2, y 3, y 4 0, y 7 unrestricted in sign. Statement Showing Inventory Holding Cost under Current System Particulars Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Opening Inventory* (A) ,030 Add: Production* 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 Less: Demand* 3,150 3,760 4,060 3,350 3,650 4,830 Closing Inventory* (B) ,030 - A B Average Inventory Inventory Holding Rs.70 22,750 46,900 39,200 45,850 66,850 36,050 (*) in terms of standard labour hours Inventory Holding Cost for the six months = Rs.2,57,600 (Rs.22,750+ Rs.46,900 + Rs.39,200 + Rs.45,850 + Rs.66,850 +Rs.36,050) Calculation of Relevant Overtime Cost under JIT System Particulars Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Demand* 3,150 3,760 4,060 3,350 3,650 4,830 Production* 3,150 3,760 4,060 3,350 3,650 4,830
5 Normal Availability* 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 3,800 Shortage (=Overtime*) (C) ,030 C 0.95 Actual Overtime Hours , Overtime Rs [110+45%] , ,72,931 (*) in terms of standard labour hours (b) Total Overtime payment = Rs.2,16,583 (Rs.43,652 + Rs.1,72,931) Therefore, saving in JIT system = Rs.2,57,600 Rs.2,16,583 Comments = Rs.41,017 Though WL is saving Rs.41,017 by changing its production system to Just-in-time but it has to consider other factors as well before taking any final call which are as follows: - (i) (ii) WL has to ensure that it receives materials from its suppliers on the exact date and at the exact time when they are needed. Credentials and reliability of supplier must be thoroughly checked. To remove any quality issues, the engineering staff must visit supplier s sites and examine their processes, not only to see if they can reliably ship high-quality parts but also to provide them with engineering assistance to bring them up to a higher standard of product. (iii) WL should also aim to improve quality at its process and design levels with the purpose of achieving Zero Defects in the production process. (iv) WL should also keep in mind the efficiency of its work force. WL must ensure that labour s learning curve has reached at steady rate so that they are capable of performing a variety of operations at effective and efficient manner. The workforce must be completely retrained and focused on a wide range of activities. Opportunity Cost of Labour - The Tg 2 labour has zero opportunity cost as there is no other use for the time already paid for and is available. However, TTL needs to pay an additional amount for Tg 1 labour. This amount can be save if the special job were not there. Tg 1 labour: Hours Required 250 Hours Available 150 Extra Hours Needed 100 Cost per hour (Rs.630/42hrs) Rs. 15 Opportunity Cost Rs. 1,500 Thus, the Opportunity Cost of Labour for completing the special job is Rs.1,500. Opportunity Cost of Material - TTL has no alternative use for the Tr 1, they must dispose of it at a cost of Rs.1,250. Thus, TTL actually saves Rs.1,250 by using the materials for the KIA Industries special job. Consequently, the Opportunity Cost of Material is - Rs.1,250 (i.e., the opportunity cost of this resource is negative). The minimum price is the price at which TTL just recovers its Opportunity Cost. TTL s Total Opportunity Cost is Rs.250 (Rs.1,500 Rs.1,250). Accordingly, minimum Price for the Special Job is Rs
6 4. (a) Customer Profitability Statement (b) Particulars WX Ltd. WY Ltd. XY Bros. Sales (units) 2,000 1, Sales Revenue (A) 2,20,00,000 1,10,00,000 88,00,000 Less: Average Variable Cost (B) (Rs. 5,500 60% = 3,300 p.u.) 66,00,000 33,00,000 26,40,000 Contribution [70%of Sales] (A)-(B) 1,54,00,000 77,00,000 61,60,000 Less: Additional Overheads Delivery Cost (No. of K.M. Rs. 200) Emergency Delivery Cost (No. of Emerg. Delivery Rs. 21,000) Order Processing Cost (No. of Orders Rs. 6,000) 2,00,000 1,60,000 1,80,000 42,000 21,000-24,000 12,000 48,000 Specific Discount 55,00,000 22,00,000 13,20,000 Sales Commission 33,00,000 11,00,000 4,40,000 Advertisement Cost 8,75,000 6,15,000 4,30,000 Profit per customer* 54,59,000 35,92,000 37,42,000 Profit Margin per customer* (%) 24.81% 32.65% 42.52% Rank III II I * Before deducting general fixed overhead cost The contribution margin is 70% for each customer but when the other overheads costs per customer is included in the above profitability statement the profitability of the three customers become different. XY Bros. is the most profitable customer. to Deal with Clients (Minutes) Probability Cumulative Probability Assigned Numbers between Arrivals (Minutes) Probability Cumulative Probability Assigned Numbers
7 Client Simulation Table for between Arrivals and Service Between Arrivals Arrival In 7 Serving Out Waiting Voucher Yes Yes Total Clients in a Week of 75Hours = # Average between Arrivals = 10.4 minutes 433 (75 hours 60 minutes /10.4 # minutes) ( ) 2 out of the 12 clients receive Rs.15 voucher. So the Cost will be Rs.1, or Rs.1,083 [(2/12 433) Rs.15]. Taking Cycle as 148 minutes, Voucher Cost can be computed as follows: Rs.15 per Client [(75 hours 60 minutes /148 minutes) No. of Cycles 2 Clients per Cycle ] So, Voucher Cost will be Rs (a) (i) Transfer price per unit of product A that Division X should quote in order to meet target profit for the year: Quotation for the 40,000 units of product A should be such that meet Division X s target profit and interest cost on working capital. Therefore the minimum quote for product A will be calculated as follows: Particulars Amount Target Profit (given for the year) 2,50,00,000 Add: Interest Cost on Working Capital 1,38,00,000 Required Profit 3,88,00,000 Add: Fixed Overhead 4,00,00,000 Target Contribution 7,88,00,000 Less: Contribution Earned from external sales {60,000 units Rs. (2,500 1,600)} 5,40,00,000
8 Contribution Required from internal sales 2,48,00,000 Contribution per unit of Product A (Rs.2,48,00,000 40,000 units) 620 Transfer Price of Product A to Division Y (Variable Cost per unit + Contribution per unit) 2,220 (b) (ii) The two transfer prices based on opportunity costs: For the 30,000 units (i.e. maximum capacity maximum external market demand) at variable cost of production i.e. Rs.1,600 per unit. For the next 10,000 units (i.e. external market demand maximum possible sale) at market selling price i.e. Rs.2,500 per unit. The given information can be tabulated in following transportation problem- Manager Transfer Pricing Assignment Corporate Valuation Statutory Audit Available S 1,800 2,250 2, D 2,100 1,950 1, K 2,400 2,100 2, Required The given problem is an unbalanced transportation problem. Introducing a dummy assignment to balance it, we get- Manager Assignment Transfer Pricing Corporate Valuation Statutory Audit Dummy Available S 1,800 2,250 2, D 2,100 1,950 1, K 2,400 2,100 2, Required The objective here is to maximize total billing amount of the auditors. For achieving this objective, let us convert this maximization problem into a minimization problem by subtracting all the elements of the above payoff matrix from the highest payoff i.e. Rs.2,850. Manager Assignment Transfer Pricing Corporate Valuation Statutory Audit Dummy Available S 1, , D ,050 2, K , Required
9 Now, let us apply solution. VAM method to the above matrix for finding the initial feasible Manager Assignment Transfer Pricing Corp. Valuation Stat. Audit Dummy Avail. S 1, , / D ,050 2, /55/ , K , /33/0 150, 300, 2, Required 143/0 154/121/0 176/0 55/ The initial solution is given below. It can be seen that it is a degenerate solution since the number of allocation is 5. In order to apply optimality test, the total number of allocati ons should be 6 (m + n -1). To make the initial solution a non-degenerate, we introduce a very small quantity in the least cost independent cell which is cell of K, Statutory Audit Manager Transfer Pricing Corporate Valuation Assignment Stat. Audit Dummy S 1, ,850 D ,050 2, K , e 9
