A United Allocation Method of Spare Parts and Ground Maintenance Equipment for Civil Aircraft
|
|
|
- Joan George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A United Allocation Method of Spare Parts and Ground Maintenance Equipment for Civil Aircraft Li Yongkai 1,a,Feng Yunwen 1, Xue Xiaofeng 1 and Lu Cheng 1 1 School of Aeronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian, China Abstract. Aimed at multi-echelon inventory allocation problem with finite repair capacity for civil aircrafta united planning method based on queuing theory and Vari-Metric model is presented to deploy the aircraft spare parts and ground maintenance equipment. Through the analysis of actual engineering, the effect of repair time is quantified by the number of maintenance equipment. On this basis, the available of fleet and the cost expense are selected as the objective and constraint respectively, marginal analysis method is set as the optimization, a new allocation scheme which was suit to civil aircraft s maintenance resources is put forward. By applied examples analysis, it is shows that this method is reasonable and feasible. 1 Introduction Due to the rapid development of high-tech equipment, maintenance resources (spare parts and ground maintenance equipment) to ensure the normal use of the civil aircraft has been attached more and more importance. With complex equipment lead to fast-rising prices of spare parts and repair facilities, the contradiction of outlay and resources shortage become more prominent if we allocate maintenance resources according to the traditional method. Therefore, in order to ensure the timeliness of maintenance tasks and reduce operating costs for civil aircraft, we need to make reasonable allocation for civil aircraft s maintenance resources to seek optimal cost-effectiveness between fleet availability and cost expense of resources. In foreign countries, study on maintenance resources allocation carried out earlier than China. The classical Metric model is proposed by Sherbrooke[1], which laid a foundation for multi-echelon inventory allocation theory. Muckstadt[2] established an inventory management method for the multiorder multi-echelon case, i.e. the Mod-Metric system model. Graves[3] put forward Vari-Metric model to solve the problem of multi-echelon multi-indenture spare parts inventory control. The existing researches about multi-echelon inventory allocation had been applied to various managements of maintenance resources, however, previous studies were based on the assumption of infinite repair capacity, and the maintenance ability of each location is limited in the practical engineering. These methods failed to consider the interaction between the number of maintenance equipment and maintenance ability. In this paper, the assumption of infinite repair capacity is relaxed and the effect of repair time is quantified by the number of maintenance equipment based on M/M/c queuing theory. According to a Corresponding author : lyk56820@hotmail.com The Authors, published by EDP Sciences. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (
2 the Vari-Metric method, a calculation mode for fleet availability of civil aircraft is established. Based on that, this study put forward a united allocation method of spare parts and ground maintenance equipment for civil aircraft, resources allocation scheme is also obtained. In addition, the influence of the inventory scheme between limited and infinite repair capacity is evaluated. 2 Model descriptions In general, the maintenance points of aircraft is regarded as two-echelon inventory model, respectively, the Local Warehouse (LW) and the Central Department (CD). When the parts on the aircraft are in trouble, broken parts will be replaced if spare parts are available on the LW, otherwise, order a spare part to the CD with a (S-1,S) replenishment policy. The invalid parts are sent to repair shop at the CD unless there have adequate repair capacity on the LW. Repaired parts will act as new spare parts and replenish stocks. It should follow the principle of queuing theory in repair: the invalid parts can be repaired immediately if there have free maintenance equipment, or waiting to repair until the free maintenance facilities occurred. Which means that the maintenance process of invalid parts satisfying a first-come, first-serve(fcfs) basis. The replacement and maintenance process of the aircraft parts is shown in figure 1. aircraft parts failed repaired at the LW Yes Can invalid parts be repaired at the LW? Replacement of invalid parts Yes Is spare parts available at the LW No Is spare parts available at the CD No Order new spare parts act as new spare parts and replenishing stocks No repaired at the CD Yes Send to the LW Figure 1 The replacement and maintenance process of the aircraft parts In order to simplify the modeling process, there are some reasonable assumptions for united allocation method of spare parts and ground maintenance equipment: The failure of aircraft parts follows the Poisson process. The invalid parts can be repaired perfectly. Any aircraft part has a independent mean-time-between-maintenance (MTBM). There is no lateral supply. For a better expression of the model, the variables are listed as follows: i spare parts number. i 1, 2,3,n n j maintenance points number. CD: j 0, LW: j 1, 2,3, m k maintenance equipment number. k 1, 2,3,l S q the allocation scheme. Spare part: q 0, maintenance equipment q 1 C q purchase price. Spare part: q 0, maintenance equipment q 1 r air route number. r 1, 2,3 D flight mileage through maintenance point j at air route r. rj M the total demand of spare parts i i m the demand of spare parts i at maintenance point j. r j repair probability at maintenance point j. T the repair time of spare parts i at maintenance point j. the average demand of spare parts i getting from maintenance and resupply at maintenance 2
3 point j. P the steady state probability of spare parts i getting from maintenance and resupply at maintenance point j. O order and ship time of spare parts i from the CD to maintenance point j. f the fraction of all demands of spare parts i at the LW j. 3 Estimating the demand of spare parts 3.1 The demand model of spare parts The basic formula of spare parts demand is: M=.. AI P I. N AI.. P (1) AI.. PSV.. CT../ T. (2) Where: M -the demand number of spare parts, AI.. P- the average number of spare parts need to be repaired, SV..-repair rate per year, CT.. repair time, T. - annual working days, IN-. index number, represents the level of security. 3.2 The demand for each maintenance point For the LW maintenance points, the demand of spare parts can be determined according to the percentage of flight mileage through the LW from the total route. Define D r as the total route of air r route r, and m as the demand caused by air route r of spare parts i at maintenance point j : D r rj m Mi (3) Dr The total demand m consist of the sum of demand for all routes that pass through the LW r m m (4) For the CD maintenance points, the demand of spare parts equal to the number of spare parts that cannot be repaired at the LW. mi0 m(1r j) (5) 4 A united allocation method of maintenance resources for civil aircraft 4.1 The construction of multi-echelon spare parts inventory model According to the classic METRIC theory, the following relationships exist in inventory level[4]: S OHDIBO S is the inventory level, OH is existing inventory, DI is the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply, BO is the shortage number of spare parts. When using (S-1,S) inventory strategy, the value of S is constant, OH, DI and BO are in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Therefore, the expectation EBO (S 0) and variance VBO (S 0) of spare parts shortage can be expressed by the following formulas when the value of OH iss 0 : 3
4 EBO(S ) P(DI S 1) 2P(DI S 2)... (xs ) P(DI x) (6) XS VBO( SO ) E[ BO ( S0)] [ EBO( S0)] (7) Where, P(DI x) is the probability that the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply is x. Next, calculating P(DI x) at the LW and CD respectively. According to the Palm theorem, the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply followed from Boson distribution with mt i0 i0 mean.so the average demand i0 and steady state probability P i0 for the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply can be expressed by the following: i0 mt i0 i0 (8) Pi0() x Poisson(, x i0) (9) The expectation EBO (S) i0 and variance VBO (S) i0 of spare parts shortage at the CD can be derived from the formulas (6), (7) and (9). The average demand of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply at the LW consists of two parts: one is the fault parts for maintenance at the LW, and the other is the fault parts sent to the CD due to the lack of maintenance capability at the LW: m (rt (1 r ) O EBOi 0 mi 0) (10) The variance for the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply Var ( S ) can be expressed by the following formula: 2 Var ( S) m rti 0 (1 r ) O j f (1 f ) EBOi 0( S) f VBOi 0( S) (11) Where m (1 r ) f (12) mi 0 The steady state probability of DI x at the LW depends on the ratio of mean and variance p Var ( S). If p 1, the number of spare parts getting from maintenance and resupply followed a negative binomial distribution; else if p 1, this number according to Poisson distribution; and if p 1, selecting binomial distribution. So we can get the steady state probability P, furthermore, we obtain the expectation EBO (S) and variance VBO (S) of spare parts shortage at the LW. The total expectation of spare parts shortage consists of the expectation at all maintenance points: n n m (13) EBO (S) EBO ( S) EBO ( S) i i0 i1 i1 j1 The relationship between fleet availability A and the total expectation of spare parts shortage EBO i (S) is: n i i (14) A EBO (S) NZ i1 Where, Z i is the installed number at a plane, N is the number of aircraft in a fleet. Thus, the maximum availability of fleet equal to the minimum value for the expectation of spare parts shortage. The investment cost of all maintenance resources C is composed of two parts: the cost of purchasing spare parts and the cost of the maintenance equipment: Z i 4
