Outline. Summary. Economics 124/PP 190-5/290-5 Innovation and Technical Change. Standards and networks (2) Prof. Bronwyn H. Hall
|
|
|
- Timothy Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Economics 124/PP 190-5/290-5 Innovation and Technical Change Standards and networks (2) Prof. Bronwyn H. Hall Outline Review Competition among systems with different standards Some examples of the power of network externalities PC operating systems QWERTY keyboard layout Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Summary Technological standards are specifications (of measures or a measurement system, of functions and the way they must be performed, or of the input/output parameters. These make it possible for different components of a system work together successfully. Network goods are systems whose value to one user depends on use by others. Networks usually involve some use of standards. Demand for a network good is a function of the price and the size of the network Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
2 Summary Network externalities are the benefit or cost conferred on others when an individual chooses to purchase a network good. Positive externality arises from the fact that other people s utility is increased when someone joins a network Negative externality exists if there is another competing network good. When an individual adopts the first one, the decision is negative for the users of the second. Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Indirect network size and software Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Standards competitions Outcome of competition between two competing standards (systems) depends on whether firms prefer 1. Incompatibility likely when firms are symmetric, and when standards battle does not delay adoption too much 2. Compatibility likely when demand depends greatly on having a single standard (communications) and when battle will dissipate profits Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
3 Game theoretic analysis Simple two player game Each player has two action or strategy choices (standard 1 or standard 2) There are different payoffs for each combination of choices Dominant strategy a choice that is best regardless of what the other player does Nash equilibrium choice of strategies where neither player finds it beneficial to deviate on his own (given the other player s choice) Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Standardization game Payoff Matrix (Incompatibility) Firm 1 Standard 1 Standard 2 Standard 1 Firm 2 Standard 2 There is no dominant strategy. Nash equilibria are incompatible standards: (1,2) and (2,1) Example: consumer heterogeneity means differentiated products earn higher profits. Scotchmer shows that under some conditions this is not a stable equilibrium (each firm has an incentive to lower price or increase applications to drive the other out). Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Standardization game Payoff Matrix (Compatibility) Firm 1 Standard 1 Standard 2 Firm 2 Standard 1 Standard This is a coordination game. Best response depends on what other player does there is no dominant strategy. There are two possible Nash equilibria, (1,1) and (2,2) Example: communications network (fax, etc.) Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
4 Welfare with network competition Adoption rates for Pareto-improving standards (technologies) can be too slow (excess inertia) or too fast (excess momentum) too slow because Old technology has a large installed base and early adopters bear too large a share of the switching costs New technology is unattractive with few users New technology s advantage positive, but relatively small too fast because First adopters like the new technology and ignore their negative effects on the users of old technology Network advantage is not that large Old technology has a small installed base Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Examples of market tipping Color TV vs black & white TV Video recording: VHS versus Beta PC platforms: Apple vs IBM/MS-DOS (open standards) Browsers: Internet Explorer vs Netscape (vs Mozilla?) We look at these two more closely: PC platforms: MS Windows OS vs IBM OS(2) Keyboards: QWERTY vs Dvorak Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ IBM s OS/2 vs MS Windows Example of the power of network effects 1991 OS/2 released OS/2 sales 400K; Windows sales 18M OS/2 technically superior 32-bit OS, not available from MS until Windows 95 OS/2 failed; withdrawn from market Problem: lack of complementary software applications Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
5 QWERTY Example David asks why most keyboards have the QWERTYUIOP layout today, even though those trained on the Dvorak keyboard type more quickly. Although note that there is some debate about this assertion. History: Oct 1867 Sholes primitive typewriter patented (typebar clash problem) 1873 manufactured by Remington 1880s only 5000 typewriters in US, proliferation of competing designs 1890s QWERTY four row keyboard becomes dominant Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Sholes-Glidden typewriter Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Remington No. 2 (1878) Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
6 Why QWERTY? Touch typing invented late 1880s, made typewriters a network good because of Technical interrelatedness between keyboard layout and typist memory/skills Economies of scale in user costs of typewriting due to training each additional typist tends to join larger network Quasi-irreversibility of investment in learning how to type (sunk costs) By 1890s, significant lock-in to QWERTY layout Easier to reconfigure keyboard than typist Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Welfare with networks Lock-in to a non-optimal standard is possible The QWERTY keyboard analog HDTV in Japan, now abandoned due to superiority of digital perhaps the U. S. television standard (versus European) Small historical accidents can tip adopters to choose a standard that later users perceive as non-optimal. Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Liebowitz and Margolis Two kinds of network externalities Pecuniary with increasing returns, when demand larger, price may fall because cost is lower familiar, does not require new theory Technological true network externality, does not come through price system Network effects relatively uncommon Frequently, NW externality inframarginal externality from the,000 th user is minimal, so multiple networks can be supported if market large enough Exist but are internalized via ownership (as in our discussion of the static case with monopoly) Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
7 Liebowitz-Margolis critique of QWERTY Historically, not at all clear that Dvorak is superior 1944 study cited by David was conducted by Dvorak himself GSA study in 1956 found them to be about the same Benefit of switch may be small per typist If the standard is obviously inferior, users can coordinate to switch even after it is established Nevertheless, in some cases the required benefit from switching will have to be very large to overcome both the cost and the coordination cost for example, consider the cost of switching from the driving on the left to driving on the right in the United Kingdom What do you think? Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/ Policy toward tipping Is a single standard a bad outcome? Similar to natural monopoly discussion When do firms prefer closed standards and when do they prefer open standards? Depends to some extent on existing market power Control of the interface matters (IP) Which policy tools can achieve open standards? Limited antitrust when acts are egregious Fall 2004 (C) B H Hall Econ 124/PP 190-5/
Outline. Technological standards. Economics 124/PP 190-5/290-5 Innovation and Technical Change. Standards and networks Prof. Bronwyn H.