10 Let us test the above solution for optimality- (ui+vj) matrix for allocated cells , ,700 ui (ui+vj) matrix for un allocated cells , , ,700 ui ij = Cij (ui+vj) 1, Since, all allocations in ij = C ij (u i+v j)are non negative, the allocation is optimal. The allocation of assignments to managers and their billing amount is given below: Manager Assignment Billing Amount S Statutory Audit Rs.5,01,600 (176 hrs. x Rs.2,850) D Corporate Valuation Rs.2,35,950 (121 hrs. x Rs.1,950) K Transfer Pricing Rs.3,43,200 (143 hrs. x Rs.2,400) K Corporate Valuation Rs.69,300 (33 hrs. x Rs.2,100) Total Billing Rs.11,50, (a) Primary activities are the activities that are directly involved in transforming inputs into outputs and delivery and after-sales support to output. Following are the primary activities in the value chain of XYZ Ltd.:- (i) (ii) Inbound Logistics: These activities are related to the material handling and warehousing. It also covers transporting raw material from the supplier to the place of processing inside the factory. Operations: These activities are directly responsible for the transformation of raw material into final product for the delivery to the consumers.
11 (b) (iii) Outbound Logistics: These activities are involved in movement of finished goods to the point of sales. Order processing and distribution are major part of these activities. (iv) Marketing and Sales: These activities are performed for demand creation and customer solicitation. Communication, pricing and channel management are major part of these activities. (v) Service: These activities are performed after selling the goods to the consumers. Installation, repair and parts replacement are some examples of these activities. Computation of Requirements of the Question: (i) (ii) Actual Material Cost Incurred Material Cost Variance = (Standard Cost of Material of Actual Output) (Actual Material Cost Incurred) Or Actual Material Cost Incurred = (Standard Cost of Material of Actual Output) (Material Cost Variance) = 10,000 units 2 units Rs.15 + Rs. 50,000 = Rs.3,00,000 + Rs. 50,000 = Rs.3,50,000 Standard Cost of Materials Actually Consumed Material Price Variance = (Standard Price Actual Price) x Actual Quantity Consumed Or Standard Cost of Materials Actually Consumed = (Actual Material Cost Incurred) + (Material Price Variance) (iii) Labour Efficiency Variance (Refer to working note) = Rs.3,50,000 Rs.70,000 = Rs.2,80,000 Labour Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output Actual Hours Worked) x Standard Rate per Hour = (10,000 units 3 hours 35,000 hours) Rs.20 = (Rs.6,00,000 Rs.7,00,000) = Rs.1,00,000 (A) (iv) Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance (Refer to working note) Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output Actual Hours) x Standard Variable Overhead Rate per Hour 11
12 (v) = Rs.5 x (30,000 Hours 35,000 Hours) = Rs.25,000 (A) Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance (Refer to working note) Variable Overhead Expenditure Variance = (Budgeted Variable Overheads for Actual Hours) (Actual Variable Overheads) = (Rs.5 35,000 Hours Rs.2,00,000) = Rs.25,000 (A) (vi) Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance (Refer to working notes) Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Standard Hours for Actual Output Actual Hours) x Standard Fixed Overhead Rate per Hour = Rs.5 x (30,000 Hours 35,000 Hours) = Rs.25,000 (A) (vii) Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance (Refer to working notes) Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance = (Actual Hours Budgeted Hours) x Standard Fixed Overhead Rate per Hour (viii) Fixed Overhead Volume Variance (Refer to working note) = Rs.5 x (35,000 Hours 50,000 Hours) = Rs.75,000 (A) Fixed Overhead Volume Variance = (Actual Output Budgeted Output) x Standard Fixed Overhead Rate per Unit Working Note = Rs.15 [10,000 units (50,000 hours / 3 hours p. u.)] = Rs.1,50,000 Rs.2,50,000 = Rs.1,00,000 (A) Labour Rate Variance = (Standard Rate per Hour x Actual Hours) (Actual Labour Cost) Or Rs.50,000 = Rs.20 x Actual Hours Rs.6,50,000 Or Actual Hours = 35,000 Standard Hours = 10,000 Units 3 Hours = 30,000 Hours Budgeted Hours = 30,000 hours 100% 60%
13 Budgeted Fixed Overhead Standard fixed overhead recovery rate per hour = 50,000 Hours = Actual Fixed Overhead + Expenditure Variance = Rs.3,00,000 Rs.50,000 = Rs.2,50,000 = Rs. 2,50,000 50,000 hours = Rs.5 per hour Total Overhead Rate per Hour = Rs.10 Variable Overhead Rate per Hour (Rs.10 Rs.5) = Rs.5 Standard Fixed Overhead per Unit (3 hours Rs.5) = Rs (a) Cost is not only criterion for deciding in the favour of shut down. Non -cost factors worthy of consideration in this regard are as follows: (b) (i) (ii) Interest of workers, if the workers are discharged, it may become difficult to get skilled workers later, on reopening of the factory. Also shut-down may create problems. In the face of competition it may difficult to re-establish the market for the product. (iii) Plant may become obsolete or depreciate at a faster rate or get rusted. Thus, heavy capital expenditure may have to be incurred on re-opening. Cost Incurred Cost Classification S. No. (i) (ii) Cost Incurred Remuneration of the loan division manager. Cost of Printer Paper, File Folders, View Binders, Ink, Toner & Ribbons used in the loan division. (iii) Cost of the division s MacBook Pro purchased by the loan division manager last year. (iv) Cost of advertising in business newspaper by the bank, which is allocated to the loan division. Classification 1 Uncontrollable by the loan division manager. Controllable by the loan division manager. Controllable by the loan division manager. Uncontrollable by the loan division manager. Classification 2 Direct cost of the loan division. Direct cost of the loan division. Direct cost of the loan division. Indirect Cost of the loan division. Classification 3 Out of Pocket Cost Out of Pocket Cost Sunk Cost Out of Pocket Cost (c) (i) All activities of a firm are not subject to learning effect. Activities that have not been performed in the present operational mode, those performed by new or unfamiliar employees are subjected to learning effect, while those performed by familiar or experienced workmen will not be subjected to learning effect. 13
14 (ii) (i) In case Market Demand is High Product Beta (Lower Variable Cost and Higher Fixed Cost) (d) (e) (ii) In case Market Demand is Low Product Gama Relevant costs of producing one unit of the finished product Rs. Cost of material LN (realisable value) Cost of labour (Being sunk cost) - Out-of-pocket expenses Allocated overhead is not relevant for the decision. The customer should be charged Rs per unit. The assignment problem is special case of transportation problem; it can also be solved by transportation method. But the solution obtained by applying this method would be severely degenerate. This is because the optimality test in the transportation method requires that there must be m+n-1 allocations/assignments. But due to the special structure of assignment problem of order n n, any solution cannot have more than n assignments. Thus, the assignment problem is naturally degenerate. In order to remove degeneracy, n-1* number of dummy allocations will be required in order to proceed with the transportation method. Thus, the problem of degeneracy at each solution makes the transportation method computationally inefficient for solving an assignment problem. (*) m+n-1 - n n+n-1 - n 2n-1 - n n-1
THE PROFESSIONALS ACADEMY OF COMMERCE Mock Exam, Summer-2015 Management Accounting (Solution)
 THE PROFESSIONALS ACADEMY OF COMMERCE Mock Exam, Summer-2015 Management Accounting (Solution) Answer to Q-1 Minimum price for making 500 units of AK 100 Materials: Rs. X (500 units 4kg) Rs.8 16,000 Y (500
THE PROFESSIONALS ACADEMY OF COMMERCE Mock Exam, Summer-2015 Management Accounting (Solution) Answer to Q-1 Minimum price for making 500 units of AK 100 Materials: Rs. X (500 units 4kg) Rs.8 16,000 Y (500
(4 Marks) (b) Enumerate the industrial applications of linear programming.
