1. Introduction. 1.1 Project Background. ANTONY JOHNSTONE Transport Associate Aurecon
|
|
|
- Oliver Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANTONY JOHNSTONE Transport Associate Aurecon RAFAEL CARVAJAL Operational Modelling and Visualisation Coordinator Main Roads WA PERTH FREEWAY MODELLING In May 2015, Aurecon was engaged by the Main Roads Western Australia (MRWA) Network Operations Directorate to develop the largest transport simulation model ever built in Western Australia. The initial model was 31km in length, 170 km2 in area, and covered of Perth's Northern Freeway and surrounding suburbs. A second stage was then commenced which further extended the model area to also cover the majority of the Perth s Southern Freeway, resulting in a total modelled Freeway length of 82km. The model enabled the Main Roads Network Operations team to gain crucial insights into how the network s infrastructure will perform in future years, and to understand the impact of proposed upgrades or developments. At the time the project pushed Aimsun s pre-existing capabilities TSS has selected the Freeway Simulation Model as one of its flagship projects to present at its user group meetings around the world. 1. Introduction 1.1 Project Background In 2015, Main Roads WA commissioned Aurecon and TSS to develop a model of the Mitchell Freeway and its surrounding network for its Freeway Management Strategy. The network improvements are part of a larger suite of network upgrades being implemented through the Traffic Congestion Management Program.
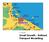
2 Figure 1 Traffic Congestion Management Program summary
3 2. Model Form 2.1 Aimsun The modelling software used in this study was Aimsun with the Hybrid model experiment type. A Hybrid model operates as a microsimulation model within user defined cordon areas, simulating individual vehicles and their interaction with other vehicles and the surrounding road environment. Outside of this cordon, a mesoscopic model environment is used to replicate the flow, delay, and route choice of variables using more simplistic algorithms. 2.2 Model Build Summary The road network was extended from the 2015 Mitchell Freeway model which was initially established through the import of the MRWA Regional Operations Model (ROM24). Further detail was then coded within the study area as well as the establishment of the initial cordon matrices. Detailed coding of lane and junction descriptions were developed using latest aerial photographs of the region and knowledge of the network operation. During the calibration process, model parameters were adjusted to align the model to that of the existing on-street behaviour. These parameters included: lane changing cooperation aggressiveness brake intensity acceleration side lane cooperation distance merging distance look ahead distance reaction time factor jam density The Aimsun version used was version (R37672 x64). 2.3 Base Model Network Microsimulation Areas The mesoscopic model area of the Hybrid model is the red cordon outside the green dotted line and covers the wider area. The key area within the green dotted line was modelled using the more detailed micro-simulation cordon environment. The micro-simulation cordon area primarily consists of the Mitchell Freeway/Kwinana Freeway corridors between Safety Bay Road and Burns Beach Road, and the connecting interchanges. A micro-simulation cordon area was also included at the intersection of Reid Highway and Wanneroo Road.
4 Figure 2 Base model network The base model network was built using available digital aerial photography, with site visits to confirm the accuracy and operation of the modelled network. Based on the supplied data, the model was constructed to a 1:1 scale, ensuring correct vehicle operation and accurate reaction to the road geometry and other vehicles. 2.4 Site Visits Site visits were undertaken using a chartered helicopter to observe and record the on-site conditions. Secondary observations for the central corridor train services and localised site visits were also undertaken.
5 3. Model Form 3.1 Traffic Demand Estimation Methodology The figure below describes the traffic demand estimation methodology. The initial traffic demand was established from the ROM24 strategic model traffic demand in the study area. The traffic counts were balanced and used in matrix furnessing, static adjustment, departure adjustment and Dynamic User Equilibrium (DUE) assignment calibration. Figure 3 Traffic demand estimation methodology 3.2 Zone Structure The foremost component in defining the zoning structure for the hybrid model was established from undertaking the static traversal procedure. Using this procedure, the static traversal OD (Origin- Destination) matrix was created, with the zone structure based on the Main Roads higher tier ROM24. Disaggregation of these ROM24 zones was undertaken where considered applicable, based on the main areas of trip generation within the study area. Disaggregation was considered necessary where there was one ROM24 zone covering several external road links, or where one ROM24 zone covered multiple internal areas that would each load a relatively high number of trips to a certain area of the network. In total 384 zones were applied to the model.
6 3.3 Trip Balancing Surveyed count data, SCATS traffic data and freeway detector data were analysed and used to develop a traffic diagram. As the count data was collected from different sources and at different times, there are discrepancies between the in/out flows in some road sections. Therefore, the counts were carefully balanced based on the flowing criteria: Minimising the difference between in and out flow of a road section (within 10 % or 100 veh/h). If there are significant differences between the 2015 and 2016 data year sources. Ensuring the entry and exit trips of an intersection are consistent with the trips in the upstream and downstream intersections. The balanced trips were applied in matrix furnessing and creating the traffic demand profile. 3.4 Demand Matrices Refinement The ROM24 cordon matrix is considered coarse in the Mitchell Freeway model area, which is not surprising given the extent of the ROM24 model area. With this, the ROM24 matrices underwent a refinement process to better reflect the traffic generators within the model area Aimsun Matrix Refinement The methodology below describes the refinement of the demand matrices. 1. The matrices were adjusted to collected survey data using the Furness method. The Furness method of matrix updating is an iterative process to derive matrices that results in the best match to survey data. Trip end totals for each Aimsun zone were formed from external link survey data, internal link survey data, and other filler zones with values based on their survey differences, surrounding land use, and number of individual households. Within this, OD pairs were also fixed to known survey values or as established during the calibration process. 2. As part of the calibration process the matrices were adjusted using the Aimsun matrix adjustment process to refine the distributions created by the ROM24 zone disaggregation. These were then checked to make sure large changes had not been made and manual refinement or containment then took place where necessary. 3. The departure adjustment was then undertaken to provide 30 minute matrices based on the 30 minute survey data sets. This allows profiles to be generated for individual OD pairs, rather than globally for all zones. 4. Lastly manual adjustments were conducted on key sections to match the observed turn counts, travel times, speed flow curves and queue lengths. All adjustments were considered minor compared to the total volumes of the sections. In summary, the following chart shows the matrix development process. Figure 4 Matrix development process
7 4. Traffic Assignment Process 4.1 Path Assignment Within Aimsun, the initial static assignment route choice was calculated using cost equations by taking into consideration section capacity and section travel times. Following this, the mesoscopic DUE assignment takes place by running the model multiple times and adjusting the paths accordingly until convergence occurs to a relative gap of 3.00%. The section capacities and global route choice parameters, including the user defined costs and attractiveness weightings were modified to aid calibration. The path assignment in the hybrid model was based on these DUE paths. Figure 5 summarises the path assignment process. Figure 5 Path assignment process 4.2 Assignment Convergence The dynamic user equilibrium assignment convergence has been used to assess the variability between each iteration. The figures below illustrate the AM and PM peak period assignment convergence respectively, and demonstrate that the model is stable. Figure 6 AM peak period assignment convergence
8 Figure 7 PM peak period assignment convergence 5. Model Calibration and Validation 5.1 Calibration Criteria Model calibration is an adjustment process to assist in the development of an accurate simulation of on-street conditions. Model calibration for this model has been based on the following criteria: Vehicle Behaviour: Undertaking a visual check to confirm the observed on-street vehicle behaviour is consistent with that observed in the model. Link Counts: Comparing observed and modelled link counts for general traffic Turn Counts: Comparing observed and modelled turning movements for general traffic Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): RMSE compares the difference between observed and modelled data. The RMSE will equate to a percentage and the percentage shall not be greater than 20% for intersection movements. Screenlines: Comparing observed and modelled total link counts for general traffic across defined boundary lines over the modelled peak hour periods.