 Economics 124/PP 190-5/290-5 Innovation and Technical Change Standards and networks Prof. Bronwyn H. Hall Outline Introduction to network economics Standards Network externalities Networks and competition
Economics 124/PP 190-5/290-5 Innovation and Technical Change Standards and networks Prof. Bronwyn H. Hall Outline Introduction to network economics Standards Network externalities Networks and competition
Competing in Standards Driven Markets
 Competing in Standards Driven Markets When can you maintain control over the use of an innovation/idea? Strong intellectual property rights First-mover advantages Customer lock-in Network effects Standards
Competing in Standards Driven Markets When can you maintain control over the use of an innovation/idea? Strong intellectual property rights First-mover advantages Customer lock-in Network effects Standards
The paper considers market equilibrium of two competitive technologies which exhibit increasing returns.
 W. B. Arthur (1989) The paper considers market equilibrium of two competitive technologies which exhibit increasing returns. Under what condition will one technology dominate the market? What properties
W. B. Arthur (1989) The paper considers market equilibrium of two competitive technologies which exhibit increasing returns. Under what condition will one technology dominate the market? What properties
The Quest for QWERTY. Tanjim Hossain and John Morgan * strong tendency for markets where platforms compete to tip to a single dominant player.
 The Quest for QWERTY Tanjim Hossain and John Morgan * In settings ranging from office suite software to online auctions, casual empiricism suggests a strong tendency for markets where platforms compete
The Quest for QWERTY Tanjim Hossain and John Morgan * In settings ranging from office suite software to online auctions, casual empiricism suggests a strong tendency for markets where platforms compete
Outline. Standards wars Compatibility decisions Public policy and standards: the government as a strategic player
 STANDARDS Overview Context: Your firm sells a product that is part of a network of products and consumers. What design should you choose? Concepts: network effects, critical mass, excess inertia, path
STANDARDS Overview Context: Your firm sells a product that is part of a network of products and consumers. What design should you choose? Concepts: network effects, critical mass, excess inertia, path
Lecture 22 - Network Externalities
 Lecture 22 - Network Externalities 14.03 pring 2003 1 Network Externalities We have mostly discussed games where one player triumphs at the expense of another. But another important class of games are
Lecture 22 - Network Externalities 14.03 pring 2003 1 Network Externalities We have mostly discussed games where one player triumphs at the expense of another. But another important class of games are
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology. Network Effects
 The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network externality)
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network externality)
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology. Network Effects
 The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 11/18/2014 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 11/18/2014 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology. Network Effects
 The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 10/28/2015 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network
The Economics of E-commerce and Technology Network Effects 1 10/28/2015 Network Effects Network Set of interconnected nodes Real network (faxes) and virtual networks (Word users) Network effect (or network
The theory of Industrial Organization
 The theory of Industrial Organization Ph. D. Program in Law and Economics Session 10: Network externalities J.L. Moraga Network Effects Network: Set of individuals and set of links between them. Physical:
The theory of Industrial Organization Ph. D. Program in Law and Economics Session 10: Network externalities J.L. Moraga Network Effects Network: Set of individuals and set of links between them. Physical:
Technology Strategy, Fall 2008 Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy, Fall 2008 Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Network Effects
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy, Fall 2008 Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Network Effects
Industrial Organization
 Industrial Organization Markets and Strategies 2nd edition Paul Belleflamme Université CatholiquedeLouvain Martin Peitz University of Mannheim University Printing House, Cambridge CB2 8BS, United Kingdom
Industrial Organization Markets and Strategies 2nd edition Paul Belleflamme Université CatholiquedeLouvain Martin Peitz University of Mannheim University Printing House, Cambridge CB2 8BS, United Kingdom
A THEORETICAL REVIEW OF NETWORK EFFECTS ON PLATFORM PRODUCTS
 A THEORETICAL REVIEW OF NETWORK EFFECTS ON PLATFORM PRODUCTS Kazuhiko Kato/Tatsuyuki Negoro 1-6-1, Nishiwaseda, Shinjyuku-ku, 169-8050 Tokyo Waseda University ABSTRACT Network effects appear to increase
A THEORETICAL REVIEW OF NETWORK EFFECTS ON PLATFORM PRODUCTS Kazuhiko Kato/Tatsuyuki Negoro 1-6-1, Nishiwaseda, Shinjyuku-ku, 169-8050 Tokyo Waseda University ABSTRACT Network effects appear to increase
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages.
 Econ 0, Sections 3 and 4, S, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = 000 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages.. Gordon is the owner
Econ 0, Sections 3 and 4, S, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = 000 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch-work in the side and bottom margins of pages.. Gordon is the owner
Game Theory Exam, June 2015
 Game Theory Exam, June 2015 Name Group: You have two and a half hours to complete the exam. I. Short questions (5 points each) I.1 Show an example of a static game that has no Nash equilibrium in pure
Game Theory Exam, June 2015 Name Group: You have two and a half hours to complete the exam. I. Short questions (5 points each) I.1 Show an example of a static game that has no Nash equilibrium in pure
From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risks and Big Rewards of Platform Markets
 From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risks and Big Rewards of Platform Markets The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risks and Big Rewards of Platform Markets The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
MIT641 Information Economics session 8 Network Externality
 MIT641 Information Economics session 8 Network Externality Dr Sittiphol Viboonthanakul Business for Rural Education and Development shineallday@yahoo.com 1 Network Externalities What are externalities?
MIT641 Information Economics session 8 Network Externality Dr Sittiphol Viboonthanakul Business for Rural Education and Development shineallday@yahoo.com 1 Network Externalities What are externalities?