 47 PAPER 5 : COST ACCOUNTING & COST SYSTEMS MAY 2003 Question No.1 is compulsory Answer any four questions from the rest. Working notes should form part of the answer. Make assumptions wherever necessary
47 PAPER 5 : COST ACCOUNTING & COST SYSTEMS MAY 2003 Question No.1 is compulsory Answer any four questions from the rest. Working notes should form part of the answer. Make assumptions wherever necessary
1). Fixed cost per unit decreases when:
 1). Fixed cost per unit decreases when: a. Production volume increases. b. Production volume decreases. c. Variable cost per unit decreases. d. Variable cost per unit increases. 2). Prime cost + Factory
1). Fixed cost per unit decreases when: a. Production volume increases. b. Production volume decreases. c. Variable cost per unit decreases. d. Variable cost per unit increases. 2). Prime cost + Factory
Particulars P Q (a) Production / Sales Quantity (units) 1,00,000 50,000. (b) Batch Size (units) 1, (c) No. of Batches (a b)
 FINAL CA NOV 2018 SUB: COSTING Topics: Simulation, CPM & PERT, Activity Based Costing, Budgetary Control, Life Cycle Costing, Standard Costing, Integral & Non- Integral Accounts. Test Code CF7 Branch (MULTIPLE)
FINAL CA NOV 2018 SUB: COSTING Topics: Simulation, CPM & PERT, Activity Based Costing, Budgetary Control, Life Cycle Costing, Standard Costing, Integral & Non- Integral Accounts. Test Code CF7 Branch (MULTIPLE)
PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS
 Value Added/ Non Value Added PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS 1. Queenstown Furniture (QF) manufactures high-quality wooden doors within the forests of Queenstown since 1952. Management
Value Added/ Non Value Added PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS 1. Queenstown Furniture (QF) manufactures high-quality wooden doors within the forests of Queenstown since 1952. Management
COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
 EXECUTIVE PROGRAMME COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SAMPLE TEST PAPER (This test paper is for practice and self study only and not to be sent to the institute) Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks : 100
EXECUTIVE PROGRAMME COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SAMPLE TEST PAPER (This test paper is for practice and self study only and not to be sent to the institute) Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks : 100
Decision Making Using Cost Concepts and CVP Analysis
 2 Decision Making Using Cost Concepts and CVP Analysis Question 1 Panchwati Cement Ltd. produces 43 grade cement for which the company has an assured market. The output for 2004 has been budgeted at 1,80,000
2 Decision Making Using Cost Concepts and CVP Analysis Question 1 Panchwati Cement Ltd. produces 43 grade cement for which the company has an assured market. The output for 2004 has been budgeted at 1,80,000
Transportation Problems
 C H A P T E R 11 Transportation Problems Learning Objectives: Understanding the feature of Assignment Problems. Formulate an Assignment problem. Hungarian Method Unbalanced Assignment Problems Profit Maximization
C H A P T E R 11 Transportation Problems Learning Objectives: Understanding the feature of Assignment Problems. Formulate an Assignment problem. Hungarian Method Unbalanced Assignment Problems Profit Maximization
PAPER 5 ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING MAY 2013
 Q.1 PAPER 5 ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING MAY 2013 (a) A process industry unit manufactures three joint products: A, B and C. C has no realisable value unless it undergoes further processing after the
Q.1 PAPER 5 ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING MAY 2013 (a) A process industry unit manufactures three joint products: A, B and C. C has no realisable value unless it undergoes further processing after the
MTP_Final_Syllabus 2016_June 2018_Set 2
 Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making DoS, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management and Decision
Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making DoS, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management and Decision
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 16 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I INTAKE VIII (GROUP A) END SEMESTER
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 16 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I INTAKE VIII (GROUP A) END SEMESTER
Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2016 Examination
 Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2016 Examination Examination Date : 26 th November 2016 Number of Pages : 07 Examination
Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2016 Examination Examination Date : 26 th November 2016 Number of Pages : 07 Examination
Answer_MTP_Final_Syllabus 2016_Dec2017_Set 1 Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making
 Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management
Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management
DEEPAK GUPTA CLASSES
 COST SHEET Q1. A Ltd. has a capacity to produce 100,000 units of the product every month. Its work costs at varying levels of production is as under: LEVEL WORK COST (Rs.per unit) 10% 400 20% 390 30% 380
COST SHEET Q1. A Ltd. has a capacity to produce 100,000 units of the product every month. Its work costs at varying levels of production is as under: LEVEL WORK COST (Rs.per unit) 10% 400 20% 390 30% 380
Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation
 Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation BY G H A N E N DR A F A G O Cost Concepts Cost refers the amount of expenses spent to generate product or services. Cost refers expenditure that may be
Cost concepts, Cost Classification and Estimation BY G H A N E N DR A F A G O Cost Concepts Cost refers the amount of expenses spent to generate product or services. Cost refers expenditure that may be
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 13 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (INTAKE VI GROUP A) END SEMESTER
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 13 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (INTAKE VI GROUP A) END SEMESTER
Basic Costing Guidance
 Basic Costing Guidance The Association of Accounting Technicians April 2010 Basic costing (BCCG) Introduction Please read this document in conjunction with the standards for all relevant units. Basic Principles
Basic Costing Guidance The Association of Accounting Technicians April 2010 Basic costing (BCCG) Introduction Please read this document in conjunction with the standards for all relevant units. Basic Principles
COST CONCEPTS IN DECISION MAKING
 CHAPTER 2 COST CONCEPTS IN DECISION MAKING BASIC CONCEPTS & FORMULAE Basic Concepts 1. Relevant cost in decision making process: Costs which are relevant for a particular business option, which are not
CHAPTER 2 COST CONCEPTS IN DECISION MAKING BASIC CONCEPTS & FORMULAE Basic Concepts 1. Relevant cost in decision making process: Costs which are relevant for a particular business option, which are not
Question Paper Accounting For Decision Making - II (MB2D2): January 2009
 Question Paper Accounting For Decision Making - II (MB2D2): January 2009 1. Prime cost plus variable overheads is Answer all 70 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. Total Marks : 100 Total
Question Paper Accounting For Decision Making - II (MB2D2): January 2009 1. Prime cost plus variable overheads is Answer all 70 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. Total Marks : 100 Total
BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme. Strategic Management Accounting. Tutorial III- Short term decision making
 BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme Strategic Management Accounting Tutorial III- Short term decision making 1. A company has the following costs and revenues relating to a product.
BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme Strategic Management Accounting Tutorial III- Short term decision making 1. A company has the following costs and revenues relating to a product.
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES SECTION I
 QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES SECTION I QUESTION ONE (a) In a recent research survey by Intelligence Consultants on the use of the services of auditing firms by various Non Governmental Organisations (NGOs)
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES SECTION I QUESTION ONE (a) In a recent research survey by Intelligence Consultants on the use of the services of auditing firms by various Non Governmental Organisations (NGOs)
Management Accounting
 THE PROFESSIONALS ACADEMY OF COMMERCE Management Accounting Mock Exam Summer-2015 May 21, 2015 Module : F (Additional reading time - 15 minutes) 100 marks 3 hours Q.1 ABC Company has received an enquiry
THE PROFESSIONALS ACADEMY OF COMMERCE Management Accounting Mock Exam Summer-2015 May 21, 2015 Module : F (Additional reading time - 15 minutes) 100 marks 3 hours Q.1 ABC Company has received an enquiry
COST. Labour. Direct
 COMMERCIAL STUDIES STD: X Chapter 10. Fundamental Concepts of Cost Concept of Cost The term cost generally means the amount of expenditure (actual or notional) incurred on, or attributable to, a given
COMMERCIAL STUDIES STD: X Chapter 10. Fundamental Concepts of Cost Concept of Cost The term cost generally means the amount of expenditure (actual or notional) incurred on, or attributable to, a given
COST ACCOUNTING QUESTION ONE
 QUESTION ONE COST ACCOUNTING a) Briefly explain the term limiting factor A limiting factor is a binding constraint upon the organization. It prevents indefinite expansion or unlimited profits. It may be
QUESTION ONE COST ACCOUNTING a) Briefly explain the term limiting factor A limiting factor is a binding constraint upon the organization. It prevents indefinite expansion or unlimited profits. It may be
Selling Price 60 Direct material 28 Direct Rs. 3 p. hr. 12 Variable overheads 6 Fixed cost (Total) 1,05,500
 Question 1 (a) PAPER 5 : ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. E Ltd. is engaged in the manufacturing of three products in its factory. The
Question 1 (a) PAPER 5 : ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. E Ltd. is engaged in the manufacturing of three products in its factory. The
1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I
 SOLUTIONS TO EERCISES EERCISE 2-1 (15 minutes) 1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I EERCISE 2-2 (15 minutes) 1. Product
SOLUTIONS TO EERCISES EERCISE 2-1 (15 minutes) 1. F; I 2. V ; D 3. V ; D 4. F; I 5. F; I 6. F; I 7. V ; D 8. F; I 9. F; I 10. V ; D 11. F; I 12. F; I 13. F; I 14. F; I EERCISE 2-2 (15 minutes) 1. Product
B.COM 2 PRIVATE COST ACCOUNTING. B.com-2 PRIVATE Annual Examination COMPILED & SOLVED BY: Jahangeer Khan
 B.COM 2 PRIVATE COST ACCOUNTING B.com-2 PRIVATE Annual Examination 20 COMPILED & SOLVED BY: Jahangeer Khan 20 Q.1: MANUFACTURING CONCERN: Consider the following information taken from the books of SAHAB
B.COM 2 PRIVATE COST ACCOUNTING B.com-2 PRIVATE Annual Examination 20 COMPILED & SOLVED BY: Jahangeer Khan 20 Q.1: MANUFACTURING CONCERN: Consider the following information taken from the books of SAHAB
B.Com II Year (Hons.) Cost Accounting Model Paper I
 Max. Marks: 100 B.Com II Year (Hons.) Cost Accounting Model Paper I Durations: 3 Hrs. Attempt all the questions. All Questions are compulsory, each question carry 20 marks. Unit I 1. A Ltd. Is the manufacturer
Max. Marks: 100 B.Com II Year (Hons.) Cost Accounting Model Paper I Durations: 3 Hrs. Attempt all the questions. All Questions are compulsory, each question carry 20 marks. Unit I 1. A Ltd. Is the manufacturer
P2 Performance Management
 Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management Examiner s Answers SECTION A Answer to Question One (a) The standard cost of the actual hours worked was 3,493-85 = 3,408. At 12 per hour the actual hours worked
Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management Examiner s Answers SECTION A Answer to Question One (a) The standard cost of the actual hours worked was 3,493-85 = 3,408. At 12 per hour the actual hours worked
The Examiner's Answers Specimen Paper. Performance Management
 The Examiner's Answers Specimen Paper P2 - SECTION A Answer to Question One The Value Chain is the concept that there is a sequence of business factors by which value is added to an organisation s products
The Examiner's Answers Specimen Paper P2 - SECTION A Answer to Question One The Value Chain is the concept that there is a sequence of business factors by which value is added to an organisation s products
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING. 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION
 MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION Structureofthelecture2 2.1 Definition of cost and related terms 2.2 Types of cost classification 2.3 Identification of cost classification 2.4 Reporting
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING 2 nd topic COST CLASSIFICATION Structureofthelecture2 2.1 Definition of cost and related terms 2.2 Types of cost classification 2.3 Identification of cost classification 2.4 Reporting
Aggregate Planning and S&OP
 Aggregate Planning and S&OP 13 OUTLINE Global Company Profile: Frito-Lay The Planning Process Sales and Operations Planning The Nature of Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning Strategies 1 OUTLINE - CONTINUED
Aggregate Planning and S&OP 13 OUTLINE Global Company Profile: Frito-Lay The Planning Process Sales and Operations Planning The Nature of Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning Strategies 1 OUTLINE - CONTINUED
HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting
 Chapter 20 HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting Lecture 08: Managerial Accounting (Concepts & Principles) Masud Jahan Department of Science and Humanities Military Institute of Science and Technology
Chapter 20 HUM 211: Financial & Managerial Accounting Lecture 08: Managerial Accounting (Concepts & Principles) Masud Jahan Department of Science and Humanities Military Institute of Science and Technology
TOPIC 7 - IAS 2 - INVENTORIES
 TOPIC 7 - IAS 2 - INVENTORIES Objective of IAS 2 to prescribe how to account for inventories. What are inventories? (a) Goods purchased for resale (b) Finished goods produced (c ) Work in progress (d)
TOPIC 7 - IAS 2 - INVENTORIES Objective of IAS 2 to prescribe how to account for inventories. What are inventories? (a) Goods purchased for resale (b) Finished goods produced (c ) Work in progress (d)