9 Table 2 AM peak link calibration results (Whole Model Area) between 7:30am and 8:30am XY Scatter Plots Criteria Modelled R 2 Value R 2 value for modelled versus observed volumes for all individual links > Line of best fit y=0.9x-1.1x y = 0.94x Links Criteria and Measures Criteria Observed Total Modelled Achieved Achieved GEH statistic < 5.0 for individual link volumes >75% of cases % GEH statistic < 7.5 for individual link volumes >80% of cases % GEH statistic < 10.0 for individual link volumes >90% of cases % <400vph within 50vph >75% of cases % vph within 12.5% >75% of cases % >2000vph within 250vph >75% of cases % Link Criteria and Measures for Volumes Greater Than 200vph Criteria Observed Total Modelled Achieved Achieved GEH statistic < 5.0 for individual link volumes >75% of cases % GEH statistic < 7.5 for individual link volumes >80% of cases % GEH statistic < 10.0 for individual link volumes >90% of cases %
10 Table 3 PM peak link calibration results (Whole Model Area) between 5:00pm and 6:00pm XY Scatter Plots Criteria Modelled R 2 Value R 2 value for modelled versus observed volumes for all individual Freeway links > Line of best fit y=0.9x-1.1x y = 0.97x Links Criteria and Measures Criteria Observed Total Modelled Achieved Achieved GEH statistic < 5.0 for individual link volumes >75% of cases % GEH statistic < 7.5 for individual link volumes >80% of cases % GEH statistic < 10.0 for individual link volumes >90% of cases % <400vph within 50vph >75% of cases % vph within 12.5% >75% of cases % >2000vph within 250vph >75% of cases % Link Criteria and Measures for Volumes Criteria Observed Modelled Achieved Greater Than 200vph Total Achieved GEH statistic < 5.0 for individual link volumes >75% of cases % GEH statistic < 7.5 for individual link volumes >80% of cases % GEH statistic < 10.0 for individual link volumes >90% of cases %
11 5.2 Validation Criteria Model validation is necessary to ensure that a model accurately represents an existing traffic situation and can be used with confidence to test alternatives. Model validation for this model has been based on the following criteria: Travel Times: Comparing observed and modelled journey travel times for general traffic over the modelled peak hour periods. Speed-Flow Data: Comparing the observed and modelling speed data at predetermined locations along the Freeway. Weaving Validation: Comparing the observed and modelling weaving volumes at predetermined locations along the Freeway. Queue Lengths: Undertaking a visual check to confirm the modelled queue operation is consistent with those observed on site. Heat Map: Comparing observed and modelled vehicle speeds along the Freeway over the peak periods. Speed-Flow Diagram: Comparing observed and modelled speed flow diagrams at predefined locations. The key aspect for the validation was the travel times as this was the main performance indicator for the option testing. The figures below show the travel times for the peak directions of travel for the peak periods. Note that with the CBD in the centre of the model, there are two peak tidal directions per period. Two sets of observed travel time data was also used for the comparisons. Figure 8 Mitchell Freeway southbound AM peak travel time
12 Figure 9 Kwinana Freeway northbound AM peak travel time Figure 10 Mitchell Freeway northbound PM peak travel time
13 Figure 11 Kwinana Freeway southbound PM peak travel time 5.3 Speed-Flow Data Validation The speed/flow validation diagrams are useful in comparing the flow breakdown at key merge points on the freeway. Finite model parameters were adjusted accordingly to get the throughput and speeds at these locations as close as possible to the observed conditions Hutton Street Southbound Figure 12 shows the Hutton Street southbound speed/flow results at this key Freeway location. Whilst the pattern is similar, the modelled data at the breakdown sits at a slightly higher speed than the observed data. Figure 12 Hutton Street Southbound Speed Flow Data Validation
14 5.3.2 Whitfords Avenue Southbound Figure 13 shows the Whitfords Avenue southbound speed/flow results. These results show a similar pattern between the modelled and observed. Figure 13 Whitfords Avenue Southbound Speed Flow Data Validation Berrigan Drive Northbound Figure 14 shows the Berrigan Drive northbound speed/flow results. These results show a similar pattern between the modelled and observed. Figure 14 Berrigan Drive Northbound Speed Flow Data Validation
15 5.3.4 Armadale Road Southbound Figure 15 shows the Armadale Road southbound speed/flow results. These results show a similar pattern between the modelled and observed. Figure 15 Armadale Road southbound Speed Flow Data Validation 6. Lessons Learnt Being such a large model, various aspects were a learning lesson. Some of these are detailed below. A huge amount of data was required and therefore a large amount of time was required to clean and process the data. Identifying the strategic model exported attributes was initially quite difficult. The impact of ghost strategic model attributes did also impact the calibration process during the static assignment stage until they were identified. While it was relatively easy to identify where in the network issues were occurring however sometimes it was difficult to identify the detailed reason for delay to occur in a meso location. The path assignment after the DUE looked more sensible with the feature disabled calculation of new paths checked. The model run time was faster than expected: 20 minutes for DUE iterations, 2 hours for Hybrid model.
16 Presenter s Bio Antony Johnstone Antony is a Chartered Transport Associate based in Perth, WA. He leads the WA Traffic and Transport Planning team and has worked on a wide range of private and public sector projects in Australasia. He has experience in a range of software with expertise in leading and managing modelling projects as well as running modelling training modules and presentations. His transport planning and traffic engineering skills have been applied to infrastructure planning, public transport design, and development assessments. Rafael Carvajal Rafael is a Civil Engineer with MBA qualifications and over 13 years experience in traffic and transport engineering. He is skilled in leading and managing modelling projects and in the development of robust models to support decision-making, solving traffic congestion issues, experienced in transport modelling, model development and skills transfer to junior team members. He is experienced and proficient in Traffic Signal Design & Operational Modelling, Traffic Management and Highways Design in urban areas. He has contributed to the evaluation of road network operations strategies, plans and operational services. Rafael has identified, recommended and implemented opportunities to improve the delivery of road network operations.
