VALUING GHG SAVINGS FROM ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN URBAN AREAS
|
|
|
- Emery Wade
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PAPER for 26 th Conference of Australian Institutes of Transport Research CSIRO TRANSPORT FUTURES Bayview Conference Centre Melbourne 8-10 December 2004 VALUING GHG SAVINGS FROM ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN URBAN AREAS Leorey Marquez (CSIRO), Nariida Smith (CSIRO) and Justine Gannon (CSIRO) ABSTRACT CSIRO is undertaking a study to establish the value of Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) for ameliorating growing environmental, economic and social impacts of increasing traffic in urban areas. This paper, reporting results from early stages of the work, discusses the benefits of estimating the relative impacts of alternative ITS measures at a detailed level across entire urban areas. The benefits of applying these estimates to calculate, over time, monetary savings of early application of ITS and some approaches to estimation are introduced. The approaches are illustrated via a case study which shows how, at a strategic planning level, estimates of the value of ITS as major tools for reducing traffic disbenefits can be obtained in a cost effective manner. CONTACT AUTHOR: Dr Nariida Smith Leader Transport Futures Team CSIRO Manufacturing & Infrastructure Technology PO Box 310 North Ryde 1670 NSW AUSTRALIA Phone Fax nariida.smith@csiro.au
2 1. INTRODUCTION The volume of traffic in urban areas across the world is increasing. Even if growth in passenger traffic finally plateaus because drivers need to time other activities such as work and sleep, freight traffic will continue to grow with freight trips occurring 24/7. Numbers of social, economic and environmental impacts are associated with this growth including injury and death from crashes, economic costs of congestion, and environment impacts from noise, air pollution and green house gas emissions. There is no single solution for the amelioration of all these problems. However we contend that Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) offer the most promising solutions in the short to medium term for two reasons: ITS can be retro-fitted. Existing roads can be instrumented with traffic management equipment. Telematic devices to improve driving efficiency can be fitted to existing vehicles The Scope of Impacts. A traffic management system that improves traffic flows would improve the efficiencies of all vehicles from heavy trucks, through to large sports utility vehicles (SUV) to old, badly tuned vehicles with low fuel efficiency. The CSIRO has commenced a research program to develop decision support tools for planners and policy makers to use in assessing the benefits for Australia, and urban Australia in particular, of widespread application of ITS technologies. This paper presents the first results of this research which is developing methodologies to: estimate the relative impacts of alternative ITS applications at a detailed network level so that the best type of ITS and the best location for that technology is identified across the urban road network to obtain maximum benefits estimate a range of social, economic and environmental cost and benefits, allowing for the best choices and best placement will differ according to the interests of stakeholders estimate the extra benefits derived from early application of the ITS and the associated value in using ITS as the major tools to reduce traffic disbenefits. As this research is part of a larger energy research initiative aimed at both energy security and reduction of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions (CSIRO, 2004), there is particular interest in valuing early intervention strategies. Global warming is cumulative so options to reduce GHG emissions in the short term are particularly valuable. However global warming is not the only cumulative impact of traffic. Numbers of health impacts are also cumulative. The impacts on the health of vulnerable populations, such as the young and the elderly, are cumulative. So too are the impacts of noise. Moreover, early monetary savings for business and the community from direct reduction in fuel costs due to congestion will translate to significant benefits over CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 1
3 time. It has recently been suggested congestion accounts for 25% of urban freight costs in one of Australia s cities (Batchelor, 2004). Since the reliability of benefits over time depend on initial impacts analysis, the first priority is to develop reliable estimates of current benefits. The benefits needed to inform strategic planning rather than those developed in impact analysis of particular projects are the focus of this work. Thus the estimation procedures cover larger areas (usually entire urban areas), longer time frames, and multiple options, so cost and time effective methods are needed. In this context, appropriate use of secondary data and choice of measurement and analysis scale is vital. This paper discusses these issues together with our suggested approaches and presents some early results from a case study. The paper is arranged as follows. The following section discusses the relative merits of Top Down and Bottom Up analyses in investigating impacts of ITS. This is followed by the introduction of the concept of Outcome Scenarios which will be used in estimating the impacts of multiple alternative ITS measures. A case study demonstrating the approach is then presented and some comments on the valuation of benefits are provided. Although these results are for an Australian city, we believe the approaches used are generally applicable to cities around the world. 2. TOP DOWN OR BOTTOM UP In Europe, the USA and Japan general global or top down estimates of the potential benefits of ITS have been made. The European Road Transport Telematics Implementation Co-ordination Organisation (ERTICO), the body coordinating ITS activities throughout Europe, predicted and was working toward a set of benefits from ITS applications by the year 2017 (ERTICO, 1998 and European Commission, 2001) including: 25% reduction in travel times 40 hours per traveller saved each year by the use of automatic tolling systems 25% reduction in freight costs by improved efficiency of freight movement and fleet operations and, 50% less pollution in city centres by using advanced traffic management systems. The Federal ITS program in the United States, funded under the Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21), has similar goals (ITS America, 2002). These include: reducing congestion to save one billion gallons of petrol per annum and the associated emissions CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 2
4 13% reduction in travel time through better road conditions and 8%-10% reduction in transit travel time and a 13% reduction in fuel consumption through better signal coordination 10% 15% reduction in truck operating costs. In Japan, ITS is expected to be the most effective measure for solving serious road traffic problems. A national project entitled "e-japan Priority Policy Program 2003" (MLIT, 2003) aims to achieve benefits such as: reduction of total loss due to traffic congestion by 6% with VICS (Vehicle Information and Communication System) via a national deployment rate of 30% elimination of about 70% of traffic congestion on Japanese expressways via ETC (Electronic Toll Collection System), AHS (Advanced Cruise-Assist Highway Systems), and other ITS deployments lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions of CO2 by about 10%-15% and nitrous oxide by 30% from improved driving efficiency through ITS. At the same time, estimates of the full local advantage of individual ITS measures via careful bottom up cost-benefit and ITS assessment programs are being published regularly. For example, the US Department of Transport collects the results of studies in an ITS Cost and Benefits Database ( which has become a primary repository of information on ITS applications for both practitioners and policy makers. Unfortunately, both the top-down and the bottom-up approaches encounter significant difficulties in providing a full estimation of the benefits of multiple, alternative, integrated ITS measures on an urban-wide scale. While it would be possible, in theory, to mount a vast costbenefit study with multiple ITS applications applied, it would be too costly in practice. At the same time, global estimates of benefits, even if they can be transferred to the local situation cannot be used to estimate the best location of alternative measures. It is particularly important that characteristics and problems associated with individual locations within urban areas be matched to the types of ITS measures that best meet these problems. A number of local studies support the expectation that the location of ITS measures affects their impacts. Thus for transport planners and policy makers seeking some concrete indications of the impacts of ITS measures in their city or region. An approach based on outcome scenarios, as detailed below, may be helpful. 3. OUTCOME SCENARIOS AND MODEL FRAMEWORK Many urban authorities have created strategic travel models based on transport modelling software platforms such as EMME2, Trips, or Transcad to assist planning and managing development. Strategic travel models include multi-modal traffic assignment capability to CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 3