5 n C c S c S 0i 0i 1k 1k i1 k1 l (15) Where, c 0i, S 0i are the purchase price and allocation scheme of i th spare parts, c 1k, S 1k are the purchase price and allocation scheme of k th maintenance equipment. Through the above analysis, the available of fleet and the cost expense are selected as the objective and constraint respectively, a multi-echelon inventory allocation method is put forward: min EBO( S) (16) st.. C C The effect of ground maintenance equipment on repair time Based on the multi-service model of queuing theory, the problem of maintenance resources allocation under the condition of limited maintenance capacity is solved. The following are the assumptions of the repair process The arrival interval of fault parts followed with negative exponent distribution (Parameters is ). The repair time followed with negative exponent distribution (Parameters is ). System capacity: infinite. Queue length: infinite. Serve regulation: first-come-first-served (FCFS). Define, s, k is the number of maintenance equipment. In order to avoid he queue k is lengthening, the repair capacity per unit time should be greater than the number of failures, i.e., s 1 The probability that a fault part does not have to wait for service when it arrives p 0 is: p 0 k 1 n n k 0 n! k!(1 s ) The number of parts waiting to be repaired in the system L q is: p 1 (17) d p k k 0 s n 0 s Lq s 2 (18) k! d s n1 k!(1 s ) According to the Little formula, the average repair time T (including service time and waiting time) of the parts in the maintenance point is obtained: L q T (19) Then take repair time T into the inventory allocation model of spare parts, a united planning method based on queuing theory and Vari-Metric model is obtained to deploy the aircraft spare parts and ground maintenance equipment. 4.3 Solving process based on marginal analysis According to the relevant literature[5], it can be proved that the expectation of spare parts shortage is a monotone increasing, convex function of inventory level, so the multi-echelon inventory allocation model can be solved by the method of marginal analysis. Step.1 Set the initial allocation of spare parts and ground maintenance equipment, which the 5
6 number of ground maintenance equipment should be avoid he queue is lengthening. Step.2 Calculate the marginal increment of spare parts and ground maintenance equipment, i.e., calculate the maximum value of i EBO (S i) EBO(Si1) ci and k EBO (S k) EBO(Sk1) ck, Increase the unit number of spare parts or ground maintenance equipment according to the maximum marginal increment. Step.3 Calculate the total investment cost C, if C C0, go to step.2; otherwise, end of the calculation. 5 Numerical example A typical numerical example is provided to illuminate the application of our model. The maintenance resources allocation problem about the engine of s aircrafts that used on American route is selected as the research object. The fleet consisted of 5 Boeing and 10 Boeing ER aircraft, the Boeing aircraft used on Chongqing - Being - San Francisco and Being - New York routes, the Boeing ER aircraft used on Being - Los Angeles, Being - Houston and Being -Washington routes. The two kinds of aircrafts were used GEnx and GE90 engine respectively, the specific parameters are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. Airport maintenance points are regarded as the Location Warehouse (LW), the company called are regarded as the Central Department (CD). A set of GE engine maintenance equipment at the LW worth $1 million, and the price of maintenance equipment at the CD is $40 million. Table 1 GEnx aeroengine parameters name The number of aircraft Installed number Flight hours/hour Mean Time Between Failure/Hour Cost/USD GEnx-2B67 engine M Repair Average Order and ship Order and ship probability at Repair probability repair time(internal)/day time(abroad)/day the at the LW(abroad) time/day LW(internal) Table 2GE90 aeroengine parameters The Mean Time Installed Flight name number of Between number hours/hour aircraft Failure/Hour Cost/USD GE90-115B engine M Repair Average Order and ship Order and ship probability at Repair probability repair time(internal)/day time(abroad)/day the at the LW(abroad) time/day LW(internal) Through the establishment of the joint allocation model proposed by this paper, the method of marginal analysis is adopted to get the fleet availability. Finally, we obtained the allocation scheme with the fleet availability of 0.96 under the investment expenses of $684 million. The allocation scheme of spare parts and ground maintenance equipment are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. The curves about expectation of spare parts shortage and fleet availability that are changed over investment cost as shown in Figure 2. Table 3 the number of spare parts Location Being Chongqing San Francisco New York The spare parts number
7 of GEnx engine location Being Los Houston Washington Angeles The spare parts number of GE90 engine Cost $ 517 million Table 4 the number of maintenance equipment Location Being Chongqing San New York Francisco The number of maintenance Los Angeles Houston Washington equipment Cost $ 167 million Figure 2The curves of expectation of spare parts shortage and fleet availability changed over cost The results show that the following two points: (1) The fleet availability increased with investment cost, but the growth trend is more and more slow. So it s usually to maintain the fleet availability between in engineering applications, some important parts such as the engine can be maintained at (2) The lack of ground maintenance equipment caused significantly impact on spare parts shortage, but when the maintenance equipment achieve a certain amount, the influence to spare parts from the number of maintenance equipment will decrease sharply. So it s impossible to improve the fleet availability through continue to increase the number of maintenance equipment. If we do not consider the impact of maintenance equipment, and using the assumption of infinite maintenance capability, we can get the engine spare parts inventory scheme under the same availability (see table 5). Table 5 the number of spare parts Location Being Chongqing The spare parts number of GEnx engine San Francisco New York location Being Los Angeles Houston Washington The spare parts number of GE90 engine Cost $ million Observing the allocation of engine spare parts under infinite maintenance capacity, we found that the effect of repair capacity for spare parts allocation scheme is mainly reflected in the CD maintenance point. This is because the CD maintenance point has a heavy maintenance task, fault parts repaired quickly and translated into stock of spare parts timely under the infinite maintenance 7