Calibration of a Micro-Simulation Model in a Large Urban Network
 in a Large Urban Network Timothy Oketch, Ph.D., P. Eng., Director, TIMCON Associates, 37 Portelli Crescent, Ajax, Ontario, LZ1 0C4, Email: TOketch@timcon.net, http://www.timcon.net (formerly Senior Project
in a Large Urban Network Timothy Oketch, Ph.D., P. Eng., Director, TIMCON Associates, 37 Portelli Crescent, Ajax, Ontario, LZ1 0C4, Email: TOketch@timcon.net, http://www.timcon.net (formerly Senior Project
Multi-Resolution Traffic Modeling for Transform 66 Inside the Beltway Projects. Prepared by George Lu, Shankar Natarajan
 Multi-Resolution Traffic Modeling for Transform 66 Inside the Beltway Projects Prepared by George Lu, Shankar Natarajan 2017 VASITE Annual Meeting, June 29, 2017 Outline Transform I-66 Inside the Beltway
Multi-Resolution Traffic Modeling for Transform 66 Inside the Beltway Projects Prepared by George Lu, Shankar Natarajan 2017 VASITE Annual Meeting, June 29, 2017 Outline Transform I-66 Inside the Beltway
Project Appraisal Guidelines
 Project Appraisal Guidelines Unit 5.2 Construction of Traffic Models February 2011 Project Appraisal Guidelines Unit 5.2 Construction of Transport Models Version Date Comments 1.0 February 2011 New Guidance
Project Appraisal Guidelines Unit 5.2 Construction of Traffic Models February 2011 Project Appraisal Guidelines Unit 5.2 Construction of Transport Models Version Date Comments 1.0 February 2011 New Guidance
Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments
 Roads Australia Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments Des Snook Main Roads Western Australia 26 September 2014 1 Roads Australia Traffic Congestion Workshop in Perth 17 September 2013
Roads Australia Report on 2013 Traffic Congestion Workshop - Developments Des Snook Main Roads Western Australia 26 September 2014 1 Roads Australia Traffic Congestion Workshop in Perth 17 September 2013
Traffic Analysis. Appendix I
 FHWA #T-A000(18) / NHDOT #13742 Bow Concord Improvements Appendix I Traffic Analysis The traffic analysis for the project was conducted using the Bow-Concord Traffic Microsimulation Model prepared specifically
FHWA #T-A000(18) / NHDOT #13742 Bow Concord Improvements Appendix I Traffic Analysis The traffic analysis for the project was conducted using the Bow-Concord Traffic Microsimulation Model prepared specifically
SERPM 7/DTA Application FSUTMS Users Group Meeting
 SERPM 7/DTA Application FSUTMS Users Group Meeting Ana Elias, PhD, PE, PTOE Leigh Ann White, PE, PTOE June, 2015 www.jacobs.com worldwide Agenda 1. Mesoscopic Modelling and Cube Avenue Principles 2. Background
SERPM 7/DTA Application FSUTMS Users Group Meeting Ana Elias, PhD, PE, PTOE Leigh Ann White, PE, PTOE June, 2015 www.jacobs.com worldwide Agenda 1. Mesoscopic Modelling and Cube Avenue Principles 2. Background
The Secrets to HCM Consistency Using Simulation Models
 The Secrets to HCM Consistency Using Simulation Models Ronald T. Milam, AICP David Stanek, PE Chris Breiland Fehr & Peers 2990 Lava Ridge Court, Suite 200 Roseville, CA 95661 r.milam@fehrandpeers.com (916)
The Secrets to HCM Consistency Using Simulation Models Ronald T. Milam, AICP David Stanek, PE Chris Breiland Fehr & Peers 2990 Lava Ridge Court, Suite 200 Roseville, CA 95661 r.milam@fehrandpeers.com (916)
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT
 9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
9. TRAVEL FORECAST MODEL DEVELOPMENT To examine the existing transportation system and accurately predict impacts of future growth, a travel demand model is necessary. A travel demand model is a computer
1 DRAFT Model Capability
 1 DRAFT Model Capability As part of the evaluation of the proposed Western Distributor, additional traffic counts and travel time surveys were collected. The model was updated and refined in several areas,
1 DRAFT Model Capability As part of the evaluation of the proposed Western Distributor, additional traffic counts and travel time surveys were collected. The model was updated and refined in several areas,
Developing a Large Scale Hybrid Simulation Model of the Minneapolis Metropolitan Area
 Developing a Large Scale Hybrid Simulation Model of the Minneapolis Metropolitan Area Derek Lehrke Minnesota Traffic Observatory, University of Minnesota 26th Annual Transportation Research Conference,
Developing a Large Scale Hybrid Simulation Model of the Minneapolis Metropolitan Area Derek Lehrke Minnesota Traffic Observatory, University of Minnesota 26th Annual Transportation Research Conference,
Stage One Reference Design Enhancements. Date: 2 October Cabinet-in-Confidence
 Stage One Reference Design Enhancements Date: 2 October 2013 Introduction This paper provides further information regarding the proposed enhancements to the Reference Design that have been identified since
Stage One Reference Design Enhancements Date: 2 October 2013 Introduction This paper provides further information regarding the proposed enhancements to the Reference Design that have been identified since
TRANSPORT MODELLING WITH REFERENCE TO THE GAUTENG FREEWAY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
 TRANSPORT MODELLING WITH REFERENCE TO THE GAUTENG FREEWAY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT A Robinson Pr.Eng. BSc. Civ.Eng (Natal); GDE (Wits) MSAICE MCILT Trading as ARTranS Consulting ABSTRACT Spiralling road construction
TRANSPORT MODELLING WITH REFERENCE TO THE GAUTENG FREEWAY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT A Robinson Pr.Eng. BSc. Civ.Eng (Natal); GDE (Wits) MSAICE MCILT Trading as ARTranS Consulting ABSTRACT Spiralling road construction
Transportation Model Report
 1. Introduction The traffic impacts of the future developments in the IL130/High Cross Road corridor for different scenarios were analyzed using a Travel Demand Model (TDM). A four step modeling process
1. Introduction The traffic impacts of the future developments in the IL130/High Cross Road corridor for different scenarios were analyzed using a Travel Demand Model (TDM). A four step modeling process
Origin-Destination Trips and Skims Matrices
 Origin-Destination Trips and Skims Matrices presented by César A. Segovia, AICP Senior Transportation Planner AECOM September 17, 2015 Today s Webinar Content Matrix Estimation Data sources Florida Application
Origin-Destination Trips and Skims Matrices presented by César A. Segovia, AICP Senior Transportation Planner AECOM September 17, 2015 Today s Webinar Content Matrix Estimation Data sources Florida Application
Applying Micro-simulation i tools for Project Development- University of Florida Traffic Seminar Jaimison Sloboden, PE RS&H
 Applying Micro-simulation i tools for Project Development- Documentation ti & QA/QC University of Florida Traffic Seminar Jaimison Sloboden, PE RS&H Overview Principles Types of Projects Correctly Scoping
Applying Micro-simulation i tools for Project Development- Documentation ti & QA/QC University of Florida Traffic Seminar Jaimison Sloboden, PE RS&H Overview Principles Types of Projects Correctly Scoping
INTERIM ADVICE NOTE 103/08. Advice Regarding the Assessment of Sites for Ramp Metering
 INTERIM ADVICE NOTE 103/08 Advice Regarding the Assessment of Sites for Ramp Metering Summary This document provides advice on identifying on-slip locations that are likely to be suitable for the implementation
INTERIM ADVICE NOTE 103/08 Advice Regarding the Assessment of Sites for Ramp Metering Summary This document provides advice on identifying on-slip locations that are likely to be suitable for the implementation
Investigating the Impacts of Fixed-Time Ramp Metering through Microsimulation
 Investigating the Impacts of Fixed-Time Ramp Metering through Microsimulation Vahid POORJAFARI a, Wen Long YUE b a PhD Candidate, School of Natural and Built Environment, University of South Australia,
Investigating the Impacts of Fixed-Time Ramp Metering through Microsimulation Vahid POORJAFARI a, Wen Long YUE b a PhD Candidate, School of Natural and Built Environment, University of South Australia,
EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION
 EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION Hussein Dia and Nick Cottman Department of Civil Engineering The University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia 4072 E-mail: H.Dia@uq.edu.au
EVALUATION OF INCIDENT MANAGEMENT BENEFITS USING TRAFFIC SIMULATION Hussein Dia and Nick Cottman Department of Civil Engineering The University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia 4072 E-mail: H.Dia@uq.edu.au
8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis
 8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis The primary purpose for using CORSIM in the context of this manual is to guide the design process and program delivery. To this point in the manual, you have been given
8.0 Chapter 8 Alternatives Analysis The primary purpose for using CORSIM in the context of this manual is to guide the design process and program delivery. To this point in the manual, you have been given
report final Decennial Model Update Executive Summary Contra Costa Transportation Authority Cambridge Systematics, Inc.