5 assign trips to various layers of transport network infrastructure. It is possible to manipulate such models to: change origins and destinations of trips, change the numbers of trips, and/or change the attributes such as maximum speed or capacity of portions of the transport network. These are changes in outcome. The models do not need to know the specific measures contributing to each unit of change. By grouping together ITS measures into generic classes that produce similar outcomes, such as increasing speed or decreasing travel time, planners can identify policy outcome scenarios that produce changes in the performance of the transport network as a result of successful implementation alternative ITS measures. In this study we considered ITS measures in generic groups that lead to four outcome scenarios. The scenarios are: Reduced Traffic Volumes: This scenario is produced by a combination of ITS technologies to improve alternative modes of travel or discouraging peak travel. These technologies include efficient operating of public transport (transit management systems); automated control of high occupancy vehicle lanes to improve compliance (road management systems); and automated toll collection allowing more widespread application of road charging and differential charging to shift traffic from peaks. Improved Highway Capacity: This scenario is produced by deploying ITS such as adaptive or integrated traffic signal management on groups of links in the network, such as freeways and arterials; and incident detection and management systems. Trip Route and Time Changes: This scenario is produced by using ITS to provide real time information to drivers with information about specific links of strategic importance in the network to promote alternative trip routes or alternative times when traffic is heavy Reduced Numbers of Freight Trips: This scenario is produced by deploying ITS to freight vehicle operation to increase loading, schedule trips more efficiently and reduce empty running. To test the effectiveness of these scenarios in their local area, the analyst needs to be able to provide estimates of the amount and location of the changes to be modelled. An extensive literature search using both the ITS Benefits and Cost Database and other sources was carried out to find reasonable estimates of the likely impacts based on currently observed results. The modelling procedure was designed to incorporate both sensitivity testing of the initial values and ongoing updates as better estimates become available. The procedure was also designed to allow for spatial variability in the application of changes. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 4
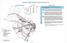
6 A prototype of the model, called the ITS-GHG Tool has been developed with the primary role of estimating the GHG impacts from selected outcome scenarios. The ITS-GHG Tool was implemented in Transcad using three components illustrated in Figure 1. Transcad was chosen as the platform for the ITS-GHG Tool as it is both a transport modelling package as required by the Route Assignment Module, as well as a geographic information system (GIS) for the spatial analysis required by the Link Emissions Module and the Long-term Impacts Module. The benefit estimation procedure is currently external to the package because it is still under development. GHG benefits and some first estimates of the values of a range of benefits are described in the case study below. Figure 1: Components of ITS-GHG Tool 4. A CASE STUDY OF SYDNEY Sydney has a good radial rail network and an extensive bus network, but as some 80% of household travel originates and ends in areas of low density, Sydney is very car dependent as evidenced by the car s 70% mode share (HTS, 2001). Freight traffic is increasing even more rapidly than car traffic with a particularly rise in light commercial vehicle traffic. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 5
7 ITS outcome scenarios were created based on the policy outcome scenarios described above to consider: Congestion Reduction: The car trip matrices for the AM Peak and the PM Peak were reduced by 15% across the board. No changes were made to the car trip matrices out of peak, or to the commercial vehicle trip matrices at any time. Better Traffic Management : For arterial roads, all relevant volume delay functions, which describe how delay builds up on a link as traffic volume approaches link capacity, were altered so that at saturation point, the road would be operating at 3kph faster than previously, and 10% would be added to the traffic capacity of the road. Improvement was restricted to arterial roads because motorways and freeways generally perform well. Real Time Information: The same volume delay changes proposed for better traffic management were applied just to the roads bearing the brunt of urban traffic flows, principal radial routes and main orbital routes. Logistics Efficiencies: Load factors were increased (i.e. higher loads per vehicle, meaning fewer vehicle trips to move a given quantity of goods around the city) with some consolidation of loads as a result (i.e. a transfer of some freight from light commercials to rigid tucks, and from rigid trucks to articulated) with spatial variation due to differing capacity for higher loads between industries. Passenger and freight trip data for four time of day periods morning and evening peaks, day inter-peak and night were provided by the Transport and Population Data Centre of the New South Wales Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources. The latest freight trip data available at the start of the work was for 1996 and thus these demonstration results are for 1996 (CTS, 1996). They are currently being revised with more recent data. However the 1996 figures are useful for demonstration purposes of relative impacts. Figure 2 shows the differences in GHG emissions from freight and passenger between scenarios and the base case over the entire urban area for an entire weekday. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 6
8 Real Time Traffic Information Logistics Changes Traffic Management Lower Congestion 0% 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% % Reduction CO2e (Urban 24hrs) Passenger Vehicles Commercial Vehicles Figure 2: Potential ITS Impacts on GHG Emissions Note that this is just an example of impacts based on implementation on sets of roads in the network. The results shown are not for the actual implementation which gives most GHG reduction but for the implementation judged by transport planners to be a likely early implementation. However the average over the day shows the impact of ITS under assumptions of implementation outcomes, which are quite conservative especially for the realtime information and better traffic management scenarios. Moreover, the average hides larger relative impacts in particular time of day periods and particular locations. The decision support tool is able to provide the emissions and changes in emissions on each and every link in the road network. It also provides vehicle kilometres travelled, vehicles hours travelled and fuel consumed (see Table 1). This provides a wealth of information for estimating savings in fuel and environmental cost due to alternative ITS measures at a very detailed level. This could be useful to a wider range of planners and policy makers other than those charged with reducing GHG emissions. The following section describes how monetary estimates of environmental savings might be estimated. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 7
9 Table 1: Scenario Impacts on Distance and Time and GHG Emissions (24 Hours) Trips ( 000) VKT ( 000) VHT ( 000) Average Speed (kph) CO2(e) Tonnes Per Day Scenario 1996 Base Lower congestion Net reduction Better traffic management Net reduction Cars 7,113 6, ,113 0 Logistical changes Net reduction Real-time traffic info. Net reduction 7, ,113 0 LCVs Rigids Artics All vehicles 7,720 7, , , ,720 0 Cars 77,469 72,259 5,210 77, , , LCVs 4,989 4, , ,977 1,012 4, Rigids 2,409 2, , , Artics All vehicles 85,546 80,290 5,256 85, ,737 1,809 85, Cars 2,371 2, , , , LCVs Rigids Artics All vehicles 2,612 2, , , , Cars LCVs Rigids Artics All vehicles Cars 16,322 14,835 1,487 15, , , LCVs 1,307 1, , , , Rigids 1,428 1, , , , Artics All vehicles 19,690 18,135 1,555 19, , , CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 8
10 VALUING ITS BENEFITS To enable different types of benefits to be compared, a common base is needed and monetary costs and benefits provide this base. Internal costs such as fuel and travel time are borne by road users and can be estimated given each user s travel distance, time and fuel use. The external costs such as noise, air pollution and global warming are borne by other individuals, and by society at large, and are therefore harder to estimate. Since many societal costs are externalities that are not traded in the market, valuation is not simple and no single method is appropriate for all cases. Most authors use an environmental valuation framework (Envalue, 1995): Valuations correspond to the aggregate payments that society (as the sum total of the individuals who make it up) would be prepared to make for these goods. (Envalue, 1995). There are numbers of recent studies estimating the environmental impacts of transport. See for instance External Costs of Transport. Accident, Environmental, and Congestion Costs in Western Europe (Infras/IWW, 2000). Table 2 shows some common methods of evaluation. Table 2: Common Methods for Valuing Transport Externalities Method Market Based Description Damage Costs: that measure the actual costs of damages or of repairing the damage; Avoidance Costs: that reflect the cost of preventing the damage Surrogate Market Based Opinion Based where actual impacts can t be measured, so proxies such as changes in property values (hedonic pricing) in areas of high traffic noise or extreme air pollution, are used Values taken from responses to surveys or expert opinions. These methods include a range of stated preference techniques which test the communities willingness to pay for an environmental gain or willingness to accept an environmental loss In general, tangible costs such as medical treatment costs are assessed using market-based methods whereas, intangible costs such as loss of quality of life or pain and suffering, are better assessed by opinion-based techniques. Average External Costs per traffic unit are estimated to allow comparisons between situations or modes. The usual per unit cost for passenger travel is vehicle passenger kilometres and for freight is tonne-kilometres i.e. the number of kilometres travelled multiplied by the number of tonnes carried. Table 3 suggested by Tsolakis and Houghton (2003) shows a range of environmental benefits estimated in this CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 9