8 capacity assumption, thereby the demand for the number of spare parts at the CD is reduced. Figure 3 comparison of limited and infinite repair capacity Due to the limited repair ability and ground equipment costs, there is a big gap of fleet availability in the same cost from whether to consider the ground maintenance equipment (see Figure 3). But with the increase in investment costs, the gap between the two is reduced gradually. The main reason is that after the maintenance equipment reached a certain number, it s influence on fleet availability decreased sharply. At this time, spare parts become the decisive element of fleet availability. To sum up, the united allocation model proposed in this paper can effectively solve the planning problem for spare parts and ground maintenance resources. 6 Summary For the current study, the spare parts inventory allocation model has the problem of over estimating the maintenance capability. In this paper, we take the allocation problem of aeroengine maintenance resources as an example, focusing on the use of M/M/c queuing model to analyze the effects of repair time from the number of maintenance equipment. A united planning model, which is used to allocate maintenance resources for civil aircraft is put forward, and the model can be solved by marginal analysis method. The research of this paper provides an effective method to reasonable allocating the maintenance resources for civil aircraft. The method can not only reduce maintenance cost, improve support efficiency of civil aircraft operation, but also enrich the theory, method and technology of maintenance resources allocation for civil aircraft. It has important application value in engineering for civil aircraft in using and development. Based on the current research, the future will consider the allocation of civil aircraft maintenance resources under the imperfect maintenance case. Acknowledgements The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No ) and Special Scientific Research Project of Civil Aircraft(MJZ-2014-F-06) References 1. Sherbrooke C C, Operations Research, 16, (1966) 2. Mcclain J O, Maxwell W L, Muckstadt J A, et al, Management Science, 30, (1984) 3. Graves S C, Management Science, 31, (1985) 4. J Xu, H Zuo, L Sun, Information Technology Journal, 13 (2014) 5. Costantino F, Gravio G D, Tronci M, Reliability Engineering System Safety, 119, (2013) 8
Examining Stock Positions in Military Logistics
 Examining Stock Positions in Military Logistics Nancy Sloan, M.S.O.R., Manuel Rossetti, Ph.D. Department of Industrial Engineering University of Arkansas Fayetteville, AR 72701, USA Abstract Decisions
Examining Stock Positions in Military Logistics Nancy Sloan, M.S.O.R., Manuel Rossetti, Ph.D. Department of Industrial Engineering University of Arkansas Fayetteville, AR 72701, USA Abstract Decisions
Principles of Inventory Management
 John A. Muckstadt Amar Sapra Principles of Inventory Management When You Are Down to Four, Order More fya Springer Inventories Are Everywhere 1 1.1 The Roles of Inventory 2 1.2 Fundamental Questions 5
John A. Muckstadt Amar Sapra Principles of Inventory Management When You Are Down to Four, Order More fya Springer Inventories Are Everywhere 1 1.1 The Roles of Inventory 2 1.2 Fundamental Questions 5
An optimal approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking
 An optimal approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking R.J.I. Basten M.C. van der Heijden J.M.J. Schutten February 17, 2010 1 Introduction We propose a method that
An optimal approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking R.J.I. Basten M.C. van der Heijden J.M.J. Schutten February 17, 2010 1 Introduction We propose a method that
Expediting in Two-Echelon Spare Parts Inventory Systems
 Expediting in Two-Echelon Spare Parts Inventory Systems Melvin Drent and Joachim Arts University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg Centre for Logistics and Supply Chain Management, melvin.drent@uni.lu, joachim.arts@uni.lu
Expediting in Two-Echelon Spare Parts Inventory Systems Melvin Drent and Joachim Arts University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg Centre for Logistics and Supply Chain Management, melvin.drent@uni.lu, joachim.arts@uni.lu
Spare Parts Inventory Management with Demand Lead Times and Rationing
 Spare Parts Inventory Management with Demand Lead Times and Rationing Yasar Levent Kocaga Alper Sen Department of Industrial Engineering Bilkent University Bilkent, Ankara 06800, Turkey {yasarl,alpersen}@bilkent.edu.tr
Spare Parts Inventory Management with Demand Lead Times and Rationing Yasar Levent Kocaga Alper Sen Department of Industrial Engineering Bilkent University Bilkent, Ankara 06800, Turkey {yasarl,alpersen}@bilkent.edu.tr
RISK-POOLING EFFECTS OF DIRECT SHIPPING IN A ONE-WAREHOUSE N-RETAILER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 RISK-POOLING EFFECTS OF DIRECT SHIPPING IN A ONE-WAREHOUSE N-RETAILER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Sangwook Park* I. Introduction N. The Model U. Model and Assumptions V. Concludin~ remarks ID. Previous Study I.
RISK-POOLING EFFECTS OF DIRECT SHIPPING IN A ONE-WAREHOUSE N-RETAILER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Sangwook Park* I. Introduction N. The Model U. Model and Assumptions V. Concludin~ remarks ID. Previous Study I.
D.K.M.COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS), VELLORE-1. OPERATIONS RESEARCH
 D.K.M.COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS), VELLORE-1. OPERATIONS RESEARCH UNIT-1 DECISION THEORY SECTION -A 1. Define Essential Elements in Decision Model? 2. Explain steps in Decision theory approach. 3. A
D.K.M.COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS), VELLORE-1. OPERATIONS RESEARCH UNIT-1 DECISION THEORY SECTION -A 1. Define Essential Elements in Decision Model? 2. Explain steps in Decision theory approach. 3. A
Analysis and Design of the Logistics System for Rope Manufacturing Plant
 Analysis and Design of the Logistics System for Rope Manufacturing Plant Xue Sun 1,2,*, Chao-Chin Wu 3, and Liang-Rui Chen 2 1 College of Urban Rail Transit and Logistics, Beijing Union University, Beijing,
Analysis and Design of the Logistics System for Rope Manufacturing Plant Xue Sun 1,2,*, Chao-Chin Wu 3, and Liang-Rui Chen 2 1 College of Urban Rail Transit and Logistics, Beijing Union University, Beijing,
AFTER SALES SERVICES FOR REPAIRABLE PARTS WITH SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS
 AFTER SALES SERVICES FOR REPAIRABLE PARTS WITH SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School at the University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
AFTER SALES SERVICES FOR REPAIRABLE PARTS WITH SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENTS A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School at the University of Missouri In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Optimizing the Safety Stock Inventory Cost Under Target Service Level Constraints
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 Dissertations and Theses 2012 Optimizing the Safety Stock Inventory Cost Under Target Service Level Constraints
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Masters Theses 1911 - February 2014 Dissertations and Theses 2012 Optimizing the Safety Stock Inventory Cost Under Target Service Level Constraints
The integration of online and offline channels
 The integration of online and offline channels Zihan Zhou, Qinan Wang Nanyang Business School, Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 69798 zzhou6@e.ntu.edu.sg Abstract We study a
The integration of online and offline channels Zihan Zhou, Qinan Wang Nanyang Business School, Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 69798 zzhou6@e.ntu.edu.sg Abstract We study a
Computing small-fleet aircraft availabilities including redundancy and spares
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln U.S. Air Force Research U.S. Department of Defense 2002 Computing small-fleet aircraft availabilities including redundancy
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln U.S. Air Force Research U.S. Department of Defense 2002 Computing small-fleet aircraft availabilities including redundancy
The Staffing Problem of the N-Design Multi-Skill Call Center Based on Queuing Model
 3rd International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor etwork (WCS 06) The Staffing Problem of the -Design Multi-Skill Call Center Based on Queuing Model Chun-Yan Li, De-Quan Yue Zhijiang College
3rd International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor etwork (WCS 06) The Staffing Problem of the -Design Multi-Skill Call Center Based on Queuing Model Chun-Yan Li, De-Quan Yue Zhijiang College
A SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF THE VARI-METRIC REPAIRABLE INVENTORY OPTIMIZATION PROCEDURE FOR THE U.S. COAST GUARD. Michael Freimer
 Proceedings of the 2005 Winter Simulation Conference M. E. Kuhl, N. M. Steiger, F. B. Armstrong, and J. A. Joines, eds. A SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF THE VARI-METRIC REPAIRABLE INVENTORY OPTIMIZATION PROCEDURE
Proceedings of the 2005 Winter Simulation Conference M. E. Kuhl, N. M. Steiger, F. B. Armstrong, and J. A. Joines, eds. A SIMULATION ANALYSIS OF THE VARI-METRIC REPAIRABLE INVENTORY OPTIMIZATION PROCEDURE
Chapter 7A Waiting Line Management. OBJECTIVES Waiting Line Characteristics Suggestions for Managing Queues Examples (Models 1, 2, 3, and 4)
 Chapter 7A Waiting Line Management 1 OBJECTIVES Waiting Line Characteristics Suggestions for Managing Queues Examples (Models 1, 2, 3, and 4) Components of the Queuing System 2 Customer Arrivals Servicing
Chapter 7A Waiting Line Management 1 OBJECTIVES Waiting Line Characteristics Suggestions for Managing Queues Examples (Models 1, 2, 3, and 4) Components of the Queuing System 2 Customer Arrivals Servicing
^ Springer. The Logic of Logistics. Theory, Algorithms, and Applications. for Logistics Management. David Simchi-Levi Xin Chen Julien Bramel
 David Simchi-Levi Xin Chen Julien Bramel The Logic of Logistics Theory, Algorithms, and Applications for Logistics Management Third Edition ^ Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 What Is Logistics Management?