 final report prepared for Contra Costa Transportation Authority prepared by with Dowling Associates Caliper Corporation June 2003 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... ES-1 2.0 Data Development... ES-5
final report prepared for Contra Costa Transportation Authority prepared by with Dowling Associates Caliper Corporation June 2003 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... ES-1 2.0 Data Development... ES-5
Traffic Control in Action. Prof. Markos Papageorgiou Dynamic Systems and Simulation Laboratory, Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece
 Traffic Control in Action Prof. Markos Papageorgiou Dynamic Systems and Simulation Laboratory, Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece 1. INTRODUCTION Man has reached to the moon but even ants were
Traffic Control in Action Prof. Markos Papageorgiou Dynamic Systems and Simulation Laboratory, Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece 1. INTRODUCTION Man has reached to the moon but even ants were
Appendix B5 PT Model Validation
 Appendix B5 PT Model Validation PT Model Validation Report Sheffield and Rotherham Public Transport Model Report for Sheffield City Council August 2009 Document Control Project Title: MVA Project Number:
Appendix B5 PT Model Validation PT Model Validation Report Sheffield and Rotherham Public Transport Model Report for Sheffield City Council August 2009 Document Control Project Title: MVA Project Number:
VEHICLE PROBES AS REAL-TIME ATMS SOURCES OF DYNAMIC O-D AND TRAVEL TIME DATA. Abstract
 VEHICLE PROBES AS REAL-TIME ATMS SOURCES OF DYNAMIC O-D AND TRAVEL TIME DATA M Van Aerde, B Hellinga, L Yu, and H Rakha Department of Civil Engineering Queen's University, Kingston, Canada Fax: 613-545
VEHICLE PROBES AS REAL-TIME ATMS SOURCES OF DYNAMIC O-D AND TRAVEL TIME DATA M Van Aerde, B Hellinga, L Yu, and H Rakha Department of Civil Engineering Queen's University, Kingston, Canada Fax: 613-545
N4 Collooney to Castlebaldwin Road Scheme
 Traffic Analysis Brief of Evidence N4 Collooney to Castlebaldwin Road Scheme Presented by: Declan Keenan and Shane Dunny of AECOM Designer AECOM Lower Ground Floor Grand Canal House Upper Grand Canal Street
Traffic Analysis Brief of Evidence N4 Collooney to Castlebaldwin Road Scheme Presented by: Declan Keenan and Shane Dunny of AECOM Designer AECOM Lower Ground Floor Grand Canal House Upper Grand Canal Street
Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018
 Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018 GTA creating transport that works 01 Preliminaries GTA creating transport that works Review scope : Review
Fishermans Bend Integrated Transport Plan Peer Review John Kiriakidis, GTA Consultants 28/03/2018 GTA creating transport that works 01 Preliminaries GTA creating transport that works Review scope : Review
CHAPTER 2: MODELING METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER 2: MODELING METHODOLOGY 2.1 PROCESS OVERVIEW The methodology used to forecast future conditions consisted of traditional traffic engineering practices and tools with enhancements to more accurately
CHAPTER 2: MODELING METHODOLOGY 2.1 PROCESS OVERVIEW The methodology used to forecast future conditions consisted of traditional traffic engineering practices and tools with enhancements to more accurately
GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA!
 International Experiences Driving Managed Mobility GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA! Darren Henderson, WSP USA M1, Melbourne, VIC MANAGED FREEWAYS The most important transportation strategy you ve probably never
International Experiences Driving Managed Mobility GOOD ONYA, AUSTRALIA! Darren Henderson, WSP USA M1, Melbourne, VIC MANAGED FREEWAYS The most important transportation strategy you ve probably never
Volume to Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning. Hiron Fernando, BSCE. A Thesis CIVIL ENGINEERING
 Volume to Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning by Hiron Fernando, BSCE A Thesis In CIVIL ENGINEERING Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Texas Tech
Volume to Capacity Estimation of Signalized Road Networks for Metropolitan Transportation Planning by Hiron Fernando, BSCE A Thesis In CIVIL ENGINEERING Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Texas Tech
Standardization of Travel Demand Models
 Standardization of Travel Demand Models TNMUG Meeting November 14, 2013 The North Carolina Experience Leta F. Huntsinger, Ph.D., P.E. and Rhett Fussell, P.E. Background } North Carolina Profile } 18 MPOs,
Standardization of Travel Demand Models TNMUG Meeting November 14, 2013 The North Carolina Experience Leta F. Huntsinger, Ph.D., P.E. and Rhett Fussell, P.E. Background } North Carolina Profile } 18 MPOs,
Quantifying the performance of a traffic data collection system: Scout Connect match rate evaluation
 Technology Showcase Miovision Scout Quantifying the performance of a traffic data collection system: Scout Connect match rate evaluation Contents Executive summary 2 Elements of the study 2 Objectives
Technology Showcase Miovision Scout Quantifying the performance of a traffic data collection system: Scout Connect match rate evaluation Contents Executive summary 2 Elements of the study 2 Objectives
OPTIMIZING RAMP METERING STRATEGIES
 OPTIMIZING RAMP METERING STRATEGIES Presented by Kouros Mohammadian, Ph.D. Saurav Chakrabarti. ITS Midwest Annual Meeting Chicago, Illinois February 7, 2006 Background Ramp control is the application of
OPTIMIZING RAMP METERING STRATEGIES Presented by Kouros Mohammadian, Ph.D. Saurav Chakrabarti. ITS Midwest Annual Meeting Chicago, Illinois February 7, 2006 Background Ramp control is the application of
University Site: Land Between Madingley Road and Huntingdon Road (Parcel A); and
 Technical Note Project: North West Cambridge Transport Study To: Cambridgeshire County Council Subject: Additional Development Scenarios - University From: Atkins Date: 19/02/2009 cc: Executive Summary
Technical Note Project: North West Cambridge Transport Study To: Cambridgeshire County Council Subject: Additional Development Scenarios - University From: Atkins Date: 19/02/2009 cc: Executive Summary
Automating Variable Speeds and Traveler Information with Real-Time Traffic and Weather
 Automating Variable Speeds and Traveler Information with Real-Time Traffic and Weather Joshua Crain, Jim Peters, P.E., PTOE, and Carl S. Olson ABSTRACT The Highway 217 freeway in Portland, Oregon was the
Automating Variable Speeds and Traveler Information with Real-Time Traffic and Weather Joshua Crain, Jim Peters, P.E., PTOE, and Carl S. Olson ABSTRACT The Highway 217 freeway in Portland, Oregon was the
Applications of Microscopic Traffic Simulation Model for Integrated Networks
 Applications of Microscopic Traffic Simulation Model for Integrated Networks by Steven I. Chien Dept. of Civil & Environmental Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology January 13, 2006 Center for
Applications of Microscopic Traffic Simulation Model for Integrated Networks by Steven I. Chien Dept. of Civil & Environmental Engineering New Jersey Institute of Technology January 13, 2006 Center for
Framework and Guidelines for the Development of a Twin Cities Mesoscopic DTA Model
 Framework and Guidelines for the Development of a Twin Cities Mesoscopic DTA Model John Hourdos, Principal Investigator Minnesota Traffic Observatory Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering
Framework and Guidelines for the Development of a Twin Cities Mesoscopic DTA Model John Hourdos, Principal Investigator Minnesota Traffic Observatory Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering
The London Land-Use and Transport Interaction Model (LonLUTI)
 The London Land-Use and Transport Interaction Model (LonLUTI) October 2014 Contents 3 Introduction 4 Why do we need transport models? 6 TfL s suite of models 8 What is LonLUTI? 12 How was LonLUTI developed?
The London Land-Use and Transport Interaction Model (LonLUTI) October 2014 Contents 3 Introduction 4 Why do we need transport models? 6 TfL s suite of models 8 What is LonLUTI? 12 How was LonLUTI developed?