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 2 MODULE CODE: ACCT08004
 School of Business & Enterprise Paisley & Hamilton Campus Session 014-015 Trimester 1 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING MODULE CODE: ACCT08004 Date: 16 th January 015 Time: 1000-100 Answer THREE questions Question
School of Business & Enterprise Paisley & Hamilton Campus Session 014-015 Trimester 1 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING MODULE CODE: ACCT08004 Date: 16 th January 015 Time: 1000-100 Answer THREE questions Question
Section A: Summary Content Notes
 COST ACCOUNTING 30 JULY 2015 Section A: Summary Content Notes MANUFACTURING ACCOUNTS: NEW LEDGER ACCOUNTS New Ledger Accounts pertaining to manufacturing concerns are divided into the following categories:
COST ACCOUNTING 30 JULY 2015 Section A: Summary Content Notes MANUFACTURING ACCOUNTS: NEW LEDGER ACCOUNTS New Ledger Accounts pertaining to manufacturing concerns are divided into the following categories:
Aggregate Planning (session 1,2)
 Aggregate Planning (session 1,2) 1 Outline The Planning Process The Nature of Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning Strategies Capacity Options Demand Options Mixing Options to Develop a Plan Methods for
Aggregate Planning (session 1,2) 1 Outline The Planning Process The Nature of Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning Strategies Capacity Options Demand Options Mixing Options to Develop a Plan Methods for
MARGINAL COSTING CATEGORY A CHAPTER HIGH MARKS COVERAGE IN EXAM
 1 MARGINAL COSTING CATEGORY A CHAPTER HIGH MARKS COVERAGE IN EXAM Question 1 Arnav Ltd. manufacture and sales its product R-9. The following figures have been collected from cost records of last year for
1 MARGINAL COSTING CATEGORY A CHAPTER HIGH MARKS COVERAGE IN EXAM Question 1 Arnav Ltd. manufacture and sales its product R-9. The following figures have been collected from cost records of last year for
COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED & SOLD STATEMENT
 COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED & SOLD STATEMENT In order to understand the financial and cost statement of a concern we should clear about the procedure adopted by trading concern and manufacturing concern
COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED & SOLD STATEMENT In order to understand the financial and cost statement of a concern we should clear about the procedure adopted by trading concern and manufacturing concern
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior rue/false Questions F 1. he cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. Answer: rue Difficulty: Simple Learning Objective: 1 F 2. A cost can either be an asset
Chapter 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior rue/false Questions F 1. he cost of an item is the sacrifice made to acquire it. Answer: rue Difficulty: Simple Learning Objective: 1 F 2. A cost can either be an asset
P2 Performance Management
 Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management Examiner s Answers SECTION A Answer to Question One (a) Flexed Actual Budget Output (batches) 50 50 Variance Direct labour hours 68 91 93 65 24 74 adverse Direct
Performance Pillar P2 Performance Management Examiner s Answers SECTION A Answer to Question One (a) Flexed Actual Budget Output (batches) 50 50 Variance Direct labour hours 68 91 93 65 24 74 adverse Direct
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE 2.2 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING LECTURES 2 HOLY KPORTORGBI
 EXCEL PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE 2.2 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING LECTURES 2 HOLY KPORTORGBI Requirements CA Textbook Excel 2.2 Management Revision Kit Punctuality in class Weekly assignments Mocks Common mistakes
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE 2.2 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING LECTURES 2 HOLY KPORTORGBI Requirements CA Textbook Excel 2.2 Management Revision Kit Punctuality in class Weekly assignments Mocks Common mistakes
Which of the following is correct? Select correct option: Units sold=opening finished goods units + Units produced Closing finished goods units Units
 Which of the following is correct? Units sold=opening finished goods units + Units produced Closing finished goods units Units Sold = Units produced + Closing finished goods units - Opening finished goods
Which of the following is correct? Units sold=opening finished goods units + Units produced Closing finished goods units Units Sold = Units produced + Closing finished goods units - Opening finished goods
KSA Core SAP (i) Final New Financial Reporting. 1(a)
 KSA Core SAP (i) Final New Financial Reporting 1a 1b 1(a) 1b 1c 2 3a . 4a 4b 5 6a 6c 6d KSA Core SAP (i) Final New Law MCQ: 1(i) option-(c) 1(ii) option-(d) 1(iii) option -(b) 1(iv) option-(c) 1(v)
KSA Core SAP (i) Final New Financial Reporting 1a 1b 1(a) 1b 1c 2 3a . 4a 4b 5 6a 6c 6d KSA Core SAP (i) Final New Law MCQ: 1(i) option-(c) 1(ii) option-(d) 1(iii) option -(b) 1(iv) option-(c) 1(v)
B.COM II COST ACCOUNTING
 The workings under the heading of Additional Working are not required according to the requirement of the examiner. These are only for understanding the solutions. For more help, visit 2014 B.COM II COST
The workings under the heading of Additional Working are not required according to the requirement of the examiner. These are only for understanding the solutions. For more help, visit 2014 B.COM II COST
ANIL SHARMA S CLASSES
 ANIL SHARMA S CLASSES {Marks: 100} (COSTING PAPER-FULL) {Time: 3 Hours} ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Q-1: What is meant by cost
ANIL SHARMA S CLASSES {Marks: 100} (COSTING PAPER-FULL) {Time: 3 Hours} ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Q-1: What is meant by cost
Microeconomics (Cost, Ch 7)
 Microeconomics (Cost, Ch 7) Lectures 10-11-12 Feb 09/13/16, 2017 7.1 MEASURING COST: WHICH COSTS MATTER? Economic Cost versus Accounting Cost Opportunity Cost accounting cost Actual expenses plus depreciation
Microeconomics (Cost, Ch 7) Lectures 10-11-12 Feb 09/13/16, 2017 7.1 MEASURING COST: WHICH COSTS MATTER? Economic Cost versus Accounting Cost Opportunity Cost accounting cost Actual expenses plus depreciation
COST ACCOUNTING b.com part II Regular & Private (SUPPLEMENTARY) Solved Paper. Compiled & Solved by: Sameer Hussain
 COST ACCOUNTING b.com part II 2014 Regular & Private (SUPPLEMENTARY) Solved Paper Compiled & Solved by: Sameer Hussain Instructions: (1) Attempt any FIVE questions. (2) All questions carry equal marks.
