SOLUBILITY STUDY GUIDE- Multiple Choice Section
|
|
|
- Britney Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOLUBILITY STUDY GUIDE- Multiple Choice Section Multiple Choice Section: This study guide is a compilation of questions from provincial exams since I urge you to become intimately familiar with question types. You will notice that questions from one year to another are very similar in their composition. Identification of question types will allow you to be more efficient in answering these questions on the provincial examination. My recommendations for using this study guide are as follows : 1. DO ALL THE QUESTIONS in this booklet. These are actual Provincial Exam questions! Your own provincial exam and unit test will include questions similar to the ones in this booklet! 2. RESIST THE URGE TO LOOK AT THE ANSWER KEY until you have given all the questions in the section your best effort. Don t do one question, then look at the key, then do another and look at the key, and so on. Each time you look at one answer in the study guide, your eye will notice other answers around them, and this will reduce the effectiveness of those questions in helping you to learn. 3. LEARN FROM YOUR MISTAKES! If you get a question wrong, figure out why! If you are having difficulty, talk to your study partner, or maybe phone someone in your Peer Tutoring group. Get together with group members or other students from class and work on these questions together. Explain how you got your answers to tough questions to others. In explaining yourself to someone else, you will learn the material better yourself (try it!) Ask your teacher to explain the questions to you during tutorial or after school. Your goal should be to get 100% on any Chemistry 12 multiple choice test- learning from your mistakes in this booklet will really help you in your efforts to meet this goal! 4. This is REALLY CRUCIAL: DO NOT mark the answer anywhere on the questions themselves. For example, do not circle any of options A B C or D-instead use a different sheet of paper to place your answers on. By avoiding this urge, you can re-use this study guide effectively again, when preparing for your final exam. In the box to the left, put an asterisk or small note to yourself to indicate that you got the question wrong and need to come back to it. If you got the question correct initially, a check mark might be assurance that you understand this type of question and therefore can concentrate on other questions that present a challenge to you. 5. Check Off the STATUS box on the PRESCRIBED LEARNING OUTCOMES sheet. I have tried to organize the questions in the identical sequence to which they appear on your Acid Base Prescribed Learning Outcome sheet. By doing this, you can be confident that you know everything you need to know for both the UNIT EXAM and PROVINCIAL EXAM! TABLE OF CONTENTS: CONCEPT OF SOLUBILITY 1 SOLUBILITY AND PRECIPITATION 5 QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS 15 ANSWERS 21 CONCEPT OF SOLUBILITY 1. G1 Which of the following will dissolve in water to produce a molecular solution? A. CaCl 2 B. NaOH C. CH 3 OH D. Sr(OH) 2 2. G1 Which one of the following would form an ionic solution when dissolved in water? A. I 2 B. CH 3 OH C. Ca(NO 3 ) 2 D. C 12 H 22 O G1 Molecular solutions do not conduct electricity because they contain A. molecules only. B. cations and anions. C. molecules and anions. D. molecules and cations. 4. G1 When dissolved in water, which of the following produces an ionic solution? A. O 2 B. CH 4 C. CaCl 2 D. C 12 H 22 O G1 When dissolved in water, which of the following forms a molecular solution? A. HCl (g) B. NaNO 3 (s) C. CH 3 OH (l) D. K 2 SO 4(s) 6. G1 Which of the following dissolves in water to form an ionic solution? A. O 2 B. SiO 2 C. KMnO 4 D. C 12 H 22 O G1 Which of the following produces a molecular solution when dissolved in water? A. RbClO B. CH 3OH C. NH 4 SCN D. NaCH 3 COO 8. G1 Consider the following solutes: Which of the solutes above form only molecular aqueous solutions? A. I and II B. II and III C. II, III and IV D. I, II, III and IV SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 1 of 22
2 9. G3 Which of the following does not define solubility? A. the concentration of solute in a saturated solution B. the moles of solute dissolved in a given volume of solution C. the maximum mass of solute that can dissolve in a given volume of solution D. the minimum moles of solute needed to produce one litre of a saturated solution 10. G3 To determine the solubility of a solute in water, a solution must be prepared that is A. saturated. B. unsaturated. C. concentrated. D. supersaturated. 11. G3 When Ca (OH) 2 attains solubility equilibrium, the A. solution is saturated. B. ph will be less than 7. C. Trial K sp is less than the K sp. D. concentrations of the ions are equal. 12. G4 Which of the following units is commonly used to describe solubility? A. ml/s B. g/ C C. mol/l D. C/mol 13. G4 Which of the following units can be used to represent solubility? A. g B. mol C. mol/l D. ml/s 14. G4 Which of the following units could be used to describe solubility? A. g/s B. g/l C. M/L D. mol/s 15. G5 A saturated solution of NiCO 3 was evaporated to dryness. A ml sample was found to contain g NiCO 3. The molar mass of NiCO 3 is g mol. The molar solubility of NiCO 3 is: A M B M C M D M 16. G5 A student evaporated 200.0mL of a saturated solution of SrCrO 4 to dryness. The residue contained mol SrCrO 4. The solubility of SrCrO 4 is: A M B M C M D M 17. G6 In a solubility equilibrium, the A. rate of dissolving equals the rate of crystallization. B. neither dissolving nor crystallization are occurring. C. concentration of solute and solvent are always equal. D. mass of dissolved solute is greater than the mass of the solution. 18. G6 In a saturated solution of KNO 3, the rate of crystallization is A. equal to zero. B. equal to the rate of dissolving. C. less than the rate of dissolving. D. greater than the rate of dissolving. 19. G6 In a saturated solution, the rate of dissolving is A. equal to zero. B. equal to the rate of crystallization. C. less than the rate of crystallization. D. greater than the rate of crystallization. 20. G6 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 2 of 22
3 21. G6 22. G6 Consider the following equation: Which of the following graphs represents the relationship between [Ag + ] and [Cl ] in this system at a constant temperature? 23. G7 24. G8 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 3 of 22
4 25. G8 26. G8 In a 200 ml sample of 0.030M Na 3 PO 4, the [Na + ] is: A M B M C M D M 27. G8 In an experiment, mol of Fe(NO 3 ) 3 is dissolved in water to produce a 2.00 L solution. The [NO - 3 ] in this solution is A M B M C M D M 28. G8 29. G8 30. G8 A ml solution contains mol of Ba(NO 3 ) 2. The [NO 3 - ] is: A M B M C M D M 31. G8 32. G8 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 4 of 22
5 33. G8 A 3.0 L solution of NiCl 2 is found to have a chloride concentration of 0.60 M. The concentration of nickel(ii) ions in this solution is A M B M C M D. 1.2 M 34. G8 In 0.20 M Na 2 CrO 4, the ion concentrations are 35. G8 36. G8 At a certain temperature, 7.0 x10-4 mol MgSO 4 is present in ml of solution. The concentration of the Mg 2+ in this solution is A. 7.0 x 10-5 M B. 7.0 x 10-4 M C. 7.0 x 10-3 M D. 7.0 x 10-6 M SOLUBILITY AND PRECIPITATION 37. H1 Which of the following substances has the lowest solubility? A. BaS B. CuS C. FeS D. ZnS 38. H1 In a saturated solution of Zn(OH) 2, the [Zn 2+ ] is: A. less than 0.10 M B. more than 10.0 M C. more than 0.10 M, but less than 1.0 M D. more than 1.0 M, but less than 10.0 M 39. H1 Which one of the following salts is soluble? A. BaSO 4 B. CaCO 3 C. K 3 PO 4 D. Fe(OH)2 40. H1 From the list of salts below, how many are considered soluble at 25 C? CuCl 2, CaSO 4, PbS, Ag 3 PO 4 A. zero B. one C. two D. three 41. H1 Which of the following salts has the lowest solubility? A. copper(i) chloride B. ammonium sulphide C. potassium hydroxide D. mercury(ii) sulphate SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 5 of 22