I 95 EXPRESS LANES SOUTHERN TERMINUS EXTENSION TRAFFIC OPERATIONS AND SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
 I 95 EXPRESS LANES SOUTHERN TERMINUS EXTENSION TRAFFIC OPERATIONS AND SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT February 2016 INTERSTATE 95 EXPRESS LANES SOUTHERN TERMINUS EXTENSION PROJECT Commonwealth of Virginia Virginia
I 95 EXPRESS LANES SOUTHERN TERMINUS EXTENSION TRAFFIC OPERATIONS AND SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT February 2016 INTERSTATE 95 EXPRESS LANES SOUTHERN TERMINUS EXTENSION PROJECT Commonwealth of Virginia Virginia
The TIS is to be signed and sealed by a Florida Registered Professional Engineer.
 CHAPTER 900. SECTION 901. DEVELOPMENT STANDARDS INFRASTRUCTURE STANDARDS 901.5. Transportation Impact Study A. Intent and Purpose The intent and purpose of the Traffic Impact Study (TIS) is to identify
CHAPTER 900. SECTION 901. DEVELOPMENT STANDARDS INFRASTRUCTURE STANDARDS 901.5. Transportation Impact Study A. Intent and Purpose The intent and purpose of the Traffic Impact Study (TIS) is to identify
I-85 Traffic Study: A State-of-the-Practice Modeling of Freeway Traffic Operation
 I-85 Traffic Study: A State-of-the-Practice Modeling of Freeway Traffic Operation Daiheng Ni * Keith Strickland ** Chunxia Feng * * School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology,
I-85 Traffic Study: A State-of-the-Practice Modeling of Freeway Traffic Operation Daiheng Ni * Keith Strickland ** Chunxia Feng * * School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology,
AGGREGATE ANALYSIS OF TRAVELLER ADAPTATION TO TRANSPORTATION NETWORK CHANGES - A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF THE OPENING OF HIGHWAY
 AGGREGATE ANALYSIS OF TRAVELLER ADAPTATION TO TRANSPORTATION NETWORK CHANGES - A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF THE OPENING OF HIGHWAY 407 Bruce R. Hellinga and David K. Tsui 2 Department of Civil Engineering
AGGREGATE ANALYSIS OF TRAVELLER ADAPTATION TO TRANSPORTATION NETWORK CHANGES - A STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF THE OPENING OF HIGHWAY 407 Bruce R. Hellinga and David K. Tsui 2 Department of Civil Engineering
TAG UNIT M3.1. Highway Assignment Modelling. January Department for Transport. Transport Analysis Guidance (TAG)
 TAG UNIT M3.1 January 2014 Department for Transport Transport Analysis Guidance (TAG) https://www.gov.uk/transport-analysis-guidance-webtag This TAG Unit is guidance for the MODELLING PRACTITIONER This
TAG UNIT M3.1 January 2014 Department for Transport Transport Analysis Guidance (TAG) https://www.gov.uk/transport-analysis-guidance-webtag This TAG Unit is guidance for the MODELLING PRACTITIONER This
Highways England s Regional Traffic Models Challenges over the past year Saturn User Group 2 nd November Alison Cox
 Highways England s Regional Traffic Models Challenges over the past year Saturn User Group 2 nd November 2016 Alison Cox Background to RTMs 5 models covering England Overlapping areas to consider potential
Highways England s Regional Traffic Models Challenges over the past year Saturn User Group 2 nd November 2016 Alison Cox Background to RTMs 5 models covering England Overlapping areas to consider potential
Traffic Data Quality Analysis. James Sturrock, PE, PTOE, FHWA Resource Center Operations Team
 Traffic Analysis James Sturrock, PE, PTOE, FHWA Resource Center Operations Team Source Material Traffic Measurement http://ntl.bts.gov/lib/jpodocs/repts_te/14058.htm Seven DEADLY Misconceptions about Information
Traffic Analysis James Sturrock, PE, PTOE, FHWA Resource Center Operations Team Source Material Traffic Measurement http://ntl.bts.gov/lib/jpodocs/repts_te/14058.htm Seven DEADLY Misconceptions about Information
INTERIM ADVICE NOTE (IAN 36/01) THE USE AND APPLICATION OF MICRO- SIMULATION TRAFFIC MODELS
 INTERIM ADVICE NOTE (IAN 36/01) THE USE AND APPLICATION OF MICRO- SIMULATION TRAFFIC MODELS June 2001 Table of Contents Foreword 1 Background 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Design Manual for Roads and Bridges-
INTERIM ADVICE NOTE (IAN 36/01) THE USE AND APPLICATION OF MICRO- SIMULATION TRAFFIC MODELS June 2001 Table of Contents Foreword 1 Background 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 The Design Manual for Roads and Bridges-
Transport Model for Scotland. Kevin Lumsden MVA
 1. INTRODUCTION Transport Model for Scotland Kevin Lumsden MVA Transport Model for Scotland (TMfS) is a multi-modal transport demand and assignment model with an interactive Land Use model. The model area
1. INTRODUCTION Transport Model for Scotland Kevin Lumsden MVA Transport Model for Scotland (TMfS) is a multi-modal transport demand and assignment model with an interactive Land Use model. The model area
Technical Memorandum. 720 SW Washington Suite 500 Portland, OR dksassociates.com. DATE: July 12, 2017
 Technical Memorandum DATE: July 12, 2017 TO: Kay Bork City of Veneta Bill Johnston, AICP Oregon Department of Transportation Christina McDaniel-Wilson, PE Oregon Department of Transportation Keith Blair,
Technical Memorandum DATE: July 12, 2017 TO: Kay Bork City of Veneta Bill Johnston, AICP Oregon Department of Transportation Christina McDaniel-Wilson, PE Oregon Department of Transportation Keith Blair,
Analytical Tools and Decision Support Systems SANDAG I-15 ICM. ITS PA January 30 th, 2014
 Analytical Tools and Decision Support Systems SANDAG I-15 ICM ITS PA January 30 th, 2014 Project Partners/Stakeholders National ICM Evaluator National AMS Contractor 2 San Diego I-15 Corridor 21 mile corridor
Analytical Tools and Decision Support Systems SANDAG I-15 ICM ITS PA January 30 th, 2014 Project Partners/Stakeholders National ICM Evaluator National AMS Contractor 2 San Diego I-15 Corridor 21 mile corridor
Model Construction and Calibration Technical Documentation Draft
 430 IACC Building Fargo, ND 58105 Tel 701-231-8058 Fax 701-231-1945 www.ugpti.org www.atacenter.org Model Construction and Calibration Technical Documentation Draft January, 2004 Prepared for: Bismarck/Mandan
430 IACC Building Fargo, ND 58105 Tel 701-231-8058 Fax 701-231-1945 www.ugpti.org www.atacenter.org Model Construction and Calibration Technical Documentation Draft January, 2004 Prepared for: Bismarck/Mandan
Information sheet: STRATEGIC CASE: DEFINING PROBLEMS AND BENEFITS WELL
 NZ TRANSPORT AGENCY Business Case Approach information sheet Strategic case: defining problems and benefits well June 2017 Information sheet: STRATEGIC CASE: DEFINING PROBLEMS AND BENEFITS WELL This information
NZ TRANSPORT AGENCY Business Case Approach information sheet Strategic case: defining problems and benefits well June 2017 Information sheet: STRATEGIC CASE: DEFINING PROBLEMS AND BENEFITS WELL This information
Jose Osiris Vidaña-Bencomo Doctoral Candidate and Graduate Assistant Research University of Texas at El Paso
 Development of a Large Scale Traffic Simulation Model to Improve the Flow of Commercial Vehicles from Maquiladora Industry to International Border- Crossings Jose Osiris Vidaña-Bencomo Doctoral Candidate
Development of a Large Scale Traffic Simulation Model to Improve the Flow of Commercial Vehicles from Maquiladora Industry to International Border- Crossings Jose Osiris Vidaña-Bencomo Doctoral Candidate
An Integrated Transport - Economics Model for Ontario
