Title. Author(s)Osaki, Shogo; Sakai, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationJournal of the Electrochemical Society, 157(8): E117. Issue Date
|
|
|
- Bernard Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title Direct Production of Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr Biomedical A Author(s)Osaki, Shogo; Sakai, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationJournal of the Electrochemical Society, 157(8): E117 Issue Date Doc URL Rights The Electrochemical Society, Inc All rights may not be reproduced, resold, distributed, or modif (ECS). The archival version of this work was publish Type article File Information JES157-8_e117-e121.pdf Instructions for use Hokkaido University Collection of Scholarly and Aca
2 /2010/157 8 /E117/5/$28.00 The Electrochemical Society E117 Direct Production of Ti 29Nb 13Ta 4.6Zr Biomedical Alloy from Oxide Mixture in Molten CaCl 2 Shogo Osaki, z Hiroshi Sakai, and Ryosuke O. Suzuki Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University, Sapporo , Japan A process based on the principle of the Ono Suzuki process involving electrolysis and the calciothermic coreduction of an oxide mixture consisting of TiO 2,Nb 2 O 5,Ta 2 O 5, and ZrO 2 for producing Ti 29Nb 23Ta 4.6Zr TNTZ was proposed. Ca was produced by the electrolysis of CaO in molten CaCl 2 by applying a voltage of 3.2 V between a carbon anode and Ti cathode at 1173 K. The residual oxygen concentration in the obtained powder decreased monotonically with an increase in the supplied electric charge. An oxygen concentration of 0.19 mass % was attained by supplying the electrical charge around 3 times larger than that necessary to generate the stoichiometrically required amount of Ca. This sample consisted of a Ti-based body-centered cubic solid solution and a small amount of hexagonal close-packed hcp solid solution. The inhomogeneity in the composition was suppressed to a relatively low level so that it could be easily improved by heat-treatment. After sintering at 1300 K for 54 ks, for example, the Tiand Zr-rich hcp phase disappeared and the composition achieved the targeted value. The results of this study indicate that the OS process can be applied to directly produce TNTZ alloy from an oxide mixture The Electrochemical Society. DOI: / All rights reserved. Manuscript submitted January 25, 2010; revised manuscript received April 26, Published June 3, In recent years, new processes for producing Ti or Ti-based alloys have been investigated. The Ono Suzuki OS process is one such process. 1-6 A schematic representation of the OS process is shown in Fig. 1. The OS process involves calciothermic reduction and Ca recycling. Ca is produced by the electrolysis of CaO in molten CaCl 2 electrolyte; Ca has a strong reducing capacity, and therefore, it can reduce various types of oxides. When a carbon anode and Ti cathode are used, the electrolysis reactions at the electrodes are expressed as follows At the anode: O 2 +C CO/CO 2 +e 1 At the cathode: Ca 2+ +2e Ca 2 The overall reaction is expressed as follows CaO + C Ca + CO/CO 2 3 The calciothermic reduction of a metal oxide for example, TiO 2 is expressed as follows TiO 2 +2Ca Ti + 2CaO 4 CaO that is formed as a by-product immediately dissolves in the molten CaCl 2, where CaO is electrolyzed again. These reactions permit the recycling of Ca used as a reducing agent and the continuous reduction of oxides in the same molten CaCl 2 bath. Because of the wide solubility of CaO, the dissolution of O 2 from the oxide at the cathode was also studied as the direct electro-deoxidation, 7-10 which has been applied to TiO 2 using CaCl 2 melt especially applying a low electrochemical potential such as 2.0 V. At a voltage higher than the theoretical decomposition voltage of CaO, the OS process has been successfully applied to the reduction of single oxides such as TiO and V 2 O Recently, the principle of the OS process was applied to the synthesis of Ti V Cr hydrogen-storage alloy 12 and Ti 6Al 4V aerospace alloy. 13 In this study, we attempted to directly produce Ti 29Nb 13Ta 4.6Zr TNTZ alloy from an oxide mixture, as shown in Fig. 1. TNTZ alloy is a newly developed alloy that is used for biomedical purposes and is expected to find wide-ranging applications because of its advantageous properties. Its constituent elements, namely Ti, Nb, Ta, and Zr, are nontoxic to biological bodies. In addition, it has a low Young s modulus of 60 GPa, much lower than that of pure Ti, which is beneficial in implant applications, and its mechanical strength is similar to that of Ti 6Al 4V alloy. 14 However, as is common in the case of Ti-based alloys, a method for producing TNTZ alloy remains complicated and expensive because the above-mentioned constituent elements need to be reduced individually before they are mixed. Furthermore, alloying methods such as arc melting require a considerable amount of electric power. If reduction and alloying could be carried out simultaneously, or more specifically, if the alloy could be directly produced from the oxide mixture, the production process could be considerably simplified; in fact, such an optimization might lead to TNTZ alloys finding wideranging applications. The OS process could serve as this type of novel process for producing Ti-based alloys, because Ca can reduce most oxides and an alloy is synthesized simultaneously from the reduced metals during the process, as shown in Fig. 1, if some oxides are used as starting materials. In the production of TNTZ alloys, as shown in Fig. 2, 15 the constituent oxides can be reduced to their metallic phases by Ca because CaO is the most thermodynamically stable among the oxides shown in Fig. 2. Using an oxide mixture that consists of TiO 2,Nb 2 O 5,Ta 2 O 5, and ZrO 2 as the starting material, the individual oxides can be reduced simultaneously to form an alloy. The calciothermic coreduction of the oxide mixture is expressed as follows TiO 2 +Nb 2 O 5 +Ta 2 O 5 + ZrO 2 +Ca TNTZ + CaO 5 CaO + C Ca + CO/CO 2 6 In this study, we attempted to produce TNTZ alloy experimentally according to the reaction given in Eq. 5 and 6. The residual oxygen concentration and elemental distribution of the obtained sample were analyzed to confirm whether reduction and alloying proceeded successfully. z s.osaki@eng.hokudai.ac.jp Figure 1. Principle of OS process for TNTZ alloy formation.