11 manner for Australian conditions as an example. While some of these figures will be site specific and benefit transfer cannot really be applied to other sites, they do provide some indication of the potential scope and magnitude of the value of benefits. Table 3: Calibrated values of total environmental costs (2001 Australian Dollars). (Source: Tsolakis and Houghton, 2003) Cars (AUD$ per 1000 vehiclekm) Light Duty Trucks (AUD$ per 1000 tonne-km) Heavy Duty Trucks (AUD$ per 1000 tonne-km) Air Pollution Noise (site specific) Climate change Nature and Landscape (site specific) Upstream/Downstream costs Urban Separation Costs Average Note: Climate change costs are based on 8% CO 2 emission target Unfortunately a simple linking of cost per distance travelled for passenger vehicles or load by distance for freight vehicles will not suffice for estimating ITS benefits. As can be seen from Table 1 under the Better Traffic Management scenario, GHG, in CO2 equivalent emissions, fell but the distance travelled VKT actually rose slightly due to smoother traffic flows. Therefore estimating change in GHG cost using $ per 1000 vkt would indicate increased GHG cost when clearly less GHG should mean reduced costs. The first step in solving this problem is to assemble dollar costs for environmental impacts of transport based on effects rather than causes. Thus instead of basing GHG costs on distance travelled, they are based on emissions. Such methods of estimation are less used because they add complexity. It is no longer possible to simply add all the environmental costs per vehicle kilometre and multiply by the vehicles kilometres to get total cost. However simplicity in calculation is not an advantage if it gives a wrong answer. Thus a set of costs based on quantity of GHG emissions is being developed as are new estimates of the other environmental costs of transport, few of which are simply due to distance travelled. Fortunately as can be seen from Table 2 estimations of environmental damage are based on effects, for example willingness to pay to avoid air pollution, so it is possible to develop a set of benefits linked to emission and other effects of traffic. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 10
12 The first of the estimates for this study relate to GHG abatement. Using the European Union abatement cost of 38 (A$65) per tonne of CO 2, which is based on a Kyoto protocol emission target of 8%, the monetary savings from reducing GHG and hence limiting climate change by ITS measures were calculated for CO2-equivalent emissions and scenarios for the Sydney of As can be seen, these benefits alone are significant and the total benefit from all environmental impacts will be greater. The challenge is to make sure that current estimates as well as long-term forecasts, drawn from multiple sources, are comparable with those of other benefits. Table 4: Indicative daily GHG savings due to ITS measures for 1996 Sydney Scenario Lower congestion Better traffic management Logistics changes Real-time traffic information Cars 96,700 21,300 5,300 27,000 Reduction from 1996 Base Case (2004 AUD) LCVs 1,800 1,500 14,100 2,400 Rigids 1, ,200 1,700 Artics , All vehicles 101,100 24,200 42,400 31,700 The data from this analysis, when used in conjunction with costing data for the implementation and operation of each of the scenarios will enable detailed economic analysis to assist policy decision makers and investors on whether to implement these technologies and where. This information would also form the basis of a better understanding of who the benefits are attributed to, as the basis for any cost sharing arrangements that may lead to public private partnership funding arrangements. CONCLUSION This paper has argued that since ITS can be retrofitted, existing infrastructure and vehicles can have wide spread impacts on the efficiency of all vehicles, old and new, large and small. ITS measures are particularly valuable for reducing the negative impacts of road traffic. However their value may be under-appreciated. In this context, it is particularly useful for planners and policy makers to have tools that estimate benefits. There are numbers of options available for estimation of local benefits of particular projects at micro level. At the other end of the scale, global estimates of benefits at macro level are available. However there is a need for meta-level estimation methods and tools to assess urban wide benefits of ITS, which can incorporate detailed examinations of network level impacts, since ITS implementations are CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 11
13 clearly location specific, but can also give the city wide assessment of impacts needed by policy makers. A potentially cost effective method for estimating daily benefits of ITS measures has been developed. While the case study application estimates GHG impacts for global warming, the detailed information on distances, times, fuel and emissions can have wider application in the estimation of other environmental benefits. However in common with other efficiency measures which reduce impacts without reducing travel, the benefits cannot be simply estimated using the typical costs by distance travelled, as impact changes while distance does not. There is value in developing methods which allow for this assessment of ITS for two reasons. First efficiency measures for ITS are particularly attractive when they limit the disadvantages of traffic while retaining the benefits of travel mobility for the community and access to goods and services for business and industry. Secondly, they can be implemented early and therefore have cumulative advantage over time. Ongoing research will provide methods for estimating those advantages. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS: The authors wish to thank Dr. John Wright and the CSIRO Energy Transformed Flagship for their continuing support for research on low energy vehicles and intelligent transport systems. The authors also wish to thank Dr. Rocco Zito and Prof. Michael Taylor of the Transport Systems Center (UNISA) for making the results of their emissions modelling work available for this study. Finally, the authors are grateful for the contributions and guidance on transport modelling for the Sydney GMR provided by the NSW Transport and Population Data Centre (TPDC). REFERENCES CSIRO, 2004, Energy Transformed. accessed June Batchelor, P., 2004 Transport Ministers Address at Victorian Supply Chain Summit. Melbourne, August ERTICO, 1998 Intelligent City Transport: a Guidebook to Intelligent Transport Systems Brussels: ERTICO European Commission, 2001 White Paper- European Transport Policy for 2010: Time to Decide accessed June ITS America, 2002, Delivering the future of transportation: the national intelligent transport systems program plan: A ten-year vision, January MLIT, 2003, ITS Handbook , Japanes Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, accessed June US Dept of Transport website CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 12
14 EMME/2 Release 9.0 User s Manual, Inro Consultants Trips Website, accessed June HTS, 2001, Key Transport Indicators. Transport and Population Data Centre, accessed June CTS, 1996, Commercial Transport Study, Transport and Population Data Centre, accessed June Envalue, 1995, A searchable environmental valuation database, NSW Environmental Protection Authority, accessed June Infras/IWW, 2000, External Costs of Transports - Accidents, Environmental and Congestion Costs in Western Europe, Union Internationale des Chemins de Fer UIR, Brussels. Tsolakis, D. and N. Houghton, 2003, Valuing environmental externalities, Proceedings of the 21 st ARRB and 11 th REAAA Conference, May 2003, Cairns, Queensland, Australia. CSIRO Transport Futures 26 th CAITR, December 2004 page 13
Submission in response to: New South Wales Draft Climate Change Strategic Plan and. Draft Plan to Save Energy and Money
 Submission in response to: New South Wales Draft Climate Change Strategic Plan and Draft Plan to Save Energy and Money December 2016 1 This document has been prepared by the Freight on Rail Group (the
Submission in response to: New South Wales Draft Climate Change Strategic Plan and Draft Plan to Save Energy and Money December 2016 1 This document has been prepared by the Freight on Rail Group (the
National Transport Commission Submission to Infrastructure Victoria
 National Transport Commission Submission to Infrastructure Victoria Automated and zero emission vehicles March 2018 Submission outline 1 Introduction 3 1.1 The purpose of this submission 3 About the NTC
National Transport Commission Submission to Infrastructure Victoria Automated and zero emission vehicles March 2018 Submission outline 1 Introduction 3 1.1 The purpose of this submission 3 About the NTC
Environmental Parameter Values [PV4]
![Environmental Parameter Values [PV4] Environmental Parameter Values [PV4]](/thumbs/84/91038484.jpg) Environmental Parameter Values [PV4] Providing Feedback This draft document has been published for stakeholder feedback. Submissions are due Monday 9 February 2015 All submissions should be in writing
Environmental Parameter Values [PV4] Providing Feedback This draft document has been published for stakeholder feedback. Submissions are due Monday 9 February 2015 All submissions should be in writing
A more detailed description of Transportation, and its programs and initiatives can be found at
 Business Plan 2018 21 Transportation Accountability Statement This business plan was prepared under my direction, taking into consideration our government s policy decisions as of March 7, 2018. original
Business Plan 2018 21 Transportation Accountability Statement This business plan was prepared under my direction, taking into consideration our government s policy decisions as of March 7, 2018. original
Reducing CO2 and Energy Use Through Livable Communities: What s s Possible and Next Steps
 Reducing CO2 and Energy Use Through Livable Communities: What s s Possible and Next Steps November 12, 2010 By Michael Replogle, Global Policy Director and Founder Institute for Transportation and Development
Reducing CO2 and Energy Use Through Livable Communities: What s s Possible and Next Steps November 12, 2010 By Michael Replogle, Global Policy Director and Founder Institute for Transportation and Development
MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND. John de Pont, TERNZ
 MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND John de Pont, TERNZ ABSTRACT Over the last 10 years, road freight in New Zealand has grown at approximately 1.3 times the rate of growth of real gross domestic product (RGDP) and
MODELLING FREIGHT DEMAND John de Pont, TERNZ ABSTRACT Over the last 10 years, road freight in New Zealand has grown at approximately 1.3 times the rate of growth of real gross domestic product (RGDP) and
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October David Gargett and David Cosgrove
 27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Organisation(s): Predicting traffic growth in Australian cities David Gargett and David
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Organisation(s): Predicting traffic growth in Australian cities David Gargett and David
Project 24 Rail Transport Energy Efficiency and Sustainability. Project background Commenced July Completed December 2006
 Rail Research Industry Report Project 24 Rail Transport Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Project background Commenced July 2002 - Completed December 2006 Results and Outcomes: 1. Energy efficiency
Rail Research Industry Report Project 24 Rail Transport Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Project background Commenced July 2002 - Completed December 2006 Results and Outcomes: 1. Energy efficiency
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion
 Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
1 DRAFT Model Capability
 1 DRAFT Model Capability As part of the evaluation of the proposed Western Distributor, additional traffic counts and travel time surveys were collected. The model was updated and refined in several areas,
1 DRAFT Model Capability As part of the evaluation of the proposed Western Distributor, additional traffic counts and travel time surveys were collected. The model was updated and refined in several areas,
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links
 Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Intelligent Transport Systems Action Plan - Key questions and answers
 MEMO/08/789 Brussels, 16 December 2008 Intelligent Transport Systems Action Plan - Key questions and answers Summary Typical and well known ITS application are the so-called "GPS" navigation systems in
MEMO/08/789 Brussels, 16 December 2008 Intelligent Transport Systems Action Plan - Key questions and answers Summary Typical and well known ITS application are the so-called "GPS" navigation systems in
Urban Congestion The COAG Review
 Urban Congestion The COAG Review Lindsay. Jacob 1, Anthony. Ockwell 2, David. Gargett 1, David. Cosgrove 1 1 Department of Transport & Regional Services, Canberra, ACT, Australia 2 Meyrick & Associates,
Urban Congestion The COAG Review Lindsay. Jacob 1, Anthony. Ockwell 2, David. Gargett 1, David. Cosgrove 1 1 Department of Transport & Regional Services, Canberra, ACT, Australia 2 Meyrick & Associates,
Benefit Cost Analysis Narrative
 Chicago Region Environmental and Transportation Efficiency Program (CREATE) Grade Separations of: GS21a - Union Pacific and 95 th Street GS11 - Belt Railway Company of Chicago and Columbus Ave. GS 9 -
Chicago Region Environmental and Transportation Efficiency Program (CREATE) Grade Separations of: GS21a - Union Pacific and 95 th Street GS11 - Belt Railway Company of Chicago and Columbus Ave. GS 9 -
INTEGRATED TRANSPORT PLANNING: A QUEENSLAND EXPERIENCE
 INTEGRATED TRANSPORT PLANNING: A QUEENSLAND EXPERIENCE Louw, J. Queensland Transport. ABSTRACT Transport plays a vital role in maintaining quality of life and enhancing attractiveness for industry development
INTEGRATED TRANSPORT PLANNING: A QUEENSLAND EXPERIENCE Louw, J. Queensland Transport. ABSTRACT Transport plays a vital role in maintaining quality of life and enhancing attractiveness for industry development
ITS Action Plan- Internet Consultation
 ITS Action Plan- Internet Consultation * What are Intelligent transport Systems (ITS)? Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) are generally defined as a collection of applications and services based on advanced
ITS Action Plan- Internet Consultation * What are Intelligent transport Systems (ITS)? Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) are generally defined as a collection of applications and services based on advanced
Illawarra Business Chamber/Illawarra First. Submission on NSW Draft Freight and Ports Plan
 Illawarra Business Chamber/Illawarra First Submission on NSW Draft Freight and Ports Plan Illawarra Business Chamber A division of the NSW Business Chamber Level 1, 87-89 Market Street WOLLONGONG NSW 2500
Illawarra Business Chamber/Illawarra First Submission on NSW Draft Freight and Ports Plan Illawarra Business Chamber A division of the NSW Business Chamber Level 1, 87-89 Market Street WOLLONGONG NSW 2500
Transport and Main Roads measuring congestion
 Transport and Main Roads measuring congestion Frans Dekker David Johnston International Roads Federation/Roads Australia Conference Sydney, 2015 1 Overview 1. The why 2. What we do 3. Prioritisation tools
Transport and Main Roads measuring congestion Frans Dekker David Johnston International Roads Federation/Roads Australia Conference Sydney, 2015 1 Overview 1. The why 2. What we do 3. Prioritisation tools
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT. accompanying document to the COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 16.12.2008 SEC(2008) 3084 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT accompanying document to the COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION Action Plan for the
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 16.12.2008 SEC(2008) 3084 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT accompanying document to the COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION Action Plan for the
Regional Evaluation Decision tool for Smart Growth
 Regional Evaluation Decision tool for Smart Growth Maren Outwater, Robert Cervero, Jerry Walters, Colin Smith, Christopher Gray, Rich Kuzmyak Objectives This project is one of the SHRP 2 Capacity projects
Regional Evaluation Decision tool for Smart Growth Maren Outwater, Robert Cervero, Jerry Walters, Colin Smith, Christopher Gray, Rich Kuzmyak Objectives This project is one of the SHRP 2 Capacity projects
Transportation Planning and Climate Change
 Transportation Planning and Climate Change Analysis and Use of New Tools in the Central Puget Sound Region New Partners for Smart Growth Conference February 4, 2010 2 Agenda Setting the Stage Climate Change
Transportation Planning and Climate Change Analysis and Use of New Tools in the Central Puget Sound Region New Partners for Smart Growth Conference February 4, 2010 2 Agenda Setting the Stage Climate Change
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004
 Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
Appendix L Greenhouse Gas 4-part Strategy
 Appendix L Greenhouse Gas 4-part Strategy Supplementary information regarding options for further reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the Puget Sound region State and Federal Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Appendix L Greenhouse Gas 4-part Strategy Supplementary information regarding options for further reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the Puget Sound region State and Federal Greenhouse Gas Emissions
UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK
 Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
Abstract UK Road Pricing Feasibility Study: Modelling the Impacts Elizabeth Cox 1 UK In July 2003, the UK government set up a comprehensive study to examine how a new system of charging for road use could
7.0 Benefit/Cost Analysis
 7.0 Benefit/Cost Analysis 7.0 Benefit/Cost Analysis This section presents detailed instructions on how to conduct benefit-cost analysis using a spreadsheet tool developed for the Phase I evaluation; this
7.0 Benefit/Cost Analysis 7.0 Benefit/Cost Analysis This section presents detailed instructions on how to conduct benefit-cost analysis using a spreadsheet tool developed for the Phase I evaluation; this
MOBILITICS. Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles. June 12, 2018
 MOBILITICS Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles June 12, 2018 Connected and Automated Vehicles are everywhere. Light Duty (personal or shared) Shuttles Bus Freight Parcel Delivery
MOBILITICS Scenario Planning and Modeling Connected & Automated Vehicles June 12, 2018 Connected and Automated Vehicles are everywhere. Light Duty (personal or shared) Shuttles Bus Freight Parcel Delivery
QUT Digital Repository:
 QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ Sirikijpanichkul, Ackchai and Ferreira, Luis (2008) Modelling Impacts of Urban Freight Terminal Location Decisions. In Mao, Baohua and Tian, Zongzhong
QUT Digital Repository: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/ Sirikijpanichkul, Ackchai and Ferreira, Luis (2008) Modelling Impacts of Urban Freight Terminal Location Decisions. In Mao, Baohua and Tian, Zongzhong
The Auckland Transport Models Project - Overview and Use to Date -
 The Auckland Transport Models Project - Overview and Use to Date - John Davies (Auckland Regional Council) Jojo Valero (Auckland Regional Council) David Young (David Young Consulting) Auckland Transport
The Auckland Transport Models Project - Overview and Use to Date - John Davies (Auckland Regional Council) Jojo Valero (Auckland Regional Council) David Young (David Young Consulting) Auckland Transport
Final Report Basic Analysis (Phase A) Final Version 10/24/2017
 BaslerFonds, Swiss Association of Cities, and Additional Partners Use of Automated Vehicles in Everyday Life - Potential Applications and Effects in Switzerland Final Report Basic Analysis (Phase A) Final
BaslerFonds, Swiss Association of Cities, and Additional Partners Use of Automated Vehicles in Everyday Life - Potential Applications and Effects in Switzerland Final Report Basic Analysis (Phase A) Final
The Western Corridor Transportation Study A Bold New Step in a Brave New World or Traditional Transport Planning Recycled?