 An Integrated Transport - Economics Model for Ontario by Sundar Damodaran, Ph.D., P.Eng. Ministry of Transportation, Ontario Paper prepared for presentation at the Travel Demand Modeling: Applications
An Integrated Transport - Economics Model for Ontario by Sundar Damodaran, Ph.D., P.Eng. Ministry of Transportation, Ontario Paper prepared for presentation at the Travel Demand Modeling: Applications
Congestion Management Safety Plan Phase 4
 AUGUST 2018 Congestion Management Safety Plan Phase 4 Executive Summary Report for MnDOT Metro District Prepared by: SRF Consulting Group, Inc. and Sambatek, Inc. BACKGROUND The Congestion Management Safety
AUGUST 2018 Congestion Management Safety Plan Phase 4 Executive Summary Report for MnDOT Metro District Prepared by: SRF Consulting Group, Inc. and Sambatek, Inc. BACKGROUND The Congestion Management Safety
1. Controlling the number of vehicles that are allowed to enter the freeway,
 Chapter 25 Ramp Metering 25.1 Introduction Ramp metering can be defined as a method by which traffic seeking to gain access to a busy highway is controlled at the access point via traffic signals. This
Chapter 25 Ramp Metering 25.1 Introduction Ramp metering can be defined as a method by which traffic seeking to gain access to a busy highway is controlled at the access point via traffic signals. This
DEVELOPMENT, ANALYSIS, AND DESIGN OF A NEW PARKWAY AT GRADE INTERSECTION (PAGI)
 2013 ITE Western District Annual Meeting COCEPT DEVELOPMET, AALYSIS, AD DESIG OF A EW PARKWAY AT GRADE ITERSECTIO (PAGI) Lead Author: James M. Witkowski, PhD Supporting Author: Darrell Truitt, PE The Pima
2013 ITE Western District Annual Meeting COCEPT DEVELOPMET, AALYSIS, AD DESIG OF A EW PARKWAY AT GRADE ITERSECTIO (PAGI) Lead Author: James M. Witkowski, PhD Supporting Author: Darrell Truitt, PE The Pima
Appendix 1. Problem Identification for MoTI Business Cases
 Guidelines for Preparing MoTI Business Cases Appendix 1 Problem Identification for MoTI Business Cases Prepared By: Planning and Programming Branch Infrastructure Department BC Ministry of Transportation
Guidelines for Preparing MoTI Business Cases Appendix 1 Problem Identification for MoTI Business Cases Prepared By: Planning and Programming Branch Infrastructure Department BC Ministry of Transportation
Special Issue: Intelligent Transportation Systems
 Journal of Advanced Transportation, Vol. 36 No. 3, pp. 225-229 www. advanced-transport. corn EDITORIAL Special Issue: Intelligent Transportation Systems Guest Editor: William H.K. Lam Recent rapid development
Journal of Advanced Transportation, Vol. 36 No. 3, pp. 225-229 www. advanced-transport. corn EDITORIAL Special Issue: Intelligent Transportation Systems Guest Editor: William H.K. Lam Recent rapid development
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links
 Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Transportation Problems and Issues Excerpts from WWW Links Reference Bok, D. (2018). Transportation policy and planning. https://www.hks.harvard.edu/courses/transportation-policy-and-planning Transportation
Connecting Land Use & Transportation
 Connecting Land Use & Transportation 2010 APA Upper Midwest Planning Conference Mankato, Minnesota Presented by: Gina Mitchell, AICP Bryan Nemeth, PE, PTOE Bolton & Menk, Inc. 1 Outline Developing a land
Connecting Land Use & Transportation 2010 APA Upper Midwest Planning Conference Mankato, Minnesota Presented by: Gina Mitchell, AICP Bryan Nemeth, PE, PTOE Bolton & Menk, Inc. 1 Outline Developing a land
Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction
 Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction Kevin D. Moriarty Research Assistant Transportation Engineering November 16, 2006 Overview Introduction
Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction Kevin D. Moriarty Research Assistant Transportation Engineering November 16, 2006 Overview Introduction
ACCURACY OF TRAFFIC COUNT DATA USED FOR CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION OF HIGHWAY MODELS
 ACCURACY OF TRAFFIC COUNT DATA USED FOR CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION OF HIGHWAY MODELS Reza Tolouei BEng MSc PhD MCIHT (corresponding author) Principal Consultant AECOM AECOM House 63-77 Victoria Street
ACCURACY OF TRAFFIC COUNT DATA USED FOR CALIBRATION AND VALIDATION OF HIGHWAY MODELS Reza Tolouei BEng MSc PhD MCIHT (corresponding author) Principal Consultant AECOM AECOM House 63-77 Victoria Street
Project Appraisal Guidelines for National Roads Unit Data Collection
 Project Appraisal Guidelines for National Roads Unit 5.2 - Data Collection October 2016 TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is responsible
Project Appraisal Guidelines for National Roads Unit 5.2 - Data Collection October 2016 TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is responsible
Modeling Truck Movements: A Comparison between the Quick Response Freight Manual (QRFM) and Tour-Based Approaches
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 5 Issue 11 November 2016 PP. 45-51 Modeling Truck Movements: A Comparison between the Quick
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 5 Issue 11 November 2016 PP. 45-51 Modeling Truck Movements: A Comparison between the Quick
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources)
 Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
Urban Transport Modeling (based on these two sources) A Transportation Modeling Primer May, 1995 Edward A. Beimborn Center for Urban Transportation Studies University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee http://www.uwm.edu/dept/c
Traffic Impact Studies
 G U I D E Ministry of Transportation General Guidelines for the Preparation of Traffic Impact Studies L I N E S January 2008 1.0 Introduction: The main purpose of a Traffic Impact Study (TIS) is to demonstrate
G U I D E Ministry of Transportation General Guidelines for the Preparation of Traffic Impact Studies L I N E S January 2008 1.0 Introduction: The main purpose of a Traffic Impact Study (TIS) is to demonstrate
CE 452 Traffic Impact Assessment
 CE 452 Traffic Impact Assessment 1 Why Required? New developments Produce/ attract new traffic Production: Residences Attraction: Shops, Offices, Schools, Hospitals etc. etc. Changes in traffic pattern
CE 452 Traffic Impact Assessment 1 Why Required? New developments Produce/ attract new traffic Production: Residences Attraction: Shops, Offices, Schools, Hospitals etc. etc. Changes in traffic pattern
Freight Transportation Planning and Modeling Spring 2012
 Freight Model Validation Techniques Abstract Several reviews of validation techniques for statewide passenger and freight models have been published over the past several years. In this paper I synthesize
Freight Model Validation Techniques Abstract Several reviews of validation techniques for statewide passenger and freight models have been published over the past several years. In this paper I synthesize
Database and Travel Demand Model
 Database and Travel Demand Model 7 The CMP legislation requires every CMA, in consultation with the regional transportation planning agency (the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) in the Bay
Database and Travel Demand Model 7 The CMP legislation requires every CMA, in consultation with the regional transportation planning agency (the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) in the Bay
report Smart Growth - Refined Transport Modelling