3 E118 Figure 4. The change in anodic current density vs time. Figure 2. Oxygen partial pressure of the oxides in the system of Ti Nb Ta Zr. Experimental Figure 3 shows the experimental apparatus used for carrying out the reduction of the oxide mixture and electrolysis. Molten CaCl 2 with 0.5 mol % CaO dissolved in it was used as the electrolyte. The mass of mixed salt was approximately 600 g. The anode was made of carbon and had a diameter of 10 mm, giving an active surface area of approximately 15 cm 2 when it was immersed in the molten salt. The cathode was made of Ti net and had a diameter of 12 mm; it had a cylindrical basketlike shape to hold the starting sample. The oxide powders, namely TiO 2, Nb 2 O 5, Ta 2 O 5, and ZrO 2, were weighted at the targeted composition with a mass ratio of TNTZ; Figure 3. The experimental apparatus. they were then mixed thoroughly in mortar, before being inserted into the cathode. The mass of the starting oxide mixture was fixed at 2.00 g in all the experiments. The electrolysis vessel was evacuated at 873 K for approximately 30 ks to remove water present in the electrolyte. Electrolysis was carried out under a constant potential of 3.2 V at 1173 K in Ar gas atmosphere. Q/Q 0 was used as an indicator to order the degree of reduction. Here, Q denotes the supplied charge and is calculated by integrating the measured current against time; Q 0 denotes the theoretical charge and is defined as the electricity required to generate a stoichiometric amount of Ca as given in Eq. 5. In this study, Q 0 was evaluated to be 8322 C. After stopping electrolysis, the cathode was removed from the bath and cooled in Ar atmosphere. The reduced sample was sequentially washed with distilled water, acetic acid, ethanol, and acetone. It was then analyzed by X-ray diffractometry XRD and electron probe microanalysis EPMA. The oxygen concentration of samples was also analyzed by using an IR absorption method with carbon crucible under He atmosphere using a LECO TC600 oxygen analyzer. Several reduced samples were sintered for future application in powder metallurgy. The samples were pressed into a pellet 10 mm in diameter and thickness on the order of a few millimeters at 450 MPa and then sintered in Ar atmosphere at 1300 K for 54 ks. The specimens were then analyzed by XRD and EPMA again. Results and Discussion Current density. Figure 4 shows the change in anodic current density during electrolysis. The current exhibited a comparatively large value at the initial stage; it then gradually decreased and approached a low and constant value. Under the assumption that the electrical carrier in molten CaCl 2 was mainly oxygen ions and the anodic reaction involves the evolution of CO and CO 2 gas, namely the consumption of oxygen ions, the large current would be attributable to the high reaction rate due to the high concentration of dissolved O 2. The amount of O 2 decreased during the electrolysis, as indicated by Eq. 1, and the current due to O 2 decreased. In contrast, the amount of dissolved O 2 increased when reduction or deoxidation occurred effectively along with the generation of a large amount of CaO. Therefore, these changes in the dissolved O 2 are attributed to the current change. After the complete reduction and removal of O 2, the current should be zero. However, as shown in Fig. 4, a certain constant current continued to flow even at this final stage. This was due to the occurrence of parasite reactions in which Ca saturated in the molten salt reduced CO and CO 2 gas evolving at the anode. Phases identified by XRD. Figure 5 shows the XRD results of the reduced samples obtained at Q/Q 0 = 57, 115, 165, 262, and
4 E119 Figure 6. The change in oxygen concentration vs supplied charge. Figure 5. XRD patterns of reduced samples. 323%, as shown in Fig. 4. In Fig. 5, and correspond to hexagonal close-packed hcp and body-centered cubic bcc solid solutions, respectively. At Q/Q 0 = 57%,,, CaTiO 3, and ZrO 2 were found. This indicates that the generation of Nb and Ta, which have a bcc structure, occurred effectively during electrolysis. However, TiO 2 would react with CaO dissolved in the molten salt to form the composite oxide CaTiO 3. ZrO 2 remained in the oxide form at this stage. This implies that the reduction behavior reduction rate could be classified into two groups, as predicted by the Ellingham diagram Fig. 2. In other words, the free energy change in the chemical reaction oxygen removal from the oxide can be classified into two groups: a group of Ta and Nb, and another of Ti and Zr. The elements in the latter group are more stable than those in the former. At Q/Q 0 = 115%, CaTiO 3 disappeared and CaZrO 3 was formed. In previous studies, 6,16 it was reported that CaTiO 3 was formed when the OS process reduced the TiO 2 starting material. In this study, it was confirmed that ZrO 2, whose metal has properties similar to those of Ti, also forms a composite oxide CaZrO 3. When the electric charge reached 165% of the theoretical value, only the and phases were found. Therefore, at this stage, all oxides might have been reduced to the metallic phase. At 262%, the XRD pattern obtained was similar to that obtained at 165%. The smaller intensity of the peak indicated the transformation of to. At 323%, TiC precipitation was observed. This is due to the generation of carbon via the reduction of CO and CO 2 as a parasite reaction or the direct reaction with Ti. To suppress TiC formation, the Ca-rich area should be separated from the anodic reaction area. At all stages, a residual phase was detected; in contrast, it was reported that the TNTZ alloy had a single phase. 17 Oxygen concentration. Figure 6 shows the relationship between the residual oxygen concentration of the reduced sample and the supplied electric charge. The oxygen concentration decreased with an increase in the supplied electric charge, and it finally reached 0.23 mass % at Q/Q 0 = 262% without TiC precipitation and 0.19 mass % at Q/Q 0 = 323%. A comparison of Fig. 6 with Fig. 5 indicated that the reduction completed before Q/Q 0 = 160%, following which deoxidation from the oxygen metal solid solution proceeded. The phase detected at Q/Q 0 = 115% included CaZrO 3. Previously reported 18 arc-melted TNTZ alloys contained mass % oxygen, and the increase in the oxygen concentration caused a larger mechanical strength that was offset by a smaller elongation. A TNTZ alloy including mass % oxygen could be employed for a variety of applications. 19 Therefore, when producing TNTZ by our approach, it was concluded that the reduction and deoxidation proceeded sufficiently and the targeted residual oxygen concentration had been achieved. Elemental distribution. Figures 7-10 show scanning electron microscopic SEM images and the concentration mappings of the four elements in the reduced powders obtained for Q/Q 0 = 57, 115, 165, and 262%, respectively. In all figures, the brighter red color indicates a higher concentration. At Q/Q 0 = 57%, most parts of the sample were in the form of fine particles having a diameter on the order of submicrometers. The constituent elements dispersed over the entire area; however, all were not present at the same location because alloying did not proceed sufficiently. At Q/Q 0 = 115%, it was clearly recognized that Nb and Ta existed at the same location. This implies that the alloying of Nb and Ta proceeded until this period. However, Ti existed more widely than Nb or Ta and some parts of -Ti did not react with other elements. Zr localized at some parts, probably in the form of CaZrO 3. Figure 11 shows a magnified view of this sample. Table I lists the results of local elemental analyses carried out at the three positions shown in Fig. 11. Some rectangular blocks existed in this powder at locations that were rich in Nb and Ta. Therefore, this block was considered as a Nb Ta-based bcc -solid solution with Figure 7. Color online SEM image and elemental concentration mappings of the sample obtained at Q/Q 0 = 57%.
5 E120 Figure 8. Color online SEM image and elemental concentration mappings of the sample obtained at Q/Q 0 = 115%. Figure 11. SEM image of the sample obtained at Q/Q 0 = 115%. The analytical values at A, B, and C are given in Table I mass % Ti. The fine particles marked as C are considered as -Ti containing a larger amount of oxygen. Three types of elements coexisted, although the morphologies of the particles were dissimilar. The mixing of the constituent elements occurred at the oxide and alloy particle level, in addition to the individual reduction of elemental oxides. At Q/Q 0 = 165%, all of the constituent elements shown in Fig. 9 have spread more widely than those shown in Fig. 8. All of the starting oxides including ZrO 2 were reduced to the metallic state at this stage and the sample formed secondary particles having a diameter of approximately 200 m. At Q/Q 0 = 262% Fig. 10, the elemental distribution became almost homogeneous, and the size of the secondary particles remained unchanged. Table II lists the results of local elemental analyses carried out at eight positions over the image shown in Fig. 10. This image was chosen at random and the spot size of a few micrometers was used. The deviations of the values listed in Table II are the standard deviation. Although Fig. 10 suggests that the four elements distributed homogeneously over a wide area, the measured compositions at eight locations exhibited slight variations. This study showed that the reduction and deoxidation proceeded sufficiently and that the alloying proceeded simultaneously in molten CaCl 2. However, a residual phase probably exists due to differences in the reduction behavior of the constituent oxides. The differences in the reduction rate lead to variations in the elements in the reduced powders. This is because the initial product Nb and Ta metals form blocks, whereas the delayed product Ti and Zr cannot Table I. Local elemental analyses results at three positions in Fig. 11. Figure 9. Color online SEM image and elemental concentration mappings of the sample obtained at Q/Q 0 = 165%. Position Concentration C/mass % Ti Nb Ta Zr Ca O A B C Table II. Local elemental analyses results for the powder shown in Fig. 10. Concentration C/mass % Position Ti Nb Ta Zr Figure 10. Color online SEM image and elemental concentration mappings of the sample obtained at Q/Q 0 = 262%. a b c d e f g h Average TNTZ