David Simchi-Levi Xin Chen Julien Bramel The Logic of Logistics Theory, Algorithms, and Applications for Logistics Management Third Edition ^ Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 What Is Logistics Management?
Modelling Multiechelon Inventory Systems for Repairable Items using Spreadsheets
 Modelling Multiechelon Inventory Systems for Repairable Items using Spreadsheets 1 Dinesh Shenoy, 2 Hoshiar Mal 1,2 Department of Operations Management, FLAME University, Lavale, Pune, Maharastra, INDIA.
Modelling Multiechelon Inventory Systems for Repairable Items using Spreadsheets 1 Dinesh Shenoy, 2 Hoshiar Mal 1,2 Department of Operations Management, FLAME University, Lavale, Pune, Maharastra, INDIA.
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010
 WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010 PhD Preliminary Examination Candidate Name: 1- Sensitivity Analysis (20 points) Answer ALL Questions Question 1-20
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010 PhD Preliminary Examination Candidate Name: 1- Sensitivity Analysis (20 points) Answer ALL Questions Question 1-20
Lecture 45. Waiting Lines. Learning Objectives
 Lecture 45 Waiting Lines Learning Objectives After completing the lecture, we should be able to explain the formation of waiting lines in unloaded systems, identify the goal of queuing ( waiting line)
Lecture 45 Waiting Lines Learning Objectives After completing the lecture, we should be able to explain the formation of waiting lines in unloaded systems, identify the goal of queuing ( waiting line)
Introduction - Simulation. Simulation of industrial processes and logistical systems - MION40
 Introduction - Simulation Simulation of industrial processes and logistical systems - MION40 1 What is a model? A model is an external and explicit representation of part of reality as seen by the people
Introduction - Simulation Simulation of industrial processes and logistical systems - MION40 1 What is a model? A model is an external and explicit representation of part of reality as seen by the people
Mass Customized Large Scale Production System with Learning Curve Consideration
 Mass Customized Large Scale Production System with Learning Curve Consideration KuoWei Chen and Richard Lee Storch Industrial & Systems Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, U.S.A {kwc206,rlstorch}@uw.edu
Mass Customized Large Scale Production System with Learning Curve Consideration KuoWei Chen and Richard Lee Storch Industrial & Systems Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, U.S.A {kwc206,rlstorch}@uw.edu
Joint optimization of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocks Basten, R.J.I.; Heijden, van der, M.C.; Schutten, J.M.J.
 Joint optimization of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocks Basten, R.J.I.; Heijden, van der, M.C.; Schutten, J.M.J. Published: 01/01/2011 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version
Joint optimization of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocks Basten, R.J.I.; Heijden, van der, M.C.; Schutten, J.M.J. Published: 01/01/2011 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version
Queueing Theory and Waiting Lines
 Queueing Theory and Waiting Lines Most waiting line problems are trying to find the best service Large staff => Good Service Small staff => Poor Service What is Best It depends on the organization! Most
Queueing Theory and Waiting Lines Most waiting line problems are trying to find the best service Large staff => Good Service Small staff => Poor Service What is Best It depends on the organization! Most
Hamdy A. Taha, OPERATIONS RESEARCH, AN INTRODUCTION, 5 th edition, Maxwell Macmillan International, 1992
 Reference books: Anderson, Sweeney, and Williams, AN INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT SCIENCE, QUANTITATIVE APPROACHES TO DECISION MAKING, 7 th edition, West Publishing Company,1994 Hamdy A. Taha, OPERATIONS
Reference books: Anderson, Sweeney, and Williams, AN INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT SCIENCE, QUANTITATIVE APPROACHES TO DECISION MAKING, 7 th edition, West Publishing Company,1994 Hamdy A. Taha, OPERATIONS
An Efficient Heuristic Optimization Algorithm for a Two-Echelon (R, Q) Inventory System. Abstract
 An Efficient Heustic Optimization Algothm for a Two-Echelon (R, Q) Inventory System Authors and Affiliations: Mohammad H. Al-Rifai, Ph.D., Propak Corporation Manuel D. Rossetti, Ph. D., University of Arkansas
An Efficient Heustic Optimization Algothm for a Two-Echelon (R, Q) Inventory System Authors and Affiliations: Mohammad H. Al-Rifai, Ph.D., Propak Corporation Manuel D. Rossetti, Ph. D., University of Arkansas
Numerical investigation of tradeoffs in production-inventory control policies with advance demand information
 Numerical investigation of tradeoffs in production-inventory control policies with advance demand information George Liberopoulos and telios oukoumialos University of Thessaly, Department of Mechanical
Numerical investigation of tradeoffs in production-inventory control policies with advance demand information George Liberopoulos and telios oukoumialos University of Thessaly, Department of Mechanical
Integrated planning of operations and spare parts logistics under uncertainty in the supply chain of maintenance service providers
 Integrated planning of operations and spare parts logistics under uncertainty in the supply chain of maintenance service providers Masoumeh Kazemi Zanjani, JEng, PhD Concordia University, Montreal, Canada
Integrated planning of operations and spare parts logistics under uncertainty in the supply chain of maintenance service providers Masoumeh Kazemi Zanjani, JEng, PhD Concordia University, Montreal, Canada
Spare parts allocation fuzzy systems approach
 Spare parts allocation fuzzy systems approach LES M. SZTANDERA Computer Information Systems Philadelphia University School House Lane and Henry Avenues Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19144-5497 UNITED STATES
Spare parts allocation fuzzy systems approach LES M. SZTANDERA Computer Information Systems Philadelphia University School House Lane and Henry Avenues Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19144-5497 UNITED STATES
Queuing Theory 1.1 Introduction
 Queuing Theory 1.1 Introduction A common situation occurring in everyday life is that of queuing or waiting in a line. Queues (waiting lines) are usually seen at bus stop, ticket booths, doctor s clinics,
Queuing Theory 1.1 Introduction A common situation occurring in everyday life is that of queuing or waiting in a line. Queues (waiting lines) are usually seen at bus stop, ticket booths, doctor s clinics,
Rotables stocking and repair : a Markov approach
 Rotables stocking and repair : a Markov approach Citation for published version (APA): de Haas, H. F. M. (1992). Rotables stocking and repair : a Markov approach. (TU Eindhoven. Fac. TBDK, Vakgroep LBS
Rotables stocking and repair : a Markov approach Citation for published version (APA): de Haas, H. F. M. (1992). Rotables stocking and repair : a Markov approach. (TU Eindhoven. Fac. TBDK, Vakgroep LBS
Deriving the Exact Cost Function for a Two-Level Inventory System with Information Sharing
 Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering Vol. 2, No., pp 4-5 Spring 28 Deriving the Exact Cost Function for a Two-Level Inventory System with Information Sharing R. Haji *, S.M. Sajadifar 2,2 Industrial
Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering Vol. 2, No., pp 4-5 Spring 28 Deriving the Exact Cost Function for a Two-Level Inventory System with Information Sharing R. Haji *, S.M. Sajadifar 2,2 Industrial
This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 6(4): 1400-1411, 2012 ISSN 1995-0756 1400 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Joint Production and Economic
Advances in Environmental Biology, 6(4): 1400-1411, 2012 ISSN 1995-0756 1400 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Joint Production and Economic
University Question Paper Two Marks
 University Question Paper Two Marks 1. List the application of Operations Research in functional areas of management. Answer: Finance, Budgeting and Investment Marketing Physical distribution Purchasing,
University Question Paper Two Marks 1. List the application of Operations Research in functional areas of management. Answer: Finance, Budgeting and Investment Marketing Physical distribution Purchasing,
Chapter 14. Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models
 Chapter 4 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Tenth Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Jeff Heyl 2008 Prentice-Hall,
Chapter 4 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Tenth Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Jeff Heyl 2008 Prentice-Hall,
Textbook: pp Chapter 12: Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models
 1 Textbook: pp. 445-478 Chapter 12: Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models 2 Learning Objectives (1 of 2) After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Describe the trade-off curves for cost-of-waiting
1 Textbook: pp. 445-478 Chapter 12: Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models 2 Learning Objectives (1 of 2) After completing this chapter, students will be able to: Describe the trade-off curves for cost-of-waiting
An Approach to Predicting Passenger Operation Performance from Commuter System Performance
 An Approach to Predicting Passenger Operation Performance from Commuter System Performance Bo Chang, Ph. D SYSTRA New York, NY ABSTRACT In passenger operation, one often is concerned with on-time performance.