Industrial. Organization. Markets and Strategies. 2nd edition. Paul Belleflamme Universite Catholique de Louvain. Martin Peitz University of Mannheim
 Industrial Organization Markets and Strategies 2nd edition Paul Belleflamme Universite Catholique de Louvain Martin Peitz University of Mannheim CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List offigures xiii
Industrial Organization Markets and Strategies 2nd edition Paul Belleflamme Universite Catholique de Louvain Martin Peitz University of Mannheim CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List offigures xiii
McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Standards Battles and Design Dominance McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies,
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 Standards Battles and Design Dominance McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies,
Competition Law and Innovation: Dissecting the Interplay. Wolfgang Kerber Philipps-Universität Marburg
 Competition Law and Innovation: Dissecting the Interplay Wolfgang Kerber Philipps-Universität Marburg 12 th Annual Conference of the GCLC Dynamic Markets and Dynamic Enforcement: Which Competition Policy
Competition Law and Innovation: Dissecting the Interplay Wolfgang Kerber Philipps-Universität Marburg 12 th Annual Conference of the GCLC Dynamic Markets and Dynamic Enforcement: Which Competition Policy
Industrial Organization Lecture 11: Network Effects
 Industrial Organization Lecture 11: Network Effects Nicolas Schutz Nicolas Schutz Network Effects 1 / 40 Introduction Network effects, or network externalities are said to exist when the benefit that a
Industrial Organization Lecture 11: Network Effects Nicolas Schutz Nicolas Schutz Network Effects 1 / 40 Introduction Network effects, or network externalities are said to exist when the benefit that a
Standards Battles and Design Dominance. Copyright 2013 by Professor D. J. Lee, Kyung Hee Univ. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 4 Standards Battles and Design Dominance Copyright 2013 by Professor D. J. Lee, Kyung Hee Univ. All rights reserved. Prologue 1: VHS and Betamax - A dominant design in VCR industry Please watch
Chapter 4 Standards Battles and Design Dominance Copyright 2013 by Professor D. J. Lee, Kyung Hee Univ. All rights reserved. Prologue 1: VHS and Betamax - A dominant design in VCR industry Please watch
underlying these concepts is more complex than the standard material taught in a principles class. The importance of network
 Network Externalities and Standardization: A Classroom Demonstration Christopher Ruebeck, Sarah Stafford, Nicola Tynan, William Alpert, Gwendolyn Ball, and Bridget Butkevich * Abstract: This paper presents
Network Externalities and Standardization: A Classroom Demonstration Christopher Ruebeck, Sarah Stafford, Nicola Tynan, William Alpert, Gwendolyn Ball, and Bridget Butkevich * Abstract: This paper presents
Chapter 15 Oligopoly
 Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Chapter 15 Oligopoly BEFORE YOU READ THE CHAPTER Summary This chapter explores oligopoly, a market structure characterized by a few firms producing a product that mayor may
Goldwasser AP Microeconomics Chapter 15 Oligopoly BEFORE YOU READ THE CHAPTER Summary This chapter explores oligopoly, a market structure characterized by a few firms producing a product that mayor may
OLIGOPOLY AND DUOPOLY. Asst.. Prof. Dr. Serdar AYAN
 OLIGOPOLY AND DUOPOLY Asst.. Prof. Dr. Serdar AYAN WHAT IS OLIGOPOLY? Oligopoly is a market type in which: A small number of firms compete. Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms.. WHAT
OLIGOPOLY AND DUOPOLY Asst.. Prof. Dr. Serdar AYAN WHAT IS OLIGOPOLY? Oligopoly is a market type in which: A small number of firms compete. Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms.. WHAT
Do not open this exam until told to do so. Solution
 Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Fall 003 Final (Version): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solution Final (Version
Do not open this exam until told to do so. Department of Economics College of Social and Applied Human Sciences K. Annen, Fall 003 Final (Version): Intermediate Microeconomics (ECON30) Solution Final (Version
MOT Seminar. John Musacchio 4/16/09
 Game Theory MOT Seminar John Musacchio johnm@soe.ucsc.edu 4/16/09 1 Who am I? John Musacchio Assistant Professor in ISTM Joined January 2005 PhD from Berkeley in Electrical l Engineering i Research Interests
Game Theory MOT Seminar John Musacchio johnm@soe.ucsc.edu 4/16/09 1 Who am I? John Musacchio Assistant Professor in ISTM Joined January 2005 PhD from Berkeley in Electrical l Engineering i Research Interests
Economics of two-sided markets
 Economics of two-sided markets basato su: Rysman M. (2009) The Economics of Two-Sided Markets, Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 23, Number 3 Summer 2009 Pages 125 143! Davide Castellani Dipartimento
Economics of two-sided markets basato su: Rysman M. (2009) The Economics of Two-Sided Markets, Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 23, Number 3 Summer 2009 Pages 125 143! Davide Castellani Dipartimento
Network Effects and Microsoft
 Timothy F. Bresnahan * Abstract Economic theories of network effects have a number of testable implications. Testing of the theory by econometric methods, however, has proved difficult. I turn to documentary
Timothy F. Bresnahan * Abstract Economic theories of network effects have a number of testable implications. Testing of the theory by econometric methods, however, has proved difficult. I turn to documentary
Chapter 9: Static Games and Cournot Competition
 Chapter 9: Static Games and Cournot Competition Learning Objectives: Students should learn to:. The student will understand the ideas of strategic interdependence and reasoning strategically and be able
Chapter 9: Static Games and Cournot Competition Learning Objectives: Students should learn to:. The student will understand the ideas of strategic interdependence and reasoning strategically and be able
Ross School of Business at the University of Michigan Independent Study Project Report
 Ross School of Business at the University of Michigan Independent Study Project Report TERM : Winter 1999 COURSE : CS 750 PROFESSOR : Allen Afuah STUDENT : Nitin Pai TITLE : Establishing standards : improving