 Anthony W Brennand 1, Graham Taylor 2 and Steven Knowles 3 1 Greater Wellington Regional Council, Wellington, New Zealand 2 Transit New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand 3 Maunsell Limited, Wellington,
Anthony W Brennand 1, Graham Taylor 2 and Steven Knowles 3 1 Greater Wellington Regional Council, Wellington, New Zealand 2 Transit New Zealand, Wellington, New Zealand 3 Maunsell Limited, Wellington,
Sustainable Transportation in New Zealand
 One of a number of discussion papers produced by the IPENZ Presidential Task Committee on Sustainability during 2003 and 2004. Andrew G. Macbeth, MWH New Zealand Ltd. ( andrew.g.macbeth@mwhglobal.com )
One of a number of discussion papers produced by the IPENZ Presidential Task Committee on Sustainability during 2003 and 2004. Andrew G. Macbeth, MWH New Zealand Ltd. ( andrew.g.macbeth@mwhglobal.com )
Key Questions in International Transport Policy
 Key Questions in International Transport Policy Jari Kauppila, Senior Economist InterTran seminar Helsinki, 30 Nov 2015 Intergovernmental Organisation 57 member countries (23 non-oecd) focussing on transport
Key Questions in International Transport Policy Jari Kauppila, Senior Economist InterTran seminar Helsinki, 30 Nov 2015 Intergovernmental Organisation 57 member countries (23 non-oecd) focussing on transport
INNOVATIVE CONCEPTS AND NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REGIONAL MULTI-JURISDICTIONAL INTEGRATED TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT
 INNOVATIVE CONCEPTS AND NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REGIONAL MULTI-JURISDICTIONAL INTEGRATED TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT Joseph K. Lam, P.Eng., President, Systems Business Perry Craig, P.Eng., Principal, Systems Business
INNOVATIVE CONCEPTS AND NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR REGIONAL MULTI-JURISDICTIONAL INTEGRATED TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT Joseph K. Lam, P.Eng., President, Systems Business Perry Craig, P.Eng., Principal, Systems Business
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT
 9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
Government Policy Statement on Land Transport 2018/ /28. DRAFT (FOR ENGAGEMENT ) NOT GOVERNMENT POLICY February 2017
 DRAFT (FOR ENGAGEMENT ) NOT GOVERNMENT POLICY February 2017 Government Policy Statement on Land Transport 2018/19 2027/28 DRAFT GOVERNMENT POLICY STATEMENT Contents 1 Land transport context 1 A: Role of
DRAFT (FOR ENGAGEMENT ) NOT GOVERNMENT POLICY February 2017 Government Policy Statement on Land Transport 2018/19 2027/28 DRAFT GOVERNMENT POLICY STATEMENT Contents 1 Land transport context 1 A: Role of
Nature Conservation Council of NSW. Sustainable Transport Policy
 Nature Conservation Council of NSW Sustainable Transport Policy (As endorsed by the Annual Conference, October 2002) Introduction In 1999 substantial work was undertaken to draft an NCC Sustainable Transport
Nature Conservation Council of NSW Sustainable Transport Policy (As endorsed by the Annual Conference, October 2002) Introduction In 1999 substantial work was undertaken to draft an NCC Sustainable Transport
Sustainable Transport in the 21st Century
 FUELLING THE CLIMATE 2011 Sustainable Transport in the 21st Century European Perspectives Hamburg, 20 May 2011 Matthew Ledbury, Community of European Railway and Infrastructure Companies (CER) 1 CER CONTENTS
FUELLING THE CLIMATE 2011 Sustainable Transport in the 21st Century European Perspectives Hamburg, 20 May 2011 Matthew Ledbury, Community of European Railway and Infrastructure Companies (CER) 1 CER CONTENTS
Putting travellers in the picture
 M 3 MATTISSE Overview Brochure Putting travellers in the picture MATTISSE delivers the essential information for people on the move MATTISSE (Midlands Advanced Transportation and Telematics Information
M 3 MATTISSE Overview Brochure Putting travellers in the picture MATTISSE delivers the essential information for people on the move MATTISSE (Midlands Advanced Transportation and Telematics Information
Mr. Sungwon LEE The Korea Transport Institute
 SEMINAR ON OVERCOMING BORDER CROSSING OBSTACLES 5-6 March 2009, Paris IMPROVING EFFICIENCY IN THE LOGISTICS SECTOR FOR SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT DEVELOPMENT IN THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA Mr. Sungwon LEE The Korea
SEMINAR ON OVERCOMING BORDER CROSSING OBSTACLES 5-6 March 2009, Paris IMPROVING EFFICIENCY IN THE LOGISTICS SECTOR FOR SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORT DEVELOPMENT IN THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA Mr. Sungwon LEE The Korea
The True Costs of Transport
 NEW UPDATE STUDY ON EXTERNAL COSTS Time to Act Measuring the external costs of European transport modes The volume of transport in Europe has more than doubled since 1970 1. This increase in transport
NEW UPDATE STUDY ON EXTERNAL COSTS Time to Act Measuring the external costs of European transport modes The volume of transport in Europe has more than doubled since 1970 1. This increase in transport
Congestion Management Process (CMP)
 Congestion Management Process (CMP) Introduction The Congestion Management Process (CMP) is a systematic, data-driven, and regionally accepted approach that aims to improve the performance of the transportation
Congestion Management Process (CMP) Introduction The Congestion Management Process (CMP) is a systematic, data-driven, and regionally accepted approach that aims to improve the performance of the transportation
ITS and Air Quality A Critical Look
 ITS and Air Quality A Critical Look April 6, 2005 1.212 Introduction to ITS Professor Joseph Sussman Doctoral Candidate, Technology, Management and Policy Engineering Systems Division, MIT Outline Is ITS
ITS and Air Quality A Critical Look April 6, 2005 1.212 Introduction to ITS Professor Joseph Sussman Doctoral Candidate, Technology, Management and Policy Engineering Systems Division, MIT Outline Is ITS
Transportation Cost Analysis:
 Victoria Transport Policy Institute www.vtpi.org info@vtpi.org 1250 Rudlin Street, Victoria, BC, V8V 3R7, CANADA Phone & Fax (250) 360-1560 Efficiency - Equity - Clarity Transportation Cost Analysis: Techniques,
Victoria Transport Policy Institute www.vtpi.org info@vtpi.org 1250 Rudlin Street, Victoria, BC, V8V 3R7, CANADA Phone & Fax (250) 360-1560 Efficiency - Equity - Clarity Transportation Cost Analysis: Techniques,
Moving Freight An update on road freight network access
 Moving Freight An update on road freight network access Roads Australia Network Reliability Workshop Russell Hoelzl Director (Freight) 23 June 2015 1 Our values 2 Queensland freight movement General freight
Moving Freight An update on road freight network access Roads Australia Network Reliability Workshop Russell Hoelzl Director (Freight) 23 June 2015 1 Our values 2 Queensland freight movement General freight
Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally. Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia. 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
 Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia Sustainable Urban Design and Development ~ Role of EST Country Report
Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia Sustainable Urban Design and Development ~ Role of EST Country Report
Greater Golden Horseshoe Transportation Plan
 Greater Golden Horseshoe Transportation Plan Transportation Profile Executive Summary October 2017 PREPARED BY Urban Strategies Inc. and HDR for the Ministry of Transportation TRANSPORTATION PROFILE -
Greater Golden Horseshoe Transportation Plan Transportation Profile Executive Summary October 2017 PREPARED BY Urban Strategies Inc. and HDR for the Ministry of Transportation TRANSPORTATION PROFILE -
Multi-modality assessments in promoting sustainable urban traffic