6 42. H1 43. H1 A soluble magnesium salt is A. MgSO 3 B. MgCO 3 C. Mg(NO 3 ) 2 D. Mg 3 (PO 4 ) H1 Which of the following compounds could be used to prepare a 0.20 M solution of hydroxide ion? A. KOH B. Fe(OH) 3 C. Mg(OH) 2 D. Zn(OH) H1 Which of the following has a solubility of less than 0.10 M? A. SrS B. SrCl 2 C. SrSO 4 D. Sr(OH) H1 Which of the following is the least soluble in water at 25 C? A. CaSO 4 B. BaSO 4 C. CuSO 4 D. MgSO H1 Which of the following will be most soluble in water at 25 C? A. AgI B. PbS C. MgSO 4 D. Ba(OH) H1 The least soluble salt in water is A. BaS B. AlCl 3 C. CaSO 3 D. ZnSO H1 Which of the following compounds will form a saturated solution with the greatest concentration of Ag +? A. AgI B. AgBr C. AgIO 3 D. AgBrO H1 Which of the following is most soluble? A. Na 2 S B. CaSO 4 C. PbCO 3 D. Zn(OH) H1 Which of the following saturated solutions has the lowest [SO 2 4 ] at 25 C? A. SrSO 4 B. PbSO 4 C. CaSO 4 D. BaSO H1 Which of the following compounds is the least soluble in water? A. H 2 S B. KNO 3 C. ZnSO 4 D. Ca(OH) H1 Which of the following saturated solutions has the greatest [CO 2 3 ]? A. SrCO 3 B. CaCO 3 C. BaCO 3 D. MgCO 54. H1 The least soluble salt in water is A. CaS B. CaSO 4 C. CaC 2 O 4 D. Ca(NO 3 ) H1 At 25 C, which of the following compounds would dissolve to form a saturated solution with the greatest [Pb 2+ ]? A. PbI 2 B. PbCl 2 C. PbBr 2 D. Pb(IO 3 ) H1 Which of the following compounds is the least soluble in water? A. CaS B. Fe(OH) 3 C. KMnO 4 D. NH 4 HC 2 O H2 Which of the following will not produce a precipitate when equal volumes of 0.20M solutions are combined? SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 6 of 22
7 58. H2 Consider the following 0.10mL solutions: Equal moles of AgNO 3 are added to each solution. It is observed that a precipitate forms in all but one solution. Which solution does not form a precipitate? A. Cl - B. Br C. IO 3 D. BrO H2 Consider the following experiment: The unknown solution could contain: A. 0.20M OH - B. 0.20M NO3 - C. 0.20M PO D. 0.20M SO H2 61. H2 62. H2 If equal volumes of 0.2 M KBr and 0.2 M FeSO 4 are mixed, then A. no precipitate will be observed. B. a precipitate of FeBr will be observed. 2 C. a precipitate of K SO will be observed. 2 4 D. a precipitate of both K2SO 4 and FeBr 2 will be observed. 63. H2 Which of the following occurs when equal volumes of 0.20M MgS and 0.20M ZnSO 4 are mixed? A. A precipitate does not form. B. A precipitate of ZnS forms. C. A precipitate of MgSO forms. D. Precipitates of MgSO and ZnS form H2 When a student mixes equal volumes of 0.20 M Na2S and 0.20 M Sr(OH) 2, A. no precipitate forms. B. a precipitate of only SrS forms. C. a precipitate of only NaOH forms. D. precipitates of both NaOH and SrS form. SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 7 of 22
8 65. H2 When 0.20 M Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is added to an equal volume of 0.20 M CaCl 2, A. AlCl 3 precipitates. B. CaSO 4 precipitates. C. AlCl 3 and CaSO 4 precipitate. D. no precipitate forms. 66. H2 When equal volumes of 0.2 M K 2 CO 3 and 0.2 M Na 3 PO 4 are mixed, A. no precipitate will form. B. a precipitate of K 3 PO 4 will form. C. a precipitate of Na 2 CO 3 will form. D. a precipitate of both K 3 PO 4 and Na 2 CO 3 will form. 67. H2 When equal volumes of 0.2 M NH 4 Cl and 0.2 M CuSO 4 are combined, A. a precipitate does not form. B. a precipitate of CuCl 2 forms. C. a precipitate of (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 forms. D. a precipitate of both (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 and CuCl 2 forms. 68. H2 A dilute solution of AgNO 3 is added dropwise to each of the following test tubes until a precipitate forms in each tube. Which solution requires the lowest [Ag + ] to just begin precipitation? A. NaCl B. FeCl 3 C. CuCl 2 D. NH 4 Cl 69. H2 Which of the following 0.20M solutions will not form a precipitate when mixed with an equal volume of 0.20 M Sr (OH) 2? A. CaS B. NH 4 Cl C. Na 2 SO 4 D. Ba(NO 3 ) H2 Consider the following anions: When 10.0 ml of 0.20 M Pb (NO 3 ) 2 are added to each of the above, precipitates form in: A. I and II only. B. I and III only. C. II and III only. D. I, II and III. 71. H2 When equal volumes of M ZnSO and M Sr (OH) are combined, 4 2 A. no precipitate forms. B. a precipitate of only SrSO forms. 4 C. a precipitate of only Zn (OH) forms. D. precipitates of both SrSO 4 and Zn(OH) 2 form H2 When equal volumes of M SrBr 2 and M AgNO 3 are combined, A. no precipitate forms. B. a precipitate of only AgBr forms. C. a precipitate of only Sr(NO 3 ) 2 forms. D. precipitates of both AgBr and Sr(NO 3 ) 2 form. 73. H3 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 8 of 22
9 74. H3 75. H3 76. H3 77. H3 78. H4 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 9 of 22
10 79. H4 80. H4 Which of the following ions could be added to an aqueous mixture containing Pb 2+ and Ba 2+ to separate the ions by precipitating one of them? A. I B. NO 3 3 C. PO 4 2 D. SO H4 A solution of AgNO 3 is slowly added to a mixture containing 0.10 M I,Cl,Br and IO 3. The precipitate which forms first is: A. AgI B. AgCl C. AgBr D. AgIO H4 Which of the following ions could be used to separate Cl - 2- (aq ) from SO 4 (aq) by precipitation? A. Ag + B. Ca 2+ + C. NH 4 D. Pb H4 Which of the following could be used to separate Pb 2+ from Ba 2+ by precipitation? A. Na 2 S B. NaOH C. Na 2 CO 3 D. Na 2 SO H4 To remove Mg 2+ from a solution by precipitation, a student should add: A. NaI B. KOH C. Li 2 SO 4 D. (NH 4 ) 2 S 85. H4 Which of the following causes a precipitate to form when Sr 2+ (aq) is added but not when Zn 2+ (aq) is added: A. S 2 B. Cl 2 C. SO 4 2 D. CO H4 Which of the following anions could be used to separate Pb 2+ from Ba 2+ by precipitation? A. Cl B. OH C. NO 3 2 D. CO H4 A solution contains two cations, each having a concentration of M. When an equal volume of 0.20 M OH is added, these cations are removed from the solution by precipitation. These ions are A. Ba 2+ and K + B. Sr 2+ and Na + C. Mg 2+ and Sr 2+ D. Mg 2+ and Ca H5 89. H5 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 10 of 22
11 90. H5 Consider the following equilibrium: Which of the following will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right? 91. H5 92. H5 A student could precipitate silver chloride from a saturated solution of silver chloride by adding A. water. B. sodium iodide. C. sodium nitrate. D. sodium chloride. 93. H5 Consider the following equilibrium system: Which of the following changes would result in more PbI 2 dissolving? A. adding more PbI 2 B. increasing the pressure C. adding some Pb(NO 3 ) 2 D. increasing the temperature 94. H5 In which of the following would solid AgCl be most soluble? A. 1 M HCl B. 1 M MgCl 2 C. 1 M AgNO 3 D. 1M NH 4 NO H5 Consider the following equilibrium: Which of the following reagents, when added to the equilibrium system, would cause more CaCO 3 to dissolve? A. KNO 3 (s) B. CaCO 3(s) C. H 2 C 2 O 4(s) D. Na 2 CO 3(s) 96. H5 Consider the following equilibrium: Sodium chloride is added to a saturated solution of AgCl. The amount of solid AgCl will A. increase as the equilibrium shifts to the left. B. decrease as the equilibrium shifts to the left. C. increase as the equilibrium shifts to the right. D. decrease as the equilibrium shifts to the right. SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 11 of 22