An Approach to Predicting Passenger Operation Performance from Commuter System Performance Bo Chang, Ph. D SYSTRA New York, NY ABSTRACT In passenger operation, one often is concerned with on-time performance.
An approximate approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking
 An approximate approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking R.J.I. Basten, M.C. van der Heijden, J.M.J. Schutten Beta Working Paper series 347 BETA publicatie WP
An approximate approach for the joint problem of level of repair analysis and spare parts stocking R.J.I. Basten, M.C. van der Heijden, J.M.J. Schutten Beta Working Paper series 347 BETA publicatie WP
Multi-Echelon Network Evaluation and Inventory Strategy. Boxi Xu Patrick Scott MIT Master of Supply Chain Management Class of 2017
 Multi-Echelon Network Evaluation and Inventory Strategy Boxi Xu Patrick Scott MIT Master of Supply Chain Management Class of 2017 Overview Thesis sponsor Major global oil field service company Objective
Multi-Echelon Network Evaluation and Inventory Strategy Boxi Xu Patrick Scott MIT Master of Supply Chain Management Class of 2017 Overview Thesis sponsor Major global oil field service company Objective
INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF QUEUES 16.1 Introduction
 INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF QUEUES 16.1 Introduction The study of waiting lines, called queuing theory is one of the oldest and most widely used Operations Research techniques. Waiting lines are
INTRODUCTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF QUEUES 16.1 Introduction The study of waiting lines, called queuing theory is one of the oldest and most widely used Operations Research techniques. Waiting lines are
Through Life Availability Simulation
 Through Life Availability Simulation Greg van Bavel Department of National Defence Centre for Operational Research and Analysis Presented to the OmegaPS Analyzer UGM 2017 November 9 Her Majesty the Queen
Through Life Availability Simulation Greg van Bavel Department of National Defence Centre for Operational Research and Analysis Presented to the OmegaPS Analyzer UGM 2017 November 9 Her Majesty the Queen
Factory Operations Research Center (FORCe II)
 Factory Operations Research Center (FORCe II) SRC/ISMT 2004-OJ-1214 Configuration, monitoring and control of semiconductor supply chains Jan. 7, 2005 Shi-Chung Chang (task 1) Argon Chen (task 2) Yon Chou
Factory Operations Research Center (FORCe II) SRC/ISMT 2004-OJ-1214 Configuration, monitoring and control of semiconductor supply chains Jan. 7, 2005 Shi-Chung Chang (task 1) Argon Chen (task 2) Yon Chou
Multi-echelon Inventory Control with Integrated Shipment Decisions
 Multi-echelon Inventory Control with Integrated Shipment Decisions Stenius, Olof 2014 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Stenius, O. (2014). Multi-echelon Inventory Control with
Multi-echelon Inventory Control with Integrated Shipment Decisions Stenius, Olof 2014 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Stenius, O. (2014). Multi-echelon Inventory Control with
Availability Modeling of Grid Computing Environments Using SANs
 Availability Modeling of Grid Computing Environments Using SANs Reza Entezari-Maleki Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran E-mail: entezari@ce.sharif.edu Ali
Availability Modeling of Grid Computing Environments Using SANs Reza Entezari-Maleki Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran E-mail: entezari@ce.sharif.edu Ali
A multi-item spare parts inventory model with customer differentiation
 A multi-item spare parts inventory model with customer differentiation Citation for published version (APA): Kranenburg, A. A., & Houtum, van, G. J. J. A. N. (2004). A multi-item spare parts inventory
A multi-item spare parts inventory model with customer differentiation Citation for published version (APA): Kranenburg, A. A., & Houtum, van, G. J. J. A. N. (2004). A multi-item spare parts inventory
B.V. Patel Institute of Business Management, Computer & Information Technology, Uka Tarsadia University : Managerial Economics
 Unit-1 Introduction of Managerial Economics and Cost Analysis Answer the following. (1 mark) 1. Define Managerial Economics? 2. How does Managerial Economics help managers to become efficient and competent?
Unit-1 Introduction of Managerial Economics and Cost Analysis Answer the following. (1 mark) 1. Define Managerial Economics? 2. How does Managerial Economics help managers to become efficient and competent?