6 E121 Table III. Local elemental analyses results for the sintered pellet shown in Fig. 12. Concentration C/mass % Position Ti Nb Ta Zr a b c d e f g h Average TNTZ Figure 12. Color online SEM image and elemental concentration mappings of the pellet after sintering. diffuse well into the blocks. Zr acts as an hcp stabilizing element in Ti alloy, whereas Nb and Ta act as bcc stabilizing elements. 20 Therefore, the variability of elements causes the residual phase. Improvement by heat-treatment. From the viewpoint of future applications in powder metallurgy, we attempted to sinter the reduced powder to improve the compositional homogeneity. The powder obtained at Q/Q 0 = 262% was pressed into a pellet at 450 MPa and then sintered in Ar atmosphere at 1300 K for 54 ks. After cooling, the pellet was analyzed by XRD and EPMA. The analytical results are shown in Fig. 12 and 13 and Table III. Figure 12 shows the SEM image and elemental distribution randomly selected in the sample, and Table III lists the analytical results at eight positions of this image. The compositional homogeneity was improved after the heat-treatment, and the analyzed compositions approached the targeted values with low variability. Figure 13 shows XRD patterns of the unsintered powder, sintered Figure 13. Comparison of XRD patterns. pellet, and solution-treated sample. 17 The sintered pellet had a single phase and its XRD pattern agrees with that reported in a previous study. 17 Conclusions We proposed a process based on the principle of the OS process involving Ca coreduction and electrochemical recycling of Ca for producing Ti-based alloys. An oxide mixture consisting of TiO 2, Nb 2 O 5,Ta 2 O 5, and ZrO 2 was reduced simultaneously to form an alloy powder in molten CaCl 2. The oxygen concentration decreased monotonically with an increase in the supplied electric charge and reached 0.23 mass % without TiC contamination. The reduced sample with a low oxygen concentration was detected as a mixture of and phases, and its inhomogeneity was suppressed to a relatively low level although the reduction rates of the constituent oxides were different. The sample obtained after sintering had a single phase with the targeted compositions. These facts indicate that the OS process can be applied to directly produce TNTZ alloy from an oxide mixture. References 1. R. O. Suzuki and K. Ono, Aqueous and Electrochemical Processing, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Warrendale, PA R. O. Suzuki and S. Inoue, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 34, R. O. Suzuki, K. Teranuma, and K. Ono, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 34, K. Ono and R. O. Suzuki, Materia Japan (Bulletin of The Japan Institute of Metals), 41, R. O. Suzuki, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 66, R. O. Suzuki and S. Fukui, Mater. Trans., 45, G. Z. Chen, D. J. Fray, and T. W. Farthing, Nature (London), 407, K. Dring, R. Dashwood, and D. Inman, J. Electrochem. Soc., 152, E G. Z. Chen and D. J. Fray, J. Electrochem. Soc., 149, E C. Schwandt and D. J. Fray, Electrochim. Acta, 51, Y. Oka and R. O. Suzuki, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 72, Y. Kano and R. O. Suzuki, Ti-2007 Science and Technology, The Japan Institute of Metals H. Sakai, Y. Oka, and R. O. Suzuki, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 72, D. Kuroda, M. Niinomi, H. Fukui, M. Morinaga, A. Suzuki, and J. Hasegawa, Tetsu to Hagane, 86, A. Roine, HSC Chemistry, Version 6.1, Outotec Research Oy, Pori, Finland K. Kobayashi, Y. Oka, and R. O. Suzuki, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 72, ; Mater. Trans., 50, D. Kuroda, M. Niinomi, H. Fukui, A. Suzuki, and J. Hasegawa, Tetsu to Hagane, 86, M. Nakai, M. Niinomi, T. Akahori, H. Ishikawa, and M. Ogawa, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 72, F. Geng, M. Niinomi, M. Nakai, T. Akahori, and H. Tsutsumi, in Proceedings of the Processing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials XVIII (PFAMXVIII), 176th Committee on Process Created Materials Function, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, p H. Okamoto, ASM Handbook, p. 3, ASM International, OH 1992.
Current Activities of OS Process Using Molten CaO+CaCl 2
 Current Activities of OS Process Using Molten CaO+CaCl 2 Ryosuke O. Suzuki Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University 1. Direct Production of Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr Biomedical Alloy Appling the principle
Current Activities of OS Process Using Molten CaO+CaCl 2 Ryosuke O. Suzuki Faculty of Engineering, Hokkaido University 1. Direct Production of Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr Biomedical Alloy Appling the principle
Title. Author(s)Oka, Yuichi; Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationECS Transactions, 16(49): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Direct Reduction of Liquid V2O5 in Molten CaCl2 Author(s)Oka, Yuichi; Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationECS Transactions, 16(49): 255-264 Issue Date 2009 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/50032 Rights
Title Direct Reduction of Liquid V2O5 in Molten CaCl2 Author(s)Oka, Yuichi; Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationECS Transactions, 16(49): 255-264 Issue Date 2009 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/50032 Rights
Title. Author(s)Suzuki, Ryosuke O.; Matsuura, Fumiya; Natsui, Shungo. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Conversion of CO2 to CO gas using molten CaCl2 and Z Author(s)Suzuki, Ryosuke O.; Matsuura, Fumiya; Natsui, Shungo Issue Date 2017-10 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67371 Type proceedings File
Title Conversion of CO2 to CO gas using molten CaCl2 and Z Author(s)Suzuki, Ryosuke O.; Matsuura, Fumiya; Natsui, Shungo Issue Date 2017-10 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67371 Type proceedings File
Direct reduction processes for titanium oxide in mol. The final publication is available at Instructions for use
 Title Direct reduction processes for titanium oxide in mol Author(s)Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationJOM : Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Issue Date 2007-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/50035
Title Direct reduction processes for titanium oxide in mol Author(s)Suzuki, Ryosuke O. CitationJOM : Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Issue Date 2007-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/50035
An investigation of electro-deoxidation process for producing titanium from dense titanium dioxide cathode
 An investigation of electro-deoxidation process for producing titanium from dense titanium dioxide cathode Zhi-Yuan CHEN 1),2)*, Kuo-Chih CHOU 1),2) and Fu-Shen LI 2) 1) State Key Laboratory of Advanced
An investigation of electro-deoxidation process for producing titanium from dense titanium dioxide cathode Zhi-Yuan CHEN 1),2)*, Kuo-Chih CHOU 1),2) and Fu-Shen LI 2) 1) State Key Laboratory of Advanced
DIRECT REDUCTION OF VANADIUM OXIDE IN MOLTEN CaCl 2
 Sohn International Symposium ADVANCED PROCESSING OF METALS AND MATERIALS VOLUME 3 - THERMO AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL PRINCIPLES: SPECIAL MATERIALS and AQUEOUS AND ELECTROCHEMICAL PROCESSING Edited by F. Kongoli
Sohn International Symposium ADVANCED PROCESSING OF METALS AND MATERIALS VOLUME 3 - THERMO AND PHYSICOCHEMICAL PRINCIPLES: SPECIAL MATERIALS and AQUEOUS AND ELECTROCHEMICAL PROCESSING Edited by F. Kongoli
Fundamental Aspects of Calciothermic Process to Produce Titanium
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1660 to 1664 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in Titanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Fundamental Aspects of Calciothermic
Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1660 to 1664 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in Titanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Fundamental Aspects of Calciothermic
ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT
 ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT Yasushi Katayama Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University 3-14-1, Hiyoshi,
ELECTROCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE THIN FILM IN LiCl-KCl-CaCl 2 EUTECTIC MELT Yasushi Katayama Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University 3-14-1, Hiyoshi,
Reduction of TiO 2 in Molten CaCl 2 by Ca Deposited during CaO Electrolysis
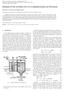 Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1665 to 1671 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in tanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Reduction of O 2 in Molten
Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1665 to 1671 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in tanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Reduction of O 2 in Molten
Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium-bearing compounds to titanium-silicon alloys in molten calcium chloride
 Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium-bearing compounds to titanium-silicon alloys in molten calcium chloride Xingli ZOU, and Xionggang LU Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Metallurgy and Materials
Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium-bearing compounds to titanium-silicon alloys in molten calcium chloride Xingli ZOU, and Xionggang LU Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Metallurgy and Materials
MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder. the original is available online at Instructions for use
 Title MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder Author(s)Tsuchida, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Satoshi CitationEURO CERAMICS VIII, PTS 1-3: 85-88 Issue Date 2004 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/15876
Title MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder Author(s)Tsuchida, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Satoshi CitationEURO CERAMICS VIII, PTS 1-3: 85-88 Issue Date 2004 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/15876
Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure on Liquidus for the CaO SiO 2 FeO x System at K
 , pp. 2040 2045 Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure on Liquidus for the CaO SiO 2 FeO x System at 1 573 K Hisao KIMURA, Shuji ENDO 1), Kohei YAJIMA 2) and Fumitaka TSUKIHASHI 2) Institute of Industrial Science,
, pp. 2040 2045 Effect of Oxygen Partial Pressure on Liquidus for the CaO SiO 2 FeO x System at 1 573 K Hisao KIMURA, Shuji ENDO 1), Kohei YAJIMA 2) and Fumitaka TSUKIHASHI 2) Institute of Industrial Science,
Title. CitationFluid phase equilibria, 385: Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Solubility of gaseous carbon dioxide in molten LiCl- Author(s)Wakamatsu, Takafumi; Uchiyama, Takuya; Natsui, Shung CitationFluid phase equilibria, : - Issue Date 0-0- Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net//0
Title Solubility of gaseous carbon dioxide in molten LiCl- Author(s)Wakamatsu, Takafumi; Uchiyama, Takuya; Natsui, Shung CitationFluid phase equilibria, : - Issue Date 0-0- Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net//0
Anhui University of Technology, School of Metallurgy and Resource, Maanshan, China. (Received 14 October 2012; accepted 28 January 2013)
 J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 49 (1) B (2013) 71-76 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, Section B: Metallurgy DEPOLARIZED -BASED GAS ANODES FOR ELECTROWINNING OF SILVER IN MOLTEN CHLORIDES S. Xiao a,*,
J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 49 (1) B (2013) 71-76 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, Section B: Metallurgy DEPOLARIZED -BASED GAS ANODES FOR ELECTROWINNING OF SILVER IN MOLTEN CHLORIDES S. Xiao a,*,
ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL
 80 ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL Roy G. Baggerly Boeing Research & Technology, Northwest Analytical Laboratories ABSTRACT: Nitinol is a shape memory
80 ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL Roy G. Baggerly Boeing Research & Technology, Northwest Analytical Laboratories ABSTRACT: Nitinol is a shape memory
Atmosphere Controlled Hot Thermocouple Method and Crystallization Phenomenon of CaO Al 2 O 3 Eutectic Slag
 , pp. 1967 1973 Atmosphere Controlled Hot Thermocouple Method and Crystallization Phenomenon of CaO Al 2 O 3 Eutectic Slag Yoshiaki KASHIWAYA, 1) Yasuaki KUSADA 2) and Ryosuke O. SUZUKI 3) 1) Graduate
, pp. 1967 1973 Atmosphere Controlled Hot Thermocouple Method and Crystallization Phenomenon of CaO Al 2 O 3 Eutectic Slag Yoshiaki KASHIWAYA, 1) Yasuaki KUSADA 2) and Ryosuke O. SUZUKI 3) 1) Graduate
A Study on the Formation of Magnetic Refrigerant La(Fe,Si) 13
 A Study on the Formation of Magnetic Refrigerant La(Fe,Si Compounds by Spark Plasma Sintering H. Tsuji, A.T. Saito, T. Kobayashi, S. Sakurada Corporate Research & Development Center, Toshiba Corp. Kawasaki,
A Study on the Formation of Magnetic Refrigerant La(Fe,Si Compounds by Spark Plasma Sintering H. Tsuji, A.T. Saito, T. Kobayashi, S. Sakurada Corporate Research & Development Center, Toshiba Corp. Kawasaki,
Oxygen Permeability through Internal Oxidation Zone in Fe Cr Alloys under Dry and Humid Conditions at 973 and K
 , pp. 259 263 Oxygen Permeability through Internal Oxidation Zone in Fe Cr Alloys under Dry and Humid Conditions at 973 and 1 073 K Asep Ridwan SETIAWAN, 1) Mohd HANAFI BIN ANI, 2) Mitsutoshi UEDA, 2)
, pp. 259 263 Oxygen Permeability through Internal Oxidation Zone in Fe Cr Alloys under Dry and Humid Conditions at 973 and 1 073 K Asep Ridwan SETIAWAN, 1) Mohd HANAFI BIN ANI, 2) Mitsutoshi UEDA, 2)
Title. Citation Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 75. Issue Date Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/ Type.
 Title Rapid reduction of titanium dioxide nano-parti Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Yoshida, Masumi; Matsuura, S Author(s) Suzuki, Ryosuke O. Citation Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 75 Issue Date 2014-09
Title Rapid reduction of titanium dioxide nano-parti Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Yoshida, Masumi; Matsuura, S Author(s) Suzuki, Ryosuke O. Citation Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 75 Issue Date 2014-09
Influence of Sulfur on the Reaction between MnO SiO 2 FeO Oxide and Fe Mn Si Solid Alloy by Heat Treatment
 , pp. 2678 2686 Influence of Sulfur on the Reaction between MnO SiO 2 FeO Oxide and Fe Mn Si Solid Alloy by Heat Treatment Kyung-Ho KIM, 1) * Hiroyuki SHIBATA 2) and Shin-ya KITAMURA 2) 1) Formerly Graduate
, pp. 2678 2686 Influence of Sulfur on the Reaction between MnO SiO 2 FeO Oxide and Fe Mn Si Solid Alloy by Heat Treatment Kyung-Ho KIM, 1) * Hiroyuki SHIBATA 2) and Shin-ya KITAMURA 2) 1) Formerly Graduate
Mechanical Properties of a -Type Titanium Alloy Cast Using a Calcia Mold for Biomedical Applications
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 1 (21) pp. 136 to 142 #21 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Mechanical Properties of a -Type Titanium Alloy Cast Using a Calcia Mold for Biomedical Applications Harumi
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 1 (21) pp. 136 to 142 #21 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Mechanical Properties of a -Type Titanium Alloy Cast Using a Calcia Mold for Biomedical Applications Harumi
Mechanical Properties and Phase Stability of Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O Alloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 5 (27) pp. 1124 to 113 #27 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Mechanical Properties and Phase Stability of Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O Alloys Tadahiko Furuta 1,
Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 5 (27) pp. 1124 to 113 #27 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Mechanical Properties and Phase Stability of Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O Alloys Tadahiko Furuta 1,
Synthesis of Ultra Fine Titanium-Tungsten Carbide Powder from Titanium Dioxide and Ammonium Metatungstate
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 187 to 191 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Synthesis of Ultra Fine Titanium-Tungsten Carbide Powder from Titanium Dioxide and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 187 to 191 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Synthesis of Ultra Fine Titanium-Tungsten Carbide Powder from Titanium Dioxide and
Niobium Powder Production in Molten Salt by Electrochemical Pulverization
 Niobium Powder Production in Molten Salt by Electrochemical Pulverization Boyan Yuan * and Toru H. Okabe ** *: Graduate Student, Department of Materials Engineering, University of Tokyo **: Associate Professor,
Niobium Powder Production in Molten Salt by Electrochemical Pulverization Boyan Yuan * and Toru H. Okabe ** *: Graduate Student, Department of Materials Engineering, University of Tokyo **: Associate Professor,
Formation and Mechanical Properties of Mg 97 Zn 1 RE 2 Alloys with Long-Period Stacking Ordered Structure
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 11 (2007) pp. 2986 to 2992 #2007 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Formation and Mechanical Properties of Mg 97 Zn 1 RE 2 Alloys with Long-Period
Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 11 (2007) pp. 2986 to 2992 #2007 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Formation and Mechanical Properties of Mg 97 Zn 1 RE 2 Alloys with Long-Period