Ross School of Business at the University of Michigan Independent Study Project Report TERM : Winter 1999 COURSE : CS 750 PROFESSOR : Allen Afuah STUDENT : Nitin Pai TITLE : Establishing standards : improving
From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risk of Platform Markets
 strategy+business ISSUE 73 WINTER 2013 From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risk of Platform Markets Companies like dating sites and online auctions that link complementary partners can dominate for years
strategy+business ISSUE 73 WINTER 2013 From Netscape to eharmony: The High Risk of Platform Markets Companies like dating sites and online auctions that link complementary partners can dominate for years
Two-Sided Markets and the Sharing Economy:
 Two-Sided Markets and the Sharing Economy: Nuances, Challenges, and Cautionary Notes Michael R. Baye Prepared for the 2 nd Annual BCCP Conference on Regulatory Challenges in Digital Markets Berlin, June
Two-Sided Markets and the Sharing Economy: Nuances, Challenges, and Cautionary Notes Michael R. Baye Prepared for the 2 nd Annual BCCP Conference on Regulatory Challenges in Digital Markets Berlin, June
SI Information Economics, Winter 2009
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2009-01 SI 646 - Information Economics, Winter 2009 McCabe, Mark McCabe, M. (2009, January 23). Information Economics. Retrieved from Open.Michigan
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2009-01 SI 646 - Information Economics, Winter 2009 McCabe, Mark McCabe, M. (2009, January 23). Information Economics. Retrieved from Open.Michigan
AP Microeconomics: Test 5 Study Guide
 AP Microeconomics: Test 5 Study Guide Mr. Warkentin nwarkentin@wyomingseminary.org 203 Sprague Hall 2017-2018 Academic Year Directions: The purpose of this sheet is to quickly capture the topics and skills
AP Microeconomics: Test 5 Study Guide Mr. Warkentin nwarkentin@wyomingseminary.org 203 Sprague Hall 2017-2018 Academic Year Directions: The purpose of this sheet is to quickly capture the topics and skills
Web Marketing & Digital Advertising Digital technologies and market changes
 Web Marketing & Digital Advertising Digital technologies and market changes A.A. 2018-2019 Costanza Nosi UNIVERSITÀ LUMSA WHAT DOES DIGITAL MEAN? Digital data is also called binary data because it is usually
Web Marketing & Digital Advertising Digital technologies and market changes A.A. 2018-2019 Costanza Nosi UNIVERSITÀ LUMSA WHAT DOES DIGITAL MEAN? Digital data is also called binary data because it is usually
Economic Theory and Practices Telecommunication Policy and Regulation for Competition
 Topics Economic Theory and Practices Telecommunication Policy and Regulation for Competition Workshop on Telecommunication Policy and Regulation for Competition Bangkok, Thailand, 11-15 July 2005 Part
Topics Economic Theory and Practices Telecommunication Policy and Regulation for Competition Workshop on Telecommunication Policy and Regulation for Competition Bangkok, Thailand, 11-15 July 2005 Part
Managing Technological Innovation
 Articles Managing Technological Innovation Technological Innovation Definition: The process of developing new, marketed products and/or new production and delivery systems. Burgelman et al. 1A. Tinkering/
Articles Managing Technological Innovation Technological Innovation Definition: The process of developing new, marketed products and/or new production and delivery systems. Burgelman et al. 1A. Tinkering/
Network Economics. for the MBA class. Networks, Telecommunications Economics, and Digital Convergence. Prof. Nicholas Economides.
 Network Economics for the MBA class Networks, Telecommunications Economics, and Digital Convergence Prof. Nicholas Economides January 2006 This course is about the economics of network industries. The
Network Economics for the MBA class Networks, Telecommunications Economics, and Digital Convergence Prof. Nicholas Economides January 2006 This course is about the economics of network industries. The
Inaccuracies in Fable of the Fable
 Inaccuracies in Fable of the Fable Although Mr. Brooks brings up some reasonable points, many of his points are either off base or are just plainly wrong. This note examines his claims, using his headers
Inaccuracies in Fable of the Fable Although Mr. Brooks brings up some reasonable points, many of his points are either off base or are just plainly wrong. This note examines his claims, using his headers
Module 32. Game Theory. Module Objectives. Module Outline. I. Games Oligopolists Play
 Module 32 Game Theory Module Objectives Students will learn in this module: How our understanding of oligopoly can be enhanced by using game theory. The concept of the prisoners dilemma. How repeated interactions
Module 32 Game Theory Module Objectives Students will learn in this module: How our understanding of oligopoly can be enhanced by using game theory. The concept of the prisoners dilemma. How repeated interactions
1. What are Network Effects?
 Network Externalities (Effects) S. J. Liebowitz Stephen E. Margolis S. J. Liebowitz: Management School, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, Texas 75083 Stephen E. Margolis: Department of Economics,
Network Externalities (Effects) S. J. Liebowitz Stephen E. Margolis S. J. Liebowitz: Management School, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, Texas 75083 Stephen E. Margolis: Department of Economics,
Industrial Organization. Networks
 In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Industrial Organization 44772 (1392-93 1 st term) Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Networks Network externalities What
In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Industrial Organization 44772 (1392-93 1 st term) Dr. S. Farshad Fatemi Networks Network externalities What
Oligopoly C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T. When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to
 Oligopoly CHAPTER17 C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1 Describe and identify oligopoly and explain how it arises. 2 Explain the dilemma
Oligopoly CHAPTER17 C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1 Describe and identify oligopoly and explain how it arises. 2 Explain the dilemma
Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry s output.