 Juha Hulkkonen Climate Neutral Cities, 23rd September 2009, Geneva Multi-modality assessments in promoting sustainable urban traffic Table of contents Multimodal transport maturity assessment model Project
Juha Hulkkonen Climate Neutral Cities, 23rd September 2009, Geneva Multi-modality assessments in promoting sustainable urban traffic Table of contents Multimodal transport maturity assessment model Project
Transportation Concurrency
 2015 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
2015 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
Transportation Concurrency
 2017 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
2017 Frequently Asked Questions About. Transportation Concurrency Q. What is Transportation Concurrency? A. Transportation Concurrency is both a State law requirement and a City pre-application development
6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS
 6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS 6.1 MODEL RUN SUMMARY NOTEBOOK The Model Run Summary Notebook (under separate cover) provides documentation of the multiple
6.0 CONGESTION HOT SPOT PROBLEM AND IMPROVEMENT TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL ANALYSIS 6.1 MODEL RUN SUMMARY NOTEBOOK The Model Run Summary Notebook (under separate cover) provides documentation of the multiple
17 July Jeff Tryens Executive Director SA Strategic Plan: Community Connection GPO Box 2343 ADELAIDE SA Dear Jeff
 Royal Automobile Association of South Australia Inc. ABN 90 020 001 807 101 Richmond Road, Mile End, SA 5031 Phone (08) 8202 4600 Fax (08) 82024520 www.raa.net 17 Jeff Tryens Executive Director SA Strategic
Royal Automobile Association of South Australia Inc. ABN 90 020 001 807 101 Richmond Road, Mile End, SA 5031 Phone (08) 8202 4600 Fax (08) 82024520 www.raa.net 17 Jeff Tryens Executive Director SA Strategic
Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally. Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia. 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
 Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia Sustainable Urban Design and Development ~ Role of EST Country Report
Intergovernmental Eleventh Regional Environmentally Sustainable Transport (EST) Forum in Asia 2-5 October 2018 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia Sustainable Urban Design and Development ~ Role of EST Country Report
WELLINGTON NORTHERN CORRIDOR. Project Summary Statement 21 December 2009
 WELLINGTON NORTHERN CORRIDOR Project Summary Statement 21 December 2009 1 Table of Contents 1. Purpose of Document 2. Strategic Context 3. Benefits 4. Project Scope and Economics 5. Implementation Plan
WELLINGTON NORTHERN CORRIDOR Project Summary Statement 21 December 2009 1 Table of Contents 1. Purpose of Document 2. Strategic Context 3. Benefits 4. Project Scope and Economics 5. Implementation Plan
Regional Performance Measures Annual Progress Report TPO Board - 2/4/2016 Presentation by: Chris Wichman, Senior Planner
 2015 TPO Board - 2/4/2016 Presentation by: Chris Wichman, Senior Planner Overview History and definition of performance-based planning & programming Review of 2015 TPO Board Action Requested 2 History
2015 TPO Board - 2/4/2016 Presentation by: Chris Wichman, Senior Planner Overview History and definition of performance-based planning & programming Review of 2015 TPO Board Action Requested 2 History
Bus Industry Confederation Response to COAG Road Reform Plan Funding and Implementation Issues Paper. Submission by the Bus Industry Confederation
 Bus Industry Confederation Response to COAG Road Reform Plan Funding and Implementation Issues Paper Submission by the Bus Industry Confederation May 2011 Bus Industry Confederation Inc. Last Updated 08
Bus Industry Confederation Response to COAG Road Reform Plan Funding and Implementation Issues Paper Submission by the Bus Industry Confederation May 2011 Bus Industry Confederation Inc. Last Updated 08
Queensland Freight Strategy
 Department of Transport and Main Roads Queensland Freight Strategy Advancing Freight in Queensland 1 The State of Queensland, March 2019. Published by the Department of Transport and Main Roads, 1 William
Department of Transport and Main Roads Queensland Freight Strategy Advancing Freight in Queensland 1 The State of Queensland, March 2019. Published by the Department of Transport and Main Roads, 1 William
Transport, Health & Safety. Driving better public health outcomes
 Transport, Health & Safety Driving better public health outcomes Assoc. Professor Brett Hughes Director, Curtin - Monash Accident Research Centre, Curtin University School of Public Health May 2010 Overview
Transport, Health & Safety Driving better public health outcomes Assoc. Professor Brett Hughes Director, Curtin - Monash Accident Research Centre, Curtin University School of Public Health May 2010 Overview
RISSB Cost-Benefit Analysis
 Rail Industry Safety and Standards Board RISSB Cost-Benefit Analysis Board Briefing - Board Briefing Board Briefing Prepared for Rail Industry Safety and Standards Board Prepared by AECOM Australia Pty
Rail Industry Safety and Standards Board RISSB Cost-Benefit Analysis Board Briefing - Board Briefing Board Briefing Prepared for Rail Industry Safety and Standards Board Prepared by AECOM Australia Pty
Calculating Mode Shift and Congestion Relief-Related Greenhouse Gas Displacement For the Current Year (see last slide for contact information)
 Calculating Mode Shift and Congestion Relief-Related Greenhouse Gas Displacement For the Current Year (see last slide for contact information) 1 Step 1: Estimate Reductions in Annual Auto Vehicles Miles
Calculating Mode Shift and Congestion Relief-Related Greenhouse Gas Displacement For the Current Year (see last slide for contact information) 1 Step 1: Estimate Reductions in Annual Auto Vehicles Miles
Draft Submission to the Inquiry into National Freight and Supply Chain Priorities. August 2017
 Draft Submission to the Inquiry into National Freight and Supply Chain Priorities August 2017 KEY POINTS Local government welcomes the government s development of a new freight and ports plan and looks
Draft Submission to the Inquiry into National Freight and Supply Chain Priorities August 2017 KEY POINTS Local government welcomes the government s development of a new freight and ports plan and looks
GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA!
 International Experiences Driving Managed Mobility GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA! Darren Henderson, WSP USA M1, Melbourne, VIC MANAGED FREEWAYS The most important transportation strategy you ve probably never
International Experiences Driving Managed Mobility GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA! Darren Henderson, WSP USA M1, Melbourne, VIC MANAGED FREEWAYS The most important transportation strategy you ve probably never
INCIDENT MANAGEMENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT & OPERATIONS (TSM&O) FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION DISTRICT SIX
 INCIDENT ROAD RANGERS RISC IRV Road Rangers Service Patrols provide motorist assistance and incident management services in Miami-Dade County 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. The fleet assists stranded
INCIDENT ROAD RANGERS RISC IRV Road Rangers Service Patrols provide motorist assistance and incident management services in Miami-Dade County 24 hours per day, 7 days per week. The fleet assists stranded
Long-term Plan Transport Proposal. 29 October 2014
 Long-term Plan Transport Proposal 29 October 2014 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Two Networks... 5 What will it cost?... 12 What are the benefits?... 15 Meeting the government s transport objectives...
Long-term Plan Transport Proposal 29 October 2014 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Two Networks... 5 What will it cost?... 12 What are the benefits?... 15 Meeting the government s transport objectives...