Effect of Amorphous Transformation on Electrochemical Capacities of Rare Earth Mg Based Alloys
 Z. Phys. Chem. 220 (2006) 631 639 / DOI 10.1524/zpch.2006.220.5.631 by Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, München Effect of Amorphous Transformation on Electrochemical Capacities of Rare Earth Mg Based Alloys
Z. Phys. Chem. 220 (2006) 631 639 / DOI 10.1524/zpch.2006.220.5.631 by Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, München Effect of Amorphous Transformation on Electrochemical Capacities of Rare Earth Mg Based Alloys
Relationship between Hydrogen Absorption and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Immersed in Acidic Fluoride Solutions
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 5 (29) pp. 1183 to 1189 #29 The Japan Institute of Metals Relationship between Hydrogen Absorption and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Immersed in Acidic Fluoride
Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 5 (29) pp. 1183 to 1189 #29 The Japan Institute of Metals Relationship between Hydrogen Absorption and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Immersed in Acidic Fluoride
Sealing Mechanism of Anodic Porous Oxide Films Formed on Aluminum in Lithium Hydroxide Solution
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1463-1468 1463 Sealing Mechanism of Anodic Porous
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1463-1468 1463 Sealing Mechanism of Anodic Porous
Influence of Steel Grade on Oxidation Rate of Molten Steel in Tundish
 , pp. 831 840 Influence of Steel Grade on Oxidation Rate of Molten Steel in Tundish Katsuhiro SASAI and Akihiro MATSUZAWA Oita R & D Laboratories, Nippon Steel Corporation, 1 Oaza-Nishinosu, Oita, Oita-ken,
, pp. 831 840 Influence of Steel Grade on Oxidation Rate of Molten Steel in Tundish Katsuhiro SASAI and Akihiro MATSUZAWA Oita R & D Laboratories, Nippon Steel Corporation, 1 Oaza-Nishinosu, Oita, Oita-ken,
SiC/Aluminum Composites Fabricated by in situ Processing using Reactive Infiltration Aid
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1886-1890 1886 /Aluminum Composites Fabricated
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1886-1890 1886 /Aluminum Composites Fabricated
Experimental apparatus
 Experimental apparatus Metallothermic Reduction Components of reaction capsule Ta crucible Stainless steel foil Reaction capsule Reaction capsule Stainless steel reaction capsule Sc 2 O 3 or ScF 3 (+Al+CaCl
Experimental apparatus Metallothermic Reduction Components of reaction capsule Ta crucible Stainless steel foil Reaction capsule Reaction capsule Stainless steel reaction capsule Sc 2 O 3 or ScF 3 (+Al+CaCl
MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY
 Association of Metallurgical Engineers Serbia and Montenegro Scientific paper AME UDC:669.715.17.2:62.192.4=2 MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY V. MAKSIMOVIĆ 1,
Association of Metallurgical Engineers Serbia and Montenegro Scientific paper AME UDC:669.715.17.2:62.192.4=2 MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY V. MAKSIMOVIĆ 1,
Formation and Soft Magnetic Properties of Co Fe Si B Nb Bulk Glassy Alloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 5 (2002) pp. 1230 to 1234 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Formation and Soft Magnetic Properties of Co Fe Si B Nb Bulk Glassy Alloys Akihisa
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 5 (2002) pp. 1230 to 1234 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Formation and Soft Magnetic Properties of Co Fe Si B Nb Bulk Glassy Alloys Akihisa
Keisuke Ueda 1; * 2, Tomo Ogura 1, Shumpei Nishiuchi 1; * 3, Kenji Miyamoto 2, Toshikazu Nanbu 2 and Akio Hirose 1. 1.
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 52, No. 5 (2011) pp. 967 to 973 Special Issue on uminium loys 2010 #2011 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Effects of -Based loys Coating on Mechanical Properties and Interfacial
Materials Transactions, Vol. 52, No. 5 (2011) pp. 967 to 973 Special Issue on uminium loys 2010 #2011 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Effects of -Based loys Coating on Mechanical Properties and Interfacial
Development of Glassy Alloy Separators for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 46, No. 7 (2005) pp. 1706 to 1710 #2005 The Japan Institute of Metals Development of Glassy Alloy Separators for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Akihisa Inoue
Materials Transactions, Vol. 46, No. 7 (2005) pp. 1706 to 1710 #2005 The Japan Institute of Metals Development of Glassy Alloy Separators for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Akihisa Inoue
Fabrication and thermal properties of Al 2 TiO 5 /Al 2 O 3 composites
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2010 Fabrication and thermal properties of Al 2 TiO 5 /Al 2 O 3 composites M. LI, F. CHEN, Q. SHEN *, L. ZHANG State Key Lab of Advanced Technology for Materials
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2010 Fabrication and thermal properties of Al 2 TiO 5 /Al 2 O 3 composites M. LI, F. CHEN, Q. SHEN *, L. ZHANG State Key Lab of Advanced Technology for Materials
Influence of TiC on the Viscosity of CaO MgO Al 2 O 3 SiO 2 TiC Suspension System
 , pp. 922 927 Influence of TiC on the Viscosity of CaO MgO Al 2 O 3 SiO 2 TiC Suspension System Guo-Hua ZHANG, 1,2) * Yu-Lan ZHEN 1,2) and Kuo-Chih CHOU 1,2) 1) State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy,
, pp. 922 927 Influence of TiC on the Viscosity of CaO MgO Al 2 O 3 SiO 2 TiC Suspension System Guo-Hua ZHANG, 1,2) * Yu-Lan ZHEN 1,2) and Kuo-Chih CHOU 1,2) 1) State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy,
DEVELOPMENT OF HEAT RESISTANT Pb-FREE JOINTS BY TLPS PROCESS OF Ag AND Sn-Bi-Ag ALLOY POWDERS
 J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 48 (3) B (2012) 413-418 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, Section B: Metallurgy DEVELOPMENT OF HEAT RESISTANT Pb-FREE JOINTS BY TLPS PROCESS OF Ag AND Sn-Bi-Ag ALLOY POWDERS
J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 48 (3) B (2012) 413-418 Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, Section B: Metallurgy DEVELOPMENT OF HEAT RESISTANT Pb-FREE JOINTS BY TLPS PROCESS OF Ag AND Sn-Bi-Ag ALLOY POWDERS
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Low-Temperature Molten-Salt Production of Silicon Nanowires by the Electrochemical Reduction of CaSiO 3 Yifan Dong, Tyler Slade, Matthew J. Stolt, Linsen Li, Steven N. Girard, Liqiang
Supporting Information Low-Temperature Molten-Salt Production of Silicon Nanowires by the Electrochemical Reduction of CaSiO 3 Yifan Dong, Tyler Slade, Matthew J. Stolt, Linsen Li, Steven N. Girard, Liqiang
Effects of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High-strength Hot-rolled Steel Plates Containing Cu, Cr and Ni
 , pp. 692 698 Effects of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High-strength Hot-rolled Steel Plates Containing Cu, Cr and Ni Sung-Joon KIM, Chang Gil LEE, Tae-Ho LEE and Sunghak
, pp. 692 698 Effects of Coiling Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of High-strength Hot-rolled Steel Plates Containing Cu, Cr and Ni Sung-Joon KIM, Chang Gil LEE, Tae-Ho LEE and Sunghak
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS) and Okabe Lab.
 Institute of Industrial Science (IIS) and Okabe Lab. Ryosuke Matsuoka Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo 1 Institute of Industrial Science (IIS) http://www.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ 2 About
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS) and Okabe Lab. Ryosuke Matsuoka Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo 1 Institute of Industrial Science (IIS) http://www.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ 2 About
Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF
 Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF Vladimír Danielik*, Pavel Fellner, Marta Ambrová, Oldřich Matal a Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials, Faculty
Corrosion of Nickel-Chromium Alloy in the Molten Mixture LiF-NaF-KF Vladimír Danielik*, Pavel Fellner, Marta Ambrová, Oldřich Matal a Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials, Faculty
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells
 Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
Novel Mn 1.5 Co 1.5 O 4 spinel cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Huanying Liu, a, b Xuefeng Zhu, a * Mojie Cheng, c You Cong, a Weishen Yang a * a State Key Laboratory of Catalysis,
STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING
 STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING K. Tomolya 1, D. Janovszky 2, A. Sycheva 3, A. Roósz 4 1 Ph.D. Research fellow, 2 Ph.D. Senior research fellow, 3 Ph.D. Research
STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING K. Tomolya 1, D. Janovszky 2, A. Sycheva 3, A. Roósz 4 1 Ph.D. Research fellow, 2 Ph.D. Senior research fellow, 3 Ph.D. Research
Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained by Crystallization of Cast Amorphous Phase
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2337 to 2341 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2337 to 2341 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained
Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium.