12 97. H5 Consider the following equilibrium: When Br - (aq) is added to a saturated solution of AgCl, A. more AgCl dissolves and its solubility product increases. B. more AgCl precipitates and its solubility product decreases. C. more AgCl dissolves and its solubility product remains constant. D. more AgCl precipitates and its solubility product remains constant. 98. H5 Magnesium carbonate would be most soluble in a solution of A. MgCl 2 B. NaNO 3 C. Na 2 CO 3 D. Mg(NO 3 ) H5 Consider the following solubility equilibrium: The addition of which of the following substances would decrease the solubility of MgCO 3? A. H 2 O B. NaCl C. NaOH D. Na 2 CO H5 The greatest mass of solid SnS will dissolve in 1.0 L of A. H 2 O B M MgS C M (NH 4 ) 2 S D M Sn (NO 3 ) H5 Consider the following equilibrium: A saturated solution of MgCO 3 is in contact with undissolved solute. More MgCO 3 s ( ) can be dissolved by adding solid A. oxalic acid. B. sodium carbonate. C. magnesium chloride. D. magnesium carbonate H5 When solid AgBr is added to a saturated solution of AgBr, the reaction rates can be described as: 103. H5 Which of the following describes the changes in ion concentrations when 1.0 g of solid ZnS is added to a saturated solution of ZnS? SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 12 of 22
13 104. H5 Consider the following graph for a saturated Ag 2 CO 3 solution: What change occurred at time t 1? A. Water was added. B. AgNO 3 (s) was added. C. Na 2 CO 3 (s) was added. D. The temperature was increased H5 The solubility of PbI 2 will increase with the addition of A. PbI 2 B. heat. C. water. D. Pb (NO 3 ) H5 Consider the following equilibrium: The equilibrium will shift left upon the addition of A. H 2 O (l) B. SrF 2 (s) C. SrCl 2 (s) D. NaNO 3 (s ) 107. H5 Consider the solubility equilibrium: An additional piece of solid CaCO 3 is added to the equilibrium above. The rate of dissolving and rate of crystallization have 108. H5 Silver chloride, AgCl, would be least soluble in A. 1.0 M HCl B. 1.0 M NaNO 3 C. 1.0 M ZnCl 2 D. 1.0 M AgNO H H5 Consider the following solubility equilibrium: Which of the following will result in an increase of [Ba 2+ ]? A. adding water B. adding BaS (s) C. adding BaSO 3 (s) D. adding Na 2SO 3 (s) SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 13 of 22
14 111. H6 During a lab on qualitative analysis, an unknown solution containing one cation was analyzed and the following data were collected: Which one of the following cations is found in the unknown solution? A. Mg 2+ B. Ca 2+ C. Sr 2+ D. Ba H6 A nitrate solution containing an unknown cation is added to each of the following three test tubes. A precipitate forms in one test tube only. The unknown cation is A. Ag + B. Ca 2+ C. Sr 2+ D. NH H6 A solution containing a single unknown cation is added to three test tubes. The following anions were added and observations were recorded: The solution contains: A. Sr 2+ B. Ag + or Pb 2+ C. Ca 2+ or Ba 2+ D. K +,NH 4 + or H H6 A student wishes to identify an unknown cation in a solution. A precipitate does not form with the addition of SO 4 2, but does form with the addition of S 2. Which of the following is the unknown cation? A. Ag + B. Mg 2+ C. Ca 2+ D. Cu H6 A solution containing an unknown cation was added to three solutions and the following observations were recorded: The unknown cation is: A. Pb 2+ B. Sr 2+ C. Ca 2+ D. Ag H6 2 2 A solution contains a mixture of SO 4 and S. Which of the following cations could be used to remov e only the SO 2 4 from the solution by precipitation? A. K + B. Sr 2+ C. Pb 2+ D. Cu H7 Which of the following would precipitate the Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ found in hard water? A. S 2 B. PO4 3 C. SO4 2 D. CH 3COO 118. H Which of the following could be used to precipitate both Mg and Ca from hard water? A. lithium sulphate B. sodium phosphate C. potassium sulphide D. ammonium chloride SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 14 of 22
15 119. H7 Two ions found in hard water are Ca 2+ and Mg 2+. Which of the following will precipitate only one of these ions? A. I B. S C. SO 4 D. CO I1 QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS 121. I1 Consider the following equilibrium: 122. I2 Which of the following will increase the solubility of ammonium chloride? A.stirring the solution B.adding more water C.adding more NH 4 Cl (s) D. increasing the temperature 123. I2 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 15 of 22
16 124. I I I I2 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 16 of 22
17 128. I I I3 A compound has a solubility of 7.1x10-5 at 25 o C. The compound is: A. CuS B. AgBr C. CaCO 3 D. CaSO I I I I3 At a certain temperature, the solubility of BaF 2 is 7.4x10-3 moles per litre. The K sp of BaF 2 is A B C D SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 17 of 22
18 135. I3 The solubility of manganese(ii) sulphide is M at 25 C. The solubility product constant is A B C D I3 The solubility of barium fluoride is M. The solubility product constant is: A B C D I3 The solubility of MnS is M, at 25 C. The K sp value is A B C D I3 At 25 C, the solubility of an unknown compound is 7.1x10-5 M. The compound is A. CuI B. AgI C. CaCO 3 D. CaSO I3 The solubility of barium oxalate, BaC 2 O 4,is 4.8 x10-4 M. The value of K sp is A. 2.3 x 10-7 B. 4.8 x 10-4 C. 2.4 x 10-4 D. 2.2 x I3 The solubility of PbS is M. What is the value of K sp for PbS? A B C D I3 The solubility of FeF 2 is 8.4x10-3 M. The K sp value is A. 5.9 x10-7 B. 2.4 x10-6 C. 7.1 x10-5 D. 8.4 x I3 The solubility of SnS is 3.2 x 10-3 M. The value of K sp is A. 1.0 x10-5 B. 3.2 x 10-3 C. 6.4 x 10-3 D. 5.7 x I3 The solubility of Mn (IO 3 ) 2 is 4.8 x10-3 M. What is the value of K sp? A. 1.1x10-7 B. 4.4 x 10-7 C. 7.1 x 10-6 D. 1.1 x I I4 The solubility of magnesium carbonate is: A M B M C M D M 146. I4 The molar solubility of iron(ii) sulphide is A M B M C M D M 147. I4 At 25 C, the solubility of Mg (OH) 2 is A M B M C M D M 148. I4 The solubility of AgBrO 3 is A M B M C M D M 149. I I4 The solubility of MgCO 3 is A. 4.6x10-11 M B. 6.8 x 10-6 M C. 1.4 x 10-5 M D. 2.6 x 10-3 M 151. I4 At 25 C, the solubility of AgBr is A. 2.9 x10-25 M B. 5.4 x M C. 2.7 x M D. 7.3 x 10-7 M SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 18 of 22
19 152. I4 The solubility of SrF 2 is A. 4.3 x10-9 M B. 6.6 x10-5 M C. 1.0 x10-3 M D. 1.6 x10-3 M 153. I5 In an experiment, a student mixes equal volumes of M Pb 2+ ions with M I ions. The trial ion product is A B C D I5 When equal volumes of M AgNO 3 and M NaBrO 3 are mixed, the trial ion product (TIP) is A. less than K sp and a precipitate forms. B. greater than K sp and a precipitate forms. C. less than K sp and no precipitate forms. D. greater than K sp and no precipitate forms I I5 When equal volumes of 2.0 M Pb(NO 3 ) 2 and 2.0 M KCl are mixed, A. a precipitate forms because trial ion product <K sp B. a precipitate forms because trial ion product >K sp C. a precipitate does not form because trial ion product <K sp D. a precipitate does not form because trial ion product >K sp 157. I5 When solutions of Pb(NO 3 ) 2 and NaCl are mixed, the trial ion product (Trial K sp ) is 9.8x10-6. Which of the following statements is true? A. A precipitate forms because Ksp > B. A precipitate forms because Ksp < C. A precipitate does not form because Ksp < D. A precipitate does not form because Ksp > I5 When equal volumes of 0.20M Pb(NO 3 ) 2 and 0.20 M KI are mixed together, A. a precipitate forms since Trial Ion Product > K sp B. a precipitate forms since Trial Ion Product < K sp C. no precipitate forms since Trial Ion Product > K sp D. no precipitate forms since Trial Ion Product < K sp 159. I5 If the Trial Ion Product for AgBrO 3 is calculated to be , then A. a precipitate forms because the Trial Ion Product > K sp B. a precipitate forms because the Trial Ion Product < K sp C. no precipitate forms because the Trial Ion Product > K sp D. no precipitate forms because the Trial Ion Product < K sp 160. I5 When equal volumes of M Ca(NO 3 ) 2 and 0.20 M Na 2 SO 4 are combined, A. a precipitate forms because Trial Ion Product > K sp B. a precipitate forms because Trial Ion Product < K sp C. no precipitate forms because Trial Ion Product > K sp D. no precipitate forms because Trial Ion Product < K sp 161. I6 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 19 of 22