Stocking strategy for service parts : a case study
 Stocking strategy for service parts : a case study Botter, R.; Fortuin, L. Published: 01/01/1998 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and volume
Stocking strategy for service parts : a case study Botter, R.; Fortuin, L. Published: 01/01/1998 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and volume
and type II customers arrive in batches of size k with probability d k
 xv Preface Decision making is an important task of any industry. Operations research is a discipline that helps to solve decision making problems to make viable decision one needs exact and reliable information
xv Preface Decision making is an important task of any industry. Operations research is a discipline that helps to solve decision making problems to make viable decision one needs exact and reliable information
1 Introduction Importance and Objectives of Inventory Control Overview and Purpose of the Book Framework...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Importance and Objectives of Inventory Control... 1 1.2 Overview and Purpose of the Book... 2 1.3 Framework... 4 2 Forecasting... 7 2.1 Objectives and Approaches... 7 2.2
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Importance and Objectives of Inventory Control... 1 1.2 Overview and Purpose of the Book... 2 1.3 Framework... 4 2 Forecasting... 7 2.1 Objectives and Approaches... 7 2.2
A Simple EOQ-like Solution to an Inventory System with Compound Poisson and Deterministic Demand
 A Simple EOQ-like Solution to an Inventory System with Compound Poisson and Deterministic Demand Katy S. Azoury San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA Julia Miyaoka* San Francisco
A Simple EOQ-like Solution to an Inventory System with Compound Poisson and Deterministic Demand Katy S. Azoury San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA Julia Miyaoka* San Francisco
Code No: RR Set No. 1
 Code No: RR410301 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 OPERATIONS RESEARCH ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Code No: RR410301 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 OPERATIONS RESEARCH ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Techniques of Operations Research
 Techniques of Operations Research C HAPTER 2 2.1 INTRODUCTION The term, Operations Research was first coined in 1940 by McClosky and Trefthen in a small town called Bowdsey of the United Kingdom. This
Techniques of Operations Research C HAPTER 2 2.1 INTRODUCTION The term, Operations Research was first coined in 1940 by McClosky and Trefthen in a small town called Bowdsey of the United Kingdom. This
4. Management Information Systems and Decision Support Systems
 4. Management Information Systems and Decision Support Systems As we have seen, a transaction processing system serves as the foundation for the other systems. Transaction processing systems are operational
4. Management Information Systems and Decision Support Systems As we have seen, a transaction processing system serves as the foundation for the other systems. Transaction processing systems are operational
Top 10 Tasks Complete Sample Work Order Status Updates for Quality Assurance During Upgrade/Repair Simulations
 Top 10 Tasks Complete Sample Work Order Status Updates for Quality Assurance During Upgrade/Repair Simulations 03/01/2017 Here we describe simulation models for repair processes of field-level aircraft,
Top 10 Tasks Complete Sample Work Order Status Updates for Quality Assurance During Upgrade/Repair Simulations 03/01/2017 Here we describe simulation models for repair processes of field-level aircraft,
Mathematical approach to the analysis of waiting lines
 Queueing Theory Mathematical approach to the analysis of waiting lines This theory is applicable to a wide range of service operations, including call centers, banks, post offices, restaurants, theme parks,
Queueing Theory Mathematical approach to the analysis of waiting lines This theory is applicable to a wide range of service operations, including call centers, banks, post offices, restaurants, theme parks,
Chapter 13. Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models
 Chapter 13 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Eleventh Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Brian Peterson Learning
Chapter 13 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models To accompany Quantitative Analysis for Management, Eleventh Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna Power Point slides created by Brian Peterson Learning
A decision aid for make-to-order and make-to-stock classification
 Chapter 3 A decision aid for make-to-order and make-to-stock classification Managers in food processing industries find it difficult to decide which products to make to order and which products to stock.
Chapter 3 A decision aid for make-to-order and make-to-stock classification Managers in food processing industries find it difficult to decide which products to make to order and which products to stock.
Integrated Inventory Model with Decreasing Probability of Imperfect Maintenance in a Supply Chain
 , March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Integrated Inventory Model with Decreasing Probability of Imperfect Maintenance in a Supply Chain Ming Feng Yang, Chien Min Su, Ming Cheng Lo, Hsu Hsin Lee and Wei Chung
, March 13-15, 2013, Hong Kong Integrated Inventory Model with Decreasing Probability of Imperfect Maintenance in a Supply Chain Ming Feng Yang, Chien Min Su, Ming Cheng Lo, Hsu Hsin Lee and Wei Chung
Routing and Inventory Allocation Policies in Multi-Echelon. Distribution Systems
 Routing and Inventory Allocation Policies in Multi-Echelon Distribution Systems Routing and Inventory Allocation Policies in Multi-Echelon Distribution Systems Sangwook Park College of Business Administration
Routing and Inventory Allocation Policies in Multi-Echelon Distribution Systems Routing and Inventory Allocation Policies in Multi-Echelon Distribution Systems Sangwook Park College of Business Administration
Study on Predictive Maintenance Strategy
 , pp.52-56 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.137.10 Study on Predictive Maintenance Strategy Wang Hongxia, Ye Xiaohui, Yin Ming Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China 25523224@QQ.com Abstract.
, pp.52-56 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.137.10 Study on Predictive Maintenance Strategy Wang Hongxia, Ye Xiaohui, Yin Ming Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China 25523224@QQ.com Abstract.
Research on the Impact of Big Data on Logistics
 Research on the Impact of Big Data on Logistics Yaxing Wang 1,*, Lijie Feng 1, Heyu Chang 1 and Min Wu 1 1 School of management and engineering, Zhengzhou University, China Corresponding Email:615871159@qq.com
Research on the Impact of Big Data on Logistics Yaxing Wang 1,*, Lijie Feng 1, Heyu Chang 1 and Min Wu 1 1 School of management and engineering, Zhengzhou University, China Corresponding Email:615871159@qq.com
Justifying Advanced Finite Capacity Planning and Scheduling
 Justifying Advanced Finite Capacity Planning and Scheduling Charles J. Murgiano, CPIM WATERLOO MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE 1. Introduction How well your manufacturing company manages production on the shop
Justifying Advanced Finite Capacity Planning and Scheduling Charles J. Murgiano, CPIM WATERLOO MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE 1. Introduction How well your manufacturing company manages production on the shop
Sven Axsäter. Inventory Control. Third Edition. Springer
 Sven Axsäter Inventory Control Third Edition Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Importance and Objectives of Inventory Control 1 1.2 Overview and Purpose of the Book 2 1.3 Framework 4 2 Forecasting
Sven Axsäter Inventory Control Third Edition Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Importance and Objectives of Inventory Control 1 1.2 Overview and Purpose of the Book 2 1.3 Framework 4 2 Forecasting
Discrete and dynamic versus continuous and static loading policy for a multi-compartment vehicle
 European Journal of Operational Research 174 (2006) 1329 1337 Short Communication Discrete and dynamic versus continuous and static loading policy for a multi-compartment vehicle Yossi Bukchin a, *, Subhash
European Journal of Operational Research 174 (2006) 1329 1337 Short Communication Discrete and dynamic versus continuous and static loading policy for a multi-compartment vehicle Yossi Bukchin a, *, Subhash
WAITING LINE MODELS Introduction
 WAITING LINE MODELS Introduction Professor Robert Saltzman Operations Analysis Queuing Analysis: The Study of Waiting Lines Lines are everywhere in the service sector: Grocery store checkout Airport bag
WAITING LINE MODELS Introduction Professor Robert Saltzman Operations Analysis Queuing Analysis: The Study of Waiting Lines Lines are everywhere in the service sector: Grocery store checkout Airport bag
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS ANALYSIS OF A PROPOSAL TO IMPLEMENT THE READINESS-BASED SPARING PROCESS IN THE BRAZILIAN NAVY by Régis M. Nogueira June 2017 Thesis Advisor: Co-Advisor:
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS ANALYSIS OF A PROPOSAL TO IMPLEMENT THE READINESS-BASED SPARING PROCESS IN THE BRAZILIAN NAVY by Régis M. Nogueira June 2017 Thesis Advisor: Co-Advisor:
Managing Decentralized Inventory and Transhipment