 report Smart Growth - Refined Transport Modelling report Smart Growth - Refined Transport Modelling Prepared for Smart Growth By Beca Carter Hollings & Ferner Ltd November 2002 8111359/210 Rev A L1:90421
report Smart Growth - Refined Transport Modelling report Smart Growth - Refined Transport Modelling Prepared for Smart Growth By Beca Carter Hollings & Ferner Ltd November 2002 8111359/210 Rev A L1:90421
Evaluation of Truck Signal Priority at N Columbia Blvd and Martin Luther King Jr. Blvd Intersection
 Portland State University PDXScholar Civil and Environmental Engineering Master's Project Reports Civil and Environmental Engineering 2014 Evaluation of Truck Signal Priority at N Columbia Blvd and Martin
Portland State University PDXScholar Civil and Environmental Engineering Master's Project Reports Civil and Environmental Engineering 2014 Evaluation of Truck Signal Priority at N Columbia Blvd and Martin
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion
 Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
Network Operation Planning - A new approach to managing congestion Andrew Wall VicRoads, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 1 Introduction Congestion is an unavoidable aspect of most urban cities. However, there
Public Submission by Alcoa World Alumina Australia on the Train Management Guidelines as submitted by WestNet Rail
 Public Submission by Alcoa World Alumina Australia on the Train Management Guidelines as submitted by WestNet Rail Prepared for: Rail Access Regulator Office of the Rail Access Regulator Level 27, 197
Public Submission by Alcoa World Alumina Australia on the Train Management Guidelines as submitted by WestNet Rail Prepared for: Rail Access Regulator Office of the Rail Access Regulator Level 27, 197
FREEWAY PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM (PeMS): AN OPERATIONAL ANALYSIS TOOL
 FREEWAY PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM (PeMS): AN OPERATIONAL ANALYSIS TOOL Tom Choe Office of Freeway Operations California Department of Transportation District 7 120 S Spring Street Los Angeles, CA
FREEWAY PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM (PeMS): AN OPERATIONAL ANALYSIS TOOL Tom Choe Office of Freeway Operations California Department of Transportation District 7 120 S Spring Street Los Angeles, CA
Use Big Data and Modeling Tools To Decipher Traffic Patterns: Case Studies in Virginia
 Use Big Data and Modeling Tools To Decipher Traffic Patterns: Case Studies in Virginia Agenda Need for O-D Data O-D Data Collection A Primer Big Data and StreetLight Data Use Modeling Tool for O-D Estimation
Use Big Data and Modeling Tools To Decipher Traffic Patterns: Case Studies in Virginia Agenda Need for O-D Data O-D Data Collection A Primer Big Data and StreetLight Data Use Modeling Tool for O-D Estimation
Travel Time in Macroscopic Traffic Models for Origin-Destination Estimation
 University of Wisconsin Milwaukee UWM Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations May 2013 Travel Time in Macroscopic Traffic Models for Origin-Destination Estimation Eric Youngblom University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
University of Wisconsin Milwaukee UWM Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations May 2013 Travel Time in Macroscopic Traffic Models for Origin-Destination Estimation Eric Youngblom University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG
 Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG Arash Mirzaei North Central Texas Council Of Governments For University of Texas at Arlington ITE Student Chapter March 9, 2005 Agenda Background DFW Regional Model Structure
Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG Arash Mirzaei North Central Texas Council Of Governments For University of Texas at Arlington ITE Student Chapter March 9, 2005 Agenda Background DFW Regional Model Structure
Surrogate safety assessment for a tight urban diamond interchange using micro-simulation
 Publish Information: Chen, S., H. Liu, Z. Tian, and D. H. Jeryl (2009). Surrogate Safety Assessment for A Tight Urban Diamond Interchange Using Micro-simulation. Advances in Transportation Studies, an
Publish Information: Chen, S., H. Liu, Z. Tian, and D. H. Jeryl (2009). Surrogate Safety Assessment for A Tight Urban Diamond Interchange Using Micro-simulation. Advances in Transportation Studies, an
CHAPTER 2 - TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL DEVELOPMENT
 CHAPTER 2 - TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL DEVELOPMENT 2.1 EXISTING TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL In order to accurately project future year traffic volumes within this regional study area, it was first necessary to construct
CHAPTER 2 - TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL DEVELOPMENT 2.1 EXISTING TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL In order to accurately project future year traffic volumes within this regional study area, it was first necessary to construct
Ramp Metering. Chapter Introduction Metering strategies Benefits Objectives
 Chapter 46 Ramp Metering Traffic signal on merge ramp Direction of travel Merge lane Vehicle detectors monitoring traffic density through lane occupancy Figure 46.1: Schematic diagram of ramp metering
Chapter 46 Ramp Metering Traffic signal on merge ramp Direction of travel Merge lane Vehicle detectors monitoring traffic density through lane occupancy Figure 46.1: Schematic diagram of ramp metering
DEVELOPMENT OF RIGA-MINSK TRANSPORT CORRIDOR SIMULATION MODEL
 Transport and Telecommunication, 2010, Volume 11, No 1, 38 47 Transport and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosova 1, Riga, LV-1019, Latvia DEVELOPMENT OF RIGA-MINSK TRANSPORT CORRIDOR SIMULATION MODEL
Transport and Telecommunication, 2010, Volume 11, No 1, 38 47 Transport and Telecommunication Institute, Lomonosova 1, Riga, LV-1019, Latvia DEVELOPMENT OF RIGA-MINSK TRANSPORT CORRIDOR SIMULATION MODEL
Apply DynusT Model for Incident Management along Loop 101 Corridor
 Apply DynusT Model for Incident Management along Loop 101 Corridor Lili(Leo) Luo, P.E. ITS/Safety Engineer Sarath Joshua, P.E. ITS/Safety Program Manager What do Transportation Models do? Help us answer
Apply DynusT Model for Incident Management along Loop 101 Corridor Lili(Leo) Luo, P.E. ITS/Safety Engineer Sarath Joshua, P.E. ITS/Safety Program Manager What do Transportation Models do? Help us answer
Variable Speed Advisory/Limit and Coordinated Ramp Metering for Freeway Traffic Control
 Variable Speed Advisory/Limit and Coordinated Ramp Metering for Freeway Traffic Control Project Meeting Caltrans DRI Xiao-Yun Lu and Steven Shladover California PATH Program, U. C. Berkeley Sept 7, 2012
Variable Speed Advisory/Limit and Coordinated Ramp Metering for Freeway Traffic Control Project Meeting Caltrans DRI Xiao-Yun Lu and Steven Shladover California PATH Program, U. C. Berkeley Sept 7, 2012
CORSIM Modeling Guidelines
 CORSIM Modeling Guidelines September 2012 Nevada Department of Transportation 1263 S. Stewart Street Carson City, Nevada 89712 775-888-7000 www.nevadadot.com Brian E. Sandoval Governor Rudy Malfabon, P.E.
CORSIM Modeling Guidelines September 2012 Nevada Department of Transportation 1263 S. Stewart Street Carson City, Nevada 89712 775-888-7000 www.nevadadot.com Brian E. Sandoval Governor Rudy Malfabon, P.E.
Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin
 Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin A. Pugh B.E. (Hons), Member A.W.A. Sales and Support Manager, Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, Australia S. Ratcliffe B.Sc(Hons), Grad Dip
Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin A. Pugh B.E. (Hons), Member A.W.A. Sales and Support Manager, Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, Australia S. Ratcliffe B.Sc(Hons), Grad Dip
Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities
 Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities By Dr. Michael Anderson and Mary Catherine Dondapati Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of
Effectively Using the QRFM to Model Truck Trips in Medium-Sized Urban Communities By Dr. Michael Anderson and Mary Catherine Dondapati Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering The University of
EU-TP0103 Traffic and accidents monitoring system on ANAS National Road Network. Pier Paolo Cartolano
 EU-TP0103 Traffic and accidents monitoring system on ANAS National Road Network Pier Paolo Cartolano What is ANAS S.p.A. National Ordinary Roads and Highways Total Investments 25.369 Km 2,1 billion of
EU-TP0103 Traffic and accidents monitoring system on ANAS National Road Network Pier Paolo Cartolano What is ANAS S.p.A. National Ordinary Roads and Highways Total Investments 25.369 Km 2,1 billion of
The Economics of Urban Road Pricing
 The Economics of Urban Road Pricing Capita Selecta Erik T Verhoef Free University Amsterdam Outline Basic economic motivation Statics versus dynamics Second-best aspects Conclusions Basic motivation road
The Economics of Urban Road Pricing Capita Selecta Erik T Verhoef Free University Amsterdam Outline Basic economic motivation Statics versus dynamics Second-best aspects Conclusions Basic motivation road
Dynamic Lane Merge Systems
 Dynamic Lane Merge Systems Acknowledgements Maryland State Highway Administration University of Maryland, College Park Michigan Department of Transportation Wayne State University Lane Merging Issues Merging
Dynamic Lane Merge Systems Acknowledgements Maryland State Highway Administration University of Maryland, College Park Michigan Department of Transportation Wayne State University Lane Merging Issues Merging
Woodburn Interchange Project Transportation Technical Report
 Final Report Woodburn Interchange Project Transportation Technical Report Prepared for Oregon Department of Transportation April 212 Prepared by DKS Associates Contents Methodologies... 4 Volume Development...
Final Report Woodburn Interchange Project Transportation Technical Report Prepared for Oregon Department of Transportation April 212 Prepared by DKS Associates Contents Methodologies... 4 Volume Development...
REAL-TIME MERGING TRAFFIC CONTROL AT CONGESTED FREEWAY OFF-RAMP AREAS
 REAL-TIME MERGING TRAFFIC CONTROL AT CONGESTED FREEWAY OFF-RAMP AREAS By Anastasia Spiliopoulou* PhD Dynamic Systems and Simulation Laboratory Department of Production Engineering and Management Technical
REAL-TIME MERGING TRAFFIC CONTROL AT CONGESTED FREEWAY OFF-RAMP AREAS By Anastasia Spiliopoulou* PhD Dynamic Systems and Simulation Laboratory Department of Production Engineering and Management Technical
Fargo Moorhead MPO 2010 Regional Travel Demand Model Update Technical Report-DRAFT. June 2013
 430 IACC Building Fargo, ND 58105 Tel 701-231-8058 Fax 701-231-1945 www.ugpti.org www.atacenter.org Fargo Moorhead MPO 2010 Regional Travel Demand Model Update Technical Report-DRAFT June 2013 Prepared
430 IACC Building Fargo, ND 58105 Tel 701-231-8058 Fax 701-231-1945 www.ugpti.org www.atacenter.org Fargo Moorhead MPO 2010 Regional Travel Demand Model Update Technical Report-DRAFT June 2013 Prepared
Regional Travel Demand Management Plan
 Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 Quality for life Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 For more information, contact: Greater Wellington 142 Wakefield
Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 Quality for life Regional Travel Demand Management Plan Adopted October 2009 For more information, contact: Greater Wellington 142 Wakefield
Development of a New Strategic Transport Planning Model for Adelaide
 Development of a New Strategic Transport Planning Model for Adelaide Nicholas Holyoak 1, Michael Taylor 1, Lindsay Oxlad 2 and John Gregory 3 1 Transport Systems Centre, University of South Australia,
Development of a New Strategic Transport Planning Model for Adelaide Nicholas Holyoak 1, Michael Taylor 1, Lindsay Oxlad 2 and John Gregory 3 1 Transport Systems Centre, University of South Australia,
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004
 Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
Project Appraisal Using PRISM Simon Hubbard 28 th September 2004 Introduction : Overview of Presentation - Option Appraisal Policy Context - Potential PRISM Applications - Use of the Model / Scale of the
City of Tacoma TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN DRAFT
 City of Tacoma TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN 140 APPENDICES Appendix A Model Documentation MEMORANDUM Date: November 26, 2014 To: City of Tacoma, Department of Public Works From: Chris Breiland, Fehr & Peers
City of Tacoma TRANSPORTATION MASTER PLAN 140 APPENDICES Appendix A Model Documentation MEMORANDUM Date: November 26, 2014 To: City of Tacoma, Department of Public Works From: Chris Breiland, Fehr & Peers
Loop 289 Corridor Study Phase I
 2008 Loop 289 Corridor Study Phase I Hongchao Liu, Pavan Evuri, and Hao Xu Multidisciplinary Research in Transportation Texas Tech University August 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES... III LIST OF
2008 Loop 289 Corridor Study Phase I Hongchao Liu, Pavan Evuri, and Hao Xu Multidisciplinary Research in Transportation Texas Tech University August 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES... III LIST OF
WIN-WIN DYNAMIC CONGESTION PRICING FOR CONGESTED URBAN AREAS
 1 WIN-WIN DYNAMIC CONGESTION PRICING FOR CONGESTED URBAN AREAS Aya Aboudina, Ph.D. Student University of Toronto Baher Abdulhai, Ph.D., P.Eng. University of Toronto June 12 th, 2012 ITS Canada - ACGM 2012
1 WIN-WIN DYNAMIC CONGESTION PRICING FOR CONGESTED URBAN AREAS Aya Aboudina, Ph.D. Student University of Toronto Baher Abdulhai, Ph.D., P.Eng. University of Toronto June 12 th, 2012 ITS Canada - ACGM 2012
Fishermans Bend. Integrated Transport Plan Victorian Planning Panels. Cccc Eco City World Summit July Neal Giles, Fishermans Bend Taskforce
 Fishermans Bend Cccc Eco City World Summit July 2017 Integrated Transport Plan Victorian Planning Panels Neal Giles, Image: Lensaloft Aerial Photography Key Challenges The network needs to change The framework
Fishermans Bend Cccc Eco City World Summit July 2017 Integrated Transport Plan Victorian Planning Panels Neal Giles, Image: Lensaloft Aerial Photography Key Challenges The network needs to change The framework
Roadway Traffic Assignment (Last Edit August 26, 2005)
 Roadway Traffic Assignment (Last Edit August 26, 2005) This chapter focuses on the Roadway Traffic Assignment module of the Dallas-Fort Worth Regional Travel Model (DFWRTM). Based on the input vehicle
Roadway Traffic Assignment (Last Edit August 26, 2005) This chapter focuses on the Roadway Traffic Assignment module of the Dallas-Fort Worth Regional Travel Model (DFWRTM). Based on the input vehicle
Evaluation Summary for the San Diego Testbed. Final Report August 2017 FHWA-JPO
 Analysis, Modeling, and Simulation (AMS) Testbed Development and Evaluation to Support Dynamic Mobility Applications (DMA) and Active Transportation and Demand Management (ATDM) Programs Evaluation Summary
Analysis, Modeling, and Simulation (AMS) Testbed Development and Evaluation to Support Dynamic Mobility Applications (DMA) and Active Transportation and Demand Management (ATDM) Programs Evaluation Summary
Evaluation Study of Inflow Traffic Control by Ramp Metering on Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway
 Evaluation Study of Inflow Traffic Control by Ramp Metering on Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway 1 Tsubota, Y., 2 M. Iwata and 2 H. Kawashima 1 Obirin University, 2 Keio University, E-Mail: masafumi@ae.keio.ac.jp
Evaluation Study of Inflow Traffic Control by Ramp Metering on Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway 1 Tsubota, Y., 2 M. Iwata and 2 H. Kawashima 1 Obirin University, 2 Keio University, E-Mail: masafumi@ae.keio.ac.jp