IDS. Pavement Cost Impact Assessment from Increased Vehicle Mass Limits - Calculation Sheet Guide
 IDS Pavement Cost Impact Assessment from Increased Vehicle Mass Limits - Pavement Cost Impact Assessment from Increased Vehicle Mass Limits This document has been prepared for the benefit of the IDS. No
IDS Pavement Cost Impact Assessment from Increased Vehicle Mass Limits - Pavement Cost Impact Assessment from Increased Vehicle Mass Limits This document has been prepared for the benefit of the IDS. No
Transport Model for Scotland. Kevin Lumsden MVA
 1. INTRODUCTION Transport Model for Scotland Kevin Lumsden MVA Transport Model for Scotland (TMfS) is a multi-modal transport demand and assignment model with an interactive Land Use model. The model area
1. INTRODUCTION Transport Model for Scotland Kevin Lumsden MVA Transport Model for Scotland (TMfS) is a multi-modal transport demand and assignment model with an interactive Land Use model. The model area
Australia's transport is falling behind on energy efficiency
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2014 Australia's transport is falling behind on
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2014 Australia's transport is falling behind on
Vehicle kilometres travelled by road. Summary. Environmental Report Card March Getting worse. Total distance travelled (Total VKT)
 Vehicle kilometres travelled by road Environmental Report Card March 2009 Summary Transport is a vital link that brings people and goods together across New Zealand. We rely on it to get to work and for
Vehicle kilometres travelled by road Environmental Report Card March 2009 Summary Transport is a vital link that brings people and goods together across New Zealand. We rely on it to get to work and for
Urban Traffic Management Approaches to Achieve Sustainability
 Urban Traffic Management Approaches to Achieve Sustainability Prof. Dr.-Ing. Manfred Boltze Transport Planning and Traffic Engineering, Technische Universität Darmstadt Conference The Future of Traffic
Urban Traffic Management Approaches to Achieve Sustainability Prof. Dr.-Ing. Manfred Boltze Transport Planning and Traffic Engineering, Technische Universität Darmstadt Conference The Future of Traffic
ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF SUSTAINABLE MOBILITY
 DIRECTORATE GENERAL FOR INTERNAL POLICIES POLICY DEPARTMENT B: STRUCTURAL AND COHESION POLICIES TRANSPORT AND TOURISM ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF SUSTAINABLE MOBILITY STUDY Abstract This study highlights the economic
DIRECTORATE GENERAL FOR INTERNAL POLICIES POLICY DEPARTMENT B: STRUCTURAL AND COHESION POLICIES TRANSPORT AND TOURISM ECONOMIC ASPECTS OF SUSTAINABLE MOBILITY STUDY Abstract This study highlights the economic
Perspectives on Intelligent Transportation and Telematics
 Perspectives on Intelligent Transportation and Telematics Workshop on Intelligent Transportation and Telematic Systems University of California, San Diego Ronald E. Boenau, P.E. Federal Transit Administration
Perspectives on Intelligent Transportation and Telematics Workshop on Intelligent Transportation and Telematic Systems University of California, San Diego Ronald E. Boenau, P.E. Federal Transit Administration
How Future Vehicles Will Revolutionise Freight Logistics - Creating Australia s Logistics Future. Dr Steve Nuttall Director, ACA Research May 2017
 How Future Vehicles Will Revolutionise Freight Logistics - Creating Australia s Logistics Future Dr Steve Nuttall Director, ACA Research May 2017 Content 2 4 6 CAV In Logistics: Science Fiction Or Fact?
How Future Vehicles Will Revolutionise Freight Logistics - Creating Australia s Logistics Future Dr Steve Nuttall Director, ACA Research May 2017 Content 2 4 6 CAV In Logistics: Science Fiction Or Fact?
Investigating the Environmental Costs of Deteriorating Road Conditions in South Africa
 Investigating the Environmental Costs of Deteriorating Road Conditions in South Africa L Mashoko, W L Bean*, W JvdM STEYN* CSIR, Built Environment, P O Box 395, Pretoria, 0001 Tel: 012 841-4466; Email:
Investigating the Environmental Costs of Deteriorating Road Conditions in South Africa L Mashoko, W L Bean*, W JvdM STEYN* CSIR, Built Environment, P O Box 395, Pretoria, 0001 Tel: 012 841-4466; Email:
Transportation Vision and Challenges for the Future Industry Perspective
 Transportation Vision and Challenges for the Future Industry Perspective C. Michael Walton, Ph.D., P.E. PE The University of Texas at Austin 1 2 3 4 5 We have two classes of forecasters: Those who don
Transportation Vision and Challenges for the Future Industry Perspective C. Michael Walton, Ph.D., P.E. PE The University of Texas at Austin 1 2 3 4 5 We have two classes of forecasters: Those who don
Buffalo Niagara Integrated Corridor Management Project. ENTERPRISE Webinar Keir Opie, Cambridge Systematics September 26, 2016
 Buffalo Niagara Integrated Corridor Management Project ENTERPRISE Webinar Keir Opie, Cambridge Systematics September 26, 2016 1 Buffalo-Niagara ICM Corridors I-190 ICM Corridor Cross Border Corridor 2
Buffalo Niagara Integrated Corridor Management Project ENTERPRISE Webinar Keir Opie, Cambridge Systematics September 26, 2016 1 Buffalo-Niagara ICM Corridors I-190 ICM Corridor Cross Border Corridor 2
Drivers of Congestion Growth & Change
 Drivers of Congestion Growth & Change A Congestion Blueprint Transport Policy Branch, Department of Transport and Main Roads 1 Our values, our diversity 2 Queensland Government s objectives for the community
Drivers of Congestion Growth & Change A Congestion Blueprint Transport Policy Branch, Department of Transport and Main Roads 1 Our values, our diversity 2 Queensland Government s objectives for the community
Telematics System dedicated for Provisioning of On-Line Information about Predicted Occupancy of Highway Parking Areas
 Telematics System dedicated for Provisioning of On-Line Information about Predicted Occupancy of Highway Parking Areas Tomas ZELINKA, Michal JERABEK, Martin SROTYR, Zdenek LOKAJ, Petr KUMPOST Faculty of
Telematics System dedicated for Provisioning of On-Line Information about Predicted Occupancy of Highway Parking Areas Tomas ZELINKA, Michal JERABEK, Martin SROTYR, Zdenek LOKAJ, Petr KUMPOST Faculty of
Asset Management Plan Strategic Context
 Asset Management Plan 2012 2015 Strategic Context Asset Management Plan 2012 2015 Strategic Context Quality Record Sheet REPORT STATUS Final ORIGINATOR Asset Management Unit Infrastructure Division Contributors:
Asset Management Plan 2012 2015 Strategic Context Asset Management Plan 2012 2015 Strategic Context Quality Record Sheet REPORT STATUS Final ORIGINATOR Asset Management Unit Infrastructure Division Contributors:
This presentation is one of the support materials prepared for the capacity building program Building Leaders in Urban Transport Planning (LUTP).
 1 Cluster 1/Module 2 (C1/M2): Complexity of Urban Transport. This presentation is one of the support materials prepared for the capacity building program Building Leaders in Urban Transport Planning (LUTP).
1 Cluster 1/Module 2 (C1/M2): Complexity of Urban Transport. This presentation is one of the support materials prepared for the capacity building program Building Leaders in Urban Transport Planning (LUTP).
Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments
 Roads Australia Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments Des Snook Main Roads Western Australia 26 September 2014 1 Roads Australia Traffic Congestion Workshop in Perth 17 September 2013
Roads Australia Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments Des Snook Main Roads Western Australia 26 September 2014 1 Roads Australia Traffic Congestion Workshop in Perth 17 September 2013
Introduction to Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Transportation Systems 1 PART III: TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION 2 Chapter 24: Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) 3 Introduction ITS combines high technology and improvements in information
Introduction to Transportation Systems 1 PART III: TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION 2 Chapter 24: Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) 3 Introduction ITS combines high technology and improvements in information
CIVE 240. Urban Issues in North America. Adedamola, Adedapo (Dami) Department of Civil Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo.