 Managing Decentralized Inventory and Transhipment Moshe Dror mdror@eller.arizona.edu Nichalin Suakkaphong nichalin@email.arizona.edu Department of MIS University of Arizona Fleet Size Mix and Inventory
Managing Decentralized Inventory and Transhipment Moshe Dror mdror@eller.arizona.edu Nichalin Suakkaphong nichalin@email.arizona.edu Department of MIS University of Arizona Fleet Size Mix and Inventory
An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems
 An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems Srinivasan Jagannathan & Kevin C. Almeroth Department of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, CA 936-5 fjsrini,almerothg@cs.ucsb.edu
An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems Srinivasan Jagannathan & Kevin C. Almeroth Department of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, CA 936-5 fjsrini,almerothg@cs.ucsb.edu
Scheduling theory, part 1
 Scheduling theory, part 1 Aperiodic jobs Pontus Ekberg Uppsala University 2017-09-01 Real-time systems? Not necessarily fast but always predictable 2 Real-time systems: theory & practice Practice Building
Scheduling theory, part 1 Aperiodic jobs Pontus Ekberg Uppsala University 2017-09-01 Real-time systems? Not necessarily fast but always predictable 2 Real-time systems: theory & practice Practice Building
The 2x2 Exchange Economy. Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/2 (Lecture 8, Micro Theory I)
 The 2x2 Exchange Economy Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/2 (Lecture 8, Micro Theory I) Road Map for Chapter 3 Pareto Efficiency Allocation (PEA) Cannot make one better off without hurting others Walrasian (Price-taking)
The 2x2 Exchange Economy Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/2 (Lecture 8, Micro Theory I) Road Map for Chapter 3 Pareto Efficiency Allocation (PEA) Cannot make one better off without hurting others Walrasian (Price-taking)
The economics of competitive markets Rolands Irklis
 The economics of competitive markets Rolands Irklis www. erranet.org Presentation outline 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Consumer s demand 3. Producer costs and supply decisions 4. Market equilibrium
The economics of competitive markets Rolands Irklis www. erranet.org Presentation outline 1. Introduction and motivation 2. Consumer s demand 3. Producer costs and supply decisions 4. Market equilibrium
Aviation Management System
 Aviation Management System 1 2 Silver Wings Aircraft Aviation Management System represents a functional high end suite of integrated applications that fully addresses the needs of aircraft maintenance
Aviation Management System 1 2 Silver Wings Aircraft Aviation Management System represents a functional high end suite of integrated applications that fully addresses the needs of aircraft maintenance
General Equilibrium for the Exchange Economy. Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/9 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I)
 General Equilibrium for the Exchange Economy Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/9 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) What s in between the lines? And God said, 2 Let there be light and there was light. (Genesis 1:3,
General Equilibrium for the Exchange Economy Joseph Tao-yi Wang 2013/10/9 (Lecture 9, Micro Theory I) What s in between the lines? And God said, 2 Let there be light and there was light. (Genesis 1:3,
How to Determine if You Need an RFID Tracking Solution
 How to Determine if You Need an RFID Tracking Solution The Returnable Container Challenge Returnable transport items (RTIs) are a critical component of many supply chains. RTIs include reusable totes,
How to Determine if You Need an RFID Tracking Solution The Returnable Container Challenge Returnable transport items (RTIs) are a critical component of many supply chains. RTIs include reusable totes,
Differential Analysis: Relevant Costs the Key to Decision Making
 April 30, 2014 Differential Analysis: Relevant Costs the Key to Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
April 30, 2014 Differential Analysis: Relevant Costs the Key to Decision Making Today s Agenda Relevant Costs vs. Irrelevant Costs Differential Approach vs. Total Cost Approach Product Transfer Decision
LECTURE 13 (and forward): TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION
 Introduction to Tranportation Systems 1.201J/11.545J/ESD.210J Fall 2006 LECTURE 13 (and forward): TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION DISPLAYS October 24 (and forward), 2006 SPEAKER: Joseph M. Sussman MIT Traveler
Introduction to Tranportation Systems 1.201J/11.545J/ESD.210J Fall 2006 LECTURE 13 (and forward): TRAVELER TRANSPORTATION DISPLAYS October 24 (and forward), 2006 SPEAKER: Joseph M. Sussman MIT Traveler
Research of Inbound Mode for Automobile Parts Logistics Based on the Second Factory of Company H
 Journal of Investment and Management 2016; 5(4): 34-38 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jim doi: 10.11648/j.jim.20160504.12 ISSN: 2328-7713 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7721 (Online) Research of Inbound
Journal of Investment and Management 2016; 5(4): 34-38 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jim doi: 10.11648/j.jim.20160504.12 ISSN: 2328-7713 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7721 (Online) Research of Inbound
SERVICE TOOLS: WHY BOTHER?
 SERVICE TOOLS: WHY BOTHER? Optimization of stock levels for service tool inventory SECOND ISRAELI-DUTCH WORKSHOP ON QUEUEING THEORY SEPTEMBER 29 - OCTOBER 1, 2010 INGRID VLIEGEN 1 Co-authors: Ana Bušić
SERVICE TOOLS: WHY BOTHER? Optimization of stock levels for service tool inventory SECOND ISRAELI-DUTCH WORKSHOP ON QUEUEING THEORY SEPTEMBER 29 - OCTOBER 1, 2010 INGRID VLIEGEN 1 Co-authors: Ana Bušić
Analysis of The Time Value for Public Transport Passenger by Using Random Regret Minimization
 Analysis of The Time Value for Public Transport Passenger by Using Random Regret Minimization Medis Surbakti 1 and Fransiscus Pinem 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
Analysis of The Time Value for Public Transport Passenger by Using Random Regret Minimization Medis Surbakti 1 and Fransiscus Pinem 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
WE consider the dynamic pickup and delivery problem
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 53, NO. 6, JULY 2008 1419 A Dynamic Pickup and Delivery Problem in Mobile Networks Under Information Constraints Holly A. Waisanen, Devavrat Shah, and Munther
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 53, NO. 6, JULY 2008 1419 A Dynamic Pickup and Delivery Problem in Mobile Networks Under Information Constraints Holly A. Waisanen, Devavrat Shah, and Munther
Chapter C Waiting Lines
 Supplement C Waiting Lines Chapter C Waiting Lines TRUE/FALSE 1. Waiting lines cannot develop if the time to process a customer is constant. Answer: False Reference: Why Waiting Lines Form Keywords: waiting,
Supplement C Waiting Lines Chapter C Waiting Lines TRUE/FALSE 1. Waiting lines cannot develop if the time to process a customer is constant. Answer: False Reference: Why Waiting Lines Form Keywords: waiting,
Use of Queuing Models in Health Care - PPT
 University of Wisconsin-Madison From the SelectedWorks of Vikas Singh December, 2006 Use of Queuing Models in Health Care - PPT Vikas Singh, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Available at: https://works.bepress.com/vikas_singh/13/
University of Wisconsin-Madison From the SelectedWorks of Vikas Singh December, 2006 Use of Queuing Models in Health Care - PPT Vikas Singh, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Available at: https://works.bepress.com/vikas_singh/13/
1 Introduction 1. 2 Forecasting and Demand Modeling 5. 3 Deterministic Inventory Models Stochastic Inventory Models 63
 CONTENTS IN BRIEF 1 Introduction 1 2 Forecasting and Demand Modeling 5 3 Deterministic Inventory Models 29 4 Stochastic Inventory Models 63 5 Multi Echelon Inventory Models 117 6 Dealing with Uncertainty
CONTENTS IN BRIEF 1 Introduction 1 2 Forecasting and Demand Modeling 5 3 Deterministic Inventory Models 29 4 Stochastic Inventory Models 63 5 Multi Echelon Inventory Models 117 6 Dealing with Uncertainty
Midterm for CpE/EE/PEP 345 Modeling and Simulation Stevens Institute of Technology Fall 2003
 Midterm for CpE/EE/PEP 345 Modeling and Simulation Stevens Institute of Technology Fall 003 The midterm is open book/open notes. Total value is 100 points (30% of course grade). All questions are equally
Midterm for CpE/EE/PEP 345 Modeling and Simulation Stevens Institute of Technology Fall 003 The midterm is open book/open notes. Total value is 100 points (30% of course grade). All questions are equally
A Study on the Optimum Bucket Size for Master Scheduling:
 The Josai Journal of Business Administration 2010, Vols.6 & 7, No.1, 19 30 2010, Josai University A Study on the Optimum Bucket Size for Master Scheduling: For the Case of Hierarchically Structured Products
The Josai Journal of Business Administration 2010, Vols.6 & 7, No.1, 19 30 2010, Josai University A Study on the Optimum Bucket Size for Master Scheduling: For the Case of Hierarchically Structured Products
ISyE 3133B Sample Final Tests
 ISyE 3133B Sample Final Tests Time: 160 minutes, 100 Points Set A Problem 1 (20 pts). Head & Boulders (H&B) produces two different types of shampoos A and B by mixing 3 raw materials (R1, R2, and R3).