COST ACCOUNTING b.com part II 2014 Regular & Private (SUPPLEMENTARY) Solved Paper Compiled & Solved by: Sameer Hussain Instructions: (1) Attempt any FIVE questions. (2) All questions carry equal marks.
Learning Curve Theory
 16 Learning Curve Theory Question 1 An electronics firm which has developed a new type of fire-alarm system has been asked to quote for a prospective contract. The customer requires separate price quotations
16 Learning Curve Theory Question 1 An electronics firm which has developed a new type of fire-alarm system has been asked to quote for a prospective contract. The customer requires separate price quotations
BUY ASSETS INVENTORY BUSINESSES
 HOW WE BUY ASSETS INVENTORY BUSINESSES AND EXCESS FROM WE WOULD LIKE TO PURCHASE YOUR ASSETS AND COMPLETE PRODUCT INVENTORY AND PAY YOU IN 24 HOURS. Dear friend, We are interested in purchasing your complete
HOW WE BUY ASSETS INVENTORY BUSINESSES AND EXCESS FROM WE WOULD LIKE TO PURCHASE YOUR ASSETS AND COMPLETE PRODUCT INVENTORY AND PAY YOU IN 24 HOURS. Dear friend, We are interested in purchasing your complete
MGT402 Cost Accounting
 MGT402 Cost Accounting Which of the following statement measures the financial position of the entity on particular time? Income Statement Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement Statement of Retained Earning
MGT402 Cost Accounting Which of the following statement measures the financial position of the entity on particular time? Income Statement Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement Statement of Retained Earning
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs
 Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
10-1. Learning Objective. Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision.
 10-1 Learning Objective Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 10-2 Relevant Costs and Benefits A relevant cost is a cost that differs between alternatives. A relevant benefit
10-1 Learning Objective Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 10-2 Relevant Costs and Benefits A relevant cost is a cost that differs between alternatives. A relevant benefit
3 CVP Analysis and Decision making
 3 CVP Analysis and Decision making LEARNING OBJECTIVES : After studying this unit you will be able to : Understand meaning and theory of Marginal Costing. Explain difference between Marginal Costing and
3 CVP Analysis and Decision making LEARNING OBJECTIVES : After studying this unit you will be able to : Understand meaning and theory of Marginal Costing. Explain difference between Marginal Costing and
1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting period.
 Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting
Chapter 02 Cost Concepts and Behavior True / False Questions 1. The cost of an item is the sacrifice of resources made to acquire it. True False 2. An expense is a cost charged against revenue in an accounting
University Question Paper Two Marks
 University Question Paper Two Marks 1. List the application of Operations Research in functional areas of management. Answer: Finance, Budgeting and Investment Marketing Physical distribution Purchasing,
University Question Paper Two Marks 1. List the application of Operations Research in functional areas of management. Answer: Finance, Budgeting and Investment Marketing Physical distribution Purchasing,
TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM AND VARIANTS
 TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM AND VARIANTS Introduction to Lecture T: Welcome to the next exercise. I hope you enjoyed the previous exercise. S: Sure I did. It is good to learn new concepts. I am beginning to
TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM AND VARIANTS Introduction to Lecture T: Welcome to the next exercise. I hope you enjoyed the previous exercise. S: Sure I did. It is good to learn new concepts. I am beginning to
COST AUDIT REPORT THE THAL INDUSTRIES CORPORATION LIMITED YEAR ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, Submitted By:
 COST AUDIT REPORT THE THAL INDUSTRIES CORPORATION LIMITED YEAR ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2014 Submitted By: Ashiq & Company Chartered Accountants Office No-9, First Floor Liberty Center, LMQ Road, Multan Tel:
COST AUDIT REPORT THE THAL INDUSTRIES CORPORATION LIMITED YEAR ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2014 Submitted By: Ashiq & Company Chartered Accountants Office No-9, First Floor Liberty Center, LMQ Road, Multan Tel:
Accounting Technicians Ireland 2 nd Year Examination: Summer 2016 Paper: MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
 Accounting Technicians Ireland 2 nd Year Examination: Summer 2016 Paper: MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Monday 16 May 2016 2.30 p.m. to 5.30 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES In this examination paper the symbol
Accounting Technicians Ireland 2 nd Year Examination: Summer 2016 Paper: MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Monday 16 May 2016 2.30 p.m. to 5.30 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES In this examination paper the symbol
SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS. June KB 2 Business Management Accounting. All Rights Reserved
 SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS KB 2 Business Management Accounting June 2017 All Rights Reserved Answer 01 Relevant Learning Outcome/s: SECTION 1 1.2.1 Assess the key features of marginal costing and throughput accounting
SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS KB 2 Business Management Accounting June 2017 All Rights Reserved Answer 01 Relevant Learning Outcome/s: SECTION 1 1.2.1 Assess the key features of marginal costing and throughput accounting
INTER CA MAY PAPER 3 : COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUTING Branch: Multiple Date: Page 1
 INTER CA MAY 2018 PAPER 3 : COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUTING Branch: Multiple Date: Note: Question 1 is compulsory. Attempt any five from the rest. Note: All questions are compulsory. Question 1 (5 Marks
INTER CA MAY 2018 PAPER 3 : COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUTING Branch: Multiple Date: Note: Question 1 is compulsory. Attempt any five from the rest. Note: All questions are compulsory. Question 1 (5 Marks
Chapter 12 Applications in Manufacturing Sector. Book:- Waman S Jawadekar
 Chapter 12 Applications in Manufacturing Sector Book:- Waman S Jawadekar Introduction This chapter is an introduction to the business applications of MIS. For each application, inputs, which are processed
Chapter 12 Applications in Manufacturing Sector Book:- Waman S Jawadekar Introduction This chapter is an introduction to the business applications of MIS. For each application, inputs, which are processed
2. Standard costs imply a) Predetermined cost for a period b) Incurred cost c) Conversion cost d) Incremental cost
 QUESTION BANK PAPER: COST ACCOUNTING COURSE: B.Com (Semester IV) MCQs 1. The basic objective of cost accounting is a) Recording of cost b) Reporting of cost c) Cost control d) EarningProfit 2. Standard
QUESTION BANK PAPER: COST ACCOUNTING COURSE: B.Com (Semester IV) MCQs 1. The basic objective of cost accounting is a) Recording of cost b) Reporting of cost c) Cost control d) EarningProfit 2. Standard
Test Series: October, 2014
 MOCK TEST PAPER 2 FINAL COURSE: GROUP II PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Question No. 1 is compulsory Answer any five questions from the remaining six questions Test Series: October, 2014 Time
MOCK TEST PAPER 2 FINAL COURSE: GROUP II PAPER 5: ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Question No. 1 is compulsory Answer any five questions from the remaining six questions Test Series: October, 2014 Time
Type of Inventory. OVERVIEW In case of manufacturing concerns. Stores and Spares. Formulae for Determining Cost of Inventory
 CHAPTER 4 INVENTORIES LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Understand the meaning of term 'Inventory'. Learn the technique of Specific identification method, FIFO, Average