 Topic 8 Chapter 13 Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition Econ 203 Topic 8 page 1 Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry
Topic 8 Chapter 13 Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition Econ 203 Topic 8 page 1 Oligopoly: How do firms behave when there are only a few competitors? These firms produce all or most of their industry
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 27. Oligopoly and Strategic Behavior
 Chapter 27 Oligopoly and Introduction On a typical day, United Parcel Service will transport over 10 million packages. UPS and its main rival, FedEx Ground, earn more than three-fourths of total revenue
Chapter 27 Oligopoly and Introduction On a typical day, United Parcel Service will transport over 10 million packages. UPS and its main rival, FedEx Ground, earn more than three-fourths of total revenue
Managerial Economics
 This paper has 10 pages (including the coversheet) THE UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE MELBOURNE BUSINESS SCHOOL Managerial Economics A/Prof. Joshua Gans and Dr Vivek Chaudhri Final Exam: Semester 1, 1998 Reading
This paper has 10 pages (including the coversheet) THE UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE MELBOURNE BUSINESS SCHOOL Managerial Economics A/Prof. Joshua Gans and Dr Vivek Chaudhri Final Exam: Semester 1, 1998 Reading
Network Externalities, Technological Progress, and the Competition of Market Contracts
 Network Externalities, Technological Progress, and the Competition of Market Contracts by Marcel Thum May 1993 Abstract Network externalities are used to describe the fact that many modern products become
Network Externalities, Technological Progress, and the Competition of Market Contracts by Marcel Thum May 1993 Abstract Network externalities are used to describe the fact that many modern products become
ANSWER OUTLINE. DATE: Thursday, March 12, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2009
 ANSWER OUTLINE Midterm Exam (80 Points Total) Leigh Tesfatsion DATE: Thursday, March 12, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2009 NOTE: Please answer ALL FOUR questions included on this test. In answering these questions,
ANSWER OUTLINE Midterm Exam (80 Points Total) Leigh Tesfatsion DATE: Thursday, March 12, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2009 NOTE: Please answer ALL FOUR questions included on this test. In answering these questions,
29/02/2016. Market structure II- Other types of imperfect competition. What Is Monopolistic Competition? OTHER TYPES OF IMPERFECT COMPETITION
 Market structure II- Other types of imperfect competition OTHER TYPES OF IMPERFECT COMPETITION Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which many firms
Market structure II- Other types of imperfect competition OTHER TYPES OF IMPERFECT COMPETITION Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which many firms
MICROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH OLIGOPOLY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CHARACTERISTICS OF OLIGOPOLY A market is an oligopoly when: Nature of Good: The goods for sale are Setting Price: The sellers are - There are producers - Firms are One firm
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CHARACTERISTICS OF OLIGOPOLY A market is an oligopoly when: Nature of Good: The goods for sale are Setting Price: The sellers are - There are producers - Firms are One firm
Innovation, Openness & Platform Control
 Innovation, Openness & Platform Control Geoffrey Parker Tulane University Marshall Van Alstyne Boston University & MIT Sponsored by NSF IIS-0338662, and grants from CISCO & Microsoft Corporations Motivation
Innovation, Openness & Platform Control Geoffrey Parker Tulane University Marshall Van Alstyne Boston University & MIT Sponsored by NSF IIS-0338662, and grants from CISCO & Microsoft Corporations Motivation
Lecture 21: Strategic Interaction and Game Theory
 Lecture 2: Strategic Interaction and Game Theory EC DD & EE / Manove Strategic Interaction p What types of firms are most likely to engage in costly rent-seeking? EC DD & EE / Manove Monopoly>Rent Seeking
Lecture 2: Strategic Interaction and Game Theory EC DD & EE / Manove Strategic Interaction p What types of firms are most likely to engage in costly rent-seeking? EC DD & EE / Manove Monopoly>Rent Seeking
Oligopoly. Quantity Price(per year) 0 $120 2,000 $100 4,000 $80 6,000 $60 8,000 $40 10,000 $20 12,000 $0
 Oligopoly 1. Markets with only a few sellers, each offering a product similar or identical to the others, are typically referred to as a. monopoly markets. b. perfectly competitive markets. c. monopolistically
Oligopoly 1. Markets with only a few sellers, each offering a product similar or identical to the others, are typically referred to as a. monopoly markets. b. perfectly competitive markets. c. monopolistically
Economics 220C Empirical Methods in Industrial Organization. Bronwyn H. Hall Economics, UC Berkeley Spring 2005
 Economics 220C Empirical Methods in Industrial Organization Bronwyn H. Hall Economics, UC Berkeley Spring 2005 Goals for this course 1. Survey various styles of research in the field with representative
Economics 220C Empirical Methods in Industrial Organization Bronwyn H. Hall Economics, UC Berkeley Spring 2005 Goals for this course 1. Survey various styles of research in the field with representative
HANDBOOK OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATION
 EtEIEIBEIBBEIEHEIBEIBEIEHEtEIEIEIEIBBEIE HANDBOOK OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATION VOLUME 3 Edited by MARK ARMSTRONG Department of Economics, University College of London and ROBERT PORTER Department of Economics,
EtEIEIBEIBBEIEHEIBEIBEIEHEtEIEIEIEIBBEIE HANDBOOK OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATION VOLUME 3 Edited by MARK ARMSTRONG Department of Economics, University College of London and ROBERT PORTER Department of Economics,
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TYING, UPGRADES, AND SWITCHING COSTS IN DURABLE-GOODS MARKETS. Dennis W. Carlton Michael Waldman
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TYING, UPGRADES, AND SWITCHING COSTS IN DURABLE-GOODS MARKETS Dennis W. Carlton Michael Waldman Working Paper 11407 http://www.nber.org/papers/w11407 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TYING, UPGRADES, AND SWITCHING COSTS IN DURABLE-GOODS MARKETS Dennis W. Carlton Michael Waldman Working Paper 11407 http://www.nber.org/papers/w11407 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