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 3254-3263 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium. Popoola A.P.I
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6 (2011) 3254-3263 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Performance Evaluation of Zinc Deposited Mild Steel in Chloride Medium. Popoola A.P.I
Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends
 Special Issue Oxygen Storage Materials for Automotive Catalysts Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions 1 Review Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends Hideo Sobukawa This review summarizes
Special Issue Oxygen Storage Materials for Automotive Catalysts Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions 1 Review Development of Ceria-Zirconia Solid Solutions and Future Trends Hideo Sobukawa This review summarizes
Influences of graphite anode area on electrolysis of solid metal oxides in molten salts
 J Solid State Electrochem (2014) 18:3317 3325 DOI 10.1007/s10008-014-2645-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Influences of graphite area on electrolysis of solid metal oxides in molten salts Hualin Chen & Xianbo Jin & Linpo
J Solid State Electrochem (2014) 18:3317 3325 DOI 10.1007/s10008-014-2645-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Influences of graphite area on electrolysis of solid metal oxides in molten salts Hualin Chen & Xianbo Jin & Linpo
Xiao YANG, Hiroyuki MATSUURA and Fumitaka TSUKIHASHI
 , pp. 702 711 Reaction Behavior of P 2 O 5 at the Interface between Solid 2CaO SiO 2 and Liquid CaO SiO 2 FeO x P 2 O 5 Slags Saturated with Solid 5CaO SiO 2 P 2 O 5 at 1 573 K Xiao YANG, Hiroyuki MATSUURA
, pp. 702 711 Reaction Behavior of P 2 O 5 at the Interface between Solid 2CaO SiO 2 and Liquid CaO SiO 2 FeO x P 2 O 5 Slags Saturated with Solid 5CaO SiO 2 P 2 O 5 at 1 573 K Xiao YANG, Hiroyuki MATSUURA
Effect of Chromium on Nitrogen Solubility in Liquid Fe Cr Alloys Containing 30 mass% Cr
 ISIJ International, Vol. 49 (009), No., pp. 668 67 Effect of Chromium on Nitrogen Solubility in Liquid Fe Alloys Containing 30 mass% Wan-Yi KIM, ) Chang-Oh LEE, ) Chul-Wook YUN ) and Jong-Jin PAK ) ) Formerly
ISIJ International, Vol. 49 (009), No., pp. 668 67 Effect of Chromium on Nitrogen Solubility in Liquid Fe Alloys Containing 30 mass% Wan-Yi KIM, ) Chang-Oh LEE, ) Chul-Wook YUN ) and Jong-Jin PAK ) ) Formerly
Effect of Silicon Carbide on Reactions between Molten Steel and Fused Magnesia Silicon Carbide Composite Refractory
 Effect of Silicon Carbide on Reactions between Molten Steel and Fused Magnesia Silicon Carbide Composite Refractory Interactions between MgO SiC composite and liquid steel resulted in decomposition of
Effect of Silicon Carbide on Reactions between Molten Steel and Fused Magnesia Silicon Carbide Composite Refractory Interactions between MgO SiC composite and liquid steel resulted in decomposition of
Oxidation of Chromium
 Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
X-ray Spectroscopic Analysis of Solid State Reaction during Mechanical Alloying of Molybdenum and Graphite Powder Mixture
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2292 to 2296 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals X-ray Spectroscopic Analysis of Solid State Reaction during Mechanical Alloying of lybdenum and Powder
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2292 to 2296 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals X-ray Spectroscopic Analysis of Solid State Reaction during Mechanical Alloying of lybdenum and Powder
Liquid Solubility of Manganese and Its Influence on Grain Size of Mg-Al Alloys* 1
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 47, No. 8 (2006) pp. 1968 to 1974 #2006 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Liquid Solubility of Manganese and Its Influence on Grain Size of Mg-Al Alloys* 1 Yosuke Tamura,
Materials Transactions, Vol. 47, No. 8 (2006) pp. 1968 to 1974 #2006 The Japan Institute of Light Metals Liquid Solubility of Manganese and Its Influence on Grain Size of Mg-Al Alloys* 1 Yosuke Tamura,
Effect of Li Addition on Synthesis of Mg-Ti BCC Alloys by means of Ball Milling
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 2 (07) pp. 121 to 126 #07 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Li Addition on Synthesis of - BCC Alloys by means of Ball Milling Kohta Asano, Hirotoshi Enoki and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 48, No. 2 (07) pp. 121 to 126 #07 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Li Addition on Synthesis of - BCC Alloys by means of Ball Milling Kohta Asano, Hirotoshi Enoki and
Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened Pure Titanium
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) 381 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) : 381-392 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) 381 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43(2) : 381-392 http://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/ Contributed Paper Corrosion Resistant Evaluation of Oxygen Solid-Solution Strengthened
THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY TITANIUM ALLOYS WITH METALS OF IV VIII GROUPS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
 DOI: 10.2478/v10077-008-0004-7 A.V. Dobromyslov Institute of Metal Physics, Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Еkaterinburg, Russia THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY
DOI: 10.2478/v10077-008-0004-7 A.V. Dobromyslov Institute of Metal Physics, Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Еkaterinburg, Russia THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY
Densification and dielectric properties of barium neodymium titanium oxide ceramics
 Materials Science and Engineering B98 (2003) 33/37 www.elsevier.com/locate/mseb Densification and dielectric properties of barium neodymium titanium oxide ceramics Chung-Hsin Lu *, Yung-Hsiang Huang Electronic
Materials Science and Engineering B98 (2003) 33/37 www.elsevier.com/locate/mseb Densification and dielectric properties of barium neodymium titanium oxide ceramics Chung-Hsin Lu *, Yung-Hsiang Huang Electronic
Microstructural Characterization of Aluminum Powder Liquid Coating on IN 738 Superalloy
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.17 No.2 pp. 75-79, 2007 Microstructural Characterization of Aluminum Powder Liquid Coating on IN 738 Superalloy Patama VISUTTIPITUKUL 1*, Nuntiya LIMVANUTPONG
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.17 No.2 pp. 75-79, 2007 Microstructural Characterization of Aluminum Powder Liquid Coating on IN 738 Superalloy Patama VISUTTIPITUKUL 1*, Nuntiya LIMVANUTPONG
Thermodynamic Interaction between Chromium and Aluminum in Liquid Fe Cr Alloys Containing 26 mass% Cr
 ISIJ International, Vol. 51 (2011), o. 2, pp. 208 213 Thermodynamic Interaction between Chromium and uminum in Liquid Fe loys Containing 26 mass% Jong-h J, 1) Moon-Sic JUG, 1) Jong-Hyun PARK, 1) Chang-h
ISIJ International, Vol. 51 (2011), o. 2, pp. 208 213 Thermodynamic Interaction between Chromium and uminum in Liquid Fe loys Containing 26 mass% Jong-h J, 1) Moon-Sic JUG, 1) Jong-Hyun PARK, 1) Chang-h
Form of Al Ti Oxide Produced by Al Ti Deoxidation Reaction at 1873 and 1473 K
 Form of Al Ti Oxide Produced by Al Ti Deoxidation Reaction at 1873 and 1473 K Hiroyuki Matsuura Lecturer Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of
Form of Al Ti Oxide Produced by Al Ti Deoxidation Reaction at 1873 and 1473 K Hiroyuki Matsuura Lecturer Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of
Aging of Cu-3 at% Ti Alloys in Hydrogen Atmosphere: Influence of Hydrogen Pressure on Strength and Electrical Conductivity* 1
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 52, No. 4 (2) pp. 65 to 69 Special Issue on Advanced Materials for Hydrogen Energy Applications #2 Journal of Japan Research Institute for Advanced Copper-Base Materials and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 52, No. 4 (2) pp. 65 to 69 Special Issue on Advanced Materials for Hydrogen Energy Applications #2 Journal of Japan Research Institute for Advanced Copper-Base Materials and
Thermal Conductivity and Sintering Behavior of Hafnia-based Thermal Barrier Coating Using EB-PVD
 Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-131 Thermal Conductivity and Sintering Behavior of Hafnia-based Thermal Barrier Coating Using EB-PVD
Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-131 Thermal Conductivity and Sintering Behavior of Hafnia-based Thermal Barrier Coating Using EB-PVD
Production of Titanium Powder Directly from Titanium Ore by Preform Reduction Process (PRP)
 Production of Titanium Powder Directly from Titanium Ore by Preform Reduction Process (PRP) Haiyan Zheng 1 & Toru H. Okabe 2 1: Department of Materials Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, The
Production of Titanium Powder Directly from Titanium Ore by Preform Reduction Process (PRP) Haiyan Zheng 1 & Toru H. Okabe 2 1: Department of Materials Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, The
Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as. Negative Electrode Materials
 Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
Supplementary Information: Alkaline Rechargeable Ni/Co Batteries: Cobalt Hydroxides as Negative Electrode Materials X. P. Gao, S. M. Yao, T. Y. Yan, Z. Zhou Institute of New Energy Material Chemistry,
Influence of Niobium or Molybdenum in Titanium Alloy for Permanent Implant Application Yuswono Marsumi 1, a and Andika Widya Pramono 1,b
 Advanced Materials Research Vol. 900 (2014) pp 53-63 (2014) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.900.53 Influence of Niobium or Molybdenum in Titanium Alloy for Permanent
Advanced Materials Research Vol. 900 (2014) pp 53-63 (2014) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.900.53 Influence of Niobium or Molybdenum in Titanium Alloy for Permanent
Nanocrystalline structure and Mechanical Properties of Vapor Quenched Al-Zr-Fe Alloy Sheets Prepared by Electron-Beam Deposition
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 10 (2003) pp. 1948 to 1954 Special Issue on Nano-Hetero Structures in Advanced Metallic Materials #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Nanocrystalline structure and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 10 (2003) pp. 1948 to 1954 Special Issue on Nano-Hetero Structures in Advanced Metallic Materials #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Nanocrystalline structure and
Fabrication of Ni-Al Intermetallic Compounds on the Al Casting alloy by SHS Process
 Fabrication of Ni-Al Intermetallic Compounds on the Al Casting alloy by SHS Process G.S. Cho *, K.R. Lee*, K.H. Choe*, K.W. Lee* and A. Ikenaga** *Advanced Material R/D Center, KITECH, 994-32 Dongchun-dong,
Fabrication of Ni-Al Intermetallic Compounds on the Al Casting alloy by SHS Process G.S. Cho *, K.R. Lee*, K.H. Choe*, K.W. Lee* and A. Ikenaga** *Advanced Material R/D Center, KITECH, 994-32 Dongchun-dong,
Aluminization of High Purity Nickel by Powder Liquid Coating
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) 331 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) : 331-339 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Aluminization of High Purity Nickel by Powder Liquid Coating
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) 331 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009; 36(3) : 331-339 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper Aluminization of High Purity Nickel by Powder Liquid Coating
Wettability between Porous MgAl 2 O 4 Substrates and Molten Iron
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 11 (2009) pp. 2552 to 2556 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Wettability between Porous MgAl 2 O 4 Substrates and Molten Iron Naotaka Fukami*, Ryohei Wakamatsu*,
Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 11 (2009) pp. 2552 to 2556 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Wettability between Porous MgAl 2 O 4 Substrates and Molten Iron Naotaka Fukami*, Ryohei Wakamatsu*,
Method Excitation signal applied Wave response based on method Linear Differential pulse Square wave Cyclic Developed current recorded
 Voltammetry Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Working electrode (microelectrode) place where redox occurs surface area few mm 2 to limit current
Voltammetry Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Working electrode (microelectrode) place where redox occurs surface area few mm 2 to limit current
Improved high-q microwave dielectric resonator using CuO-doped MgNb 2 O 6 ceramics
 Materials Research Bulletin 38 (2003) 1091 1099 Improved high-q microwave dielectric resonator using CuO-doped MgNb 2 O 6 ceramics Cheng-Shing Hsu a, Cheng-Liang Huang a,*, Jing-Fang Tseng a, Chi-Yuen
Materials Research Bulletin 38 (2003) 1091 1099 Improved high-q microwave dielectric resonator using CuO-doped MgNb 2 O 6 ceramics Cheng-Shing Hsu a, Cheng-Liang Huang a,*, Jing-Fang Tseng a, Chi-Yuen
Influence of Spraying Conditions on Properties of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Coating by Gas Tunnel Type Plasma Spraying
 Influence of Spraying Conditions on Properties of Zr-Based Metallic Glass by Gas Tunnel Type Plasma Spraying KOBAYASHI Akira *, KURODA Toshio *, KIMURA Hisamichi ** and INOUE Akihisa ** Abstract Metallic
Influence of Spraying Conditions on Properties of Zr-Based Metallic Glass by Gas Tunnel Type Plasma Spraying KOBAYASHI Akira *, KURODA Toshio *, KIMURA Hisamichi ** and INOUE Akihisa ** Abstract Metallic
Effect of Decarburization on Microstructure of DC-Plasma Nitrided H 13 Tool Steel
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.16 No.2 pp.16, 2006 Effect of Decarburization on Microstructure of DCPlasma Nitrided H 13 Tool Steel Patama VISUTTIPITUKUL 1*, Chuleeporn PAARAI 2 and Kuwahara
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.16 No.2 pp.16, 2006 Effect of Decarburization on Microstructure of DCPlasma Nitrided H 13 Tool Steel Patama VISUTTIPITUKUL 1*, Chuleeporn PAARAI 2 and Kuwahara
Effect of Pickling Solution on the Surface Morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy Investment Cast K Mutombo 1, a and P Rossouw 2
 Effect of Pickling Solution on the Surface Morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy Investment Cast K Mutombo 1, a and P Rossouw 2 1,2 Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), South Africa a kmutombo@csir.co.za
Effect of Pickling Solution on the Surface Morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy Investment Cast K Mutombo 1, a and P Rossouw 2 1,2 Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), South Africa a kmutombo@csir.co.za
Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 6 (21) pp. 119 to 1113 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy S. A.
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 6 (21) pp. 119 to 1113 #21 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Anodizing Potential on the Surface Morphology and Corrosion Property of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy S. A.
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 1, 2013, 38-47 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS Suman Pawar* Department
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 1, 2013, 38-47 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS Suman Pawar* Department
Deoxidation of NiTi Alloy Melts Using Metallic Barium
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 49, No. 2 (28) pp. 289 to 293 #28 The Japan Institute of Metals Deoxidation of NiTi Alloy Melts Using Metallic Barium Susumu Miyamoto*, Masatoshi Watanabe, Takayuki Narushima
Materials Transactions, Vol. 49, No. 2 (28) pp. 289 to 293 #28 The Japan Institute of Metals Deoxidation of NiTi Alloy Melts Using Metallic Barium Susumu Miyamoto*, Masatoshi Watanabe, Takayuki Narushima
Experimental technique. Revision 1. Electroplating an iron key with copper metal
 Experimental technique. Revision 1 Electroplating an iron key with copper metal Aim To investigate whether Faraday s laws apply to the electroplating of a brass key with nickel Procedure The apparatus
Experimental technique. Revision 1 Electroplating an iron key with copper metal Aim To investigate whether Faraday s laws apply to the electroplating of a brass key with nickel Procedure The apparatus
Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore
 , pp. 570 575 Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore Daisuke NOGUCHI, 1) * Ko-ichiro OHNO, 2) Takayuki MAEDA, 2) Kouki NISHIOKA 3) and Masakata SHIMIZU
, pp. 570 575 Effect of CO Gas Concentration on Reduction Rate of Major Mineral Phase in Sintered Iron Ore Daisuke NOGUCHI, 1) * Ko-ichiro OHNO, 2) Takayuki MAEDA, 2) Kouki NISHIOKA 3) and Masakata SHIMIZU
Microstructural Evolution of Ti-Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 117 to 122 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Microstructural Evolution of -Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying Hiroyuki Hosokawa, Kiyotaka Kato, Koji
Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 117 to 122 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Microstructural Evolution of -Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying Hiroyuki Hosokawa, Kiyotaka Kato, Koji
An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 3 (2003) pp. 389 to 395 #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1 Rongguang
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 3 (2003) pp. 389 to 395 #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals An XPS and Atomic Force Microscopy Study of the Micro-Wetting Behavior of Water on Pure Chromium* 1 Rongguang
IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY
 IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Jonas O. RABE, Ute RABE, Sigrun HIRSEKORN Fraunhofer Institute
IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Jonas O. RABE, Ute RABE, Sigrun HIRSEKORN Fraunhofer Institute
In-situ Observation of Microstructure Change in Steel by EBSD
 NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL TECHNICAL REPORT No. 114 MARCH 2017 Technical Report UDC 621. 785. 36 In-situ Observation of Microstructure Change in Steel by EBSD Masayuki WAKITA* Seiichi SUZUKI Abstract
NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL TECHNICAL REPORT No. 114 MARCH 2017 Technical Report UDC 621. 785. 36 In-situ Observation of Microstructure Change in Steel by EBSD Masayuki WAKITA* Seiichi SUZUKI Abstract
a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as
 EXERCISES KJM5120 Chapter 5; Diffusion 1. Random (self) diffusion a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as 1 n D = s 6 t 2 where n/t represents the jump frequency
EXERCISES KJM5120 Chapter 5; Diffusion 1. Random (self) diffusion a) The self-diffusion coefficient of a metal with cubic structure can be expressed as 1 n D = s 6 t 2 where n/t represents the jump frequency
Annealing Effect on Mechanical Properties of Ti-Al Alloy/Pure Ti Harmonic-Structured Composite by MM/SPS Process
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Annealing Effect on Mechanical Properties of Ti-Al Alloy/Pure Ti Harmonic-Structured Composite by MM/SPS Process To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Annealing Effect on Mechanical Properties of Ti-Al Alloy/Pure Ti Harmonic-Structured Composite by MM/SPS Process To cite this article:
Comparison between Reducibilities of Columnar Silico-ferrite of Calcium and Aluminum (SFCA) Covered with Slag and Acicular SFCA with Fine Pores
 ISIJ International, Vol. 58 (2018), ISIJ International, No. 4 Vol. 58 (2018), No. 4, pp. 642 651 Comparison between Reducibilities of Columnar Silico-ferrite of Calcium and Aluminum (SFCA) Covered with
ISIJ International, Vol. 58 (2018), ISIJ International, No. 4 Vol. 58 (2018), No. 4, pp. 642 651 Comparison between Reducibilities of Columnar Silico-ferrite of Calcium and Aluminum (SFCA) Covered with
Tensile Property, Corrosion Resistance and Cytocompatibility of Tungsten Short Fiber Reinforced Ti 6Al 4V Alloy
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 12 (2002) pp. 2995 to 2999 Special Issue on Biomaterials and Bioengineering c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Tensile Property, Corrosion Resistance and Cytocompatibility
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 12 (2002) pp. 2995 to 2999 Special Issue on Biomaterials and Bioengineering c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals Tensile Property, Corrosion Resistance and Cytocompatibility
MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY
 MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Sigrun HIRSEKORN, Jonas RABE, Ute RABE, FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Campus E3 1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany INTRODUCTION
MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Sigrun HIRSEKORN, Jonas RABE, Ute RABE, FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Campus E3 1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany INTRODUCTION
Electrical conductivity of molten fluoride oxide melts with high addition of aluminium fluoride
 Electrical conductivity of molten fluoride oxide melts with high addition of aluminium fluoride Emília Kubiňáková, Ján Híveš, Vladimír Danielik Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials,
Electrical conductivity of molten fluoride oxide melts with high addition of aluminium fluoride Emília Kubiňáková, Ján Híveš, Vladimír Danielik Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Technology and Materials,
A study on the process of removing sulfide in steel surface layer by molten salt electrolysis
 A study on the process of removing sulfide in steel surface layer by molten salt electrolysis Liguang ZHU 1), Ying XU 2),Xingjuan WANG 1) and Xinhua ZHU 1) 1) College of Metallurgy Science and Engineering,
A study on the process of removing sulfide in steel surface layer by molten salt electrolysis Liguang ZHU 1), Ying XU 2),Xingjuan WANG 1) and Xinhua ZHU 1) 1) College of Metallurgy Science and Engineering,
Enrichment of Phosphorus Oxide in Steelmaking Slag by Utilizing Capillary Action
 J. Sustain. Metall. (2016) 2:38 43 DOI 10.1007/s40831-015-0035-3 THEMATIC SECTION: SLAG VALORISATION TODAY Enrichment of Phosphorus Oxide in Steelmaking Slag by Utilizing Capillary Action Shohei Koizumi
J. Sustain. Metall. (2016) 2:38 43 DOI 10.1007/s40831-015-0035-3 THEMATIC SECTION: SLAG VALORISATION TODAY Enrichment of Phosphorus Oxide in Steelmaking Slag by Utilizing Capillary Action Shohei Koizumi
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Supplementary Material: Development of the Fray-Farthing-Chen Cambridge Process: Towards the Sustainable Production of Titanium and Its Alloys
 Supplementary Material: Development of the Fray-Farthing-Chen Cambridge Process: Towards the Sustainable Production of Titanium and Its Alloys DI HU 1, 2, 4, ALEKSEI DOLGANOV 1, MINGCHAN MA 1, BIYASH BHATTACHARYA
Supplementary Material: Development of the Fray-Farthing-Chen Cambridge Process: Towards the Sustainable Production of Titanium and Its Alloys DI HU 1, 2, 4, ALEKSEI DOLGANOV 1, MINGCHAN MA 1, BIYASH BHATTACHARYA
Corrosion Characteristics of RAFM Steels and Unalloyed Metals in Static Pb-17Li )
 Corrosion Characteristics of RAFM Steels and Unalloyed Metals in Static Pb-17Li ) Masatoshi KONDO and Takeo MUROGA 1) Tokai University, 4-1-1 Kitakaname, Hiratsuka-shi, Kanagawa 259-1292, Japan 1) National
Corrosion Characteristics of RAFM Steels and Unalloyed Metals in Static Pb-17Li ) Masatoshi KONDO and Takeo MUROGA 1) Tokai University, 4-1-1 Kitakaname, Hiratsuka-shi, Kanagawa 259-1292, Japan 1) National
Isothermal Aging Behavior of Beta Titanium Manganese Alloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (29) pp. 2737 to 2743 Special Issue on Low Cost Reduction Processes, Roles of Low Cost Elements and Interstitial Elements, and Microstructural Control for Generalization
Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (29) pp. 2737 to 2743 Special Issue on Low Cost Reduction Processes, Roles of Low Cost Elements and Interstitial Elements, and Microstructural Control for Generalization
Dynamic Young s Modulus and Mechanical Properties of Ti Hf Alloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1549 to 1554 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in Titanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Dynamic Young s Modulus and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 5 (2004) pp. 1549 to 1554 Special Issue on Recent Research and Developments in Titanium and Its Alloys #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals Dynamic Young s Modulus and
PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 10, No. 2, April - June 2015, p. 715-719 PREPARATION OF NEODYMIUM HYDROXIDE NANORODS AND NEODYMIUM OXIDE NANORODS BY A HYDROTHERMAL METHOD N. EKTHAMMATHAT
Table of Contents. Preface...
 Preface... xi Chapter 1. Metallurgical Thermochemistry... 1 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Quantities characterizing the state of a system and its evolution... 3 1.2.1. The types of operations... 3 1.2.2.
Preface... xi Chapter 1. Metallurgical Thermochemistry... 1 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Quantities characterizing the state of a system and its evolution... 3 1.2.1. The types of operations... 3 1.2.2.
In-situ X-ray Diffraction of Corrosion Products Formed on Iron Surfaces
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 46, No. 3 (2005) pp. 637 to 642 #2005 The Mining and Materials Processing Institute of Japan In-situ X-ray Diffraction of Corrosion Products Formed on Iron Surfaces Yohei Takahashi
Materials Transactions, Vol. 46, No. 3 (2005) pp. 637 to 642 #2005 The Mining and Materials Processing Institute of Japan In-situ X-ray Diffraction of Corrosion Products Formed on Iron Surfaces Yohei Takahashi