CHAPTER 4 INVENTORIES LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Understand the meaning of term 'Inventory'. Learn the technique of Specific identification method, FIFO, Average
Relevant Costs for Decision Making
 Relevant Costs for Decision Making Chapter Thirteen 13-2 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 13-3 Cost Concepts for Decision Making A relevant cost is
Relevant Costs for Decision Making Chapter Thirteen 13-2 Learning Objective 1 Identify relevant and irrelevant costs and benefits in a decision. 13-3 Cost Concepts for Decision Making A relevant cost is
ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS GUIDE ( ) E.C.O.-10
 1 ASSIGMET SOLUTIOS GUIDE (2016-2017) E.C.O.-10 Elements of Costing Disclaimer/Special ote: These are just the sample of the Answers/Solutions to some of the Questions given in the Assignments. These Sample
1 ASSIGMET SOLUTIOS GUIDE (2016-2017) E.C.O.-10 Elements of Costing Disclaimer/Special ote: These are just the sample of the Answers/Solutions to some of the Questions given in the Assignments. These Sample
Performance Management
 Monitoring Test MT Performance Management F5PM-MTA-Z6-A Answers & Marking Scheme 06 DeVry/Becker Educational Development Corp. RODBER CO Linear programming model x = monthly production of product X y =
Monitoring Test MT Performance Management F5PM-MTA-Z6-A Answers & Marking Scheme 06 DeVry/Becker Educational Development Corp. RODBER CO Linear programming model x = monthly production of product X y =
MTP_Final_ Syllabus 2012_December 2017_Set 2 Paper 15- Business Strategy & Strategic Cost Management
 Paper 15- Business Strategy & Strategic Cost Management Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountant of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15- Business Strategy &
Paper 15- Business Strategy & Strategic Cost Management Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountant of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15- Business Strategy &
Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination
 Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2017 Solutions, Examiners Comments & Marking Scheme NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting Technicians
Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2017 Solutions, Examiners Comments & Marking Scheme NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting Technicians
Problem Exercise 3-12
 Exercise 3-12 1. The overhead applied to Ms. Miyami s account would be computed as follows: 2002 2001 Estimated overhead cost (a)... $144,000 $144,000 Estimated professional staff hours (b)... 2,250 2,400
Exercise 3-12 1. The overhead applied to Ms. Miyami s account would be computed as follows: 2002 2001 Estimated overhead cost (a)... $144,000 $144,000 Estimated professional staff hours (b)... 2,250 2,400
PAPER 5 : COST MANAGEMENT QUESTIONS
 Decision Making - Profit Maximization PAPER 5 : COST MANAGEMENT QUESTIONS 1. ABC Co Ltd which produces household electronic gadget HIFY had 90% capacity utilization (4.5 lakh units) current year of Department
Decision Making - Profit Maximization PAPER 5 : COST MANAGEMENT QUESTIONS 1. ABC Co Ltd which produces household electronic gadget HIFY had 90% capacity utilization (4.5 lakh units) current year of Department
(ALL BATCHES) DATE: MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours
 (ALL BATCHES) DATE: 20.09.2018 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours PAPER 3 : COST ACCOUNTING Answer to questions are to be given only in English except in the case of candidates who have opted for Hindi
(ALL BATCHES) DATE: 20.09.2018 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours PAPER 3 : COST ACCOUNTING Answer to questions are to be given only in English except in the case of candidates who have opted for Hindi
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2016 Exam Paper, Solutions & Examiner s Comments Page 1 of 24 NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting
Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2016 Exam Paper, Solutions & Examiner s Comments Page 1 of 24 NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting
MTP_Final_Syllabus 2016_June 2018_Set 1
 Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making DoS, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management and Decision
Paper 15 Strategic Cost Management and Decision Making DoS, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 15 - Strategic Cost Management and Decision
Chapter 17 Job Order Costing Study Guide Solutions Fill-in-the-Blank Equations. Exercises. 1. Estimated activity base. 2. Underapplied. 3.
 Chapter 17 Job Order Costing Study Guide Solutions Fill-in-the-Blank Equations 1. Estimated activity base 2. Underapplied 3. Overapplied Exercises 1. An automobile manufacturer produces various lines of
Chapter 17 Job Order Costing Study Guide Solutions Fill-in-the-Blank Equations 1. Estimated activity base 2. Underapplied 3. Overapplied Exercises 1. An automobile manufacturer produces various lines of
Chapter 11. Decision Making and Relevant Information Linear Programming as a Decision Facilitating Tool
 Chapter 11 Decision Making and Relevant Information Linear Programming as a Decision Facilitating Tool 1 Introduction This chapter explores cost accounting for decision facilitating purposes It focuses
Chapter 11 Decision Making and Relevant Information Linear Programming as a Decision Facilitating Tool 1 Introduction This chapter explores cost accounting for decision facilitating purposes It focuses
Process Costing Joint and By Product CA Past Years Exam Question
 CA R. K. Mehta Process Costing Joint and By Product CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 May, 2012 A product passes through two processes A and B. During the year, the input to Process A of Basic raw
CA R. K. Mehta Process Costing Joint and By Product CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 May, 2012 A product passes through two processes A and B. During the year, the input to Process A of Basic raw
An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes
 CHAPTER 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Overview This chapter introduces the basic terminology of cost accounting. Communication among managers and management accountants is greatly facilitated
CHAPTER 2 An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Overview This chapter introduces the basic terminology of cost accounting. Communication among managers and management accountants is greatly facilitated
SYLLABUS. Class B.Com IV Sem. (All) Subject: Cost Accounting
 CLASS:-B.Com. IV Semester SYLLABUS Class B.Com IV Sem. (All) Subject: Cost Accounting Unit-I Unit- II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Cost: Meaning, Concept and Classification. Elements of Cost, Nature & Importance,
CLASS:-B.Com. IV Semester SYLLABUS Class B.Com IV Sem. (All) Subject: Cost Accounting Unit-I Unit- II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Cost: Meaning, Concept and Classification. Elements of Cost, Nature & Importance,
9.15 BOOKS RECOMMENDED
 241 5. What are the advantages of Cost Accounting? 6. What are the essentials of good costing system? 7. What are the various elements of costs? 8. Write short notes on: a) Cost centres b) Cost units c)
241 5. What are the advantages of Cost Accounting? 6. What are the essentials of good costing system? 7. What are the various elements of costs? 8. Write short notes on: a) Cost centres b) Cost units c)
Paper 8- Cost Accounting
 Paper 8- Cost Accounting Dos, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 8- Cost Accounting Full Marks : 100 Time allowed: 3 hours Section A Question
Paper 8- Cost Accounting Dos, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 8- Cost Accounting Full Marks : 100 Time allowed: 3 hours Section A Question
MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar
 MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L10 - Working Capital Management www.mba638.wordpress.com Learning Objectives 1. Model the cash conversion cycle and explain its components. 2.
MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L10 - Working Capital Management www.mba638.wordpress.com Learning Objectives 1. Model the cash conversion cycle and explain its components. 2.
MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar
 MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L9 - Working Capital Management www.mba638.wordpress.com Learning Objectives 1. Model the cash conversion cycle and explain its components. 2.
MBF1223 Financial Management Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L9 - Working Capital Management www.mba638.wordpress.com Learning Objectives 1. Model the cash conversion cycle and explain its components. 2.
AGGREGATE PLANNING PROBLEMS
 AGGREGATE PLANNING PROBLEMS Problem 1. ABC Corporation has developed a forecast for a group of items that has the following seasonal demand pattern. Quarter Demand Cumulative Demand 1 22 22 2 17 39 3 4
AGGREGATE PLANNING PROBLEMS Problem 1. ABC Corporation has developed a forecast for a group of items that has the following seasonal demand pattern. Quarter Demand Cumulative Demand 1 22 22 2 17 39 3 4
Operation and supply chain management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Operation and supply chain management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 37 Transportation and Distribution Models In this lecture, we
Operation and supply chain management Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 37 Transportation and Distribution Models In this lecture, we
SUPPLY. definition: Supply means the quantity offered for sale by sellers at particular prices, during a certain period of time.
 SUPPLY definition: Supply means the quantity offered for sale by sellers at particular prices, during a certain period of time. First factor affecting price is demand. Second factor affecting price is
SUPPLY definition: Supply means the quantity offered for sale by sellers at particular prices, during a certain period of time. First factor affecting price is demand. Second factor affecting price is
MGT402 Cost and management accounting. All online solved quiz by Fahid Mehmood (22/2/2014)
 MGT402 Cost and management accounting All online solved quiz by Fahid Mehmood (22/2/2014) Figure 1 Hope this file will help you n remember me in your prays Ist quiz solved by Fahid Mehmood (11/11/2013)
MGT402 Cost and management accounting All online solved quiz by Fahid Mehmood (22/2/2014) Figure 1 Hope this file will help you n remember me in your prays Ist quiz solved by Fahid Mehmood (11/11/2013)
10 Joint Products & By Products
 10 Joint Products & By Products BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE Basic Concepts 1. Joint Products and By-Products (i) Joint Products - Two or more products of equal importance, produced, simultaneously from
10 Joint Products & By Products BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE Basic Concepts 1. Joint Products and By-Products (i) Joint Products - Two or more products of equal importance, produced, simultaneously from
OPERATIONAL CASE STUDY February 2018 EXAM ANSWERS. Variant 5. The February 2018 exam can be viewed at
 OPERATIONAL CASE STUDY February 2018 EXAM ANSWERS Variant 5 The February 2018 exam can be viewed at SECTION 1 - BRIEFING NOTE SUPPLIER EVALUATION Financial stability: Financial stability of our suppliers
OPERATIONAL CASE STUDY February 2018 EXAM ANSWERS Variant 5 The February 2018 exam can be viewed at SECTION 1 - BRIEFING NOTE SUPPLIER EVALUATION Financial stability: Financial stability of our suppliers
Time: 60 Minutes Record : 10 Skill Test : 20 Total Marks : 30 Note: Problems are to be solved by using computers (Excel or any accounting package).
 Computer Lab - Practical Question Bank FACULTY OF COMMERCE, OSMANIA UNIVERSITY ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- B.Com (General) III
Computer Lab - Practical Question Bank FACULTY OF COMMERCE, OSMANIA UNIVERSITY ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- B.Com (General) III
COST ACCOUNTING B.com-2 Regular Annual Examination 2015
 B.com-2 COST ACCOUNTING Compiled & Solved By: JAHANGEER KHAN Q.1: MANUFACTURING CONCERN: Record of Muqeem and Baber shows the following information for 2015: Sales 500 T.V Sets Material Purchased Direct
B.com-2 COST ACCOUNTING Compiled & Solved By: JAHANGEER KHAN Q.1: MANUFACTURING CONCERN: Record of Muqeem and Baber shows the following information for 2015: Sales 500 T.V Sets Material Purchased Direct
Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination. Management Accounting (MA / OL 1-201)
 Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination Examination Date : 17 th November 2018 Number of Pages : 06 Examination
Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination Examination Date : 17 th November 2018 Number of Pages : 06 Examination
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Code: MB0048. Section-A
 Time: 2 hours OPERATIONS RESEARCH Code: MB0048 Max.Marks:140 Section-A Answer the following 1. Which of the following is an example of a mathematical model? a. Iconic model b. Replacement model c. Analogue
Time: 2 hours OPERATIONS RESEARCH Code: MB0048 Max.Marks:140 Section-A Answer the following 1. Which of the following is an example of a mathematical model? a. Iconic model b. Replacement model c. Analogue
CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction. Simulation for general business management
 CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction Simulation for general business management What is Cesim SimFirm? Cesim SimFirm is an online business simulation game that develops students understanding of the complexity of
CESIM SIMFIRM Introduction Simulation for general business management What is Cesim SimFirm? Cesim SimFirm is an online business simulation game that develops students understanding of the complexity of
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Pricing Decisions & Profitability Analysis
 Pricing Decisions & Profitability Analysis Economic theory The optimum selling price is the price at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. 1 Problems with applying economic theory 1. Difficult and
Pricing Decisions & Profitability Analysis Economic theory The optimum selling price is the price at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. 1 Problems with applying economic theory 1. Difficult and
Overheads/Job and Batch Costing. RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service
 CA R. K. Mehta Overheads/Job and Batch Costing CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 Nov, 2006 RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service departments Human
CA R. K. Mehta Overheads/Job and Batch Costing CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 Nov, 2006 RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service departments Human
P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination
 Management Level Paper P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination Examiner s Answers Note: Some of the answers that follow are fuller and more comprehensive than would be expected from a well-prepared
Management Level Paper P2 Performance Management September 2014 examination Examiner s Answers Note: Some of the answers that follow are fuller and more comprehensive than would be expected from a well-prepared