The Business of Open Standards in the E&P Industry. Michael Glinsky Chris Haase
 The Business of Open Standards in the E&P Industry Michael Glinsky Chris Haase Something for a businessman to think about Business opportunity Consumers Suppliers Business proposal Description Example
The Business of Open Standards in the E&P Industry Michael Glinsky Chris Haase Something for a businessman to think about Business opportunity Consumers Suppliers Business proposal Description Example
Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of Legal Norms &
 Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of John Asker February 7, 2013 Yale Law School Roadmap Build on case studies of environments where extra-legal norms are at least as important as formal
Analytic Preliminaries for Social Acceptability of John Asker February 7, 2013 Yale Law School Roadmap Build on case studies of environments where extra-legal norms are at least as important as formal
Answer Outline. DATE: Thursday, March 13, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2008
 Answer Outline Midterm Exam (80 Points Total) Leigh Tesfatsion DATE: Thursday, March 13, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2008 QUESTION 1:SHORT ANSWERS [15 Points Total, 5 Points Each Part A-C (About 15 Minutes)]
Answer Outline Midterm Exam (80 Points Total) Leigh Tesfatsion DATE: Thursday, March 13, 11:00am Econ 308, Spring 2008 QUESTION 1:SHORT ANSWERS [15 Points Total, 5 Points Each Part A-C (About 15 Minutes)]
Incentives for Market Research: Preemption and Learning Effects
 Incentives for Market Research: Preemption and Learning Effects Peter M. Kort, Pauli Murto, and Grzegorz Pawlina April 25, 2005 Preliminary and incomplete. Please do not quote. Abstract This paper is about
Incentives for Market Research: Preemption and Learning Effects Peter M. Kort, Pauli Murto, and Grzegorz Pawlina April 25, 2005 Preliminary and incomplete. Please do not quote. Abstract This paper is about
PRICE OF ANARCHY: QUANTIFYING THE INEFFICIENCY OF EQUILIBRIA. Zongxu Mu
 PRICE OF ANARCHY: QUANTIFYING THE INEFFICIENCY OF EQUILIBRIA Zongxu Mu The Invisible Hand Equilibria and Efficiency Central to free market economics The Wealth of Nations (Smith, 1776) led by an invisible
PRICE OF ANARCHY: QUANTIFYING THE INEFFICIENCY OF EQUILIBRIA Zongxu Mu The Invisible Hand Equilibria and Efficiency Central to free market economics The Wealth of Nations (Smith, 1776) led by an invisible
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Attempt all the questions. The allocation of marks is shown in brackets.
 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Game Theory Autumn Semester 2017 18 2 hours and 30 minutes Attempt all the questions. The allocation of marks is shown in brackets. Please leave this exam paper on
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Game Theory Autumn Semester 2017 18 2 hours and 30 minutes Attempt all the questions. The allocation of marks is shown in brackets. Please leave this exam paper on
Market Structure. Monopolistic Oligopoly. By Asst. Prof. Kessara Thanyalakpark, Ph.D.
 Market Structure Monopolistic Oligopoly By Asst. Prof. Kessara Thanyalakpark, Ph.D. Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic Characteristics A hybrid market between competitive and monopoly market Large numbers
Market Structure Monopolistic Oligopoly By Asst. Prof. Kessara Thanyalakpark, Ph.D. Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic Characteristics A hybrid market between competitive and monopoly market Large numbers
Static (or Simultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Information
 Static (or Simultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Information Dominated Strategies Nash Equilibrium F.Valognes - Game Theory - Chp 2 1 Outline of Static Games of Complete Information Introduction to games
Static (or Simultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Information Dominated Strategies Nash Equilibrium F.Valognes - Game Theory - Chp 2 1 Outline of Static Games of Complete Information Introduction to games
Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4)
 Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4) Slide 1 Generic Business Strategies Michael Porter (1980) suggested three generic strategies in positioning products or services. Cost leadership
Competition and Strategies (Courcoubetis&Weber: Chapter 6.4) Slide 1 Generic Business Strategies Michael Porter (1980) suggested three generic strategies in positioning products or services. Cost leadership
Business Austan Goolsbee Technology and Policy in the Telecom, Media, and Technology Industries Final Exam Answers
 Business 33221 Austan Goolsbee Technology and Policy in the Telecom, Media, and Technology Industries Final Exam Answers 1. (40 points) From a news report two weeks ago: "Mozilla has accused Microsoft
Business 33221 Austan Goolsbee Technology and Policy in the Telecom, Media, and Technology Industries Final Exam Answers 1. (40 points) From a news report two weeks ago: "Mozilla has accused Microsoft
Oligopoly is a market structure in which Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms. A small number of firms compete.
 15 OLIGOPOLY What Is Oligopoly? Oligopoly is a market structure in which Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms. A small number of firms compete. Oligopoly sell (but more than two) of
15 OLIGOPOLY What Is Oligopoly? Oligopoly is a market structure in which Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms. A small number of firms compete. Oligopoly sell (but more than two) of
ECO 610: Lecture 9. Oligopoly, Rivalry, and Strategic Behavior
 ECO 610: Lecture 9 Oligopoly, Rivalry, and Strategic Behavior Oligopoly, Rivalry, and Strategic Behavior: Outline Porter s Five Forces Model: when does internal rivalry get interesting? Oligopoly: definition
ECO 610: Lecture 9 Oligopoly, Rivalry, and Strategic Behavior Oligopoly, Rivalry, and Strategic Behavior: Outline Porter s Five Forces Model: when does internal rivalry get interesting? Oligopoly: definition
Review Chapters 1 & 2
 Review Chapters 1 & 2 ECON 1 Midterm 1 Review Session Scarcity or No Free Lunch Principle. Cost-Benefit Principle. Reservation Price. Economic Surplus = Benefit Cost. Opportunity Cost (DO NOT FORGET!!).
Review Chapters 1 & 2 ECON 1 Midterm 1 Review Session Scarcity or No Free Lunch Principle. Cost-Benefit Principle. Reservation Price. Economic Surplus = Benefit Cost. Opportunity Cost (DO NOT FORGET!!).
Innovation from a micro-economic perspective
 Innovation from a micro-economic perspective An introductory overview to some themes of the week Luigi Marengo St. Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa, l.marengo@sssup.it Why Study the Economics of Science
Innovation from a micro-economic perspective An introductory overview to some themes of the week Luigi Marengo St. Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa, l.marengo@sssup.it Why Study the Economics of Science
Game Theory and Economics
 and Economics Game theory is the study of how people behave in strategic situations. Strategic decisions are those in which each person, in deciding what actions to take, must consider how others might
and Economics Game theory is the study of how people behave in strategic situations. Strategic decisions are those in which each person, in deciding what actions to take, must consider how others might
Technology Strategy Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Strategic Management of Platforms
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.912 Technology Strategy Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Strategic Management of Platforms
Topics in ALGORITHMIC GAME THEORY *
 Topics in ALGORITHMIC GAME THEORY * Spring 2012 Prof: Evdokia Nikolova * Based on slides by Prof. Costis Daskalakis Let s play: game theory society sign Let s play: Battle of the Sexes Theater Football
Topics in ALGORITHMIC GAME THEORY * Spring 2012 Prof: Evdokia Nikolova * Based on slides by Prof. Costis Daskalakis Let s play: game theory society sign Let s play: Battle of the Sexes Theater Football
2013 sample MC CH 15. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: 2013 sample MC CH 15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Monopolistic competition is identified by a. many firms producing a slightly
Class: Date: 2013 sample MC CH 15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Monopolistic competition is identified by a. many firms producing a slightly
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page.
 Econ 0, Section 2, S0, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page..
Econ 0, Section 2, S0, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page..
Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page.
 Econ 0, Section 2, S0, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = 2 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page..
Econ 0, Section 2, S0, Schroeter Exam #4, Special code = 2 Choose the single best answer for each question. Do all of your scratch work in the margins or in the blank space at the bottom of the last page..
Chapter 12. A Game Theoretic Approach to Strategic Behavior
 Chapter 12 A Game Theoretic Approach to Strategic Behavior Chapter Outline An Introduction to the Theory of Games Prisoner s Dilemma Nash Equilibrium Maximin Strategy Strategies for Repeated Play Sequential
Chapter 12 A Game Theoretic Approach to Strategic Behavior Chapter Outline An Introduction to the Theory of Games Prisoner s Dilemma Nash Equilibrium Maximin Strategy Strategies for Repeated Play Sequential
Questions similar to the ones below have been found adequate to bring out the key issues in the case study.
 APPLE TEACHING NOTE The case can be used to illustrate the issues of make or buy and managing the supply chain. It is best used in the middle part of an operations strategy course. It not only introduces
APPLE TEACHING NOTE The case can be used to illustrate the issues of make or buy and managing the supply chain. It is best used in the middle part of an operations strategy course. It not only introduces
Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 41
 Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 41 Game Theory Strategic thinking is the art of outdoing an adversary, knowing that the adversary is trying to do the same to you. Dixit and Nalebuff Game theory is used
Microeconomics LESSON 6 ACTIVITY 41 Game Theory Strategic thinking is the art of outdoing an adversary, knowing that the adversary is trying to do the same to you. Dixit and Nalebuff Game theory is used
Graham Romp Dynamic Game Theory.
 Graham Romp Dynamic Game Theory. In the previous chapter we focused on static games. However for many important economic applications we need to think of the game as being played over a number of time
Graham Romp Dynamic Game Theory. In the previous chapter we focused on static games. However for many important economic applications we need to think of the game as being played over a number of time
Econ 101A Solutions for Final exam - Fall 2006
 Econ 101A Solutions for Final exam - Fall 2006 Problem 1. Shorter problems. (35 points) Solve the following shorter problems. 1. Consider the following (simultaneous) game of chicken. This is a game in
Econ 101A Solutions for Final exam - Fall 2006 Problem 1. Shorter problems. (35 points) Solve the following shorter problems. 1. Consider the following (simultaneous) game of chicken. This is a game in
The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation
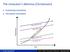 The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation 1 Change Management Peter G. Klein University of Missouri September 2009 Some recent trends Increased role of information
The innovator s dilemma (Christensen) Sustaining innovation Disruptive innovation 1 Change Management Peter G. Klein University of Missouri September 2009 Some recent trends Increased role of information
Lecture 21: Strategic Interaction and Game Theory
 Lecture : Strategic Interaction and Game Theory EC DD & EE / Manove Strategic Interaction p EC DD & EE / Manove Clicker Question p Strategic Interaction In perfectly competitive markets (like the market
Lecture : Strategic Interaction and Game Theory EC DD & EE / Manove Strategic Interaction p EC DD & EE / Manove Clicker Question p Strategic Interaction In perfectly competitive markets (like the market
Dynamic Network Competition Very Preliminary and incomplete
 Dynamic Network Competition Very Preliminary and incomplete Hanna Ha laburda Bruno Jullien Yaron Yehezkel June 19, 2013 Abstract This paper considers a dynamic platform competition in a market with network
Dynamic Network Competition Very Preliminary and incomplete Hanna Ha laburda Bruno Jullien Yaron Yehezkel June 19, 2013 Abstract This paper considers a dynamic platform competition in a market with network
Open Access To Broadband Networks: A Case Study Of The AOL/Time Warner Merger. by Daniel L. Rubenfeld & Hal J. Singer
 Open Access To Broadband Networks: A Case Study Of The AOL/Time Warner Merger by Daniel L. Rubenfeld & Hal J. Singer Presented by Kevin Morgan and Michael Lewis Outline Introduction: the key players Horizontal
Open Access To Broadband Networks: A Case Study Of The AOL/Time Warner Merger by Daniel L. Rubenfeld & Hal J. Singer Presented by Kevin Morgan and Michael Lewis Outline Introduction: the key players Horizontal
Microeconomics Sixth Edition
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Microeconomics Sixth Edition 17 Oligopoly Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What outcomes are possible
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Microeconomics Sixth Edition 17 Oligopoly Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What outcomes are possible
Compatibility and the Creation of Shared Networks. Nicholas Economides
 Chapter 3 in Electronic Services Networks, M.E. Guerrin-Calvert and S.S. Wildman (eds), Praeger, New York, 1991. Compatibility and the Creation of Shared Networks Nicholas Economides Many networks start
Chapter 3 in Electronic Services Networks, M.E. Guerrin-Calvert and S.S. Wildman (eds), Praeger, New York, 1991. Compatibility and the Creation of Shared Networks Nicholas Economides Many networks start
Erik den Hartigh 1 Delft University of Technology and TVA developments bv. Ton van Asseldonk TVA developments bv
 Business ecosystems: A research framework for investigating the relation between network structure, firm strategy, and the pattern of innovation diffusion Erik den Hartigh 1 Delft University of Technology
Business ecosystems: A research framework for investigating the relation between network structure, firm strategy, and the pattern of innovation diffusion Erik den Hartigh 1 Delft University of Technology
H3 Economics: Game Theory and the Economics of Cooperation. theme 2: firms and market failure game theory notes
 theme 2: firms and market failure game theory notes introduction dominant strategies, Nash equilibrium and Prisoner s Dilemma repeated games sequential games entry deterrence strategic trade limitations
theme 2: firms and market failure game theory notes introduction dominant strategies, Nash equilibrium and Prisoner s Dilemma repeated games sequential games entry deterrence strategic trade limitations
FINAL Version A Friday, June 11, 2004 FILL IN THE BLANK. (5 points per blank)
 ECN 460/560, Spring 2004 Prof. Bruce Blonigen SS#: FINAL Version A Friday, June 11, 2004 FILL IN THE BLANK. (5 points per blank) 1) In the theory of the firm, the short-run is defined as that period of
ECN 460/560, Spring 2004 Prof. Bruce Blonigen SS#: FINAL Version A Friday, June 11, 2004 FILL IN THE BLANK. (5 points per blank) 1) In the theory of the firm, the short-run is defined as that period of
Lecture 13(i) Announcements. Lecture on Game Theory. Average of HW 1-9 posted at Moodle. Two more to go: HW 10 due Tues, Dec 8 HW 11 due Tues, Dec 15
 Lecture 13(i) Announcements Average of HW 1-9 posted at Moodle Two more to go: HW 10 due Tues, Dec 8 HW 11 due Tues, Dec 15 We drop the two lowest homeworks. If you skip HW 10 and HW 11, the current average
Lecture 13(i) Announcements Average of HW 1-9 posted at Moodle Two more to go: HW 10 due Tues, Dec 8 HW 11 due Tues, Dec 15 We drop the two lowest homeworks. If you skip HW 10 and HW 11, the current average
Econ 3542: Experimental and Behavioral Economics Exam #1 Review Questions
 Econ 3542: Experimental and Behavioral Economics Exam #1 Review Questions Chapter 1 (Intro) o Briefly describe the early history of market experiments. Chamberlin s original pit market experiments (1948)
Econ 3542: Experimental and Behavioral Economics Exam #1 Review Questions Chapter 1 (Intro) o Briefly describe the early history of market experiments. Chamberlin s original pit market experiments (1948)
The 3 Fundamentals of Systems Management
 The 3 Fundamentals of Systems Management Dell October 2007 There are three fundamental components to desktop and notebook systems management Deploy; Monitor; and Change (Update). There are many subelements,
The 3 Fundamentals of Systems Management Dell October 2007 There are three fundamental components to desktop and notebook systems management Deploy; Monitor; and Change (Update). There are many subelements,
Economics of Industrial Organization. Lecture 14: Intellectual Property Rights and Patent Policy
 Economics of Industrial Organization Lecture 14: Intellectual Property Rights and Patent Policy Patents; government-granted monopoly We have spent much of this course consider the problems of monopoly
Economics of Industrial Organization Lecture 14: Intellectual Property Rights and Patent Policy Patents; government-granted monopoly We have spent much of this course consider the problems of monopoly
Algoritmi Distribuiti e Reti Complesse (modulo II) Luciano Gualà
 Algoritmi Distribuiti e Reti Complesse (modulo II) Luciano Gualà guala@mat.uniroma2.it www.mat.uniroma2.it/~guala Algorithmic Game Theory Algorithmic Issues in Non-cooperative (i.e., strategic) Distributed
Algoritmi Distribuiti e Reti Complesse (modulo II) Luciano Gualà guala@mat.uniroma2.it www.mat.uniroma2.it/~guala Algorithmic Game Theory Algorithmic Issues in Non-cooperative (i.e., strategic) Distributed
Analyze different types of non zero sum games. Hawk vs. Dove game. Advertising problem. Problem of companies polluting the environment.
 Unit 3 GME THEORY Lesson 31 Learning Objective: nalyze different types of non zero sum games Hawk vs. game. dvertising problem. Problem of companies polluting the environment. Rationalizability or Iterative
Unit 3 GME THEORY Lesson 31 Learning Objective: nalyze different types of non zero sum games Hawk vs. game. dvertising problem. Problem of companies polluting the environment. Rationalizability or Iterative