20 162. I6 What is the maximum [Sr 2+ ] that can exist in a solution of 0.10 M Na 2 SO 4? A M B M C M D M 163. I6 What is the maximum [Ag + ] that can exist in 0. 20M NaBrO 3? A M B M C M D M 164. I6 At 25 C, the maximum [Zn 2+ ] that can exist in M Na 2 S is A x10-26 M B. 2.0 x M C x M D. 4.5 x M 165. I6 The maximum [SO 2 4 ] that can exist in 1.0x10-3 M Ca(NO 3 ) 2 without a precipitate forming is A. 7.1x10-5 M B. 1.0 x 10-3 M C. 8.4 x 10-3 M D. 7.1 x 10-2 M 166. I6 Solid NaBrO 3 is added to a M Ag + solution. What is the [BrO 3 ] when a precipitate first forms? A. 2.8 x10-9 M B. 5.3 x 10-7 M C. 5.3 x 10-3 M D. 1.0 x 10-2 M 167. I I I7 SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 20 of 22
21 ANSWER KEY: CONCEPT OF SOLUBILITY: 1. C 2. C 3. A 4. C 5. C 6. C 7. B 8. B 9. B 10. A 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. B 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. B 19. B 20. D 21. A 22. A 23. D 24. B 25. D 26. D 27. C 28. B 29. D 30. D 31. C 32. C 33. A 34. A 35. D 36. C SOLUBILITY AND PRECIPITATION: 37. B 53. D 38. A 54. C 39. C 55. B 40. B 56. B 41. A 57. C 42. A 58. D 43. C 59. A 44. A 60. D 45. C 61. B 46. B 62. A 47. C 63. B 48. C 64. A 49. D 65. B 50. A 66. A 51. D 67. A 52. D 68. B 69. B 70. D 71. D 72. B 73. D 74. D 75. A 76. B 77. D 78. D 79. D 80. A 81. A 82. B 83. A 84. B 85. C 86. A 87. D 88. D 89. A 90. B 91. C 92. D 93. D 94. D 95. C 96. A 97. C 98. B 99. D 100. A 101. A 102. A 103. D 104. B 105. B 106. C 107. A 108. C 109. C 110. B 111. B 112. C 113. B 114. D 115. B 116. B SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 21 of 22
22 117. B 118. B 119. C QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS: 120. D 121. D 122. B 123. A 124. A 125. C 126. B 127. B 128. D 129. A 130. C 131. B 132. B 133. B 134. A 135. A 136. B 137. A 138. C 139. A 140. A 141. B 142. A 143. B 144. C 145. D 146. D 147. D 148. D 149. C 150. D 151. D 152. C 153. A 154. C 155. B 156. B 157. D 158. A 159. D 160. A 161. B 162. B 163. C 164. C 165. D 166. C 167. D 168. C 169. B SAHOTA 03 Solubility Study Guide - Multiple Choice - Page 22 of 22
1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is.. The precipitate which forms first is
 CHEMISTRY 12 UNIT 3 - REVIEW Ksp Part A - Multiple Choice 1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is A. Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 (s) 3 Fe 2+ (aq) + 2 SO 4 3 (aq)
CHEMISTRY 12 UNIT 3 - REVIEW Ksp Part A - Multiple Choice 1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is A. Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 (s) 3 Fe 2+ (aq) + 2 SO 4 3 (aq)
Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility
 Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility The Answer is A Answer A is the primary condition for solubility equilibrium. Remember the solution is also called saturated. B, of course is wrong because these opposing
Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility The Answer is A Answer A is the primary condition for solubility equilibrium. Remember the solution is also called saturated. B, of course is wrong because these opposing
Equilibria of Slightly Soluble Ionic Compounds: We lied to you in chem 115
 Precipitation Reactions Predicting Whether a Precipitate Will Form Note the ions present in the reactants Consider all possible cation-anion combinations Use the solubility rules to decide whether any
Precipitation Reactions Predicting Whether a Precipitate Will Form Note the ions present in the reactants Consider all possible cation-anion combinations Use the solubility rules to decide whether any
Unit 3 - Solubility Practice Test # 2
 1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
Solutions Unit Exam Name Date Period
 Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Last Update: 27Nov2008 Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Last Update: 27Nov2008 Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Exercise 6a. Balancing equations
 Exercise 6a Balancing equations Balance the following equations. To get you started _ indicates the first six questions where numbers need to be inserted to achieve the balance. In one or two difficult
Exercise 6a Balancing equations Balance the following equations. To get you started _ indicates the first six questions where numbers need to be inserted to achieve the balance. In one or two difficult
Duncan. UNIT 8 - Chemical Equations BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 14.) C2H6 + O2 CO2 + H2O. 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.
 BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 1.) CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.) N2 + H2 NH3 5.) KI + Cl2 KCl + I2 6.) HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + H2O 7.) KClO3 KCl + O2 8.) K3PO4 + HCl KCl
BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 1.) CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.) N2 + H2 NH3 5.) KI + Cl2 KCl + I2 6.) HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + H2O 7.) KClO3 KCl + O2 8.) K3PO4 + HCl KCl
Combination Reactions 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O. 2Na + I 2 2NaI. Ca + Cl 2 CaCl 2. C + O 2 CO 2 or 2C + O 2 2CO 3H 2 + N 2 2NH 3
 Combination Reactions Predict the product and write balanced reactions for each of the following. 1. Hydrogen burned in oxygen. 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O 2. Sodium plus iodine. 2Na + I 2 2NaI 3. Calcium burned
Combination Reactions Predict the product and write balanced reactions for each of the following. 1. Hydrogen burned in oxygen. 2H 2 + O 2 2H 2 O 2. Sodium plus iodine. 2Na + I 2 2NaI 3. Calcium burned
Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products. Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint.
 Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint. For reactions with a transition metal, the most likely charge on the metal
Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint. For reactions with a transition metal, the most likely charge on the metal
Solubility Equilibrium
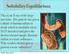 Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
INTERPRETING CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND SYMBOLS
 INTERPRETING CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND SYMBOLS THE FORMULA OR SYMBOL REPRESENTS: CHEMICAL FORMULA OR SYMBOL NUMBER OF ATOMS TOTAL CHARGE NUMBER OF PROTONS NUMBER OF ELECTRONS Atom Molecule Monatomic Cation
INTERPRETING CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND SYMBOLS THE FORMULA OR SYMBOL REPRESENTS: CHEMICAL FORMULA OR SYMBOL NUMBER OF ATOMS TOTAL CHARGE NUMBER OF PROTONS NUMBER OF ELECTRONS Atom Molecule Monatomic Cation
Chapter 18 Homework Answers
 Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.19 (a) AgI(s) Ag + + I K sp = [Ag + ][I ] (b) Ag PO (s) Ag + + PO K sp = [Ag + ] [PO ] (c) PbCrO (s) Pb + + CrO K sp = [Pb + ][CrO ] (d) Al(OH) (s) Al + + OH K sp = [Al +
Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.19 (a) AgI(s) Ag + + I K sp = [Ag + ][I ] (b) Ag PO (s) Ag + + PO K sp = [Ag + ] [PO ] (c) PbCrO (s) Pb + + CrO K sp = [Pb + ][CrO ] (d) Al(OH) (s) Al + + OH K sp = [Al +
Exercises. Solubility Equilibria. a. AgC 2 H 3 O 2 b. Al(OH) 3 c. Ca 3 (PO 4 ) Write balanced equations for the dissolution reactions and the
 766 Active Learning Questions These questions are designed to be used by groups of students in class. 1. Which of the following will affect the total amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount
766 Active Learning Questions These questions are designed to be used by groups of students in class. 1. Which of the following will affect the total amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount
Chapter six. Precipitate is separated by filtration, washing,drying and finally is accurately weighed.