 CIVE 240 Urban Issues in North America Adedamola, Adedapo (Dami) Department of Civil Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo. ON, N2L 3G1 Objectives of the Lecture In the context of sustainable growth
CIVE 240 Urban Issues in North America Adedamola, Adedapo (Dami) Department of Civil Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo. ON, N2L 3G1 Objectives of the Lecture In the context of sustainable growth
AS THE EFFECT ON BRIDGE BARRIERS
 ABSTRACT AS5100.2 2017 THE EFFECT ON BRIDGE BARRIERS David Coe, Senior Principal, Pitt & Sherry The revision to AS5100 in 2017 resulted in significant changes to the design loading and impact heights for
ABSTRACT AS5100.2 2017 THE EFFECT ON BRIDGE BARRIERS David Coe, Senior Principal, Pitt & Sherry The revision to AS5100 in 2017 resulted in significant changes to the design loading and impact heights for
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004
 27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Organisation(s): Economic development and investment in transportation infrastructure an
27th Australasian Transport Research Forum, Adelaide, 29 September 1 October 2004 Paper title: Author(s) name(s): Organisation(s): Economic development and investment in transportation infrastructure an
Developing a Low Emission Vehicle Strategy for SA Discussion Paper (Nov 2010)
 Developing a Low Emission Vehicle Strategy for SA Discussion Paper (Nov 2010) DTEI and the Climate Change Division of the Department of the Premier and Cabinet has released a Discussion Paper dealing with
Developing a Low Emission Vehicle Strategy for SA Discussion Paper (Nov 2010) DTEI and the Climate Change Division of the Department of the Premier and Cabinet has released a Discussion Paper dealing with
50 YOUNG PEOPLE IN STICKING TOGETHER PROJECT COMPARED TO JOBACTIVE CONTROL GROUP
 Providing proven, sustained attachment to the labour market for young Australians who have experienced long-term unemployment. A model that translates easily to people of all ages who are long-term unemployed,
Providing proven, sustained attachment to the labour market for young Australians who have experienced long-term unemployment. A model that translates easily to people of all ages who are long-term unemployed,
Report on National Activities and Projects Regarding ITS Priority Areas
 Republic of Cyprus Report on National Activities and Projects Regarding ITS Priority Areas Implementing Co-ordinating Agency: Public Works Department, Ministry of Communications and Works, 165 Strovolos
Republic of Cyprus Report on National Activities and Projects Regarding ITS Priority Areas Implementing Co-ordinating Agency: Public Works Department, Ministry of Communications and Works, 165 Strovolos
Greater Newcastle Transport Plan
 Greater Newcastle Transport Plan Engineers Australia submission 16 February 2018 11 National Circuit, Barton ACT 2600 Tel: 02 6270 6555 Email: publicaffairs@engineersaustralia.org.au www.engineersaustralia.org.au
Greater Newcastle Transport Plan Engineers Australia submission 16 February 2018 11 National Circuit, Barton ACT 2600 Tel: 02 6270 6555 Email: publicaffairs@engineersaustralia.org.au www.engineersaustralia.org.au
Northern Virginia Region Draft Needs Summary
 Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
AN EXAMINATION OF POTENTIALS IN APPLICATION OF SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORTATION PERFORMANCE INDICATORS (STPI) TO SRI LANKA
 AN EXAMINATION OF POTENTIALS IN APPLICATION OF SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORTATION PERFORMANCE INDICATORS (STPI) TO SRI LANKA C. Hewawasam 1, J.M.S.J. Bandarara 2, 1 Lecturer, Department of Town & Country Planning,
AN EXAMINATION OF POTENTIALS IN APPLICATION OF SUSTAINABLE TRANSPORTATION PERFORMANCE INDICATORS (STPI) TO SRI LANKA C. Hewawasam 1, J.M.S.J. Bandarara 2, 1 Lecturer, Department of Town & Country Planning,
Introduction. 1 McKinstry/Bounajm. 1 In this paper, any reference to short lines also includes regional railways.
 Investigating the Social Benefits of Short Line Freight Railways in Canada Robert McKinstry, Railway Association of Canada Fares Bounajm, Railway Association of Canada Introduction The Canada Transportation
Investigating the Social Benefits of Short Line Freight Railways in Canada Robert McKinstry, Railway Association of Canada Fares Bounajm, Railway Association of Canada Introduction The Canada Transportation
State Strategies to Reduce Traffic Congestion. National Conference of State Legislatures November, 2007
 State Strategies to Reduce Traffic Congestion National Conference of State Legislatures November, 2007 More People More Freight 40 million more people in last 15 years Highway travel increase 1990-2003,
State Strategies to Reduce Traffic Congestion National Conference of State Legislatures November, 2007 More People More Freight 40 million more people in last 15 years Highway travel increase 1990-2003,
JULY This guide is to be used for the Sustainable Transport Credits in the Transport Category.
 JULY 2015 This guide is to be used for the Sustainable Transport Credits in the Transport Category. For information on this document, please contact: Green Building Council of Australia (02) 8239 6218
JULY 2015 This guide is to be used for the Sustainable Transport Credits in the Transport Category. For information on this document, please contact: Green Building Council of Australia (02) 8239 6218
Implications of Automated Vehicles for Long-Range Planning in the GGH
 Ministry of Transportation Implications of Automated Vehicles for Long-Range Planning in the GGH Michael Casey, Ministry of Transportation Spring Pragma Conference Tomorrow Has Arrived: Cities and Autonomous
Ministry of Transportation Implications of Automated Vehicles for Long-Range Planning in the GGH Michael Casey, Ministry of Transportation Spring Pragma Conference Tomorrow Has Arrived: Cities and Autonomous
Transport Domain Plan. Draft list of Enduring Questions
 Transport Domain Plan Draft list of Engagement Draft v1.0 August 2014 Introduction The Transport Domain Plan is jointly led by Statistics NZ and the Ministry of Transport. It is a project that will identify
Transport Domain Plan Draft list of Engagement Draft v1.0 August 2014 Introduction The Transport Domain Plan is jointly led by Statistics NZ and the Ministry of Transport. It is a project that will identify
Deployment and Evaluation of ITS Technology in Work Zones
 Deployment and Evaluation of ITS Technology in Work Zones Authors: Rob Bushman, P.Eng. University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada e-mail: rjb230@mail.usask.ca phone: (306) 653-6600 fax:
Deployment and Evaluation of ITS Technology in Work Zones Authors: Rob Bushman, P.Eng. University of Saskatchewan Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada e-mail: rjb230@mail.usask.ca phone: (306) 653-6600 fax:
EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION
 EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION Hussein Dia and Nick Cottman Department of Civil Engineering The University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia 4072 E-mail: H.Dia@uq.edu.au
EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION Hussein Dia and Nick Cottman Department of Civil Engineering The University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia 4072 E-mail: H.Dia@uq.edu.au
Workshop #3 Needs Assessment. Ministry of Transportation IBI Group March 27, 2014
 Workshop #3 Ministry of Transportation IBI Group Opening Remarks and Introductions page 1 Study Overview and Update page 2 History of the Study This study builds upon the 2002 MTO study Simcoe Area Transportation
Workshop #3 Ministry of Transportation IBI Group Opening Remarks and Introductions page 1 Study Overview and Update page 2 History of the Study This study builds upon the 2002 MTO study Simcoe Area Transportation
IMPACT STUDY ON INTELLIGENT MOBILITY. A sustainability impact framework and case analysis of energy and environment
 IMPACT STUDY ON INTELLIGENT MOBILITY A sustainability impact framework and case analysis of energy and environment April 2013 Foreword For many years, the industry and its detractors have identified the
IMPACT STUDY ON INTELLIGENT MOBILITY A sustainability impact framework and case analysis of energy and environment April 2013 Foreword For many years, the industry and its detractors have identified the
Developments in Cooperative Intelligent Vehicle- Highway Systems and Human Factors Implications
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2001 Driving Assessment Conference Aug 17th, 12:00 AM Developments in Cooperative Intelligent Vehicle- Highway Systems and Human Factors
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2001 Driving Assessment Conference Aug 17th, 12:00 AM Developments in Cooperative Intelligent Vehicle- Highway Systems and Human Factors
Zenith Model Recalibration and Validation Version Review of VISTA. February Public Transport Victoria
 Zenith Model Recalibration and Validation Version 3.0.0 Review of VISTA February 2014 Public Transport Victoria Page Intentionally Left Blank Review of VISTA Draft Report Project No. ZML-VIC-Year4 COPYRIGHT:
Zenith Model Recalibration and Validation Version 3.0.0 Review of VISTA February 2014 Public Transport Victoria Page Intentionally Left Blank Review of VISTA Draft Report Project No. ZML-VIC-Year4 COPYRIGHT:
