Willow Company produces lawn mowers. One of its plants produces two versions of mowers: a basic model and a deluxe model. The deluxe model has a
|
|
|
- Henry Wright
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Illustration Problem 2: Production-Based Costing vs. Activity Based Costing Willow Company produces lawn mowers. One of its plants produces two versions of mowers: a basic model and a deluxe model. The deluxe model has a sturdier frame, a higher horsepower engine, a wider blade, and mulching capability. At the beginning of the year, the following data were prepared p for this plant:
2 Basic Model Deluxe Model Expected quantity 40,000 20,000 Selling price $180 $360 Pi Prime Costs $80 $160 Machine hours 5,000 5,000 Direct labor hours 10,000 10,000 Engineering i support (hours) 1,500 4,500 Receiving (orders processed) Material handling (number of moves) 2,000 4,000 Purchasing (number of requisitions) Maintenance (hours used) 1,000 3,000 Paying suppliers (invoices processed) Setting up equipment (number of setups) 20 60
3 Additionally, the following overhead activity costs are reported: Maintaining i i equipment $114,000 Engineering support 120,000 Material handling? Setting up equipment 96,000 Purchasing materials 60,000 Receiving gg goods 40,000 Paying suppliers 30,000 Providing space 20,000 TOTAL $?
4 Other Information: Facility-level costs are allocated in proportion to machine hours (provides a measure of time the facility is used by each product). Material handling uses three inputs: two forklifts, gasoline to operate the forklift, and three operators. The three operators are paid a salary of $40,000 each. The operators spend 25 percent of their time on the receiving activity and 75 percent on moving goods (material handling). Gasoline costs $3 per move. Depreciation amounts to $6,000 per forklift per year.
5 REQUIRED: 1. Calculate the cost of the material-handling activity. Label the cost assignments as driver tracing and direct tracing. Identify the resource drivers. 2. Calculate the cost per unit for each product using direct labor hours to assign all overhead costs. 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. 4. Using the pool rates computed in Requirement 2, calculate the cost per unit for each product. Compare these costs with those calculated using functional-based costing. Which cost is most accurate? Explain.
6 1. Calculate the cost of the material-handling activity. Label the cost assignments as driver tracing and direct tracing. Identify the resource drivers. Labor and gasoline are driver tracing: Labor: [3 people x $40,000 = $120,000] (0.75 x $120,000) = $ 90,000 Time = resource driver = DLH (direct labor hrs) Gasoline: ($3 x 6,000 moves)= 18,000 Moves = resource driver Depreciation: ($6,000 x 2 forklifts) = 12,000 Direct tracing Total Cost $120,000000
7 2. Calculate the cost per unit for each product using direct labor hours to assign all overhead costs. Plug in Material handling cost that was just figured to get total overhead activity costs: Maintaining equipment $114,000 Engineering support 120,000 Material handling 120, Setting up equipment 96,000 Purchasing materials 60,000 Receiving goods 40,000 Paying suppliers 30,000 Providing space 20,000 TOTAL $600,000
8 2. Calculate the cost per unit for each product using direct labor hours to assign all overhead costs. Plant-wide rate: (10,000 Basic DLH + 10,000 Deluxe DLH = 20,000 DLH) $600,000 / 20,000 DLH = $30 / DLH Unit Cost: Cost per Unit Basic Deluxe Prime Costs $80.00 $ Overhead: Basic: $30/DLH x 10,000 DLH = $300,000 $300,000 / 40,000 units = $7.50/unit 7.50 Deluxe: $30/DLH x 10,000 DLH = $300,000 $300,000 / 20,000 units = $15.00/unit Total $87.50 $175.00
9 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 1: LEVEL ACTIVITY DRIVER Unit Level: Batch Level: None Material Handling Setting Up Equip # Moves # Setups Product- Sustaining: Maintaining Equip Eng. Support Maint. Hrs. Used Eng. Support Hrs. Purchasing Mat. Receiving Goods Paying Suppliers # Requisitions # Rec. Orders # Invoices Facility Level: Providing Space Machine Hrs.
10 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 2: COST DRIVER: CONSUMPTION BASIC MODEL DELUXE MODEL POOL MEASURE # Moves # Setups B A 2000/6000 = /80 = /6000 = /80 = T C H Batch Level Costs: 2,000 moves for Basic / Total # moves 6,000 = ,000 moves for Deluxe / Total # moves 6,000 = 0.67
11 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 2: COST DRIVER: CONSUMPTION MEASURE Maint. hours used Eng. Support hours # Requisitions processed # Rec. orders processed # Invoices P S R U O S D T U A C I T N - I N G BASIC MODEL DELUXE MODEL POOL 1000/4000 = 0.25 R U 3000/4000 = /6000 = /6000 = /300 = /300 = /750 = /750 = /750 = /750 = Product-Sustaining Costs: 1,000 Maint. hrs. for Basic (3,000 for Deluxe) / 4,000 Total Maint. hrs. = 0.25 Basic (0.75 Deluxe) 1,500 Eng. Support hrs. for Basic (4,500 for Deluxe) / 6,000 Total hrs. = 0.25 Basic (0.75 Deluxe) 100 Requisitions Processed for Basic (200 for Deluxe) / 300 Total Req. = 0.33 Basic (O.67 Deluxe) 250 Rec. orders processed for Basic (500 for Deluxe ) / 750 Total orders = 0.33 Basic (0.67 Deluxe) 250 Invoices for Basic (500 for Deluxe ) / 750 Total Invoices = 0.33 Basic (0.67 Deluxe)
12 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 3: COST DRIVER: CONSUMPTION MEASURE Machine Hours F A C I L I T Y BASIC MODEL DELUXE MODEL POOL 5,000/10,000, = ,000/10,000, = A Facility Level Costs: 5,000 Machine hrs. for Basic (5,000 for Deluxe) / 10,000 Total Machine hrs. = 0.50 Basic (0.50 Deluxe)
13 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 3: COST DRIVER: CONSUMPTION BASIC MODEL DELUXE MODEL POOL MEASURE # Moves # Setups B A T C H P S Maint. hours used R U Eng. Support hours O S D T # Requisitions U A processed C I T N # Rec. orders processed - I # Invoices N Machine Hours F A C I L I T Y G 2000/6000 = /80 = /4000 = /6000 = /300 = /750 = /750 = /6000 = /80 = /4000 = /6000 = /300 = /750 = /750 = ,000/10,000 = ,000/10,000 =
14 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 4: Batch-Level Activities: Pool 1: Material Handling $120,000 Divide By # Moves / 6,000 (2,000 Basic + 4,000 Deluxe) Pool Rate $ Pool 2: Setting Up Equip $96,000 Divide By # of Setups / 80 (20 Basic + 60 Deluxe) Pool Rate $ 1,200
15 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 4 Product-Sustaining Level Activities: Pool 3: Maintenance $114,000 Engineering g 120,000 Total $234,000 Divide By Maint. Hrs / 4,000 (1,000 Basic + 3,000 Deluxe) Pool Rate $ Note: Engineering hours could also be used as a driver. The activities are grouped together because they have the same process, are both product level, and have the same consumption ratios (0.25 and 0.75). $234,000 / 6,000 Engineering hours = $39.00 Pool Rate
16 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 4: Product-Sustaining Level Activities: Pool 4: Purchasing $ 60,000 Receiving 40,000 Paying Suppliers 30, Total $130,000 Divide by # of Rec. Orders / 750 (250 Basic Deluxe) Pool Rate $
17 3. Form homogeneous cost pools and calculate pool rates. Explain why you group activities into pools. STEP 4: Facility Level Activities: Pool 5: Providing Space $20,000 Divide By Mach. Hrs. / 10,000 (5,000 Basic + 5,000 Deluxe) Pool Rate $ 2.00
18 4. Using the pool rates computed in Requirement 3, Calculate the cost per unit for each product. Unit Cost: Basic Deluxe Overhead: Pool 1: 2,000 x $20 (moves) 40,000 4,000 x $20 (moves) 80,000 Pool 2: 20 x $1,200 (setups) 24, x $1,200 (setups) 72,000
19 4. Using the pool rates computed in Requirement 3, Calculate the cost per unit for each product. Unit Cost: Basic Deluxe Overhead: Pool 3: 1,000 x $ (maint. hrs.) 58, ,000 x $58.50 (maint. hrs.) 175,500 Alt. Pool 3 w/ Eng. hrs.: 1,500 x $39 (eng. hrs.) 58,500 4,500 x $39 (eng. hrs.) 175,500 Pool 4: 250 x $ (rec. orders) 43, x $ (rec. orders) 86,665665
20 4. Using the pool rates computed in Requirement 3, Calculate the cost per unit for each product. Unit Cost: Basic Deluxe Overhead: Pool 5: 5,000 x $2 (mach. hrs.) 10, ,000 x $2 (mach. hrs.) 10,000 TOTAL: $ 175,833 $424,165 Divide By # Units Produced / 40,000 / 20,000 Unit Cost $ 4.40 $ Pi Prime Cost Total ABC Unit Cost $84.40 $181.21
Overcosting and Undercosting (Example 1 at the end of these notes)
 Chapter 5 Activity-Based Costing Overcosting and Undercosting (Example 1 at the end of these notes) Distortions from inaccurate costing Activities/Resources/Cost Drivers Steps in ABC Identify resources
Chapter 5 Activity-Based Costing Overcosting and Undercosting (Example 1 at the end of these notes) Distortions from inaccurate costing Activities/Resources/Cost Drivers Steps in ABC Identify resources
Activity-Based Costing Systems
 4 Activity-Based Costing Systems 4-2 Learning Objective 1 4-3 Traditional Costing Systems Traditional cost systems were created when manufacturing processes were labor intensive. A single company-wide
4 Activity-Based Costing Systems 4-2 Learning Objective 1 4-3 Traditional Costing Systems Traditional cost systems were created when manufacturing processes were labor intensive. A single company-wide
Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 5 Activity-Based Costing and Activity-Based Management
 Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 5 Activity-Based Costing and Activity-Based Management 5.1 Objective 5.1 1) Which of the following statements is true of a
Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis, 16e, Global Edition (Horngren) Chapter 5 Activity-Based Costing and Activity-Based Management 5.1 Objective 5.1 1) Which of the following statements is true of a
REVIEW FOR EXAM NO. 1, ACCT-2302 (SAC) (Chapters 14-16)
 A. Chapter 14 (Managerial Accounting). 1. Purposes and Principles. (Page 632) REVIEW FOR EXAM NO. 1, ACCT-2302 (SAC) (Chapters 14-16) a. Provides economic/financial information (both historical and estimated)
A. Chapter 14 (Managerial Accounting). 1. Purposes and Principles. (Page 632) REVIEW FOR EXAM NO. 1, ACCT-2302 (SAC) (Chapters 14-16) a. Provides economic/financial information (both historical and estimated)
Activity-Based Costing. Managerial Accounting, Fourth Edition
 Study Objectives Study CHAPTER Objectives 4 Activity-Based Costing Managerial Accounting, Fourth Edition Study Objectives 1. Recognize the difference between traditional costing and activity based costing.
Study Objectives Study CHAPTER Objectives 4 Activity-Based Costing Managerial Accounting, Fourth Edition Study Objectives 1. Recognize the difference between traditional costing and activity based costing.
Activity Based Costing
 Activity Based Costing 1 Existing Single Indirect- Cost Pool System Cole Corporation manufactures two types of cell phones a standard type (S) and one complex type with additional functions (C). To cost
Activity Based Costing 1 Existing Single Indirect- Cost Pool System Cole Corporation manufactures two types of cell phones a standard type (S) and one complex type with additional functions (C). To cost
Activity Based Costing
 Activity Based Costing Existing Single Indirect- Cost Pool System Cole Corporation manufactures two types of cell phones a standard type (S) and one complex type with additional functions (C). To cost
Activity Based Costing Existing Single Indirect- Cost Pool System Cole Corporation manufactures two types of cell phones a standard type (S) and one complex type with additional functions (C). To cost
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING SPRING 2014 MIDTERM EXAM. PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May.
 PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May. Factory utilities $ 13,500 Direct labor $79,100 Depreciation on factory Sales salaries 48,400 equipment 12,650 Property taxes
PROBLEM 1 Kennedy Company reports the following costs and expenses in May. Factory utilities $ 13,500 Direct labor $79,100 Depreciation on factory Sales salaries 48,400 equipment 12,650 Property taxes
rate is used to apply overhead costs to products. Our purpose in this section is to provide a detailed example of cost flows in an ABC system.
 Appendix 6A Cost Flows in an -Based Costing System 6A-1 Cost Flows in an -Based Costing System In Chapter 4, we discussed the flow of costs in a job-order costing system. The flow of costs through raw
Appendix 6A Cost Flows in an -Based Costing System 6A-1 Cost Flows in an -Based Costing System In Chapter 4, we discussed the flow of costs in a job-order costing system. The flow of costs through raw
Acct 1B Week 8, Chap 7
 Acct 1B Week 8, Chap 7 Activity Based Costing (ABC) Instructor: Michael Booth Cabrillo College Activity Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making Global Business Situation Using technology and productivity
Acct 1B Week 8, Chap 7 Activity Based Costing (ABC) Instructor: Michael Booth Cabrillo College Activity Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making Global Business Situation Using technology and productivity
5-54 Volume-based Costing Versus ABC
 5-54 Volume-based Costing Versus ABC 1. Product A Product B Product C Materials $50.00 $114.40 $65.00 Labor 20.00 12.00 10.00 Overhead* 116.00 69.60 58.00 Total Cost $186.00 $ 196.00 $133.00 *overhead
5-54 Volume-based Costing Versus ABC 1. Product A Product B Product C Materials $50.00 $114.40 $65.00 Labor 20.00 12.00 10.00 Overhead* 116.00 69.60 58.00 Total Cost $186.00 $ 196.00 $133.00 *overhead
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
 13. Nonvalue-added activities are unnecessary activities or activities that are necessary but inefficient and improvable. An example is moving goods. Nonvalue-added costs are those costs caused by nonvalue-added
13. Nonvalue-added activities are unnecessary activities or activities that are necessary but inefficient and improvable. An example is moving goods. Nonvalue-added costs are those costs caused by nonvalue-added
Activity Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making. M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías
 Activity Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Ejemplo 1. Portland Power Company 2 Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide managers with cost information
Activity Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making M. En C. Eduardo Bustos Farías 1 Ejemplo 1. Portland Power Company 2 Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide managers with cost information
AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING
 TM 3-1 AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING A. The documents in a job-order costing system. 1. Materials requisition form. 2. Direct labor time ticket. 3. Job cost sheet. B. Applying overhead using a predetermined
TM 3-1 AGENDA: JOB-ORDER COSTING A. The documents in a job-order costing system. 1. Materials requisition form. 2. Direct labor time ticket. 3. Job cost sheet. B. Applying overhead using a predetermined
1. Amounts (in thousands) Molding Component Assembly Total
 5-32 (30 min.) Plantwide versus department overhead cost rates. 1. Amounts (in thousands) Molding Component Assembly Total Manufacturing department overhead $21,000 $16,200 $22,600 $59,800 Service departments:
5-32 (30 min.) Plantwide versus department overhead cost rates. 1. Amounts (in thousands) Molding Component Assembly Total Manufacturing department overhead $21,000 $16,200 $22,600 $59,800 Service departments:
COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION A
 COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION A (Chapters 1-4) Approximate Problem Topic Points Minutes A - I Multiple Choice... 20 20 A - II Cost of Goods Manufactured and Sold... 20 15 A - III Job Order Cost Accounting...
COMPREHENSIVE EXAMINATION A (Chapters 1-4) Approximate Problem Topic Points Minutes A - I Multiple Choice... 20 20 A - II Cost of Goods Manufactured and Sold... 20 15 A - III Job Order Cost Accounting...
Practice Quiz Questions
 Fundamentals of Product and Service Costing: Practice Quiz Questions 1 Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following statements is correct? a) A cost flow diagram is helpful by providing a graphical representation
Fundamentals of Product and Service Costing: Practice Quiz Questions 1 Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following statements is correct? a) A cost flow diagram is helpful by providing a graphical representation
ACCTG 221 / ABC Costing
 ACCTG 221 / ABC Costing ACTIVITY BASED COSTING SYSTEMS First identifies activities in an organization and then assigns the cost of each activity to products and services based on actual consumption The
ACCTG 221 / ABC Costing ACTIVITY BASED COSTING SYSTEMS First identifies activities in an organization and then assigns the cost of each activity to products and services based on actual consumption The
Chapter 5: Activity-Based Costing
 Chapter 5: -Based ing Management System: A cost-management system (CMS) is a collection of tools and techniques that identifies how management s decisions affect costs. Traditional (Peanut Butter) ing:
Chapter 5: -Based ing Management System: A cost-management system (CMS) is a collection of tools and techniques that identifies how management s decisions affect costs. Traditional (Peanut Butter) ing:
Management Accounting for Multinational Companies. Solution to the Wilkerson Case. Igor Baranov. Executive Summary
 Management Accounting for Multinational Companies Solution to the Wilkerson Case Igor Baranov Executive Summary Taking into account the difference among product and high proportion of overheads, Wilkerson
Management Accounting for Multinational Companies Solution to the Wilkerson Case Igor Baranov Executive Summary Taking into account the difference among product and high proportion of overheads, Wilkerson
Traditional Costing Systems
 Traditional Costing Systems Product Costs Direct labor Direct materials Factory Overhead Direct labor and direct materials are easy to trace to products. The problem comes with factory overhead. Traditional
Traditional Costing Systems Product Costs Direct labor Direct materials Factory Overhead Direct labor and direct materials are easy to trace to products. The problem comes with factory overhead. Traditional
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation
 Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
Chapter 02 - Cost Concepts and Cost Allocation Student: 1. Product costs for a manufacturing company consist of direct materials, direct labor, and overhead. 2. Period cost and product cost are synonymous
INTER CA NOVEMBER 2018
 Answer 1 INTER CA NOVEMBER 2018 Sub: COSTING Topics Introduction, Cost Sheet, Standard Costing, Integral and Non- Integral Accounts, Activity Based Costing Test Code N14 Branch: Multiple Date: Note : All
Answer 1 INTER CA NOVEMBER 2018 Sub: COSTING Topics Introduction, Cost Sheet, Standard Costing, Integral and Non- Integral Accounts, Activity Based Costing Test Code N14 Branch: Multiple Date: Note : All
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions 1. A cost not relevant to deciding whether to purchase a new machine is: a) The cost of the new machine b) Lower maintenance costs for the new machine c) The cost of the old machine
Multiple Choice Questions 1. A cost not relevant to deciding whether to purchase a new machine is: a) The cost of the new machine b) Lower maintenance costs for the new machine c) The cost of the old machine
TUTORIAL -ABC. Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Pelawat Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka
 TUTORIAL -ABC Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Pelawat Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka TOTAL COST for a COST OBJECT EXAMPLE: 1 Direct Cost (Labor Material) Overhead
TUTORIAL -ABC Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Pelawat Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka TOTAL COST for a COST OBJECT EXAMPLE: 1 Direct Cost (Labor Material) Overhead
Cost Accounting. Multiple Choice Questions:
 Multiple Choice Questions: 1- The Value Chain a- Involves external companies as well as internal activities. b- Is the sequence of business functions in which customer usefulness is added to products or
Multiple Choice Questions: 1- The Value Chain a- Involves external companies as well as internal activities. b- Is the sequence of business functions in which customer usefulness is added to products or
PAPER 4 QUESTION ONE. The ABC system can therefore be described as constituting the following stages:
 QUESTION ONE PAPER 4 Activity based costing is a method of costing products in which an attempt is made to reflect more accurately in the product costs those, activities which influence the level of overheads.
QUESTION ONE PAPER 4 Activity based costing is a method of costing products in which an attempt is made to reflect more accurately in the product costs those, activities which influence the level of overheads.
CHAPTER 26 (FIN MAN); CHAPTER 11 (MAN) COST ALLOCATION AND ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING
 (FIN MAN); CHAPTER 11 (MAN) COST ALLOCATION AND ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Management desires accurate product costs so that its decisions regarding products are correct. Managers are
(FIN MAN); CHAPTER 11 (MAN) COST ALLOCATION AND ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Management desires accurate product costs so that its decisions regarding products are correct. Managers are
Chapter 3 Activity-Based Costing
 Chapter 3 -Based Costing Solutions to Questions 3-1 The most common methods of assigning overhead costs to products are plantwide overhead rates, departmental overhead rates, and activity-based costing.
Chapter 3 -Based Costing Solutions to Questions 3-1 The most common methods of assigning overhead costs to products are plantwide overhead rates, departmental overhead rates, and activity-based costing.
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Key Topics to Know Cost of good sold statement is prepared from the finished goods inventory account. Cost of goods sold statement has the same format as in financial accounting. Cost
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Key Topics to Know Cost of good sold statement is prepared from the finished goods inventory account. Cost of goods sold statement has the same format as in financial accounting. Cost
Designing cost accounting systems. by David Derichs Lecture 1 Helsinki, 02 January 2018
 Designing cost accounting systems by David Derichs Lecture 1 Helsinki, 02 January 2018 Cost Accounting History Approaches to cost accounting I II i ii iii Traditional ABC TDABC I. The history of cost accounting
Designing cost accounting systems by David Derichs Lecture 1 Helsinki, 02 January 2018 Cost Accounting History Approaches to cost accounting I II i ii iii Traditional ABC TDABC I. The history of cost accounting
Cost Systems. Terms Cost Accounting Process Cost System Job Order Cost System
 Terms Cost Accounting Process Cost System Job Order Cost System Cost Systems Job-Order Costing Used for custom or unique items Each job is accounted for separately Measures cost based on completed job
Terms Cost Accounting Process Cost System Job Order Cost System Cost Systems Job-Order Costing Used for custom or unique items Each job is accounted for separately Measures cost based on completed job
SOLUTIONS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS CHAPTER 11
 SOLUTIONS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS CHAPTER 11 DEVELOP YOUR UNDERSTANDING Question 11.1 Absorption cost for one food processor Materials: 22,500 2,000 food processors 11.25 Direct labour: 16,500 2,000
SOLUTIONS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS CHAPTER 11 DEVELOP YOUR UNDERSTANDING Question 11.1 Absorption cost for one food processor Materials: 22,500 2,000 food processors 11.25 Direct labour: 16,500 2,000
ACG 2071 Managerial Accounting Spring 2018 Exam #4 Sample Review Problems
 Page 1 ACG 2071 Managerial Accounting Spring 2018 Exam #4 Sample Review Problems This is an independent effort. Do your own work! The ACE tutors and the SI may not assist you on this sample exam prior
Page 1 ACG 2071 Managerial Accounting Spring 2018 Exam #4 Sample Review Problems This is an independent effort. Do your own work! The ACE tutors and the SI may not assist you on this sample exam prior
Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Managerial Level May 2016 Examination. Integrative Management Accounting (IMA / ML 1-301)
 Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Managerial Level May 2016 Examination Examination Date : 14 th May 2016 Number of Pages : 06 Examination Time: 9.30
Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Managerial Level May 2016 Examination Examination Date : 14 th May 2016 Number of Pages : 06 Examination Time: 9.30
Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination. Management Accounting (MA / OL 1-201)
 Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination Examination Date : 17 th November 2018 Number of Pages : 06 Examination
Copyright Reserved Serial No Institute of Certified Management Accountants of Sri Lanka Operational Level November 2018 Examination Examination Date : 17 th November 2018 Number of Pages : 06 Examination
CHAPTER 7 Accounting 1B. Activity-Based Costing(ABC): A tool to Aid Decision Making
 CHAPTER 7 Accounting 1B Activity-Based Costing(ABC): A tool to Aid Decision Making Global Business Situation Using technology and productivity More emphasis on cost measurement and control Increasingly
CHAPTER 7 Accounting 1B Activity-Based Costing(ABC): A tool to Aid Decision Making Global Business Situation Using technology and productivity More emphasis on cost measurement and control Increasingly
MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar
 1 MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L8 Activity-Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making www.notes638.wordpress.com 2 Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide
1 MBP1133 Managerial Accounting Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L8 Activity-Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making www.notes638.wordpress.com 2 Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide
Chapter 2: Costing Systems: Job Order Costing
 Chapter 2: Costing Systems: Job Order Costing Student: 1. A job order costing system measures costs of each processes using an inventory account for each. 2. The computations for costs to be transferred
Chapter 2: Costing Systems: Job Order Costing Student: 1. A job order costing system measures costs of each processes using an inventory account for each. 2. The computations for costs to be transferred
Practice assessment model answers
 Practice assessment model answers Management Accounting: Decision and Control (MDCL) Practice assessment 1 (for Live assessments from 5 March 2018) Version 1.1 published 6 February 2018 Copyright 2018
Practice assessment model answers Management Accounting: Decision and Control (MDCL) Practice assessment 1 (for Live assessments from 5 March 2018) Version 1.1 published 6 February 2018 Copyright 2018
Activity- Based Costing
 Activity- Based Costing McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Two-Stage Progress Using Direct Labor Hours Power Costs Indirect Labor Factory Supplies
Activity- Based Costing McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Two-Stage Progress Using Direct Labor Hours Power Costs Indirect Labor Factory Supplies
Activity-Based Costing and Analysis
 A Look Back Chapters 2 and 3 described costing systems used by companies to accumulate product costing information for the reporting of inventories and cost of goods sold. 4Chapter Learning Objectives
A Look Back Chapters 2 and 3 described costing systems used by companies to accumulate product costing information for the reporting of inventories and cost of goods sold. 4Chapter Learning Objectives
COST MANAGEMENT. Key Definitions UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
 COST MANAGEMENT Key Definitions 2014 UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE Week 1: Accounting Information for Management 1. Management Accounting: Management Accounting measures and reports financial information as
COST MANAGEMENT Key Definitions 2014 UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE Week 1: Accounting Information for Management 1. Management Accounting: Management Accounting measures and reports financial information as
Activity Based Costing Learning Objectives
 Activity Based Costing 5 Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to Discuss the limitations of using only unit-based drivers to assign costs. Provide a detailed description
Activity Based Costing 5 Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to Discuss the limitations of using only unit-based drivers to assign costs. Provide a detailed description
3. Which is not an inventory account manufacturing companies have: a) Raw Materials b) Manufacturing Overhead c) Work in Process d) Finished Goods
 Chapter 1 Question Review 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of managerial accounting: a) Emphasizes decisions affecting the future b) Mandatory for external reports c) Need not follow GAAP
Chapter 1 Question Review 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of managerial accounting: a) Emphasizes decisions affecting the future b) Mandatory for external reports c) Need not follow GAAP
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Suggested Solutions to Practice Questions Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie Table of Contents Part 1:... 2 Part 2:... 8 Part 3:... 14 Part 4:...
Management Accounting Suggested Solutions to Practice Questions Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie Table of Contents Part 1:... 2 Part 2:... 8 Part 3:... 14 Part 4:...
2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. Job Costing Systems
 Job Costing Systems Types of Product-Costing Systems Process Costing Job-Order Costing Used for production of large, unique, high-cost items. Built to order rather than mass produced. Many costs can be
Job Costing Systems Types of Product-Costing Systems Process Costing Job-Order Costing Used for production of large, unique, high-cost items. Built to order rather than mass produced. Many costs can be
Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting
 Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting 2.1-1 Retailers sell their products to other wholesalers. Answer: False LO: 2-1 EOC: E
Managerial Accounting, 2e Braun/Tietz/Harrison Test Item File Chapter 2: Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting 2.1-1 Retailers sell their products to other wholesalers. Answer: False LO: 2-1 EOC: E
activity-based EXAMPLE 1 See Table 1 opposite.
 01 technical activity-based RELEVANT to ACCA QUAlification paper F5 Conventional costing distinguishes between variable and fixed costs. Typically, it is assumed that variable costs vary with the number
01 technical activity-based RELEVANT to ACCA QUAlification paper F5 Conventional costing distinguishes between variable and fixed costs. Typically, it is assumed that variable costs vary with the number
Cost Behavior. Material Cost: Direct material: 1. seen in the final product 2. economic/visible to trace Indirect Material:
 1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Cost A cost is the value of economic resources (e.g., money) sacrificed or used up to achieve a particular objective (e.g., produce a product or perform
1 Chapter 2 Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes Cost A cost is the value of economic resources (e.g., money) sacrificed or used up to achieve a particular objective (e.g., produce a product or perform
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR SECOND, FOURTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION FIN2033 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING DMGW-E-F-2/13,
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR SECOND, FOURTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION FIN2033 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING DMGW-E-F-2/13,
CONVERTING SIMULATION DATA TO COMPARATIVE INCOME STATEMENTS
 CONVERTING SIMULATION DATA TO COMPARATIVE INCOME STATEMENTS L. Leslie Gardner Mary E. Grant Laurie J. Rolston If a manufacturing system was a money amplifier, an accountant would see it like this: 2 If
CONVERTING SIMULATION DATA TO COMPARATIVE INCOME STATEMENTS L. Leslie Gardner Mary E. Grant Laurie J. Rolston If a manufacturing system was a money amplifier, an accountant would see it like this: 2 If
Inventory Cost Accounting Tips and Tricks. Nick Bergamo, Senior Manager Linda Pei, Senior Manager
 1 Inventory Cost Accounting Tips and Tricks Nick Bergamo, Senior Manager Linda Pei, Senior Manager 2 Disclaimer The material appearing in this presentation is for informational purposes only and is not
1 Inventory Cost Accounting Tips and Tricks Nick Bergamo, Senior Manager Linda Pei, Senior Manager 2 Disclaimer The material appearing in this presentation is for informational purposes only and is not
CONTACT HOURS FOR CALLS WEDNESDAYS AND THURSDAYS, 6PM TO 7PM. Production and sales volumes (units) 30,000 50,000. Raw material usage (kg) per unit 4 6
 MAAGEMET IFORMATIO - COST ACCOUTIG ASPECT WEEK 6 QUESTIOS COTACT UMBER 08038400843 COTACT HOURS FOR CALLS WEDESDAYS AD THURSDAYS, 6PM TO 7PM TOPIC: ACTIVITY BASE COSTIG VIDEO LECTURE CHEPTER: 12 QUESTIO
MAAGEMET IFORMATIO - COST ACCOUTIG ASPECT WEEK 6 QUESTIOS COTACT UMBER 08038400843 COTACT HOURS FOR CALLS WEDESDAYS AD THURSDAYS, 6PM TO 7PM TOPIC: ACTIVITY BASE COSTIG VIDEO LECTURE CHEPTER: 12 QUESTIO
CHAPTER 5: COST MANAGEMENT IN AUTOMATED BUSINESS: ABC, ABM AND TQM Pearson Education. All rights reserved.
 CHAPTER 5: COST MANAGEMENT IN AUTOMATED BUSINESS: ABC, ABM AND TQM Learning Objectives 1. Explain how broad averaging undercosts and overcosts products or services 2. Present three guidelines for refining
CHAPTER 5: COST MANAGEMENT IN AUTOMATED BUSINESS: ABC, ABM AND TQM Learning Objectives 1. Explain how broad averaging undercosts and overcosts products or services 2. Present three guidelines for refining
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Job Order Costing ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. The difference between job order costing and process costing relates to the type of product or service the company provides, and whether that product
Chapter 2 Job Order Costing ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. The difference between job order costing and process costing relates to the type of product or service the company provides, and whether that product
Chapter 6. The Production Process
 Chapter 6 The Production Process 1 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the master data associated with the production process. 2. Identify the key steps in the production process and the data, documents, and
Chapter 6 The Production Process 1 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the master data associated with the production process. 2. Identify the key steps in the production process and the data, documents, and
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) & Activity-Based Management (ABM)
 Chapter 5: Activity-Based Costing (ABC) & Activity-Based Management (ABM) Horngren 13e 5-1 A SIMPLE COSTING SYSTEM 5-2 AN ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING SYSTEM 5-3 ABC s 7 Steps Step 1: Identify the products that
Chapter 5: Activity-Based Costing (ABC) & Activity-Based Management (ABM) Horngren 13e 5-1 A SIMPLE COSTING SYSTEM 5-2 AN ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING SYSTEM 5-3 ABC s 7 Steps Step 1: Identify the products that
(Total 25 Marks) Question No. 02
 UNIVERSITY OF KELANIYA Faculty of Commerce and Management Studies Bachelor of Business Management (Special) Degree in Accountancy Examinations June/July-2015 2013/2014 Academic year Year I First Semester
UNIVERSITY OF KELANIYA Faculty of Commerce and Management Studies Bachelor of Business Management (Special) Degree in Accountancy Examinations June/July-2015 2013/2014 Academic year Year I First Semester
COST SHEET. Samir K Mahajan
 COST SHEET Samir K Mahajan COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Prime cost: It is the aggregate of direct material cost, direct labour cost and direct expenses. Prime cost or Direct cost = Direct materials + Direct
COST SHEET Samir K Mahajan COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Prime cost: It is the aggregate of direct material cost, direct labour cost and direct expenses. Prime cost or Direct cost = Direct materials + Direct
JOB COSTING AND OVERHEAD
 JOB COSTING AND OVERHEAD Key Topics to Know Differences and similarities between job order and process costing Key document is the Job Cost Sheet Flow of product costs through inventory accounts to cost
JOB COSTING AND OVERHEAD Key Topics to Know Differences and similarities between job order and process costing Key document is the Job Cost Sheet Flow of product costs through inventory accounts to cost
BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme. Strategic Management Accounting. Tutorial III- Short term decision making
 BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme Strategic Management Accounting Tutorial III- Short term decision making 1. A company has the following costs and revenues relating to a product.
BSc. (Applied Accounting) General/Special Degree Programme Strategic Management Accounting Tutorial III- Short term decision making 1. A company has the following costs and revenues relating to a product.
Unleash Hidden Profits: Make Your Supply Chain Work for You
 Unleash Hidden Profits: Make Your Supply Chain Work for You Objective Learn how you can Reduce Working Capital Improve Cash Flow Increase Profits by improving how you manage your materials and supply chain
Unleash Hidden Profits: Make Your Supply Chain Work for You Objective Learn how you can Reduce Working Capital Improve Cash Flow Increase Profits by improving how you manage your materials and supply chain
CIPS Knowledge Works. Activity Based Costing (ABC) - What the buyer needs to know. Contents
 CIPS Knowledge Works Activity Based Costing (ABC) - What the buyer needs to know Contents 1. Why Activity Based Costing? pg3 2. Some Definitions pg4 3. Some Terminology pg4 4. ABC and Purchasing pg5 5.
CIPS Knowledge Works Activity Based Costing (ABC) - What the buyer needs to know Contents 1. Why Activity Based Costing? pg3 2. Some Definitions pg4 3. Some Terminology pg4 4. ABC and Purchasing pg5 5.
Chapter 24 Differential Analysis and Product Pricing Study Guide Do You Know?
 Chapter 24 Differential Analysis and Product Pricing Study Guide Do You Know? Learning Objective 1: Prepare differential analysis reports for a variety of managerial decisions. How to prepare a differential
Chapter 24 Differential Analysis and Product Pricing Study Guide Do You Know? Learning Objective 1: Prepare differential analysis reports for a variety of managerial decisions. How to prepare a differential
Activity Based Costing: A Decision Making Tool. with Dr. Joseph Ugras December 2017
 Activity Based Costing: A Decision Making Tool with Dr. Joseph Ugras December 2017 1 7-2 Learning Objectives Know the Need for Cost and Profitability Understand how traditional and activity-based costing
Activity Based Costing: A Decision Making Tool with Dr. Joseph Ugras December 2017 1 7-2 Learning Objectives Know the Need for Cost and Profitability Understand how traditional and activity-based costing
Chapter 3 Systems Design: Job-Order Costing
 Chapter 3 Systems Design: Job-Order Costing Solutions to Questions 3-1 By definition, manufacturing overhead consists of costs that cannot be practically traced to products or jobs. Therefore, if these
Chapter 3 Systems Design: Job-Order Costing Solutions to Questions 3-1 By definition, manufacturing overhead consists of costs that cannot be practically traced to products or jobs. Therefore, if these
TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR
 18-11 C 2 Cost TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR Cost Activity Activity Cost Cost behavior refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of business activity. Total fixed
18-11 C 2 Cost TYPES OF COST CLASSIFICATIONS CLASSIFICATION BY BEHAVIOR Cost Activity Activity Cost Cost behavior refers to how a cost will react to changes in the level of business activity. Total fixed
CA Final, Paper 5, Advanced management Accounting, Chapter 1 Developments in Business Environment :Part 3. CA. Anurag Singal B.Com(H), ACA.
 CA Final, Paper 5, Advanced management Accounting, Chapter 1 Developments in Business Environment :Part 3 CA. Anurag Singal B.Com(H), ACA. Understand the concept of Target Costing Understand the concept
CA Final, Paper 5, Advanced management Accounting, Chapter 1 Developments in Business Environment :Part 3 CA. Anurag Singal B.Com(H), ACA. Understand the concept of Target Costing Understand the concept
Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100
 KEY - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 1 Date : 20/08/2018 Subject & Code : Cost Management Name of faculty : Dr.R.Duraipandian Note: Answer all questions (17MBAFM305) Max Marks : 40 Section : Finance Time: 8:30
KEY - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 1 Date : 20/08/2018 Subject & Code : Cost Management Name of faculty : Dr.R.Duraipandian Note: Answer all questions (17MBAFM305) Max Marks : 40 Section : Finance Time: 8:30
- Product costing Systems are used to compute the product cost per unit. - Product cost per unit is needed for a variety of purpose:
 Introduction: - Product costing Systems are used to compute the product cost per unit. - Product cost per unit is needed for a variety of purpose: o In financial accounting; Used to value inventory and
Introduction: - Product costing Systems are used to compute the product cost per unit. - Product cost per unit is needed for a variety of purpose: o In financial accounting; Used to value inventory and
Part 1: Answer the following questions (1,2,3, and 4) Q1: Choose the right answer. (20 points)
 Islamic university Gaza College of commerce Accounting department Final exam 2016-2017 Managerial Accounting 60 points Sunday 28.05.2017 Mohammed Alashi Name: Id:.. Part 1: Answer the following questions
Islamic university Gaza College of commerce Accounting department Final exam 2016-2017 Managerial Accounting 60 points Sunday 28.05.2017 Mohammed Alashi Name: Id:.. Part 1: Answer the following questions
A presentation by Prof Tripurari Jha M.Com, CS-Executive, CA-IPCC, Research Scholar (PhD) UGC NET Lecturer in Accountancy, Balbharati s MJP College,
 A presentation by Prof Tripurari Jha M.Com, CS-Executive, CA-IPCC, Research Scholar (PhD) UGC NET Lecturer in Accountancy, Balbharati s MJP College, Kandivali (W), Mumbai. Activity-Based Costing 2 In contrast
A presentation by Prof Tripurari Jha M.Com, CS-Executive, CA-IPCC, Research Scholar (PhD) UGC NET Lecturer in Accountancy, Balbharati s MJP College, Kandivali (W), Mumbai. Activity-Based Costing 2 In contrast
ACTIVITY BASED COSTING PERFORMANCE MEASUREMNENT ABC. Benchmarking
 PERFORMANCE MEASUREMNENT Benchmarking Measuring and benchmarking supply chain performance is a vital first step in any reengineering programme. Understanding the differences between value adding time and
PERFORMANCE MEASUREMNENT Benchmarking Measuring and benchmarking supply chain performance is a vital first step in any reengineering programme. Understanding the differences between value adding time and
Modul ke: Akuntansi Biaya. Activity Accounting. Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis. Suryadharma Sim, SE, M. Ak. Program Studi S1 Manajemen
 Modul ke: 14 Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Akuntansi Biaya Activity Accounting Suryadharma Sim, SE, M. Ak Program Studi S1 Manajemen Activity-Based Costing An accounting method that identifies the activities
Modul ke: 14 Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Akuntansi Biaya Activity Accounting Suryadharma Sim, SE, M. Ak Program Studi S1 Manajemen Activity-Based Costing An accounting method that identifies the activities
Activity-Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making
 Activity-Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making Chapter 8 McGraw-Hil/Irwin Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide managers with cost information for strategic and other decisions
Activity-Based Costing: A Tool to Aid Decision Making Chapter 8 McGraw-Hil/Irwin Activity Based Costing (ABC) ABC is designed to provide managers with cost information for strategic and other decisions
Chapter 2--Basic Cost Management Concepts
 Chapter 2--Basic Cost Management Concepts Student: 1. The cost management information system is primarily concerned with producing outputs for internal users using inputs and processes needed to satisfy
Chapter 2--Basic Cost Management Concepts Student: 1. The cost management information system is primarily concerned with producing outputs for internal users using inputs and processes needed to satisfy
SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME
 All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 13 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (INTAKE VI GROUP A) END SEMESTER
All Rights Reserved No. of Pages - 13 No of Questions - 07 SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING AND BUSINESS BSc. (APPLIED ACCOUNTING) GENERAL / SPECIAL DEGREE PROGRAMME YEAR I SEMESTER I (INTAKE VI GROUP A) END SEMESTER
Overheads/Job and Batch Costing. RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service
 CA R. K. Mehta Overheads/Job and Batch Costing CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 Nov, 2006 RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service departments Human
CA R. K. Mehta Overheads/Job and Batch Costing CA Past Years Exam Question Question : 1 Nov, 2006 RST Ltd. has two production departments Machining and Finishing. There are three service departments Human
Full file at Chapter 02 - Basic Cost Management Concepts
 CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS Learning Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word cost. 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs, and expenses. 3. Describe the role of costs in
CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS Learning Objectives 1. Explain what is meant by the word cost. 2. Distinguish among product costs, period costs, and expenses. 3. Describe the role of costs in
CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS
 CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. An accounting information system is a system consisting of interrelated manual and computer parts, using processes such as collecting, recording,
CHAPTER 2 BASIC COST MANAGEMENT CONCEPTS DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. An accounting information system is a system consisting of interrelated manual and computer parts, using processes such as collecting, recording,
Ch.4 Evaluating Requisitions.
 Module 1 : Purchasing Process. Ch.4 Evaluating Requisitions. Edited by Dr. Seung Hyun Lee (Ph.D., CPM) IEMS Research Center, E-mail : lkangsan@iems.co.kr Cost/Benefit Analysis. Classification of Costs
Module 1 : Purchasing Process. Ch.4 Evaluating Requisitions. Edited by Dr. Seung Hyun Lee (Ph.D., CPM) IEMS Research Center, E-mail : lkangsan@iems.co.kr Cost/Benefit Analysis. Classification of Costs
Full file at https://fratstock.eu
 CHAPTER 2 QUESTIONS 1. The two major objectives of materials control are (1) physical control or safeguarding the materials and (2) control of the investment in materials. 2. The controls established for
CHAPTER 2 QUESTIONS 1. The two major objectives of materials control are (1) physical control or safeguarding the materials and (2) control of the investment in materials. 2. The controls established for
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2016 Exam Paper, Solutions & Examiner s Comments Page 1 of 24 NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting
Management Accounting 2 nd Year Examination May 2016 Exam Paper, Solutions & Examiner s Comments Page 1 of 24 NOTES TO USERS ABOUT THESE SOLUTIONS The solutions in this document are published by Accounting
Can Innovation of Time Driven ABC System Replace Conventional ABC System?
 Can Innovation of Time Driven ABC System Replace Conventional ABC System? Tan Ming Kuang Accounting Department, Maranatha Christian University Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to analyze the differences
Can Innovation of Time Driven ABC System Replace Conventional ABC System? Tan Ming Kuang Accounting Department, Maranatha Christian University Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to analyze the differences
COST C O S T COST 1/12/2011
 Chapter 3 COST CONCEPT AND DESIGN ECONOMICS C O S T Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka COST Cost is not a simple concept. It is important
Chapter 3 COST CONCEPT AND DESIGN ECONOMICS C O S T Ir. Haery Sihombing/IP Pensyarah Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Melaka COST Cost is not a simple concept. It is important
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior
 2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
2 Cost Concepts and Behavior Solutions to Review Questions 2-1. Cost is a more general term that refers to a sacrifice of resources and may be either an opportunity cost or an outlay cost. An expense is
Part 1: Answer the following questions (1,2,3, and 4) Q1: Choose the right answer. (20 points)
 Islamic university Gaza College of commerce Accounting department Final exam 2016-2017 Managerial Accounting Sunday 28.05.2017 Mohammed Alashi Name: Id:.. Part 1: Answer the following questions (1,2,3,
Islamic university Gaza College of commerce Accounting department Final exam 2016-2017 Managerial Accounting Sunday 28.05.2017 Mohammed Alashi Name: Id:.. Part 1: Answer the following questions (1,2,3,
COST SHEET. Samir K Mahajan
 COST SHEET Samir K Mahajan COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Prime cost or Direct cost : It is the aggregate of direct material cost, direct labour cost and direct expenses. i.e. Prime cost or Direct cost = Direct
COST SHEET Samir K Mahajan COMPONENTS OF TOTAL COST Prime cost or Direct cost : It is the aggregate of direct material cost, direct labour cost and direct expenses. i.e. Prime cost or Direct cost = Direct
Chapter 4. Systems Design: Process Costing. Types of Costing Systems Used to Determine Product Costs. Job-order Costing.
 4-1 Chapter 4 Systems Design: Process Costing Types of Costing Systems Used to Determine Product Costs Process Costing Job-order Costing F Many units of a single, homogeneous product flow evenly through
4-1 Chapter 4 Systems Design: Process Costing Types of Costing Systems Used to Determine Product Costs Process Costing Job-order Costing F Many units of a single, homogeneous product flow evenly through
MOCK TEST PAPER INTERMEDIATE (NEW): GROUP I PAPER 3: COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
 MOCK TEST PAPER INTERMEDIATE (NEW): GROUP I PAPER 3: COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Test Series: March 2018 Answers are to be given only in English except in the case of the candidates who have opted for
MOCK TEST PAPER INTERMEDIATE (NEW): GROUP I PAPER 3: COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Test Series: March 2018 Answers are to be given only in English except in the case of the candidates who have opted for
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs
 Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
Lecture 2: Flow of resource costs Cost Object: anything for which a separate measurement of costs is required, e.g. products, services, customers, projects, processes, segments of the value chain, divisions/departments,
Part 1 Study Unit 5. Cost Accumulations Systems Jim Clemons, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM
 Part 1 Study Unit 5 Cost Accumulations Systems Jim Clemons, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM 1 Overview Cost accounting systems record manufacturing activities using a perpetual inventory system, which continuously
Part 1 Study Unit 5 Cost Accumulations Systems Jim Clemons, CMA Ronald Schmidt, CMA, CFM 1 Overview Cost accounting systems record manufacturing activities using a perpetual inventory system, which continuously
Direct and Indirect Costs
 Accounting presentation created by Rex A Schildhouse 2015-01-01 www.schildhouse.com Created by Rex A Schildhouse, www.schildhouse.com Slide 1 There are three costs associated with manufacturing a product.
Accounting presentation created by Rex A Schildhouse 2015-01-01 www.schildhouse.com Created by Rex A Schildhouse, www.schildhouse.com Slide 1 There are three costs associated with manufacturing a product.
CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
 CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING The Basic Objectives of Accounting Basic objective of accounting is to provide stakeholders with useful information about a business enterprise in order to
CHAPTER ONE: OVEVIEW OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING The Basic Objectives of Accounting Basic objective of accounting is to provide stakeholders with useful information about a business enterprise in order to
Chapter 4 Activity-based Costing Systems
 Chapter 4 Activity-based Costing Systems ABC costing may use five different cost categories that reflect different levels of production activities and that sum to total production costs. Unit-level cost:
Chapter 4 Activity-based Costing Systems ABC costing may use five different cost categories that reflect different levels of production activities and that sum to total production costs. Unit-level cost:
Managerial Accounting Prof. Dr. Vardaraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Managerial Accounting Prof Dr Vardaraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 11 Lecture - 25 Activity Based Costing and Management Today, we will continue our discussion
Managerial Accounting Prof Dr Vardaraj Bapat School of Management Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module - 11 Lecture - 25 Activity Based Costing and Management Today, we will continue our discussion
Intermediate Management Accounting Primer
 Intermediate Management Accounting Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada, CPA Canada, CPA are trademarks and/or certification marks of the Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada. 2019, Chartered
Intermediate Management Accounting Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada, CPA Canada, CPA are trademarks and/or certification marks of the Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada. 2019, Chartered
Match the activity pool with an appropriate activity measure. Your answers: Customer orders. Product design c-:i ~ Number of product designs
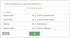 Match the activity pool with an appropriate activity measure. ~ Your answer is correct Your answers: Customer orders IHI ~ Number of customer orders Product design c-:i ~ Number of product designs l J
Match the activity pool with an appropriate activity measure. ~ Your answer is correct Your answers: Customer orders IHI ~ Number of customer orders Product design c-:i ~ Number of product designs l J