 Gravimetric Analysis Chapter six Gravimetric Analysis :- Is one of the most accurate and precise methods of quantative analysis.it is based on the measurements of the mass of solid product of a chemical
Gravimetric Analysis Chapter six Gravimetric Analysis :- Is one of the most accurate and precise methods of quantative analysis.it is based on the measurements of the mass of solid product of a chemical
JSUNIL TUTORIAL, SAMASTIPUR
 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Q 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Ans. Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper.
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Q 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Ans. Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper.
Solubility Equi librium Ksp. Chapter 17 Sections
 Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 1 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 1 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Predicting Reaction Products
 Predicting Reaction Products Once you classify a chemical reaction, write the products and balance the reaction. Review Diatomic Molecules! Elements that exist only as compounds in the natural world: Iodine
Predicting Reaction Products Once you classify a chemical reaction, write the products and balance the reaction. Review Diatomic Molecules! Elements that exist only as compounds in the natural world: Iodine
Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN. 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O. 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2
 Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O 4 3. CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2 6. Pb(NO 3 ) 2 + HCl PbCl 2 + HNO 3 7. BaO 2 BaO + O 2 8. Al
Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O 4 3. CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2 6. Pb(NO 3 ) 2 + HCl PbCl 2 + HNO 3 7. BaO 2 BaO + O 2 8. Al
Oxidation and Reduction
 Oxidation and Reduction An oxidation reaction is one in which oxygen is added to a substance. Example: Methane is oxidised when it burns in air. Oxygen is added to the carbon in methane, forming carbon
Oxidation and Reduction An oxidation reaction is one in which oxygen is added to a substance. Example: Methane is oxidised when it burns in air. Oxygen is added to the carbon in methane, forming carbon
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16)
 Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
Solubility Equi librium Ksp. Chapter 17 Sections
 Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
Solubility Equi librium Ksp Chapter 17 Sections 17.4 17.6 Precipitation Reactions Earlier in this course, we considered precipitation reactions zinc nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
14.4 (Chp16) Solubility and Solubility Product
 14.4 (Chp16) Solubility and Solubility Product What drives substances to dissolve and others to remain as a precipitate? Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Solubility and Solubility
14.4 (Chp16) Solubility and Solubility Product What drives substances to dissolve and others to remain as a precipitate? Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Solubility and Solubility
Sn 2+ (aq) + 2 Ag + (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) + 2 Ag(s),
 1. Which change in oxidation number represents oxidation? A) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) B) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn(s) C) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn 2+ (aq) D) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn(s) E) Sn(s) Sn 2 (aq) 2. In the reaction Sn 2+ (aq) + 2
1. Which change in oxidation number represents oxidation? A) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) B) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn(s) C) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn 2+ (aq) D) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn(s) E) Sn(s) Sn 2 (aq) 2. In the reaction Sn 2+ (aq) + 2
Solve: 1. a 4 a 5 = 2. ( )/10 4 = 3. a(2a) 2 = 4. (6-1 ) 3 = a /10 4 a(4a 2 ) a 3
 Solve: 1. a 4 a 5 = 2. (10 2 10 3 )/10 4 = 3. a(2a) 2 = 4. (6-1 ) 3 = a 9 10 5 /10 4 a(4a 2 ) 6 2 10 1 4a 3 5. 12y 2 / 4y 3 = 6. (a 3 ) 0 = 7. x 2 y 4 z 3 x 1 y 2 z 5 = 3y -1 1 x 1 y 2 z -2 Solve for x:
Solve: 1. a 4 a 5 = 2. (10 2 10 3 )/10 4 = 3. a(2a) 2 = 4. (6-1 ) 3 = a 9 10 5 /10 4 a(4a 2 ) 6 2 10 1 4a 3 5. 12y 2 / 4y 3 = 6. (a 3 ) 0 = 7. x 2 y 4 z 3 x 1 y 2 z 5 = 3y -1 1 x 1 y 2 z -2 Solve for x:
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
 1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
Lecture 11. Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water
 Lecture 11 Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Soluble Compounds Exceptions Acetates, Nitrates, Chlorates Na +, K +, NH 4 + compounds None None Halides ( Cl -, Br -, I - ) Ag +, Hg 2 2+, Cu +, Pb 2+
Lecture 11 Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Soluble Compounds Exceptions Acetates, Nitrates, Chlorates Na +, K +, NH 4 + compounds None None Halides ( Cl -, Br -, I - ) Ag +, Hg 2 2+, Cu +, Pb 2+
AP*Chemistry Solubility Equilibria
 AP*Chemistry Solubility Equilibria SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA (K sp, THE SOLUBILITY PRODUCT) Saturated solutions of salts are another type of chemical equilibria. Remember those solubility rules? The fine print
AP*Chemistry Solubility Equilibria SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA (K sp, THE SOLUBILITY PRODUCT) Saturated solutions of salts are another type of chemical equilibria. Remember those solubility rules? The fine print
21. sodium nitrite 31. potassium carbonate. 23. aluminum hydroxide 33. nickel (II) carbonate. 24. ammonium hydroxide 34.
 N.E. Packet 1 Nomenclature WS 1 (Ionic Compounds) Name: Date: Per: Write the name for each of the following compounds. 1. CaCO 3 11. BaSO 4 2. FeO 12. Zn(NO 3 ) 2 3. K 2 SO 3 13. CuSO 4 4. AgCl 14. AlCl
N.E. Packet 1 Nomenclature WS 1 (Ionic Compounds) Name: Date: Per: Write the name for each of the following compounds. 1. CaCO 3 11. BaSO 4 2. FeO 12. Zn(NO 3 ) 2 3. K 2 SO 3 13. CuSO 4 4. AgCl 14. AlCl
Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format
 Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format Problems on Reacting Masses of Solids Section 1 1. What is the mass of magnesium
Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format Problems on Reacting Masses of Solids Section 1 1. What is the mass of magnesium
Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015
 Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following solubility product expressions is incorrect? a. Cu
Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following solubility product expressions is incorrect? a. Cu
Chemistry. TOPIC : Redox Reactions. products are PH3 and NaH2PO2. This reaction is an examplee of. (b) Reduction (d) Neutralization
 TOPIC : Redox Reactions Date : Marks : 1 mks Time : ½ hr 1. When P reacts with caustic soda, the products are PH and NaHPO. This reaction is an examplee of (a) Oxidation (c) Oxidation and reduction (redox)
TOPIC : Redox Reactions Date : Marks : 1 mks Time : ½ hr 1. When P reacts with caustic soda, the products are PH and NaHPO. This reaction is an examplee of (a) Oxidation (c) Oxidation and reduction (redox)
PO 4 NH 4 H + + SO 3
 KEY TO AP CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE 196882, 198588, 199093, 1995 Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. H 2 S + Ag 1+ Ag 2 S + H + 2. An excess of sodium
KEY TO AP CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE 196882, 198588, 199093, 1995 Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. H 2 S + Ag 1+ Ag 2 S + H + 2. An excess of sodium
Chapter 9. Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria
 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Name: Mods: Date Agenda Homework
 Name: Mods: UNIT 6 FORMULA WRITING, FORMULA WEIGHTS, and PERCENT COMPOSITION Date Agenda Homework Wed Dec 3 Thurs Dec 4 Fri Dec 5 Mon Dec 8 Tues Dec 9 Wed Dec 10 (1/2 Day) Thurs Dec 11 Fri Dec 12 Mon Dec
Name: Mods: UNIT 6 FORMULA WRITING, FORMULA WEIGHTS, and PERCENT COMPOSITION Date Agenda Homework Wed Dec 3 Thurs Dec 4 Fri Dec 5 Mon Dec 8 Tues Dec 9 Wed Dec 10 (1/2 Day) Thurs Dec 11 Fri Dec 12 Mon Dec
[ Cl ] - [[Mg 2+ ] ] Experiment 7: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. transfer e -
![[ Cl ] - [[Mg 2+ ] ] Experiment 7: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. transfer e - [ Cl ] - [[Mg 2+ ] ] Experiment 7: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. transfer e -](/thumbs/74/70175814.jpg) Experiment 7: OxidationReduction Reactions PURPOSE Become familiar with the concepts of oxidation and reduction and how these reactions occur. Carry out several such reactions and learn to recognize when
Experiment 7: OxidationReduction Reactions PURPOSE Become familiar with the concepts of oxidation and reduction and how these reactions occur. Carry out several such reactions and learn to recognize when
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Equilibrium problems involve 3 parts: The End of Equilibrium! K sp. (well, for us!) What is the solubility of FeCO 3?
 Slide 1 The End of Equilibrium! (well, for us!) 1 Slide 2 K sp What is the solubility of FeCO 3? Solubility = MAXIMUM amount of a compound that can dissolve in water. This is actually an equilibrium. 2
Slide 1 The End of Equilibrium! (well, for us!) 1 Slide 2 K sp What is the solubility of FeCO 3? Solubility = MAXIMUM amount of a compound that can dissolve in water. This is actually an equilibrium. 2
Qualitative Analysis. István Szalai. Institute of Chemistry, Eötvös University
 Institute of Chemistry, Eötvös University 2016 Cations (Group I-III) The cations of Group I can be precipitated as sulfides from acidic solution (ph 2) by H 2 S; the precipitates are insoluble in (NH 4
Institute of Chemistry, Eötvös University 2016 Cations (Group I-III) The cations of Group I can be precipitated as sulfides from acidic solution (ph 2) by H 2 S; the precipitates are insoluble in (NH 4
Solution 2: Class X Chapter-4 Analytical Chemistry Chemistry. Book Name: Selina Concise EXERCISE- 1 (A)
 EXERCISE- 1 (A) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Write the probable colour of the following salts. (a) Ferrous salts (b) Ammonium salts (c) Cupric salts (d) Calcium salts (e) Aluminium Salts Solution
EXERCISE- 1 (A) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Write the probable colour of the following salts. (a) Ferrous salts (b) Ammonium salts (c) Cupric salts (d) Calcium salts (e) Aluminium Salts Solution
1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = g/mol)?
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM II Answer Key March 22, 2013 1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = 102.894 g/mol)? A. 4.65 ml B. 10.9 ml C. 11 ml D. 235 ml E. 240 ml
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM II Answer Key March 22, 2013 1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = 102.894 g/mol)? A. 4.65 ml B. 10.9 ml C. 11 ml D. 235 ml E. 240 ml
Electrochemistry Written Response
 Electrochemistry Written Response January 1999 7. Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: RuO 4 + P Ru(OH) 2 2+ + H 3 PO 3 (acid) (3 marks) 8. A technician tests the concentration of methanol,
Electrochemistry Written Response January 1999 7. Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: RuO 4 + P Ru(OH) 2 2+ + H 3 PO 3 (acid) (3 marks) 8. A technician tests the concentration of methanol,
Ionic Bonding Drill. Compound Formula. tin (II) nitride. silver oxide. lithium sulfide. magnesium sulfide. copper (I) nitride.
 tin (II) nitride silver oxide lithium sulfide magnesium sulfide copper (I) nitride boron iodide potassium fluoride potassium bromide sodium phosphide iron (II) chloride copper (I) bromide lead (II) sulfide
tin (II) nitride silver oxide lithium sulfide magnesium sulfide copper (I) nitride boron iodide potassium fluoride potassium bromide sodium phosphide iron (II) chloride copper (I) bromide lead (II) sulfide
CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas
 CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas 1. What are the two different ions present in the compound FeCl3? A) Fe 2+, Cl 3- B) Fe 3+, Cl 3- C) Fe +, Cl - D)
CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas 1. What are the two different ions present in the compound FeCl3? A) Fe 2+, Cl 3- B) Fe 3+, Cl 3- C) Fe +, Cl - D)
Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR
 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 1 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR Instructions: Attempt all questions Circle the most connective alternative with either a blue or black ink-but not a pencil. 1.
Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 1 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR Instructions: Attempt all questions Circle the most connective alternative with either a blue or black ink-but not a pencil. 1.
CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A
 CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A 1. Consider the following reaction: A + B C + D What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction to always be spontaneous? ΔH ΔS A. + + B. C. + D. + 2. What is
CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A 1. Consider the following reaction: A + B C + D What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction to always be spontaneous? ΔH ΔS A. + + B. C. + D. + 2. What is
Thermal decomposition. Metal carbonates
 Decomposition reactions Copy correctly Up to 3% of a workbook Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is subject to the New Zealand Copyright Act which limits copying to 3% of this workbook. Many compounds
Decomposition reactions Copy correctly Up to 3% of a workbook Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is subject to the New Zealand Copyright Act which limits copying to 3% of this workbook. Many compounds
2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1
 2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4
2/24/2003 OFB Chapter 9 1 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4
Partner: Cathy 22 March Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions
 Partner: Cathy 22 March 2012 Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the cations and anions components in the unknown solution. This
Partner: Cathy 22 March 2012 Separation and Qualitative Determination of Cations and Anions Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the cations and anions components in the unknown solution. This
3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem?
![3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem? 3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem?](/thumbs/83/87492512.jpg) 1 of 6 10/20/2009 3:52 AM 1. [7 points] What is the correct name for ZnF 2? (a) zinc fluorine (b) zinc (II) fluoride (c) zinc fluoride (d) fluoride zinc 2. [7 points] What is the correct name for P 2 O
1 of 6 10/20/2009 3:52 AM 1. [7 points] What is the correct name for ZnF 2? (a) zinc fluorine (b) zinc (II) fluoride (c) zinc fluoride (d) fluoride zinc 2. [7 points] What is the correct name for P 2 O
ANALYTICAL LABORATORY MANUAL I QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ANIONS CATIONS
 ANALYTICAL LABORATORY MANUAL I QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ANIONS CATIONS ANKARA UNIVERSITY, FACULTY OF PHARMACY DEPARTMENT OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ANIONS... 2
ANALYTICAL LABORATORY MANUAL I QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ANIONS CATIONS ANKARA UNIVERSITY, FACULTY OF PHARMACY DEPARTMENT OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY TABLE OF CONTENTS 1) QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS OF ANIONS... 2
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1998
 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1998 (One Hour and a Half) Answer to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1998 (One Hour and a Half) Answer to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
Sodium Peroxides (Na 2 O 2 ): Preparation: It is formed by heating the metal in excess of air or oxygen at 300, which is free from
 S-Block Elements Generally one question was asked every year from this topic. This is completely theoretical and little memory based. Last minute revision generally helps. The general trends in the properties
S-Block Elements Generally one question was asked every year from this topic. This is completely theoretical and little memory based. Last minute revision generally helps. The general trends in the properties
The ion with Vanadium in its oxidation state of 5 exists as a solid compound in the form of a VO 3
 Chemistry of some Transition elements: V, Mn, Co, Cu, Cr and Ag Vanadium Vanadium has four main oxidation states. Each one has a different colour. VO 2 VO 2 V 3 V 2 O.N. 5 yellow O.N. 4 blue O.N. 3 green
Chemistry of some Transition elements: V, Mn, Co, Cu, Cr and Ag Vanadium Vanadium has four main oxidation states. Each one has a different colour. VO 2 VO 2 V 3 V 2 O.N. 5 yellow O.N. 4 blue O.N. 3 green
Summer Assignment Coversheet
 Summer Assignment Coversheet Course: A.P. Chemistry Teachers Names: Mary Engels Assignment Title: Summer Assignment A Review Assignment Summary/Purpose: To review the Rules for Solubility, Oxidation Numbers,
Summer Assignment Coversheet Course: A.P. Chemistry Teachers Names: Mary Engels Assignment Title: Summer Assignment A Review Assignment Summary/Purpose: To review the Rules for Solubility, Oxidation Numbers,
Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium
 Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium 1 What we Skipped Ch. 8 discussed Activity (γ) This is what should be used in equilibrium calculations rather than conc. (molarity) In Ch. 9 in later chapters, you will
Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium 1 What we Skipped Ch. 8 discussed Activity (γ) This is what should be used in equilibrium calculations rather than conc. (molarity) In Ch. 9 in later chapters, you will
Chemical Formulas. In a chemical formula, the element with the positive charge is always written first.
 Bonding Part 2 Chemical Formulas Chemical formulas a group of chemical symbols and numbers that represent the number of atoms of each element that make up a compound. ( H O) 2 In a chemical formula, the
Bonding Part 2 Chemical Formulas Chemical formulas a group of chemical symbols and numbers that represent the number of atoms of each element that make up a compound. ( H O) 2 In a chemical formula, the
Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O
 Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O Which of these is the correct chemical formula for a molecule of oxygen? A. O B. O -2 C. O +2 D. O 2 Which of
Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O Which of these is the correct chemical formula for a molecule of oxygen? A. O B. O -2 C. O +2 D. O 2 Which of
85 Q.14 In which of the following substances does nitrogen have the lowest oxidation number?
 Redox and electrolysis / Section 3 / Sect3pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.5 The element with an atomic number of 19 is likely to be A. an oxidizing agent. B. a reducing agent. C. a non-metal. D. chemically
Redox and electrolysis / Section 3 / Sect3pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.5 The element with an atomic number of 19 is likely to be A. an oxidizing agent. B. a reducing agent. C. a non-metal. D. chemically
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals
 Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Procedure All solutions should be mixed thoroughly after any additions. Clearly record all observations (indicating what you did), even
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Procedure All solutions should be mixed thoroughly after any additions. Clearly record all observations (indicating what you did), even
CHM101 SECOND EXAM 162. Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017
 Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017 Student no. Section: Useful Information:Gas Constant R= 0.08206 L.atm/K.mol, Specific heat of H 2 O=4.18 J/g. C 1 atm. = 760 mmhg. H 1 He 2 1.000 4
Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017 Student no. Section: Useful Information:Gas Constant R= 0.08206 L.atm/K.mol, Specific heat of H 2 O=4.18 J/g. C 1 atm. = 760 mmhg. H 1 He 2 1.000 4
Compiled by Rahul Arora What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it?
 Rahul Arora 12. What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it? 13. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 In the above equation, name the compound which is oxidized and which is reduced? 14. Match the
Rahul Arora 12. What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it? 13. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 In the above equation, name the compound which is oxidized and which is reduced? 14. Match the
ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE B.P
 01 ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE B.P AIPO 4 1 / 117 121.95 80.00% 02 ALUMINUM mono-stearate, PURE 2 / 117 AI(OH) 2 (C 17 H 344.45 (as all) 7.50-8.50% 3 / 117 15Kg. 03 ALUMINUM di-stearate, PURE AI(OH)(C 17 H 35 COO)
01 ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE B.P AIPO 4 1 / 117 121.95 80.00% 02 ALUMINUM mono-stearate, PURE 2 / 117 AI(OH) 2 (C 17 H 344.45 (as all) 7.50-8.50% 3 / 117 15Kg. 03 ALUMINUM di-stearate, PURE AI(OH)(C 17 H 35 COO)
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals. Prelab. 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following:
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does
Chemistry Test Paper
 Chemistry Test Paper [Time:1 1 hrs] [M. Marks : 80] 2 Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
Chemistry Test Paper [Time:1 1 hrs] [M. Marks : 80] 2 Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
Ionic Naming Quiz #1. Ionic Naming Quiz #1. March 26, Day 05 Ionic Quiz, SDR Note, Exit Card.notebook
 Ionic Naming Quiz #1 Name the following ionic compounds: 1) NaBr sodium bromide 2) Sc(OH) 3 scandium hydroxide 3) V 2 (SO 4 ) 3 vanadium (III) sulfate 4) NH 4 F ammonium fluoride 5) CaCO 3 calcium carbonate
Ionic Naming Quiz #1 Name the following ionic compounds: 1) NaBr sodium bromide 2) Sc(OH) 3 scandium hydroxide 3) V 2 (SO 4 ) 3 vanadium (III) sulfate 4) NH 4 F ammonium fluoride 5) CaCO 3 calcium carbonate
Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE
 Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE Salient Features Extensive coverage of the syllabus in an effortless and easy to grasp format Neat
Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE Salient Features Extensive coverage of the syllabus in an effortless and easy to grasp format Neat
Precipitation Reactions and Gravimetric Analysis
 Precipitation Reactions and Gravimetric Analysis Titrations where the titrant forms a precipitate with the analyte. Not always so straightforward a number of requirements need to be met. Precipitation
Precipitation Reactions and Gravimetric Analysis Titrations where the titrant forms a precipitate with the analyte. Not always so straightforward a number of requirements need to be met. Precipitation
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1 I) Very Short Type Questions (1 mark) 1. What is the relationship between decomposition and combustion
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1 I) Very Short Type Questions (1 mark) 1. What is the relationship between decomposition and combustion
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
 Q 1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry What weight of AgCI will be precipitated when a solution containing 4.77 g of NaCI is added to a solution of 5.77 g of AgNO 3? (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) Q 2. One gram
Q 1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry What weight of AgCI will be precipitated when a solution containing 4.77 g of NaCI is added to a solution of 5.77 g of AgNO 3? (IIT JEE 1978 3 Marks) Q 2. One gram
Quantitive Chemistry Question paper
 Quantitive Chemistry Question paper Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Chemistry CCEA Quantitative Chemistry Quantitive Chemistry Question paper Time Allowed: 93 minutes Score: /77 Percentage:
Quantitive Chemistry Question paper Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Chemistry CCEA Quantitative Chemistry Quantitive Chemistry Question paper Time Allowed: 93 minutes Score: /77 Percentage:
DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes
 1 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 14 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions - This paper consists of 50 compulsory objective questions - Answer the questions by writing the correct
1 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 14 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions - This paper consists of 50 compulsory objective questions - Answer the questions by writing the correct
Ionic Naming Quiz #1. Ionic Naming Quiz #2 Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds:
 Ionic Naming Quiz #1 Name the following ionic compounds: 1) NaBr sodium bromide 2) Sc(OH) 3 scandium hydroxide 3) V 2 (SO 4 ) 3 vanadium (III) sulfate 4) NH 4 F ammonium fluoride 5) CaCO 3 calcium carbonate
Ionic Naming Quiz #1 Name the following ionic compounds: 1) NaBr sodium bromide 2) Sc(OH) 3 scandium hydroxide 3) V 2 (SO 4 ) 3 vanadium (III) sulfate 4) NH 4 F ammonium fluoride 5) CaCO 3 calcium carbonate
McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017
 112 version last name first name signature McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017 50375 / 50380 Reminder: Be sure and correctly bubble in your name, uteid, and version number on your bubblesheet. The Periodic
112 version last name first name signature McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017 50375 / 50380 Reminder: Be sure and correctly bubble in your name, uteid, and version number on your bubblesheet. The Periodic
Total Grade /150 Checked by
 FIRST LETTER OF YOUR LAST NAME CHEMISTRY 1127 EXAM I NAME (PRINT) SECTION SIGNATURE TA PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS Do NOT begin the exam until asked to do so. There are 8 numbered pages, a useful
FIRST LETTER OF YOUR LAST NAME CHEMISTRY 1127 EXAM I NAME (PRINT) SECTION SIGNATURE TA PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS Do NOT begin the exam until asked to do so. There are 8 numbered pages, a useful
Please write the balanced net ionic reaction for each one. Then answer the accompanying question.
 AP Chemistry Net Ionic Rx Practice Test A CLASS SET PLEASE RETURN!! Please write the balanced net ionic reaction for each one. Then answer the accompanying question. 1) A piece of potassium is dropped
AP Chemistry Net Ionic Rx Practice Test A CLASS SET PLEASE RETURN!! Please write the balanced net ionic reaction for each one. Then answer the accompanying question. 1) A piece of potassium is dropped
GraspIT AQA GCSE Chemical changes
 A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Hardness. Concentration is. What s the concentration of red triangles? What s in your pipes? 500 ml
 Slide 1 Hardness What s in your pipes? Slide 2 What s the concentration of red triangles? 500 ml 1 g 1 g 1 g A. 10 B. 10 C. D. 1 g 1 g It s all of the above! Slide 3 Concentration is any statement of the
Slide 1 Hardness What s in your pipes? Slide 2 What s the concentration of red triangles? 500 ml 1 g 1 g 1 g A. 10 B. 10 C. D. 1 g 1 g It s all of the above! Slide 3 Concentration is any statement of the
Test sticks and test papers for semi-quantitative determinations
 QUANTOFIX test sticks for semi-quantitative determinations QUANTOFIX test sticks meet the most important requirements for a modern quick-test: rapid dip and read convenient the analysis can be carried
QUANTOFIX test sticks for semi-quantitative determinations QUANTOFIX test sticks meet the most important requirements for a modern quick-test: rapid dip and read convenient the analysis can be carried
Topic 2.6 GROUP 2, THE ALKALINE EARTH METALS
 Topic 2.6 GROUP 2, THE ALKALINE EARTH METALS Trends in size, first ionization energy and electronegativity Trends in reaction with water Trends in solubility of group 2 sulphates and hydroxides PROPERTIES
Topic 2.6 GROUP 2, THE ALKALINE EARTH METALS Trends in size, first ionization energy and electronegativity Trends in reaction with water Trends in solubility of group 2 sulphates and hydroxides PROPERTIES
Ksp Take Home Recitation
 Ksp Take Home Recitation Names: Compound Formula Ksp at 298 K, 1 atm Aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 1.3x10-33 Aluminum phosphate Al(PO4)3 9.84x10-21 Aluminum nitrate Al(NO3)3 1.6x10-2 Barium carbonate BaCO3
Ksp Take Home Recitation Names: Compound Formula Ksp at 298 K, 1 atm Aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 1.3x10-33 Aluminum phosphate Al(PO4)3 9.84x10-21 Aluminum nitrate Al(NO3)3 1.6x10-2 Barium carbonate BaCO3
Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals. Prelab. 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following:
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does a double
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does a double
*20GSD5201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C2 Higher Tier WEDNESDAY 15 JUNE 2016, AFTERNOON [GSD52] *GSD52* *G5802* TIME 1 hour 15 minutes.
![*20GSD5201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C2 Higher Tier WEDNESDAY 15 JUNE 2016, AFTERNOON [GSD52] *GSD52* *G5802* TIME 1 hour 15 minutes. *20GSD5201* Double Award Science: Chemistry. Unit C2 Higher Tier WEDNESDAY 15 JUNE 2016, AFTERNOON [GSD52] *GSD52* *G5802* TIME 1 hour 15 minutes.](/thumbs/84/89360002.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] *GSD52* *G5802* *GSD52* WEDNESDAY 15 JUNE 2016, AFTERNOON TIME
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] *GSD52* *G5802* *GSD52* WEDNESDAY 15 JUNE 2016, AFTERNOON TIME
What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen?
 EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs energy
 THERMODYNAMIC VALUES AT STANDARD STATE (298K) Data Retrieved From: Kots, Treichal, Weaver Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity (Sixth Edition) COPYRIGHT 2006 Species Name Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs
THERMODYNAMIC VALUES AT STANDARD STATE (298K) Data Retrieved From: Kots, Treichal, Weaver Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity (Sixth Edition) COPYRIGHT 2006 Species Name Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs
EXPERIMENT 15C. Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste
 EXPERIMENT 15C Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste The following experiment is intended to continue the introduction of qualitative analysis through
EXPERIMENT 15C Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste The following experiment is intended to continue the introduction of qualitative analysis through
Page 2. Q is calcium or magnesium 1. M1.(a) bromide 1. R is aluminium 1. chloride 1. S is iron(iii) 1. sulfate. Mark this question independently
 M.(a) Q is calcium or magnesium bromide R is aluminium chloride S is iron(iii) sulfate Mark this question independently (b) Ba 2+ + SO 4 2 BaSO 4 [Fe(H 2O) 6] 3+ + 3OH Fe(H 2O) 3(OH) 3 + 3H 2O 2[Fe(H 2O)
M.(a) Q is calcium or magnesium bromide R is aluminium chloride S is iron(iii) sulfate Mark this question independently (b) Ba 2+ + SO 4 2 BaSO 4 [Fe(H 2O) 6] 3+ + 3OH Fe(H 2O) 3(OH) 3 + 3H 2O 2[Fe(H 2O)
Inorganic Naming Worksheet
 Inorganic Naming Worksheet A) Write the formulas for the following names: 1. ammonium sulfite 2. sodium nitrite 3. cupric bromate 4. aluminum sulfate 5. potassium nitrate 6. ferrous bicarbonate 7. lead
Inorganic Naming Worksheet A) Write the formulas for the following names: 1. ammonium sulfite 2. sodium nitrite 3. cupric bromate 4. aluminum sulfate 5. potassium nitrate 6. ferrous bicarbonate 7. lead
1. Name the first element by its name. 2. The second element has the ending ide. 3. The number of atoms of each element is indicated with Greek
 Binary compounds containing two nonmetals 1. Name the first element by its name. 2. The second element has the ending ide. 3. The number of atoms of each element is indicated with Greek prefixes. Greek
Binary compounds containing two nonmetals 1. Name the first element by its name. 2. The second element has the ending ide. 3. The number of atoms of each element is indicated with Greek prefixes. Greek
9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds
 9.2 Group II Content 9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) describe
9.2 Group II Content 9.2.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group II metals magnesium to barium and their compounds Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) describe
REMOVAL OF HARDNESS BY PRECIPITATION
 REMOVAL OF HARDNESS BY PRECIPITATION Hardness divalent cations If hardness is too high Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ + Fe 2+ + Mn 2+ + Sr 2+... precipitation of soap, scaling on pipes, boilers, cooling towers, heat exchangers.
REMOVAL OF HARDNESS BY PRECIPITATION Hardness divalent cations If hardness is too high Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ + Fe 2+ + Mn 2+ + Sr 2+... precipitation of soap, scaling on pipes, boilers, cooling towers, heat exchangers.
6 METALS & NON METALS
 Grade-8 Chemistry Chapter- 6 METALS & NON METALS 1. What happens in each of the following cases? a) Magnesium is burnt in oxygen. Ans: When magnesium burns in oxygen it produces magnesium oxide with dazzling
Grade-8 Chemistry Chapter- 6 METALS & NON METALS 1. What happens in each of the following cases? a) Magnesium is burnt in oxygen. Ans: When magnesium burns in oxygen it produces magnesium oxide with dazzling
Quiz 2 practice Quiz
 Name: ate: 1. The following data were recorded while determining the solubility of a certain salt. Temp. ( C) 10 20 30 40 50 Grams Solute/ 100 g H 2 O 30 33 36 39 42 Which graph best represents the solubility
Name: ate: 1. The following data were recorded while determining the solubility of a certain salt. Temp. ( C) 10 20 30 40 50 Grams Solute/ 100 g H 2 O 30 33 36 39 42 Which graph best represents the solubility
Question Answer Notes Marks number 1 (a) (i) Any two from: 2 M1 calcium/solid/it disappears
 Answer Notes Marks (a) (i) Any two from: M calcium/solid/it disappears ACCEPT dissolves / gets smaller IGNORE mass decreases M bubbles (of gas) / fizzing / effervescence ACCEPT gas given off IGNORE hydrogen
Answer Notes Marks (a) (i) Any two from: M calcium/solid/it disappears ACCEPT dissolves / gets smaller IGNORE mass decreases M bubbles (of gas) / fizzing / effervescence ACCEPT gas given off IGNORE hydrogen
NOMENCLATURE (ie naming compounds)
 NOMENCLATURE (ie naming compounds) An ionic compounds (salt) may be any one of thousands of chemical compounds How do chemists describe which salt they are discussing? There is a system that we will follow
NOMENCLATURE (ie naming compounds) An ionic compounds (salt) may be any one of thousands of chemical compounds How do chemists describe which salt they are discussing? There is a system that we will follow
GraspIT AQA GCSE Chemical changes
 A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY
 FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY 2.11 GROUP II ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.11.1 explain why these are regarded as s-block elements; 2.11.2 recall and explain the
FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY 2.11 GROUP II ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.11.1 explain why these are regarded as s-block elements; 2.11.2 recall and explain the
NANDI NORTH DISTRICT JOINT MOCK EVALUATION TEST 2013
 NAME:. SIGNATURE: INDEX NO:. DATE :.. 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 THEORY JULY / AUGUST 2013 TIME: 2 HOURS NANDI NORTH DISTRICT JOINT MOCK EVALUATION TEST 2013 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)
NAME:. SIGNATURE: INDEX NO:. DATE :.. 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 THEORY JULY / AUGUST 2013 TIME: 2 HOURS NANDI NORTH DISTRICT JOINT MOCK EVALUATION TEST 2013 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS
 JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS CHEMISTRY (2014) 91. In paints dispersed phase and dispersion medium are (1) solid and liquid (2) liquid and solid (3) liquid and liquid (4) gas and liquid 92. Which statement is
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS CHEMISTRY (2014) 91. In paints dispersed phase and dispersion medium are (1) solid and liquid (2) liquid and solid (3) liquid and liquid (4) gas and liquid 92. Which statement is