ISyE 3133B Sample Final Tests Time: 160 minutes, 100 Points Set A Problem 1 (20 pts). Head & Boulders (H&B) produces two different types of shampoos A and B by mixing 3 raw materials (R1, R2, and R3).
European Journal of Operational Research
 European Journal of Operational Research 214 (2011) 179 198 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Operational Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejor Invited Review
European Journal of Operational Research 214 (2011) 179 198 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Operational Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejor Invited Review
Queuing Models. Queue. System
 Queuing Models Introduction The goal of Queuing model is achievement of an economical balance between the cost of providing service and the cost associated with the wait required for that service This
Queuing Models Introduction The goal of Queuing model is achievement of an economical balance between the cost of providing service and the cost associated with the wait required for that service This
RAMCO AVIATION SOLUTION
 contents RAMCO AVIATION SOLUTION ENHANCEMENT NOTIFICATION Version 5.8.3 Materials 2017 Ramco Systems Ltd. All rights reserved. All trademarks acknowledged ramco 2017 Ramco Systems Ltd. All rights reserved.
contents RAMCO AVIATION SOLUTION ENHANCEMENT NOTIFICATION Version 5.8.3 Materials 2017 Ramco Systems Ltd. All rights reserved. All trademarks acknowledged ramco 2017 Ramco Systems Ltd. All rights reserved.
SCHEDULING AND CONTROLLING PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES
 SCHEDULING AND CONTROLLING PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University of Technology Baghdad - Iraq dr.mahmoudalnaimi@uotechnology.edu.iq
SCHEDULING AND CONTROLLING PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University of Technology Baghdad - Iraq dr.mahmoudalnaimi@uotechnology.edu.iq
Operations Research Models and Methods Paul A. Jensen and Jonathan F. Bard. Inventory Level. Figure 4. The inventory pattern eliminating uncertainty.
 Operations Research Models and Methods Paul A. Jensen and Jonathan F. Bard Inventory Theory.S2 The Deterministic Model An abstraction to the chaotic behavior of Fig. 2 is to assume that items are withdrawn
Operations Research Models and Methods Paul A. Jensen and Jonathan F. Bard Inventory Theory.S2 The Deterministic Model An abstraction to the chaotic behavior of Fig. 2 is to assume that items are withdrawn
Inventory Control. Inventory. Inventories in a manufacturing plant. Why inventory? Reasons for holding Raw Materials. Reasons for holding WIP
 Inventory Control Inventory the oldest result of the scientific management efforts inventory plays a key role in the logistical behavior of virtually all manufacturing systems the classical inventory results
Inventory Control Inventory the oldest result of the scientific management efforts inventory plays a key role in the logistical behavior of virtually all manufacturing systems the classical inventory results
Improvements of the Logistic Information System of Biomedical Products
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Improvements of the Logistic Information System 1, 2 Huawei TIAN 1 Department of economic management, 2 Small and medium-sized enterprises
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Improvements of the Logistic Information System 1, 2 Huawei TIAN 1 Department of economic management, 2 Small and medium-sized enterprises
Q&A ON THE DOUBLE-CHECKING SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM OF
 Q&A ON THE DOUBLE-CHECKING SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM OF IMPORTS OF SOME TEXTILES FROM CHINA This notice is for information purposes only and has no force in law. Please note that where legal advice is required
Q&A ON THE DOUBLE-CHECKING SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM OF IMPORTS OF SOME TEXTILES FROM CHINA This notice is for information purposes only and has no force in law. Please note that where legal advice is required
Simulation of Lean Principles Impact in a Multi-Product Supply Chain
 Simulation of Lean Principles Impact in a Multi-Product Supply Chain M. Rossini, A. Portioli Studacher Abstract The market competition is moving from the single firm to the whole supply chain because of
Simulation of Lean Principles Impact in a Multi-Product Supply Chain M. Rossini, A. Portioli Studacher Abstract The market competition is moving from the single firm to the whole supply chain because of
Production planning and. Unit 3
 1 Production planning and scheduling Unit 3 2 Background Because the aircraft manufacturing industry is highly sensitive to fluctuating demands and to their corresponding impact on production costs, a
1 Production planning and scheduling Unit 3 2 Background Because the aircraft manufacturing industry is highly sensitive to fluctuating demands and to their corresponding impact on production costs, a
Inventory Management IV
 Inventory Management IV Safety Stock Lecture 7 ESD.260 Fall 2003 Caplice Assumptions: Basic EOQ Model Demand Constant vs Variable Known vs Random Continuous vs Discrete Lead time Instantaneous Constant
Inventory Management IV Safety Stock Lecture 7 ESD.260 Fall 2003 Caplice Assumptions: Basic EOQ Model Demand Constant vs Variable Known vs Random Continuous vs Discrete Lead time Instantaneous Constant
Columbia Business School Problem Set 7: Solution
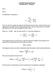 Columbia Business School roblem Set 7: Solution art 1: art a: The definition of elasticity is: ε d The term / is simply the slope of the demand function (p). (Note that this is the reciprocal of the slope
Columbia Business School roblem Set 7: Solution art 1: art a: The definition of elasticity is: ε d The term / is simply the slope of the demand function (p). (Note that this is the reciprocal of the slope
An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems
 An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems Srinivasan Jagannathan & Kevin C. Almeroth Department of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, CA 936-5 jsrini,almeroth @cs.ucsb.edu
An Adaptive Pricing Scheme for Content Delivery Systems Srinivasan Jagannathan & Kevin C. Almeroth Department of Computer Science University of California Santa Barbara, CA 936-5 jsrini,almeroth @cs.ucsb.edu
Evaluation of Ordering Systems for Multi-Echelon Inventory Control
 LICENTIATE THESIS 1994:07 L Division of Transportation and Material Flow Systems ISSN 0280 8242!SRN HLU - TH - L - - 1994/7 - L - - SE Evaluation of Ordering Systems for Multi-Echelon Inventory Control
LICENTIATE THESIS 1994:07 L Division of Transportation and Material Flow Systems ISSN 0280 8242!SRN HLU - TH - L - - 1994/7 - L - - SE Evaluation of Ordering Systems for Multi-Echelon Inventory Control
Bring order to chaos
 Quintiq Company Planner Bring order to chaos It s an ever demanding and fast-paced world. If you can t deliver on commitments, your competitors will. You ve scaled up your business with specialized equipment,
Quintiq Company Planner Bring order to chaos It s an ever demanding and fast-paced world. If you can t deliver on commitments, your competitors will. You ve scaled up your business with specialized equipment,
